Carbon Material-Reinforced Polymer Composites for Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Carbon-Reinforced Polymer Composites
2.1. Carbon-Reinforced Phenolic Resin Composites
2.2. Carbon-Reinforced Polypropylene Composites
2.3. Carbon-Reinforced Polyphenylene Sulfide Composites
2.4. Carbon-Reinforced Polybenzoxazine Composites
2.5. Carbon-Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites
3. Carbon-Reinforced Two-Polymer Composites
4. Discussion
4.1. Synthesis Methods
4.2. Production Costs
4.3. Stability of BPs
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
- (a)
- For single-polymer composites reinforced with carbon allotropes, phenolic resin, polypropylene, PPS, polybenzoxazine, and epoxy resin are the polymers more commonly used for BPs. However, more studies are required for PPS, polybenzoxazine, and epoxy resin-based composites since the studies developed to date show promising results.
- (b)
- The single-polymer composites have been reinforced using various types of carbon allotropes, mainly graphite, carbon fibers, carbon black, carbon nanotubes, and graphene. However, it is necessary to extend the study on single-polymer composites reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene since these are popular in the literature for their extraordinary electrical and mechanical properties.
- (c)
- Two-polymer composites with one, two, or three carbon allotropes have been partially explored with outstanding results. Therefore, more detailed studies on these composites should be conducted.
- (d)
- Almost all composites were produced using the compression molding technique. Nevertheless, the use of additive manufacturing could be a good strategy to produce BPs using the composites analyzed in this review.
- (e)
- Future studies should report on the properties required by the DOE and, thus, facilitate the analysis of the results.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Höök, M.; Tang, X. Depletion of Fossil Fuels and Anthropogenic Climate Change—A Review. Energy Policy 2013, 52, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.H.; Hassim, M.H.; Ng, D.K.S. Review of Evolution, Technology and Sustainability Assessments of Biofuel Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 71, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, Z.; Zafaranloo, A.; Rafiee, A.; Mérida, W.; Lipiński, W.; Khalilpour, K.R. Hydrogen as an Energy Vector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 120, 109620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, H.; Louis, C.; Jose, S.; Prakash, J.; Muthuswamy, N.; Buan, M.E.M.; Flox, C.; Chavan, S.; Shi, X.; Kauranen, P.; et al. Is the H2 Economy Realizable in the Foreseeable Future? Part I: H2 Production Methods. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 13777–13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, I.P. Hydrogen the Fuel for 21st Century. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 7368–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, P.; Poullikkas, A. A Comparative Overview of Hydrogen Production Processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Veras, T.; Mozer, T.S.; da Costa Rubim Messeder dos Santos, D.; da Silva César, A. Hydrogen: Trends, Production and Characterization of the Main Process Worldwide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 2018–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, D.J.; Malardier-Jugroot, C. Review of Hydrogen Storage Techniques for on Board Vehicle Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 14595–14617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Martínez, H.; García-Hilerio, B.; Montejo-Alvaro, F.; Gazga-Villalobos, A.; Rojas-Chávez, H.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.P. Density functional theory-based approaches to improving hydrogen storage in graphene-based materials. Molecules 2024, 29, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Escorihuela, J.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Compañ, V. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs): Advances and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Martínez, H.; Guerra-Cabrera, W.; Flores-Rojas, E.; Ruiz-Villalobos, D.; Rojas-Chávez, H.; Peña-Castañeda, Y.A.; Medina, D.I. Pt-Free Metal Nanocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Combining Experiment and Theory: An Overview. Molecules 2021, 26, 6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Padmanaban, S.; Venkitusamy, K.; Selvamuthukumaran, R.; Blaabjerg, F.; Siano, P. Recent Advances and Challenges of Fuel Cell Based Power System Architectures and Control—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Martínez, H.; Rojas-Chávez, H.; Matadamas-Ortiz, P.T.; Ortiz-Herrera, J.C.; López-Chávez, E.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Medina, D.I. Current Progress of Pt-Based ORR Electrocatalysts for PEMFCs: An Integrated View Combining Theory and Experiment. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 19, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, A.; Chaudhuri, T.; Spagnol, P. Bipolar Plates for PEM Fuel Cells: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2005, 30, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.A.; De Oliveira, M.C.L.; Ett, G.; Ett, V. Carbon Materials in Composite Bipolar Plates for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: A Review of the Main Challenges to Improve Electrical Performance. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2945–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.C.L.; Ett, G.; Antunes, R.A. Materials Selection for Bipolar Plates for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Using the Ashby Approach. J. Power Sources 2012, 206, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DOE Technical Targets for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Components. Department of Energy. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/doe-technical-targets-polymer-electrolyte-membrane-fuel-cell-components (accessed on 31 December 2023).
- Boyaci San, F.G.; Tekin, G. A Review of Thermoplastic Composites for Bipolar Plate Applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alo, O.A.; Otunniyi, I.O.; Pienaar, H.; Iyuke, S.E. Materials for Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell: Performance Criteria and Current Benchmarks. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 7, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Radzuan, N.A.; Sulong, A.B.; Sahari, J. A Review of Electrical Conductivity Models for Conductive Polymer Composite. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9262–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ling, C.Y.; Han, M.; Yong, R.Y.; Sun, D.; Chen, J. Review on Current Research of Materials, Fabrication and Application for Bipolar Plate in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 29832–29847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, C.; Naina Mohamed, S.; Devanathan, L.S. A Comprehensive Review of Current Research on Various Materials Used for Developing Composite Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 4100–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, B.D.; Huang, J.; Baird, D.G. Review of Materials and Processing Methods Used in the Production of Bipolar Plates for Fuel Cells. Int. Mater. Rev. 2007, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, N.; Dhakal, H.N.; Tjong, J.; Jaffer, S.; Yang, W.; Sain, M. Recent Advances and Future Perspectives of Carbon Materials for Fuel Cell. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Nasir, M.; Pervaiz, M.; Alothman, O.Y. A Review on Phenolic Resin and Its Composites. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 13, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilato, L. Phenolic Resins: A Century of Progress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–545. [Google Scholar]
- Okuno, K.; Woodhams, R.T. Mechanical Properties and Characterization of Phenolic Resin Syntactic Foams. J. Cell. Plast. 1974, 10, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wei, D.; Wu, Y.; Xu, T. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Graphene Oxide/Phenolic Resin Composite. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, R.; Hadianfard, M.J.; Golikand, A.N. Manufacture of a Polymer-Based Carbon Nanocomposite as Bipolar Plate of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Li, A.J.; Wang, W.Q.; Xia, L.G.; Wang, Y.M. Study on the Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Phenol Formaldehyde Resin/Graphite Composite for Bipolar Plate. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.-B.; Yang, L.; Li, J.-X.; Yang, L. Study on the Preparation and Properties of Novolac Epoxy/Graphite Composite Bipolar Plate for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 3105–3109. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, K.; Adams, D.; Hao, A.; Zheng, J.P.; Liang, Z.; Nguyen, N. Highly Conductive and Strong Graphite-Phenolic Resin Composite for Bipolar Plate Applications. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 14320–14331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchiya, A.P.; Le, N.T.; Putnam, Z.A.; Harrington, M.; Krishnan, S. Microporous Graphite Composites of Tailorable Porosity, Surface Wettability, and Water Permeability for Fuel Cell Bipolar Plates. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 10203–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, R.; Hadianfard, M.J.; Golikand, A.N. A New Equation for Predicting Electrical Conductivity of Carbon-Filled Polymer Composites Used for Bipolar Plates of Fuel Cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwan, P.; Pumchusak, J. Wet vs. Dry Dispersion Methods for Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes in the High Graphite Content Phenolic Resin Composites for Use as Bipolar Plate Application. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 158, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakate, S.R.; Sharma, S.; Chauhan, N.; Seth, R.K.; Mathur, R.B. CNTs Nanostructuring Effect on the Properties of Graphite Composite Bipolar Plate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jing, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Xie, X. Experimental Investigation of Expanded Graphite/Phenolic Resin Composite Bipolar Plate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 16240–16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, A.; Borah, M.; Pathak, A.K.; Dhakate, S.R. Effect of Filler Content on the Properties of Expanded-Graphite-Based Composite Bipolar Plates for Application in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Mater. Res. Express. 2017, 4, 095604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Park, S.; Ju, H. Effects of Type of Graphite Conductive Filler on the Performance of a Composite Bipolar Plate for Fuel Cells. Solid State Ion. 2014, 262, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykam, N.; Gautam, R.K.; Kar, K.K. Electrical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Exfoliated Graphite/Phenolic Resin Composite Bipolar Plate for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Kar, K.K. Preparation, Characterization, and Properties of Resole Type Phenolic Resin/Exfoliated Graphite Composite Bipolar Plates for PEM Fuel Cell. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2015, 7, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Kar, K.K. Synthesis and Properties of Highly Conducting Natural Flake Graphite/Phenolic Resin Composite Bipolar Plates for PEM Fuel Cells. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2016, 25, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Peng, Y.; Fan, R.; Chen, J.; Zhan, Z.; Yao, D.; Ming, P. Study on Carbon Matrix Composite Bipolar Plates with Balance of Conductivity and Flexural Strength. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Kar, K.K. The Effects of Nano-Sized Carbon Black Content and Particle Sizes on the Properties of Carbon/Phenolic Composite Bipolar Plates. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 2, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Bhowmick, A.K. A Review on the Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Graphite and Modified Graphite Reinforced Polymer Composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 638–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Kamali, B.; Kamali, A.R. Correlation between Morphological, Structural and Electrical Properties of Graphite and Exfoliated Graphene Nanostructures. Measurement 2020, 150, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfiti, E.; Berto, F. Mechanical Properties of Flexible Graphite: Review. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2020, 25, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Shao, Z.; He, L.; Gou, Y.; Sun, S. A Novel Graphite/Phenolic Resin Bipolar Plate Modified by Doping Carbon Fibers for the Application of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Kar, K.K. Synergistic Effects of Carbon Fillers of Phenolic Resin Based Composite Bipolar Plates on the Performance of PEM Fuel Cell. Fuel Cells 2016, 16, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubhra, Q.T.H.; Alam, A.K.M.M.; Quaiyyum, M.A. Mechanical properties of polypropylene composites: A review. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2013, 26, 362–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, L.; Li, S. Review of Electrical Properties for Polypropylene Based Nanocomposite. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, A.; Ronkay, F. Polypropylene as a Promising Plastic: A Review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gaxiola, D.L.; Jubinski, M.M.; Keith, J.M.; King, J.A.; Miskioglu, I. Effects of Carbon Fillers on Tensile and Flexural Properties in Polypropylene-Based Resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalyuk, O.A.; Aleshin, A.N.; Tsobkallo, E.S.; Krestinin, A.V.; Yudin, V.E. Electrical Conductivity of Polypropylene Fibers with Dispersed Carbon Fillers. Phys. Solid State 2012, 54, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Bin, Y.; Kikyotani, N.; Matsuo, M. Thermal, Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polypropylene and Carbon Filler Composites. Polym. J. 2006, 38, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alo, O.A.; Otunniyi, I.O.; Pienaar, H.C.Z. Development of Graphite-Filled Polymer Blends for Application in Bipolar Plates. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 3364–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Utkarsh; Syed, N.A.; Behravesh, A.H.; Pop-Iliev, R.; Rizvi, G. Synergistic Enrichment of Electrically Conductive Polypropylene-Graphite Composites for Fuel Cell Bipolar Plates. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 10955–10964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweiri, R.; Sahari, J. Electrical Properties of Carbon-Based Polypropylene Composites for Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC). J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, A.; Ronkay, F. Effect of Graphite and Carbon Black Fillers on the Processability, Electrical Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Based Bipolar Plates. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2013, 21, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.S.; Selamat, M.Z.; Daud, M.A.M.; Yunus, I.K.M.; Azman, M.S. Effect of Different Filler Materials in the Development of Bipolar Plate Composite for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC). Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 315, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamat, M.Z.; Jamil, A.; Hasan, R.; Dharmalingam, S. Effect of Carbon fiber Loading in Gaphite-Polypropylene Composite Properties as Bipolar Plate for Polymer Electrolyte. J. Anal. Sci. 2021, 25, 766–775. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.H.; Yen, C.Y.; Weng, C.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Ma, C.C.M.; Yang, C.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Yen, M.Y.; Hsiao, M.C.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Preparation and Properties of Carbon Nanotube/Polypropylene Nanocomposite Bipolar Plates for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 185, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, M.C.; Liao, S.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Weng, C.C.; Tsai, H.M.; Ma, C.C.M.; Lee, S.H.; Yen, M.Y.; Liu, P.I. Polypropylene-Grafted Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Polypropylene Composite Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzuan, N.A.M.; Sulong, A.B.; Somalu, M.R.; Majlan, E.H.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, M.I. Effects of Die Configuration on the Electrical Conductivity of Polypropylene Reinforced Milled Carbon Fibers: An Application on a Bipolar Plate. Polymers 2018, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Herrera, C.A.; Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Pérez-González, J.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Flores-Vela, A.; Cabañas-Moreno, J.G. Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Polypropylene/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes/Carbon Nanofibers Nanocomposites for Application in Bipolar Plates of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 26110–26125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.H.; Weng, C.C.; Yen, C.Y.; Hsiao, M.C.; Ma, C.C.M.; Tsai, M.C.; Su, A.; Yen, M.Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Liu, P.L. Preparation and Properties of Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/Polypropylene Nanocomposite Bipolar Plates for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, R.; Thommen, M.; Le Canut, J.M.; Weber, J.F.; Rytka, C.; Tsotra, P. Highly Conductive Polypropylene-Based Composites for Bipolar Plates for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2021, 21, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Radzuan, N.A.; Sulong, A.B.; Somalu, M.R.; Abdullah, A.T.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, R.E.; Majlan, E.H.; Rosli, M.I. Fibre Orientation Effect on Polypropylene/Milled Carbon Fiber Composites in the Presence of Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene as a Secondary Filler: Application on PEM Fuel Cell Bipolar Plate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 30618–30626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeetsorn, R.; Fowler, M.; Tzoganakis, C.; Wang, Y.; Taylor, M. Polypropylene Composites for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Bipolar Plates. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 264, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairan, A.; Selamat, M.Z.; Sahadan, S.N.; Malingam, S.D.; Mohamad, N. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes Loading in Multifiller Polymer Composite as Bipolar Plate for PEM Fuel Cell. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adloo, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Masoomi, M.; Pazhooh, H.N. High Performance Polymeric Bipolar Plate Based on Polypropylene/Graphite/Graphene/Nano-Carbon Black Composites for PEM Fuel Cells. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.G.; Li, A.J.; Wang, W.Q.; Yin, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Y.B. Effects of Resin Content and Preparing Conditions on the Properties of Polyphenylene Sulfide Resin/Graphite Composite for Bipolar Plate. J. Power Sources 2008, 178, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushina, A.; Satola, B.; Dyck, A.; Wagner, P. Comparative Investigation of Polyphenylene Sulfide Polymer-Graphite Bipolar Plates for Fuel Cell Application. ECS Trans. 2019, 92, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Woo, J.S.; Park, S.Y. Poly(Phenylene Sulfide)-Graphite Composites for Bipolar Plates with Preferred Morphological Orientation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, H.W.; Brady, D.G. Properties, Environmental Stability, and Molding Characteristics of Polyphenylene Sulfide. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1976, 16, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahate, A.S.; Nemade, K.R.; Waghuley, S.A. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS): State of the Art and Applications. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2013, 29, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Yang, X.D.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, T. Preparation of CF Reinforced PPS/Graphite Conductive Composite for Bipolar Plate. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 875–877, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes De Oliveira, M.C.; Sayeg, I.J.; Ett, G.; Antunes, R.A. Corrosion Behavior of Polyphenylene Sulfide–Carbon Black–Graphite Composites for Bipolar Plates of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 16405–16418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Drzal, L.T. Exploring the Potential of Exfoliated Graphene Nanoplatelets as the Conductive Filler in Polymeric Nanocomposites for Bipolar Plates. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Shi, P. Study on the Mesocarbon Microbeads/Polyphenylene Sulfide Composite Bipolar Plates Applied for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 175, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.B.; Ishida, H. Development and Characterization of High-Performance Polybenzoxazine Composites. Polym. Compos. 1996, 17, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagci, Y.; Kiskan, B.; Ghosh, N.N. Recent Advancement on Polybenzoxazine—A Newly Developed High Performance Thermoset. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 5565–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H. Overview and Historical Background of Polybenzoxazine Research. In Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 3–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kiskan, B.; Ghosh, N.N.; Yagci, Y. Polybenzoxazine-Based Composites as High-Performance Materials. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.G.; Lin, R.C.; Kuo, S.W. Polybenzoxazine/Carbon Nanotube Composites. In Advanced and Emerging Polybenzoxazine Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 725–738. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, R.; Yu, D. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Polybenzoxazine Nanocomposites: Preparation, Characterization and Properties. Polymer 2006, 47, 7711–7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Yim, J.H. A Study on the Physicochemical Properties of a Graphite/Polybenzoxazine Composite for Bipolar Plate of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueramae, I.; Pengdam, A.; Rimdusit, S. Highly Filled Graphite Polybenzoxazine Composites for an Application as Bipolar Plates in Fuel Cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3909–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuangngamphan, M.; Okhawilai, M.; Hiziroglu, S.; Rimdusit, S. Development of Highly Conductive Graphite-/Graphene-Filled Polybenzoxazine Composites for Bipolar Plates in Fuel Cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plengudomkit, R.; Okhawilai, M.; Rimdusit, S. Highly Filled Graphene-Benzoxazine Composites as Bipolar Plates in Fuel Cell Applications. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witpathomwong, S.; Okhawilai, M.; Jubsilp, C.; Karagiannidis, P.; Rimdusit, S. Highly Filled Graphite/Graphene/Carbon Nanotube in Polybenzoxazine Composites for Bipolar Plate in PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 30898–30910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani Alavijeh, M.; Kefayati, H.; Nozad Golikand, A.; Shariati, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Epoxy/Graphite/Nano-Copper Nanocomposite for the Fabrication of Bipolar Plate for PEMFCs. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2019, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, E.; Flandin, L.; Alberola, N. Polymer Composites Bipolar Plates for PEMFCs. Energy Procedia 2012, 20, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Jana, S.C. Highly Conductive Epoxy/Graphite Composites for Bipolar Plates in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigail-Cedeño, A.F.; Espinoza-Andaluz, M.; Vera, J.; Orellana-Valarezo, M.; Villacis-Balbuca, M. Influence of Different Carbon Materials on Electrical Properties of Epoxy-Based Composite for Bipolar Plate Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 2003–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suherman, H.; Sulong, A.B.; Sahari, J. Effect of the Compression Molding Parameters on the In-Plane and through-Plane Conductivity of Carbon Nanotubes/Graphite/Epoxy Nanocomposites as Bipolar Plate Material for a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alo, O.A.; Otunniyi, I.O.; Pienaar, H.c.Z. Exploring the Potential of Polyethylene/Epoxy/Graphite Composite as Bipolar Plate Material for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2289, 020007. [Google Scholar]
- Darıcık, F.; Topcu, A.; Aydın, K.; Çelik, S. Carbon Nanotube (CNT) Modified Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composite Plates for the PEM Fuel Cell Bipolar Plate Application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 1090–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Villamar, J.; Reyna, R.; Rigail-Cedeño, A.F.; Espinoza-Andaluz, M. Processing Methods of Epoxy/Graphite-Based Compounds for PEFC Bipolar Plates Using Different Secondary Fillers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 064508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeli, Y.; Johny, W.S.; Prihandoko, B.; Harjanto, S. The Effects of Carbon Black Loading on the Characteristics of Carbon Composite Bipolar Plate by Utilizing Graphite Waste Products. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2013, 268–270, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suherman, H.; Sahari, J.; Sulong, A.B.; Astuti, S.; Septe, E. Properties of Epoxy/Carbon Black/Graphite Composites for Bipolar Plate in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 911, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xia, X.H.; Yang, L.; He, Y.D.; Liu, H.B. Preparation and Characterization of Graphite/Resin Composite Bipolar Plates for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2016, 23, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alo, O.A.; Otunniyi, I.O.; Pienaar, H.C.V.Z.; Sadiku, E.R. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Epoxy Blend-Graphite/Carbon Black Composite for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Bipolar Plate. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 658–662. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, A.; Crisci, L.; Bonville, L.; Jankovic, J. An overview of bipolar plates in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2021, 13, 022701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, S.; Hussein, M.Z.; Zainal, Z.; Yusof, N.A. Carbon-based nanomaterials/allotropes: A glimpse of their synthesis, properties and some applications. Materials 2018, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, K.; Pandiyan, S.; Rajalakshmi, N.; Dhathathreyan, K.S. Cost-benefit analysis of commercial bipolar plates for PEMFC’s. J. Power Sources 2006, 161, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Huczko, A.; Oraon, R.; Adhikari, A.D.; Nayak, G.C. Magical allotropes of carbon: Prospects and applications. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 41, 257–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huya-Kouadio, J.M.; James, B.D.; Houchins, C. Meeting cost and manufacturing expectations for automotive fuel cell bipolar plates. ECS Trans 2018, 83, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Nouri, M. Effect of carbon nanotubes on dynamic mechanical properties, TGA, and crystalline structure of polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrissafis, K.; Paraskevopoulos, K.M.; Stavrev, S.Y.; Docoslis, A.; Vassiliou, A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Characterization and thermal degradation mechanism of isotactic polypropylene/carbon black nanocomposites. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 465, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, B.U.; Aytac, A. Characterization of carbon fiber-reinforced poly (phenylene sulfide) composites prepared with various compatibilizers. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.M.; Gull, N.; Munawar, M.A.; Zia, S.; Anjum, F.; Iqbal, M.S.; Jamil, T. Polyphenylene sulphide/carbon fiber composites: Study on their thermal, mechanical and microscopic properties. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, C.; Bonnaud, L.; Lligadas, G.; Ronda, J.C.; Galià, M.; Cádiz, V.; Dubois, P. Convenient and solventless preparation of pure carbon nanotube/polybenzoxazine nanocomposites with low percolation threshold and improved thermal and fire properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6814–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hosur, M.; Jeelani, S.; Mallick, P.K. Fabrication and characterization of carbon fiber reinforced clay/epoxy composite. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 5002–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, F.; Zhou, Y.; Rangari, V.K.; Jeelani, S. Testing and evaluation on the thermal and mechanical properties of carbon nano fiber reinforced SC-15 epoxy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 405, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
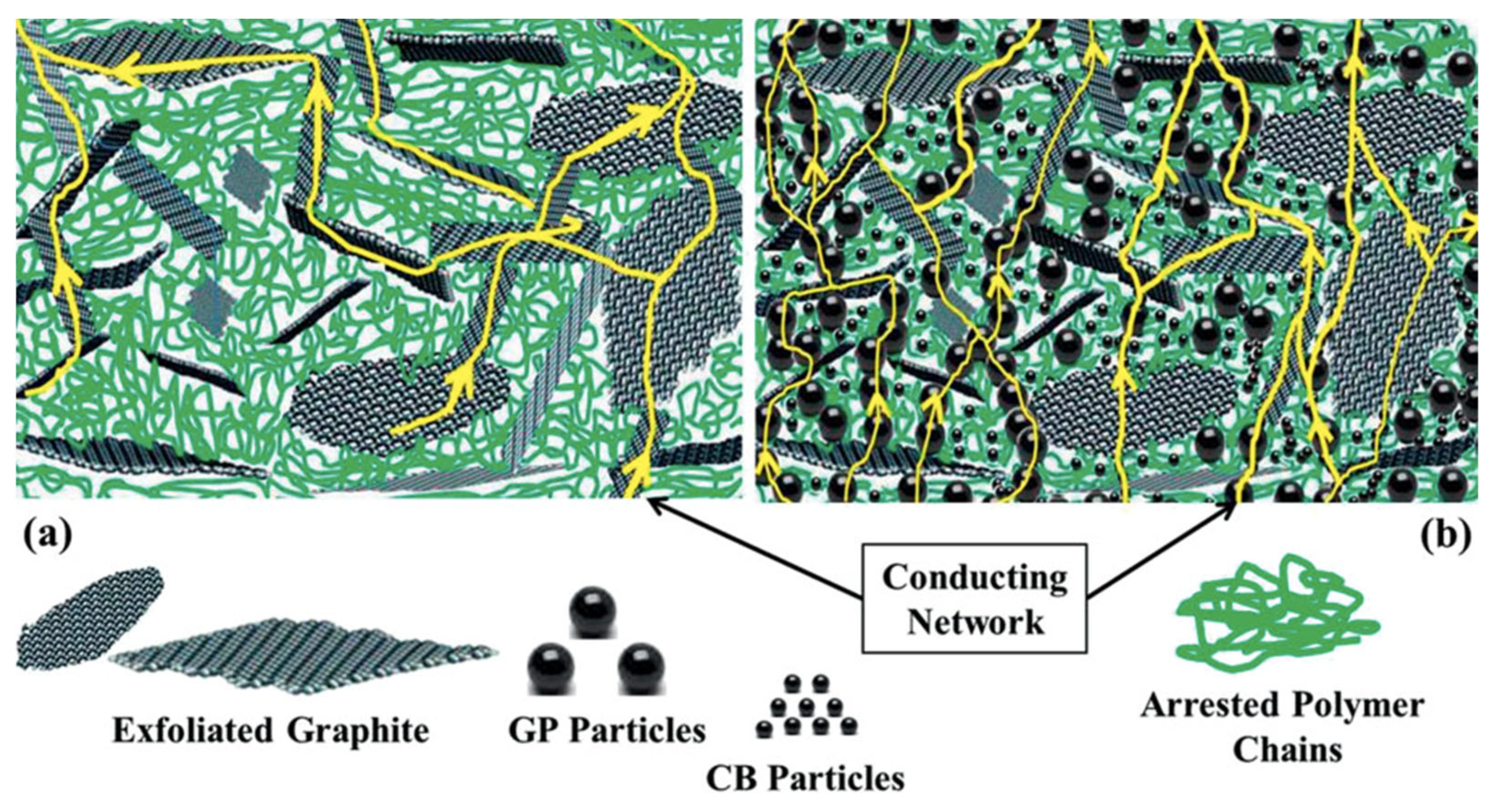
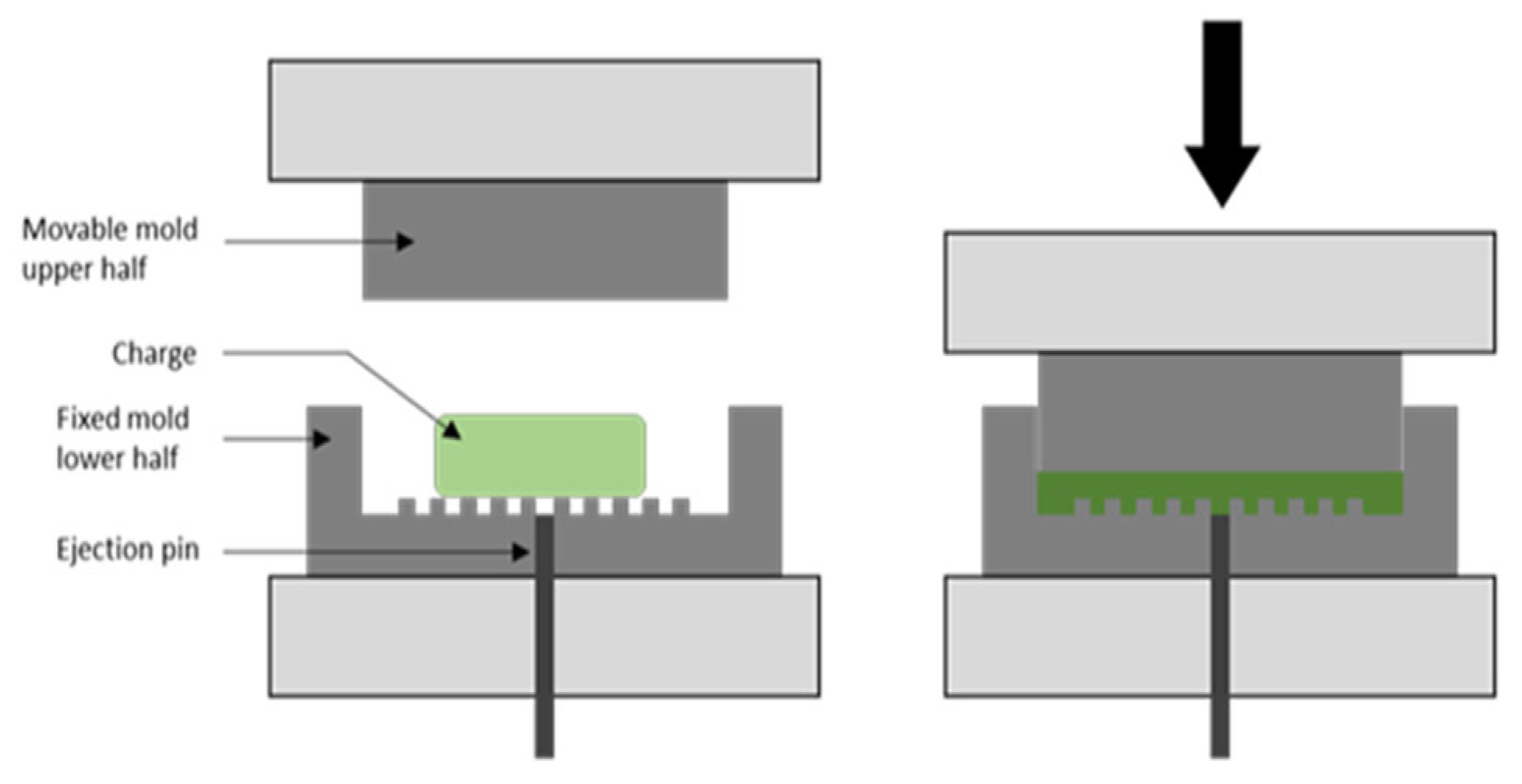
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic resin(90)-Graphite(10) [29] | 0 | 71 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Graphite(20) [29] | 2 | 70 | |
| Phenolic resin(70)-Graphite(30) [29] | 3 | 98 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Graphite(40) [29] | 15 | 97 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Graphite(50) [29] | 77 | 82 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Graphite(60) [29] | 90 | 80 | |
| Phenolic resin(30)-Graphite(70) [29] | 105 | 70 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(80) [29] | 110 | 68 | |
| Phenolic resin(35)-Graphite(65) [30] | 9 | ||
| Phenolic resin(25)-Graphite(75) [30] | 25 | 58 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(80) [30] | 55 | 53 | |
| Phenolic resin(15)-Graphite(85) [30] | 115 | 50 | |
| Phenolic resin(10)-Graphite(90) [30] | 169 | 25 | |
| Phenolic resin(35)-Graphite(65) [31] | 23 | 51 | |
| Phenolic resin(30)-Graphite(70) [31] | 26 | 48 | |
| Phenolic resin(25)-Graphite(75) [31] | 44 | 48 | |
| Phenolic resin (20)-Graphite(80) [31] | 56 | 46 | |
| Phenolic resin (15)-Graphite(85) [31] | 80 | 38 | |
| Phenolic resin(10)-Graphite(90) [31] | 82 | 26 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(80) [32] | 29 | 162 | 61 |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(80) [33] | 200 | 61 | |
| Phenolic resin(15)-Graphite(85) [33] | 230 | 34 | |
| Phenolic resin(10)-Graphite(90) [33] | 385 | 26 | |
| Phenolic resin(90)-Graphite(10) [34] | 0 | ||
| Phenolic resin(80)-Graphite(20) [34] | 2 | ||
| Phenolic resin(70)-Graphite(30) [34] | 3 | ||
| Phenolic resin(60)-Graphite(40) [34] | 15 | ||
| Phenolic resin(50)-Graphite(50) [34] | 72 | ||
| Phenolic resin(40)-Graphite(60) [34] | 95 | ||
| Phenolic resin(30-Graphite(70) [34] | 105 | ||
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(80) [34] | 109 | ||
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(80) [35] | 175 | 51 | |
| Phenolic resin(35)-Graphite(65) [36] | 10 | 80 | 40 |
| Phenolic resin(90)-Expanded graphite(10) [29] | 4 | 54 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Expanded graphite(20) [29] | 65 | 59 | |
| Phenolic resin(70)-Expanded graphite(30) [29] | 91 | 58 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Expanded graphite(40) [29] | 105 | 65 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Expanded graphite(50) [29] | 105 | 61 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Expanded graphite(60) [29] | 107 | 46 | |
| Phenolic resin(30)-Expanded graphite(70) [29] | 110 | 45 | |
| Phenolic resin(25)-Expanded graphite(75) [37] | 65 | ||
| Phenolic resin(20)-Expanded graphite(80) [37] | 63 | ||
| Phenolic resin(15)-Expanded graphite(85) [37] | 62 | ||
| Phenolic resin(60)-Expanded graphite(40) [38] | 165 | 39 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Expanded graphite(50) [38] | 225 | 43 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Expanded graphite(60) [38] | 285 | 37 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Expanded graphite(60) [32] | 80 | 132 | |
| Phenolic resin(35)-Expanded graphite(65) [32] | 100 | 130 | |
| Phenolic resin(30)-Expanded graphite(70) [32] | 130 | 122 | |
| Phenolic resin(25)-Expanded graphite(75) [32] | 160 | 115 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Expanded graphite(80) [32] | 180 | 109 | |
| Phenolic resin(15)-Expanded graphite(85) [32] | 220 | 100 | |
| Phenolic resin(90)-Expanded graphite(10) [34] | 2 | ||
| Phenolic resin(80)-Expanded graphite(20) [34] | 18 | ||
| Phenolic resin(70)-Expanded graphite(30) [34] | 65 | ||
| Phenolic resin(60)-Expanded graphite(40) [34] | 95 | ||
| Phenolic resin(50)-Expanded graphite(50) [34] | 103 | ||
| Phenolic resin(40)-Expanded graphite(60) [34] | 104 | ||
| Phenolic resin(30)-Expanded graphite(70) [34] | 106 | ||
| Phenolic resin(20)-Expanded graphite(80) [34] | 112 | ||
| Phenolic resin(25)-Lump synthetic graphite(75) [39] | 50 | 66 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Lump synthetic graphite(80) [39] | 77 | 64 | |
| Phenolic resin(15)-Lump synthetic graphite(85) [39] | 111 | 43 | |
| Phenolic resin(10)-Lump synthetic graphite(90) [39] | 118 | 32 | |
| Phenolic resin(25)-Flake synthetic graphite(75) [39] | 55 | 66 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Flake synthetic graphite(80) [39] | 85 | 65 | |
| Phenolic resin(15)-Flake synthetic graphite(85) [39] | 118 | 51 | |
| Phenolic resin(10)-Flake synthetic graphite(90) [39] | 130 | 38 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Synthetic graphite(80) [32] | 106 | 61 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Exfoliated graphite(20) [40] | 3 | ||
| Phenolic resin(70)-Exfoliated graphite(30) [40] | 32 | ||
| Phenolic resin(60)-Exfoliated graphite(40) [40] | 123 | ||
| Phenolic resin(50)-Exfoliated graphite(50) [40] | 168 | ||
| Phenolic resin(40)-Exfoliated graphite(60) [40] | 227 | ||
| Phenolic resin(30)-Exfoliated graphite(70) [40] | 308 | ||
| Phenolic resin(20)-Exfoliated graphite(80) [40] | 500 | ||
| Phenolic resin(90)-Exfoliated graphite(10) [41] | 10 | 45 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Exfoliated graphite(20) [41] | 12 | 46 | |
| Phenolic resin(70)-Exfoliated graphite(30) [41] | 125 | 46 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Exfoliated graphite(40) [41] | 160 | 48 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Exfoliated graphite(50) [41] | 310 | 54 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Exfoliated graphite(60) [41] | 375 | 48 | |
| Phenolic resin(30)-Exfoliated graphite(70) [41] | 460 | 46 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Exfoliated graphite(80) [41] | 640 | 37 | |
| Phenolic resin(70)-Flake graphite(30) [42] | 116 | 43 | |
| Phenolic resin(65)-Flake graphite(35) [42] | 134 | 42 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Flake graphite(40) [42] | 161 | 39 | |
| Phenolic resin(55)-Flake graphite(45) [42] | 214 | 35 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Flake graphite(50) [42] | 278 | 33 | |
| Phenolic resin(45)-Flake graphite(55) [42] | 322 | 27 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Flake graphite(60) [42] | 365 | 24 | |
| Phenolic resin(25)-Flake graphite(75) [39] | 105 | 50 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Flake graphite(80) [39] | 120 | 47 | |
| Phenolic resin(15)-Flake graphite(85) [39] | 148 | 42 | |
| Phenolic resin(10)-Flake graphite(90) [39] | 170 | 32 | |
| Phenolic resin(25)-Lump graphite(75) [39] | 65 | 50 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Lump graphite(80) [39] | 100 | 44 | |
| Phenolic resin(15)-Lump graphite(85) [39] | 141 | 41 | |
| Phenolic resin(10)-Lump graphite(90) [39] | 155 | 31 | |
| Phenolic resin(90)-Carbon fiber(10) [29] | 17 | 77 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Carbon fiber(20) [29] | 45 | 87 | |
| Phenolic resin(70)-Carbon fiber(30) [29] | 60 | 150 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Carbon fiber(40) [29] | 68 | 169 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Carbon fiber(50) [29] | 71 | 175 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Carbon fiber(60) [29] | 74 | 181 | |
| Phenolic resin(30)-Carbon fiber(70) [29] | 80 | 90 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Carbon fiber(80) [29] | 89 | 55 | |
| Phenolic resin(99)-Carbon fiber(1) [43] | 260 | 53 | |
| Phenolic resin(97)-Carbon fiber(3) [43] | 212 | 58 | |
| Phenolic resin(95)-Carbon fiber(5) [43] | 204 | 60 | |
| Phenolic resin(93)-Carbon fiber(7) [43] | 203 | 57 | |
| Phenolic resin(91)-Carbon fiber(9) [43] | 198 | 56 | |
| Phenolic resin(90)-Carbon fiber(10) [34] | 15 | ||
| Phenolic resin(80)-Carbon fiber(20) [34] | 28 | ||
| Phenolic resin(70)-Carbon fiber(30) [34] | 45 | ||
| Phenolic resin(60)-Carbon fiber(40) [34] | 60 | ||
| Phenolic resin(50)-Carbon fiber(50) [34] | 71 | ||
| Phenolic resin(40)-Carbon fiber(60) [34] | 75 | ||
| Phenolic resin(30)-Carbon fiber(70) [34] | 79 | ||
| Phenolic resin(20)-Carbon fiber(80) [34] | 95 | ||
| Phenolic resin(95)-Carbon black(5) [44] | 0 | 30 | |
| Phenolic resin(90)-Carbon black(10) [44] | 0.02 | 37 | |
| Phenolic resin(85)-Carbon black(15) [44] | 0.08 | 45 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Carbon black(20) [44] | 0.15 | 50 | |
| Phenolic resin(75)-Carbon black(25) [44] | 0.22 | 54 | |
| Phenolic resin(70)-Carbon black(30) [44] | 0.31 | 51 | |
| Phenolic resin(65)-Carbon black(35) [44] | 0.4 | 47 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Carbon black(40) [44] | 0.45 | 43 | |
| Phenolic resin(97.5)-Carbon black(2.5) [43] | 259 | 48 | |
| Phenolic resin(95)-Carbon black(5) [43] | 309 | 46 | |
| Phenolic resin(92.5)-Carbon black(7.5) [43] | 261 | 47 | |
| Phenolic resin(90)-Carbon black(10) [43] | 208 | 24 | |
| Phenolic resin(98.5)-Carbon black(1.5) [42] | 289 | 36 | |
| Phenolic resin(97)-Carbon black(3) [42] | 320 | 33 | |
| Phenolic resin(95.5)-Carbon black(4.5) [42] | 358 | 29 | |
| Phenolic resin(94)-Carbon black(6) [42] | 354 | 26 | |
| Phenolic resin(92.5)-Carbon black(7.5) [42] | 335 | 24 | |
| Phenolic resin(99)-MWCNTs(1) [43] | 264 | 49 | |
| Phenolic resin(98)-MWCNTs(2) [43] | 289 | 55 | |
| Phenolic resin(97)-MWCNTs(3) [43] | 268 | 55 | |
| Phenolic resin(96)-MWCNTs(4) [43] | 258 | 60 | |
| Phenolic resin(95)- MWCNTs(5) [43] | 201 | 61 |
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic resin(9.6)-Graphite(86.4)-Carbon fiber(4) [48] | 242 | 36 | |
| Phenolic resin(9.4)-Graphite(84.6)-Carbon fiber(6) [48] | 202 | 39 | |
| Phenolic resin(9.2)-Graphite(82.8)-Carbon fiber(8) [48] | 230 | 37 | |
| Phenolic resin(9)-Graphite(81)-Carbon fiber(10) [45] | 182 | 35 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Graphite(10)-Expanded graphite(10) [29] | 26 | 58 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Graphite(20)-Expanded graphite(20) [29] | 86 | 62 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Graphite(30)-Expanded graphite(30) [29] | 109 | 27 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Graphite(20)-Expanded graphite(20) [38] | 275 | 45 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Graphite(25)-Expanded graphite(25) [38] | 350 | 49 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Graphite(30)-Expanded graphite(30) [38] | 420 | 42 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Graphite(10)-Carbon fiber(10) [29] | 54 | 105 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Graphite(20)-Carbon fiber(20) [29] | 56 | 134 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Graphite(30)-Carbon fiber(30) [29] | 89 | 115 | |
| Phenolic resin(80)-Expanded graphite(10)-Carbon fiber(10) [29] | 40 | 69 | |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Expanded graphite(20)-Carbon fiber(20) [29] | 100 | 99 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Expanded graphite(30)-Carbon fiber(30) [29] | 96 | 74 | |
| Phenolic resin(19.9)-Expanded graphite(79.6)-MWCNTs(0.5) [32] | 27 | 181 | 100 |
| Phenolic resin(19.8)- Expanded graphite(79.2)-MWCNTs(1) [32] | 33 | 182 | 100 |
| Phenolic resin(19.7)- Expanded graphite(78.8)-MWCNTs(1.5) [32] | 22 | 180 | 95 |
| Phenolic resin(19.6)- Expanded graphite(78.4)-MWCNTs(2) [32] | 23 | 181 | 91 |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(79.5)-MWCNTs(0.5) [35] | 180 | 56 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(79)-MWCNTs(1) [35] | 195 | 57 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(78.5)-MWCNTs(1.5) [35] | 190 | 55 | |
| Phenolic resin(20)-Graphite(78)-MWCNTs(2) [35] | 185 | 54 | |
| Phenolic resin(34.8)-Graphite(64.7)-MWCNTs(0.5) [36] | 25 | 165 | 54 |
| Phenolic resin(35)- Graphite(64)-MWCNTs(1) [36] | 29 | 180 | 56 |
| Phenolic resin(34.5)-Graphite(64)-MWCNTs(1.5) [36] | 30 | 165 | 50 |
| Phenolic resin(34)- Graphite(64)-MWCNTs(2) [36] | 30 | 145 | 46 |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Graphite(45)-Carbon fiber(10)-Expanded graphite(5) [29] | 102 | 65 | |
| Phenolic resin(82)-Exfoliated graphite(10)-Carbon black(5)-Graphite(3) [49] | 5 | 20 | 49.5 |
| Phenolic resin(77)-Exfoliated graphite(15)-Carbon black(5)-Graphite(3) [49] | 18 | 57 | 51.5 |
| Phenolic resin(72)-Exfoliated graphite(20)-Carbon black(5)-Graphite(3) [49] | 24 | 124 | 56 |
| Phenolic resin(67)-Exfoliated graphite(25)-Carbon black(5)-Graphite(3) [49] | 48 | 220 | 58 |
| Phenolic resin(62)-Exfoliated graphite(30)-Carbon black(5)-Graphite(3) [49] | 74 | 310 | 60 |
| Phenolic resin(57)-Exfoliated graphite(35)-Carbon black(5)-Graphite(3) [49] | 97 | 375 | 62 |
| Phenolic resin(60)-Expanded graphite(20)-Graphite(16)-Carbon black(4) [38] | 160 | 38 | |
| Phenolic resin(50)-Expanded graphite(25)-Graphite(20)-Carbon Black(5) [38] | 255 | 42 | |
| Phenolic resin(40)-Expanded graphite(30)-Graphite(24)-Carbon Black(6) [38] | 400 | 39 |
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(75)-Carbon fiber(5) [61] | 263 | 40 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(70)-Carbon fiber(10) [61] | 105 | 33 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(65)-Carbon fiber(15) [61] | 93 | 28 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(60)-Carbon fiber(20) [61] | 78 | 30 | |
| Polypropylene(30)-Graphite(67.5)-Carbon black(2.5) [57] | 3 | 36 | |
| Polypropylene(25)-Graphite(72.5)-Carbon black(2.5) [57] | 9 | 37 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(77.5)-Carbon black(2.5) [57] | 21 | 28 | |
| Polypropylene(15)-Graphite(82.5)-Carbon black(2.5) [57] | 27 | 30 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(75)-Carbon black(5) [58] | 17 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(70)-Carbon black(10) [58] | 21 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(15) [58] | 25 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(20) [58] | 30 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(55)-Carbon black(25) [58] | 37 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(50)-Carbon black(30) [58] | 29 | ||
| Polypropylene(57)-Graphite(40)-Carbon black(3) [59] | 0.04 | 39 | |
| Polypropylene(54)-Graphite(40)-Carbon black(6) [59] | 0.45 | 39 | |
| Polypropylene(51)-Graphite(40)-Carbon black(9) [59] | 1 | 40.5 | |
| Polypropylene(48)-Graphite(40)-Carbon black(12) [59] | 2 | 34 | |
| Polypropylene(37)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(3) [59] | 0.8 | 40.5 | |
| Polypropylene(34)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(6) [59] | 2.5 | 37.5 | |
| Polypropylene(31)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(9) [59] | 20 | 37.5 | |
| Polypropylene(28)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(12) [59] | 75 | 35 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(75)-Carbon black(5) [60] | 18 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(70)-Carbon black(10) [60] | 21 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(15) [60] | 61 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(20) [60] | 140 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(55)-Carbon black(25) [60] | 223 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(50)-Carbon black(30) [60] | 122 | ||
| Polypropylene(28)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(7) [71] | 11 | ||
| Polypropylene(30)-Graphite(68)-MWCNTs(2) [57] | 6 | 26 | |
| Polypropylene(25)-Graphite(73)-MWCNTs(2) [57] | 9 | 28 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(78)-MWCNTs(2) [57] | 21 | 26 | |
| Polypropylene(15)-Graphite(83)-MWCNTs(2) [57] | 49 | 22 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(75)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 15 | 15 | |
| Polypropylene(19)-Graphite(80)-MWCNTs(1) [63] | 340 | 23 | |
| Polypropylene(18)-Graphite(80)-MWCNTs(2) [63] | 400 | 24 | |
| Polypropylene(16)-Graphite(80)-MWCNTs(4) [63] | 525 | 25 | |
| Polypropylene(30)-Carbon fiber(65)-Graphene(5) [68] | 3.12 | 3.49 | 162 |
| Polypropylene(25)-Carbon fiber(70)-Graphene(5) [68] | 4.93 | 2.73 | 172 |
| Polypropylene(30)-Carbon fiber(65)-MWCNTs(5) [68] | 11.51 | 7.18 | 165 |
| Polypropylene(25)-Carbon fiber(70)-MWCNTs(5) [68] | 14.76 | 11.12 | 99 |
| Polypropylene(80)-Carbon fiber(10)-MWCNTs(10) [65] | 43.1 | ||
| Polypropylene(70)-Carbon fiber(15)-MWCNTs(15) [65] | 8.2 | 45.3 | |
| Polypropylene(55)-Graphite(15)-Carbon fiber(15)-Carbon black(15) [69] | 2.5 | ||
| Polypropylene(50)-Graphite(16.66)-Carbon fiber(16.66)-Carbon black(16.66) [69] | 3.5 | ||
| Polypropylene(45)-Graphite(18.33)-Carbon fiber(18.33)-Carbon black(18.33) [69] | 6 | ||
| Polypropylene(40)-Graphite(20)-Carbon fiber(20)-Carbon black(20) [69] | 9 | ||
| Polypropylene(35)-Graphite(21.66)-Carbon fiber(21.66)-Carbon black(21.66) [69] | 20 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(65)-Carbon fiber(10)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 12 | 20 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(55)-Carbon fiber(20)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 12 | 15 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(45)-Carbon fiber(30)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 11 | 14 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(54)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(1) [70] | 114 | 16 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(53)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(2) [70] | 140 | 17 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(52)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(3) [70] | 145 | 23 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(51)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(4) [70] | 146 | 27 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(50)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(5) [70] | 150 | 30 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(49)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(6) [70] | 160 | 27 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(48)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(7) [70] | 130 | 23 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(47)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(8) [70] | 110 | 25 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(46)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(9) [70] | 109 | 26 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(45)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(10) [70] | 105 | 28 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(70)-Carbon black(5)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 7.5 | 44 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(10)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 13.5 | 20 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(15)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 15 | 17 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(55)-Carbon black(20)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 14 | 10 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(50)-Carbon black(25)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 13.5 | 9 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(65)-Expanded graphite(10)-MWCNTs(5) [67] | 15.5 | 20 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Graphite(55)-Expanded graphite(20)-MWCNT(5) [67] | 16.5 | 20 |
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyphenylene sulfide(50)-Flake graphite(50) [77] | 2 | 75 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(40)-Flake graphite(60) [77] | 39 | 72 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(35)-Flake graphite(65) [77] | 60 | 68 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(30)-Flake graphite(70) [77] | 82 | 66 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(25)-Flake graphite(75) [77] | 108 | 48 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(20)-Flake graphite(80) [77] | 120 | 45 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(10)-Flake graphite(90) [77] | 130 | 35 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(15)-Graphite(85) [78] | 36 | ||
| Polyphenylene sulfide(97.5)-Carbon fiber(2.5) [77] | 123 | 55 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(95)-Carbon fiber(5) [77] | 126 | 61 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(90)-Exfoliated graphene(10) [79] | 0.03 | 77 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(80)-Exfoliated graphene(20) [79] | 0.19 | 65 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(70)-Exfoliated graphene(30) [79] | 0.56 | 75 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(60)-Exfoliated graphene(40) [79] | 1.25 | 68 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(50)-Exfoliated graphene(50) [79] | 1.58 | 70 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(40)-Exfoliated graphene(60) [79] | 5.62 | 62 | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(30)-Mesocarbon(70) [80] | 9.31 | 64 | 45 |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(25)-Mesocarbon(75) [80] | 13.63 | 75 | 41 |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(23)-Mesocarbon(77) [80] | 15.77 | 80 | 40 |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(20)-Mesocarbon(80) [80] | 21.37 | 133.7 | 38 |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(17)-Mesocarbon(83) [80] | 22.52 | 141 | 32 |
| Polyphenylene sulfide(15)-Mesocarbon(85) [80] | 22.79 | 152 | 23 |
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polybenzoxazine(20)-Graphite(80) [87] | 198 | 54 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(15)-Graphite(85) [87] | 203 | 50 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(10)-Graphite(90) [87] | 206 | 34 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(5)-Graphite(95) [87] | 210 | 15 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(60)-Graphite(40) [88] | 0.2 | 85 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(50)-Graphite(50) [88] | 3 | 75 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(40)-Graphite(60) [88] | 12 | 62 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(30)-Graphite(70) [88] | 106 | 59 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(25)-Graphite(75) [88] | 215 | 55 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(20)-Graphite(80) [88] | 250 | 50 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(17)-Graphite(83) [89] | 284 | 58 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(90)-Graphene(10) [90] | 2 | 66 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(80)-Graphene(20) [90] | 3 | 60 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(70)-Graphene(30) [90] | 10 | 55 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(60)-Graphene(40) [90] | 39 | 54 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(50)-Graphene(50) [90] | 130 | 52 | |
| Polybenzoxazine(40)-Graphene(60) [90] | 360 | 42 |
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy resin(60)-Expanded graphite(30)-Carbon black(10) [99] | 0.00276 | ||
| Epoxy resin(30)-Expanded graphite(60)-Carbon black(10) [99] | 18.5 | ||
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(59)-Carbon black(1) [99] | 37.4 | ||
| Epoxy resin(60)-Expanded graphite(35)-Carbon black(5) [94] | 250 | 40 | |
| Epoxy resin(50)-Expanded graphite(45)-Carbon black(5) [94] | 79 | 350 | 44 |
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(55)-Carbon black(5) [94] | 470 | 56 | |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(75)-Carbon black(5) [100] | 1 | 48 | |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(70)-Carbon black(10) [100] | 0.65 | 32.3 | |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(60)-Carbon black(20) [101] | 80 | 7 | |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(55)-Carbon black(25) [101] | 120 | 14 | |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(50)-Carbon black(30) [101] | 55 | 4 | |
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(59.5)-Carbon black(0.5) [95] | 37 | ||
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(59)-Carbon black(1) [95] | 50 | ||
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(58)-Carbon back(2) [95] | 42 | ||
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(57)-Carbon black(3) [95] | 40 | ||
| Epoxy resin(60)-Expanded graphite(39.9)-Graphene(0.1) [99] | 56 | ||
| Epoxy resin(60)-Expanded graphite(39.5)-Graphene(0.5) [99] | 65.39 | ||
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(79)-MWCNT(1) [96] | 25 | 79 | |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(77.5)-MWCNT(2.5) [96] | 65 | 155 | 36 |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(75)-MWCNT(5) [96] | 75 | 180 | 45 |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(72.5)-MWCNT(7.5) [96] | 60 | 155 | 32 |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Graphite(70)-MWCNT(10) [96] | 50 | 130 | 26 |
| Epoxy resin(97.5)-Carbon fiber(1.25)-MWCNT(1.25) [98] | 120 | 46 | |
| Epoxy resin(97.75)-Carbon fiber(1.25)-MWCNT(1) [98] | 95 | 44 | |
| Epoxy resin(98)-Carbon fiber(1.25)-MWCNT(0.75) [98] | 62 | 47 | |
| Epoxy resin(98.25)-Carbon fiber(1.25)-MWCNT(0.5) [98] | 59 | 34 | |
| Epoxy resin(98.5)-Carbon fiber(1.25)-MWCNT(0.25) [98] | 52 | 36 | |
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(59.5)-Graphene(0.5) [95] | 32 | ||
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(59)-Graphene(1) [95] | 37 | ||
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(58)-Graphene(2) [95] | 32.5 | ||
| Epoxy resin(40)-Expanded graphite(57)-Graphene(3) [95] | 31 |
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy resin(31.5)-Polypropylene(38.5)-Graphite(30) [56] | 0.18 | 12.5 | 46 |
| Epoxy resin(27)-Polypropylene(33)-Graphite(40) [56] | 0.3 | 17 | 47 |
| Epoxy resin(22.5)-Polypropylene(27.5)-Graphite(50) [56] | 0.75 | 25 | 50 |
| Epoxy resin(18)-Polypropylene(22)-Graphite(60) [56] | 1.25 | 30 | 54 |
| Epoxy resin(13.5)-Polypropylene(16.5)-Graphite(70) [56] | 1.91 | 55 | 55 |
| Epoxy resin(9)-Polypropylene(11)-Graphite(80) [56] | 3.21 | 68 | 40 |
| Epoxy resin(31.5)-Polyethylene(38.5)-Graphite(30) [97] | 0.2 | 11 | 29 |
| Epoxy resin(27)-Polyethylene(33)-Graphite(40) [97] | 0.4 | 16 | 33 |
| Epoxy resin(22.5)-Polyethylene(27.5)-Graphite(50) [97] | 1.2 | 21 | 38 |
| Epoxy resin(18)-Polyethylene(22)-Graphite(60) [97] | 2.3 | 31 | 40 |
| Epoxy resin(13.5)-Polyethylene(16.2)-Graphite (70) [97] | 3 | 59 | 42 |
| Epoxy resin(9)-Polyethylene(11)-Graphite(80) [97] | 4.2 | 73 | 39 |
| Epoxy resin(10)-Phenolic resin(85)-Graphite(5) [102] | 137 | 26 | |
| Epoxy resin(15)-Phenolic resin(80)-Graphite(5) [102] | 124 | 39 | |
| Epoxy resin(20)-Phenolic resin(75)-Graphite(5) [102] | 102 | 46 | |
| Epoxy resin(25)-Phenolic resin(70)-Graphite(5) [102] | 80 | 47 | |
| Epoxy resin(30)-Phenolic resin(65)-Graphite(5) [102] | 54 | 47 | |
| Polypropylene(20)-Polyaniline(2)-Graphite(78) [58] | 7.5 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)- Polyaniline(4)-Graphite(76) [58] | 8 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)- Polyaniline(6)-Graphite(74) [58] | 9.5 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)- Polyaniline(8)-Graphite(72) [58] | 8 | ||
| Polypropylene(20)- Polyaniline(10)-Graphite(70) [58] | 5 |
| Material (wt.%) | Through-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 20 [17] | In-Plane Conductivity (S/cm) > 100 [17] | Flexural Strength (MPa) > 25 [17] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxi resin(37.5)-Polypropylene(12.5)-Graphite(49)-Carbon black(1) [103] | 0.5 | 50 | 45.5 |
| Epoxi resin(33.75)-Polypropylene(11.25)-Graphite(53)-Carbon black(2) [103] | 1 | 57 | 49 |
| Epoxi resin(30)-Polypropylene(10)-Graphite(57)-Carbon black(3) [103] | 2.5 | 65 | 52 |
| Epoxi resin(26.25)-Polypropylene(8.75)-Graphite(61)-Carbon black(4) [103] | 3 | 72 | 42 |
| Epoxi resin(22.5)-Polypropylene(7.5)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(5) [103] | 4.6 | 75 | 33 |
| Epoxi resin(18.75)-Polypropylene(6.25)-Graphite(69)-Carbon black(6) [103] | 5.9 | 83 | 32 |
| Epoxi resin (15)-Polypropylene(5)-Graphite(73)-Carbon black(7) [103] | 8.4 | 90 | 29 |
| Epoxi resin(11.25)-Polypropylene(3.75)-Graphite(77)-Carbon black(8) [103] | 9 | 93 | 19 |
| Polypropylene(23)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(5)-Graphite(67)-Carbon black(5) [71] | 5.3 | 44 | |
| Polypropylene(23)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(5)-Graphite(66.5)-Carbon black(5.5) [71] | 10 | 49 | |
| Polypropylene(23)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(5)-Graphite(66)-Carbon black(6) [71] | 15 | 51 | |
| Polypropylene(23)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(5)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(7) [71] | 105 | 44 | |
| Polypropylene(18)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(10)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(7) [71] | 28 | 39 | |
| Polypropylene(23)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(5)-Graphite(66.5)-Carbon black(5)-Graphene(0.5) [71] | 8 | 47 | |
| Polypropylene(23)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(5)-Graphite(66)-Carbon black(5)-Graphene(1) [71] | 10 | 52 | |
| Polypropylene(23)-Polypropylene maleic anhydride(5)-Graphite(65)-Carbon black(5)-Graphene(2) [71] | 7 | 48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez-Sanchez, A.; Franco-Luján, V.A.; Alfaro-López, H.M.; Hernández-Sánchez, L.; Cruz-Martínez, H.; Medina, D.I. Carbon Material-Reinforced Polymer Composites for Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Polymers 2024, 16, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050671
Gomez-Sanchez A, Franco-Luján VA, Alfaro-López HM, Hernández-Sánchez L, Cruz-Martínez H, Medina DI. Carbon Material-Reinforced Polymer Composites for Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050671
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez-Sanchez, Alejandro, Víctor A. Franco-Luján, Hilda M. Alfaro-López, Laura Hernández-Sánchez, Heriberto Cruz-Martínez, and Dora I. Medina. 2024. "Carbon Material-Reinforced Polymer Composites for Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells" Polymers 16, no. 5: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050671
APA StyleGomez-Sanchez, A., Franco-Luján, V. A., Alfaro-López, H. M., Hernández-Sánchez, L., Cruz-Martínez, H., & Medina, D. I. (2024). Carbon Material-Reinforced Polymer Composites for Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Polymers, 16(5), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050671







