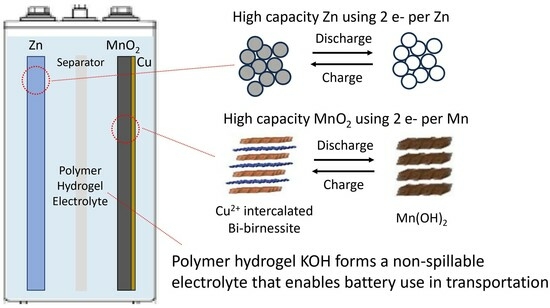
Use of Hydrogel Electrolyte in Zn-MnO2 Rechargeable Batteries: Characterization of Safety, Performance, and Cu2+ Ion Diffusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hydrogel Synthesis
2.2. Battery Preparation
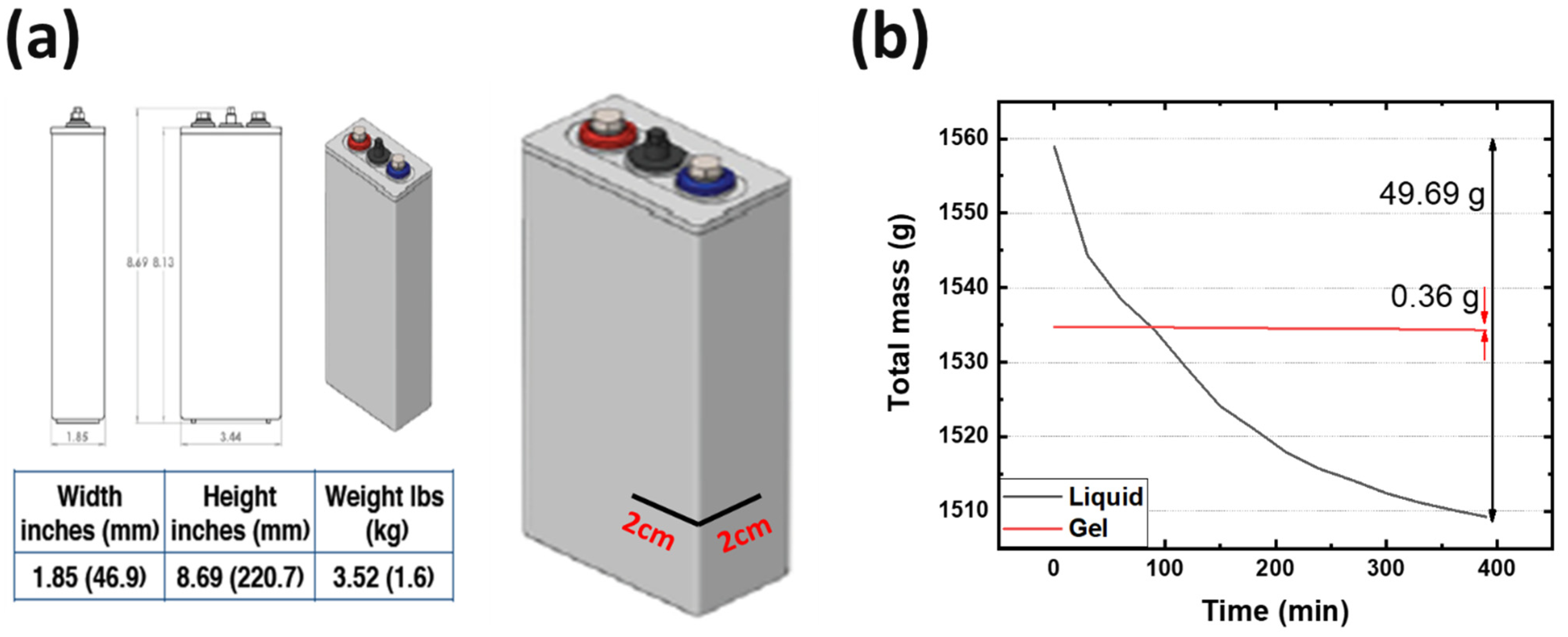
2.3. Electrolyte Spillability Safety Measurements
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
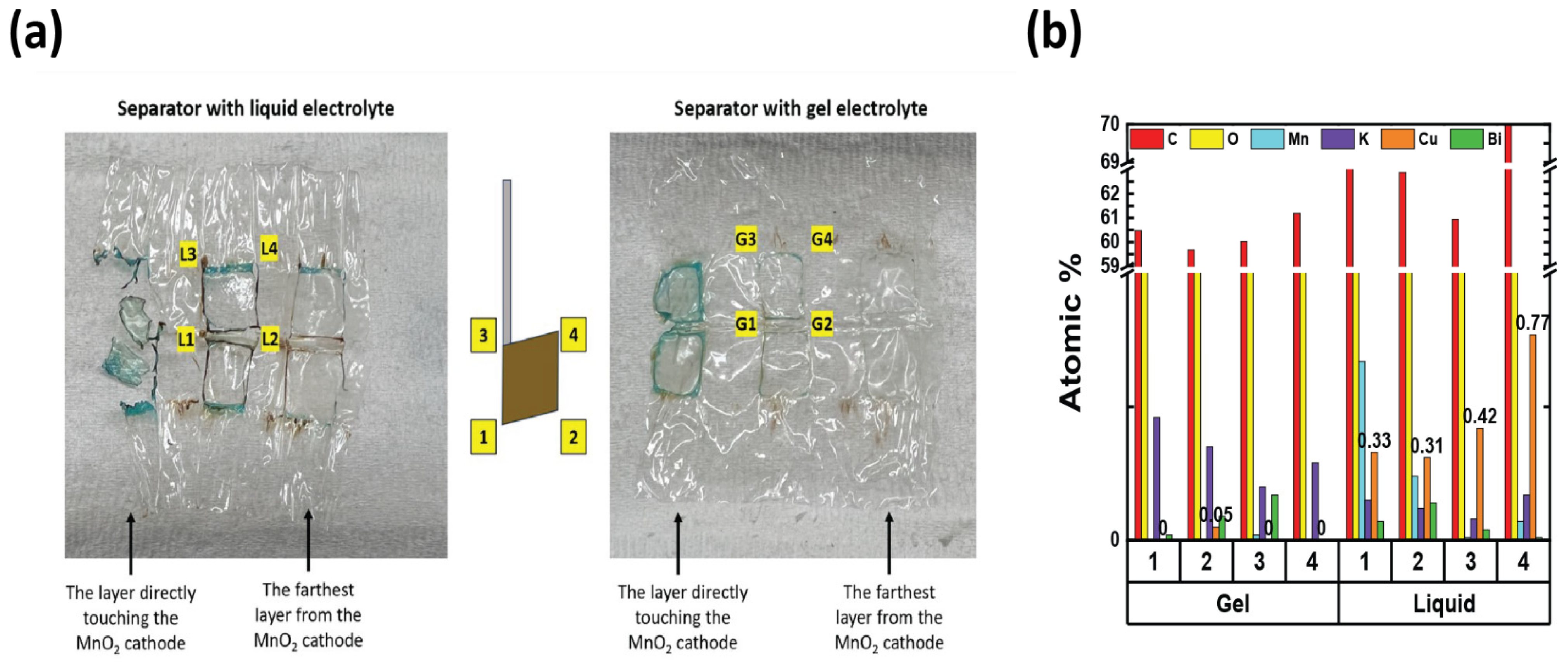
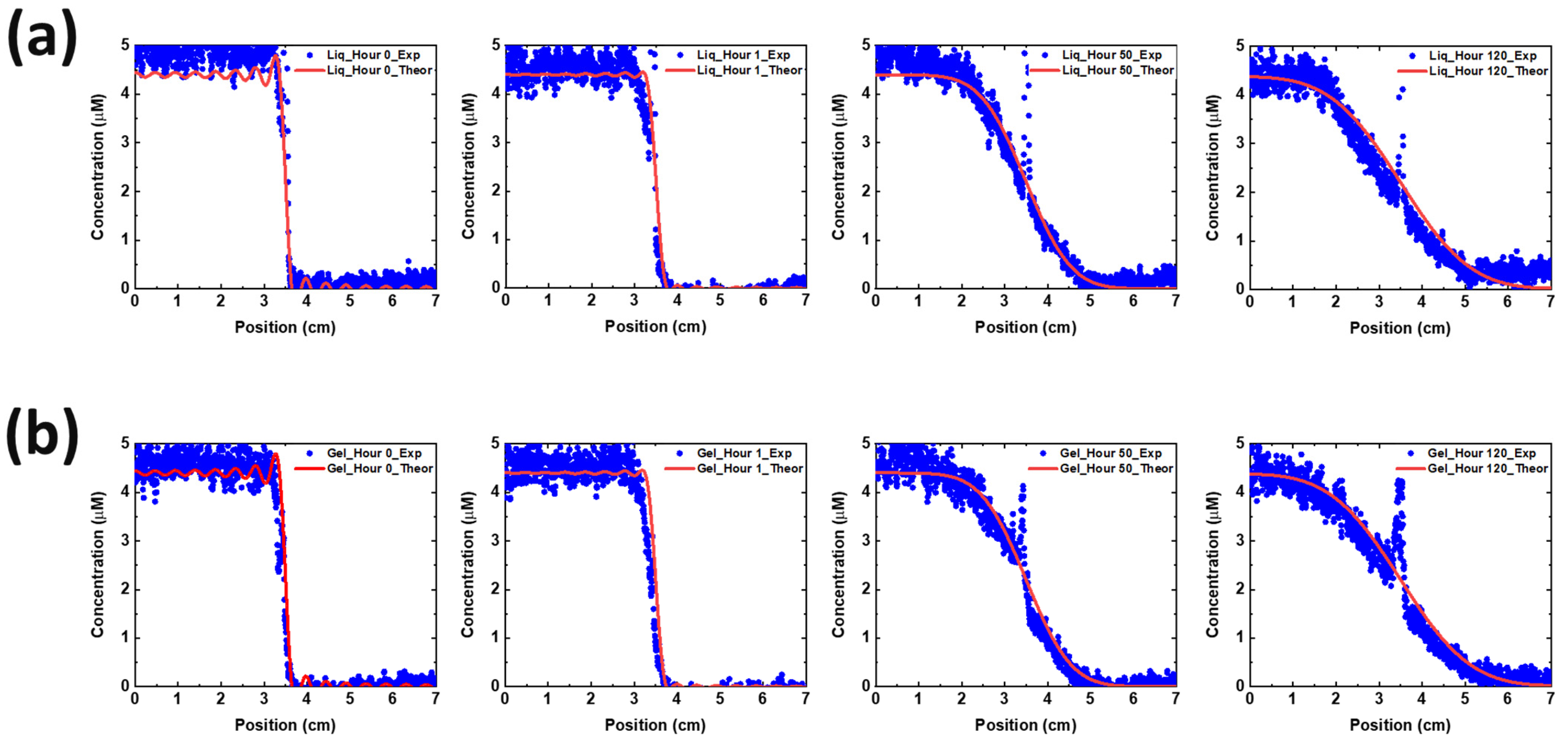
2.5. Cu Diffusion Coefficient
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Non-Spillable Hydrogel Experiment
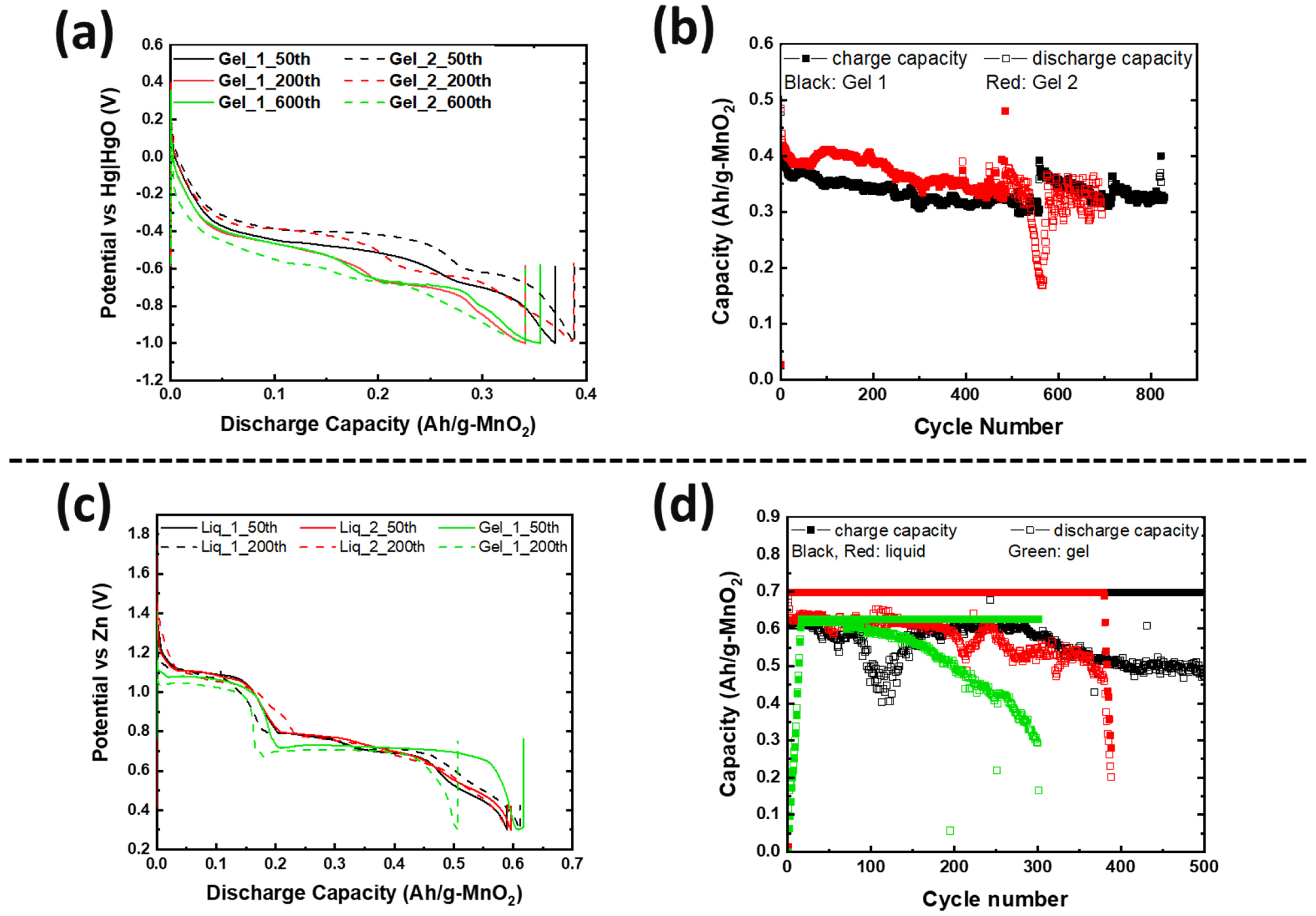
3.2. Electrochemical Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallaway, J.W.; Erdonmez, C.K.; Zhong, Z.; Croft, M.; Sviridov, L.A.; Sholklapper, T.Z.; Turney, D.E.; Banerjee, S.; Steingart, D.A. Real-time materials evolution visualized within intact cycling alkaline batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turney, D.E.; Gallaway, J.W.; Yadav, G.G.; Ramirez, R.; Nyce, M.; Banerjee, S.; Chen-Weigart, Y.K.; Wang, J.; D’Ambrose, M.J.; Kolhekar, S.; et al. Rechargeable zinc alkaline anodes for long-cycle energy storage. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4819–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingale, N.D.; Gallaway, J.W.; Nyce, M.; Couzis, A.; Banerjee, S. Rechargeability and economic aspects of alkaline zinc-manganese dioxide cells for electrical storage and load leveling. J. Power Sources 2015, 276, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.B.; Lambert, T.N.; Chalamala, B.R. Rechargeable alkaline zinc-manganese oxide batteries for grid storage: Mechanisms, challenges and developments. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 143, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrose, M.J.; Turney, D.E.; Yadav, G.G.; Nyce, M.; Banerjee, S. Material failure mechanisms of alkaline Zn rechargeable conversion electrodes. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 3381–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.E.; Turney, D.E.; Messinger, R.J.; Kiss, A.M.; Yadav, G.G.; Banerjee, S.; Lambert, T.N. Electroactive ZnO: Mechanisms, Conductivity, and Advances in Zn Alkaline Battery Cycling. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallaway, J.W.; Yadav, G.G.; Turney, D.E.; Nyce, M.; Huang, J.; Chen-Weigart, Y.-C.K.; Williams, G.; Thieme, J.; Okasinksi, J.S.; Wei, X. An operando study of the initial discharge of Bi and Bi/Cu modified MnO2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K.; Shin, J.; Chung, H.; Meng, P.Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y.S. Intercalation and Conversion Reactions of Nanosized β-MnO2 Cathode in the Secondary Zn/MnO2 Alkaline Battery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 11177–11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.G.; Gallaway, J.W.; Turney, D.E.; Nyce, M.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Banerjee, S. Regenerable Cu-intercalated MnO2 layered cathode for highly cyclable energy dense batteries. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.G.; Wei, X.; Huang, J.; Gallaway, J.W.; Turney, D.E.; Nyce, M.; Secor, J.; Banerjee, S. A conversion-based highly energy dense Cu2+ intercalated Bi-birnessite/Zn alkaline battery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15845–15854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, A.M.; Kim, M.A.; Ma, L.; Ehrlich, S.N.; Okasinksi, J.S.; Gallaway, J.W. Bismuth enables the formation of disordered birnessite in rechargeable alkaline batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 110514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, N.B.; Arnot, D.J.; Bruck, A.M.; Duay, J.; Kelly, M.; Having, R.L.; Ricketts, L.S.; Vigil, J.A.; Gallaway, J.W.; Lambert, T.N. Rechargeable alkaline Zinc/Copper oxide batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 7073–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, S.; Wu, S.; Ma, X.; Hussain, I.; Sun, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, K. Copper activated near-full two-electron Mn4+/Mn2+ redox for mild aqueous Zn/MnO2 battery. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, S.; Pan, X.; Sun, G.; Zhu, B.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Tu, F.; et al. Promoting cycle stability and rate performance of birnessite-type MnO2 cathode via cupper and bismuth dual ions pre-intercalation for aqueous zinc-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 74, 109589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Yadav, G.G.; Weiner, M.; Huang, J.; Upreti, A.; Wei, X.; Yakobov, R.; Hawkins, B.E.; Nyce, M.; Lambert, T.N.; et al. Hydroxyl conducting hydrogels enable low-maintenance commercially sized rechargeable Zn–MnO2 Batteries for Use in Solar Microgrids. Polymers 2022, 14, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y.; Ai, X. Preparation and electrochemical characterization of the alkaline polymer gel electrolyte polymerized from acrylic acid and KOH solution. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, A.A. Zn/gelled 6M KOH/O2 zinc-air battery. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.A.; Sampath, S.; Shukla, A.K. Hydrogel-polymer electrolytes for electrochemical capacitors: An overview. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, J.; Shukla, V.K. Cross-linking in hydrogels—A review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 4, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Zhong, C.; Hu, W. Potassium Polyacrylate-Based Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Practical Zn−Ni Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 22847–22857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Li, M.; Gao, G.; Fan, H.; Ma, L. The Gel-State Electrolytes in Zinc-Ion Batteries. Batteries 2022, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.; Jin, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H. Polyacrylic acid assisted synthesis of free-standing MnO2/CNTs cathode for Zinc-ion batteries. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), 49 CFR 173. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-49/subtitle-B/chapter-I/subchapter-C/part-173/subpart-E/section-173.159a?msclkid=7e67d3fdb43911ecb601bcd46a0d0bb0 (accessed on 31 December 2023).
- Vadhva, P.; Hu, J.; Johnson, M.J.; Stocker, R.; Braglia, M.; Brett, D.J.L.; Rettie, A.J.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for all-solid-state batteries: Theory, methods and future outlook. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 1930–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ji, G.; Zheng, J. A hydrogel electrolyte with ultrahigh ionic conductivity and transference number benefit from Zn2+ “highways” for dendrite-free Zn-MnO2 battery. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tél, A.; Bauer, R.A.; Varga, Z.; Zrínyi, M. Heat conduction in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 85, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jang, S.; Kim, B.-K.; Park, K. Electrochemical study of agarose hydrogels for natural convection on macroelectrodes and ultramicroelectrodes. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mole Fraction MBA:H2O | Flow from ~1 mm Gap | Flow from ~75 mm Gap |
|---|---|---|
| 2.61 × 10−5 | Flow | Flow |
| 3.40 × 10−5 | Flow | Flow |
| 3.92 × 10−5 | No Flow | Flow |
| 4.70 × 10−5 | No Flow | Flow |
| 5.20 × 10−5 | No Flow | Flow |
| 6.00 × 10−5 | No Flow | Flow |
| 6.50 × 10−5 | No Flow | No Flow |
| 7.30 × 10−5 | No Flow | No Flow |
| 7.80 × 10−5 | No Flow | No Flow |
| 1st Cycle | 5th Cycle | 12th Cycle | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid KOH Electrolyte | 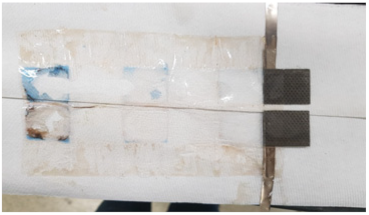 | 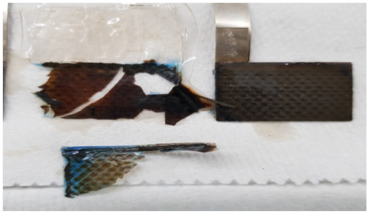 | 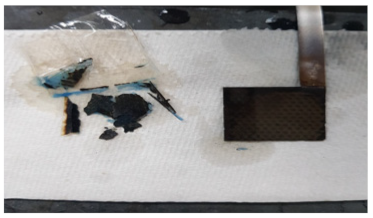 |
| Gel Electrolyte |  |  |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, J.; Turney, D.E.; Yadav, G.G.; Nyce, M.; Wygant, B.R.; Lambert, T.N.; Banerjee, S. Use of Hydrogel Electrolyte in Zn-MnO2 Rechargeable Batteries: Characterization of Safety, Performance, and Cu2+ Ion Diffusion. Polymers 2024, 16, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050658
Cho J, Turney DE, Yadav GG, Nyce M, Wygant BR, Lambert TN, Banerjee S. Use of Hydrogel Electrolyte in Zn-MnO2 Rechargeable Batteries: Characterization of Safety, Performance, and Cu2+ Ion Diffusion. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050658
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Jungsang, Damon E. Turney, Gautam Ganapati Yadav, Michael Nyce, Bryan R. Wygant, Timothy N. Lambert, and Sanjoy Banerjee. 2024. "Use of Hydrogel Electrolyte in Zn-MnO2 Rechargeable Batteries: Characterization of Safety, Performance, and Cu2+ Ion Diffusion" Polymers 16, no. 5: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050658
APA StyleCho, J., Turney, D. E., Yadav, G. G., Nyce, M., Wygant, B. R., Lambert, T. N., & Banerjee, S. (2024). Use of Hydrogel Electrolyte in Zn-MnO2 Rechargeable Batteries: Characterization of Safety, Performance, and Cu2+ Ion Diffusion. Polymers, 16(5), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050658