Injectable Thermo-Responsive Peptide Hydrogels and Its Enzyme Triggered Dynamic Self-Assembly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Characterization
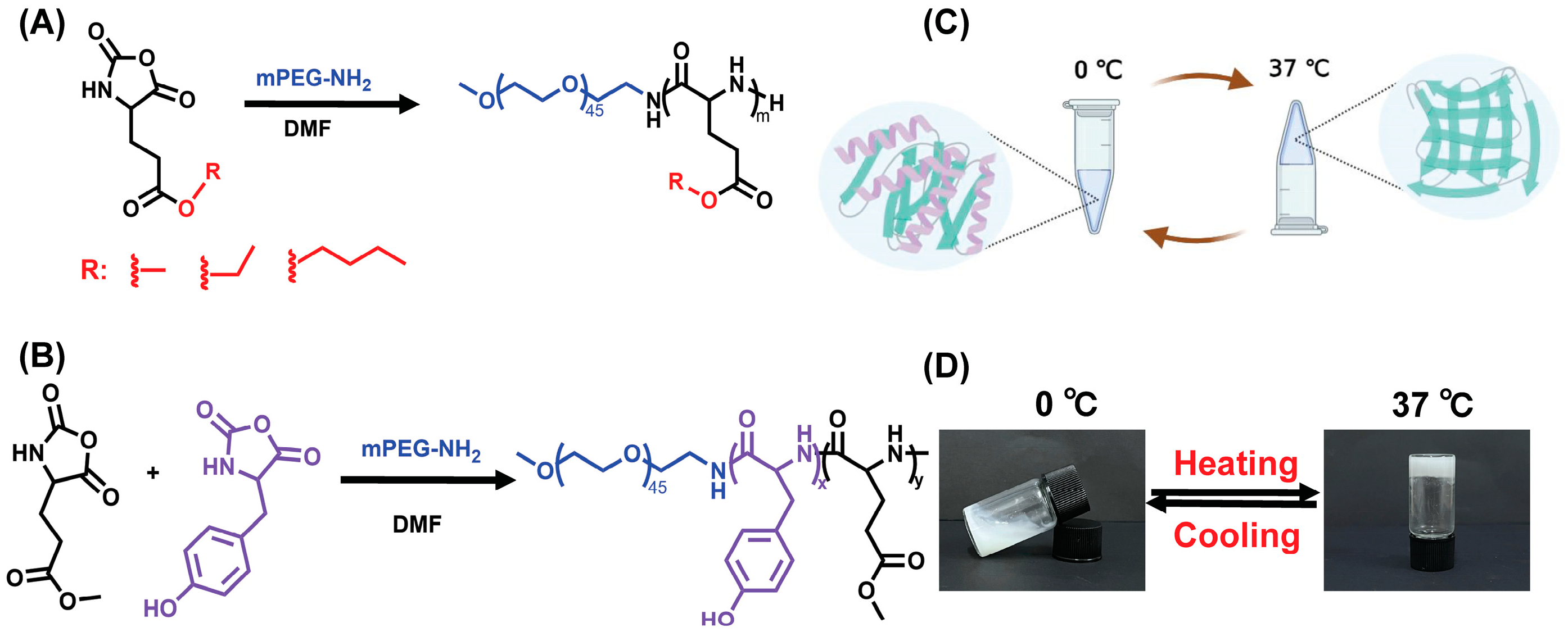
2.2. Synthesis of PEG-b-P(MGlu-co-Tyr) Copolymer
2.3. Synthesis of PEG-b-P(MGlu-co-Tyr/P)
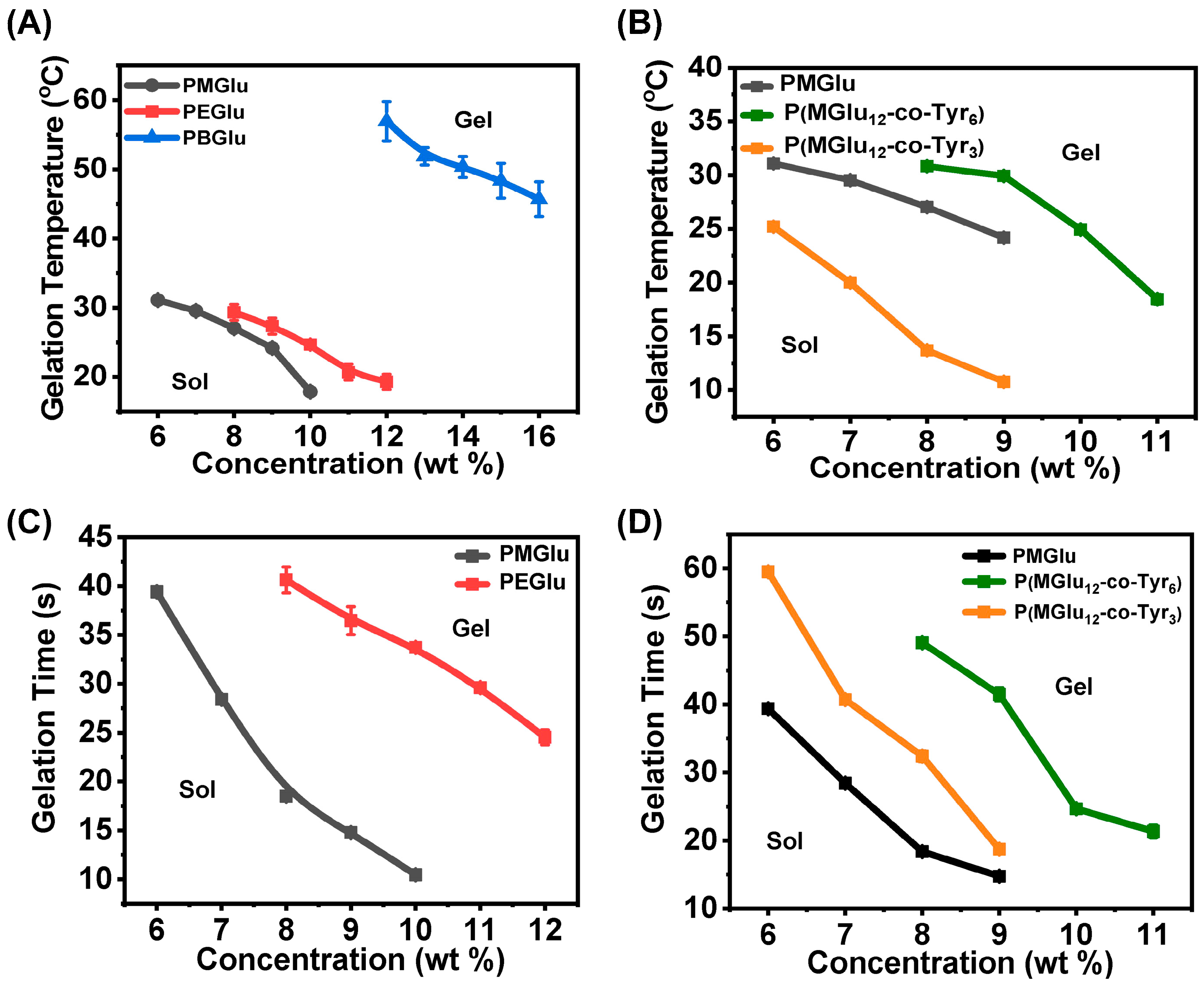
2.4. Gel Phase Diagram and Gel Time Measurement
2.5. Rheology Test
2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Analysis
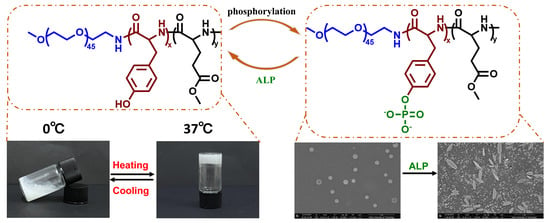
2.7. ALP Triggered Dynamic Self-Assembly
3. Results
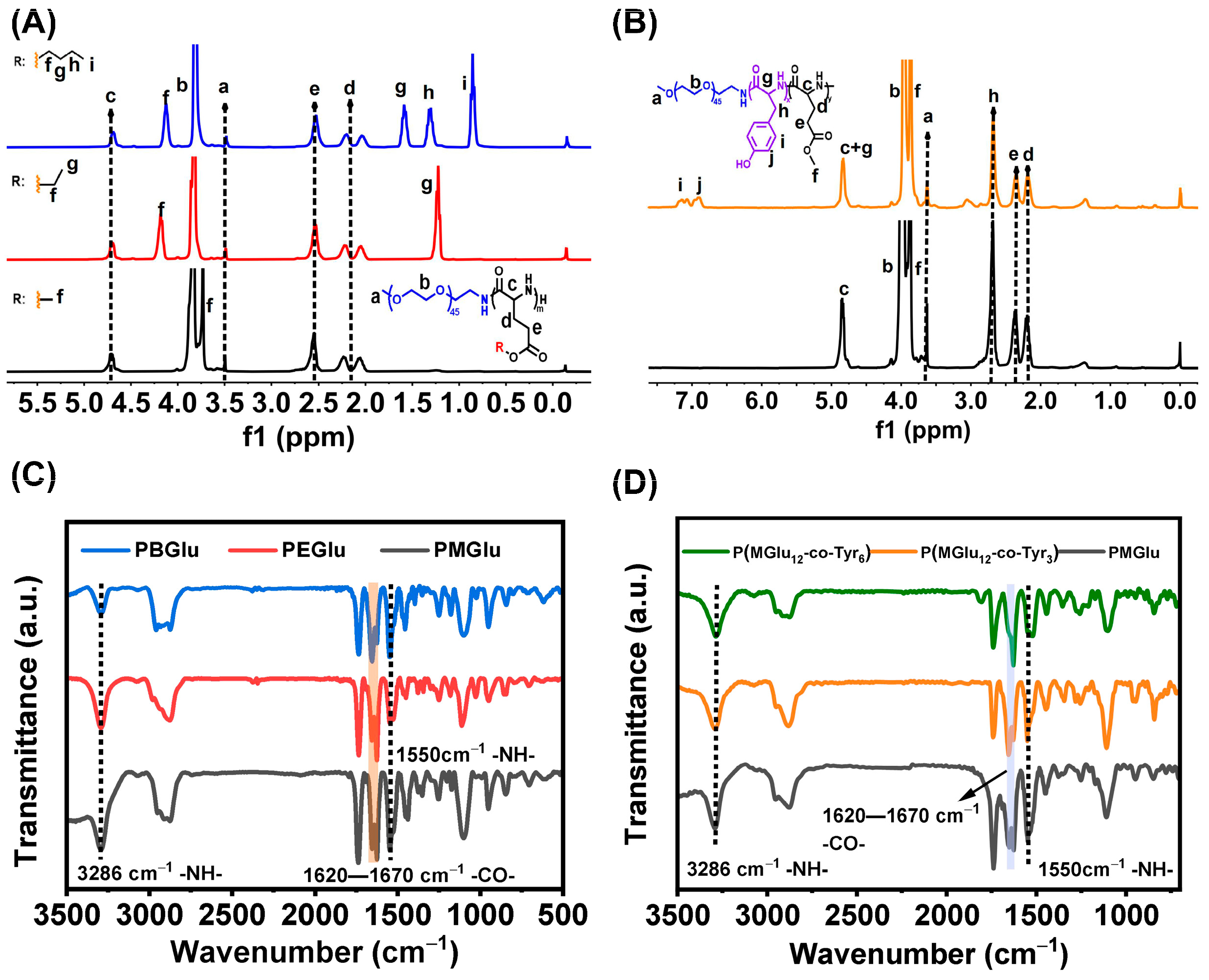
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Copolymers
3.2. Gel Phase Diagram
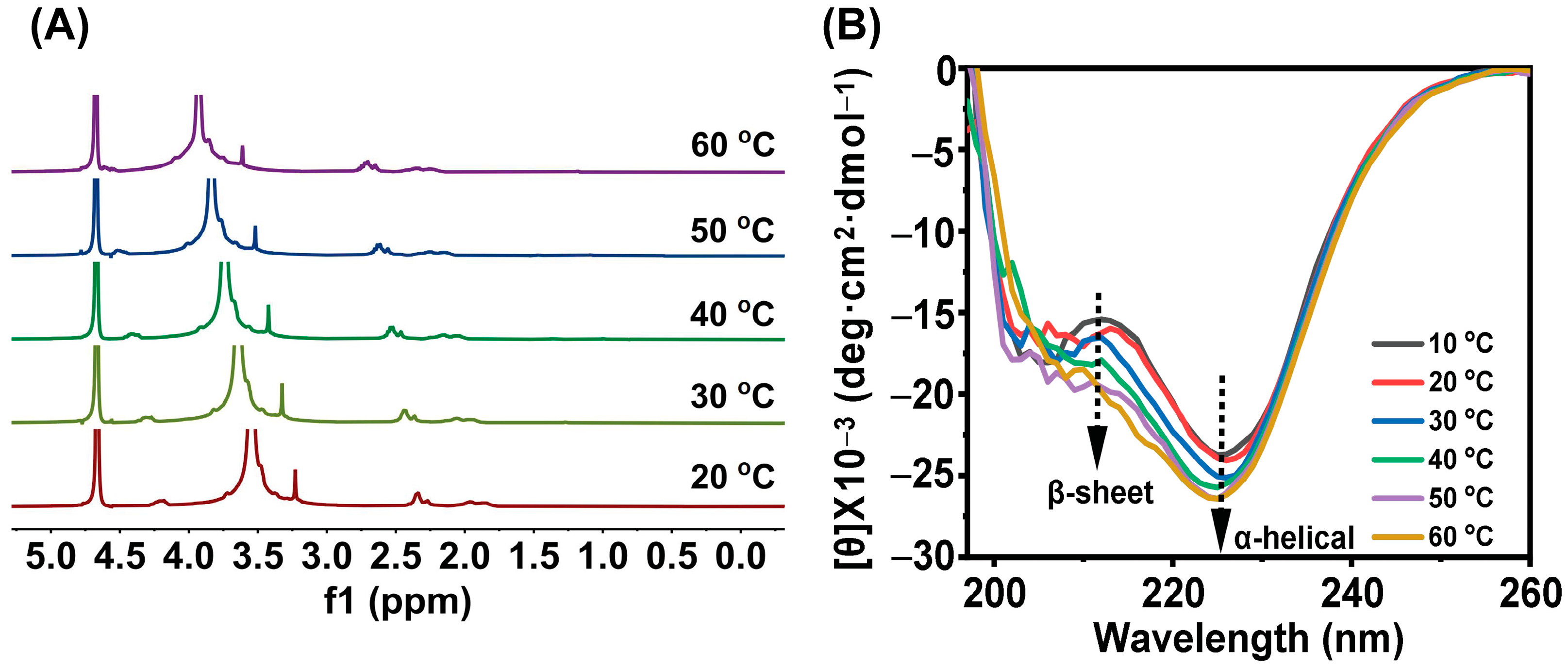
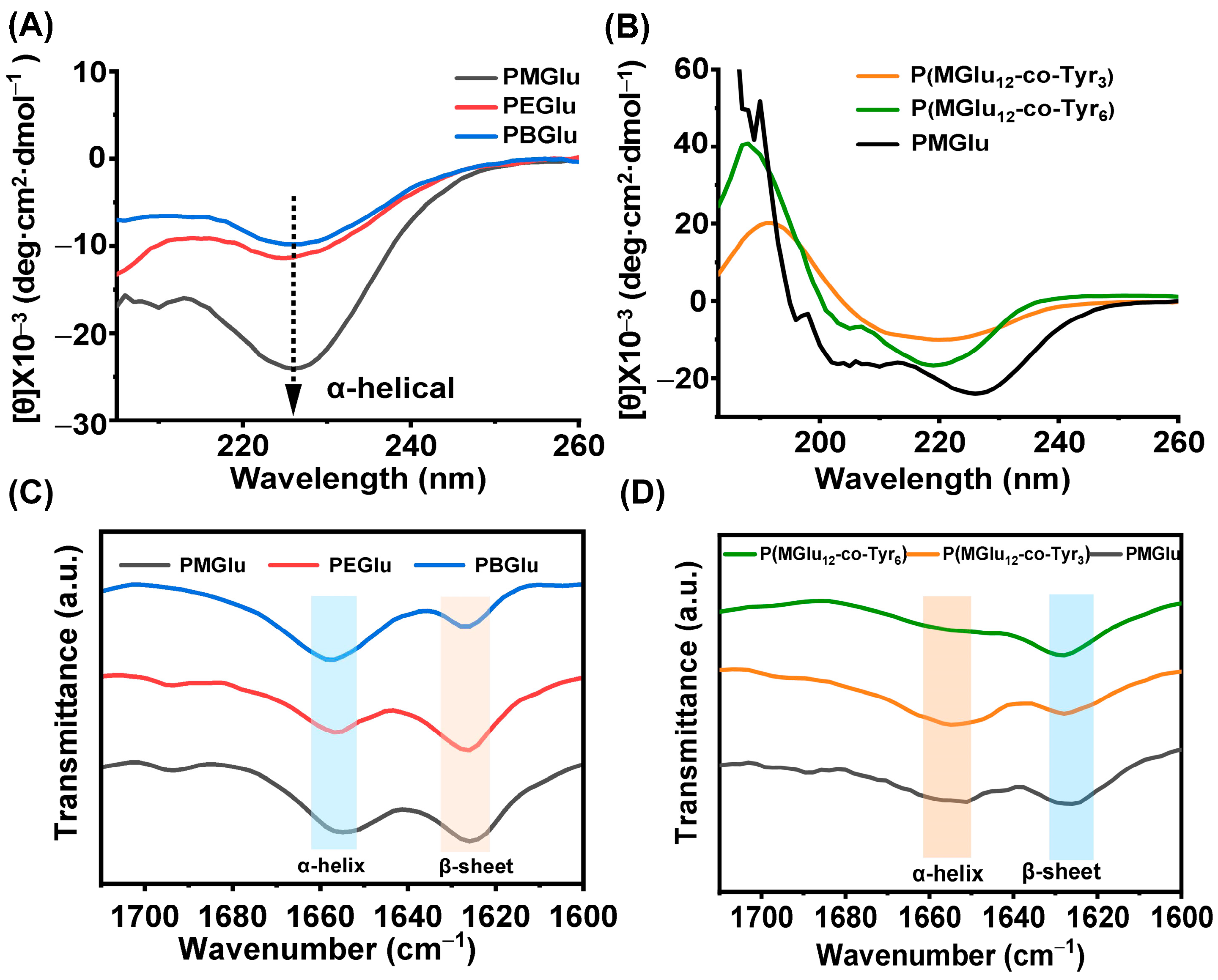
3.3. Gel Mechanism and Secondary Structure
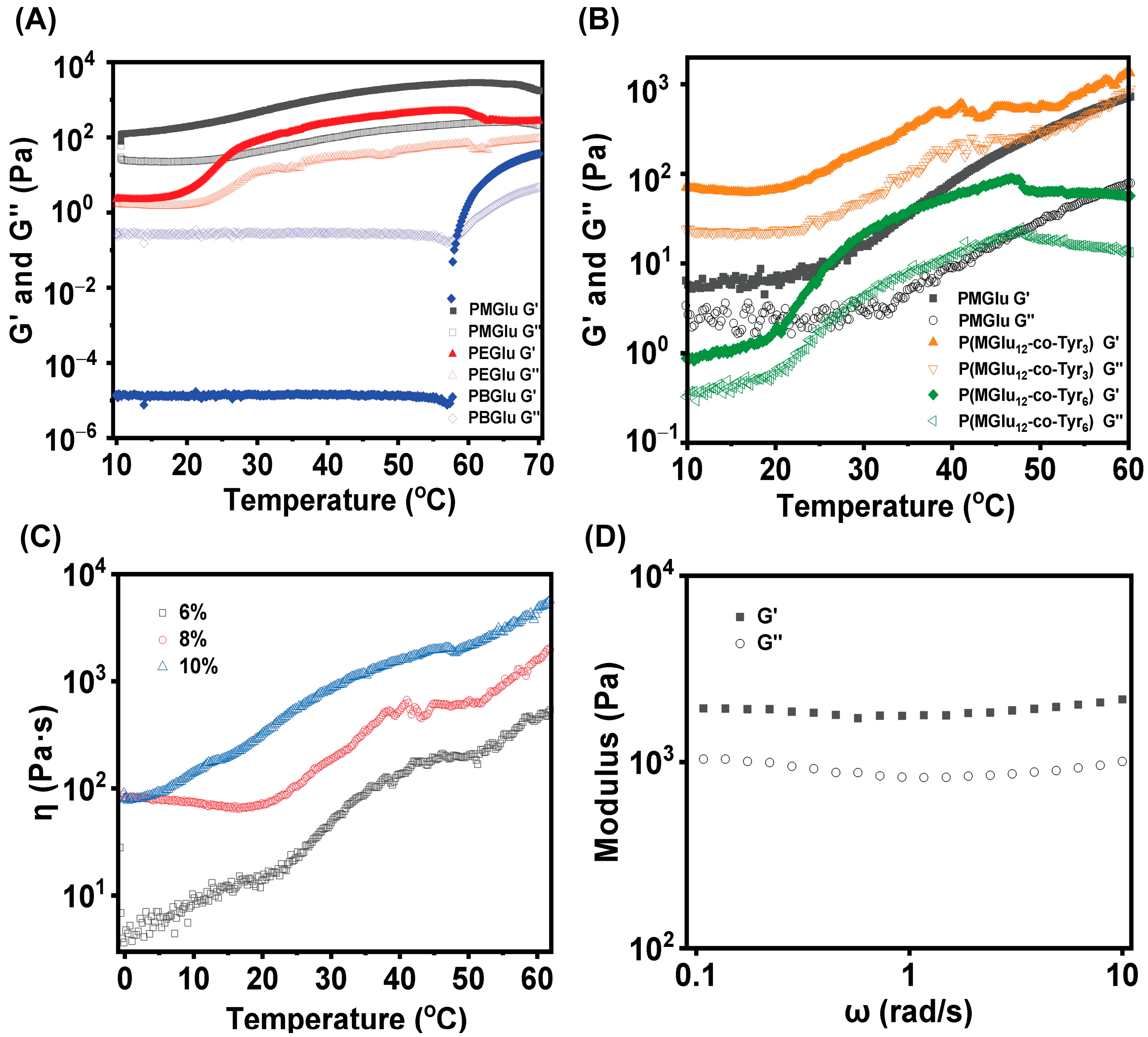
3.4. Rheology Test
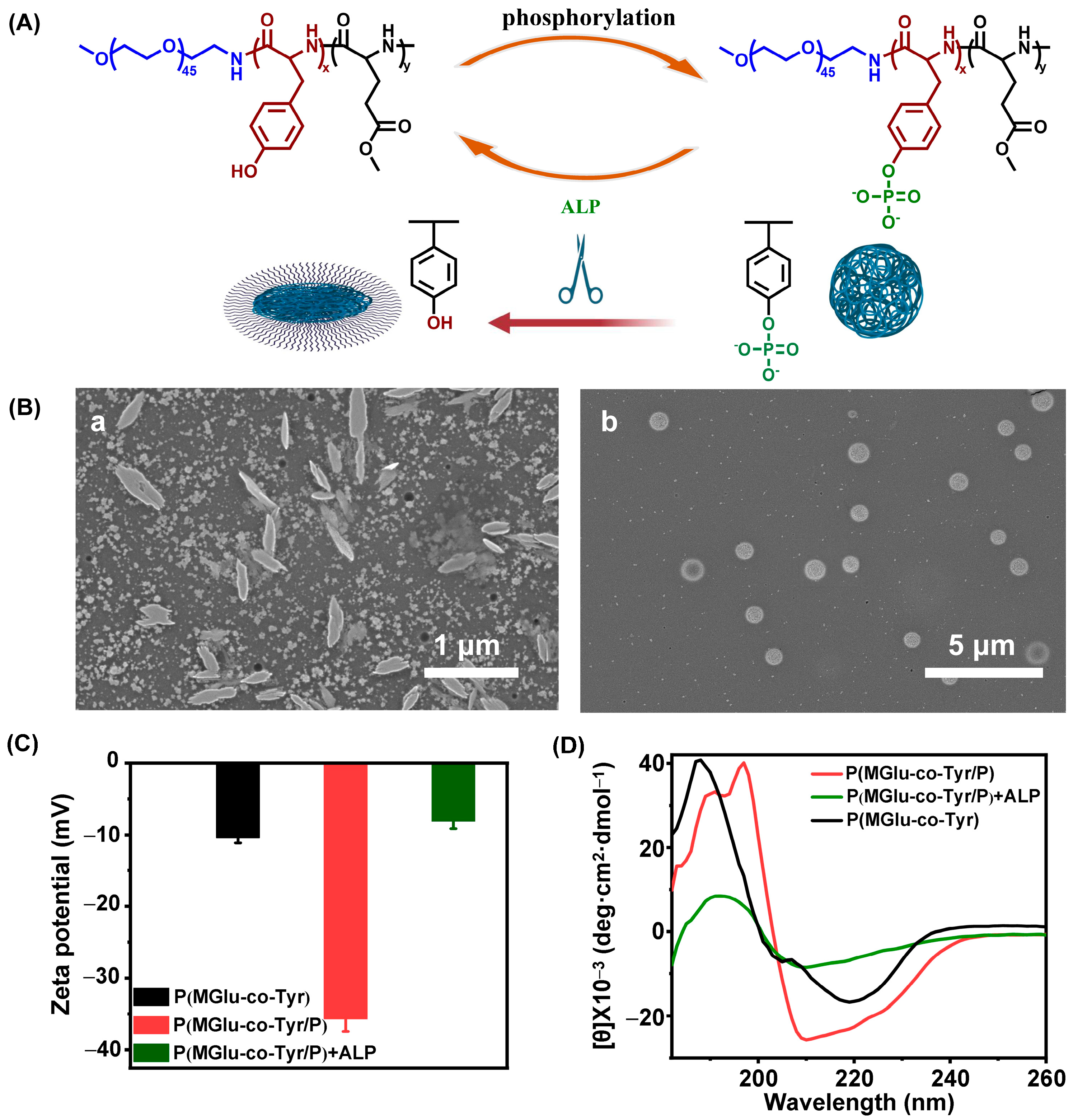
3.5. ALP Triggered Dynamic Self-Assembly
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dethe, M.R.; Prabakaran, A.; Ahmed, H. PCL-PEG copolymer based injectable thermosensitive hydrogels. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimatteo, R.; Darling, N.J.; Segura, T. In situ forming injectable hydrogels for drug delivery and wound repair. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, D.Y.; Shinde, U.P.; Yeon, B. Recent progress of in situ formed gels for biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 672–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, G. Injectable Microfluidic Hydrogel Microspheres for Cell and Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, P.; Diba, M.; Mooney, D.J. Self-healing injectable hydrogels for tissue regeneration. Chem. Rev. 2022, 123, 834–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.; Yang, X.; Chen, S. Cyclodextrin-based host–guest supramolecular hydrogels for local drug delivery. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 454, 214352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Ai, S.F.; Yang, Z.M. Peptide-based supramolecular hydrogels for local drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 482–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.S.; Cheruvu, H.S.; Mangion, S.E. Topical drug delivery: History, percutaneous absorption, and product development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 177, 113929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Jiang, C. Stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems triggered by intracellular or subcellular microenvironments. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 196, 114773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetting, M.C.; Peters, J.T.; Steichen, S.D. Stimulus-responsive hydrogels: Theory, modern advances, and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2015, 93, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darge, H.F.; Andrgie, A.T.; Tsai, H.-C. Polysaccharide and polypeptide based injectable thermo-sensitive hydrogels for local biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Lee, D.S. In situ gelling pH- and temperature-sensitive biodegradable block copolymer hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Y.; Yu, L.; Ding, J.D. PEG-based thermosensitive and biodegradable hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2021, 128, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, R. Thermosensitive Hydrogels and Advances in Their Application in Disease Therapy. Polymers 2022, 14, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Hou, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.H. Controlled synthesis and enzyme-induced hydrogelation of poly(l-phosphotyrosine)s via ring-opening polymerization of α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydride. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Stimuli-responsive polymersomes for biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, J.; Qian, C. H2O2-responsive vesicles integrated with transcutaneous patches for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano. 2017, 11, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wollenberg, A.L.; O’Shea, T.M. Conformation-directed formation of self-healing diblock copolypeptide hydrogels via polyion complexation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15114–15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J. Component effect of stem cell-loaded thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogels on cartilage repair. Acta Biomater. 2018, 73, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, D.; Ralhan, J.; Joseph, J.P. Thermoresponsive injectable hydrogel to mimic the heat- and strain-stiffening behavior of biopolymers toward muscle cell proliferation. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.C.; Yuan, F.Z. An immunomodulatory polypeptide hydrogel for osteochondral defect repair. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Injectable In Situ Forming Double-Network Hydrogel To Enhance Transplanted Cell Viability and Retention. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 5885–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, F.; Si, W. Impact of charge composition and distribution on the antibacterial properties of polypeptide coatings. ACS Macro Lett. 2022, 11, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.D.; Zhao, X.Y.; Xu, W.G. Effect of hydrophobic polypeptide length on performances of thermo-sensitive hydrogels. Molecules 2018, 23, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Lan, J.; Li, Y.H. Secondary structure-governed polypeptide cross-linked polymeric hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.J.; Xue, T.R.; Mao, J.N. Tailoring synthetic polypeptide design for directed fibril superstructure formation and enhanced hydrogel properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 5823–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.J.; Zhang, D.L.; He, C.L. Injectable thermosensitive polypeptide-based CDDP-complexed hydrogel for improving localized antitumor efficacy. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4341–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhao, D.; He, C.L. Crucial impact of residue chirality on the gelation process and biodegradability of thermoresponsive polypeptide hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3992–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.M.; Yuan, Y.N.; Li, L. Facile synthesis of high molecular weight poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(amino acid)s by relay polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y. Chiral polymer micelles alleviate adriamycin cardiotoxicity via Iron chelation and ferroptosis inhibition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, Q.H. Development of injectable thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogel as facile radioisotope and radiosensitizer hotspot for synergistic brachytherapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 114, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Deming, T.J. Methylated mono- and di(ethylene glycol)-functionalized β-sheet forming polypeptides. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisal, R.; Jayakannan, M. Tertiary-butylbenzene functionalization as a strategy for β-sheet polypeptides. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 2667–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolfson, D.N. Understanding a protein fold: The physics, chemistry, and biology of α-helical coiled coils. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenman, G.; Apter, B. Bioinspired materials: Physical properties governed by biological refolding. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 021303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, B.; Onofrei, D.; Stengel, D. Spider prey-wrapping silk is an α-helical coiled-coil/β-sheet hybrid nanofiber. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10746–10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.N.; Lewis, R.J. Structural basis for control by phosphorylation. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2209–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Fichman, G.; Schneider, J.P. Enzymatic Control of the Conformational Landscape of Self-Assembling Peptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11188–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, P.; Thirumurugan, S.; Tseng, C.-L. Synthesis of Methotrexate-Loaded Dumbbell-Shaped Titanium Dioxide/Gold Nanorods Coated with Mesoporous Silica and Decorated with Upconversion Nanoparticles for Near-Infrared-Driven Trimodal Cancer Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 33335–33347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonduelle, C. Secondary structures of synthetic polypeptide polymers. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. pH-and temperature-responsive hydrogels based on tertiary amine-modified polypeptides for stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Chem.–Asian J. 2023, 18, e202300021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, L.; Sepay, N.; Banerji, B. ß-Sheet induced helical self-assembly atructure formation by dityrosine dipeptide: Crystallographic evidence and other biophysical studies. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2022, 126, 5207–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Hanay, S.B.; Kimmins, S.D. Ion-triggered hydrogels self-assembled from statistical copolypeptides. ACS Macro Lett. 2022, 11, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Jiao, C.; Yu, B. Preparation and biomedical application of injectable hydrogels. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 4912–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, P.D.; Velu, K.; Vineeth Kumar, C. Advances in injectable hydrogel: Design, functional regulation, and biomedical applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Z. Advances and biomedical applications of polypeptide hydrogels derived from α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) polymerizations. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrasoul, M.; Ponniah, K.; Mao, A. Conformational clusters of phosphorylated tyrosine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17632–17638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.M.; Xiong, Y.T.; Lu, W.Q. Functional nanochannels for sensing tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16324–16333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.H.; Han, Z.Y.; Song, Z.Y. Bacteria-assisted activation of antimicrobial polypeptides by a random-coil to helix transition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10826–10829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Zhu, J.; Ye, H. Rational construction of protein-mimetic nano-switch systems based on secondary structure transitions of synthetic polypeptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 11206–11214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Du, X.; Yamagata, N. Enzyme-instructed self-assembly of small d-peptides as a multiple-step process for selectively killing cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3813–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, R. Enzyme-instructed assembly and disassembly processes for targeting downregulation in cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3950–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Yan, X.; Zhang, R. Enhanced cellular uptake and nuclear accumulation of drug-peptide nanomedicines prepared by enzyme-instructed self-assembly. J. Control. Release 2020, 317, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, B.; Wang, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, X. Injectable Thermo-Responsive Peptide Hydrogels and Its Enzyme Triggered Dynamic Self-Assembly. Polymers 2024, 16, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091221
Yin B, Wang R, Guo Y, Li L, Hu X. Injectable Thermo-Responsive Peptide Hydrogels and Its Enzyme Triggered Dynamic Self-Assembly. Polymers. 2024; 16(9):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091221
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Bowen, Ruoxue Wang, Yu Guo, Liuxuan Li, and Xiuli Hu. 2024. "Injectable Thermo-Responsive Peptide Hydrogels and Its Enzyme Triggered Dynamic Self-Assembly" Polymers 16, no. 9: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091221
APA StyleYin, B., Wang, R., Guo, Y., Li, L., & Hu, X. (2024). Injectable Thermo-Responsive Peptide Hydrogels and Its Enzyme Triggered Dynamic Self-Assembly. Polymers, 16(9), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091221