Reactive Deep Eutectic Solvent for an Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamate
Abstract
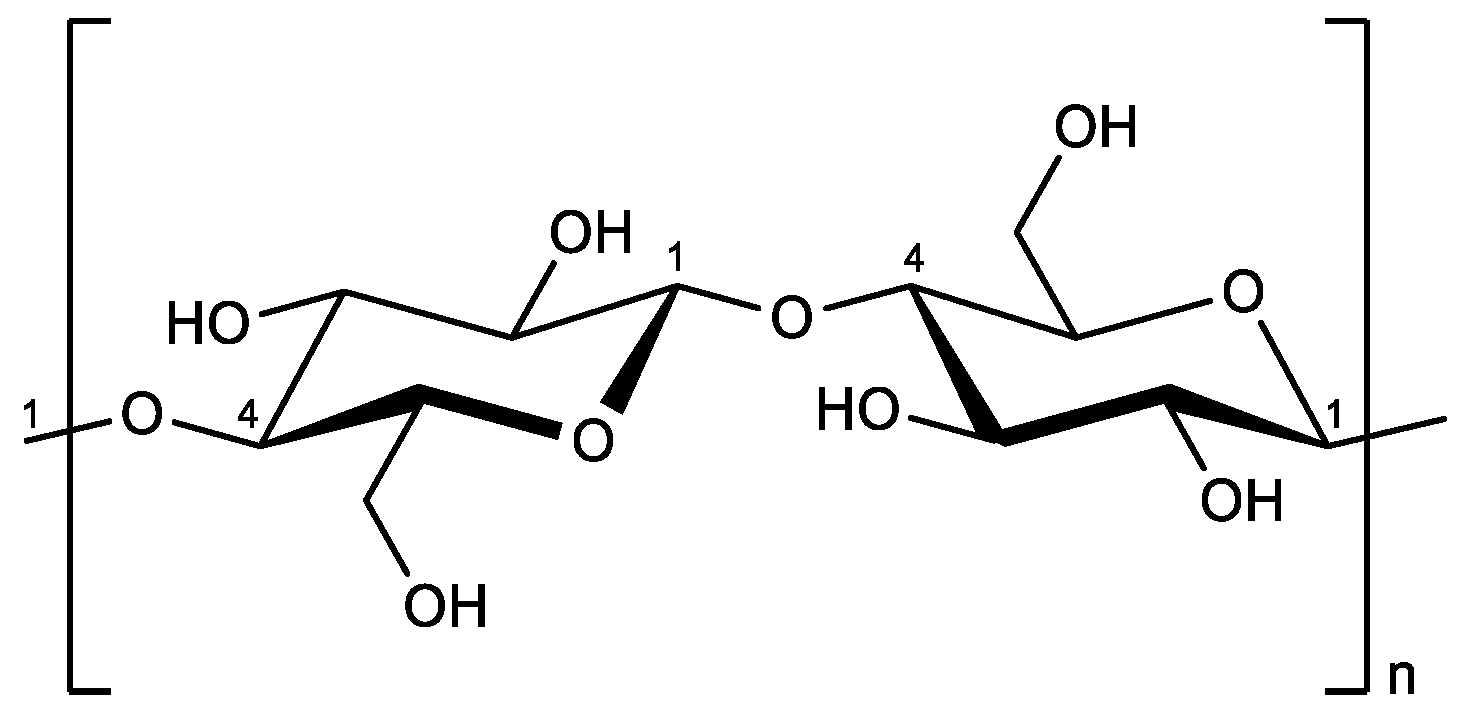
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Reactive Deep Eutectic Solvents (RDESs)
2.2.1. Preparation of DES-1 Using the Vacuum Evaporation (VE) Method
2.2.2. Preparation of DES-2 Using the Ultrasound-Assisted (US) Method
2.2.3. Preparation of DES-3 Using the Heating and Stirring (HS) Method
2.2.4. Preparation of DES-4 Using Both Ultrasonication and Vacuum Evaporation Methods
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis of RDESs
2.4. Polarized Optical Microscopy (POM) Analysis
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
2.6. Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamate (CC)
2.6.1. Experiment 1: Reaction in DES-4 Using VE
2.6.2. Experiment 2: Reaction in DES-4 Using VE and US
2.6.3. Experiment 3: Reaction in DES-4 under US in the Absence of Water
2.6.4. Experiment 4: Reaction in the Absence of DES-4 under US
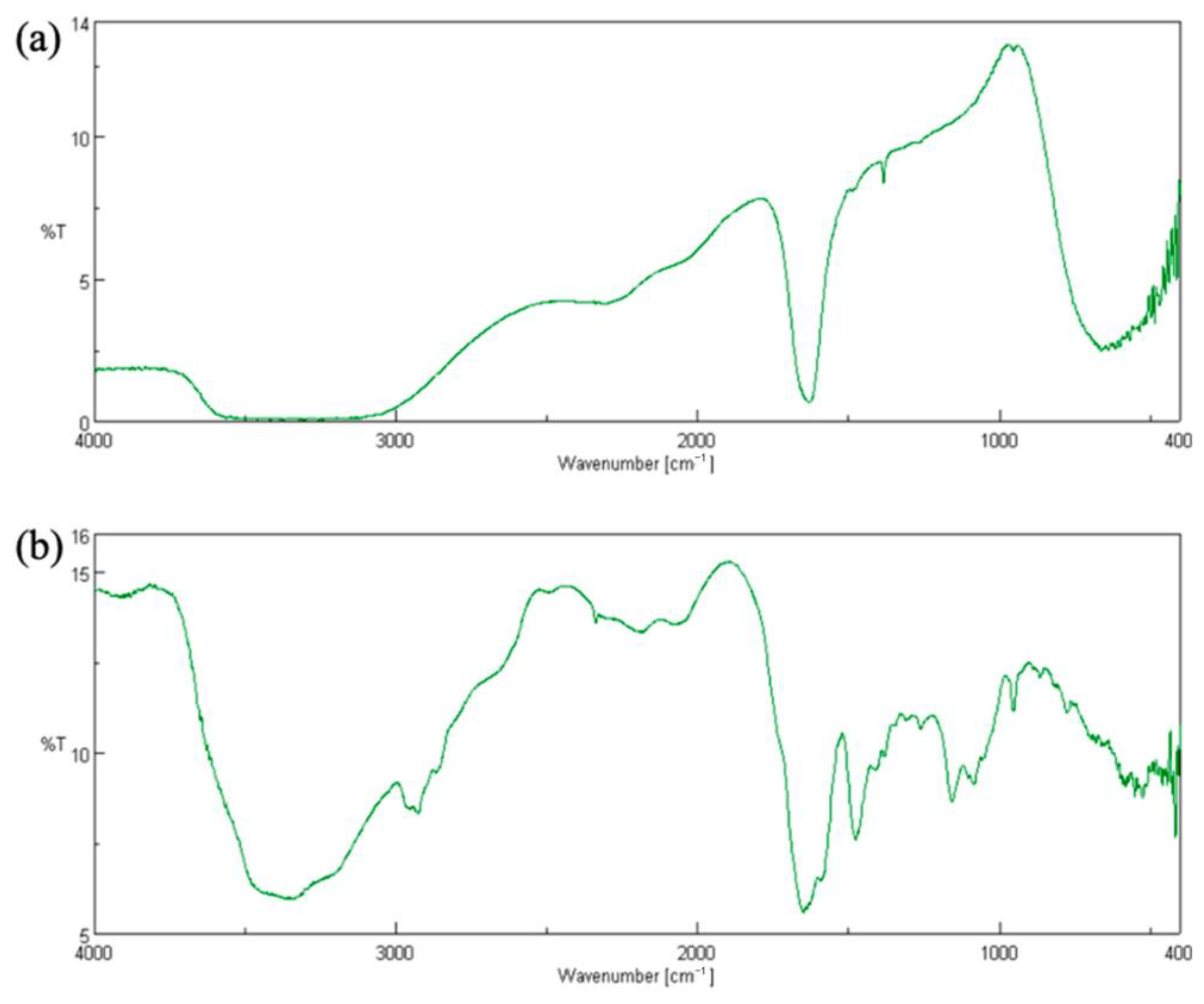
2.7. FT-IR Analysis of CC
2.8. Elemental Analysis of CC
3. Results
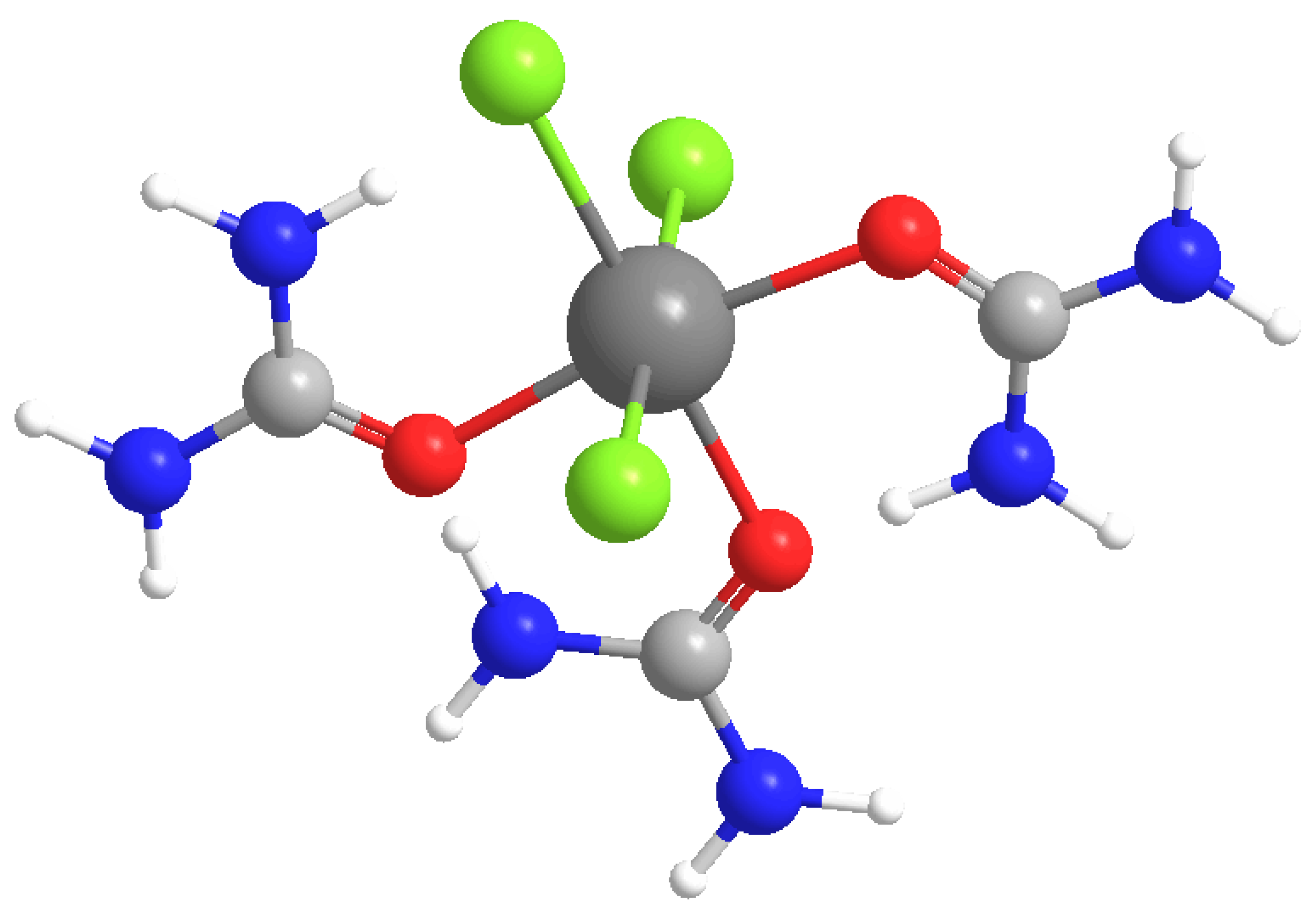
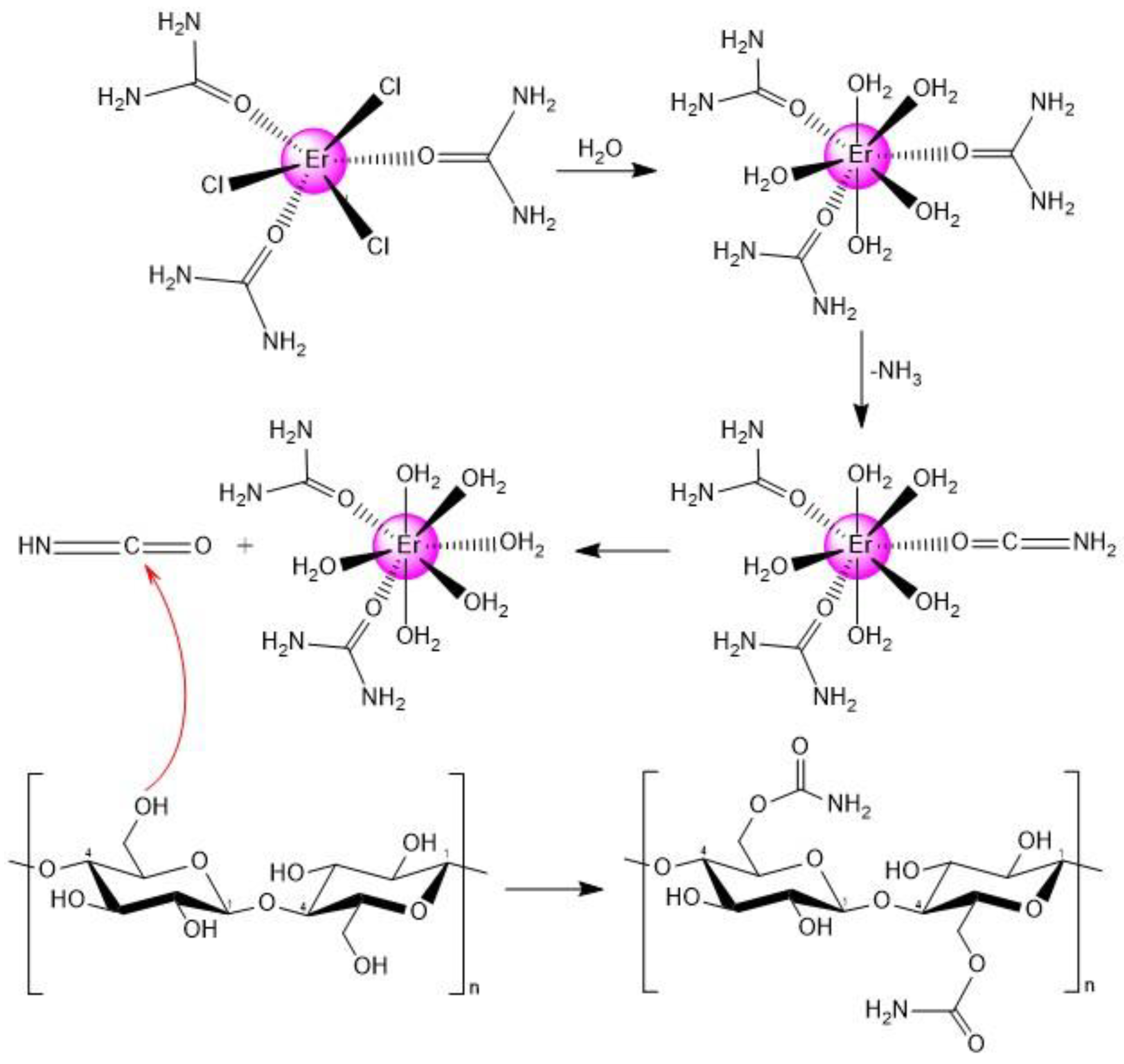
3.1. DES Formation
3.2. DES Characterization
3.3. Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamate
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Substrate | CC Preparation Method | Reaction Time (min) | N (%) a | Degree of Substitution b |
| 1 | Cellulose + H2O | Vacuum evaporation | 60 | 1.59 | 0.19 |
| 2 | Cellulose + H2O | US | 30 | 1.42 | 0.17 |
| 3 | Dried cellulose | US | 30 | 0.86 | 0.10 |
| 4 c | Cellulose + urea | Vacuum evaporation | 60 | 0.27 | 0.05 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, P.; Duarte, H.; Alves, L.; Antunes, F.; Le Moigne, N.; Dormanns, J.; Duchemin, B.; Staiger, M.P.; Medronho, B. From cellulose dissolution and regeneration to added value applications-synergism between molecular understanding and material development. In Cellulose-Fundamental Aspects and Current Trends; Intech: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, T.; Farid, A.; Haq, F.; Kiran, M.; Ullah, A.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Ghazanfar, S.; Sun, H.; Ullah, R.; et al. A Review on the Modification of Cellulose and Its Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nino, A.; Tallarida, M.A.; Algieri, V.; Olivito, F.; Costanzo, P.; De Filpo, G.; Maiuolo, L. Sulfonated Cellulose-Based Magnetic Composite as Useful Media for Water Remediation from Amine Pollutants. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Cheng, F. The Recent Progress of the Cellulose-Based Antibacterial Hydrogel. Gels 2024, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaght, F.E.; Azzaoui, K.; Idrissi, A.E.; Jodeh, S.; Khalaf, B.; Rhazi, L.; Bellaouchi, R.; Asehraou, A.; Hammouti, B.; Sabbahi, R. Synthesis, characterization, and biodegradation studies of new cellulose-based polymers. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostag, M.; Jedvert, K.; Achtel, C.; Heinze, T.; El Seoud, O.A. Recent advaces in solvents for the dissolution, shaping and derivatization of cellulose: Quaternary ammonium electrolytes and their solutions in water and molecular solvents. Molecules 2018, 23, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, D.G.; Bell, D.A.; Henderson, A. Cellulose and cellulose derivatives. In Food Polysaccharides and Their Applications, 2nd ed.; Stati Uniti, CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jedverta, K.; Heinze, T. Cellulose modification and shaping—A review. J. Polym. Engin. 2017, 37, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, B.; Karlström, G.; Stigsson, L. On the mechanism of dissolution of cellulose. J. Mol. Liq. 2010, 156, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michud, A.; Tanttu, M.; Asaadi, S.; Ma, Y.; Netti, E.; Kaariainen, P.; Persson, A.; Berntsson, A.; Hummel, M.; Sixta, H. Ioncell-F: Ionic liquid-based cellulosic textile fibers as an alternative to viscose and Lyocell. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkert, A.; Marsh, K.N.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. Ionic Liquids and their interaction with cellulose. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6712–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striegela, A. Theory and applications of DMAc/LICl in the analysis of polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 34, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, A.; Ishizu, A.; Nakano, J. Dissolution mechanism of cellulose in SO2-amine-dimethylsulfoxide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 33, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.-P.; Weigel, P.; Purz, H.; Ganster, J. Structure formation of regenerated cellulose materials from NMMO-solutions. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1473–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, T.; Koschella, A. Solvents applied in the field of cellulose chemistry-A mini review. Polim.-Cienc. E Tecnol. 2005, 15, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Voigt, W.; Fischer, K. The behaviour of cellulose in hydrated melts of the composition LiX-H2O (X=I-, NO3-, CH3COO-, ClO4-). Cellulose 1999, 6, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, V.K.; Naithani, S. Chemical functionalization of cellulose derived from nonconventional sources. In Cellulose Fibers: Bio- and Nano-Polymer Composites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H. Cellulose Carbamate: Production and Applications; VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2019; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Carbamate from Wood Pulp, Assisted by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. BioResources 2013, 8, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.; Canamares, D.; Ticona, L.A.; Pablos, J.L.; Pena, J.; Hernaiz, M.J. Highly efficient functionalization of hydroxypropyl cellulose with glucuronic acid through click chemistry under microwave irradiation as potential biomaterial with therapeutic properties. Catal. Today 2024, 429, 114495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; He, J.; Yin, C. Preparation and characterization of cellulose carbamate membrane with high strength and transparency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 38, 50068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, R.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, P. Facile preparation and performance study of antibacterial regenerated cellulose carbamate fiber based on N-halamine. Cellulose 2021, 28, 4991–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, C.V.; Rosenau, T.; Hettegger, H. Synthesis of polyanionic cellulose carbamates by homogeneous aminolysis in an ionic liquid/DMF medium. Molecules 2022, 27, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iller, E.; Stupinska, H.; Starostka, P. Properties of cellulose derivatives produced from radiation-Modified cellulose pulps. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2007, 76, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Philipp, B.; Heinze, T.; Heinze, U.; Wagenknecht, W. Comprehensive Cellulose Chemistry: Fundamentals and Analytical Methods, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1–308. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L. An efficient and environmentally friendly method for the synthesis of cellulose carbamate by microwave heating. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1504–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Kondo, T. Green Method for Production of Cellulose Multifilament from Cellulose Carbamate on a Pilot Scale. ACS Sustain. Chem. Engin. 2014, 2, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X. An efficient transformation of cellulose into cellulose carbamates assisted by microwave irradiation. Cellulose 2010, 17, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Yin, C. Preparation and characterization of cellulose carbamate regeneration membrane by supercritical carbon dioxide. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 821, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, H.; Zhou, J. Improved synthesis of cellulose carbamates with minimum urea based on an easy scale-up method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Engin. 2015, 3, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, D.; Siciliano, C.; Trombino, S.; Dumitrescu, D.E.; Suciu, F.; Di Gioia, M.L. Green solvents for the formation of amide linkages. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, H.; Singla, M. Diverse applications of ionic liquids: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118556–118574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nino, A.; Maiuolo, L.; Merino, P.; Nardi, M.; Procopio, A.; Roca-Lpez, D.; Russo, B.; Algieri, V. Efficient Organocatalyst Supported on a Simple Ionic Liquid as a Recoverable System for the Asymmetric Diels-Alder Reaction in the Presence of Water. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Costanzo, P.; De Nino, A.; Maiuolo, L.; Nardi, M.; Olivito, F.; Procopio, A. Simple and efficient Fmoc removal in ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36482–36491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Gagliardi, A.; Leggio, A.; Leotta, V.; Romio, E.; Liguori, A. N-Urethane protection of amines and amino acids in an ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 63407–63420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Barattucci, A.; Bonaccorsi, P.; Leggio, A.; Minuti, L.; Romio, E.; Temperini, A.; Siciliano, C. Deprotection/reprotection of the amino group in α-amino acids and peptides. A one-pot procedure in [Bmim][BF4] ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gericke, M.; Fardim, M.; Heinze, T. Ionic Liquids-Promising but Challenging Solvents for Homogeneous Derivatization of Cellulose. Molecules 2012, 17, 7458–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Radošević, K.; Redovniković, I.R.; Slivac, I.; Srček, V.G. Toxicity mechanisms of ionic liquids. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2017, 68, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Radošević, K.; Redovniković, I.R.; Halambek, J.; Srček, V.G. A brief overview of the potential environmental hazards of ionic liquids. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2014, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nino, A.; Merino, P.; Algieri, V.; Nardi, M.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Russo, B.; Tallarida, M.A.; Maiuolo, L. Synthesis of 1,5-functionalized 1,2,3-triazoles using ionic liquid/iron (III) chloride as an efficient and reusable homogeneous catalyst. Catalysts 2018, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents-solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Engin. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, F.P.; Vitale, P.; Capriati, V. Deep eutectic solvents and their applications as green solvents. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 21, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.A.; Baeza, A.; Chinchilla, R.; Guillena, G.; Pastor, I.M.; Ramon, D.J. Deep Eutectic Solvents: The organic reaction medium of the century. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 4, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, C.L.; Manfredi, N.; Perna, F.M.; Capriati, V.; Abbotto, A. Designing Eco-Sustainable Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells by the Use of a Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent as an Effective Electrolyte Medium. Chem.-Eur. J. 2018, 24, 17656–17659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, D.; Siciliano, C.; Di Gioia, M.L. Reactive Deep Eutectic Solvents for EDC-mediated Amide Synthesis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, D.; Marset, X.; Guillena, G.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Ramon, D.J. Visible-Light-Mediated Amide Synthesis in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taklimi, S.M.; Divsalar, A.; Ghalandari, B.; Ding, X.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Omar, K.A.; Saboury, A.A. Effects of deep eutectic solvents on the activity and stability of enzymes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Gawande, M.B. Editorial: Advances in the development and application of deep eutectic solvents. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 125871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, D.; Siciliano, C.; De Rose, R.; Trombino, S.; Cassano, R.; Di Gioia, M.L. A Bronsted Acidic Deep Eutectic Solvent for N-Boc Deprotection. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, N.; Saavedra, B.; Guillena, G.; Ramón, D.J. Indium-mediated allylation of carbonyl compounds in deep eutectic solvents. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Cassano, R.; Costanzo, P.; Cano, N.H.; Maiuolo, L.; Nardi, M.; Nicoletta, F.P.; Oliverio, M.; Procopio, A. Green synthesis of privileged benzimidazole scaffolds using active deep eutectic solvent. Molecules 2019, 24, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirvio, J.A.; Ukkola, J.; Liimatainen, H. Direct sulfation of cellulose fibers using a reactive deep eutectic solvent to produce highly charged cellulose nanofibers. Cellulose 2019, 26, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willberg-Keyriläinen, P.; Hiltunen, J.; Ropponen, J. Production of cellulose carbamate using urea-based deep eutectic solvents. Cellulose 2018, 25, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Bell, T.J.; Handaa, S.; Stoddartb, B. Cationic functionalisation of cellulose using a choline based ionic liquid analogue. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 784–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Yu, G.; Fu, Y.; Yin, C. The preparation and study of regenerated cellulose fibers by cellulose carbamate pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 7, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirviö, J.A.; Heiskanen, J.P. Synthesis of alkaline-soluble cellulose methyl carbamate using reactive deep eutectic solvent. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Xu, B.; Feng, C.; Bai, Y.; Liao, H.; Sun, S.; Giesy, J.P.; Guo, W. Copper and zinc, but not other priority toxic metals, pose risks to native aquatic species in a large urban lake in Eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfanifar, E.; Jahanjo, V.; Kasalkhe, N.; Erfanifar, E. Acute toxicity test of Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2) in sobaity seabream (Sparidebtex hasta). Environ. Sci. 2016, 1, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, C.T.; Sandstead, H.H.; Prasad, A.S.; Newberne, P.M.; Fraker, P.J. Zinc: Health effects and research priorities for the 1990s. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 5–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hjortsø, E.; Ovist, J.; Bud, M.I.; Thomsen, J.L.; Andersen, J.B.; Wiberg-Jørgensen, F.; Jensen, N.K.; Jones, R.; Reid, L.M.; Zapol, W.M. ARDS after accidental inhalation of zinc chloride smoke. Intensive Care Med. 1988, 14, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, S.; Slama, I.B.; Mrad, I.; Rihane, N.; Khemissi, W.; El Mir, L.; Rhouma, K.B.; Abdelmelek, H.; Sakly, M. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and/or zinc chloride on biochemical parameters and mineral levels in rat liver and kidney. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gómez, C.; Babin, M.; Obrador, A.; Álvarez, J.M.; Fernández, M.D. Integrating ecotoxicity and chemical approaches to compare the effects of ZnO nanoparticles, ZnO bulk, and ZnCl2 on plants and microorganisms in a natural soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 16803–16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Suzuki, K.T. Exposure, metabolism, and toxicity of rare earths and related compounds. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Procopio, A.; Dalpozzo, R.; De Nino, A.; Nardi, M.; Oliverio, M.; Russo, B. Er(OTf)3 as a Valuable Catalyst in a Short Synthesis of 2′,3′-Dideoxy Pyranosyl Nucleosides via Ferrier Rearrangement. Synthesis 2006, 15, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, L.; Russo, B.; Algieri, V.; Nardi, M.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Tallarida, M.A.; De Nino, A. Regioselective synthesis of 1,5-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazoles by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition: Role of Er(OTf)3, ionic liquid and water. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliverio, M.; Nardi, M.; Costanzo, P.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Procopio, A. Erbium salts as non-toxic catalysts compatible with alternative reaction media. Sustainability 2018, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, M.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Costanzo, P.; De Nino, A.; Maiuolo, L.; Oliverio, M.; Olivito, F.; Procopio, A. Selective acetylation of small biomolecules and their derivatives catalyzed by Er(OTf)3. Catalysts 2017, 7, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, T.R.; Kwon, H.K.; Jung, S.P. Toxicological Evaluations of Rare Earths and Their Health Impacts to Workers: A Literature Review. Saf. Health Work 2013, 4, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Guo, L.; Wu, X.; Ma, X.; Xia, Y. Urea formation from carbon dioxide and ammonia at atmospheric pressure. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2012, 10, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesiene, J.; Kazlauske, J. Functionalization of cellulose: Synthesis of water-soluble cationic cellulose derivatives. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2013, 47, 515. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, R.; Han, H.; Wu, K.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Liang, B. Preparation strategy and stability of deep eutectic solvents: A case study based on choline chloride-carboxylic acid. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, F.J.; Espino, M.; Fernández, M.A.; Silva, M.F. A greener approach to prepare natural deep eutectic solvents. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 6122–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieha, Y.-H.; Lia, Y.; Pana, Z.; Chenc, Z.; Luc, J.; Yuanc, J.; Zhua, Z.; Zhang, J. Ultrasonication-assisted synthesis of alcohol-based deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of active compounds from ginger. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, T.J. Ultrasound in synthetic organic chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1997, 26, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Overview of acidic deep eutectic solvents on synthesis, properties and applications. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, C. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of semicrystalline polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1589–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nada, A.-A.M.; Kamel, S.; El-Sakhawy, M. Thermal behavior and infrared spectroscopy of cellulose carbamates. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 70, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossy, C.; Helm, L.; Merbach, A.E. Oxygen-17 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Kinetic Study of Water Exchange on the Lanthanide (IlI). Aqua Ions Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, S.A. Establishing coordination numbers for the lanthanides in simple complexes. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2005, 8, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, M.; Susai, R. Investigation of inhibitive action of urea-Zn2+ system in the corrosion control of carbon steel in sea water. I. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 8048–8060. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Singh, R.; Chaudhary, M.; Kushwaha, S. Cellulose: A review as natural, modified, and activated carbon adsorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 1, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Shen, X. Synthesis of cellulose carbamate by supercritical CO2-assisted impregnation: Structure and rheological properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2111–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Laaksonen, A.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Ji, X. The peculiar effect of water on ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8685–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

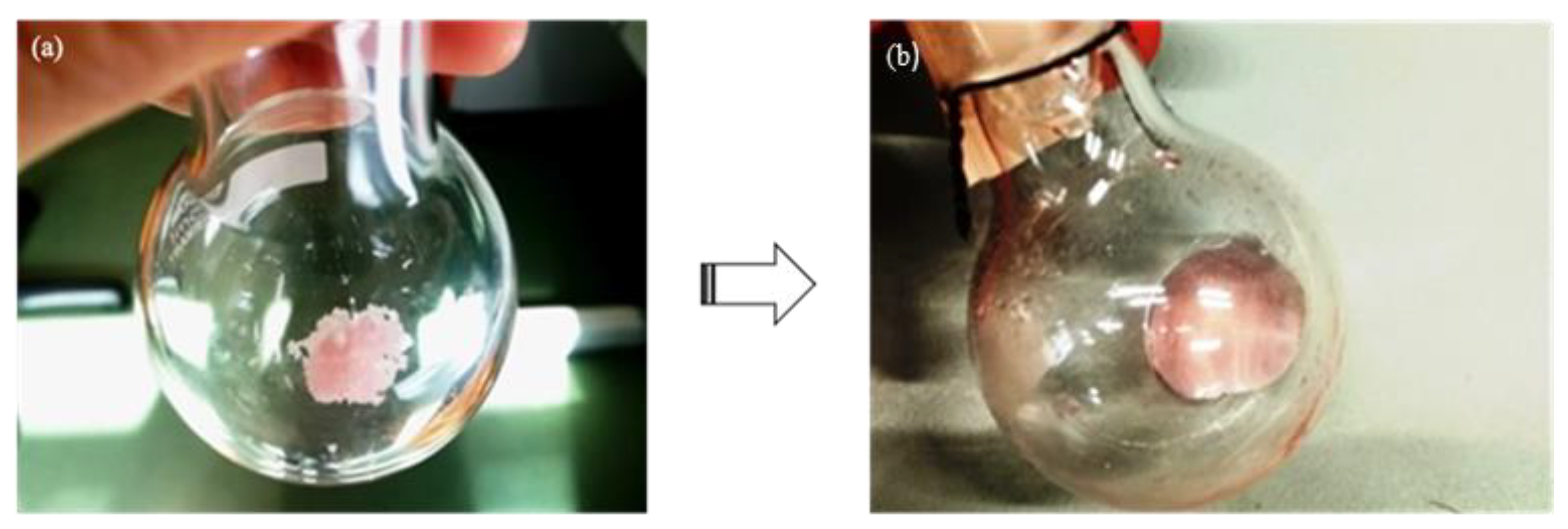


| Entry | DES | Components |
Molar Ratio | Preparation Method | Time (min) | Aspect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | ErCl3 anhydrous: urea | 1:1 | Vacuum evaporation | 60 | Pink solid |
| 2 | - | ErCl3 anhydrous: urea | 1:3 | Vacuum evaporation | 60 | Pink solid |
| 3 | - | ErCl3·6H2O: urea | 1:3 | Vacuum evaporation | 60 | Pink highly viscous liquid with particles in suspension |
| 4 | DES-1 | ErCl3·6H2O: urea (+ 20% water) | 3:10 | Vacuum evaporation | 60 |
Clear pink viscous liquid |
| 5 | - | ErCl3·6H2O: urea (+20% water) | 3:10 | Ultrasonication-assisted preparation | 30 |
Clear pink viscous liquid with particles in suspension |
| 6 | DES-2 | ErCl3·6H2O: urea (+20% water) | 3:10 | Ultrasonication-assisted preparation | 60 |
Clear pink viscous liquid |
| 7 | DES-3 | ErCl3·6H2O: urea | 3:10 | Heating and stirring | 60 |
Clear pink viscous liquid |
| 8 | DES-4 | ErCl3·6H2O: urea | 3:10 | Ultrasonication-assisted preparation and vacuum evaporation | 120 |
Clear pink viscous liquid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Algieri, V.; Maiuolo, L.; Procopio, D.; Costanzo, P.; Nicoletta, F.P.; Trombino, S.; Di Gioia, M.L.; De Nino, A. Reactive Deep Eutectic Solvent for an Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamate. Polymers 2024, 16, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060757
Algieri V, Maiuolo L, Procopio D, Costanzo P, Nicoletta FP, Trombino S, Di Gioia ML, De Nino A. Reactive Deep Eutectic Solvent for an Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamate. Polymers. 2024; 16(6):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060757
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlgieri, Vincenzo, Loredana Maiuolo, Debora Procopio, Paola Costanzo, Fiore Pasquale Nicoletta, Sonia Trombino, Maria Luisa Di Gioia, and Antonio De Nino. 2024. "Reactive Deep Eutectic Solvent for an Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamate" Polymers 16, no. 6: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060757
APA StyleAlgieri, V., Maiuolo, L., Procopio, D., Costanzo, P., Nicoletta, F. P., Trombino, S., Di Gioia, M. L., & De Nino, A. (2024). Reactive Deep Eutectic Solvent for an Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamate. Polymers, 16(6), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060757












