Effect of Irradiation Temperature and Atmosphere on Aging of Epoxy Resins for Superconducting Magnets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Samples
2.1.1. CTD101K
2.1.2. MSUT
2.1.3. MY750
2.1.4. Mix61
2.1.5. CEA Mix
2.1.6. Araldite F
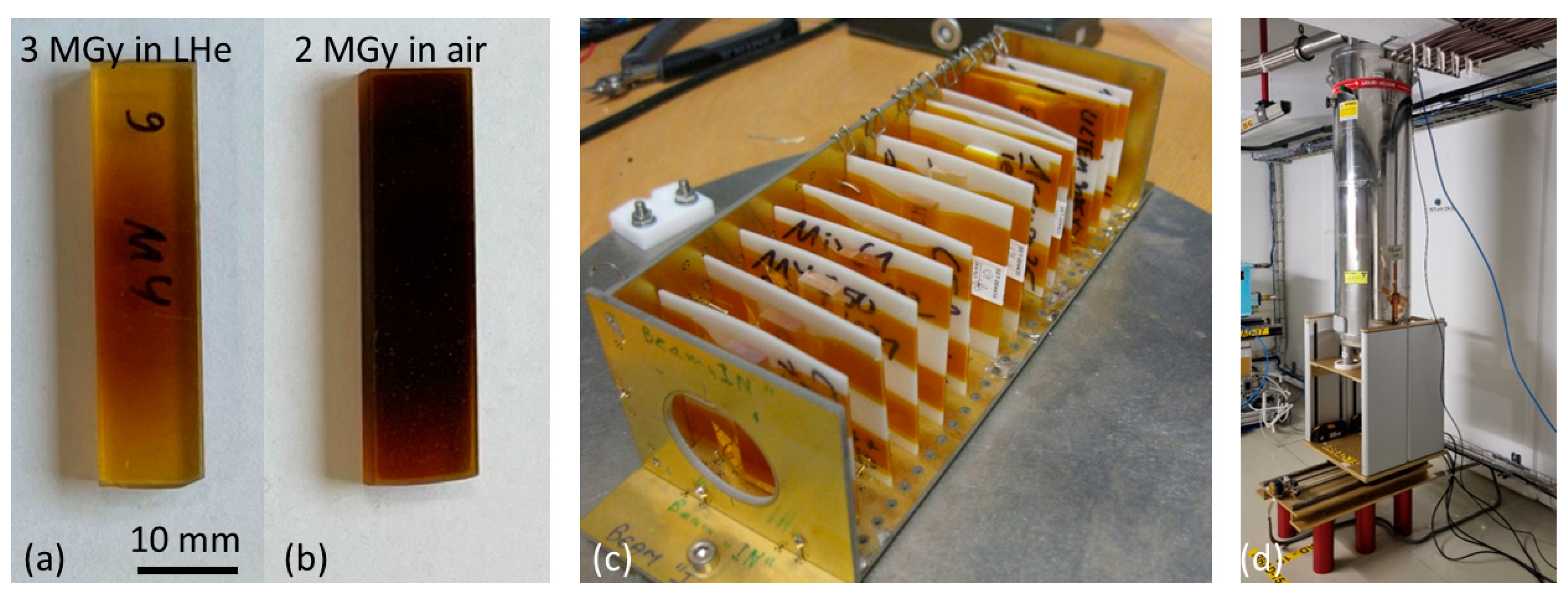
2.2. Radiation Sources
2.2.1. Gamma Irradiation
2.2.2. Proton Irradiation
2.3. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.4. Thermal Expansion Measurement with the DMA Instrument
3. Results
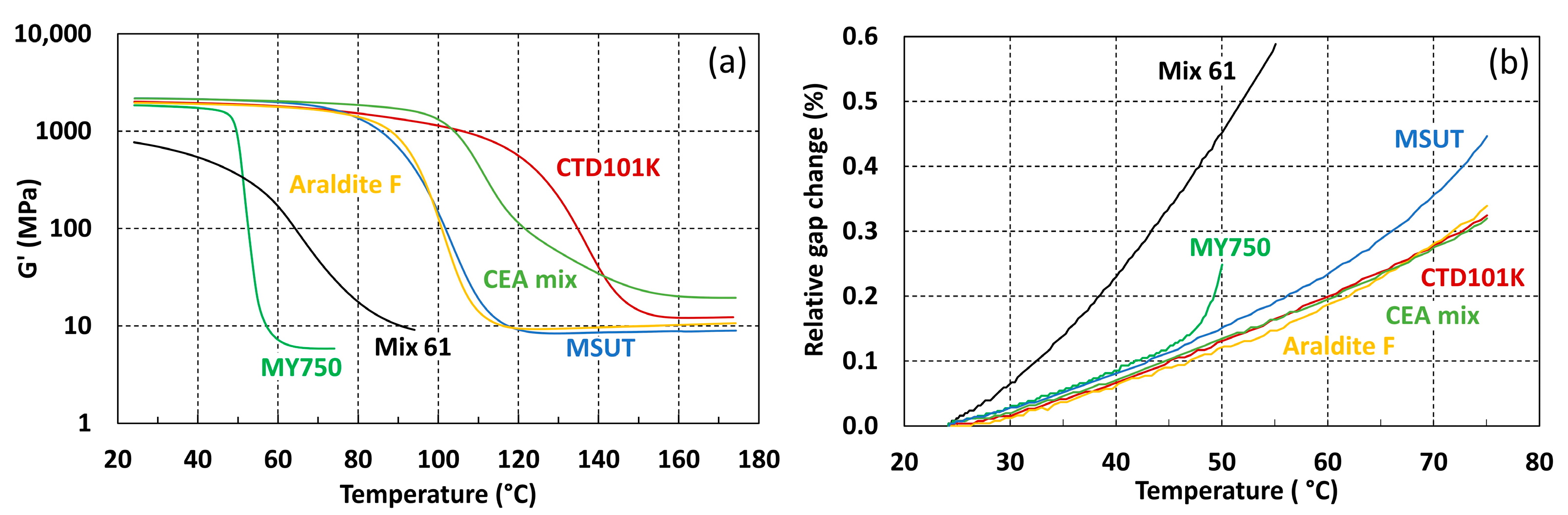
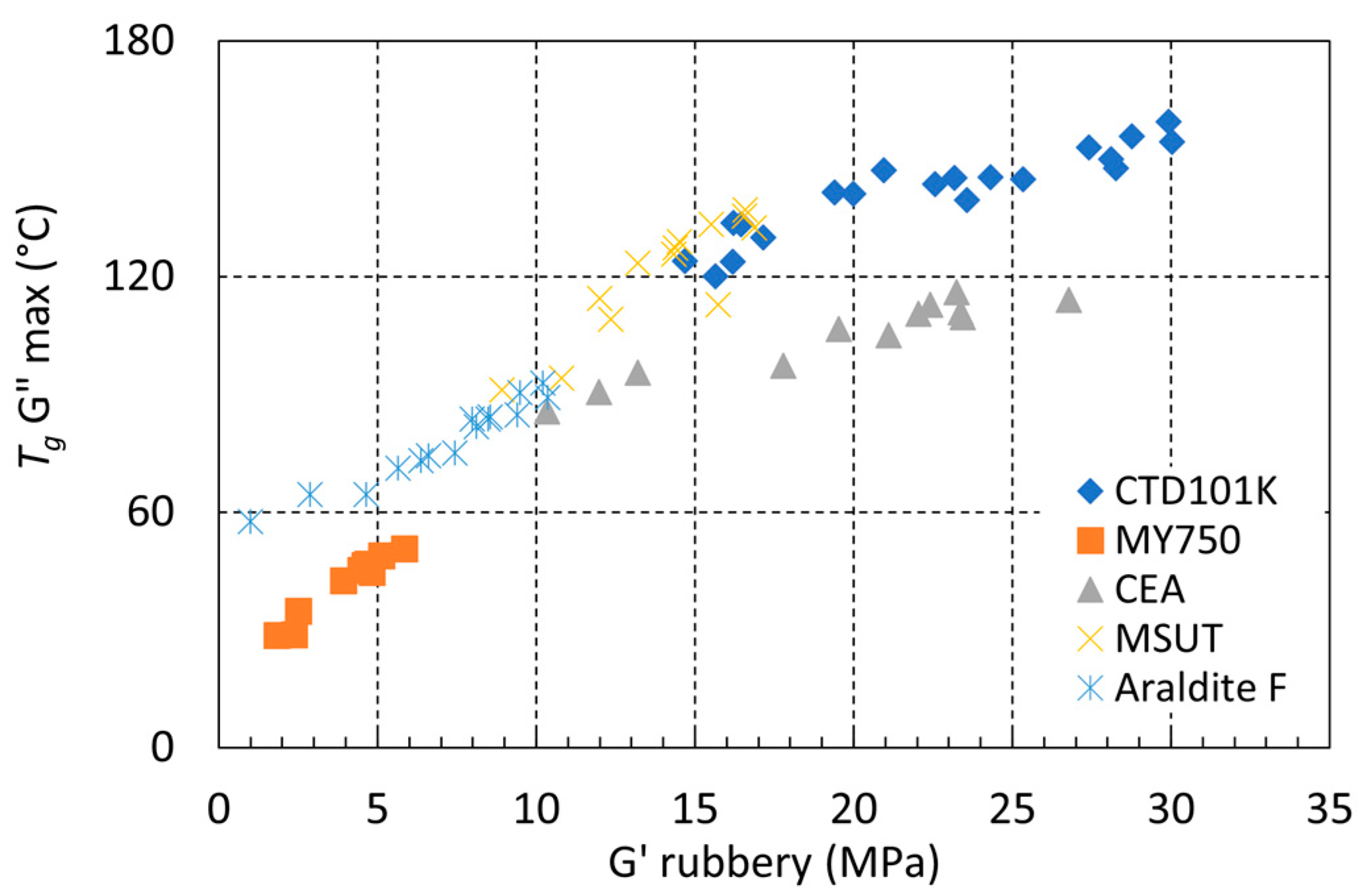
3.1. Glass Transition and Thermal Expansion of the Non-Irradiated Epoxy Resins
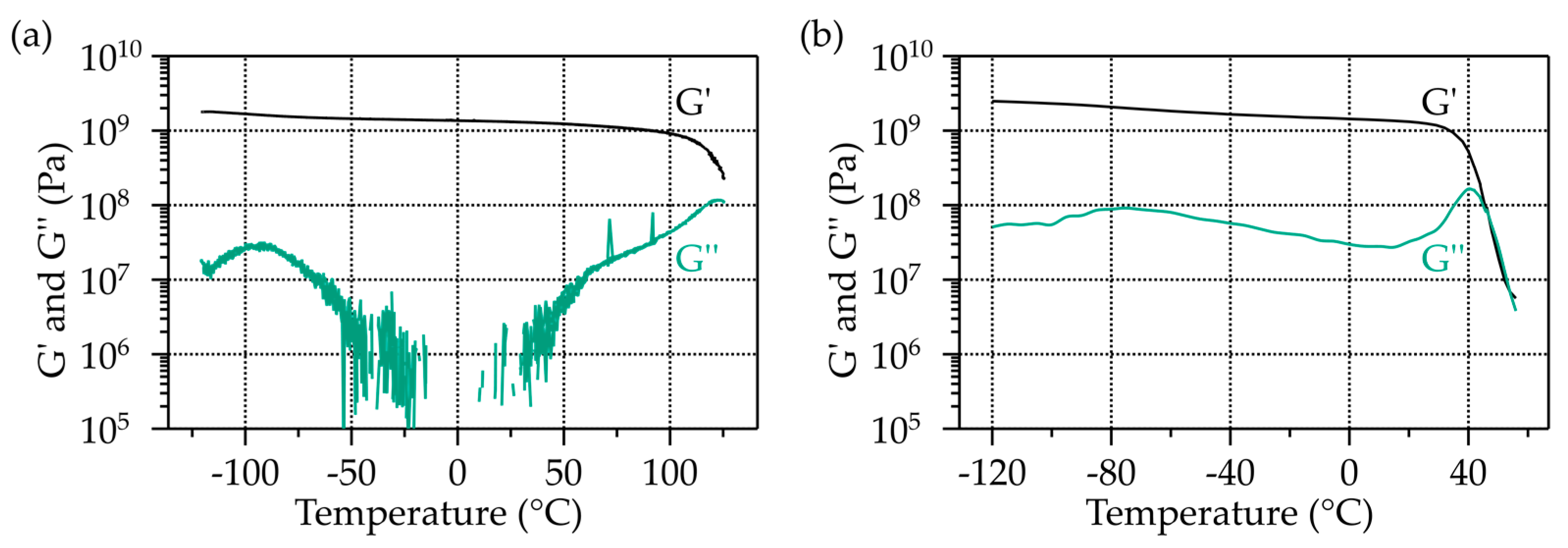
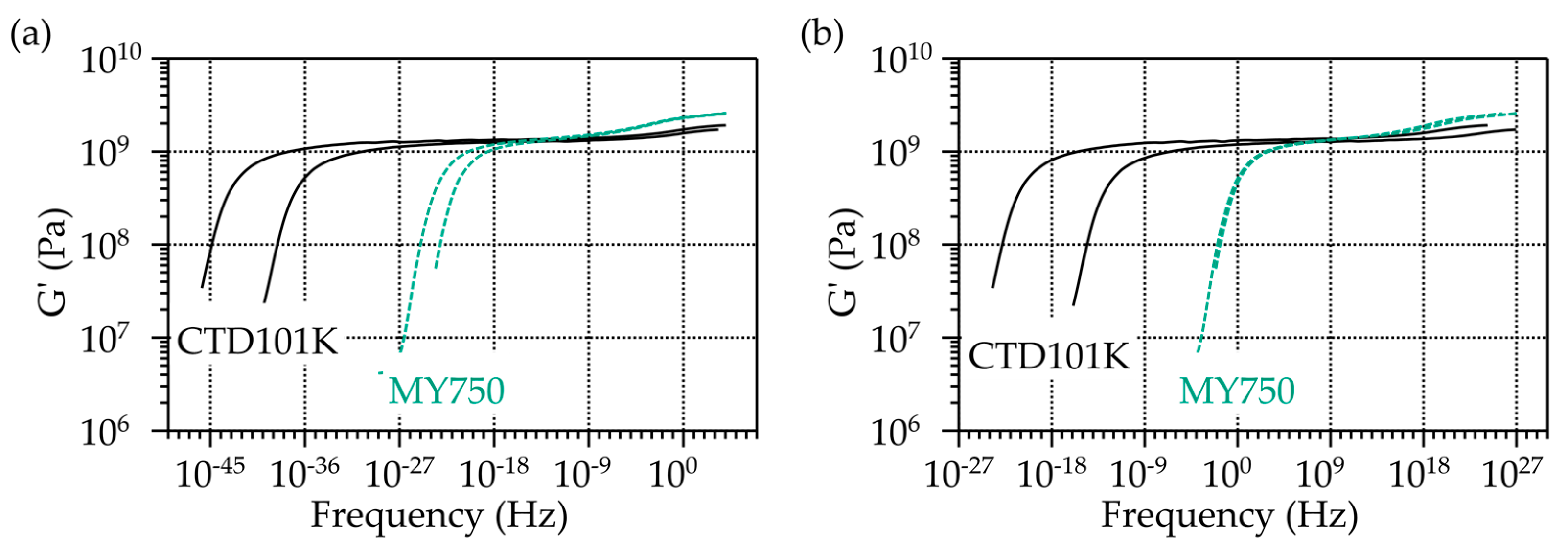
3.2. Low Temperature DMA and Master Curves of Unirradiated CTD101K and MY750
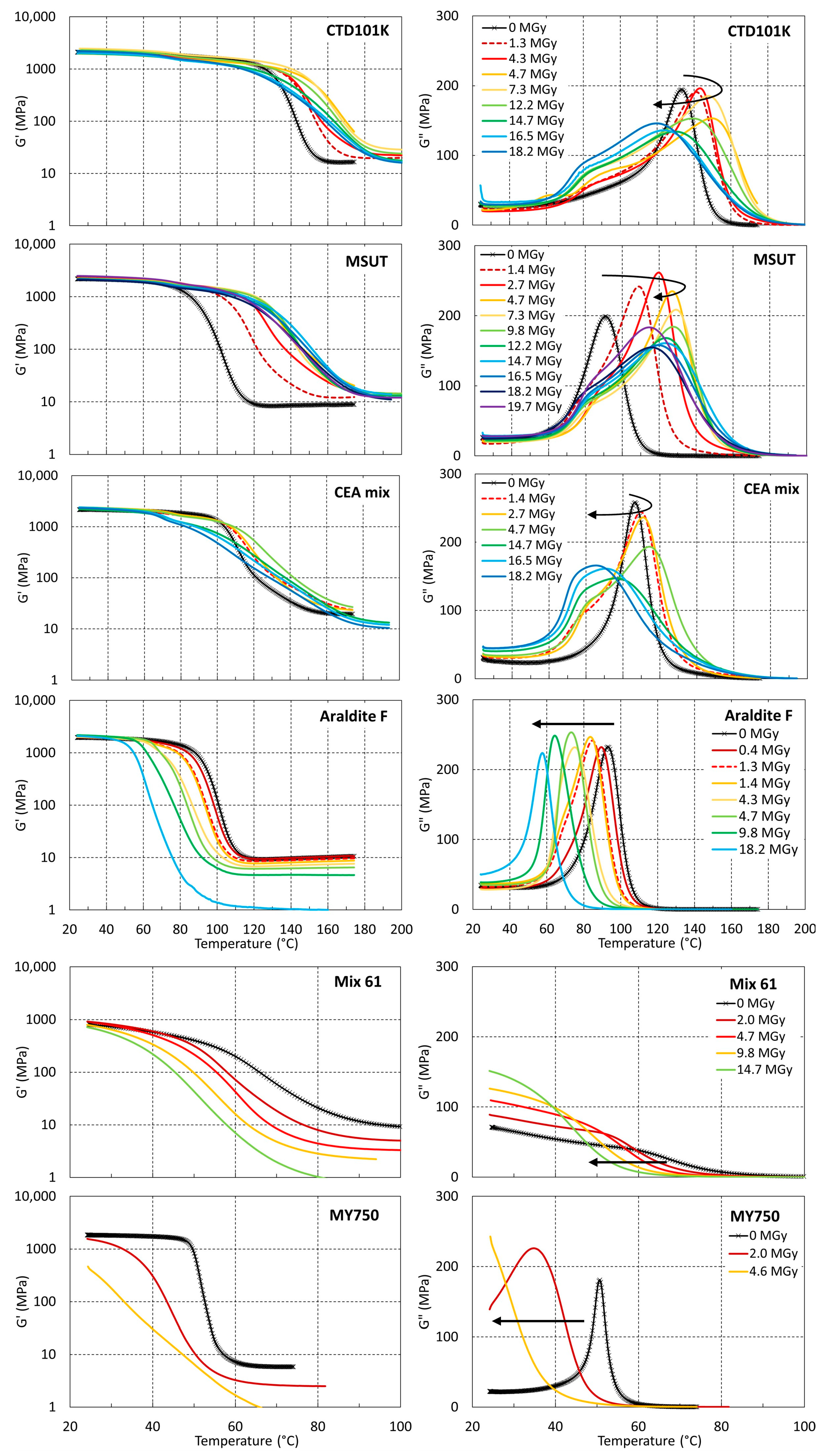
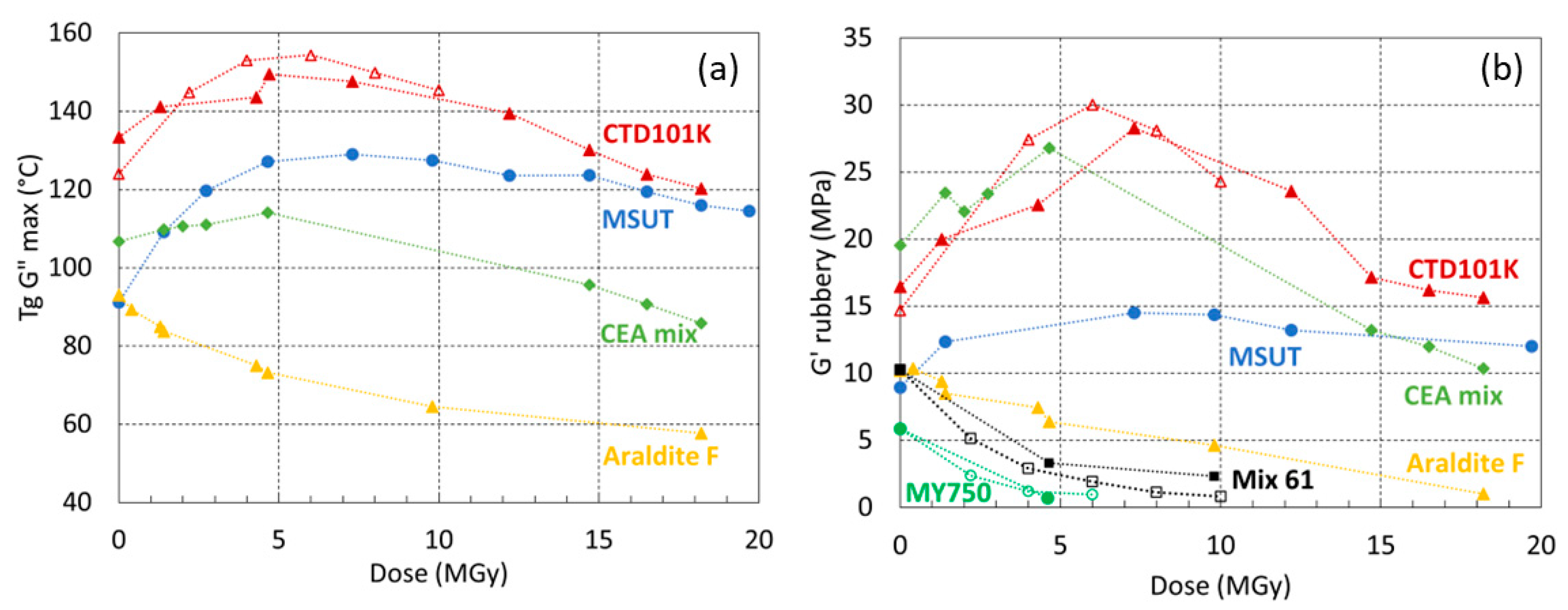
3.3. Effect of Ambient Temperature Irradiation in Air on Tg and G′rubbery
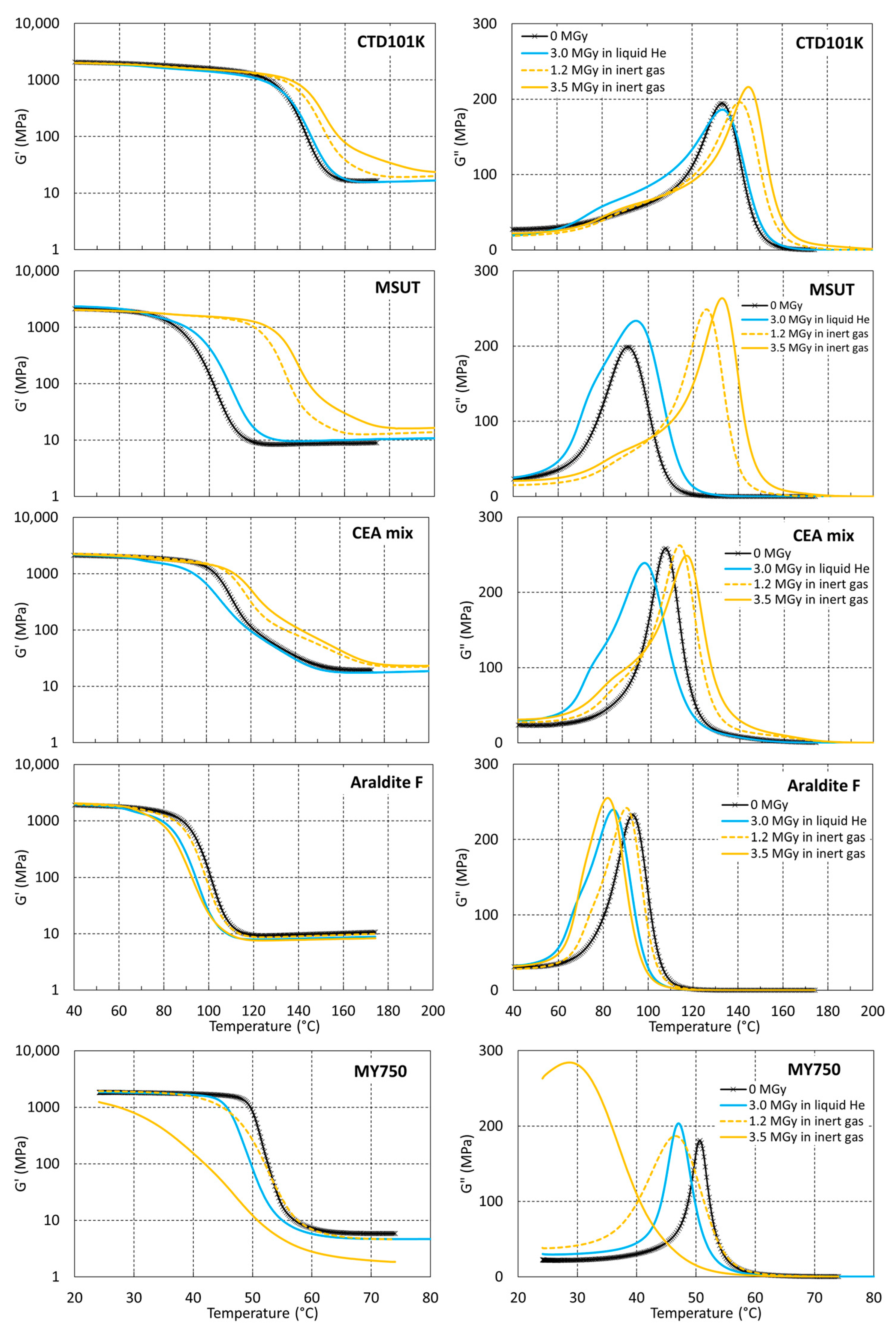
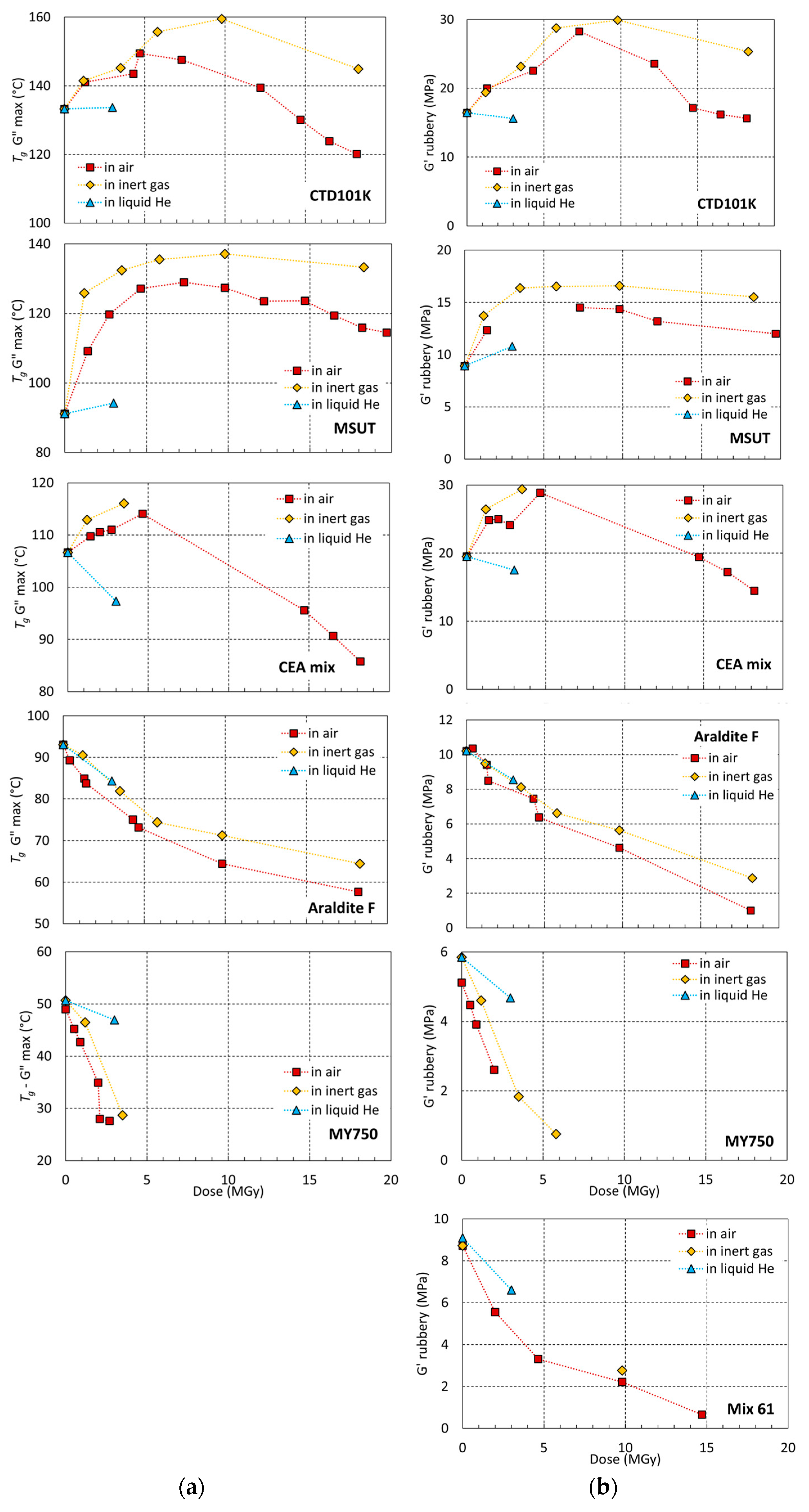
3.4. Effect of Irradiation Temperature and Atmosphere
3.5. Comparison of Tg and G′rubbery
3.6. Effect of Irradiation on Thermal Expansion
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Analytical Potential of DMA to Reveal Irradiation-Induced Aging
4.2. Effect of the Irradiation Atmosphere
4.3. Effect of the Irradiation Temperature
4.4. Comparison of the Radiation Hardness of the Different Epoxy Resin Systems
4.5. Future Irradiation Needs
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devred, A.; Bredy, P.; Durante, M.; Gourdin, C.; Rey, J.M.; Reytier, M. Insulation Systems for Nb3Sn Accelerator Magnet Coils Fabricated by the “Wind and React” Technique. In Advances in Cryogenic Engineering Materials; Balachandran, U.B., Hartwig, K.T., Gubser, D.U., Bardos, V.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, UK, 2000; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebermann, P.; Bernardi, J.; Fleiter, J.; Lackner, F.; Meuter, F.; Pieler, M.; Scheuerlein, C.; Schoerling, D.; Wolf, F.; Ballarino, A.; et al. Irreversible degradation of Nb3Sn Rutherford cables due to transversal compression stress at room temperature. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2018, 31, 065009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abada, A.; Abbrescia, M.; AbdusSalam, S.S.; Abdyukhanov, I.; Fernandez, J.A.; Abramov, A.; Aburaia, M.; Acar, A.O.; Adzic, P.R.; Agrawal, P.; et al. FCC-hh: The Hadron Collider. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 228, 755–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoerling, D.; Arbelaez, D.; Auchmann, B.; Bajko, M.; Ballarino, A.; Barzi, E.; Bellomo, G.; Benedikt, M.; Bermudez, S.I.; Bordini, B.; et al. The 16 T dipole development program for FCC and HE-LHC. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 4003109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, O.; Rossi, L. The High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider. 2015. Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/epdf/10.1142/9581 (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Arduini, G.; Bradu, B.; Brodzinski, K.; Bruce, R.; Cerutti, F.; Ciccotelli, A.; Deferne, G.; Fartoukh, S.; Fessia, P.; Garion, C.; et al. LHC Triplet Task Force Report. CERN-ATS Report-2023-0004, Geneva: CERN. 2023. Available online: https://cds.cern.ch/record/2882512/files/CERN-ACC-2023-0004.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Tavlet, M.; Fontaine, A.; Schönbacher, H. Compilation of Radiation Damage Test Data, 2nd ed.; ser. CERN Yellow Reports: Monographs; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; Available online: http://cds.cern.ch/record/357576 (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Parragh, D.M.; Scheuerlein, C.; Piccin, R.; Ravotti, F.; Pezzullo, G.; Ternova, D.; Taborelli, M.; Lehner, M.; Eisterer, M. Irradiation induced aging of epoxy resins for impregnation of superconducting magnet coils. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 7800107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. Resins for Superconducting Magnet Construction—An Overview of Requirements, Processing and Properties. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 756, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, P.E.; Munshi, N.A.; Denis, R.J. Highly radiation-resistant vacuum impregnation resin systems for fusion magnet insulation. AIP Conf. Proc. 2002, 614, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Todesco, E.; Allain, H.; Ambrosio, G.; Arduini, G.; Cerutti, F.; De Maria, R.; Esposito, L.; Fartoukh, S.; Ferracin, P.; Felice, H.; et al. A First Baseline for the Magnets in the High Luminosity LHC Insertion Regions. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2014, 24, 4003305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bottura, L.; de Rijk, G.; Rossi, L.; Tedesco, E. Advanced Accelerator Magnets for Upgrading the LHC. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2015, 25, 4002107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todesco, E.; Bajas, H.; Bajko, M.; Ballarino, A.; Bermudez, S.I.; Bordini, B.; Bottura, L.; de Rijk, G.; Devred, A.; Ramos, D.D.; et al. The High Luminosity LHC interaction region magnets towards series production. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 34, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, A.B.; Miller, T.; Arnold, J.; Huang, K.; Gephart, N.; Markewicz, W. Thermomechanical properties of a toughened epoxy for impregnating superconducting magnets. Cryogenics 1995, 35, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, W.D.; Dixon, I.R.; Dougherty, J.L.; Pickard, K.W.; Brennan, A.B. Properties of Epoxy NHMFL 61 for Superconducting Magnet Impregnation. In Proceedings of the Preprint of ICMC/CEC 1997, Portland, Oregon, 27 July–1 August 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brem, A.; Gold, B.J.; Auchmann, B.; Tommasini, D.; Tervoort, T.A. Elasticity, plasticity and fracture toughness at ambient and cryogenic temperatures of epoxy systems used for the impregnation of high-field superconducting magnets. Cryogenics 2021, 115, 103260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntsman Araldite Impregnation Resin System Araldite®CY192-1 100 pbw Aradur® HY 918-1 100 pbw Data Sheet.
- Rifflet, J.M.; Durante, M.; Segreti, M. Nb3Sn Quadrupole Development at CEA Saclay; In Proceedings of the Workshop on Accelerator Magnet Superconductors, Design and Optimization, Geneva, Switzerland, 19–23 May 2008.
- Araldite Casting Resin System. Huntsman Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.gluespec.com/Materials/SpecSheet/484420d9-3d7b-479d-a0cd-4c3204a86877 (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Ravotti, F.; Gkotse, B.; Glaser, M.; Lima, P.; Matli, E.; Moll, M. A new high-intensity proton irradiation facility at the CERN PS east area. In Proceedings of the International Conference Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics (TIPP), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2–6 June 2014; PoS(TIPP2014)354. Available online: https://pos.sissa.it/213/354/pdf (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Ravotti, F. Dosimetry Techniques and Radiation Test Facilities for Total Ionizing Dose Testing. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2018, 65, 1440–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D7028-07; Standard Test Method for Glass Transition Temperature (DMA Tg) of Polymer Matrix Composites by Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Flory, P.J. Molecular theory of rubber elasticity. Polymer 1979, 20, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T. Quantifying Polymer Crosslinking Density Using Rheology and DMA. TA Instruments. Available online: https://www.tainstruments.com/pdf/literature/RH102.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Hill, L.W. Calculation of crosslink density in short chain networks. Prog. Org. Coat. 1997, 31, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Deng, J.; Bae, C.; Xiao, X. Thermal expansion/shrinkage measurement of battery separators using a dynamic mechanical analyzer. Polym. Test. 2018, 71, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO 1183-1:2019; Plastics—Methods for Determining the Density of Non-Cellular Plastics—Part 1: Immersion Method, Liquid Pycnometer Method and Titration Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Zheng, G.; Zhu, M.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, Q. Progress in ionizing radiation resistance modification of polymer materials. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2109, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudoh, H.; Kasai, N.; Sasuga, T.; Seguchi, T. Low Temperature Gamma-ray Irradiation Effects on Polymer Materials. JAERI-Conf. 95-003. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/27/021/27021808.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Gerstenberg, H.; Gläser, W. Neutron Irradiations at Temperatures below 6 K at the Munich Research Reactor (FRM); Fakultät für Physik E21, Technische Universität München: Garching, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Idesaki, A.; Uechi, H.; Hakura, Y.; Kishi, H. Effects of gamma-ray irradiation on a cyanate ester/epoxy resin. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 98, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shundo, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Tanaka, K. Network Formation and Physical Properties of Epoxy Resins for Future Practical Applications. JACS Au 2022, 2, 1522–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idesaki, A.; Uechi, H.; Hakura, Y.; Matsuda, S.; Kishi, H. Irradiation Effects of Gamma-Rays on Cyanate Ester/Epoxy Resins. In Second Workshop on Radiation Effects in Superconducting Magnet Materials; KEK: Tsukuba, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wollmann, D.; Bernhard, A.; Cangialosi, C.; Cerutti, F.; D’Angelo, G.; Danzeca, S.; Denz, R.; Favre, M.; Garcia Alia, R.; Hagedorn, D.; et al. Characterisation of the radiation hardness of cryogenic bypass diodes for the HL-LHC inner triplet circuit. In Proceedings of the 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 19–24 May 2019; p. THPTS067. [Google Scholar]

| Material | ρ (g/cm3) | Tg (°C) | α (×10−6 K−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G′ Onset | G″ Max | tan δ Max | |||
| CTD101K | 1.22 | 118 | 122 | 140 | 60 |
| MSUT | 1.23 | 88 | 91 | 107 | 60 |
| CEA mix | 1.27 | 100 | 107 | 113 | 56 |
| Araldite F | 1.22 | 91 | 93 | 105 | 55 |
| MY750 | 1.15 | 49 | 51 | 55 | 62 |
| Mix61 | 1.14 | −38 * | n.m. | 73 | 144 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parragh, D.M.; Scheuerlein, C.; Martin, N.; Piccin, R.; Ravotti, F.; Pezzullo, G.; Koettig, T.; Lellinger, D. Effect of Irradiation Temperature and Atmosphere on Aging of Epoxy Resins for Superconducting Magnets. Polymers 2024, 16, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030407
Parragh DM, Scheuerlein C, Martin N, Piccin R, Ravotti F, Pezzullo G, Koettig T, Lellinger D. Effect of Irradiation Temperature and Atmosphere on Aging of Epoxy Resins for Superconducting Magnets. Polymers. 2024; 16(3):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030407
Chicago/Turabian StyleParragh, David Mate, Christian Scheuerlein, Noémie Martin, Roland Piccin, Federico Ravotti, Giuseppe Pezzullo, Torsten Koettig, and Dirk Lellinger. 2024. "Effect of Irradiation Temperature and Atmosphere on Aging of Epoxy Resins for Superconducting Magnets" Polymers 16, no. 3: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030407
APA StyleParragh, D. M., Scheuerlein, C., Martin, N., Piccin, R., Ravotti, F., Pezzullo, G., Koettig, T., & Lellinger, D. (2024). Effect of Irradiation Temperature and Atmosphere on Aging of Epoxy Resins for Superconducting Magnets. Polymers, 16(3), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030407







