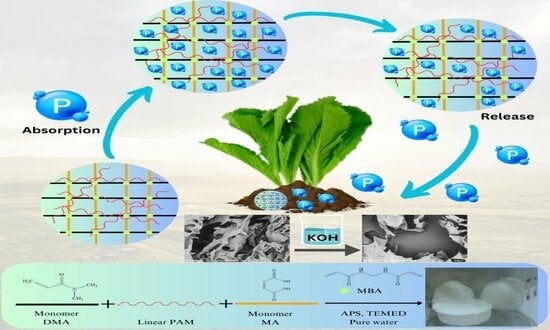
Impact of Modifications from Potassium Hydroxide on Porous Semi-IPN Hydrogel Properties and Its Application in Cultivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Semi-IPN Hydrogel
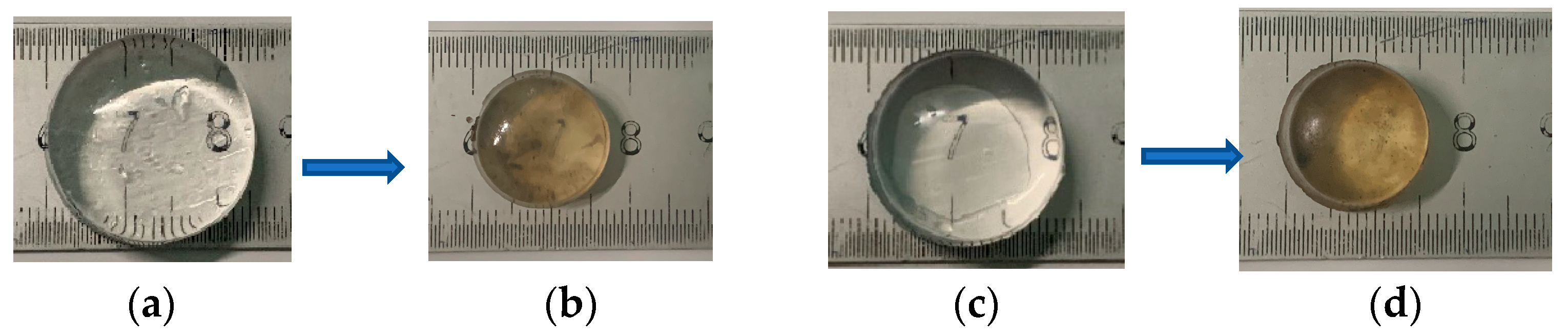
2.2.1. Preparation of Semi-IPN Hydrogel
2.2.2. Modification of Semi-IPN Hydrogel
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.4. Swelling Behavior
2.4.1. Swelling Ratio
2.4.2. Swelling Kinetics
2.5. Application for Phosphate Fertilizer
2.5.1. Phosphate Fertilizer Sorption Behavior
- ▪
- Co (mg/L): concentration of PF solution before absorption;
- ▪
- Ct (mg/L): concentration of remaining PF solution after absorption;
- ▪
- Vo (mL): volume of PF solution before absorption;
- ▪
- Vt (mL): volume of remaining PF solution after absorption;
- ▪
- M (g): weight of dried hydrogel.
2.5.2. Phosphate Fertilizer Release Behavior
2.6. The Impact of Hydrogels on Soil Properties
2.7. Plant Growth Performance
2.7.1. Prepare the Plants
2.7.2. Evaluate Plant Growth
3. Results and Discussion
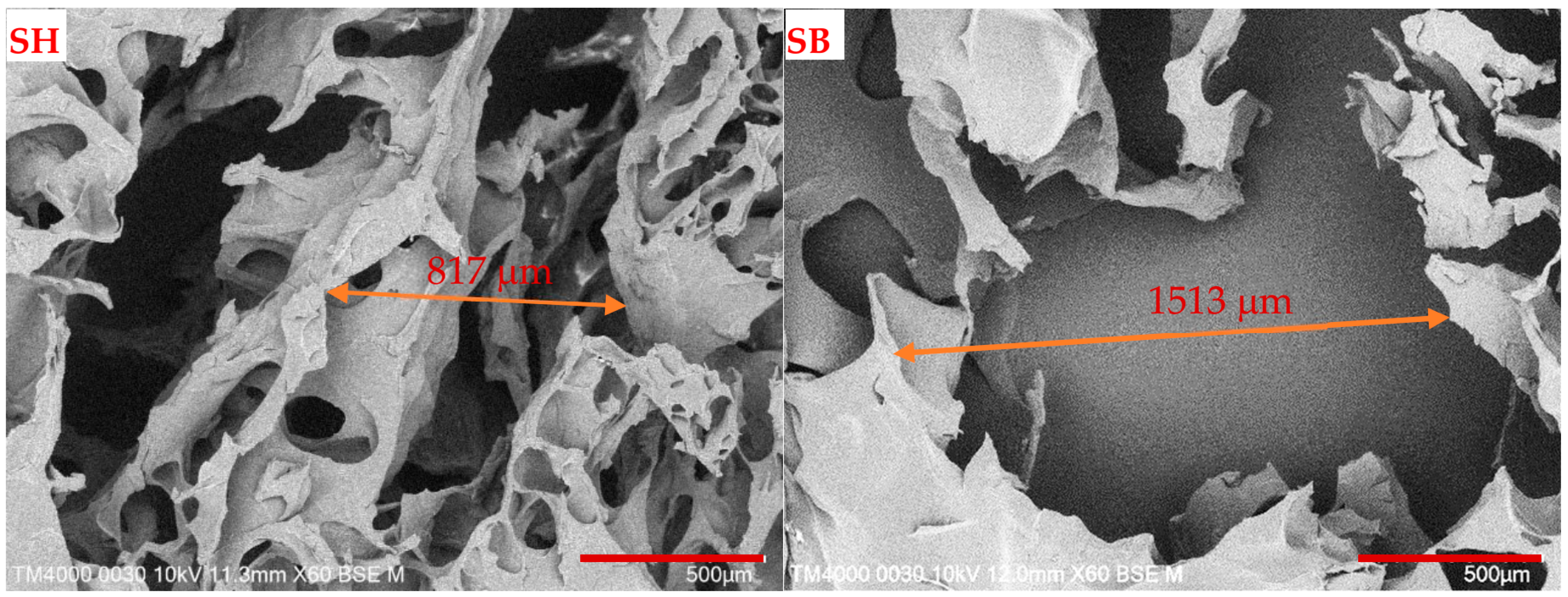
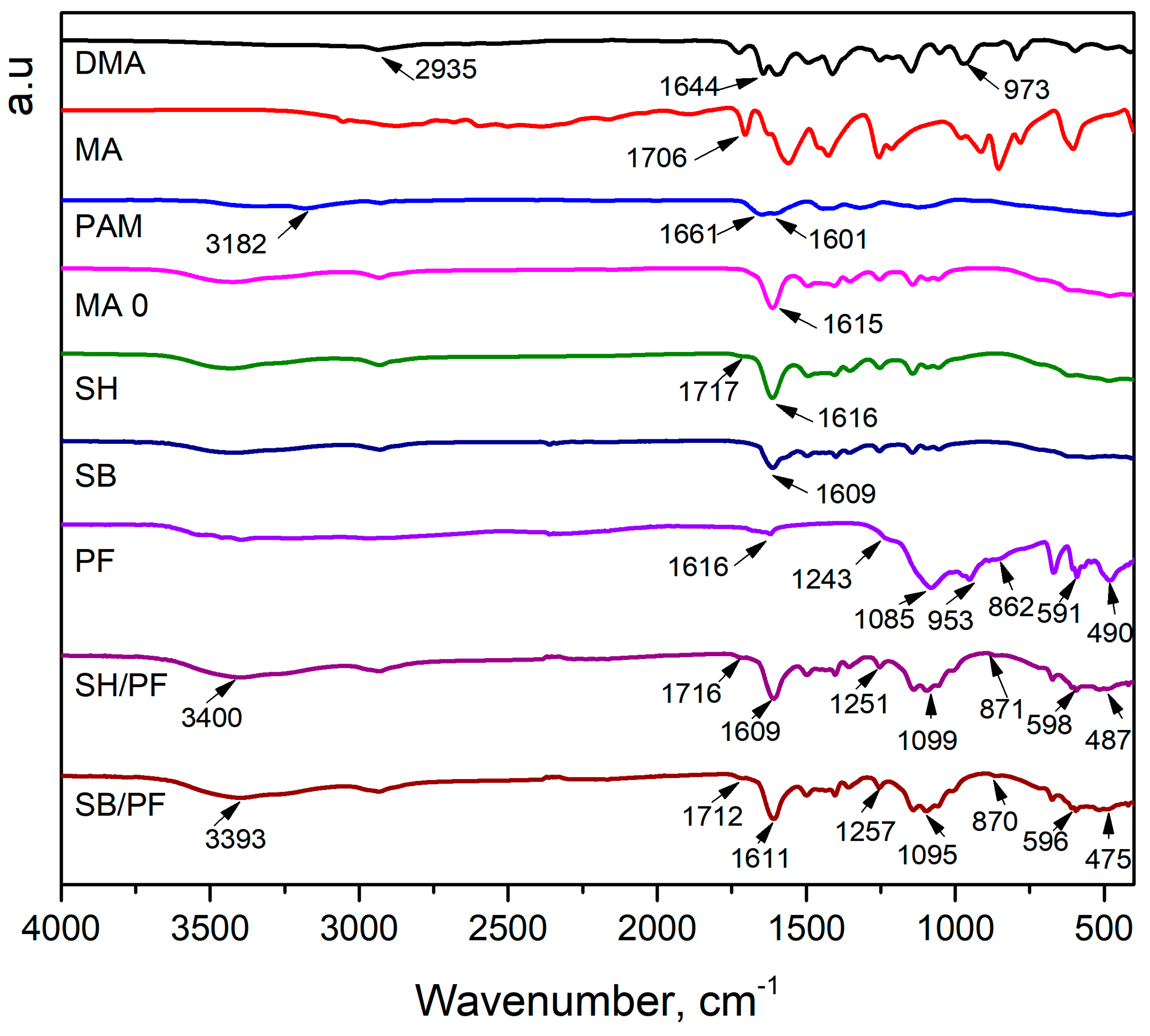
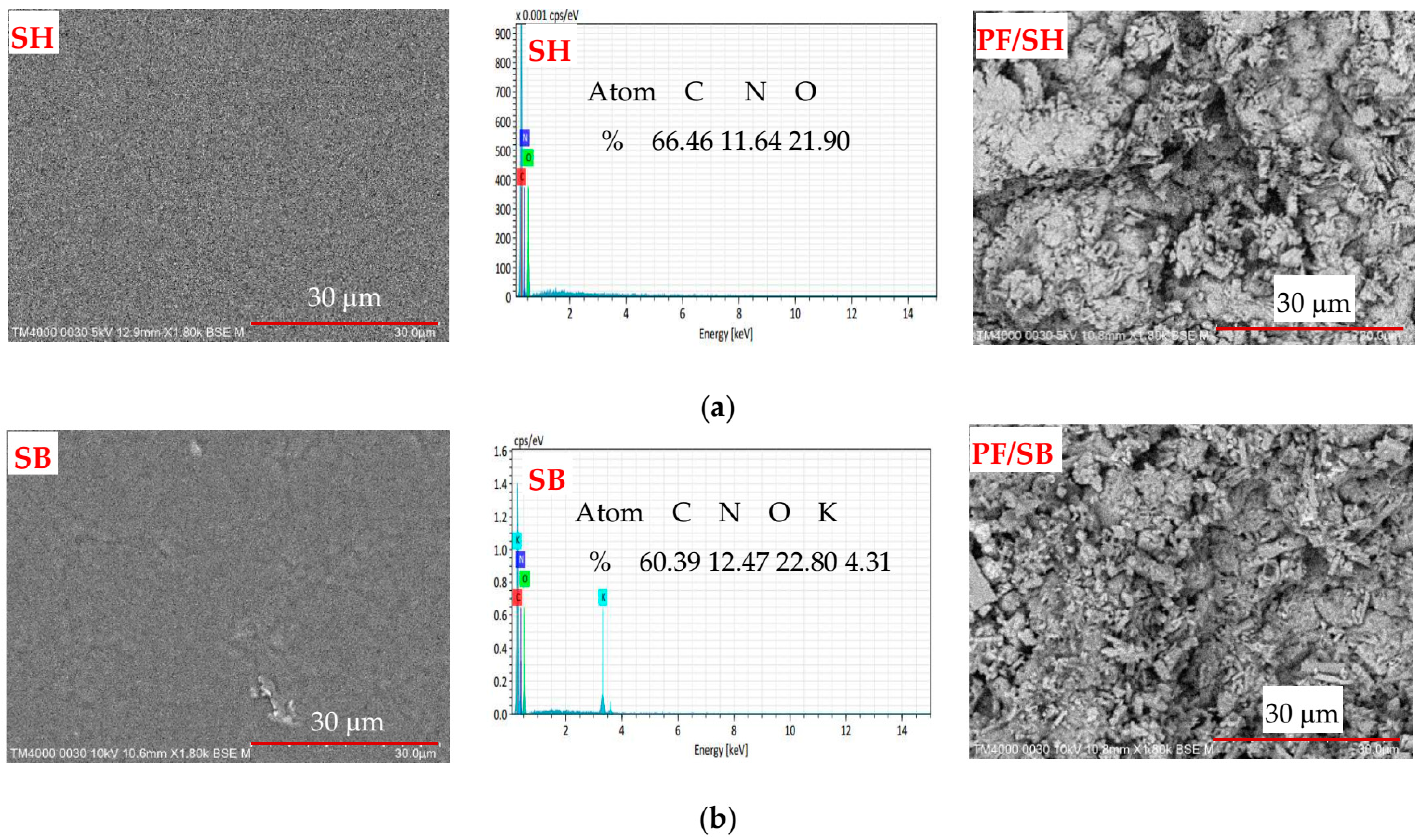
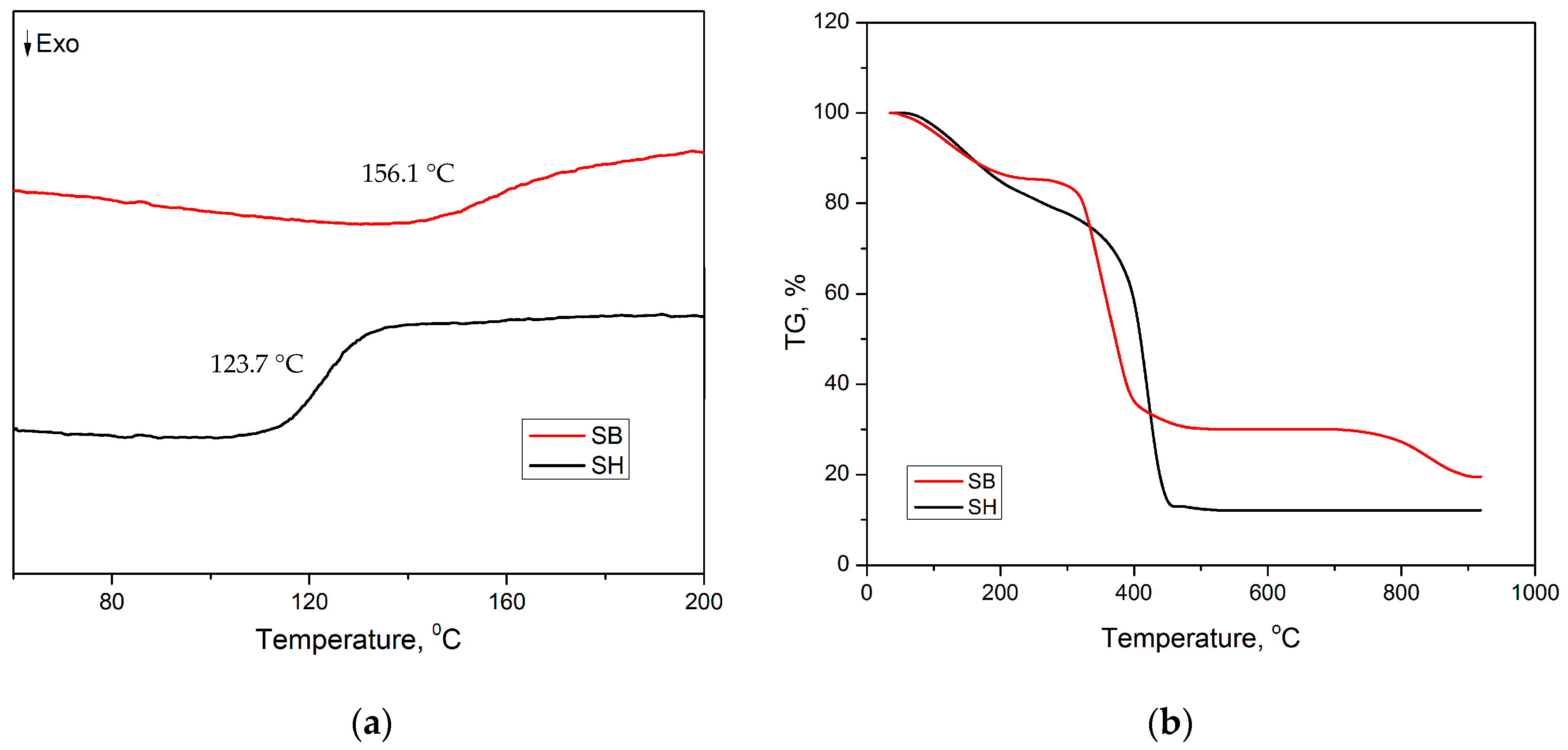
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Swelling Behavior
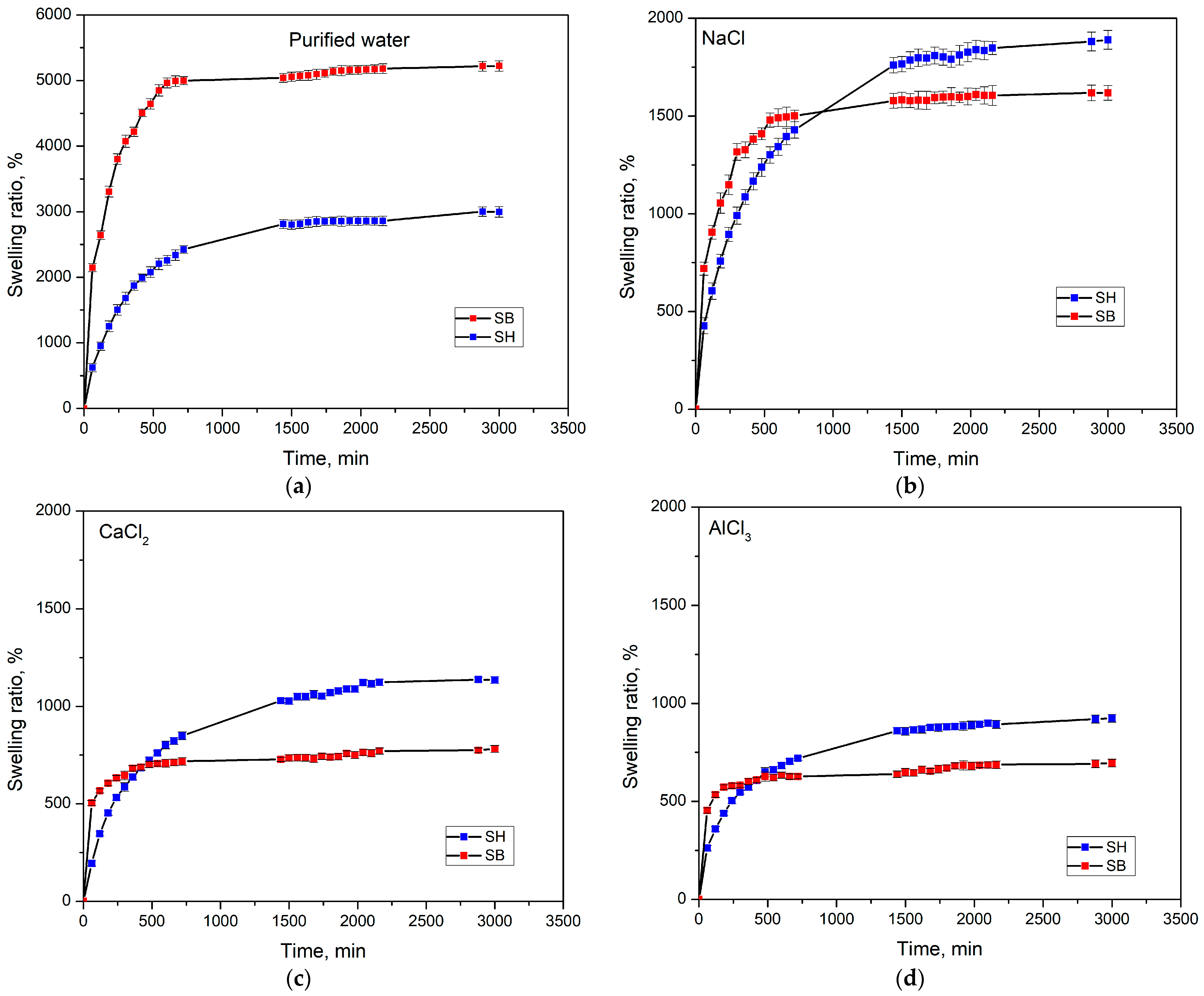
3.2.1. The Impact of Salt Environments
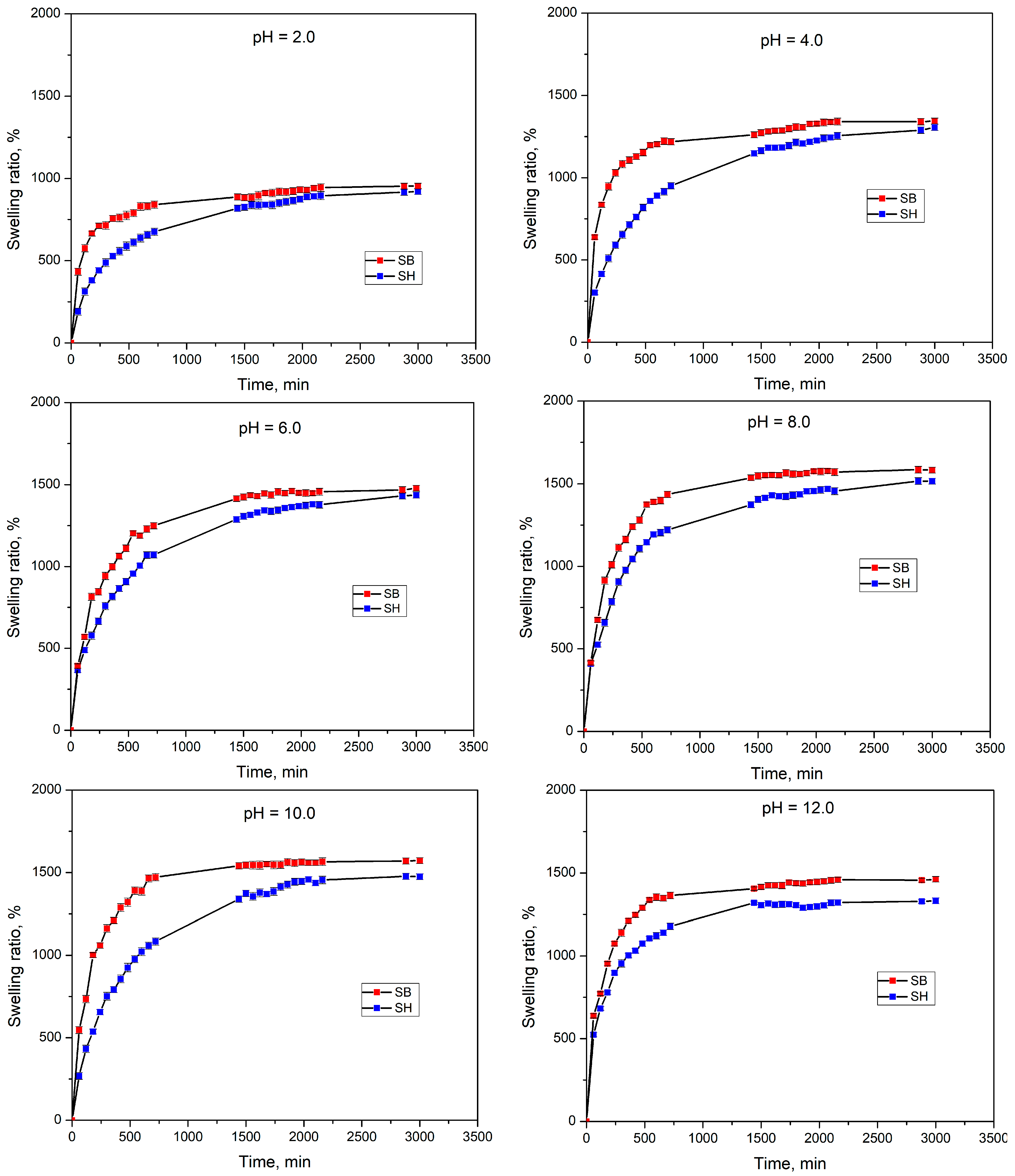
3.2.2. Swelling Behavior in pH Solutions
3.3. Release of Phosphate Fertilizer
3.3.1. Phosphate Fertilizer Sorption Behavior
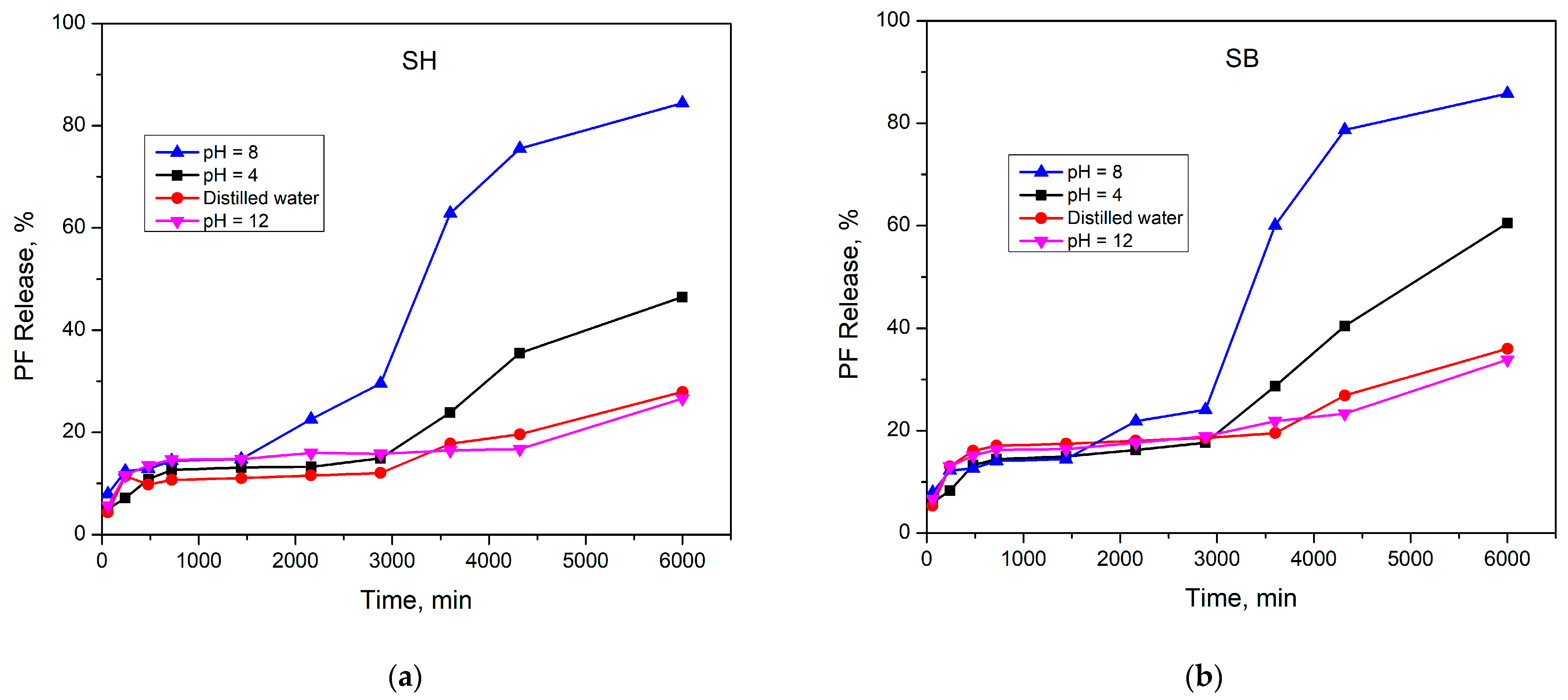
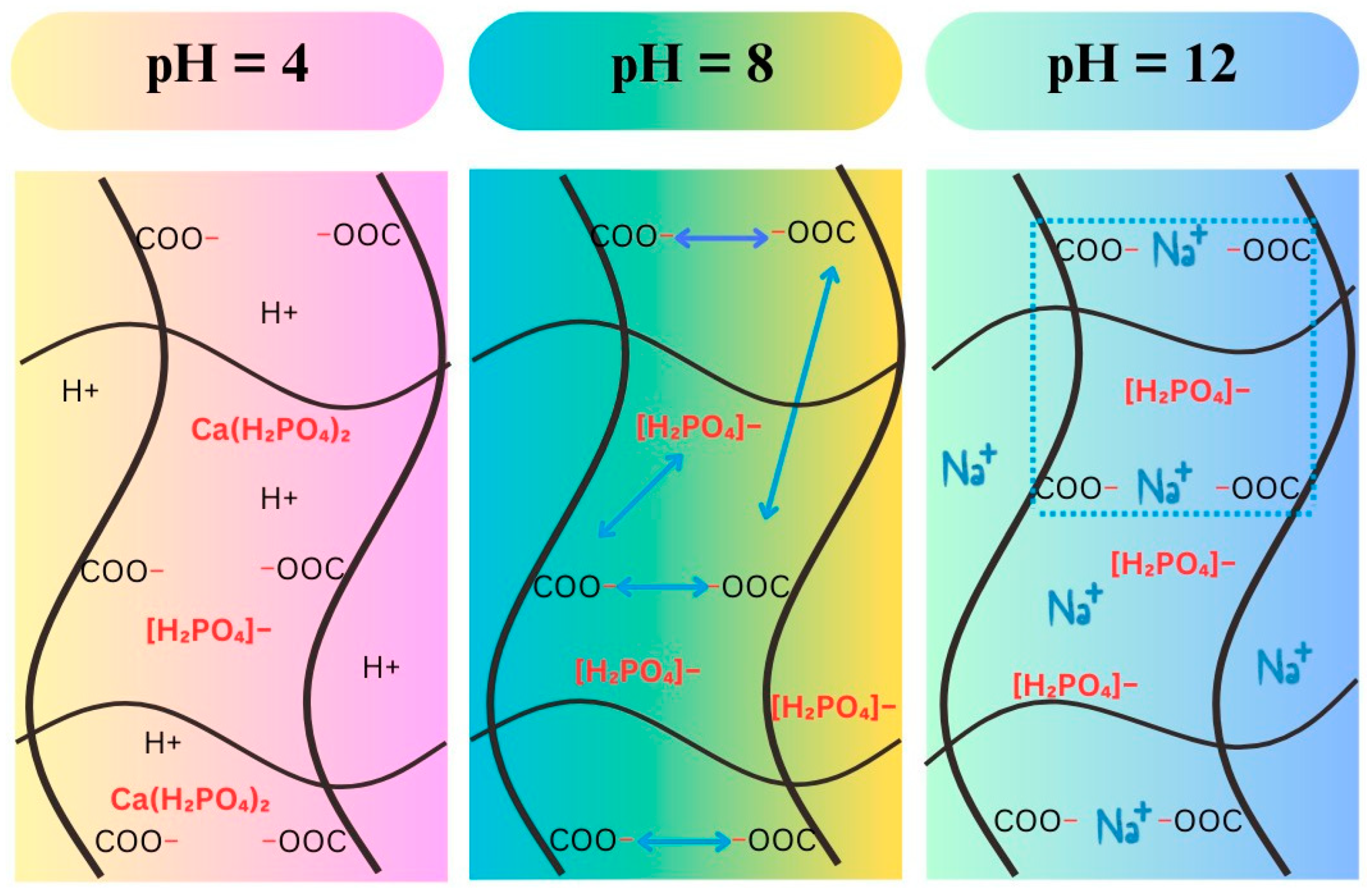
3.3.2. Phosphate Fertilizer Release Behavior
3.4. Impact of Hydrogels on Soil Properties
3.5. Plant Growth Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Lü, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Ning, P.; Liu, M. Environmentally friendly fertilizers: A review of materials used and their effects on the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, B.; Liu, M.; Lü, S. Multifunctional slow-release urea fertilizer from ethylcellulose and superabsorbent coated formulations. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, Y.; Rafii, M.Y.; Arolu, F.; Chukwu, S.C.; Salisu, M.A.; Fagbohun, I.K.; Muftaudeen, T.K.; Swaray, S.; Haliru, B.S. Superabsorbent polymer hydrogels for sustainable agriculture: A review. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, R.A. Slow release fertilizer hydrogels: A review. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 6073–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejan, P.; Khadiran, T.; Abdullah, R.; Ahmad, N. Controlled release fertilizer: A review on developments, applications and potential in agriculture. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Zeng, Q.; Li, K.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, R.; Shi, C.; Chen, T.; Xiao, C.; et al. Rapid fabrication of physically robust hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Shankar, V. Technologies for the fabrication of crosslinked polysaccharide-based hydrogels and its role in microbial three-dimensional bioprinting–A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuan, H.N.A.; Nhu, V.T.T. Synthesis and properties of pH-thermo dual responsive semi-iPN hydrogels based on N,N’-diethylacrylamide and itaconamic acid. Polymers 2020, 12, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, N.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liang, L.; An, Y.; Li, Q.; Chang, C. Biocompatible cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels with antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional hydrogels as wound dressing to enhance wound healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, H.N.A.; Phuong, H. Characterization and swelling behavior of hydrogels from N-isopropylacrylamide, N, N′-diethylacrylamide, acrylic acid, and its use for drug release. Can. J. Chem. 2023, 101, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, Y. Supramolecular adhesive hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5604–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, F.; Luo, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhuang, K.; Tan, L. Photocuring and gelatin-based antibacterial hydrogel for skin care. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 4218–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Caruso, M.R.; Milioto, S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lazzara, G. Keratin/alginate hybrid hydrogels filled with halloysite clay nanotubes for protective treatment of human hair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshallash, K.S.; Sharaf, M.; Hmdy, A.E.; Khalifa, S.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.F.; Sharaf, A.; Ibrahim, M.T.S.; Alharbi, K.; Elkelish, A. Hydrogel improved growth and productive performance of mango trees under semi-arid condition. Gels 2022, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, R.; Shi, X.; Lian, S.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, W. Synthesis of cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogel with high salt tolerance for soil conditioning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Agrawal, R.; Pfeffer, F.M.; Williams, R.; Bohidar, H.B. Hydrogels in agriculture: Prospects and challenges. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 3701–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Pirzada, T.; Opperman, C.H.; Khan, S.A. Recent advances in seed coating technologies: Transitioning toward sustainable agriculture. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 6052–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Kang, C.W. Synthesis of starch-based smart hydrogel derived from rice-cooked wastewater for agricultural use. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Gupta, R.B. Poly (N-ethylacrylamide) hydrogels for lignin separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 3406–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, H.; Goto, S.; Saito, S. Phase transition of N-substituted acrylamide gels. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 4887–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Jin, S.; Chen, S. Synthesis and characterization of fast responsive thermo-and pH-sensitive poly [(N,N-diethylacrylamide)-co-(acrylic acid)] hydrogels. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bušová, M.; Bencko, V.; Laktičová, K.V.; Holcátová, I.; Vargová, M. Risk of exposure to acrylamide. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 28, S43–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, B.; Kennedy, J.F.; Nie, J. Injectable hydrogels based on chitosan derivative/polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate/N, N-dimethylacrylamide as bone tissue engineering matrix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ma, J.; Vancso, G.J. Thermoresponsive semi-IPN hydrogel microfibers from continuous fluidic processing with high elasticity and fast actuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersen Dudu, T.; Alpaslan, D.; Aktas, N. Superabsorbent hydrogels based on N, N-dimethylacrylamide and maleic acid for applications in agriculture as water purifier and nitrogen carrier. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 8551–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, M.F.; Alam, M.M. Swelling behavior of acrylamide hydrogel in different solvents and pHs. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2005, 23, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwei, S.P.; Tuan, H.N.A.; Chiang, W.Y.; Way, T.F. Synthesis and characterization of pH and thermo dual-responsive hydrogels with a semi-IPN structure based on N-isopropylacrylamide and itaconamic acid. Materials 2018, 11, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Duan, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, G.; Ban, Q.; Lucia, L.A. A semi-interpenetrating network polyampholyte hydrogel simultaneously demonstrating remarkable toughness and antibacterial properties. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 10520–10525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.; Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; Soto, D.; Ramirez, J.; Marquez, Y.; Colina, M.; Fernández-García, M. Preparation of oxidized and grafted chitosan superabsorbents for urea delivery. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.J.; Singh, A.; Mandal, P.; Kumar, A.; Parmar, B.S. Synthesis and characterization of poly (CMC-g-cl-PAam/Zeolite) superabsorbent composites for controlled delivery of zinc micronutrient: Swelling and release behavior. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wijekoon, A.; Leipzig, N.D. 3D differentiation of neural stem cells in macroporous photopolymerizable hydrogel scaffolds. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Oropeza-Aburto, A.; Razo-Hernández, F.; Ramírez-Chávez, E.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Phospholipase DZ2 plays an important role in extraplastidic galactolipid biosynthesis and phosphate recycling in Arabidopsis roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6765–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, A.; Khayyat, M.; Azarmi-Atajan, F.; Agehara, S.; Sarkhosh, A. Soil and nutrition. In The Pomegranate: Botany, Production and Uses; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2021; pp. 285–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Whelan, M. Phosphorus activators contribute to legacy phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiriac, A.P.; Nita, L.E.; Tartau, L.; Neamtu, I.; Nistor, M.T. Semi-imprinting quercetin into poly [n, n-dimethylacrylamide-co-3, 9-divinyl-2, 4, 8, 10-tetraoxaspiro (5.5) undecane] network: Evaluation of the antioxidant character. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2338–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakan, U.; Bieerkehazhi, S.; Tolkyn, B.; Mun, G.A.; Assanov, M.; Nursultanov, M.E.; Rakhmetullayeva, R.K.; Toshtay, K.; Negim, E.S.; Ydyrys, A. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial application of copolymers based on N, N-Dimethyl acrylamide and acrylic acid. Materials 2021, 14, 6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennour, S.; Louzri, F. Study of swelling properties and thermal behavior of poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide-co-maleic acid) based hydrogels. Adv. Chem. 2014, 2014, 147398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su-Cheng, P.; Chung-Cheng, Y.; Riley, J.P. Effects of acidity and molybdate concentration on the kinetics of the formation of the phosphoantimonylmolybdenum blue complex. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 229, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, A.; Pineda, M.; Razavi, M. Assessment of soil moisture content measurement methods: Conventional laboratory oven versus halogen moisture analyzer. J. Soil Water Sci. 2020, 4, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D2216; Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Liu, Y.; Lai, Z.; Yang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Lu, M.; Chang, H.; Ding, T.; Xu, H. Thio-Michael addition of α, β-unsaturated amides catalyzed by Nmm-based ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43104–43113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaslan, D.; Erşen Dudu, T.; Kubilay, Ş.; Aktaş, N. Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible poly (maleic acid-co-citric acid) microparticles as a smart carrier for thiamine. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 6305–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.S.; Shiu, J.W.; Way, T.F.; Rwei, S.P. A thermo-responsive random copolymer of poly (NIPAm-co-FMA) for smart textile applications. Polymer 2019, 184, 121917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesanong, S.; Seangarun, C.; Boonchom, B.; Laohavisuti, N.; Chaiseeda, K.; Boonmee, W. Composition and properties of triple superphosphate obtained from oyster shells and various concentrations of phosphoric acid. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 22065–22072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheshmedzhieva, D.; Ilieva, S.; Hadjieva, B.; Galabov, B. The mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of amides: A comparative computational and experimental study of the hydrolysis of N-methylacetamide, N-methylbenzamide, and acetanilide. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2009, 22, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Saha, N.; Kitano, T.; Saha, P. Importance of viscoelastic property measurement of a new hydrogel for health care. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2009; Volume 1152, pp. 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Mahon, R.; Balogun, Y.; Oluyemi, G.; Njuguna, J. Swelling performance of sodium polyacrylate and poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) potassium salt. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaleh, H.; Atassi, Y. Up-scalable synthesis of high porous superabsorbent polymer via alkaline hydrolysis of acrylamide using microwave irradiation: Application in agriculture. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 10–26872. [Google Scholar]
- Rezanejade Bardajee, G.; Pourjavadi, A.; Soleyman, R. Novel highly swelling nanoporous hydrogel based on polysaccharide/protein hybrid backbone. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombare, N.; Mishra, S.; Shinde, R.; Siddiqui, M.Z.; Jha, U. Guar gum based hydrogel as controlled micronutrient delivery system: Mechanism and kinetics of boron release for agricultural applications. Biopolymers 2021, 112, e23418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tomlinson, M.R.; Golestanian, R.; Geoghegan, M. The interfacial behaviour of single poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide) chains as a function of pH. Nanotechnology 2007, 19, 035505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, S.K. Swelling–deswelling behavior of poly (acrylamide-co-maleic acid) hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Souza, D.; Fernandes, G.M.; Dias, B.C.; Stefanelli Junior, J.R.; Sequinel, R.; da Silveira Petruci, J.F. A Green Analytical Methodology for Detecting Adulteration in Automotive Urea-SCR Products Using Microfluidic-Paper Analytical Devices. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paarakh, M.P.; Jose, P.A.; Setty, C.M.; Peterchristoper, G.V. Release kinetics–concepts and applications. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Technol. 2018, 8, 12–20. [Google Scholar]





| Model | Mathematical Equation | |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-order (Z–O) | (8) | |
| First-order (F–O) | (9) | |
| Higuchi (H) | (10) | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas (K–P) | (11) |
| Hydrogel | Storage Modulus, G′ (Pa) | Loss Modulus, G″ (Pa) | Viscosity, η* (Pa·s) | Compressive Stress (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | 410.6 ± 10.9 | 6.2 ± 0.1 | 66.4 ± 1.7 | 585.8 ± 52.8 |
| SB | 273.6 ± 9.8 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 43.5 ± 1.6 | 436.7 ± 69.9 |
| SRmax,exp, % | SRmax,the, % | ks | n | k | D | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | SH | 3450.22 ± 43.56 | 3984.06 | 7.11 × 10−5 | 0.39 | 0.054 | 1.68 × 10−5 | 0.9478 |
| SB | 5222.11 ± 68.78 | 5276.34 | 2.15 × 10−4 | 0.18 | 0.245 | 5.96 × 10−5 | 0.8018 | |
| NaCl | SH | 1889.43 ± 61.49 | 2109.70 | 6.86 × 10−4 | 0.33 | 0.080 | 2.86 × 10−5 | 0.9618 |
| SB | 1617.93 ± 57.24 | 1669.45 | 1.50 × 10−4 | 0.16 | 0.300 | 6.97 × 10−7 | 0.8500 | |
| CaCl2 | SH | 1136.74 ± 67.43 | 1282.05 | 5.22 × 10−4 | 0.34 | 0.078 | 3.00 × 10−5 | 0.9536 |
| SB | 781.97 ± 43.24 | 781.25 | 1.27 × 10−4 | 0.08 | 0.531 | 8.38 × 10−11 | 0.9125 | |
| AlCl3 | SH | 924.32 ± 48.77 | 998.00 | 4.08 × 10−4 | 0.26 | 0.142 | 7.88 × 10−6 | 0.9671 |
| SB | 695.79 ± 53.71 | 700.28 | 1.14 × 10−4 | 0.07 | 0.560 | 1.71 × 10−11 | 0.9139 |
| SRmax,exp | SRmax,the | ks | n | k | D | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 2 | SH | 920.51 ± 14.69 | 1008.06 | 3.05 × 10−4 | 0.30 | 0.101 | 1.69 × 10−5 | 0.9695 |
| SB | 953.70 ± 13.30 | 978.47 | 9.08 × 10−4 | 0.14 | 0.333 | 1.95 × 10−5 | 0.9171 | |
| pH = 4 | SH | 1331.35 ± 22.03 | 1396.65 | 5.47 × 10−4 | 0.19 | 0.233 | 1.54 × 10−6 | 0.9216 |
| SB | 1461.85 ± 20.19 | 1508.30 | 7.50 × 10−4 | 0.16 | 0.295 | 8.19 × 10−5 | 0.8378 | |
| pH = 6 | SH | 1435.56 ± 22.36 | 1584.79 | 1.98 × 10−4 | 0.31 | 0.094 | 1.90 × 10−5 | 0.9763 |
| SB | 1477.69 ± 20.32 | 1715.27 | 2.82 × 10−4 | 0.26 | 0.134 | 1.91 × 10−5 | 0.9051 | |
| pH = 8 | SH | 1516.46 ± 17.89 | 1628.66 | 2.58 × 10−4 | 0.28 | 0.117 | 1.33 × 10−5 | 0.9316 |
| SB | 1585.08 ± 20.02 | 1680.67 | 4.07 × 10−4 | 0.24 | 0.163 | 1.34 × 10−5 | 0.8419 | |
| pH = 10 | SH | 1477.08 ± 15.79 | 1692.05 | 1.57 × 10−4 | 0.36 | 0.066 | 3.89 × 10−5 | 0.9633 |
| SB | 1572.22 ± 15.36 | 1647.45 | 5.35 × 10−4 | 0.20 | 0.222 | 4.34 × 10−5 | 0.8445 | |
| pH = 12 | SH | 1304.72 ± 20.39 | 1440.92 | 2.01 × 10−4 | 0.32 | 0.087 | 2.16 × 10−5 | 0.9782 |
| SB | 1344.59 ± 19.19 | 1377.41 | 8.11 × 10−4 | 0.14 | 0.351 | 2.46 × 10−5 | 0.8765 |
| Model | SH | SB | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 4 | pH = 8 | pH = 12 | pH = 4 | pH = 8 | pH = 12 | ||
| Z–O | Co | 9.9259 | 6.3337 | 20.8530 | 9.1705 | 4.7774 | 20.9525 |
| ko | −0.0144 | −0.0282 | −0.0046 | −0.0164 | −0.0301 | −0.0065 | |
| R2 | 0.8939 | 0.9104 | 0.7466 | 0.8835 | 0.8716 | 0.8692 | |
| F–O | Co | 16.4233 | 19.9355 | 20.8927 | 17.3744 | 20.3443 | 21.8828 |
| k1 | −3 × 10−4 | −4 × 10−4 | −2 × 10−4 | −3 × 10−4 | −4 × 10−4 | −2 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 0.9041 | 0.9307 | 0.5969 | 0.8964 | 0.9140 | 0.7128 | |
| H | kH | 0.0110 | 0.0134 | 0.0073 | 0.0106 | 0.0132 | 0.0085 |
| R2 | 0.7938 | 0.8117 | 0.7543 | 0.7424 | 0.7492 | 0.8374 | |
| K–P | n | 0.4280 | 0.5116 | 0.2443 | 0.4332 | 0.5040 | 0.2736 |
| KKP | 0.0155 | 0.0078 | 0.0956 | 0.0137 | 0.0079 | 0.0729 | |
| R2 | 0.8407 | 0.7824 | 0.8308 | 0.8087 | 0.7177 | 0.8786 | |
| Days | 0 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF/SH/Soil | 3.5 ± 0.11 | 5.3 ± 0.22 | 6.2 ± 0.19 | 12.8 ± 0.42 | 14.2 ± 0.46 | - | - |
| PF/SB/Soil | 3.5 ± 0.14 | 5.6 ± 0.17 | 6.9 ± 0.21 | 13.6 ± 0.43 | 15.3 ± 0.49 | 17.2 ± 0.54 | 17.6 ± 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuan, H.N.A.; Phan, B.T.C.; Giang, H.N.; Nguyen, G.T.; Le, T.D.H.; Phuong, H. Impact of Modifications from Potassium Hydroxide on Porous Semi-IPN Hydrogel Properties and Its Application in Cultivation. Polymers 2024, 16, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091195
Tuan HNA, Phan BTC, Giang HN, Nguyen GT, Le TDH, Phuong H. Impact of Modifications from Potassium Hydroxide on Porous Semi-IPN Hydrogel Properties and Its Application in Cultivation. Polymers. 2024; 16(9):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091195
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuan, Huynh Nguyen Anh, Bui Thi Cam Phan, Ha Ngoc Giang, Giang Tien Nguyen, Thi Duy Hanh Le, and Ho Phuong. 2024. "Impact of Modifications from Potassium Hydroxide on Porous Semi-IPN Hydrogel Properties and Its Application in Cultivation" Polymers 16, no. 9: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091195
APA StyleTuan, H. N. A., Phan, B. T. C., Giang, H. N., Nguyen, G. T., Le, T. D. H., & Phuong, H. (2024). Impact of Modifications from Potassium Hydroxide on Porous Semi-IPN Hydrogel Properties and Its Application in Cultivation. Polymers, 16(9), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091195