Effects of Ferric Ions on Cellulose Nanocrystalline-Based Chiral Nematic Film and Its Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CNC/FeCl3 Colloids
3. Results and Discussion
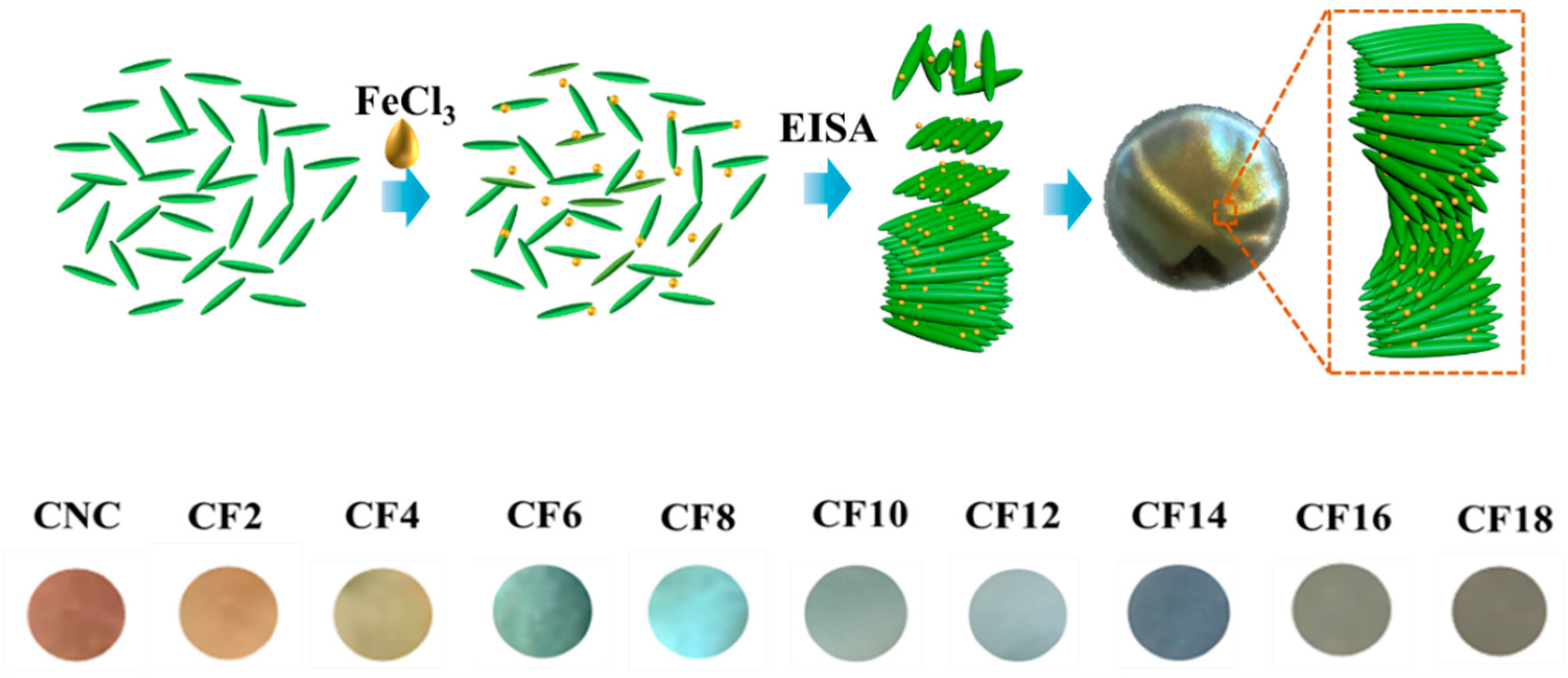
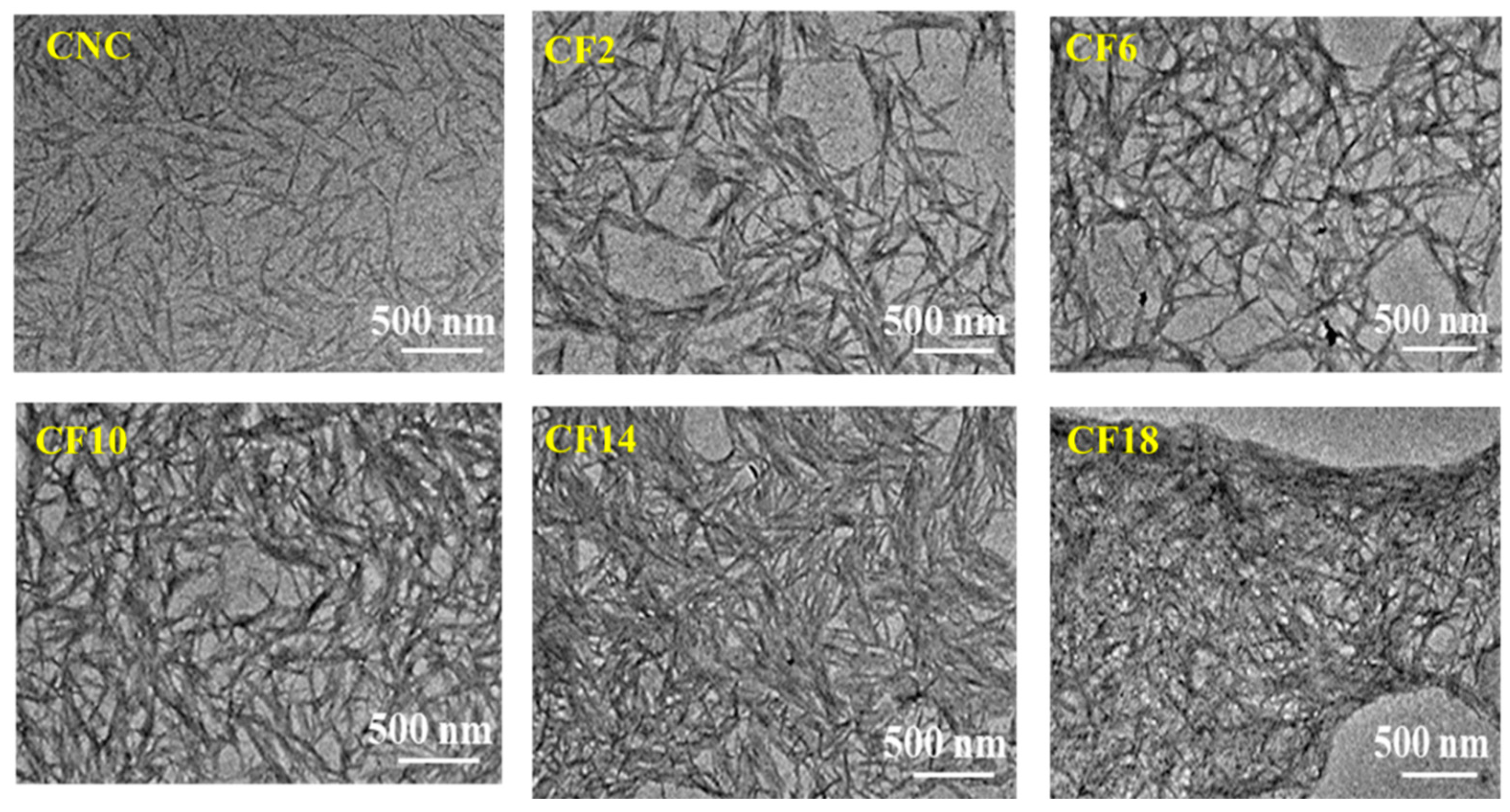
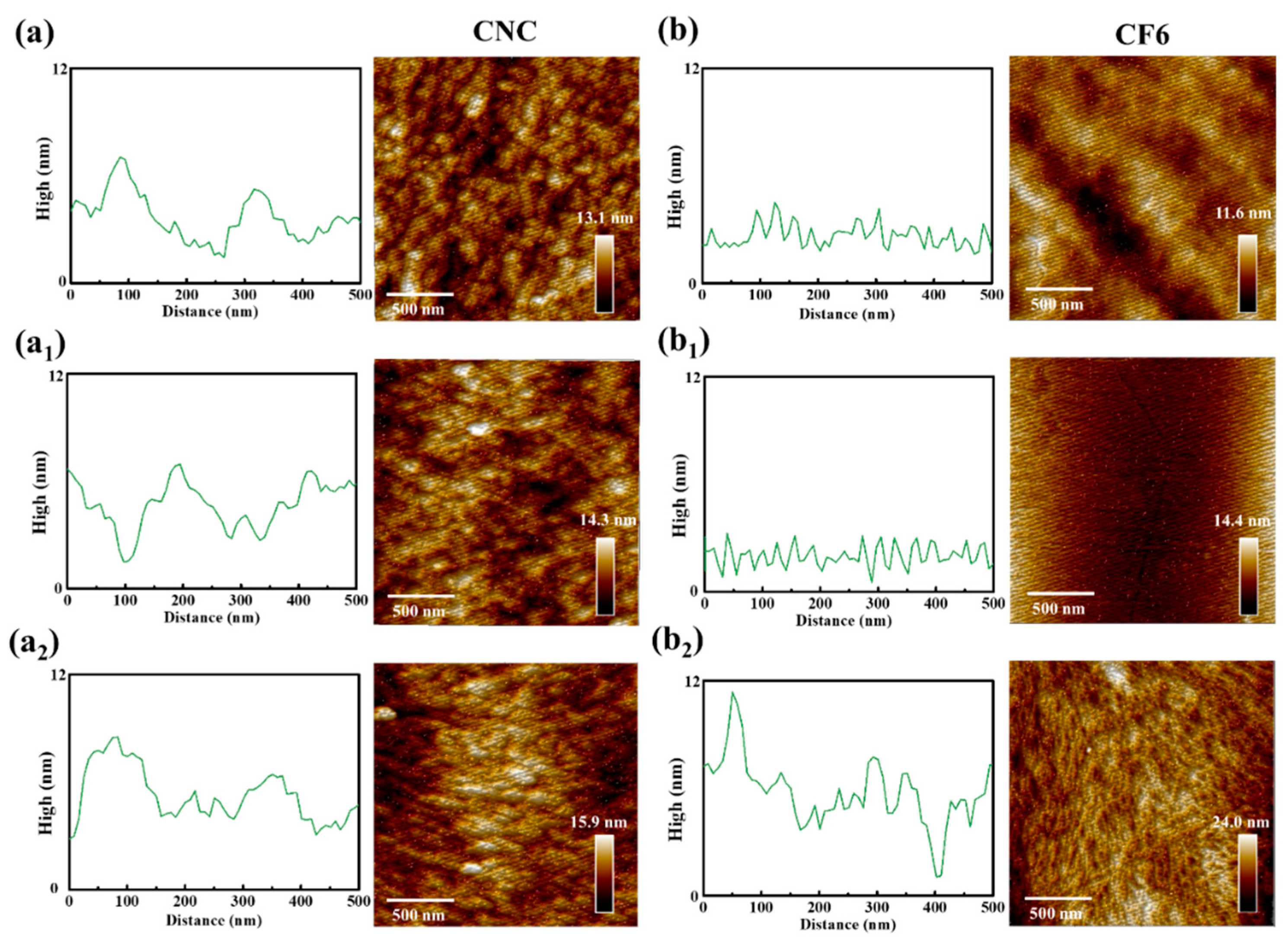
3.1. Morphological Characteristics of CNC/FeCl3 Colloids and Chiral Nematic Films
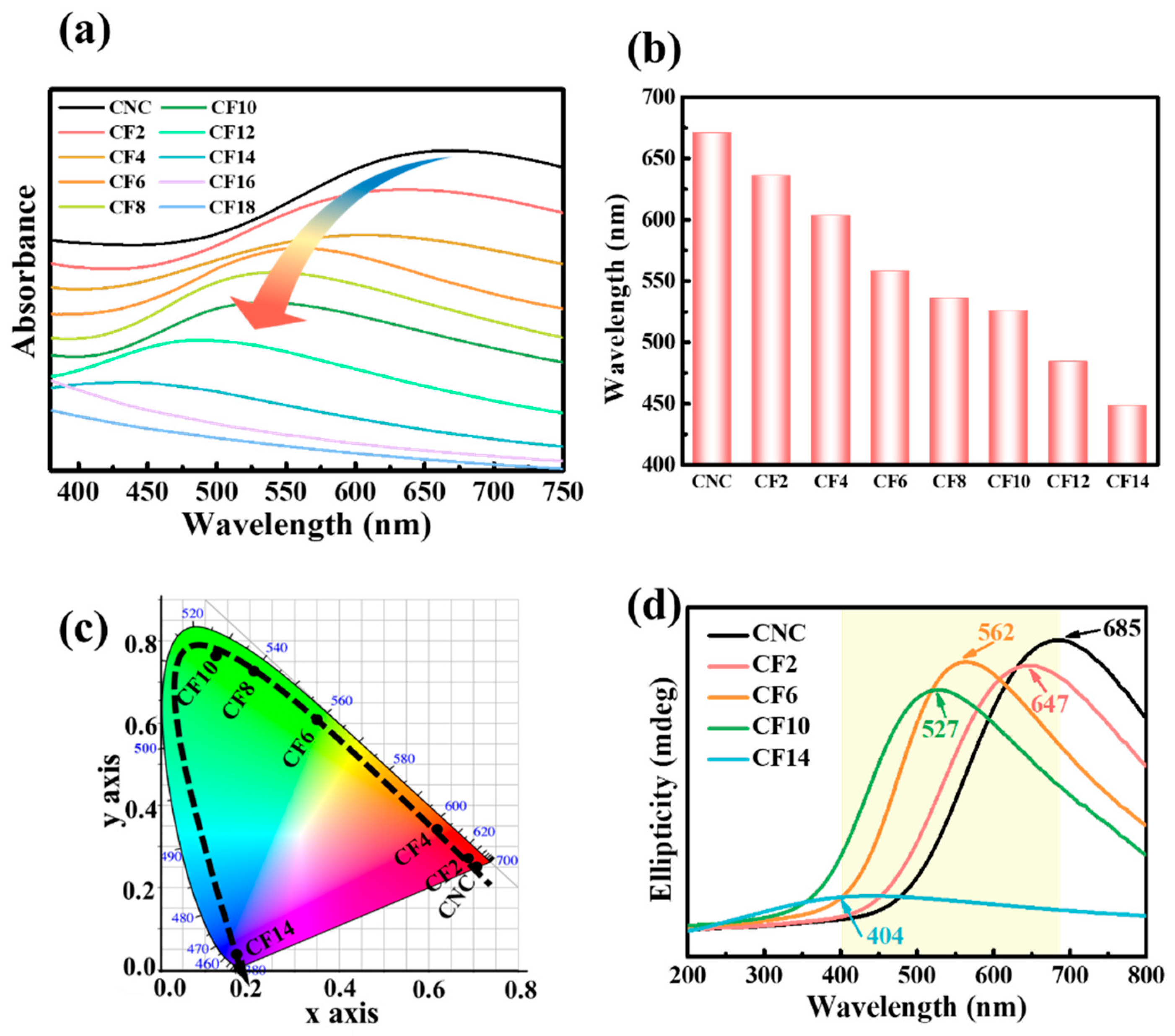
3.2. Optical Properties of CNC/FeCl3 Chiral Nematic Films
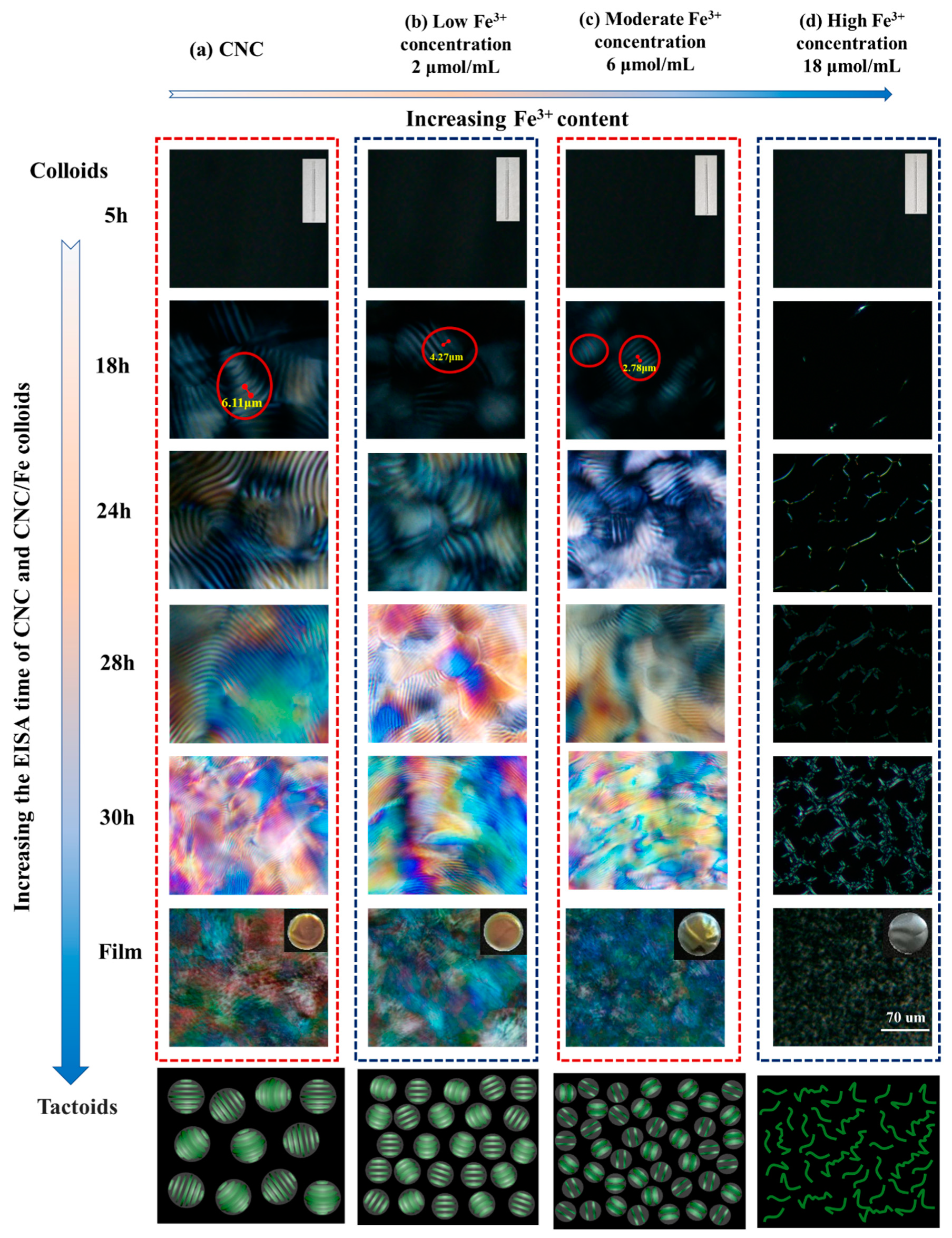
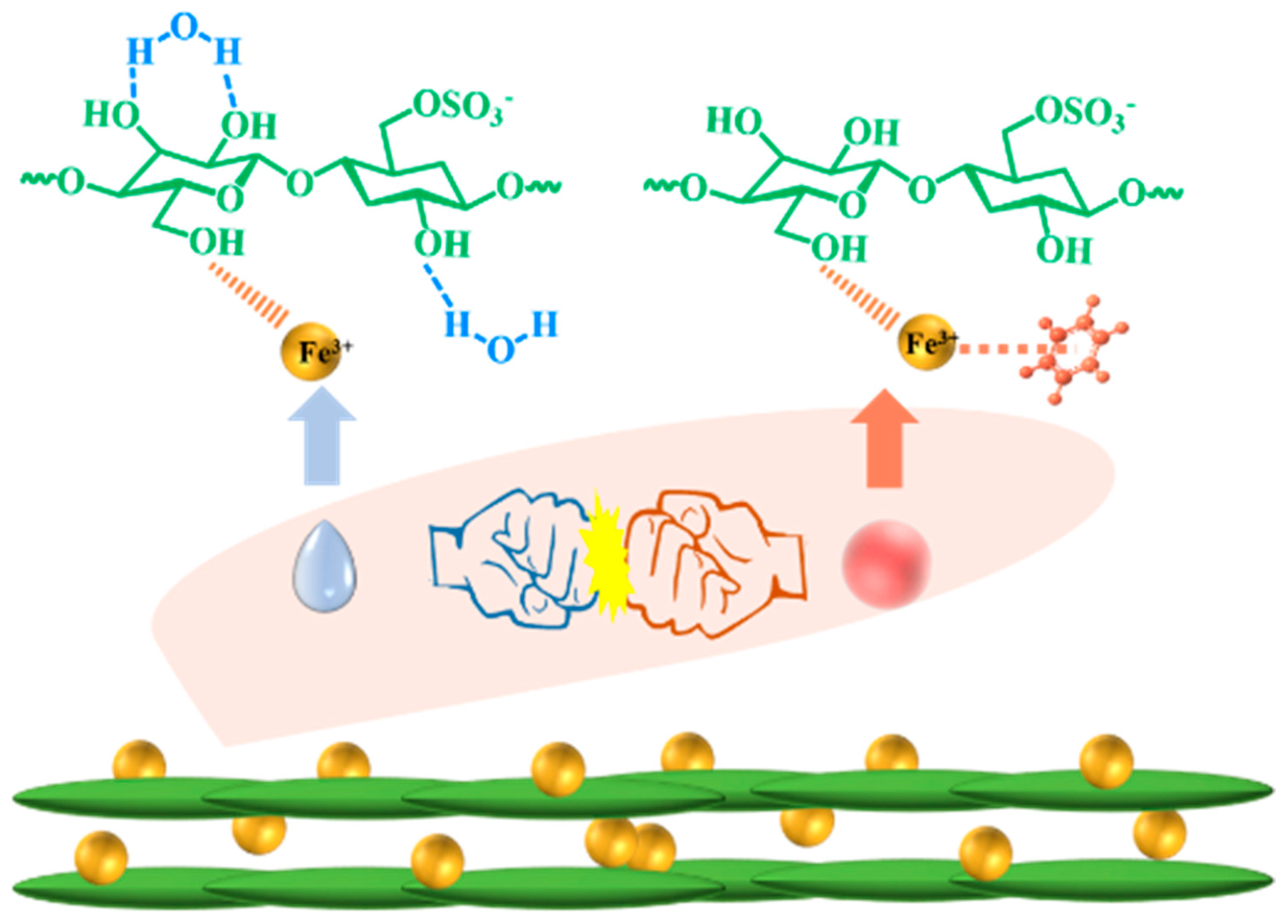
3.3. Chiral Nematic Formation of CNC/FeCl3 Iridescent Film
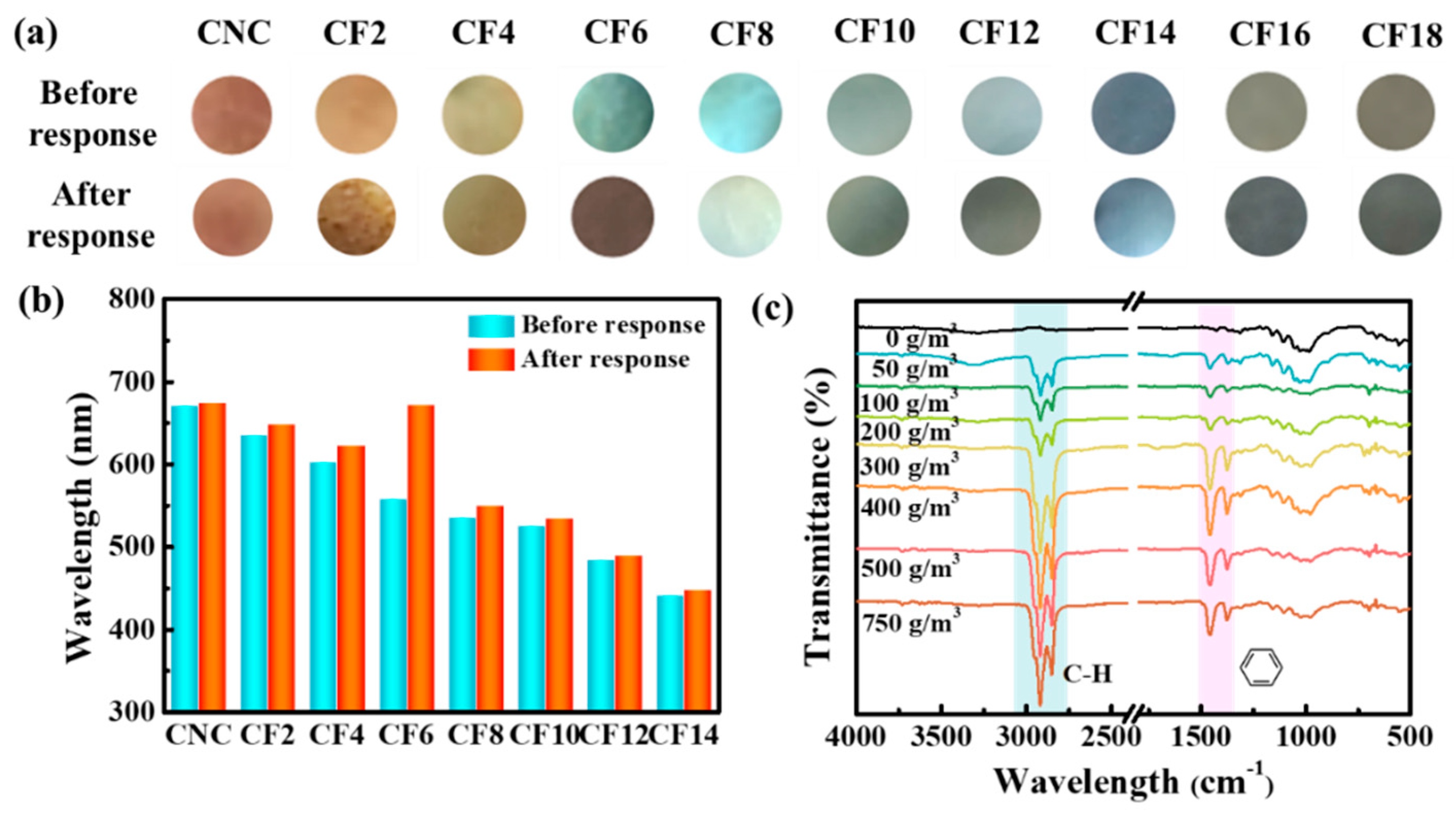
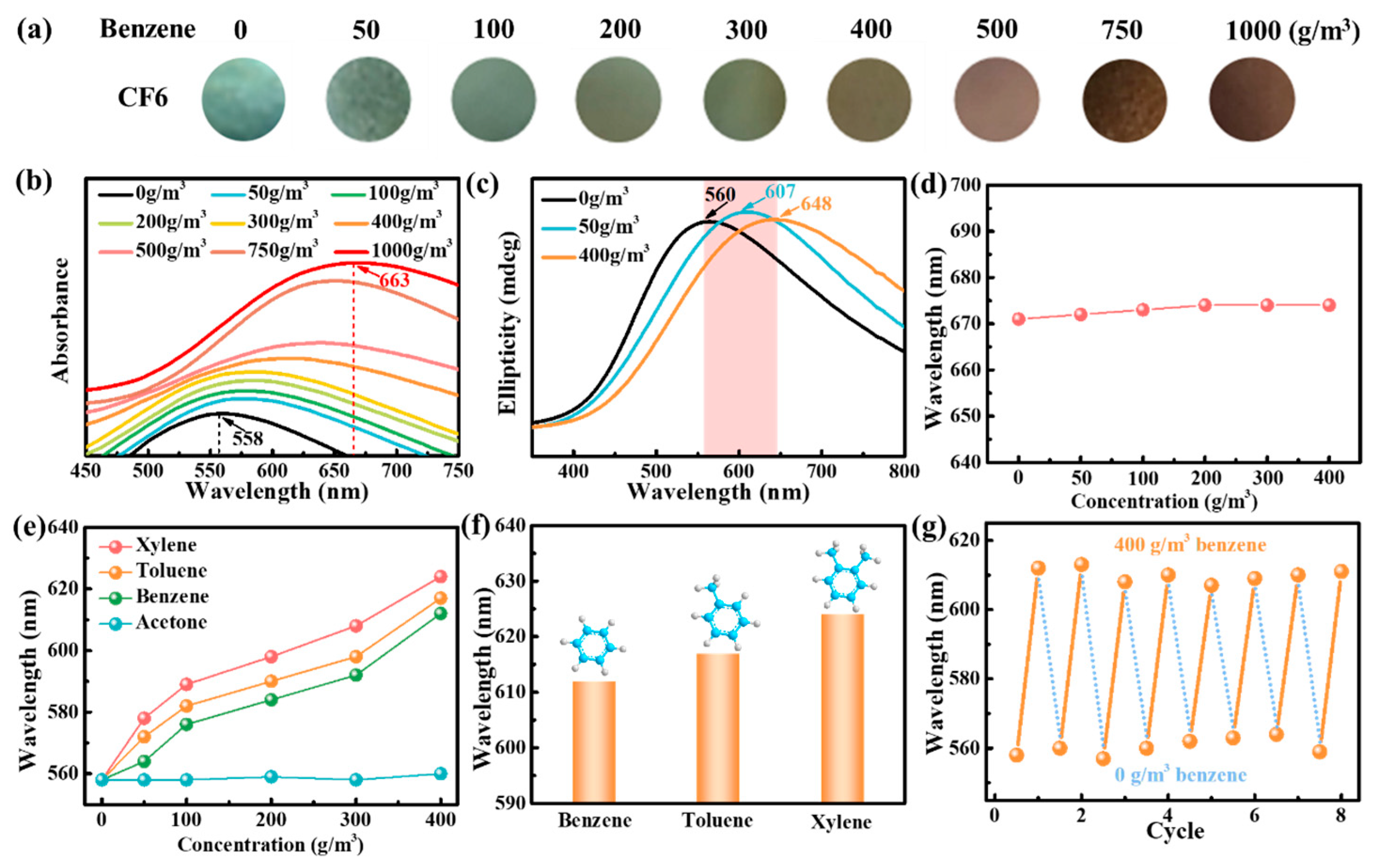
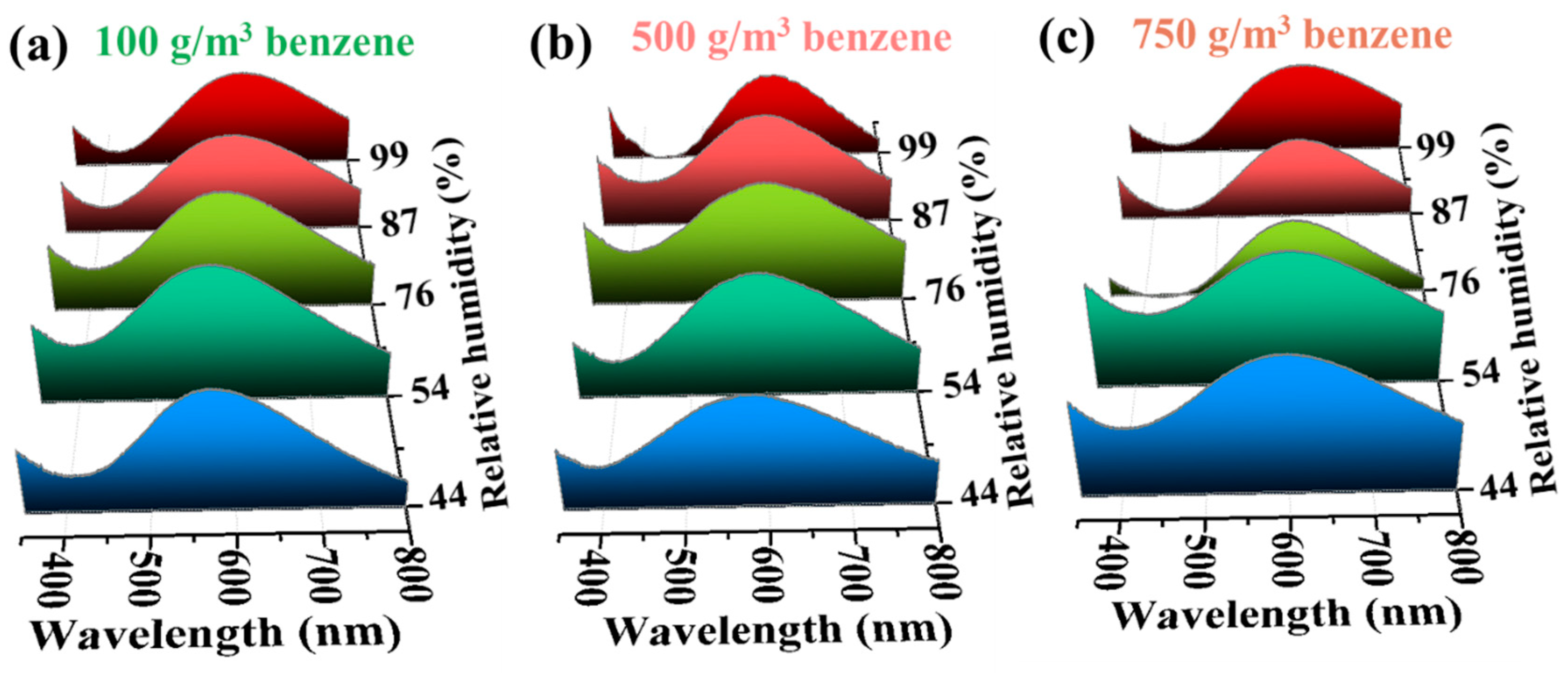
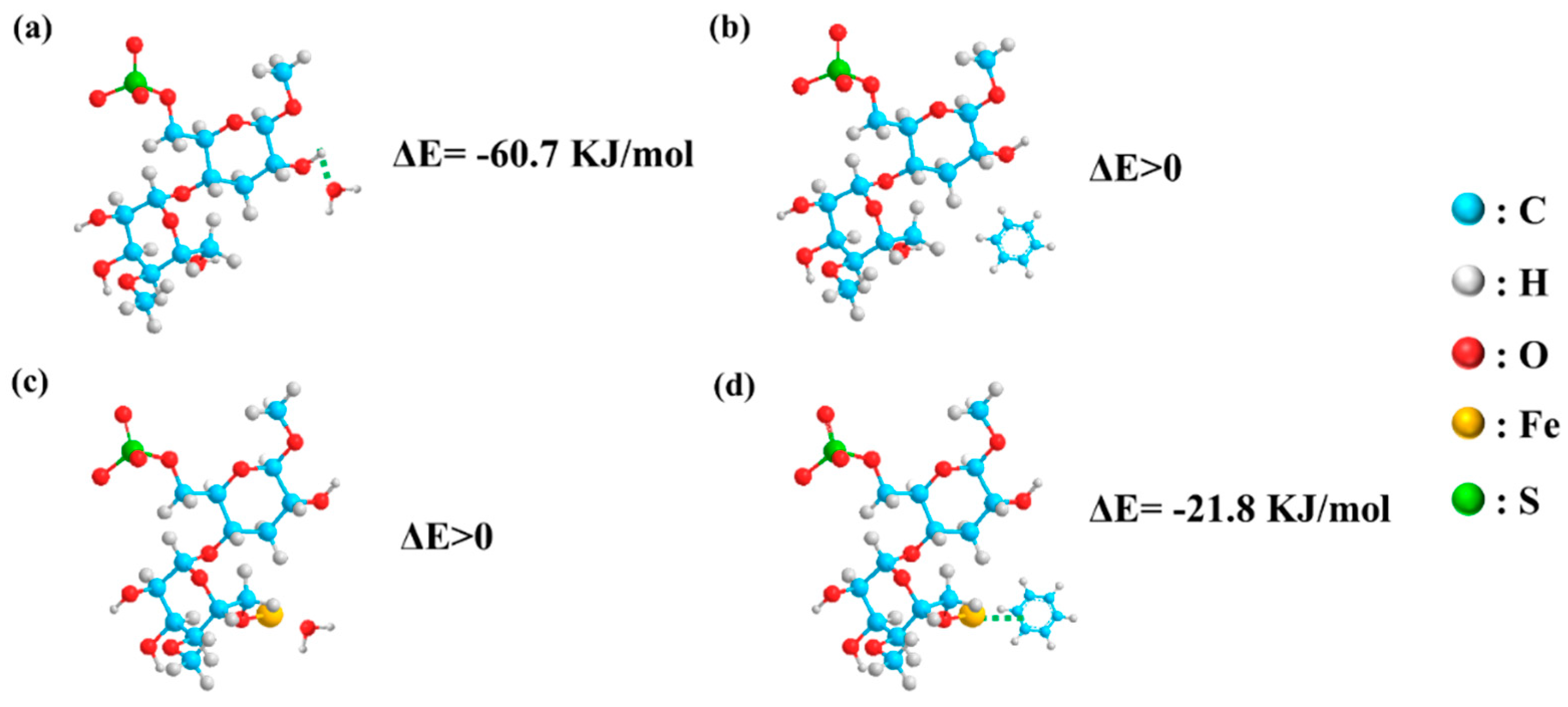
3.4. Applications for Aromatic Hydrocarbon Response
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, M.C.; Wu, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C.H.; Li, W.; Yu, H.P.; Chen, Z.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, S.X. Designing Hybrid Chiral Photonic Films with Circularly Polarized Room-Temperature Phosphorescence. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 11130–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Zhu, Z.G.; Xue, M.; Xue, F.; Wang, Q.H.; Meng, Z.H.; Lu, W.; Chen, W.; Qi, F.L.; Yan, Z.Q. Cellulose photonic crystal film sensor for alcohols. Sens. Actuators B-C 2015, 220, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.M.; Huang, Y.P.; Mei, C.T.; Zhai, S.C.; Xuan, Y.; Liu, Z.P.; Pan, M.Z.; Rojas, O.J. Chiral nematic coatings based on cellulose nanocrystals as a multiplexing platform for humidity sensing and dual anti-counterfeiting. Small 2021, 17, 2103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, S.C.; Sugiyama, J.; Pan, M.Z.; Jingbo, S.; Lu, H.Y. Dual Response of Photonic Film with Chiral Nematic Cellulose Nanocrystal: Humidity and Formaldehyde. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17833–17844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Crne, M.; Park, J.O.; Srinivasarao, M. Structural Origin of Circularly Polarized Iridescence in Jeweled Beetles. Science 2009, 325, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykov, V.P. Spontaneous emission from a medium with a band spectrum. Quantum Electron. 1975, 4, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablonovitch, E. Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid-state physics and electronics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 2059–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, V.E.; Onelli, O.D.; Steiner, L.M.; Vignolini, S. Photonics in Nature: From Order to Disorder. Funct. Surf. Biol. III 2017, 3, 53–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd-Noor, S.; Jang, H.; Baek, K.; Pei, Y.R.; Alam, A.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, I.S.; Choy, J.H.; Hyun, J.K. Ultrafast humidity-responsive structural colors from disordered nanoporous titania microspheres. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10561–10571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Yuan, X.T.; Chen, F.W.; Yang, H. Broadband Reflection in Polymer Stabilized Cholesteric Liquid Crystals via Thiol-Acrylate Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6698–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragt, A.J.J.; Broer, D.J.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Easily Processable and Programmable Responsive Semi-Interpenetrating Liquid Crystalline Polymer Network Coatings with Changing Reflectivities and Surface Topographies. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P.; Sain, M. Novel bionanocomposites: Processsing, properties and potential applications. Plast. Rubber. Compos. 2009, 38, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, C.; Song, F.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Bio-inspired non-iridescent structural coloration enabled by self-assembled cellulose nanocrystal composite films with balanced ordered/disordered arrays. Compos. Part B 2022, 229, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusuyadevi, P.R.; Shanker, R.; Cui, Y.X.; Riazanova, A.V.; Järn, M.; Jonsson, M.P.; Svagan, A.J. Photoresponsive and Polarization-Sensitive Structural Colors from Cellulose/Liquid Crystal Nanophotonic Structures. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Lee, J.K.; Gong, M.S.; Heo, K.; Chuang, W.J.; Lee, B.Y. Cellulose Nanocrystal-Based Colored Thin Films for Colorimetric Detection of Aldehyde Gases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10353–10361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.D.; Prempeh, N.; Liu, D.G.; Fan, Y.M.; Gu, M.Y.; Chang, Y. Cholesteric film of Cu(II)-doped cellulose colorimetric sensing of ammonia gas. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, A.; Zheng, C.; Tang, J.; Xie, K.; Gao, A. Light- and Humidity-Responsive Chiral Nematic Photonic Crystal Films Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24505–24511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Dong, X.; Fan, Y.N.; Yang, L.M.; He, L.; Song, F.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Chameleon-Inspired Variable Coloration Enabled by a Highly Flexible Photonic Cellulose Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 46710–46718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.D.; Zhang, Z.L.; Xue, J.; Wang, X.H.; Song, F.; Wang, X.L.; Zhu, L.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Biomimetic Optical Cellulose Nanocrystal Films with Controllable Iridescent Color and Environmental Stimuli-Responsive Chromism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5805–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.M.; Zhang, S.; Zhai, S.; Pan, M.Z. Fabrication and characterization of photonic cellulose nanocrystal films with structural colors covering full visible light. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 8756–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.M.; Lin, B.Q.; Liu, Z.P.; Rojas, O.J.; Pan, M.Z. Metal ion and ultrasonication assisted assembling chiral nematic coatings towards humidity-responsive and anti-counterfeiting. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 228, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, W.J.; Wang, L.; Tajvidi, M.; Wang, J.W.; Gardner, D.J. Transparent Multifunctional Cellulose Nanocrystal Films Prepared Using Trivalent Metal Ion Exchange for Food Packaging. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9419–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.M.; Kimura, T.; Revol, J.F. Effects of ionic strength on the isotropic chiral nematic phase transition of suspensions of cellulose crystallites. Langmuir 1996, 12, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Long, Z.; He, Z.; Fu, X.; Dong, C. Chiral Cellulose Nanocrystal Humidity-Responsive Iridescent Films with Glucan for Tuned Iridescence and Reinforced Mechanics. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 4479–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Jiang, C.; Liu, D.; Prempeh, N.; Smalyukh, I.I. Cellulose Nanocrystal/Poly(ethylene glycol) Composite as an Iridescent Coating on Polymer Substrates: Structure-Color and Interface Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 32565–32573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.P.; Liu, P.F.; Jiang, Z.G.; Yu, Z.Z. Rapidly Responsive and Flexible Chiral Nematic Cellulose Nanocrystal Composites as Multifunctional Rewritable Photonic Papers with Eco-Friendly Inks. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 5918–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Whittaker, A.K.; Zhu, S. Ultrasensitive Magnetic Tuning of Optical Properties of Films of Cholesteric Cellulose Nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9440–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Yuan, Q.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Shi, S.W.; Russell, T.P.; Wang, D. Nanorod-Surfactant Assemblies and Their Interfacial Behavior at Liquid-Liquid Interfaces. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsowitz, K.E.; Qi, H.; Hamad, W.Y.; Maclachlan, M.J. Free-standing mesoporous silica films with tunable chiral nematic structures. Nature 2010, 468, 422-U246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Browee, C. Modulating the chiral nanoarchitecture of cellulose nanocrystals through interaction with salts and polymer. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, S. Could Coulomb’s experiment result in Coulomb's law? Science 1993, 262, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehaqui, H.; Kulasinski, K.; Pfenninger, N.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Highly Carboxylated Cellulose Nanofibers via Succinic Anhydride Esterification of Wheat Fibers and Facile Mechanical Disintegration. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Renneckar, S. Supramolecular structure characterization of molecularly thin cellulose I nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive-based gas sensors for detection of benzene, toluene and xylene (BTX) gases: A review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4342–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltouny, N.A.; Ariya, P.A. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Carboxymethyl Cellulose: A Green Option for the Removal of Atmospheric Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and o-Xylene (BTEX). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12787–12795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Jiang, C.X.; Zhou, X.Y. Fabrication of Pd-decorated TiO2/MoS2 ternary nanocomposite for enhanced benzene gas sensing performance at room temperature. Talanta 2018, 182, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, S.M.; Li, J.Y.; Xing, Y.N.; Zhao, X.Y.; Li, D.J. Porous nanosheets assembled Co3O4 hierarchical architectures for enhanced BTX (Benzene, Toluene and Xylene) gas detection. Sens. Actuators B-C 2020, 315, 128120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Lin, B.; Zeng, Y.; Pan, M. Effects of Ferric Ions on Cellulose Nanocrystalline-Based Chiral Nematic Film and Its Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030399
Wang S, Lin B, Zeng Y, Pan M. Effects of Ferric Ions on Cellulose Nanocrystalline-Based Chiral Nematic Film and Its Applications. Polymers. 2024; 16(3):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030399
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuaiqi, Bingqun Lin, Yihan Zeng, and Mingzhu Pan. 2024. "Effects of Ferric Ions on Cellulose Nanocrystalline-Based Chiral Nematic Film and Its Applications" Polymers 16, no. 3: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030399
APA StyleWang, S., Lin, B., Zeng, Y., & Pan, M. (2024). Effects of Ferric Ions on Cellulose Nanocrystalline-Based Chiral Nematic Film and Its Applications. Polymers, 16(3), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030399





