Understanding the Dynamic Loss Modulus of NR/SBR Blends in the Glassy–Rubbery Transition Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dynamic Mechanical Tests
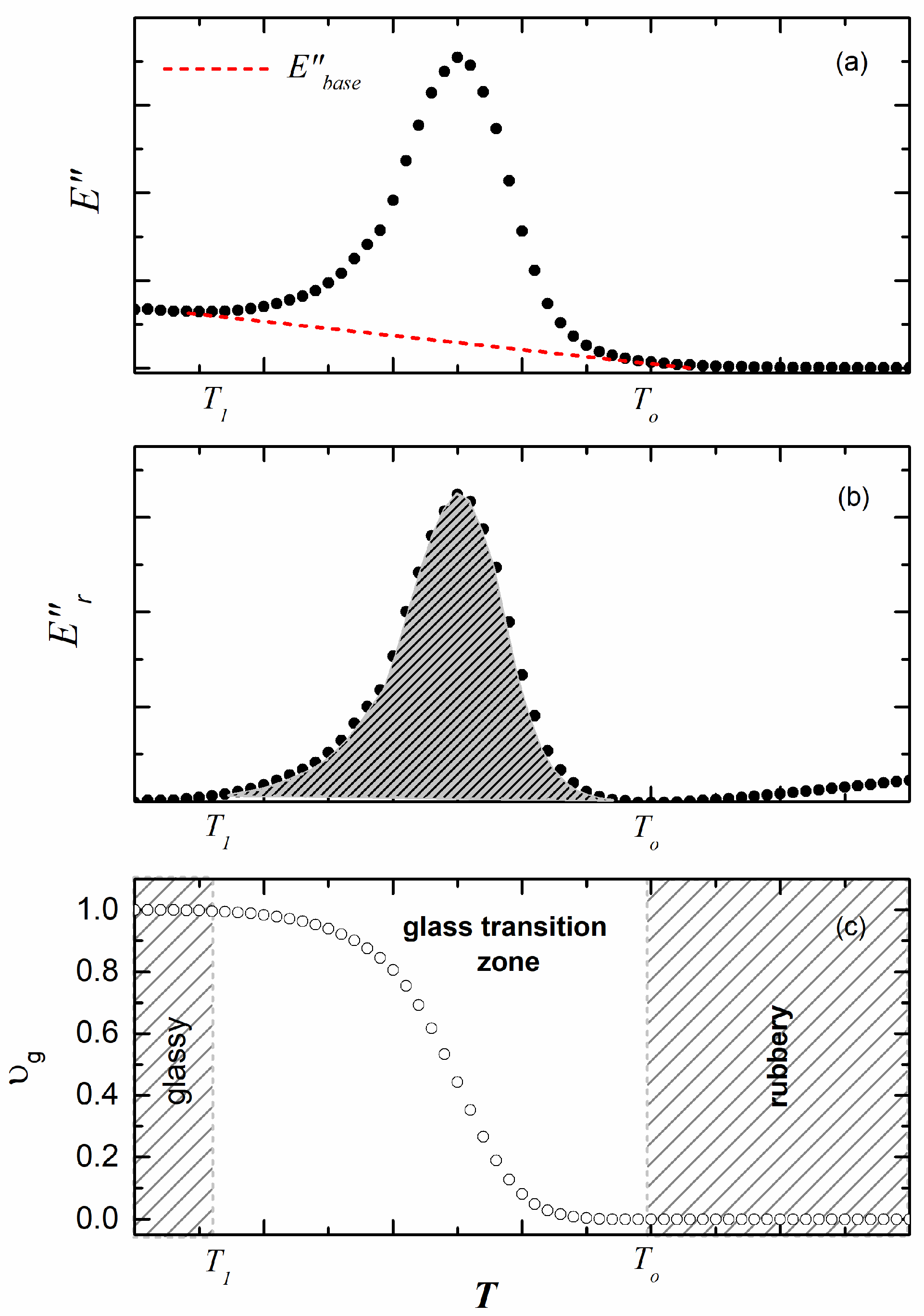
2.3. Methodology
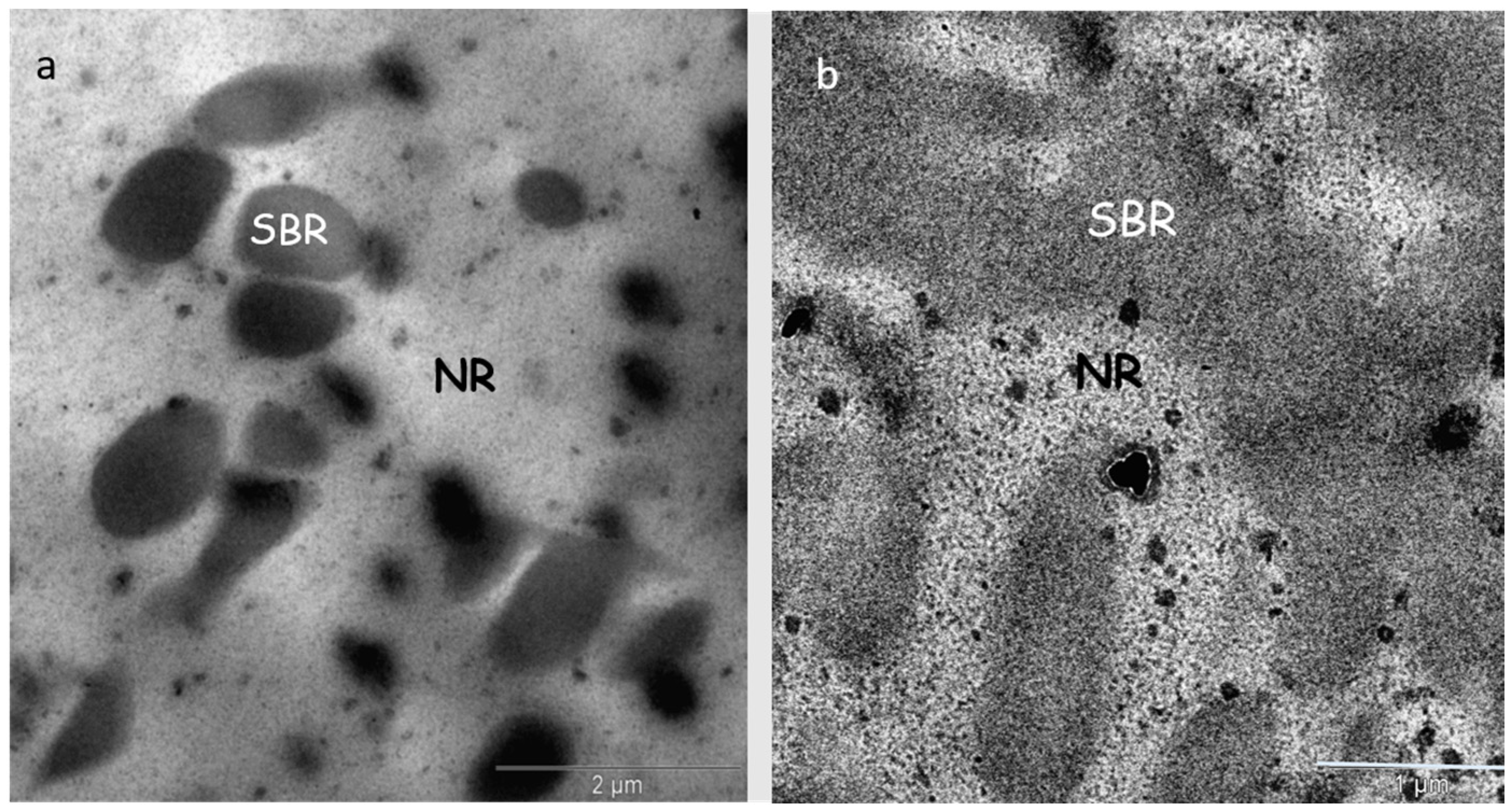
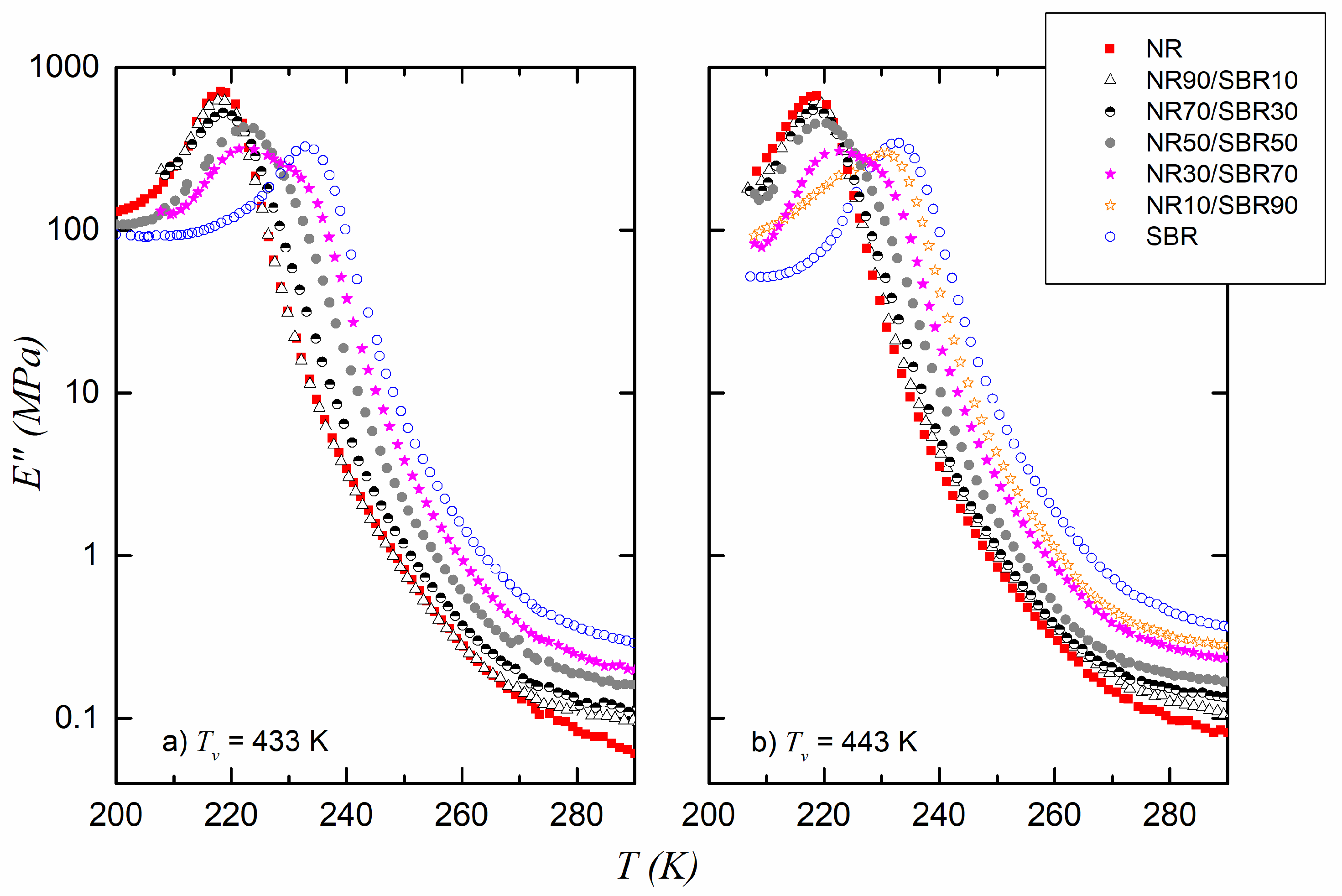
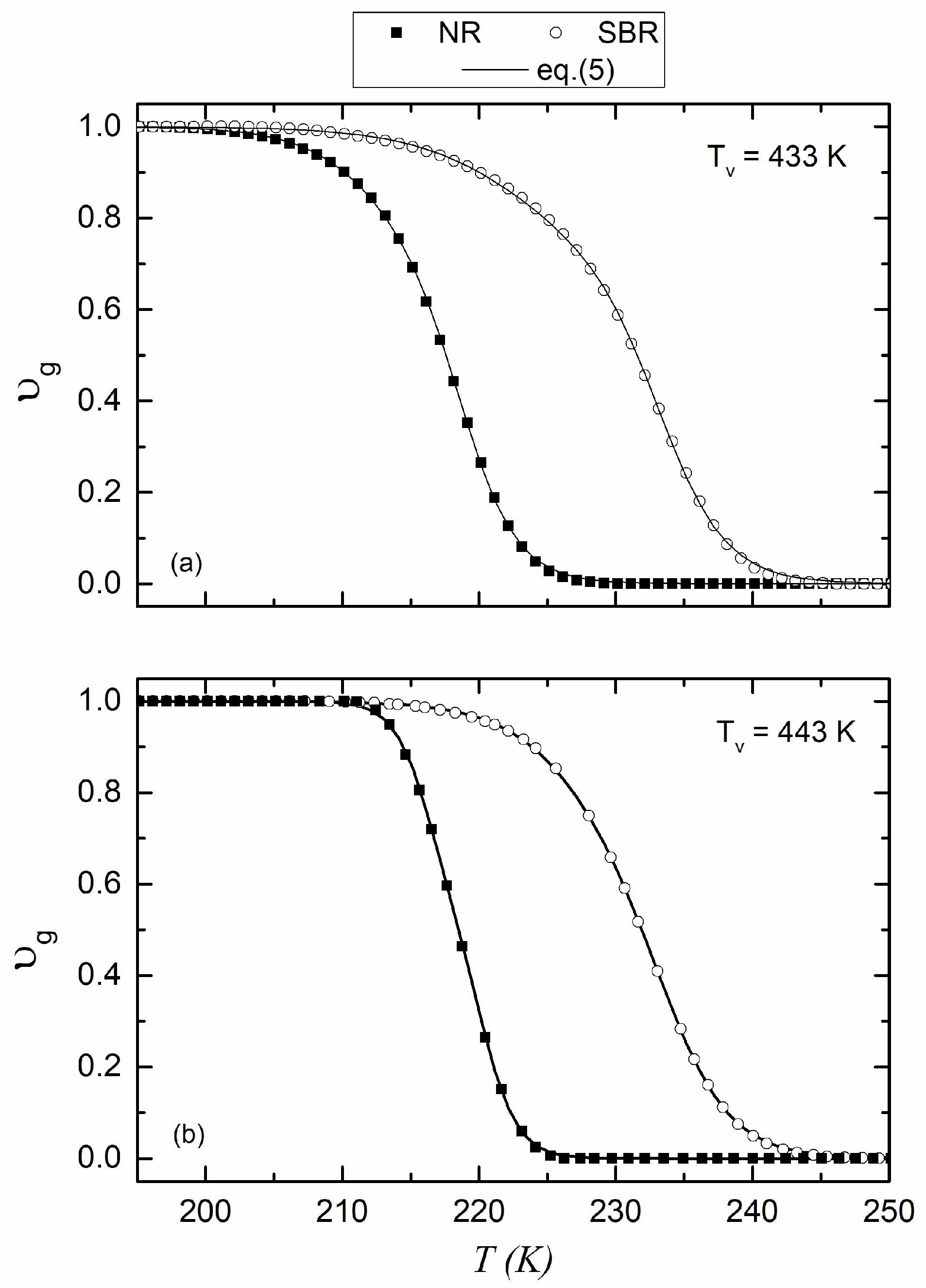
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hourston, D.J.; Song, M. Quantitative Characterization of Interfaces in Rubber-Rubber Blends by Means of Modulated-Temperature DSC. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebenik, U.; Zupančič-Valant, A.; Krajnc, M. Investigation of Rubber-Rubber Blends Miscibility. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, T.L.A.C.; Rosca, C.; Schuster, R.H.; Jacobi, M.M. Study on rubber blends: Influence of epoxidation on phase morphology and interphase. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karekar, A.; Oßwald, K.; Reincke, K.; Langer, B.; Saalwa, K. NMR Studies on the Phase-Resolved Evolution of Cross-Link Densities in Thermo-Oxidatively Aged Elastomer Blends. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 11166–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyathan, A.V.; Varghese, K.; Nair, A.S.; Thomas, S. Rubber–rubber blends: A critical review. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2020, 36, 196–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Lang, A.; Klüppel, M.; Giese, U. Influence of phase morphology on viscoelastic properties of rubber blends. In Constitutive Models for Rubber XII; Marano, A., Briatico Vangosa, F., Andena, L., Frassine, R., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, M.A.; Marzocca, A.J.; Macchi, C.; Somoza, A. Influence of vulcanization temperature on the cure kinetics and on the microstructural properties in natural rubber/styrene-butadiene rubber blends prepared by solution mixing. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 69, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, M.A.; Valentín, J.L.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Gonzalez-Jimenez, A.; Marzocca, A.J. Effect of entanglements in the microstructure of cured NR/SBR blends prepared by solution and mixing in a two-roll mill. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 81, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, M.A.; Marzocca, A.J.; Macchi, C.; Somoza, A. Natural rubber/styrene-butadiene rubber blends prepared by solution mixing: Influence of vulcanization temperature using a Semi-EV sulfur curing system on the microstructural properties. Polymer Testing 2017, 63, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klat, D.; Kepas-Suwara, A.; Lacayo-Pineda, J.; Cook, S. Morphology and nanomechanical characteristics of NR/SBR blends. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2018, 89, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klat, D.; Karimi-Varzaneh, H.A.; Lacayo-Pineda, J. Phase Morphology of NR/SBR Blends: Effect of curing temperature and curing time. Polymers 2018, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, X.; Sun, S.; Zhong, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Zuo, M.; Zheng, Q. Effect of Morphology/Structure on the Phase Behavior and Nonlinear Rheological Properties of NR/SBR Blends. Gels 2022, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzocca, A.J.; Mansilla, M.A. Dynamic mechanical properties in natural rubber/styrene-butadiene rubber blends: The local strain behavior in the glass transition region. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klüppel, M.; Schuster, R.H.; Schaper, J. Carbon black distribution in rubber blends: A dynamic-mechanical analysis. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1998, 72, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, R.H.; Meier, J.; Klüppel, M. The role of interphase in filler partition in rubber blends. Kautsch. Gummi Kunststoffe 2000, 53, 663–674. [Google Scholar]
- Wunde, M.; Klüppel, M. Influence of phase morphology and filler distribution in NR/BR and NR/SBR blends on fracture mechanical properties. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2016, 89, 588–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, J. Natural Rubber/Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Blend Composites Potentially Applied in Damping Bearings. Polymers 2024, 16, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voges, J.; Müller, M.; Lang, A.; Klüppel, M.; Juhre, D. Modeling the viscoelastic behavior of elastomer blends including a diffuse interphase. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2025, 95, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhre, D.; Voges, J.; Niemeyer, M.; Klüppel, M.; Lang, A.; Müller, M. Micromechanical modelling of the viscoelastic properties of filled elastomer blends. In Constitutive Models for Rubbers XIII; Dal, H., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setua, D.K.; Gupta, Y.N.; Kumar, S.; Awasthi, R.; Mall, A.; Sekhar, K. Determination of Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Engineering Thermoplastics at Wide Frequency Range using Havriliak–Negami Model. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Li, D. Determination of dynamic mechanical properties of carbon black filled rubbers at wide frequency range using Havriliak-Negami model. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 2015, 53, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, M.A. Influence of the Microstructure on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Natural Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber. Ph.D. Thesis, Institutional Repository, University of Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mansilla, M.A.; Ghilarducchi, A.; Salva, H.; Marzocca, A.J. Alpha (Vitrea) Transition in Vulcanized Natural Rubber/Styrene Butadiene Rubber Blends Prepared by Mechanical and Solution Mixing. Solid State Phenom. 2012, 184, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrum, N.G.; Read, B.E.; Williams, G. Anelastic and Dielectric Effects in Polymeric Solids; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 102–140. [Google Scholar]
- Akiba, M.; Hahim, A.S. Vulcanization and crosslinking in elastomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1977, 22, 475–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobol, G. The Physics of Polymers, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.Y.; Zou, S.F.; Jiang, B.Y.; Fan, B.; Hou, M.F.; Zuo, B.; Xin-Ping Wang, X.-P.; Xu, J.-T.; Fan, Z.Q. A Generalized Avrami Equation for Crystallization Kinetics of Polymers with Concomitant Double Crystallization Processes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 5908–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Burger, C.; Toki, S.; Rong, L.; Hsiao, B.S.; Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J. Crystal and Crystallites Structure of Natural Rubber and Peroxide-Vulcanized Natural Rubber by a Two-Dimensional Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction Simulation Method. II. Strain-Induced Crystallization versus Temperature-Induced Crystallization. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 9712–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.E. Free-volume theory and its application to polymer relaxation in the glassy state. In Computational Modelling of Polymers; Bicerano, J., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 297–362. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, J.H.; Di Marzio, E.A. Nature of the Glass Transition and the Glassy State. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.; Gibbs, J.H. On the Temperature Dependence of Cooperative Relaxation Properties in Glass-Forming Liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 43, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotze, W.; Sjogren, L. Relaxation processes in supercooled liquids. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1992, 55, 241–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, K.L. Universality of Low-Frequency Fluctuation, Dissipation, and Relaxation Properties of Condensed Matter, I. Comments Solid State Phys. 1979, 9, 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ngai, K.L. Universality of Low-Frequency Fluctuation, Dissipation, and Relaxation Properties of Condensed Matter, II. Comments Solid State Phys. 1980, 9, 141–155. [Google Scholar]
- Metatla, M.; Soldera, A. The Vogel−Fulcher−Tamman Equation Investigated by Atomistic Simulation with Regard to the Adam−Gibbs Model. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 9680–9685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcher, G.S. Analysis of recent measurements of the viscosity of glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1925, 8, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G.; Hesse, W. Die Abhängigkeit der Viscosität von der Temperatur bie unterkühlten Flüssigkeiten. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1926, 156, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H. Das Temperaturabhaengigkeitsgesetz der Viskositaet von Fluessigkeiten. Phys. Z. 1921, 22, 645. [Google Scholar]
- Cerveny, S.; Ghilarducci, A.; Salva, H.; Marzocca, A.J. Glass-transition and secondary relaxation in SBR-1502 from dynamic mechanical data. Polymer 2000, 41, 2227–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Liu, G.; Dong, X.; Wang, D. Correlation between Stress Relaxation Dynamics and thermochemistry for Covalent Adaptive Networks Polymer. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, A.; Hernandez, M.; Garcia, S.J.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M.; Bergmann, C.; Trimbach, J.; Blume, A. Identifying the Effect of Aromatic Oil on the Individual Component Dynamics of S-SBR/BR Blends by Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, N.; Schawe, J.E.K.; Lacayo-Pineda, J. Kinetics of the glass transition of styrene-butadiene-rubber: Dielectric spectroscopy and fast differential scanning calorimetry. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e49769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosas Fernandes, J.P.; Federico, C.E.; Lentzen, E.; Valle, N.; Basterra-Beroiz, B.; Weydert, M.; Quintana, R. Viscoelastic Properties and Sulfur Distribution at the Nanoscale in Binary Elastomeric Blends: Toward Phase-Specific Cross-Link Density Estimations. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 3287–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallon, P.E.; Mcgill, W.J. Polyisoprene, Poly(styrene-cobutadiene), and Their Blends. Part II. Vulcanization Reactions with 2-Bisbenzothiazole-2,2′-Disulfide/Sulfur. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, M.A.; Silva, L.; Salgueiro, W.; Marzocca, A.J.; Somoza, A. A Study About the Structure of Vulcanized Natural Rub-ber/Styrene Butadiene Rubber Blends and the Glass Transition Behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karekar, A.; Schicktanz, C.; Tariq, M.; Oßwald, K.; Reincke, K.; Cepus, V.; Langer, B.; Kay Saalwächter, K. Effects of artificial weathering in NR/SBR elastomer blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 208, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


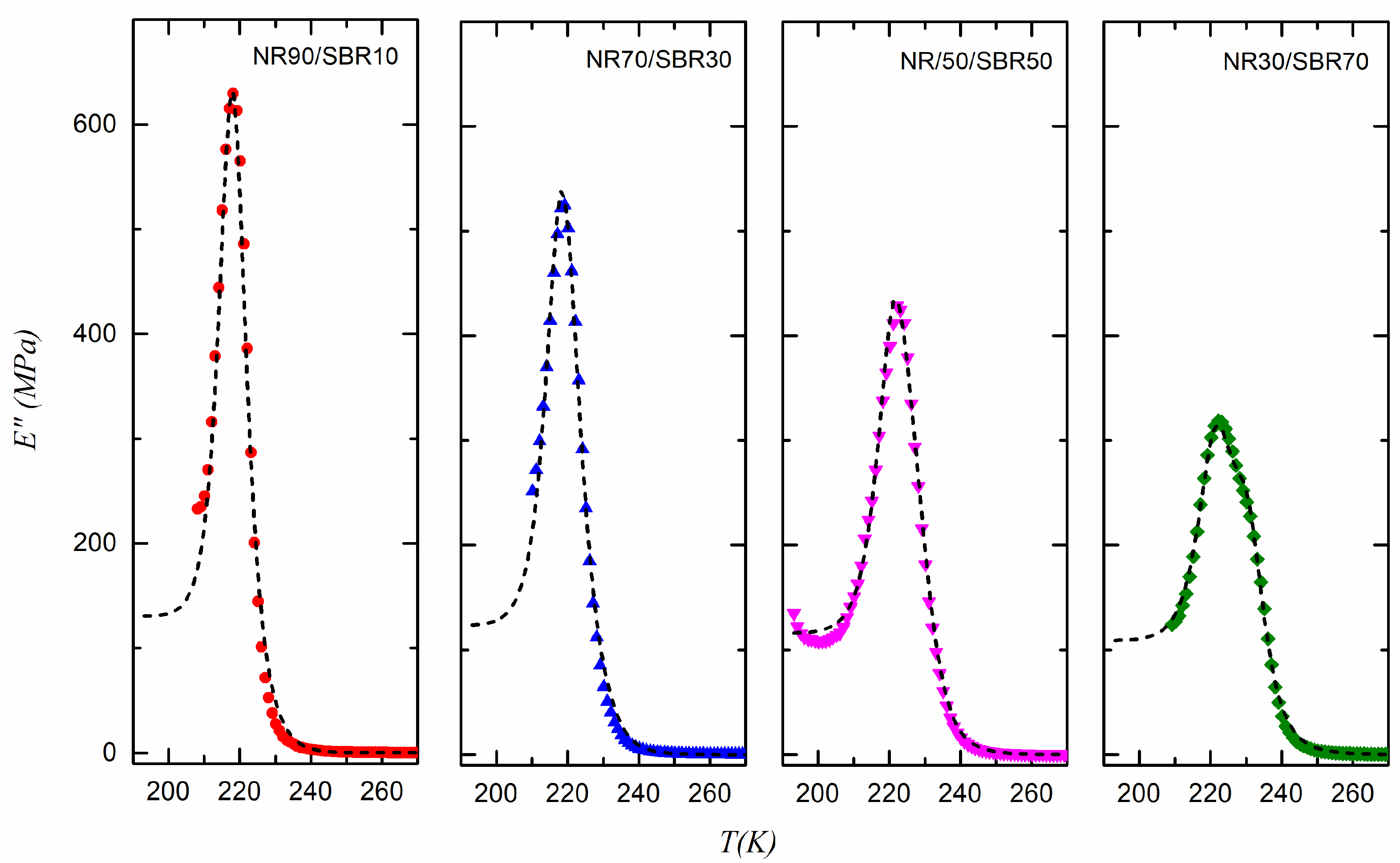
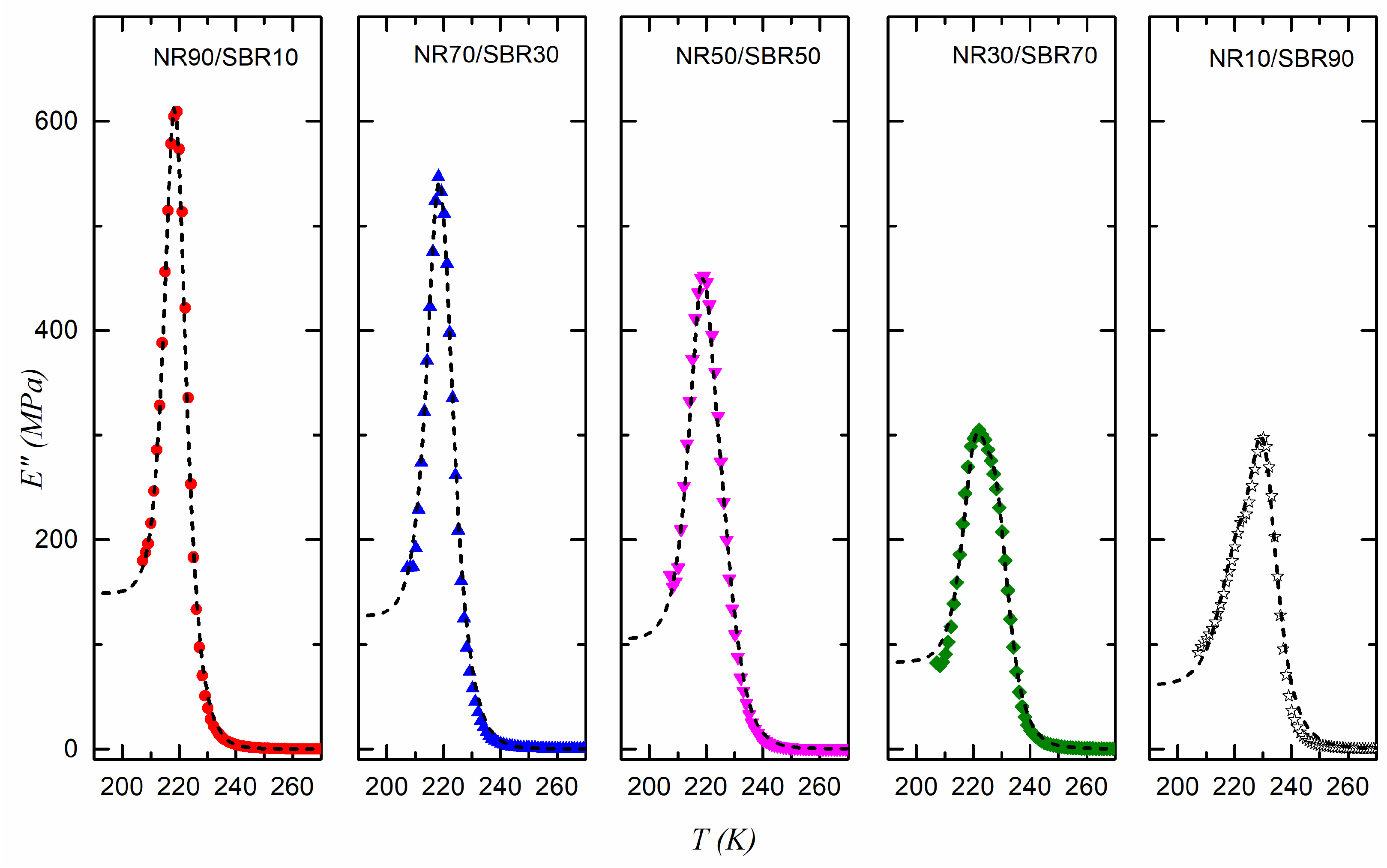
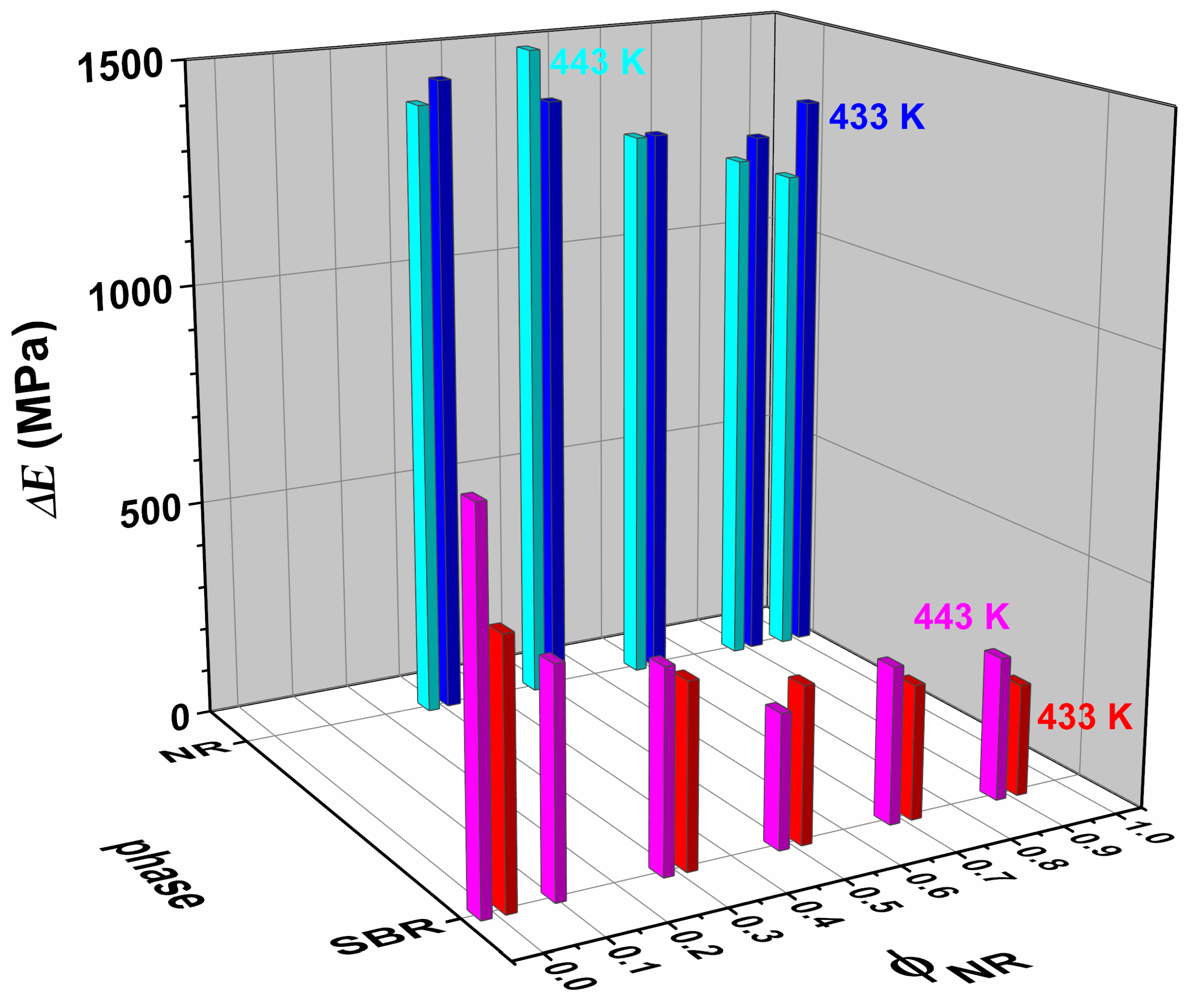

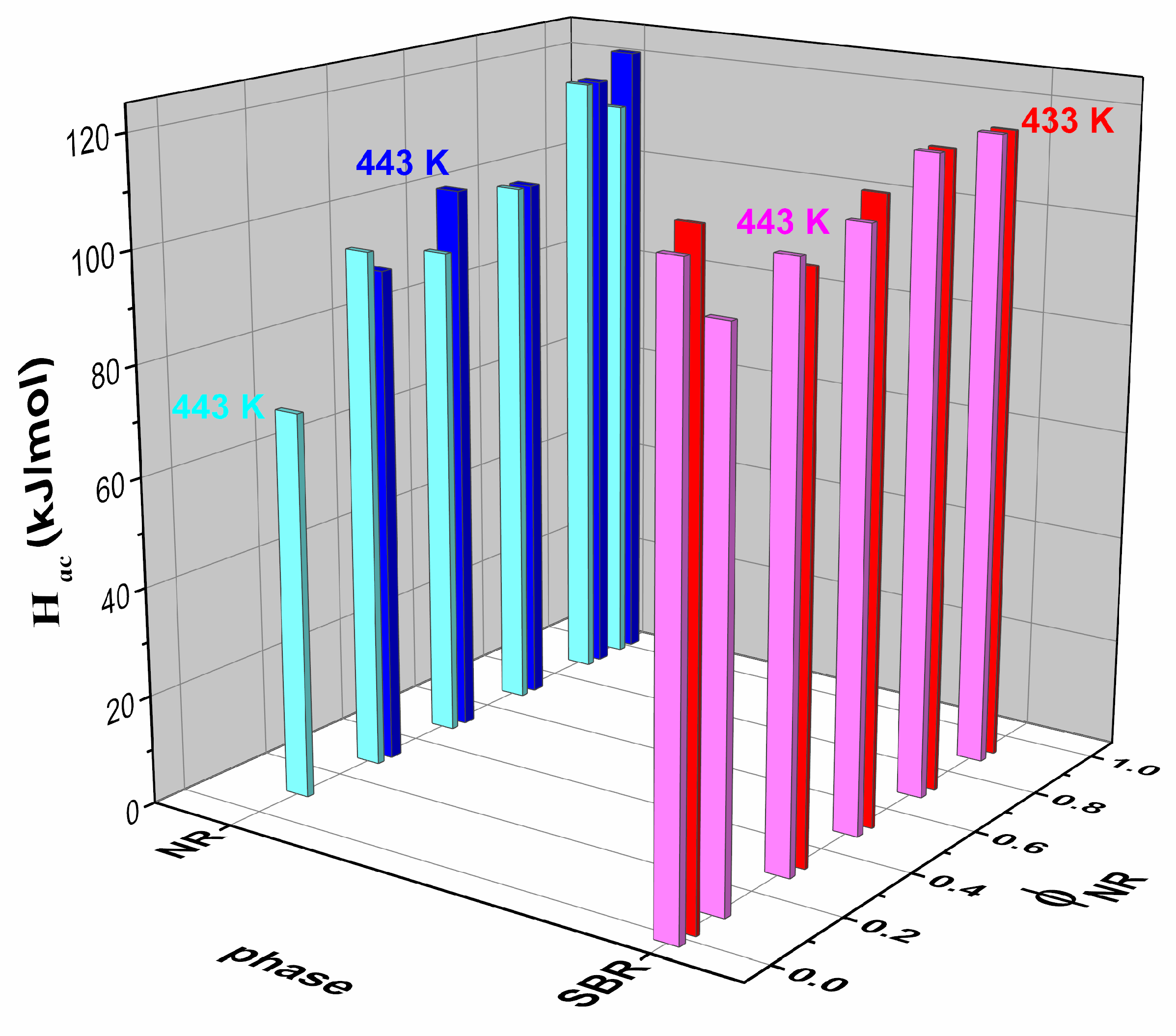
| SBR | NR10/SBR90 | NR30/SBR70 | NR50/SBR50 | NR70/SBR30 | NR90/SBR10 | NR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR (SMR20) | 0 | 10 | 30 | 50 | 70 | 90 | 100 |
| SBR-1502 | 100 | 90 | 70 | 50 | 30 | 10 | 0 |
| Stearic Acid | 2 | ||||||
| Zinc Oxide | 5 | ||||||
| Sulfur | 1.5 | ||||||
| TBBS | 1.5 | ||||||
| Tv (K) | t (min) | SBR | NR10/SBR90 | NR30/SBR70 | NR50/SBR50 | NR70/SBR30 | NR90/SBR10 | NR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 433 | t5 | 13.09 | 7.91 | 8.61 | 5.56 | 4.14 | 0.74 | 0.57 |
| 0.5 | ||||||||
| 0.57 | ||||||||
| t100 | 88.30 | 48.60 | 46.7 | 33.50 | 21.60 | 14.70 | 13.70 | |
| 443 | t5 | 5.35 | 3.45 | 3.26 | 2.80 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.40 |
| t100 | 34.40 | 25.80 | 22.10 | 17.40 | 11.40 | 7.00 | 7.70 |
| NR | SBR | |||
| Tv (K) | 433 | 443 | 433 | 443 |
| f | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.46 ± 0.05 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 0.41 ± 0.12 |
| T1 (K) | 212.62 ± 1.14 | 216.30 ± 0.20 | 223.62 ± 0.92 | 228.28 ± 1.13 |
| T2 (K) | 218.65 ± 0.14 | 220.24 ± 0.17 | 233.27 ± 0.11 | 233.60 ± 0.28 |
| k1 (K) | 3.17 ± 0.19 | 1.32 ± 0.06 | 4.36 ± 0.22 | 3.44 ± 0.11 |
| k2 (K) | 2.06 ± 0.08 | 1.32 ± 0.05 | 2.39 ± 0.08 | 2.42 ± 0.14 |
| R2 | 0.99995 | 0.99992 | 0.9999 | 0.99997 |
| NR | SBR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tv [K] | 433 | 443 | 433 | 443 | |
| [MPa] | 0.056 | 0.076 | 0.281 | 0.35 | |
| [MPa] | 133.9 | 160 | 98 | 50 | |
| VFT Equation (8) | A [s] | 3.9 × 10−16 | 4.0 × 10−16 | 1.0 × 10−13 | 0.8 × 10−13 |
| 3260 | 3250 | 2630 | 2640 | ||
| 113.9 | 114.5 | 131.5 | 131.0 | ||
| R2 | 0.9493 | 0.9153 | 0.9367 | 0.9166 | |
| Arrhenius Equation (9) | τo [s] | 2.14 × 10−31 | 5.75 × 10−29 | 1.36 × 10−28 | 9.73 × 10−28 |
| Hac [kJ/mol] | 120.6 | 110.6 | 116.4 | 112.2 | |
| R2 | 0.9543 | 0.9438 | 0.9568 | 0.9436 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzocca, A.J.; Mansilla, M.A.; Beccar Varela, M.P.; Mariani, M.C. Understanding the Dynamic Loss Modulus of NR/SBR Blends in the Glassy–Rubbery Transition Zone. Polymers 2025, 17, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101312
Marzocca AJ, Mansilla MA, Beccar Varela MP, Mariani MC. Understanding the Dynamic Loss Modulus of NR/SBR Blends in the Glassy–Rubbery Transition Zone. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101312
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzocca, Angel J., Marcela A. Mansilla, María Pía Beccar Varela, and María Cristina Mariani. 2025. "Understanding the Dynamic Loss Modulus of NR/SBR Blends in the Glassy–Rubbery Transition Zone" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101312
APA StyleMarzocca, A. J., Mansilla, M. A., Beccar Varela, M. P., & Mariani, M. C. (2025). Understanding the Dynamic Loss Modulus of NR/SBR Blends in the Glassy–Rubbery Transition Zone. Polymers, 17(10), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101312









