The Synergistic Effect of Carbon Black/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Fillers on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of EPDM Composites after Exposure to High-Pressure Hydrogen Gas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of EPDM Hybrid Composites
2.3. Viscosity and Curing Behavior
2.4. Crosslink Density
2.5. Payne Effect
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Mechanical Properties
2.8. Hydrogen Permeation Properties
2.9. Remaining Hydrogen Content
2.10. Volume Change and Mechanical Properties of the EPDM Hybrid Composites after Exposure to High-Pressure Hydrogen Gas
3. Results and Discussion
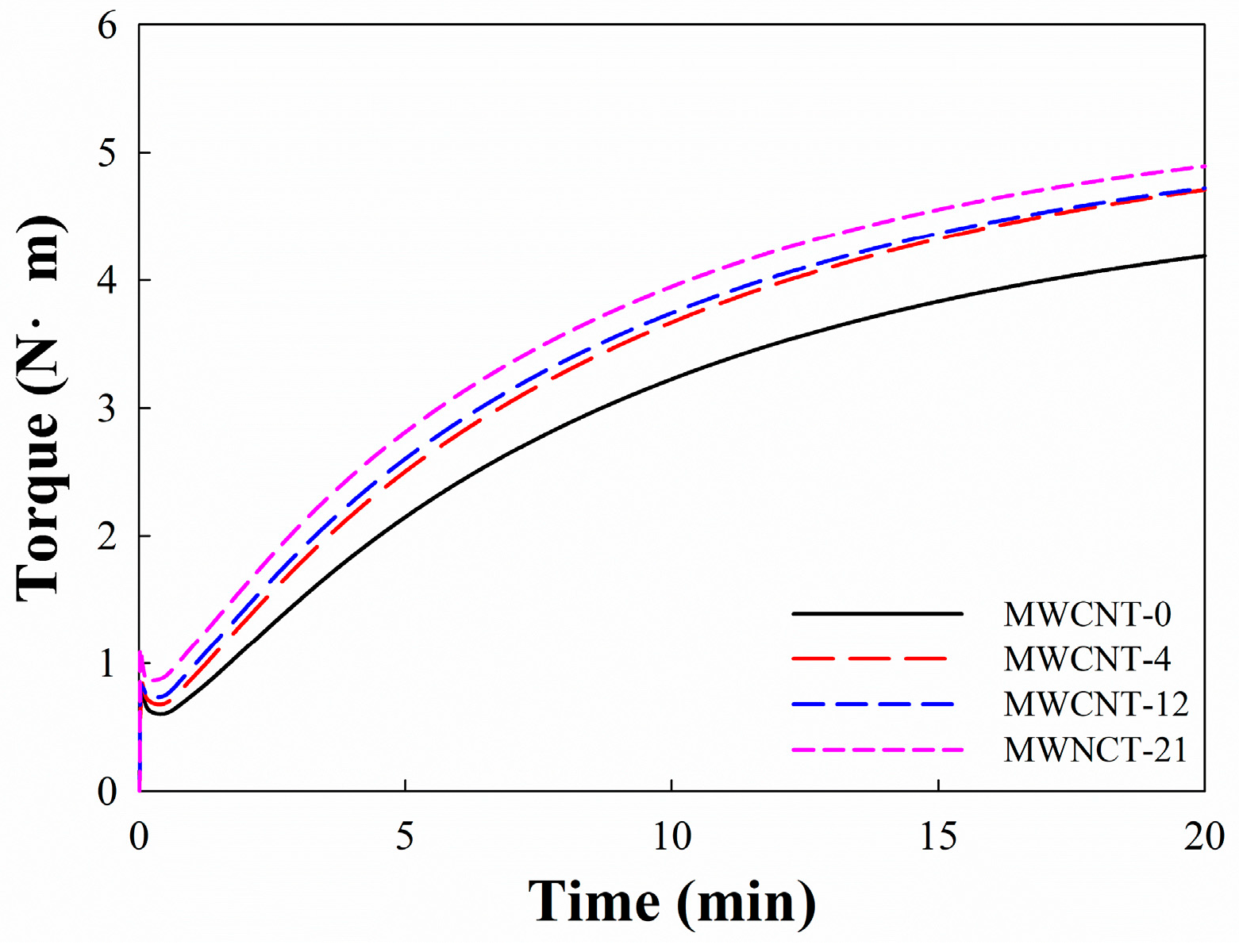
3.1. Viscosity and Curing Behavior
3.2. Crosslink Density of EPDM/CB/MWCNT Composites
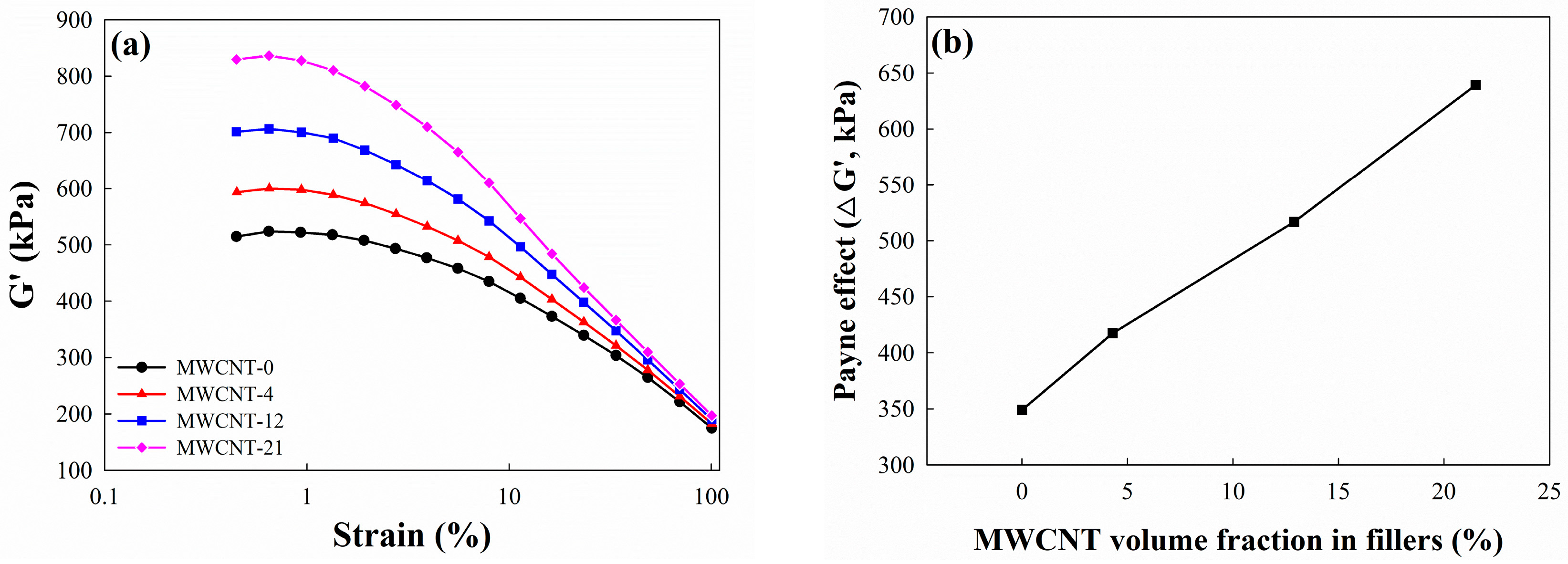
3.3. Payne Effect of EPDM Hybrid Composites
3.4. Physical and Mechanical Properties of EPDM/CB/MWCNT Composites
3.5. Hydrogen Permeation Properties of EPDM/CB/MWCNT Hybrid Composites
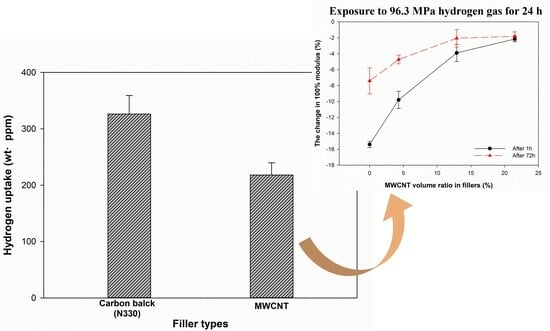
3.6. Hydrogen Uptake of EPDM/CB/MWCNT Composites
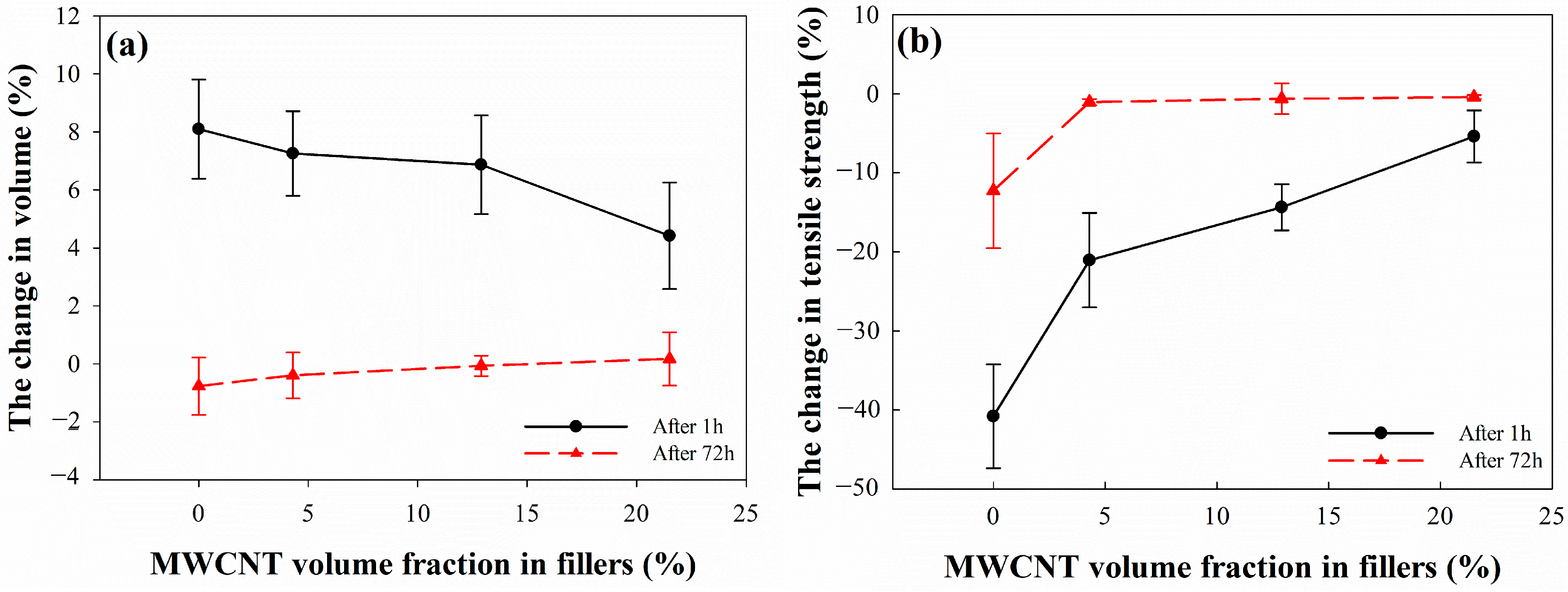
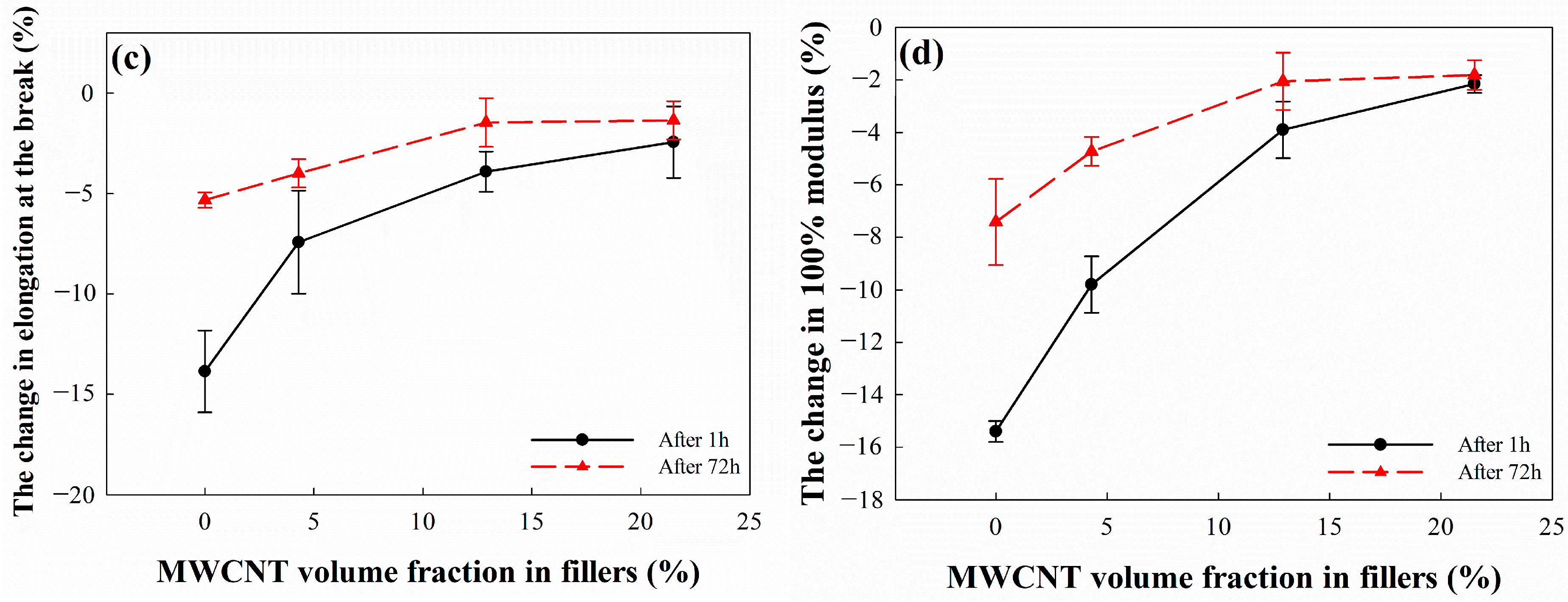
3.7. Change in Mechanical Properties of EPDM/CB/MWCNT Hybrid Composites after 96.3 MPa Hydrogen Gas Exposure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaefer, R.J. Mechanical properties of rubber. In Harris’ Shock and Vibration Handbook, 6th ed.; Piersol, A., Paez, T., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Companies Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 33.1–33.18. [Google Scholar]
- Kohls, D.J.; Beaucage, G. Rational design of reinforced rubber. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Salim, Z.A.S.; Hassan, A.; Ismail, H. A review on hybrid fillers in rubber composites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Park, B.H.; Song, H. Influence of filler type and content on properties of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) compound reinforced with carbon black or silica. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2004, 15, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurdina, A.; Mariatti, M.; Samayamutthirian, P. Effect of single-mineral filler and hybrid-mineral filler additives on the properties of polypropylene composites. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2009, 15, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junkong, P.; Kueseng, P.; Wirasate, S.; Huynh, C.; Rattanasom, N. Cut growth and abrasion behaviour, and morphology of natural rubber filled with MWCNT and MWCNT/carbon black. Polym. Test. 2015, 41, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Huang, G.; Zhang, P.; Nie, Y.; Weng, G.; Wu, J. Synergistic reinforcement of nanoclay and carbon black in natural rubber. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthivel, K.; Manikandan, K.; Prabu, B. Studies on the mechanical properties of carbon black/halloysite nanotube hybrid fillers in nitrile rubber nanocomposites. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 3627–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.A.; Ahmad, H. The properties of acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) composite with halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) and silica or carbon black. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2013, 52, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malas, A.; Das, C.K. Carbon black–clay hybrid nanocomposites based upon EPDM elastomer. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanasom, N.; Prasertsri, S. Mechanical properties, gas permeability and cut growth behaviour of natural rubber vulcanizates: Influence of clay types and clay/carbon black ratios. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Ramly, A.; Othman, N. The effect of carbon black/multiwall carbon nanotube hybrid fillers on the properties of natural rubber nanocomposites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, G.; Swain, S.K. Dispersion of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in polyacrylonitrile-co-starch copolymer matrix for enhancement of electrical, thermal, and gas barrier properties. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanath Balendran, B.; Yaragalla, S. Epoxidized natural rubber/acid functionalized carbon nanotubes composites for enhanced thermo-mechanical and oxygen barrier performance. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahamatifard, F.; Rodrigue, D.; Park, K.; Frikha, S.; Mighri, F. Natural rubber nanocomposites: Effect of carbon black/multi-walled carbon nanotubes hybrid fillers on the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2021, 60, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddini, S.; Bosnyak, C.; Henderson, N.; Ellison, C.; Paul, D. Nanocomposites from styrene–butadiene rubber (SBR) and multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) part 2: Mechanical properties. Polymer 2015, 56, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Y. Synergistic effects of carbon nanotubes and carbon black on the fracture and fatigue resistance of natural rubber composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, M.; Cipolletti, V.; Musto, S.; Cioppa, S.; Peli, G.; Mauro, M.; Gaetano, G.; Agnelli, S.; Theconis, R.; Kumar, V. Recent advancements in rubber nanocomposites. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2014, 87, 417–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnelli, S.; Cipolletti, V.; Musto, S.; Coombs, M.; Conzatti, L.; Panadini, S.; Ricco, T.; Galimberti, M. Interactive effects between carbon allotrope fillers on the mechanical reinforcement of polyisoprene based nanocomposites. EXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryu, S.R.; Sung, J.W.; Lee, D.J. Strain-induced crystallization and mechanical properties of NBR composites with carbon nanotube and carbon black. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2012, 85, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wu, J.; Zhan, Y.; Xia, H. Carbon nanotubes/carbon black synergistic reinforced natural rubber composites. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2009, 38, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Angelini, G. MWCNTs elastomer nanocomposite, part 1: The addition of MWCNTs to a natural rubber-based carbon black-filled rubber compound. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostr. 2009, 17, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, H.; Fritzsche, J.; Das, A.; Stockelhuber, K.; Jurk, R.; Heinrich, G.; Kluppel, M. Advanced elastomer nano-composites based on CNT-hybrid filler systems. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaptong, P.; Sirisinha, C.; Thepsuwan, U.; Sae-Oui, P. Properties of natural rubber reinforced by carbon black-based hybrid fillers. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, N.; Tang, Y.; Ye, L.; Fang, L. Silicone rubber nanocomposites containing a small amount of hybrid fillers with enhanced electrical sensitivity. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, M.; Coombs, M.; Riccio, P.; Riscco, T.; Passera, S.; Pandini, S.; Conzatti, L.; Ravasio, A.; Tritto, I. The role of CNTs in promoting hybrid filler networking and synergism with carbon black in the mechanical behavior of filled polyisoprene. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L. Mechanical, electrical and spectroscopic investigations of carbon nanotube-reinforced elastomers. Vib. Spectrosc. 2009, 51, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L.; Rahmani, M.; Belin, C.; Bruneel, J.L.; EI Bounia, N.E. Blends of carbon blacks and multiwall carbon nanotubes as reinforcing fillers for hydrocarbon rubbers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, L. Effect of the topology of carbon-based nanofillers on the filler networks and gas barrier properties of rubber composites. Materials 2020, 13, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, Y.Q.; Song, M. Comparative study of carbon-based nanofillers for improving the properties of HDPE for potential applications in food tray packaging. Polym. Compos. 2020, 28, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Nishimura, S. Penetrated hydrogen content and volume inflation in unfilled NBR exposed to high-pressure hydrogen–What are the characteristics of unfilled-NBR dominating them? Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18392–18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, A.; Yamabe, T.; Sato, H.; Uchida, K.; Nakayama, J.; Yamabe, J.; Nishimura, S. A visualizing study of blister initiation behavior by gas decompression. Tribol. Online 2013, 8, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promchim, J.; Kangkin, S.; Niltui, P.; Wimolmala, E.; Sombatsompop, N. Swelling and mechanical properties of (acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber)/(hydrogenated acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber) blends with precipitated silica filled in gasohol fuels. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2016, 22, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Choi, M.C.; Lee, J.H.; Yun, Y.M.; Jang, J.S.; Chung, N.K.; Jeon, S.K.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Effect of the high-pressure hydrogen gas exposure in the silica-filled EPDM sealing composites with different silica content. Polymers 2022, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.K.; Lee, C.H.; Son, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Baek, U.B.; Chung, K.S.; Choi, M.C.; Bae, J.W. Filler effects on H2 diffusion behavior in nitrile butadiene rubber blended with carbon black and silica fillers of different concentrations. Polymers 2022, 14, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.K.; Baek, U.B.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, M.C.; Bae, J.W. Hydrogen gas permeation in peroxide-crosslinked ethylene propylene diene monomer polymer composites with carbon black and silica fillers. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J., Jr. Statistical mechanics of cross-linked polymer networks II. Swelling. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornell University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Hrnjak-Murgić, Z.; Jelenčić, J.; Bravar, M.; Marović, M. Influence of the network on the interaction parameter in system EPDM vulcanizate–solvent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S.; Kim, C.; Chung, N.K. Temperature-Dependence Study on the Hydrogen Transport Properties of Polymers Used for Hydrogen Infrastructure. Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 2021, 30, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.K.; Kim, I.G.; Jeon, S.K.; Kim, K.T.; Baek, U.B.; Nahm, S.H. Volumetric analysis technique for analyzing the transport properties of hydrogen gas in cylindrical-shaped rubbery polymers. Polym. Test. 2021, 99, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Jung, J.K. Investigation of the Gas Permeation Properties Using the Volumetric Analysis Technique for Polyethylene Materials Enriched with Pure Gases under High Pressure: H2, He, N2, O2 and Ar. Polymers 2023, 15, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, A.; Whittaker, R. Low strain dynamic properties of filled rubbers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1971, 44, 440–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Payne effect of carbon black filled natural rubber compounds and their carbon black gels. Polymer 2019, 185, 121953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.B.; Mansilla, M.A.; Monsalve, L.N.; Bilbao, E.; Garraza, A.L.R.; Escobar, M.M. Elucidating the interactions between carbon nanotubes and carbon black with styrene butadiene rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikelispää, M.; Das, A.; Dierkes, W.; Vuorinen, J. The effect of partial replacement of carbon black by carbon nanotubes on the properties of natural rubber/butadiene rubber compound. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3153–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Qi, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Influence of fillers on free volume and gas barrier properties in styrene-butadiene rubber studied by positrons. Polymer 2005, 46, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Maria, H.J.; George, S.C.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Transport characteristics of organic solvents through carbon nanotube filled styrene butadiene rubber nanocomposites: The influence of rubber–filler interaction, the degree of reinforcement and morphology. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 11217–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liao, B.; Zhang, G. A review on effect of hydrogen on rubber seals used in the high-pressure hydrogen infrastructure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 23721–23738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, J.; Nishimura, S. Influence of fillers on hydrogen penetration properties and blister fracture of rubber composites for O-ring exposed to high-pressure hydrogen gas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 1977–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Ingredients (phr) | MWCNT-0 | MWCNT-4 | MWCNT-12 | MWCNT-21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 100 | 90 | 70 | 50 |
| EPDM/MWCNT MB | 0 | 11 (a) | 33 (b) | 55 (c) |
| Carbon black | 40 | 38.3 | 34.8 | 31.4 |
| Zinc oxide | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Stearic acid | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| DCP | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| TAC | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Volume fraction of MWCNT in fillers (%) | 0 | 4.3 | 12.9 | 21.5 |
| Properties | Parameters | MWCNT-0 | MWCNT-4 | MWCNT-12 | MWCNT-21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical property | Mooney viscosity (MU) | 90.3 | 102.6 | 106.9 | 113.0 |
| Cure characteristics | ML (N·m) | 0.60 | 0.68 | 0.73 | 0.86 |
| MH (N·m) | 4.19 | 4.71 | 4.72 | 4.89 | |
| Δt (N·m) | 3.59 | 4.03 | 3.99 | 4.03 | |
| T10 (min) | 1.58 | 1.43 | 1.34 | 1.27 | |
| T90 (min) | 14.95 | 14.81 | 14.54 | 14.30 | |
| Cure rate index (N·m/min) | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.37 |
| Properties | MWCNT-0 | MWCNT-4 | MWCNT-12 | MWCNT-21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 68 | 70 | 74 | 75 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 23.4 ± 1.0 | 21.6 ± 0.4 | 21.1 ± 1.9 | 21.3 ± 1.5 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 340 ± 6.9 | 319 ± 3.1 | 282 ± 21.8 | 271 ± 19.1 |
| 100% modulus (MPa) | 3.8 ± 0.0 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 6.8 ± 0.3 |
| MWCNT Volume Fraction in Fillers (%) | Permeability Coefficient (×10−10 mol/m·s·MPa) | Diffusivity Coefficient (×10−9 m2/s) | Solubility Coefficient (mol/m3·MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8.2 ± 0.05 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 39.8 ± 1.4 |
| 4.3 | 7.8 ± 0.04 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 37.3 ± 0.7 |
| 12.9 | 7.9 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 35.9 ± 0.4 |
| 21.5 | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 34.7 ± 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.; Bae, J.; Lee, J.; Yun, Y.; Jeon, S.; Chung, N.; Jung, J.; Baek, U.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; et al. The Synergistic Effect of Carbon Black/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Fillers on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of EPDM Composites after Exposure to High-Pressure Hydrogen Gas. Polymers 2024, 16, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081065
Kang H, Bae J, Lee J, Yun Y, Jeon S, Chung N, Jung J, Baek U, Lee J, Kim Y, et al. The Synergistic Effect of Carbon Black/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Fillers on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of EPDM Composites after Exposure to High-Pressure Hydrogen Gas. Polymers. 2024; 16(8):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081065
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Hyunmin, Jongwoo Bae, Jinhyok Lee, Yumi Yun, Sangkoo Jeon, Nakkwan Chung, Jaekap Jung, Unbong Baek, Jihun Lee, Yewon Kim, and et al. 2024. "The Synergistic Effect of Carbon Black/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Fillers on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of EPDM Composites after Exposure to High-Pressure Hydrogen Gas" Polymers 16, no. 8: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081065
APA StyleKang, H., Bae, J., Lee, J., Yun, Y., Jeon, S., Chung, N., Jung, J., Baek, U., Lee, J., Kim, Y., & Choi, M. (2024). The Synergistic Effect of Carbon Black/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Fillers on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of EPDM Composites after Exposure to High-Pressure Hydrogen Gas. Polymers, 16(8), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081065