Effect of Electrode Tuning on the Resistive Switching Behaviour of MXene-Based Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene Flakes
2.3. Fabrication MXene/PVDF Nanocomposite Structures
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
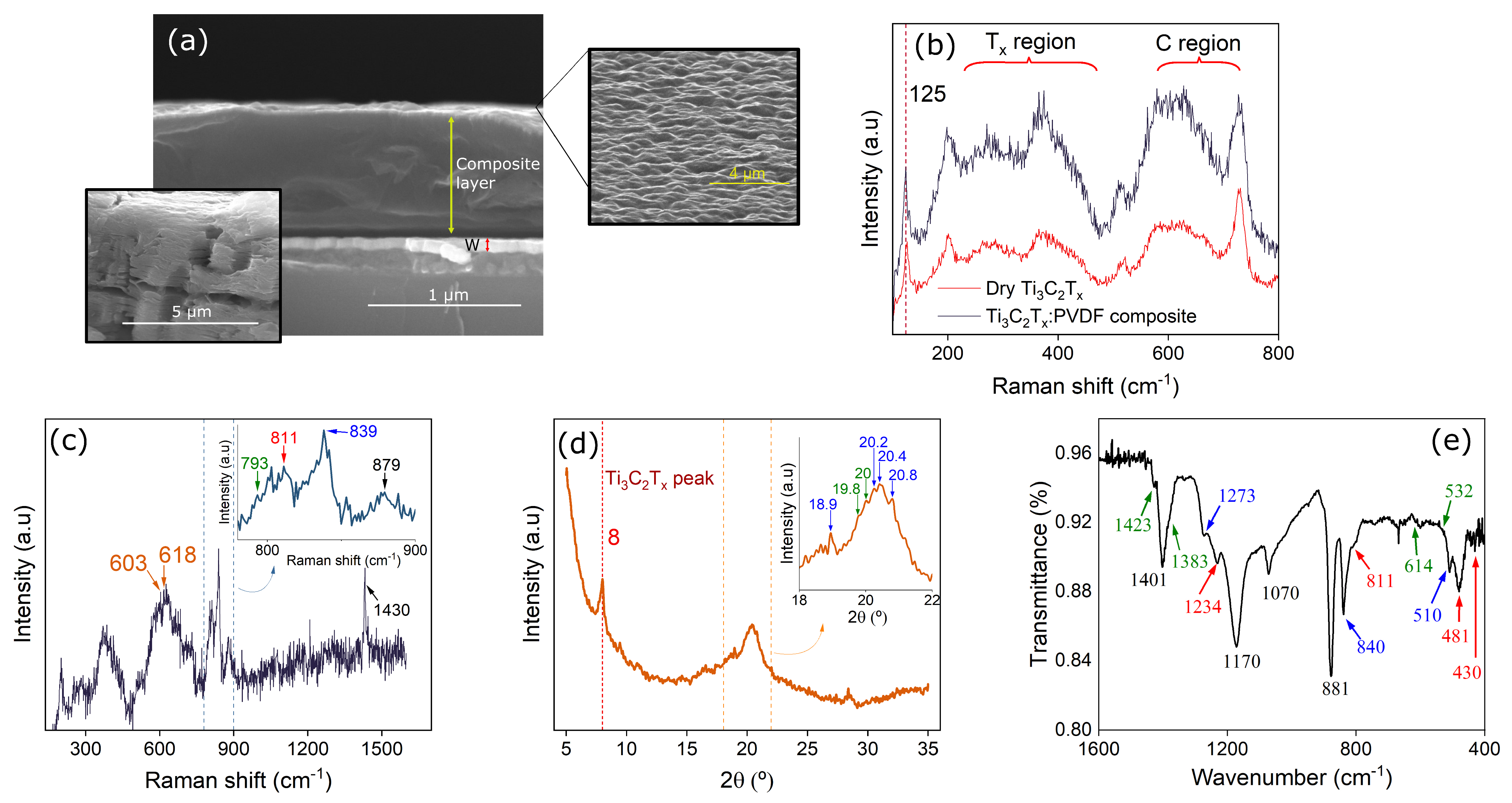
3.1. Structure Characterization
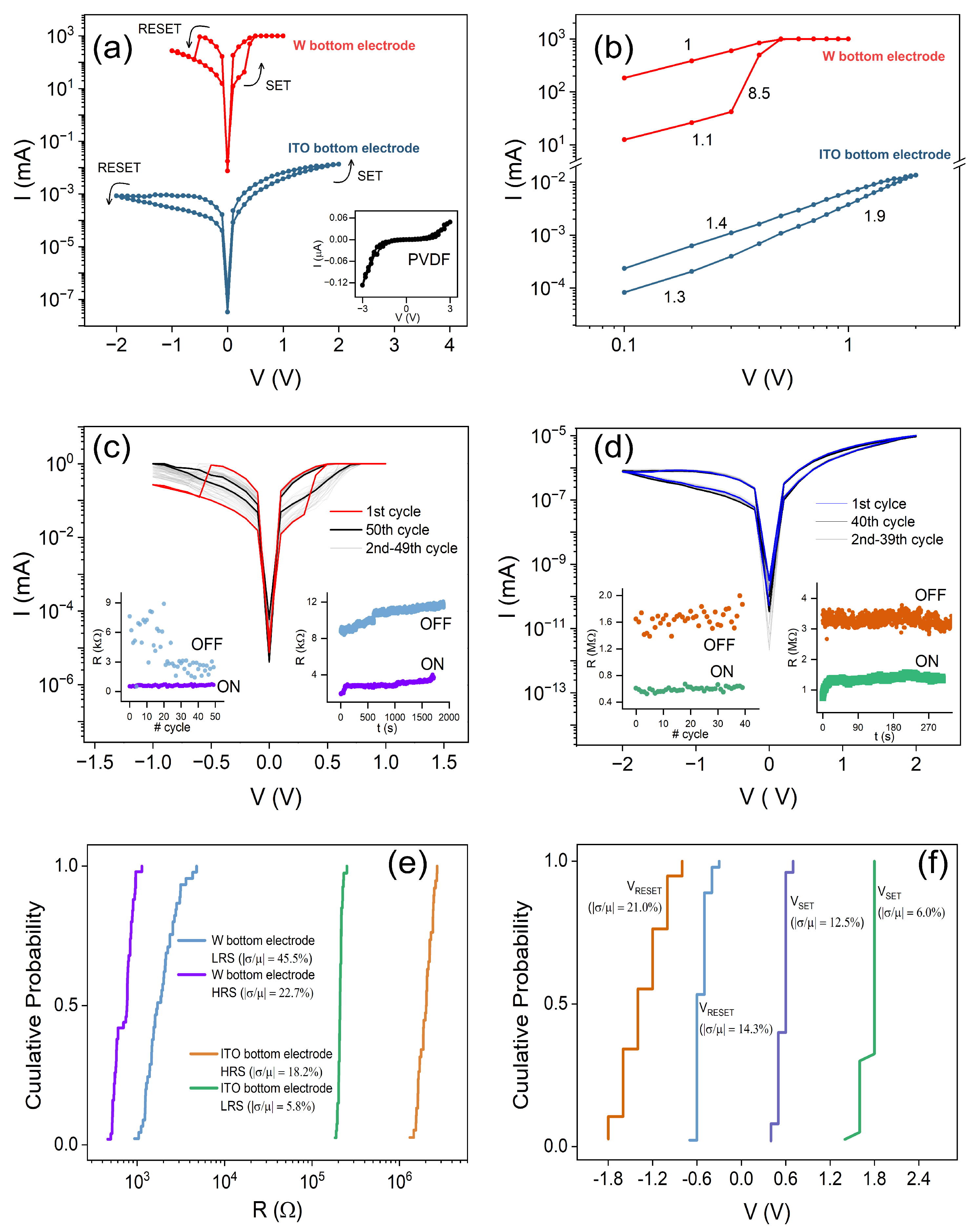
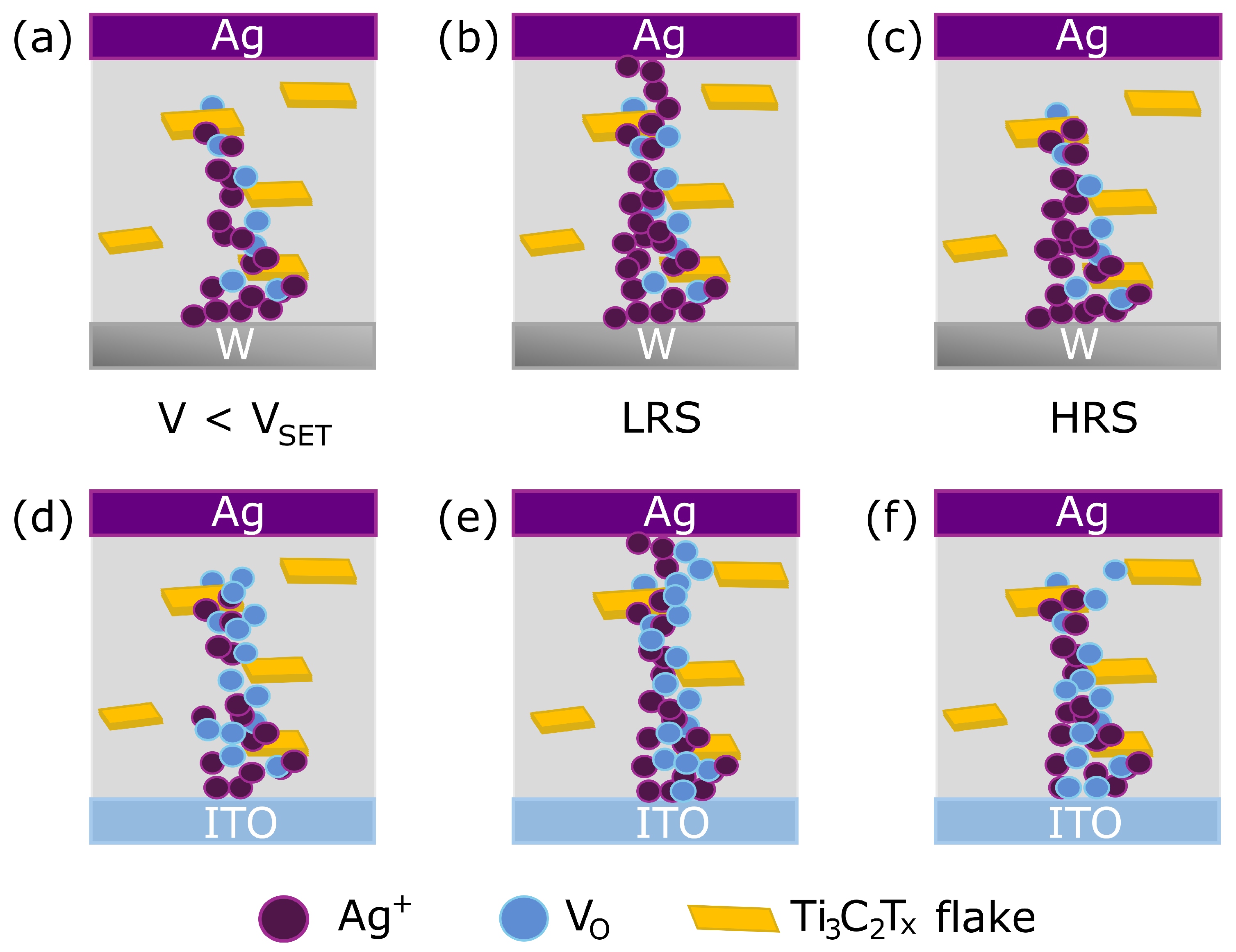
3.2. Electrical Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | Two-Dimensional |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| HRS | High resistance state |
| LRS | Low resistance state |
| MIM | Metal-Insulator-Metal |
| RS | Resistive switching |
| SCLC | Space Charge Limited Conduction |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
References
- Chua, L. Memristor—The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, C.; Castro, D.; Aroso, M.; Ventura, J.; Aguiar, P. Memristor-Based Neuromodulation Device for Real-Time Monitoring and Adaptive Control of Neuronal Populations. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waser, R.; Dittmann, R.; Staikov, G.; Szot, K. Redox-Based Resistive Switching Memories—Nanoionic Mechanisms, Prospects, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2632–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Strukov, D.B.; Stewart, D.R. Memristive devices for computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiong, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Han, J.; Ye, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Z.; et al. Designing High-Performance Storage in HfO2/BiFeO3 Memristor for Artificial Synapse Applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1901012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Cheng, C.; Huang, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Pei, W.; et al. A Self-Rectifying Synaptic Memristor Array with Ultrahigh Weight Potentiation Linearity for a Self-Organizing-Map Neural Network. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.; Acharya, A.; Tiwari, K.; Saha, P.; Sahoo, N.; Panda, D. Synaptic plasticity in zinc oxide-based flexible invisible transparent memristor by modulating oxygen concentration. J. Appl. Phys. 2024, 136, 045109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, H.M.; Wang, Z.P.; Xie, P.; Feng, Z.; Wang, J.; Mao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Han, S.T. A Perovskite Memristor with Large Dynamic Space for Analog-Encoded Image Recognition. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 21324–21333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumbhar, D.D.; Gosai, J.; Sekhar, M.R.; Mallajosyula, A.T.; Solanki, A. Hybrid Perovskite-Based Flexible and Stable Memristor by Complete Solution Process for Neuromorphic Computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2023, 9, 2200908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Hu, Z.; Yan, T.; Hong, E.; Deng, X.; Wu, L.; Fang, X. A Dual-Functional Perovskite-Based Photodetector and Memristor for Visual Memory. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Meng, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Bian, R.; Zhu, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z. 2D Material Based Synaptic Devices for Neuromorphic Computing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Cheng, S.; Qin, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, B.; Zhang, Y.; Jie, W. Low-Power Memristor Based on Two-Dimensional Materials. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 7130–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmal, K.A.; Kumbhar, D.D.; Kesavan, A.V.; Dongale, T.D.; Kim, T.G. Advancements in 2D layered material memristors: Unleashing their potential beyond memory. NPJ 2D Mater. Appl. 2024, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.M.; Samad, Y.A.; Gul, J.Z.; Saqib, M.; Khan, M.; Shaukat, R.A.; Chang, R.; Shi, Y.; Kim, W.Y. 2D materials-memristive devices nexus: From status quo to Impending applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 152, 101471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja Nibhanupudi, S.S.; Roy, A.; Veksler, D.; Coupin, M.; Matthews, K.C.; Disiena, M.; Ansh; Singh, J.V.; Gearba-Dolocan, I.R.; Warner, J.; et al. Ultra-fast switching memristors based on two-dimensional materials. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, P.; Novoselov, K.S. Recent advances in graphene and other 2D materials. Nano Mater. Sci. 2022, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yuan, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Li, D. Perspectives of 2D Materials for Optoelectronic Integration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Cheng, S.; Guo, F.; Jie, W.; Hao, J. Tunable Resistive Switching in 2D MXene Ti3C2 Nanosheets for Non-Volatile Memory and Neuromorphic Computing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 44614–44621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; et al. A New Memristor with 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene Flakes as an Artificial Bio-Synapse. Small 2019, 15, 1900107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Emerging MXene-Based Memristors for In-Memory, Neuromorphic Computing, and Logic Operation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2208320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, H.; Dias, C.; Silva, A.V.; Ventura, J. Advances on MXene-Based Memristors for Neuromorphic Computing: A Review on Synthesis, Mechanisms, and Future Directions. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 21685–21713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Anasori, B. The Rise of MXenes. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8491–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, J.L.; Hantanasirisakul, K.; Lang, A.C.; Anasori, B.; Pinto, D.; Pivak, Y.; Van Omme, J.T.; May, S.J.; Gogotsi, Y.; Taheri, M.L. Control of MXenes’ electronic properties through termination and intercalation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ashraf, I.; Mansoor, M.A.; Rizwan, S.; Iqbal, M. An Overview of Recent Advances in the Synthesis and Applications of the Transition Metal Carbide Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Xing, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Han, S.T. Emerging MXenes for Functional Memories. Small Sci. 2021, 1, 2100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kuklin, A.V.; Baev, A.; Ge, Y.; Ågren, H.; Zhang, H.; Prasad, P.N. Two-dimensional MXenes: From morphological to optical, electric, and magnetic properties and applications. Phys. Rep. 2020, 848, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M.; Mokkath, J. Surface termination dependent optical characteristics of MXene nanoflakes. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 29, 101447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Xu, S.; Lu, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, H. Surface Terminations of MXene: Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.J.; Fu, J.K.; Gao, Z.X.; Gu, S.P.; Wang, L. High-performance artificial neurons based on Ag/MXene/GST/Pt threshold switching memristors. Chin. Phys. B 2023, 32, 017304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Gu, C.; Yan, S.; Xin, Q.; Cheng, S.; Tan, P.; Wang, X.; Xiu, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; et al. MXene Quantum Dot/Polymer Hybrid Structures with Tunable Electrical Conductance and Resistive Switching for Nonvolatile Memory Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1900493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, M.; Liu, S.; Li, W.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Xuan, S.; Gong, X. Flexible polyvinylidene fluoride(PVDF)/MXene(Ti3C2Tx)/Polyimide(PI) wearable electronic for body Monitoring, thermotherapy and electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 153, 106727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, Y.; Lei, T.; Cui, Z.; Wang, H.; Qin, S. PVDF-based composites for electromagnetic shielding application: A review. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, T.; Tian, Z.; Bibi, K.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Alshareef, H.N. MXenes for Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Sadri, R.; Momodu, D.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Mohammad Haniff, M.A.S.; Wu, C.; Dee, C.F.; Ooi, P.C. N -Doped Graphene/MXene Nanocomposite as a Temperature-Adaptive Neuromorphic Memristor. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 3631–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Chen, M. Advances and prospects of PVDF based polymer electrolytes. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 64, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaev, R.; Pisarenko, T.; Sobola, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Ramazanov, S.; Trčka, T. Brief Review of PVDF Properties and Applications Potential. Polymers 2022, 14, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomaviciute-Grabusove, S.; Popov, A.; Ramanavicius, S.; Sablinskas, V.; Shevchuk, K.; Gogotsi, O.; Baginskiy, I.; Gogotsi, Y.; Ramanavicius, A. Monitoring Ti3C2Tx MXene Degradation Pathways Using Raman Spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 13184–13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grácio, M.; Teixeira, H.; Dias, C.; Ventura, J. Effect of Electrode Tuning on the Resistive Switching Behaviour of MXene-Based Composites. Polymers 2025, 17, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101309
Grácio M, Teixeira H, Dias C, Ventura J. Effect of Electrode Tuning on the Resistive Switching Behaviour of MXene-Based Composites. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101309
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrácio, Maria, Henrique Teixeira, Catarina Dias, and João Ventura. 2025. "Effect of Electrode Tuning on the Resistive Switching Behaviour of MXene-Based Composites" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101309
APA StyleGrácio, M., Teixeira, H., Dias, C., & Ventura, J. (2025). Effect of Electrode Tuning on the Resistive Switching Behaviour of MXene-Based Composites. Polymers, 17(10), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101309






