Recent Progress of Anti-Freezing, Anti-Drying, and Anti-Swelling Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications
Abstract
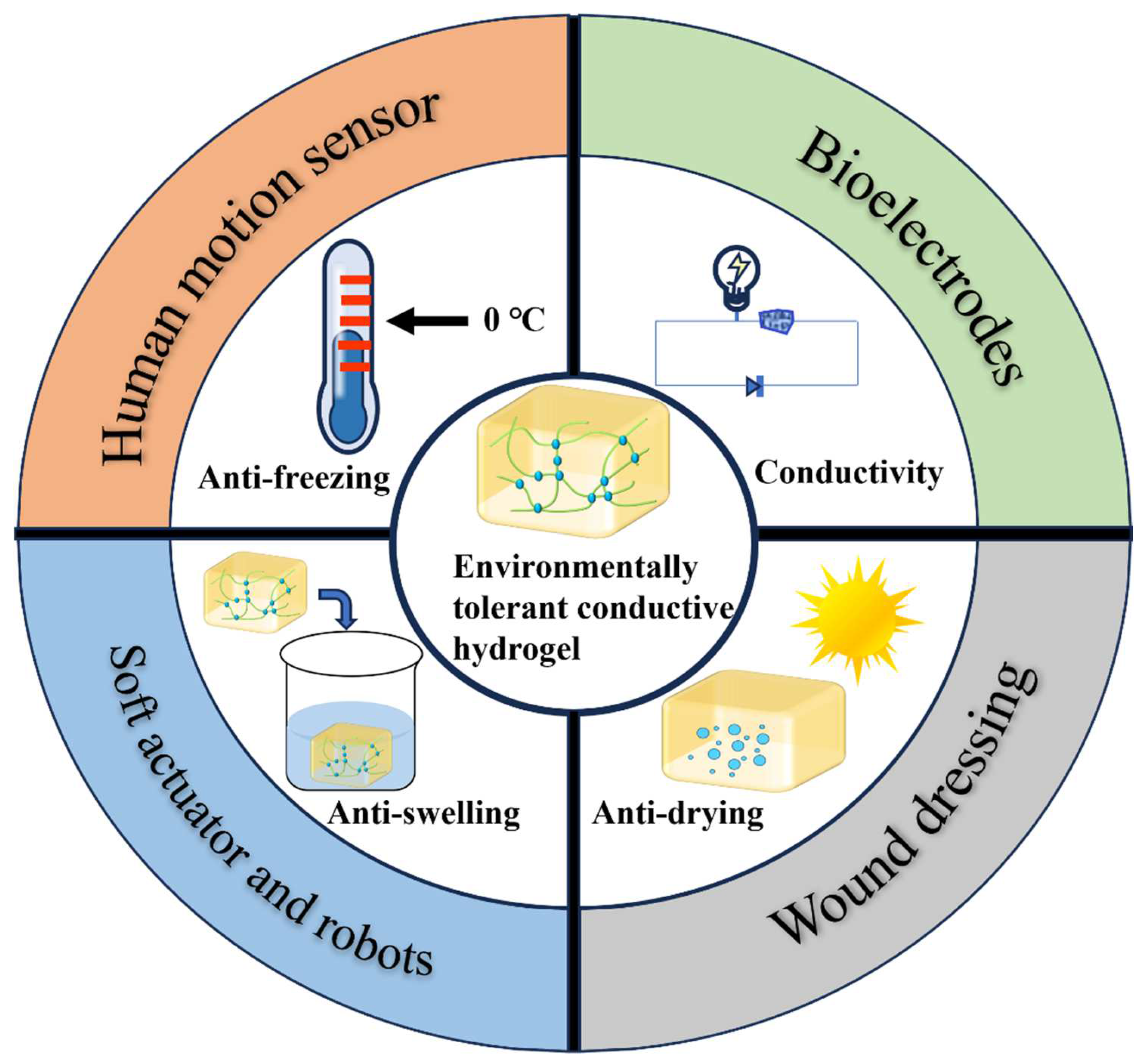
1. Introduction
2. Structure Design and ETCH Preparation Methods
2.1. ETCHs with Anti-Freezing and Anti-Drying Characteristics
2.1.1. Immersion in Salt Solution
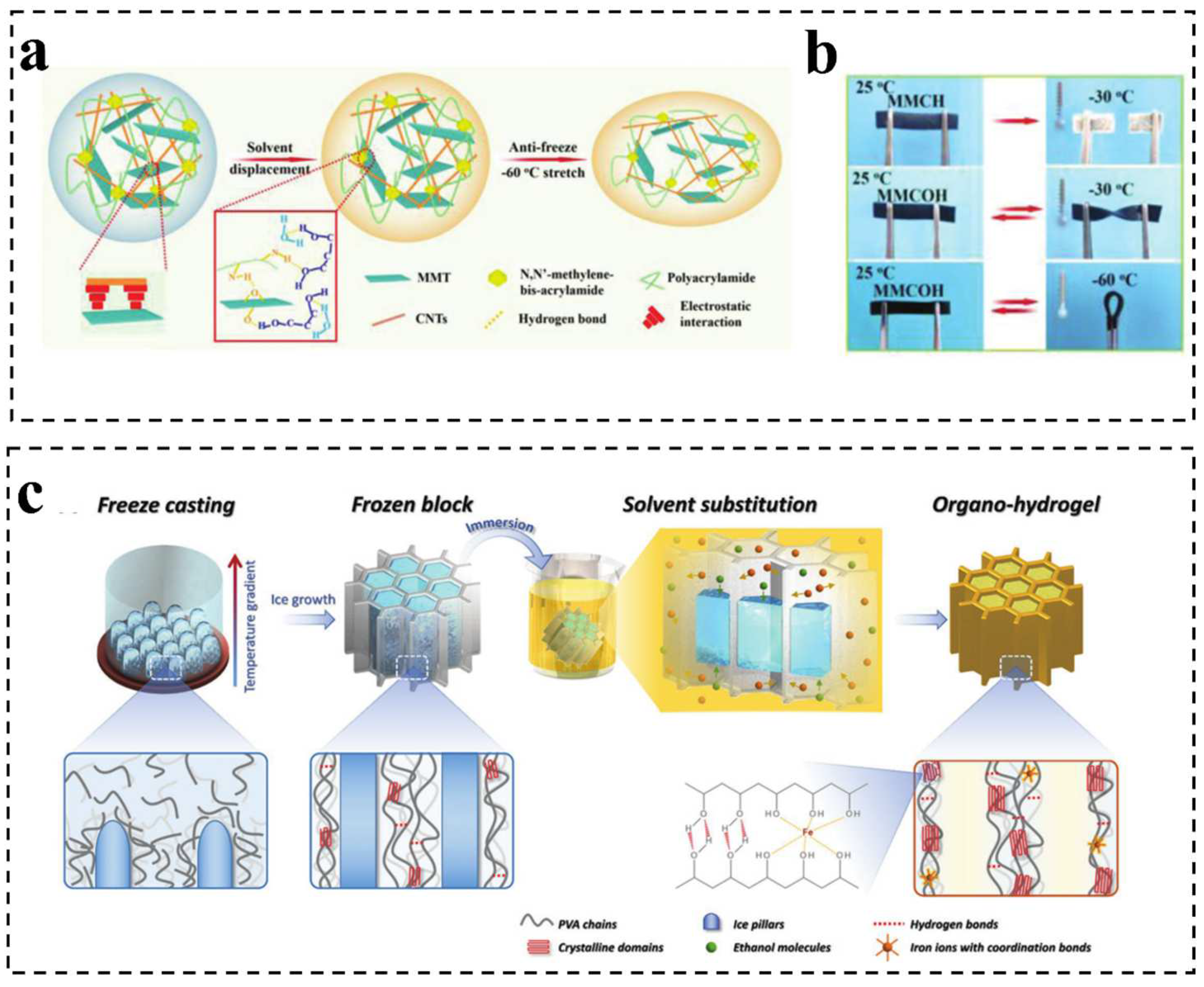
2.1.2. Incorporation of Organic Solvent
| Materials | Solvent Composition | Anti-Freezing Temperature | Anti-Drying Property | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/SNF/CN | Ethylene glycol/water | −18 °C | - | Human motion detection | [42] |
| PVA/EG | Ethylene glycol/water | −20 °C | - | Human motion monitoring | [43] |
| (PVA)/CNCs-PDDA/PA | Glycerol/water | −30 °C | - | Strain sensors | [45] |
| PVA/CNF | DMSO/water (1:2 molar ratio) | −50 °C | 85% of hydrogel weight retention after 30 days | Human motion sensor | [46] |
| AM/Cu-TA/CNF | Glycerol/water (50 wt%) | −20 °C | 70% weight retention after 7 days | Strain sensor | [47] |
| PAM/PAA/LSNs | Glycerol/water (6:1) | −60 °C | Keep the initial state for 7 days | Energy storage | [48] |
| PAM/MMT/CNTs | Glycerol/water (6:1) | −60 °C | 90% of hydrogel weight retention after 30 days | Human motion sensor | [55] |
| PVA | Ethanolic ferric chloride (2 wt%) | −30 °C | - | Strain sensor | [56] |
| Cu-TA/CNF/G | 50 wt% EG | −30 °C | 90% of hydrogel weight retention after 60 days | Human motion sensor | [57] |
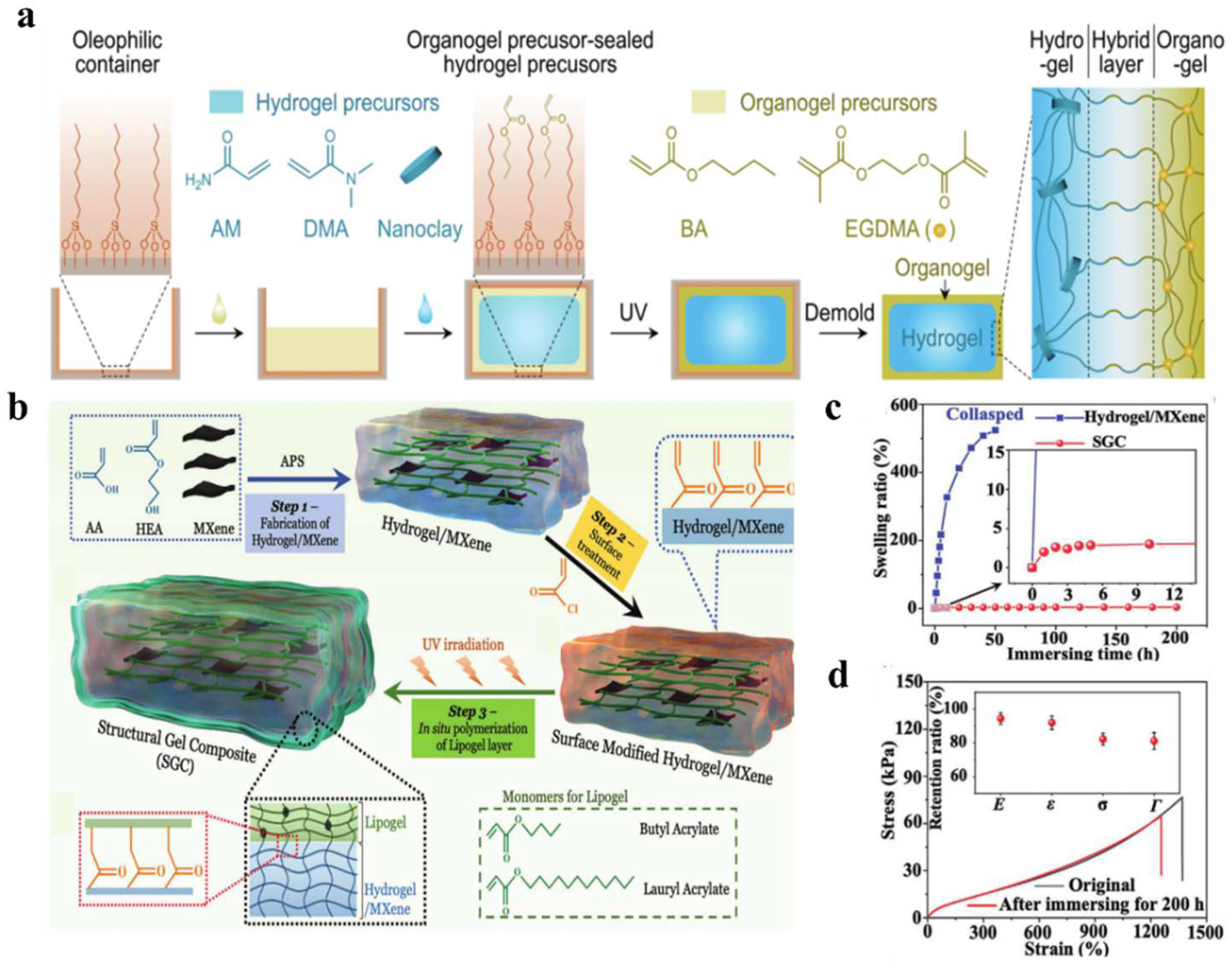
2.1.3. Surface Modification
2.1.4. Other Strategies
| Materials | Strategy | Solvent Composition | Anti-Freezing Temperature | Anti-Drying Property | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/AMY/NaCl | Organic solvent and salt solvent incorporation | Glycerol/NaCl/water | −20 °C | 85% of hydrogel weight retention after 7 days | Human motion sensor | [64] |
| SA/PAM | Organic solvent and salt solvent replacement | LiCl/CaCl2/Glycerol/water | −80 °C | 80% of hydrogel weight retention | Electronic skin | [65] |
| SBMA/AA/CS/MEA | Binary organic/water solvent and elastomer modification | DMSO/water | −30 °C | 80% of hydrogel weight retention | Human motion sensor | [66] |
| PAM/CMC | Binary salt/water solvent and elastomer modification | LiCl/water | −20 °C | 40% of hydrogel weight retention after 15 days | Human motion and strain monitor | [67] |
| AM/PVA/AFP | Nature AFP | Water | −15 °C | - | Human motion sensor | [69] |
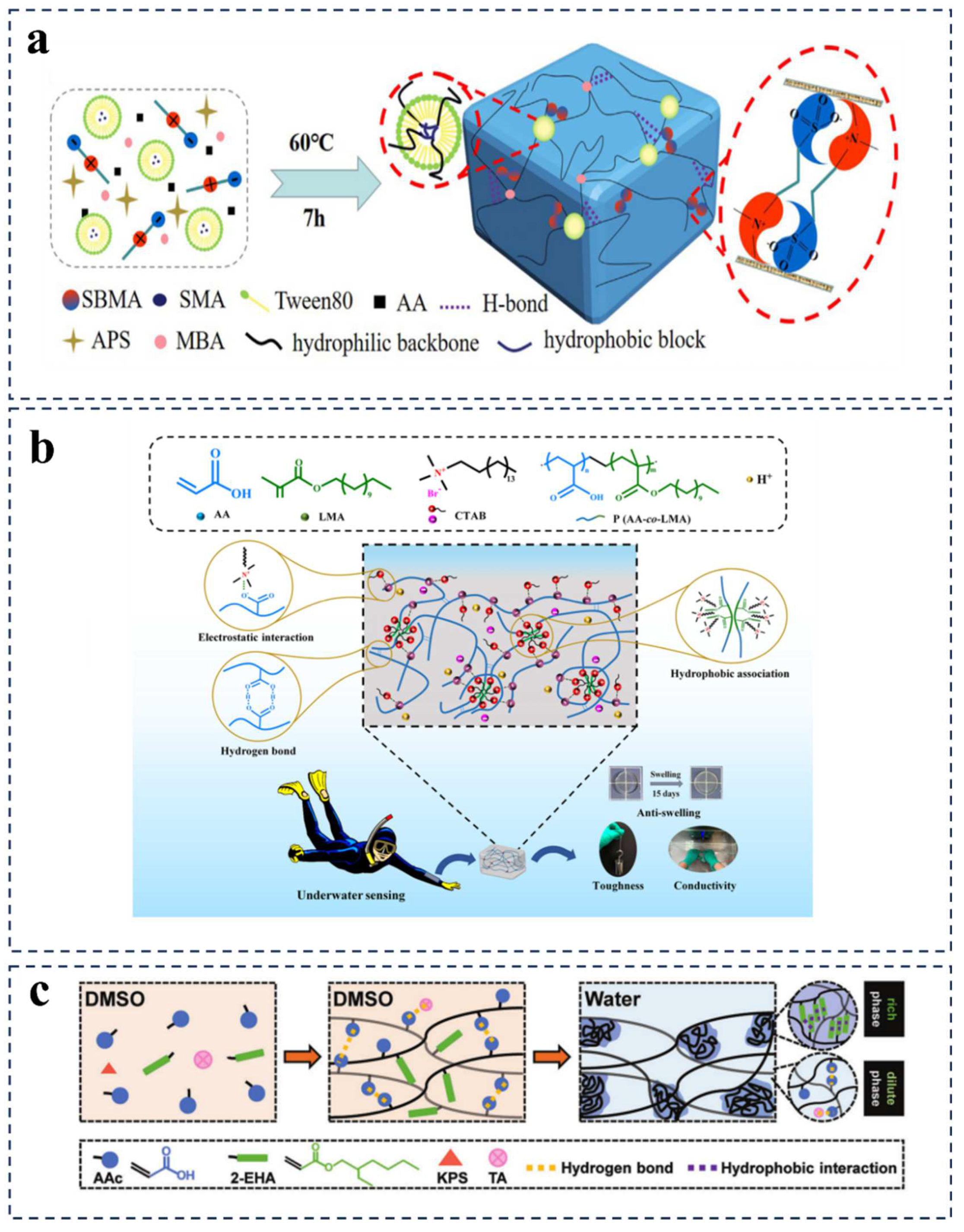
2.2. ETCHs with Anti-Swelling Ability
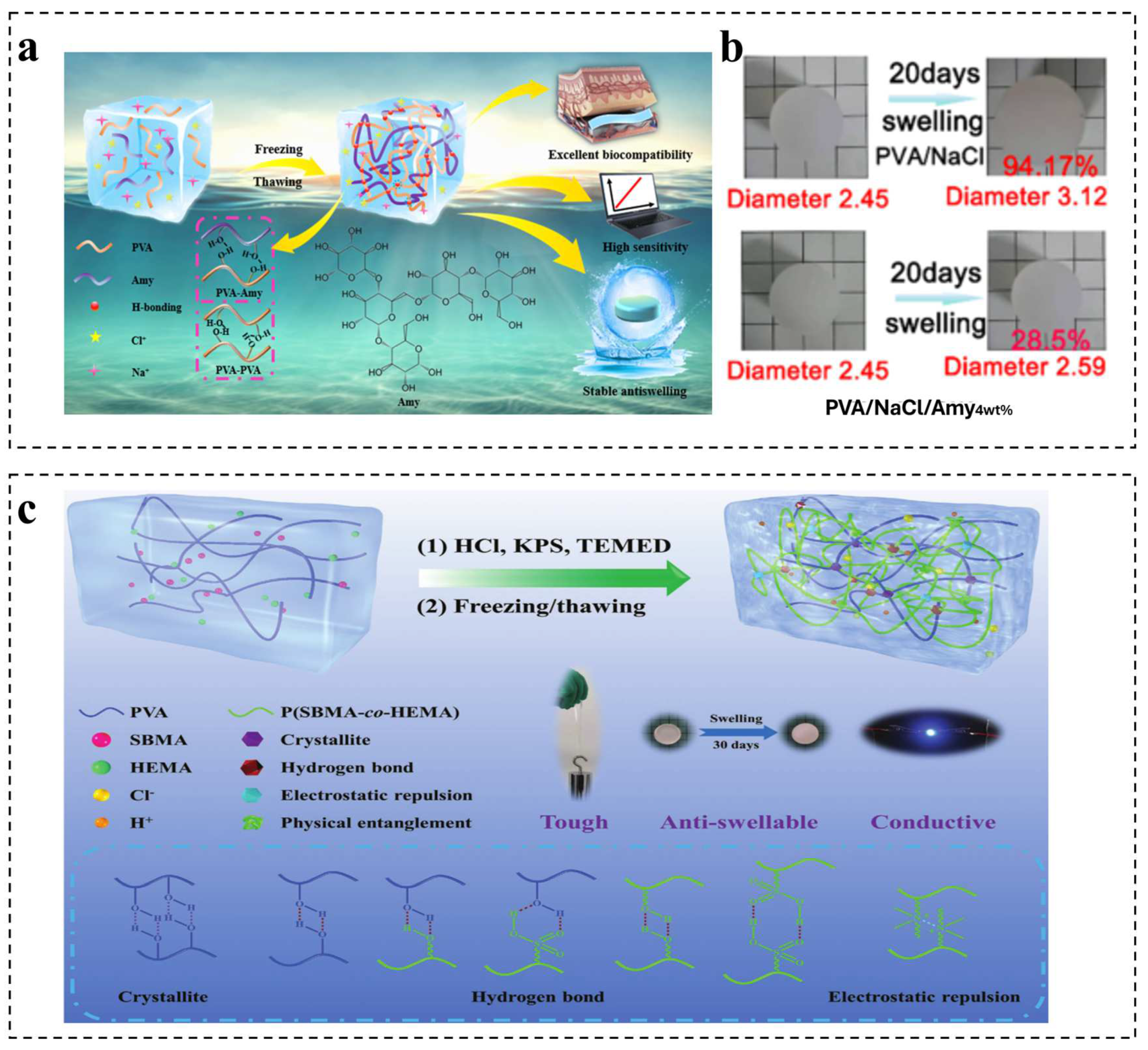
2.2.1. Physical Interaction Mechanism
2.2.2. Introduction of Hydrophobic Components Mechanism
2.2.3. Multiple Crosslinking Mechanism
3. Applications of ETCHs
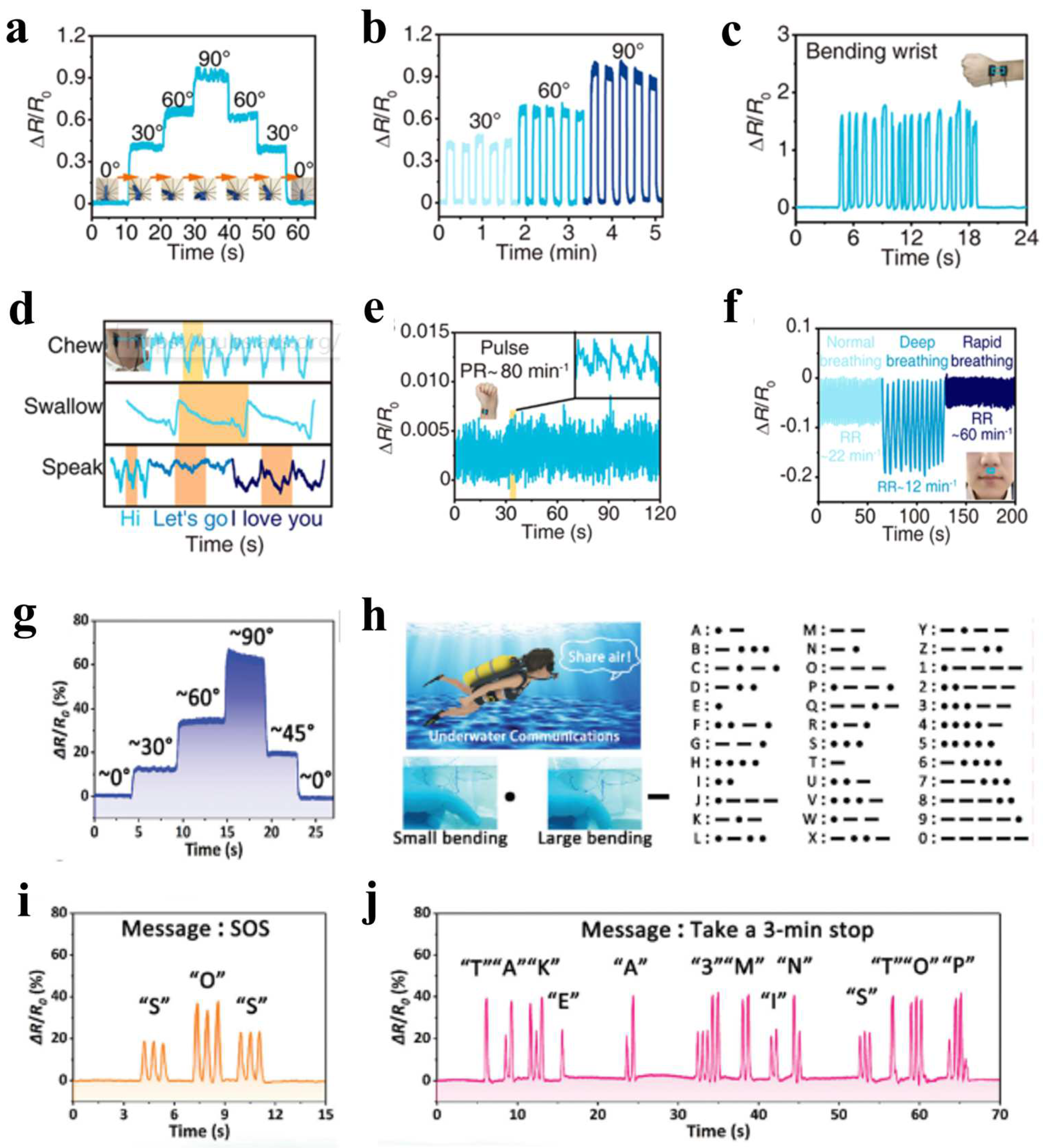
3.1. Strain Sensing and Human Motion Detection
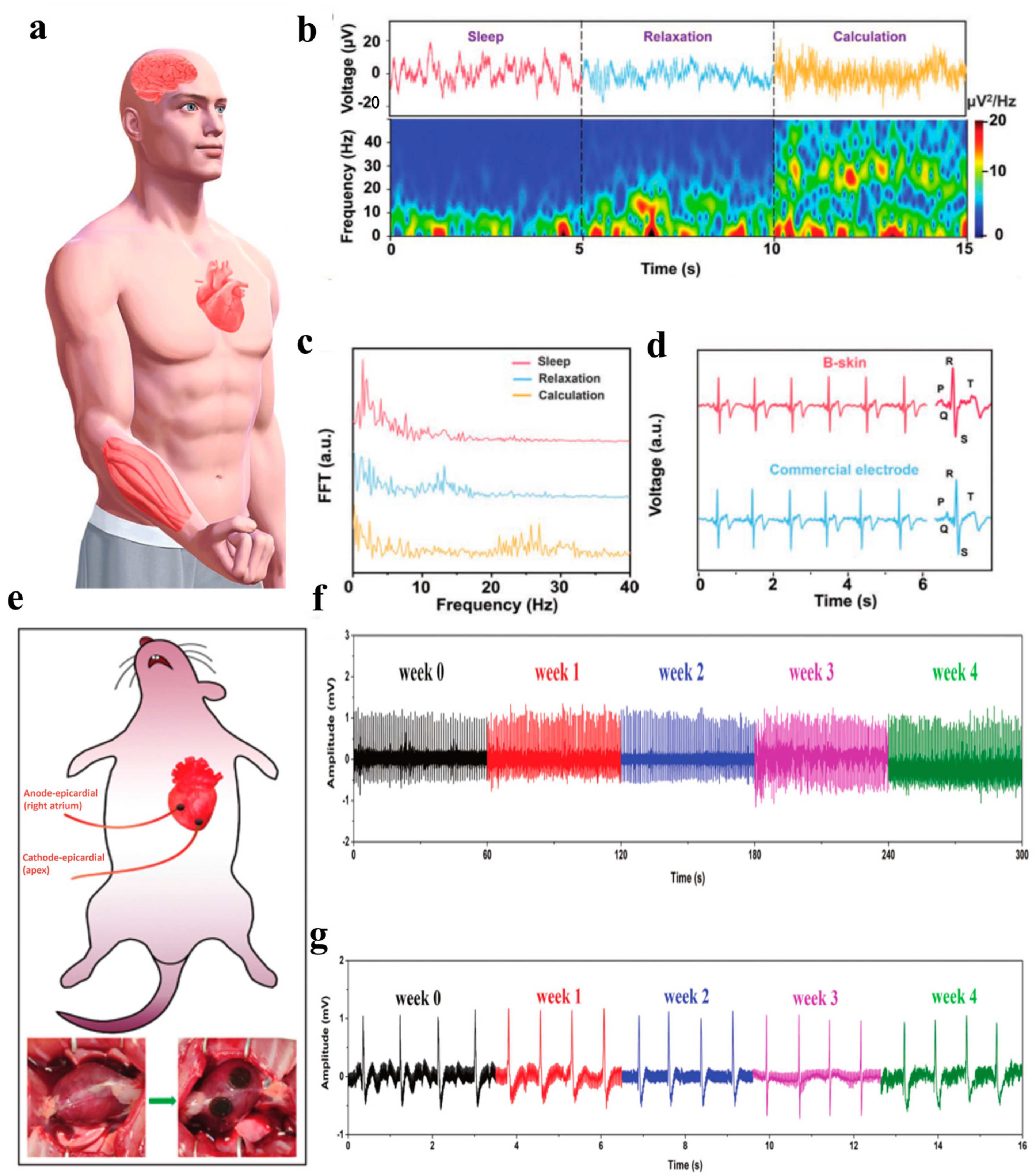
3.2. Bioelectrodes
3.3. Soft Actuator and Robotics
3.4. Wound Dressings
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ETCHs | Environmentally tolerant conductive hydrogels |
| SBMA | 3-[Dimethyl-[2-(2-methylprop-2-enoyloxy) ethyl]azaniumyl]propane-1-sulfonate |
| HEMA | 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| AA | Acrylic acid |
| PAM | Polyacrylamide |
| CS | Chitosan |
| CGO | Chitosan-modified graphene oxide |
| CNC | Cellulose nanocrystal |
| GA | Arabic gum |
| ECH | Epichlorohydrin |
| SA | Sodium alginate |
| CNF | Cellulose nanofibers |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| TA | Tannic acid |
| EG | Ethylene glycol |
| SNF | Silk nanofibers |
| CN | Carbon nitride nanosheets |
| PDDA | Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) |
| PA | Phytic acid |
| LSNs | Lignin sulfonate nanorods |
| MMT | Montmorillonite |
| G | Graphene |
| HEA | 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate |
| Th | Trehalose |
| SDS | Sodium dodecylsulfate |
| C18 | Stearylmethacrylate |
| BA | Butyl acrylate |
| DMA | N, N-dimethylacrylamide |
| AFP | Antifreeze proteins |
| AMY | Amylopectin |
| CMC | Carboxymethyl cellulose |
| VHB | acrylic elastomer |
| MEA | Ethylene glycol methyl ether acrylate |
| Gp | β-Glycerophosphate sodium |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| VBIBr | 1-butyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide |
| [BMIm]TFSI | bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| AL | Alkali lignin |
| ILs | 1-vinyl-3-butylimidazolium |
| MaPVA | Methacrylated polyvinyl alcohol |
| CMCS | Carboxymethyl chitosan |
| VBIPS | 3-(1-(4-vinylbenzyl)-1H-benzo-[d]imidazole-3-ium-3-yl) propane-1-sulfonate |
| MOF | Metal–organic framework |
| NIR | Near infrared |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram signal |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram signal |
| EMG | Electromyogram signal |
| DMAPS | [2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethyl]dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl) |
| DMAA | N,N-dimethylacrylamide |
| FFT | Fourier transform |
References
- Shi, Y.; Wang, R.; Bi, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, L.; Niu, Z. An Anti-Freezing Hydrogel Electrolyte for Flexible Zinc-Ion Batteries Operating at −70 °C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lou, D.; Wang, H.; Jiang, D.; Fang, X.; Meng, J.; Sun, X.; Li, J. One-pot synthesis of anti-freezing carrageenan/polyacrylamide double-network hydrogel electrolyte for low-temperature flexible supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, M.; Feng, L.; Hao, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Qin, G.; Sun, G.; Chen, Q. Swelling-resistant microgel-reinforced hydrogel polymer electrolytes for flexible all-in-one supercapacitors with high performances. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 7419–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Weng, L.; Zhang, X.; Guan, L.; Li, X. Constructing conductive and mechanical strength self-healing hydrogel for flexible sensor. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2023, 8, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalabianloo, N.; Can, Y.S.; Umair, M.; Sas, C.; Ersoy, C. Application level performance evaluation of wearable devices for stress classification with explainable AI. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2022, 87, 101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Chen, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Ma, P.; Dong, W. Photo-crosslinking ionic conductive PVA-SbQ/FeCl3 hydrogel sensors. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 648, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Zhu, X. Robots Built Robots: Nanorobots Customized by Intelligent Robot. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 5508–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, C.; Zhang, H.; Xie, H. Biodegradable Magnetic Hydrogel Robot with Multimodal Locomotion for Targeted Cargo Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 28922–28932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.W.; Chun, S.; Son, D.; Hu, X.; Schneider, M.; Sitti, M. A Tissue Adhesion-Controllable and Biocompatible Small-Scale Hydrogel Adhesive Robot. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dai, L.; Hunter, L.A.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. A multifunctional nanocellulose-based hydrogel for strain sensing and self-powering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 268, 118210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; He, S.; Qin, Z.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Fast self-healing zwitterion nanocomposite hydrogel for underwater sensing. Compos. Commun. 2021, 26, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, D.; Qu, R.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Song, X. Flexible sensitive hydrogel sensor with self-powered capability. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 639, 128381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, X.; Luo, C. Anisotropic hydrogels with high-sensitivity and self-adhesion for wearable sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, B.S.; Monteiro, M.V.; Ferreira, L.P.; Lavrador, P.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F. Advancing Tissue Decellularized Hydrogels for Engineering Human Organoids. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, S.; Jia, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, T. Human-tissue-inspired anti-fatigue-fracture hydrogel for a sensitive wide-range human-machine interface. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.; He, W.; He, J.; Muhammad, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z. High strength, anti-freezing and conductive silkworm excrement cellulose-based ionic hydrogel with physical-chemical double cross-linked for pressure sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Lu, J.; Huang, Z.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, H. Dual-network polyvinyl alcohol/polyacrylamide/xanthan gum ionic conductive hydrogels for flexible electronic devices. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yan, B.; Li, Y.; Lan, J.; Shi, L.; Ran, R. Antifreeze and moisturizing high conductivity PEDOT/PVA hydrogels for wearable motion sensor. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, C.; Chang, B.; Jing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Hou, C. MXene-Enabled Self-Adaptive Hydrogel Interface for Active Electroencephalogram Interactions. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19373–19384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F.; He, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, B.; Niu, S.; Han, Z.; et al. Bioinspired hydrogel actuator for soft robotics: Opportunity and challenges. Nano Today 2023, 49, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, J. Novel Glucose-Responsive Antioxidant Hybrid Hydrogel for Enhanced Diabetic Wound Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7680–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Q.; Cai, X.; Zhou, P.; Wu, Z.; Wang, B.; Ma, W.; Fu, S. Injectable hydrogels as drug delivery platform for in-situ treatment of malignant tumor. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired adhesive antioxidant antibacterial hemostatic composite hydrogel wound dressing via photo-polymerization for infected skin wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Seidi, F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H. Injectable chitosan hydrogels tailored with antibacterial and antioxidant dual functions for regenerative wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Ren, X.; Gao, G.; Duan, L. High strength, anti-freezing and strain sensing carboxymethyl cellulose-based organohydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; et al. Anti-freezing, resilient and tough hydrogels for sensitive and large-range strain and pressure sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, J.; He, R.; Zhu, C.; Cao, Y.; Qian, Z. A self-adhesive and low-temperature-tolerant strain sensor based on organohydrogel for extreme ice and snow motion monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shi, Y.; Alsaedi, M.; Wu, M.; Shi, L.; Wang, P. Hybrid Hydrogel with High Water Vapor Harvesting Capacity for Deployable Solar-Driven Atmospheric Water Generator. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11367–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Ma, Y.; et al. Environmentally Adaptive Polymer Hydrogels: Maintaining Wet-Soft Features in Extreme Conditions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, W. Development of Conductive Hydrogels for Fabricating Flexible Strain Sensors. Small 2022, 18, e2101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, E.; Zheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Cao, L.; Wu, Z. A toughened, transparent, anti-freezing and solvent-resistant hydrogel towards environmentally tolerant strain sensor and soft connection. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 656, 130390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Gao, S.; Jian, J.; Shi, X.; Lai, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, F.; Chu, F.; Zhang, D. Skin-mimicking strategy to fabricate strong and highly conductive anti-freezing cellulose-based hydrogels as strain sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Fu, W.; Xing, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, C. Advances in versatile anti-swelling polymer hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 127, 112208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Qiao, C.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Yao, J. Fabrication and Properties of Anti-freezing Gelatin Hydrogels Based on a Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 4546–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Jing, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Bai, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Wei, D. Cellulose nanocrystal based self-healing and anti-freezing arabic gum hydrogels using betaine/CaCl2 anti-freeze strategy. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7667–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.F.; Yao, J. Highly conductive and anti-freezing cellulose hydrogel for flexible sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zou, X.; Yin, H.; Huang, Y.; Dong, F.; Li, P.; Song, Y. Construction and characterization of highly stretchable ionic conductive hydrogels for flexible sensors with good anti-freezing performance. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 186, 111827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Shu, H.; Zhong, W. Ultrahigh conductivity and antifreezing zwitterionic sulfobetaine hydrogel electrolyte for low-temperature resistance flexible supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 9097–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, T.-W.; Du, Y.; Yao, B.; Duan, S.; Yan, Y.; Hua, M.; Alsaid, Y.; Zhu, X.; He, X. Tough, anti-freezing and conductive ionic hydrogels. NPG Asia Mater. 2022, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Guo, H.; Cai, C.; Li, Q.; Wen, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Ionic conductive hydrogels with long-lasting antifreezing, water retention and self-regeneration abilities. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-N.; He, X.-F.; Zeng, Z.-F.; Jiang, B.; Wu, Q.; Gong, L.-X.; Li, Y.; Bae, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, L.-C. Mechanically ductile, ionically conductive and low-temperature tolerant hydrogel enabled by high-concentration saline towards flexible strain sensor. Nano Energy 2022, 103, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Gao, J.; Xu, T.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Lu, W. Anti-freezing and antibacterial conductive organohydrogel co-reinforced by 1D silk nanofibers and 2D graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as flexible sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yin, F.; He, W.; Hang, T.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Y. Anti-freezing, recoverable and transparent conductive hydrogels co-reinforced by ethylene glycol as flexible sensors for human motion monitoring. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Raffa, P. Anti-freezing conductive zwitterionic composite hydrogels for stable multifunctional sensors. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 199, 112484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Yue, D.; Xiao, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Bai, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Wei, D. Anti-freezing and self-healing nanocomposite hydrogels based on poly(vinyl alcohol) for highly sensitive and durable flexible sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, D.; Sun, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, F. An environmentally tolerant, highly stable, cellulose nanofiber-reinforced, conductive hydrogel multifunctional sensor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Lv, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, L.; Duan, J.; Jiang, J. Mussel inspired Cu-tannic autocatalytic strategy for rapid self-polymerization of conductive and adhesive hydrogel sensors with extreme environmental tolerance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wan, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, F.; Abdulkhani, A.; Liu, X.; Nawaz, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X. Lignin nanorods reinforced nanocomposite hydrogels with UV-shielding, anti-freezing and anti-drying applications. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 187, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. Ultra-thin, transparent, anti-freezing organohydrogel film responded to a wide range of humidity and temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Li, P.; Yu, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Tong, G. Dual Network Hydrogel with High Mechanical Properties, Electrical Conductivity, Water Retention and Frost Resistance, Suitable for Wearable Strain Sensors. Gels 2023, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Luo, J.; Chang, B.; Sun, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Hou, C. High-Performance Zwitterionic Organohydrogel Fiber in Bioelectronics for Monitoring Bioinformation. Biosensors 2023, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Lv, X.; Sun, S. A highly sensitive strain sensor based on a silica@polyaniline core-shell particle reinforced hydrogel with excellent flexibility, stretchability, toughness and conductivity. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 2142–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Wu, Z.; Tao, K.; Wei, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, B.R.; Xie, X.; Wu, J. Environment tolerant, adaptable and stretchable organohydrogels: Preparation, optimization, and applications. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1356–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, G.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, K. Multifunctional Flexible Humidity Sensor Systems Towards Noncontact Wearable Electronics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, S.; Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Wan, P.; Shen, C. Environment Tolerant Conductive Nanocomposite Organohydrogels as Flexible Strain Sensors and Power Sources for Sustainable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhai, W. Strong and Tough Conductive Organo-Hydrogels via Freeze-Casting Assisted Solution Substitution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Li, X.; Yang, A.; Wu, M.; Yu, L.; Zeng, H.; Han, L. Nanomaterials-enhanced, stretchable, self-healing, temperature-tolerant and adhesive tough organohydrogels with long-term durability as flexible sensors for intelligent motion-speech recognition. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 141905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Peng, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Qu, M. Ultra-sensitive, durable and stretchable ionic skins with biomimetic micronanostructures for multi-signal detection, high-precision motion monitoring, and underwater sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 26949–26962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y. Flexible MXene-Based Hydrogel Enables Wearable Human-Computer Interaction for Intelligent Underwater Communication and Sensing Rescue. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cao, T.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Wang, K.; Fan, X. Antiliquid-Interfering, Antibacteria, and Adhesive Wearable Strain Sensor Based on Superhydrophobic and Conductive Composite Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 46022–46032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Cheng, G.; Ding, J. Tough hydrogel-elastomer hybrids hydrophobically regulated by an MXene for motion monitoring in harsh environments. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wan, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Jia, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Wetting-Enabled Three-Dimensional Interfacial Polymerization (WET-DIP) for Bioinspired Anti-Dehydration Hydrogels. Small 2023, 19, e2208157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Dai, S.; Chen, F.; Xu, B.B. A Structural Gel Composite Enabled Robust Underwater Mechanosensing Strategy with High Sensitivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. Highly conductive hydrogel sensors driven by amylose with freezing and dehydration resistances. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 12873–12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-y.; Kim, H.-J. Ultra-stretchable dual-network ionic hydrogel strain sensor with moistening and anti-freezing ability. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 166, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yuan, W. Functionally integrated conductive organohydrogel sensor for wearable motion detection, triboelectric nanogenerator and non-contact sensing. Compos. Part A 2023, 172, 107603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yue, Y.; Ding, Q.; Mei, C.; Xu, X.; Jiang, S.; He, S.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Han, J. Environment-tolerant ionic hydrogel-elastomer hybrids with robust interfaces, high transparence, and biocompatibility for a mechanical-thermal multimode sensor. InfoMat 2023, 5, e12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ding, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, L.; Tao, K.; Xie, X.; Wu, J. Ultrasensitive, stretchable, and transparent humidity sensor based on ion-conductive double-network hydrogel thin films. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2540–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xiang, P.; Dai, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, H.; Yu, J.; Gao, G.; Chen, K. Protein-assisted freeze-tolerant hydrogel with switchable performance toward customizable flexible sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liang, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Tian, Y. Skin-Inspired Ultra-Tough Supramolecular Multifunctional Hydrogel Electronic Skin for Human-Machine Interaction. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Kan, L.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N. Adaptable ionic liquid-containing supramolecular hydrogel with multiple sensations at subzero temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, P.; Li, Y.; Gao, G. Amylopectin based hydrogel strain sensor with good biocompatibility, high toughness and stable anti-swelling in multiple liquid media. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 164, 110981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Wei, H.; Lü, S. An Anti-Swellable Hydrogel Strain Sensor for Underwater Motion Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Su, Y.; Che, G.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y. Novel Lignin Hydrogel Sensors with Antiswelling, Antifreezing, and Anticreep Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 8255–8270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, T. A fully hydrophobic ionogel enables highly efficient wearable underwater sensors and communicators. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Du, Y.; Ding, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Zheng, K.; Liu, X.; et al. Self-healing liquid metal hydrogel for human-computer interaction and infrared camouflage. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2945–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, M.; Qin, S.; Wen, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Lu, H.; Meng, Q.; Cui, W.; Ran, R. Rapid Gelation of Tough and Anti-Swelling Hydrogels under Mild Conditions for Underwater Communication. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2210188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, L.; Song, B.; Bai, X.; Huang, Z.; Bu, X.; Chen, T.; Fu, H.; Guo, P. High-strain sensitive zwitterionic hydrogels with swelling-resistant and controllable rehydration for sustainable wearable sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 620, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Dong, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Lei, C. Tough, Anti-Swelling Supramolecular Hydrogels Mediated by Surfactant-Polymer Interactions for Underwater Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 30385–30397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, H.; Pi, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Cui, W.; Ran, R. Water-Induced Phase Separation for Anti-Swelling Hydrogel Adhesives in Underwater Soft Electronics. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, G. Solvent-Resistant and Nonswellable Hydrogel Conductor toward Mechanical Perception in Diverse Liquid Media. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13709–13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xiao, P.; Chen, T. Water-Resistant Conductive gels toward Underwater Wearable Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2211758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, X.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Wei, Y. Chitosan-enhanced nonswelling hydrogel with stable mechanical properties for long-lasting underwater sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 212, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Shen, J.; Wan, S.; Han, L.; Dou, G.; Sun, L. Wet-Adhesive Multifunctional Hydrogel with Anti-swelling and a Skin-Seamless Interface for Underwater Electrophysiological Monitoring and Communication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 11549–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Hou, J.; Yang, M.; Wu, G.; Sun, P. A bio-inspired, ultra-tough, high-sensitivity, and anti-swelling conductive hydrogel strain sensor for motion detection and information transmission. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 3057–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. One-Step Soaking Strategy toward Anti-Swelling Hydrogels with a Stiff “Armor”. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.Y.; Lei, X.X.; Hu, J.J.; Jiang, Y.L.; Li, Q.J.; Song, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li-Ling, J.; Xie, H.Q. Multi-crosslinking hydrogels with robust bio-adhesion and pro-coagulant activity for first-aid hemostasis and infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 16, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Lin, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, H. An All-in-One Tannic Acid-Containing Hydrogel Adhesive with High Toughness, Notch Insensitivity, Self-Healability, Tailorable Topography, and Strong, Instant, and On-Demand Underwater Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9748–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, E.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, G.; Gao, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z. Stretchable, healable, adhesive, transparent, anti-drying and anti-freezing organohydrogels toward multi-functional sensors and information platforms. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 15530–15541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Qiu, J.H.; Zhao, W.; Sakai, E.; Zhang, G.H.; Nobe, R.; Kudo, M.; Komiyama, T. Low-temperature adaptive conductive hydrogel based on ice structuring proteins/CaCl2 anti-freeze system as wearable strain and temperature sensor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; He, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zheng, S.Y.; Yang, J. Anti-Swelling Zwitterionic Hydrogels as Multi-Modal Underwater Sensors and All-in-One Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 7498–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, M. From grape seed extracts to extremely stable strain sensors with freezing tolerance, drying resistance and anti-oxidation properties. Mater. Today 2022, 33, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wen, C.; Zhao, W.; Tian, S.; Long, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sui, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J. Environment-Resistant Organohydrogel-Based Sensor Enables Highly Sensitive Strain, Temperature, and Humidity Responses. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 23692–23700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S.; Yao, X.; Han, X.; Cao, W.; Pu, J. An anti-freezing and strong wood-derived hydrogel for high-performance electronic skin and wearable sensing. Compos. Part B 2022, 239, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Cui, Y.; Song, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Neuron-Inspired Self-Powered Hydrogels with Excellent Adhesion, Recyclability and Dual-Mode Output for Multifunctional Ionic Skin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, B.; Liu, X. Skin-like hydrogel devices for wearable sensing, soft robotics and beyond. iScience 2021, 24, 103174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Oh, S.; Choi, G.; Lee, H.S. Anti-dryable, anti-freezable, and self-healable conductive hydrogel for adhesive electrodes. Compos. Interfaces 2022, 29, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.A.M.; Ghanem, L.G.; Akar, A.A.; Khedr, G.E.; Ramadan, M.; Shaheen, B.S.; Allam, N.K. Novel self-regenerative and non-flammable high-performance hydrogel electrolytes with anti-freeze properties and intrinsic redox activity for energy storage applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 16009–16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Zhu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, W.; Li, B.; Jin, R.; Han, N.; Wu, J.; et al. Sebum-Membrane-Inspired Protein-Based Bioprotonic Hydrogel for Artificial Skin and Human-Machine Merging Interface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liang, Q.; Sun, X.; Yu, D.; Huang, X.; Mugo, S.M.; Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q. Intrinsically Electron Conductive, Antibacterial, and Anti-swelling Hydrogels as Implantable Sensors for Bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yang, X.; Yan, J.; An, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xiang, D.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Anti-freezing, conductive and shape memory ionic glycerol-hydrogels with synchronous sensing and actuating properties for soft robotics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 16095–16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Qiu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Duanmu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Huang, B.; Tang, L.; Lu, B. One-pot mechanochemical assembly of lignocellulose nanofiber/graphite nanocomposites for wearable electronic devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Jin, G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; Yan, F. Poly(ionic liquid) hydrogel-based anti-freezing ionic skin for a soft robotic gripper. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, F.; Liang, Z.; Yong, Y.; Dai, S.; Li, Z. A stretchable, environmentally stable, and mechanically robust nanocomposite polyurethane organohydrogel with anti-freezing, anti-dehydration, and electromagnetic shielding properties for strain sensors and magnetic actuators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 6603–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ohm, Y.; Liao, J.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Won, P.; Roberts, P.; Carneiro, M.R.; Islam, M.F.; Ahn, J.H.; et al. A self-healing electrically conductive organogel composite. Nat. Electron. 2023, 6, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Lu, W.; Zhou, X.; Chen, T. Biomimetic anti-freezing polymeric hydrogels: Keeping soft-wet materials active in cold environments. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, K.; An, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Recent Development of Alginate-Based Materials and Their Versatile Functions in Biomedicine, Flexible Electronics, and Environmental Uses. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1302–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Ma, G.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z. Facile preparation of polysaccharides-based adhesive hydrogel with antibacterial and antioxidant properties for promoting wound healing. Colloids Surf. B 2022, 209, 112208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Smart Hydrogel Sensors with Antifreezing, Antifouling Properties for Wound Healing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Tang, P.; Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lu, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, Q.; Feng, W.; Shubhra, Q.T.H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Sponge-Like Macroporous Hydrogel with Antibacterial and ROS Scavenging Capabilities for Diabetic Wound Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2200717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials | Solvent Composition | Anti-Freezing Temperature | Anti-Drying Property | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA/PAA-CNC/betaine | CaCl2 | −30 °C | - | Motion sensor | [35] |
| Cellulose/ECH | ZnCl2/CaCl2 | −30 °C | - | Strain and pressure sensor | [36] |
| PAM/SA | LiCl | −30 °C | 92% of water retention | Motion sensor | [37] |
| SBMA/HEAA | LiCl (6 M) | −40 °C | 79.8% of water retention | Strain sensor | [38] |
| PVA | KAc (50 wt%) | −60 °C | 90% of water retention after 10 days | Soft robot and ionic skin | [39] |
| SBMA/AA | LiCl (30%) | −80 °C | 100% of water retention after 10 days | Human motion detection | [40] |
| PAM/CS/CGO | NaCl (21.2 wt%) | −56.8 °C | - | Strain sensor | [41] |
| Materials | Structure Composition | Anti-Drying | Anti-Swelling | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPU/[EMIM][TFSI]/mHNTs | Hyrdogel/acrylic elastomer (VHB) | - | Nearly non-swelling | Underwater communication | [58] |
| C18/SDS/NaCl/MXene | Hydrogel/PDMS/Triton X-100 | - | less than 2% in 30 days | Underwater communication | [59] |
| AA/HEMA/MXene/AgNPs | Hydrogel/Ecoflex/SiO2 | - | No significant change | Strain sensors | [60] |
| Th/AM/AA/MXene | Hydrogel/PDMS | 5.5% change in relative mass after 7 days | The swelling ratio less than 7% | Human motion monitoring | [61] |
| AM/DMA/BA/nanoclay | Hydrogel/organic gel layer | water retention rate of 95% after 2 days | 3–9 wt% after 7 days | Strain sensors | [62] |
| AA/HEA/MXene | Hydrogel/lipogel | - | 3% volume expansion in water for 200 h | Human motion detection | [63] |
| Materials | Interactions | Anti-Swelling Property | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA-Gp/TA-CaCl2 | Hydrogen bond | 89% of its original weight after 30 days | Electronic skin | [70] |
| PVA/AMY | Hydrogen bond | 28.55% of swelling ratio after 20 days | Strain sensor | [72] |
| PVA/poly(SBMA-HEMA) | Electrostatic interaction | 9% of swelling ratio after 30 days | Underwater motion sensor | [73] |
| PVA-AL/ILs/H2O-GLY | Hydrophobic interaction and hydrogen bond | - | Human motion sensor | [74] |
| Materials | Mechanism | Swelling Ratio | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-BuA/DMAA/IL/[BMIm]TFSI | Hydrophobic/hydrophilic structure | The swelling ratio held 3.8% after 10 days | Underwater motion sensors | [75] |
| Liquid metal/PVA/P(AAm-co-SMA) | Hydrophobic network, ionic coordination, and hydrogen bonds | Swelling ratio less than 20% after a week | Wound dressing | [76] |
| AA/SMA/SBMA | Hydrophobic and hydrogen bond | 1% volume swelling ratio after 30 days | Human motion sensor | [78] |
| AA/LMA/CTAB | Electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic associations | Around 4% of swelling ratio after 15 days | Underwater motion sensor | [79] |
| AA/EHA/TA/MWCNT | hydrophobic/hydrophilic structure | Swelling ratio less than 40% | Bioelectronics | [80] |
| AA/MEA/graphene/DMSO | Hydrophobic/hydrophilic structure | Non-swelling behavior for 500 h | Underwater motion sensors | [81] |
| Materials | Mechanism | Swelling Ratio | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA-MEA-Fe/CS | C-C covalent bond and hydrogen bond | Around 16% after 7 days | Human motion sensor | [83] |
| PAA-CS-Al3+-MXene | C-C covalent bond, hydrogen bond, and electrostatic interactions | Swelling ratio of 3.8% after 7 days | Human motion sensor | [84] |
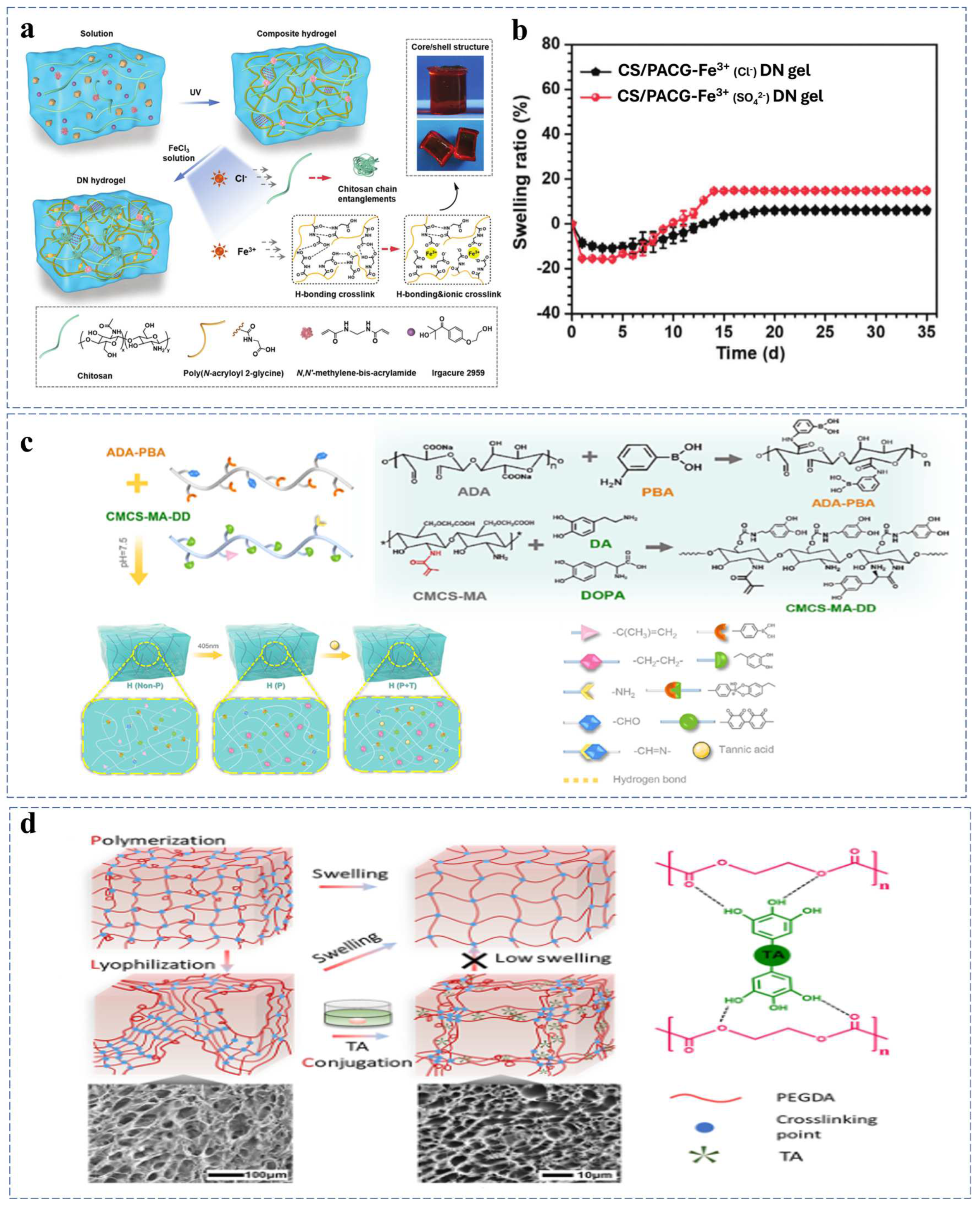
| CS/PACG | C-C covalent bond, hydrogen bond, and ionic interactions | Swelling ratio of 20% after 20 h | Wearable sensor | [86] |
| CMCS/SA/TA | C-C covalent bond, dynamic covalent bonds, and hydrogen bond | Swelling ratio of 32.4% for 30 h | Wound dressing | [87] |
| PEGDA/TA | C-C covalent bond, borate ester bond, and Schiff base bond | Swelling ratio of 20.9% after 5 days | Wound dressing | [88] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, T.; Luo, M.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X. Recent Progress of Anti-Freezing, Anti-Drying, and Anti-Swelling Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070971
Li Y, Cheng Q, Deng Z, Zhang T, Luo M, Huang X, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhao X. Recent Progress of Anti-Freezing, Anti-Drying, and Anti-Swelling Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications. Polymers. 2024; 16(7):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070971
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ying, Qiwei Cheng, Zexing Deng, Tao Zhang, Man Luo, Xiaoxiao Huang, Yuheng Wang, Wen Wang, and Xin Zhao. 2024. "Recent Progress of Anti-Freezing, Anti-Drying, and Anti-Swelling Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications" Polymers 16, no. 7: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070971
APA StyleLi, Y., Cheng, Q., Deng, Z., Zhang, T., Luo, M., Huang, X., Wang, Y., Wang, W., & Zhao, X. (2024). Recent Progress of Anti-Freezing, Anti-Drying, and Anti-Swelling Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications. Polymers, 16(7), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070971








