Computational Model for Analysing the Tooth Deflection of Polymer Gears
Abstract
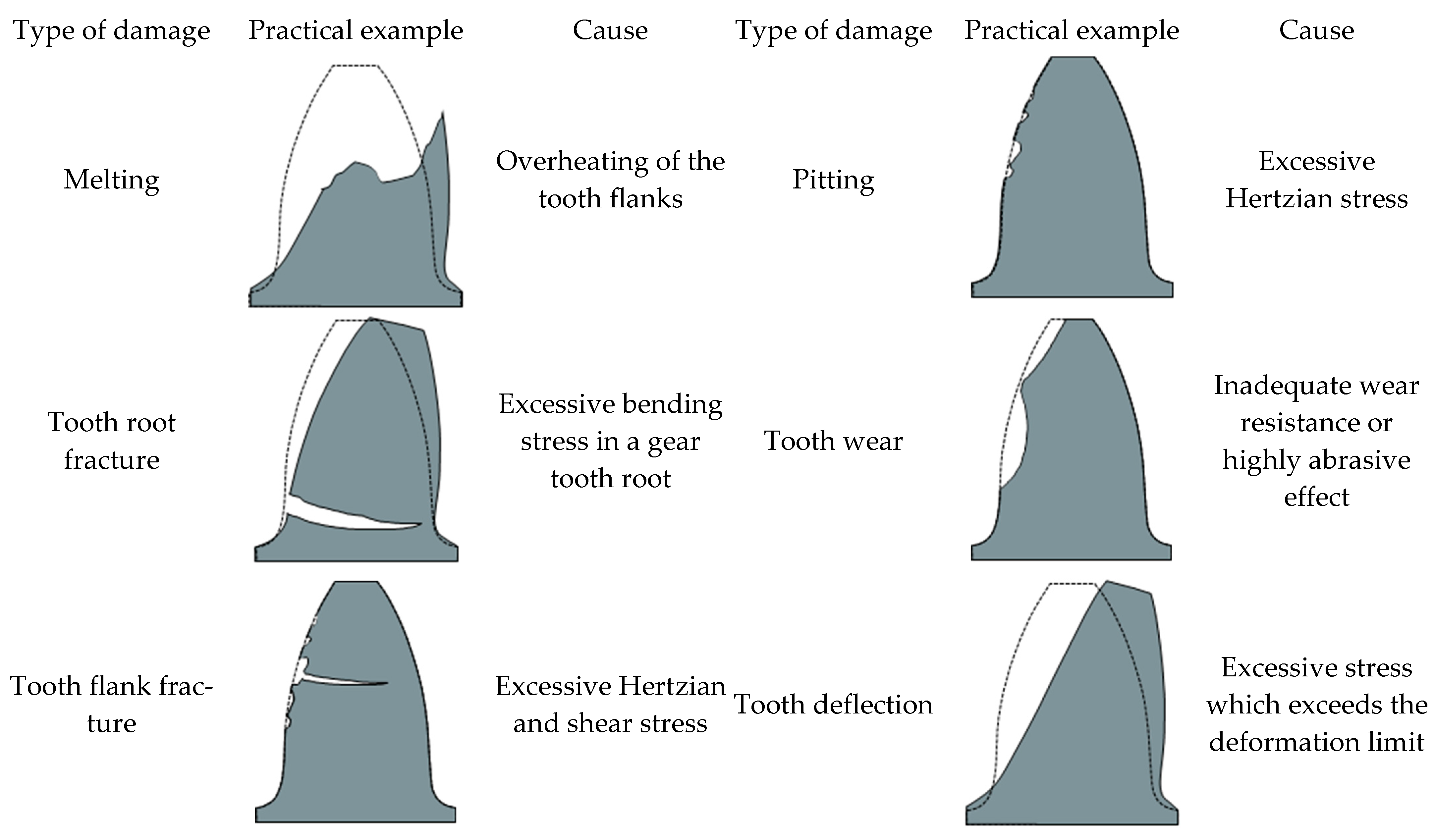
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Geometry of Analysed Gear Pair
2.2. Determination of Tooth Deflection According to VDI 2736 Guidelines
2.3. Computational Modelling
2.3.1. Geometry
2.3.2. Boundary Conditions
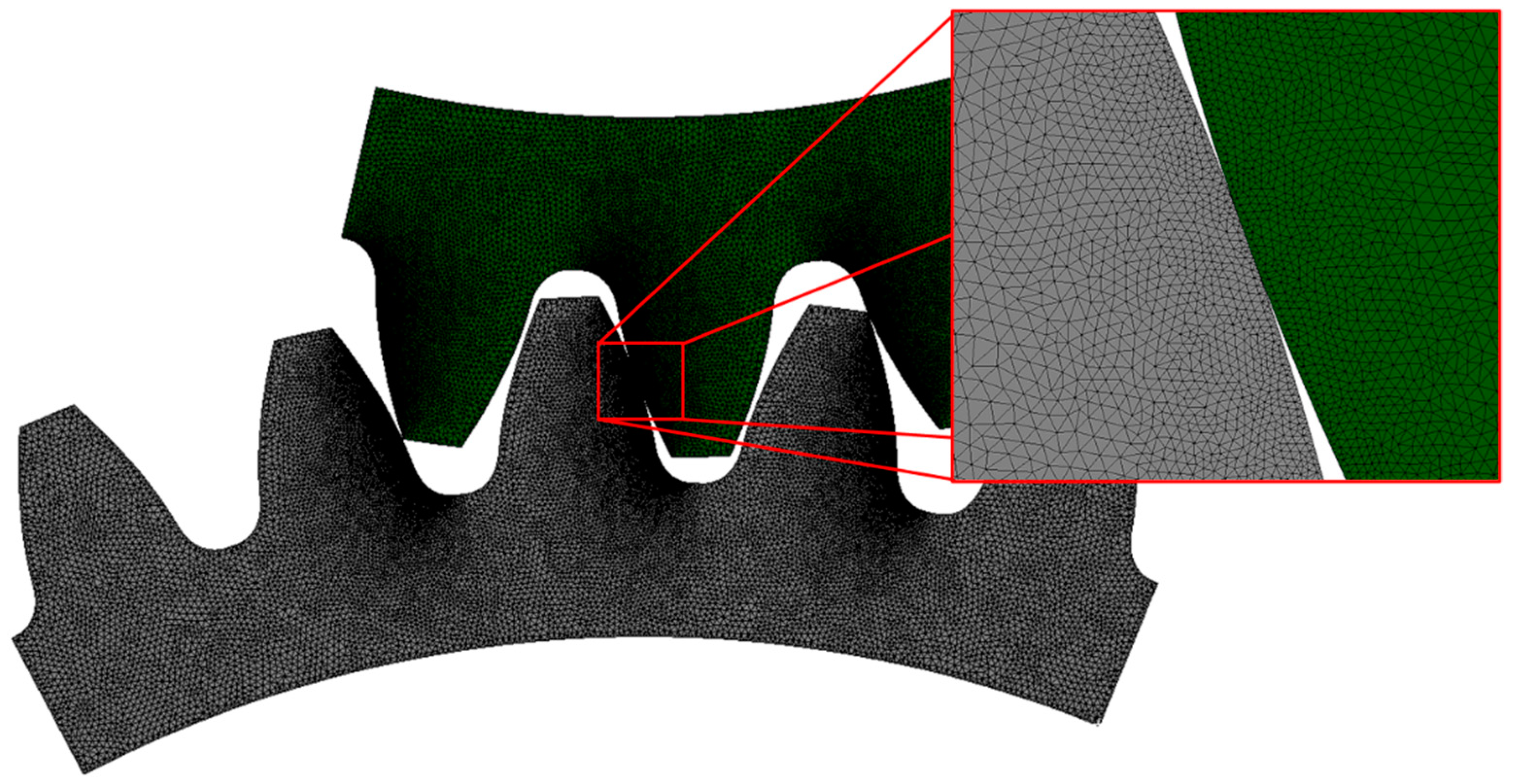
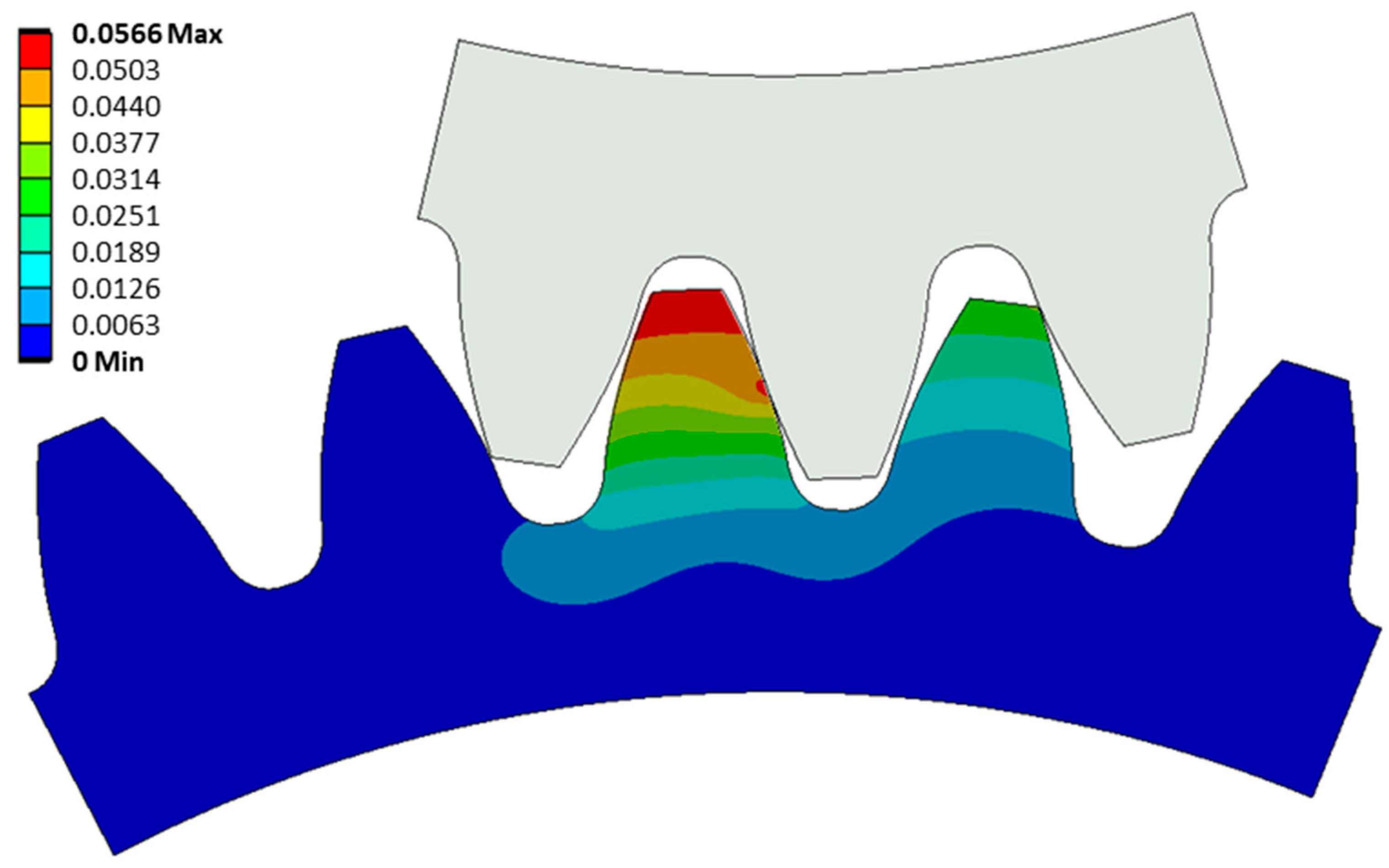
2.3.3. Finite Element Mesh
2.3.4. Numerical Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
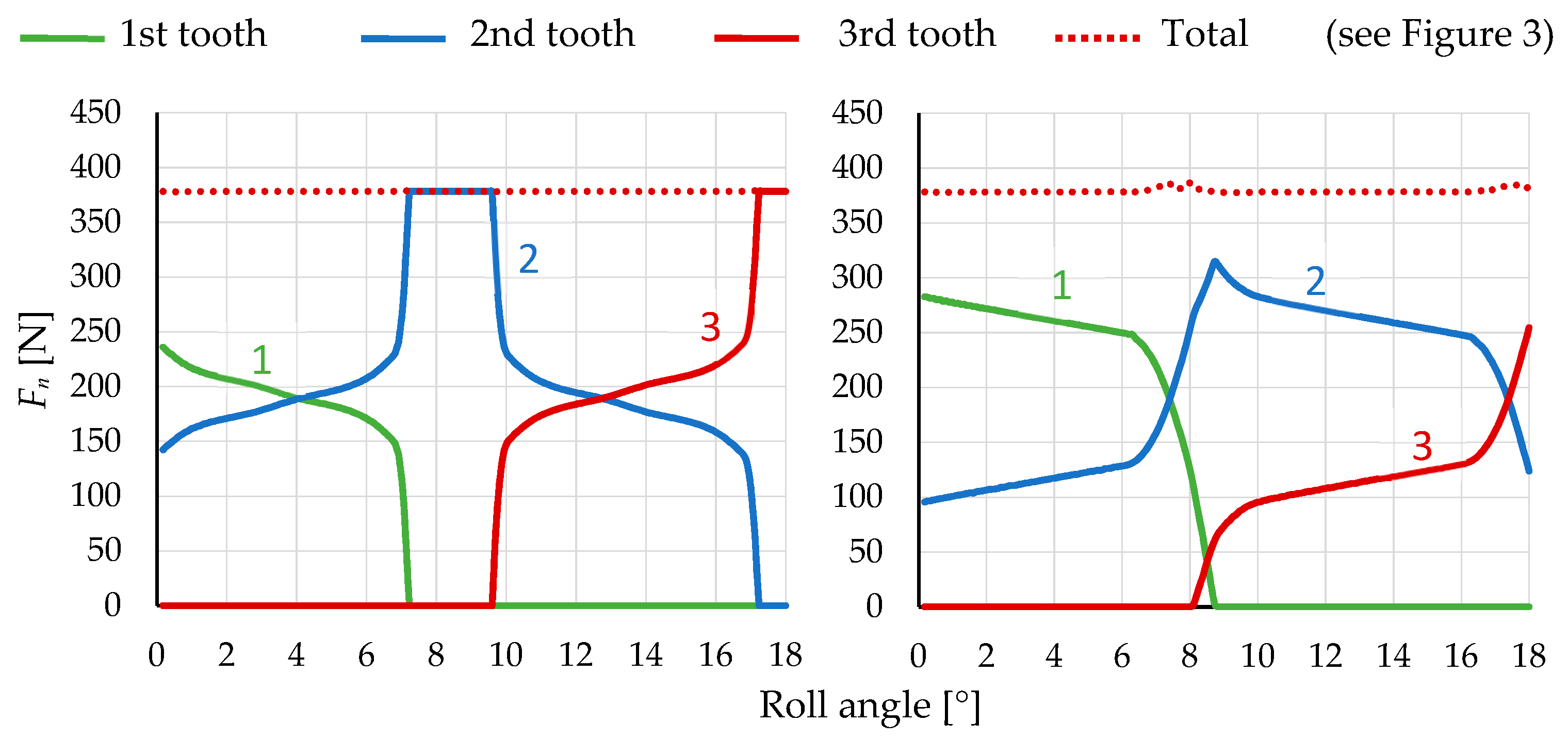
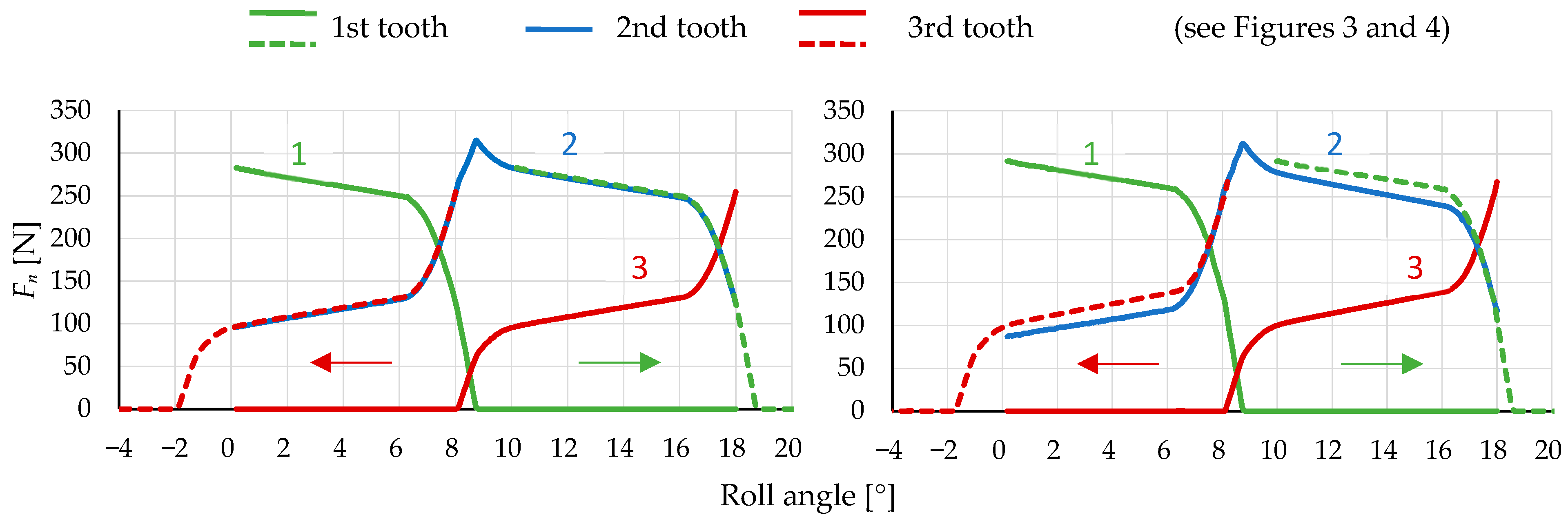
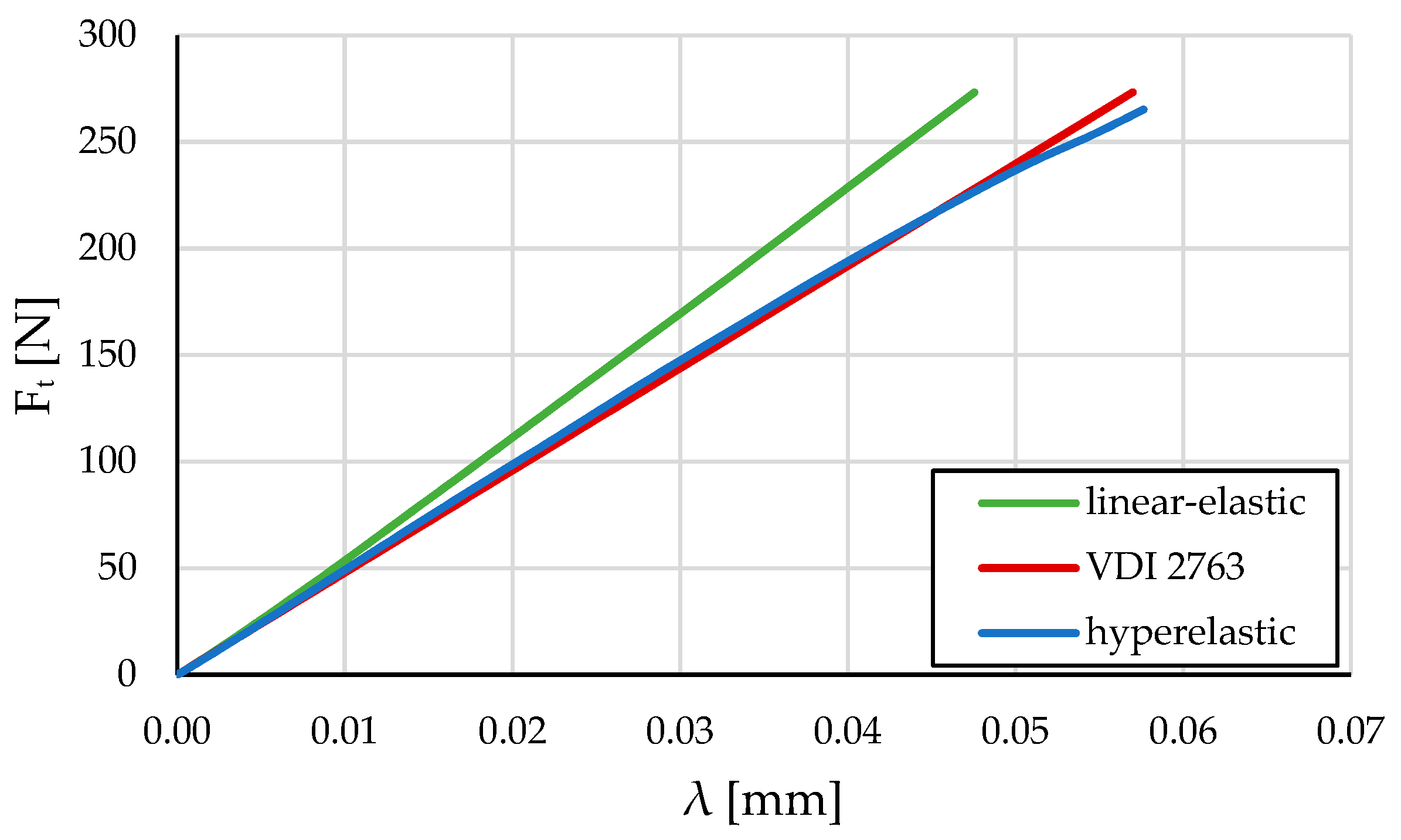
3.1. Model Comparison
3.2. Comparison between Numerical and Analytical (VDI 2736) Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muratović, E.; Muminović, A.; Delić, M.; Pervan, N.; Muminović, A.J.; Šarić, I. Potential and Design Parameters of Polyvinylidene Fluoride in Gear Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanec, B.; Glodež, S.; Belšak, A. Noise Evaluation of Coated Polymer Gears. Polymers 2023, 15, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trobentar, B.; Hriberšek, M.; Kulovec, S.; Glodež, S.; Belšak, A. Noise Evaluation of S-Polymer Gears. Polymers 2022, 14, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miler, D.; Hoić, M.; Domitran, Z.; Žeželj, D. Prediction of Friction Coefficient in Dry-Lubricated Polyoxymethylene Spur Gear Pairs. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 138, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.M.; Keogh, P.S. Wear Mechanisms in Polyoxymethylene Spur Gears. Wear 2019, 428–429, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Zhang, R.; Wei, P.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Lu, Z. The Durability Performance of Polyketone Gears under Various Lubrication Conditions. J. Tribol. 2022, 144, 091203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogačnik, A.; Tavčar, J. An Accelerated Multilevel Test and Design Procedure for Polymer Gears. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavčar, J.; Grkman, G.; Duhovnik, J. Accelerated Lifetime Testing of Reinforced Polymer Gears. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2018, 12, JAMDSM0006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, K.A.M. Wear and Mechanical Contact Behavior of Polymer Gears. J. Tribol. 2019, 141, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VDI 2736; Part 1 Thermoplastic Gear Wheels—Materials, Material Selection, Producton Methods, Production Tolerances, Form Design. Verein Deutscher Ingenieure: Harzgerode, Germany, 2016.
- VDI 2736; Part 2 Thermoplastic Gear Wheels—Cylindrical Gears—Calculation of the Load—Carrying Capacity. Verein Deutscher Ingenieure: Harzgerode, Germany, 2016.
- VDI 2736; Part 3 Thermoplastic Gear Wheels—Crossed Helical Gears—Mating Cylindrical Worm with Helical Gear—Calculation of the Load Carrying Capacity. Verein Deutscher Ingenieure: Harzgerode, Germany, 2016.
- VDI 2736; Part 4 Thermoplastic Gear Wheels—Determination of Strength Parameters on Gears. Verein Deutscher Ingenieure: Harzgerode, Germany, 2016.
- Zorko, D.; Kulovec, S.; Duhovnik, J.; Tavčar, J. Durability and Design Parameters of a Steel/PEEK Gear Pair. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 140, 825–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilvelan, S.; Gnanamoorthy, R. Damage Mechanisms in Injection Molded Unreinforced, Glass and Carbon Reinforced Nylon 66 Spur Gears. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2004, 11, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Koffi, D.; Toubal, L.; Erchiqui, F. Life and Damage Mode Modeling Applied to Plastic Gears. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 58, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Siddhartha; Singh, P.K. Polymer Spur Gears Behaviors under Different Loading Conditions: A Review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2018, 232, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarita, B.; Senthilvelan, S. Effects of Lubricant on the Surface Durability of an Injection Molded Polyamide 66 Spur Gear Paired with a Steel Gear. Tribol. Int. 2019, 137, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Siddhartha; Singh, A.K. An Investigation on the Thermal and Wear Behavior of Polymer Based Spur Gears. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochrein, J.-F.; Otto, M.; Stahl, K. Fast Tooth Deflection Calculation Method and Its Validation. Forsch. Ingenieurwes. 2022, 86, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Greenwood, D.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Goodship, V.; Shrouti, C.; Chetwynd, D.; Langlois+, P. The Wear Resistance Improvement of Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composite Gears. Wear 2019, 426–427, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Chetwynd, D.G.; Millson, M. A New Method for Testing Polymer Gear Wear Rate and Performance. Polym. Test. 2020, 82, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trobentar, B.; Glodež, S.; Zafošnik, B. Gear Tooth Deflection of Spur Polymer Gears. In Proceedings of the International Gear Conference 2014, Lyon, France, 26–28 August 2014; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Trobentar, B.; Glodež, S.; Flašker, J.; Zafošnik, B. The Influence of Surface Coatings on the Tooth Tip Deflection of Polymer Gears. Mater. Tehnol. 2016, 50, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melick, H.G.H. Tooth Bending Effects in Plastic Spur Gears. Gear Technol. 2007, 24, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Vignesh, S.; Johnney Mertens, A. Numerical Investigation on the Premature and Extended Contact Behaviour of Engineering Thermoplastic Gears and Its Effect in Gear Kinematics. Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 2023, 19, 766–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, S.; Johnney Mertens, A. A Deflection Study of Steel-Polypropylene Gear Pair Using Finite Element Analysis. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 90, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimpour, M.; Dearn, K.D.; Walton, D. A Kinematic Analysis of Meshing Polymer Gear Teeth. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2010, 224, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, C.; Wolf, M.; Schubert, D.; Drummer, D. In Situ Investigation of the Influence of Varying Load Conditions on Tooth Deformation and Wear of Polymer Gears. Forsch. Ingenieurwes. 2022, 86, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, C.; Drummer, D. Limitations of the Check Calculation for Tooth Deformation of Plastic Gears According to Gear Design Guideline VDI 2736. Polymers 2023, 15, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černe, B.; Petkovšek, M. High-Speed Camera-Based Optical Measurement Methods for in-Mesh Tooth Deflection Analysis of Thermoplastic Spur Gears. Mater. Des. 2022, 223, 111184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bončina, T.; Polanec, B.; Zupanič, F.; Glodež, S. Wear Behaviour of Multilayer Al-PVD-Coated Polymer Gears. Polymers 2022, 14, 4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 53:1998; Cylindrical Gears for General and Heavy Engineering—Standard Basic Rack Tooth Profile. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- DIN 867; Basic Rack Tooth Profiles for Involute Teeth of Cylindrical Gears for General Engineering and Heavy Engineering. German Guidelines, Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1986.
- DIN 58400; Basic Rack for Involute Teeth of Cylindrical Gears for Fine Mechanics. German Guidelines, Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1984.
- DIN 3990; Calculation of Load Capacity of Cylindrical Gears. German Standard, Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1987.
- Ansys 2023 R1 Engineering Simulation Software; Ansys: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2023.







| Parameter | Tested Gear | Supported Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Material | POM | Steel (16MnCr5) |
| Normal module m | 2.5 mm | 2.5 mm |
| Pressure angle αn | 20° | |
| Helix angle β | 0° | |
| Number of teeth z | 36 | 36 |
| Tooth width b | 14 mm | 14 mm |
| Profile shift coefficient x | 0 | 0 |
| Centre distance a | 90 mm | |
| Basic rack profile | ISO 53 [33] | |
| Young’s modulus E | 2600 MPa | 210,000 MPa |
| Poisson’s ratio ν | 0.386 | 0.280 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ignatijev, A.; Glodež, S.; Kramberger, J. Computational Model for Analysing the Tooth Deflection of Polymer Gears. Polymers 2024, 16, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050677
Ignatijev A, Glodež S, Kramberger J. Computational Model for Analysing the Tooth Deflection of Polymer Gears. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050677
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgnatijev, Aljaž, Srečko Glodež, and Janez Kramberger. 2024. "Computational Model for Analysing the Tooth Deflection of Polymer Gears" Polymers 16, no. 5: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050677
APA StyleIgnatijev, A., Glodež, S., & Kramberger, J. (2024). Computational Model for Analysing the Tooth Deflection of Polymer Gears. Polymers, 16(5), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050677






