Improving the Impact Resistance and Post-Impact Tensile Fatigue Damage Tolerance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites by Embedding the Carbon Nanoparticles in Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
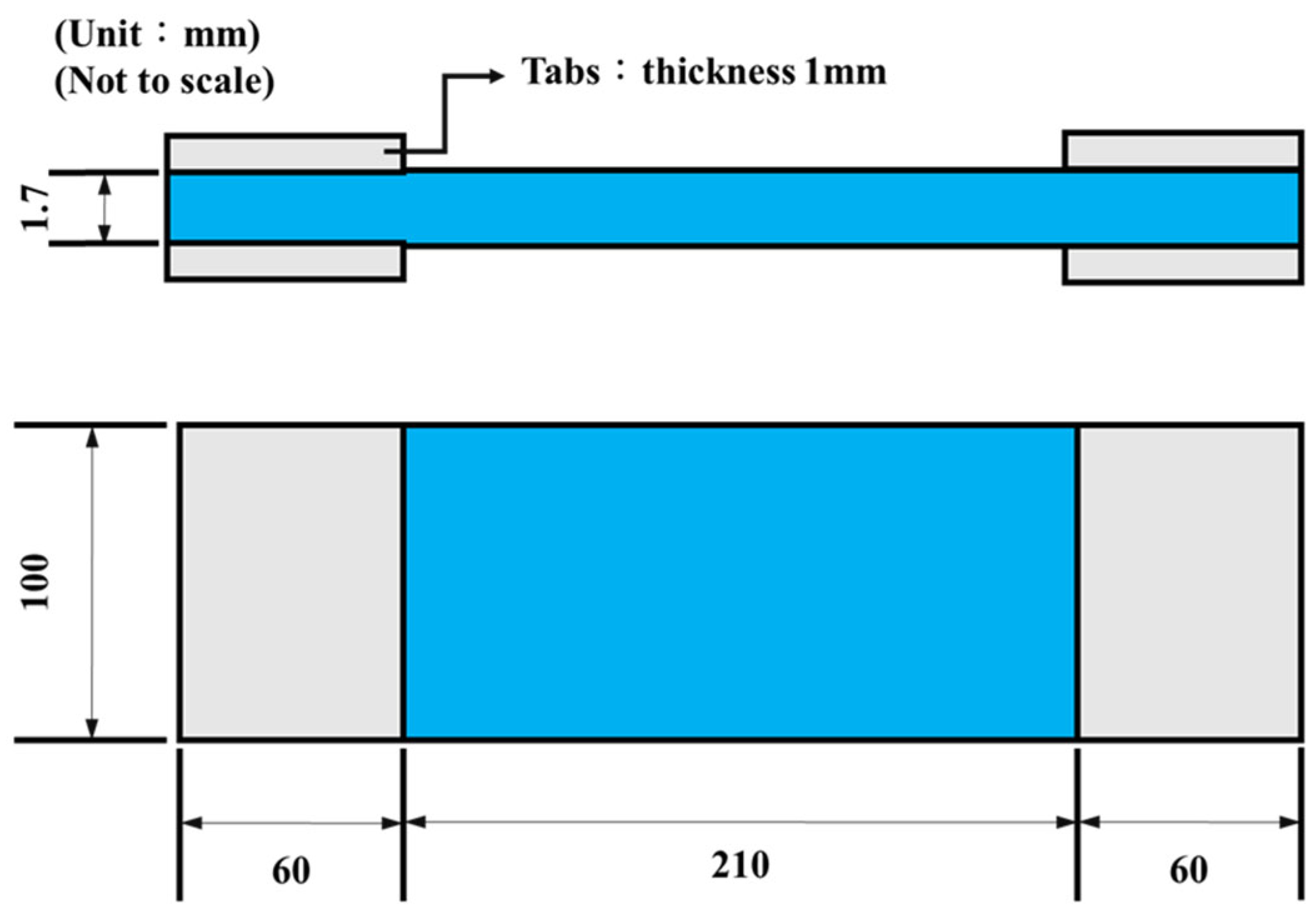
2.1. Materials and Specimen Preparation
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
3.1. Low-Velocity Impact Resistance
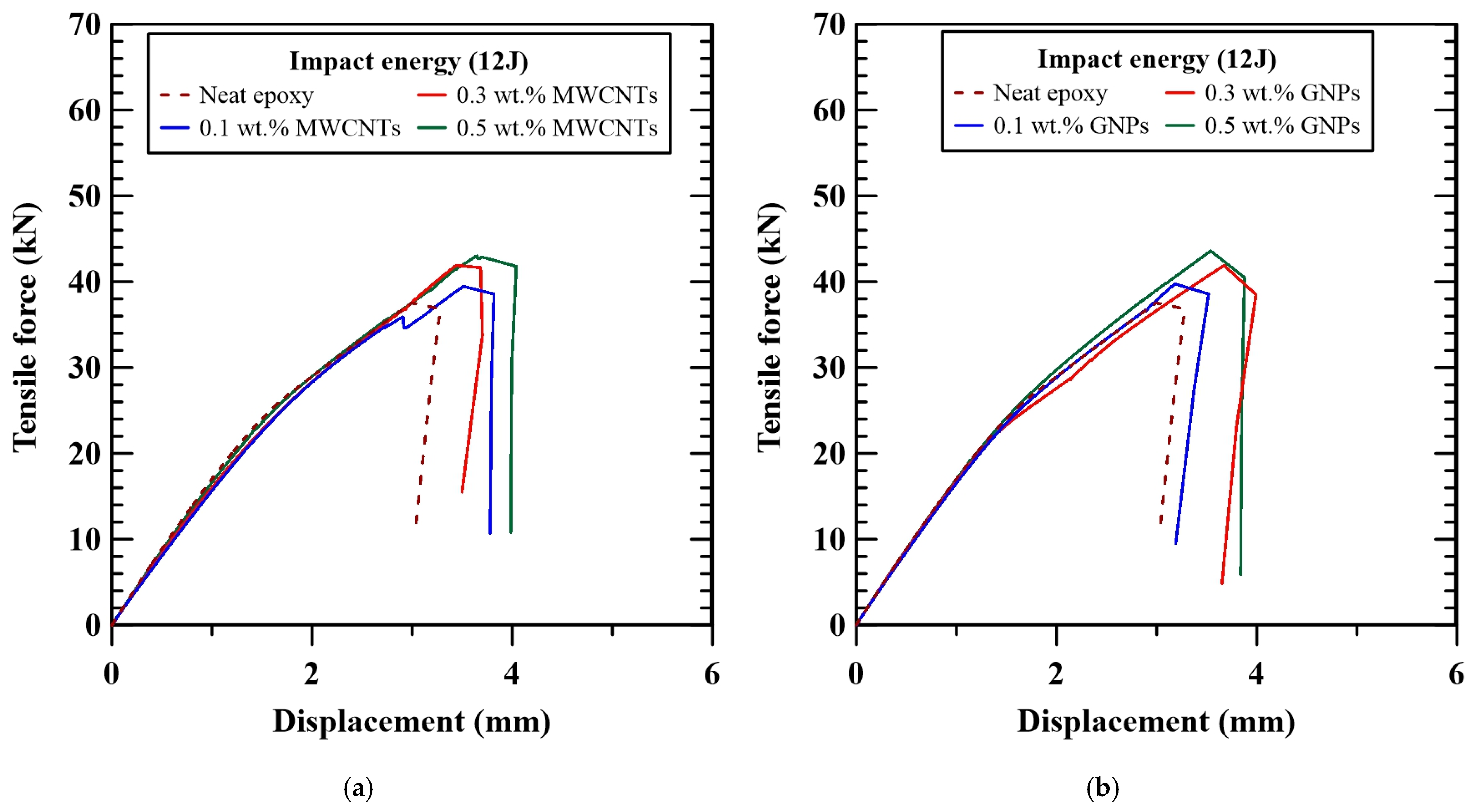
3.2. Post-Impact Statically Tensile Strength
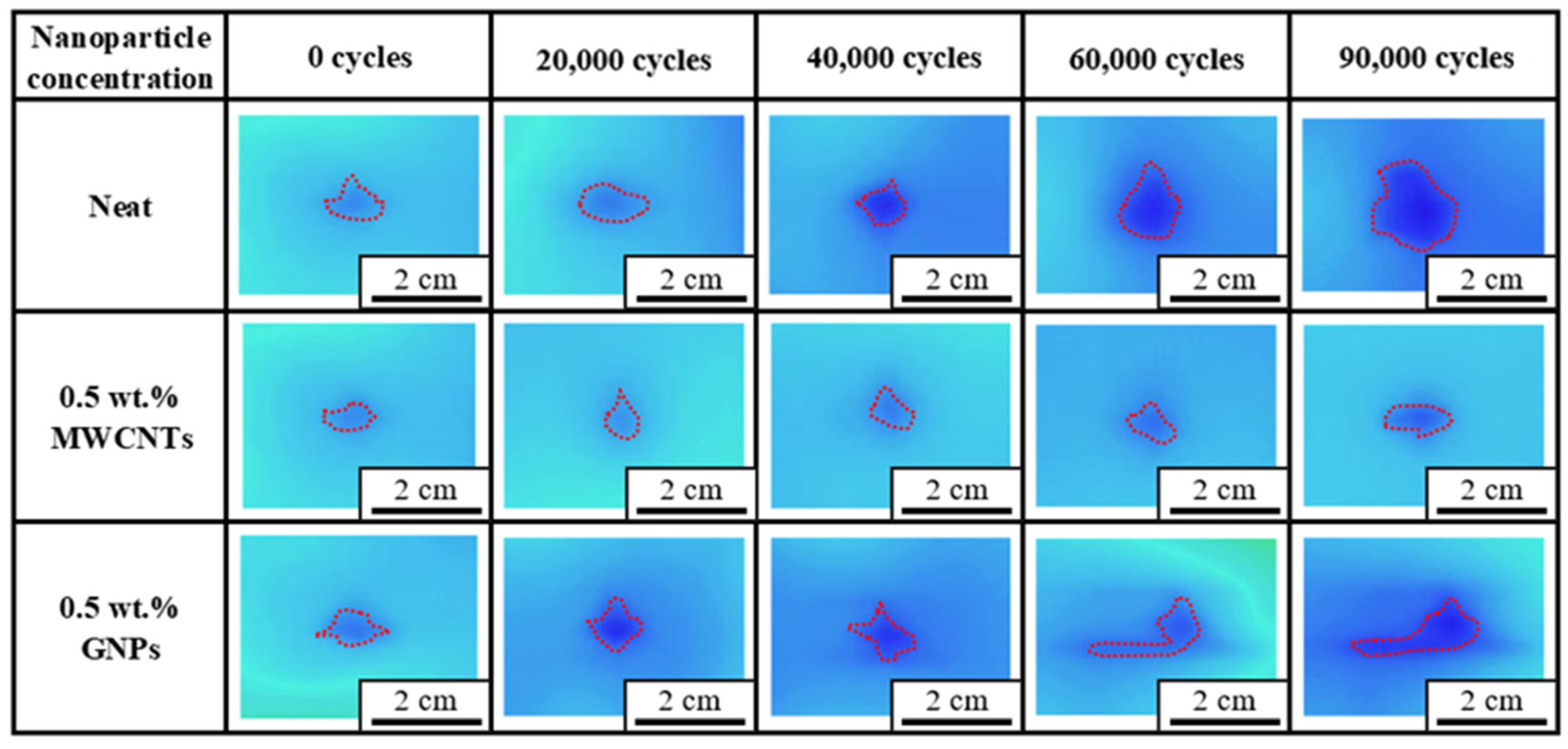
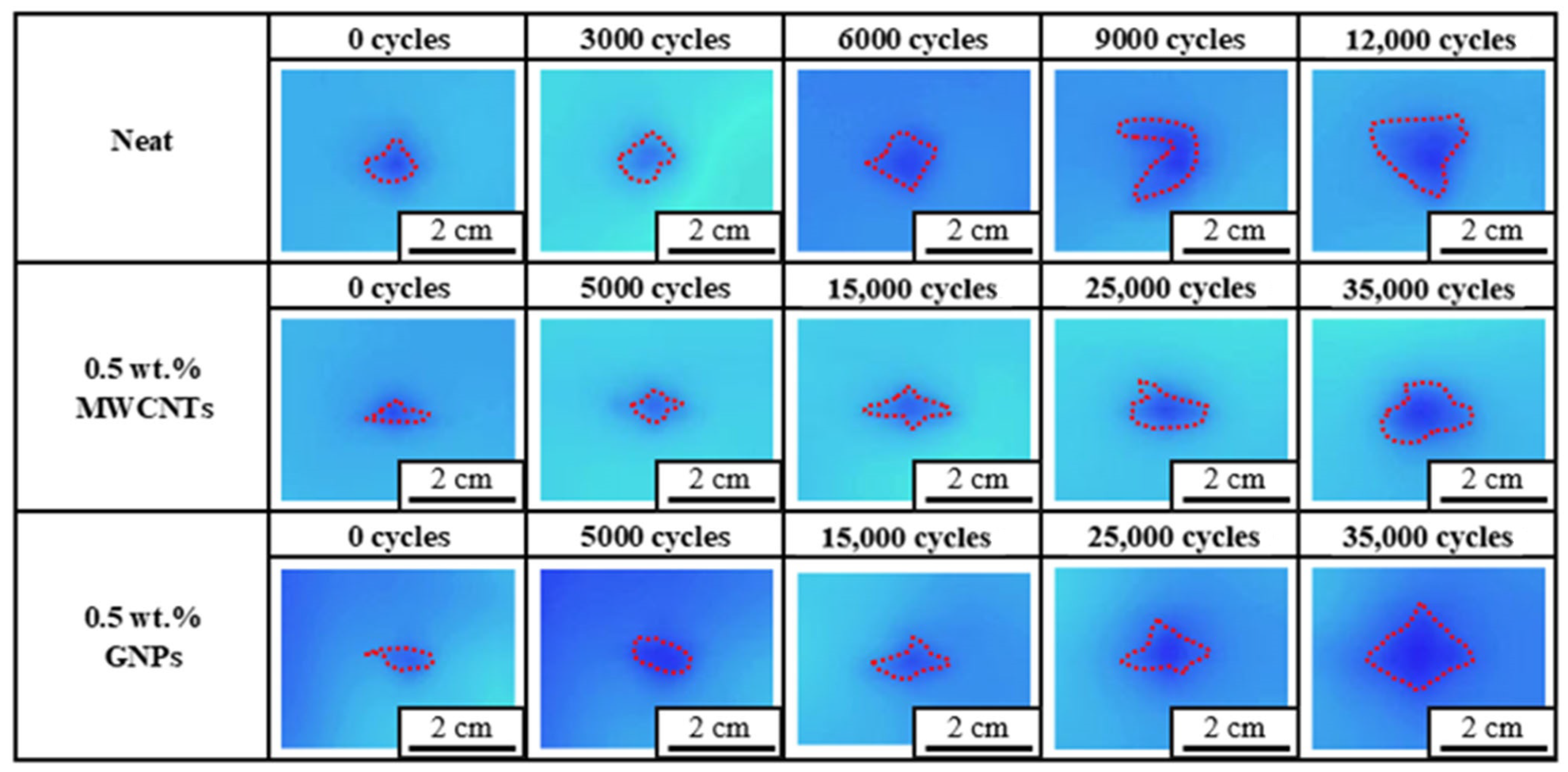
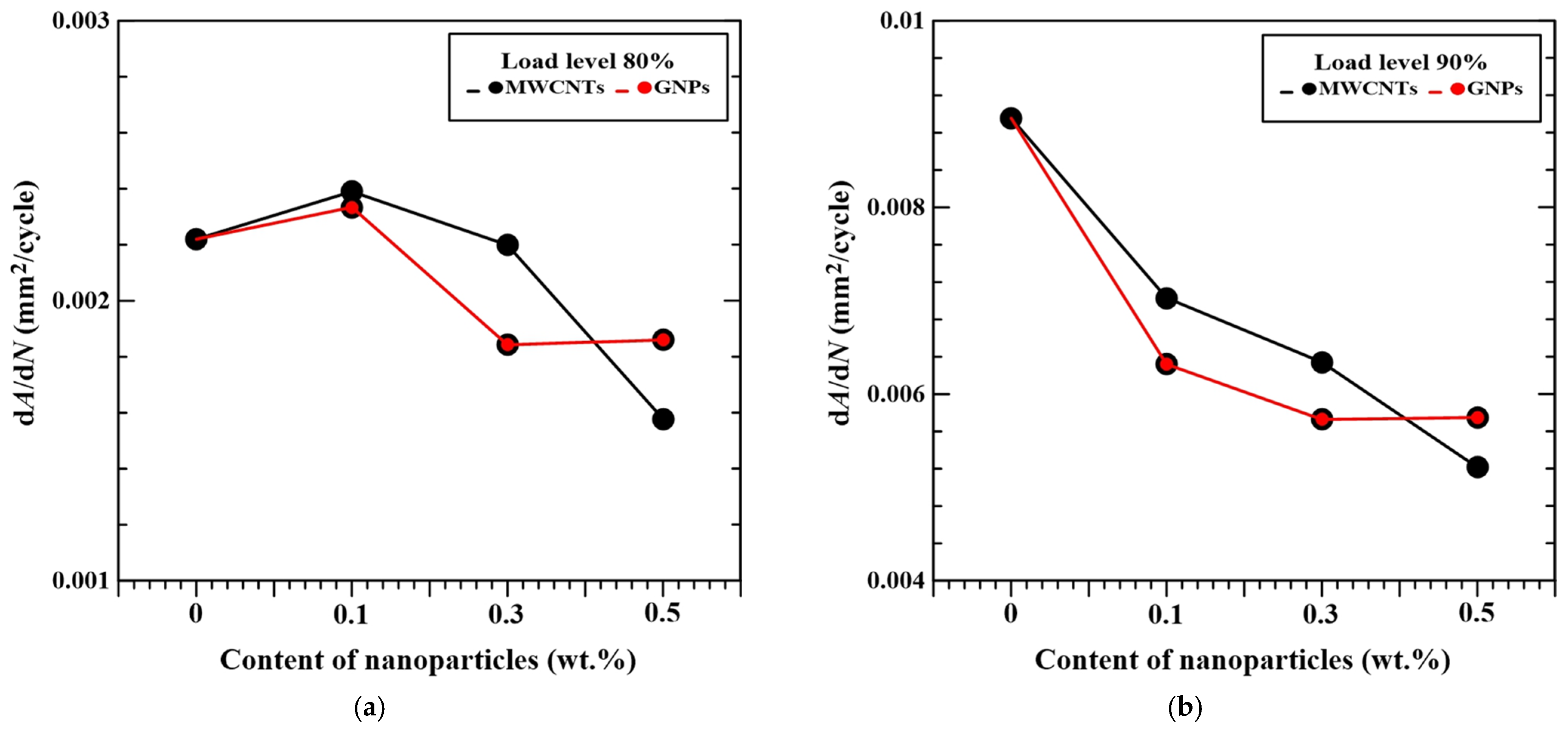
3.3. Post-Impact Tensile Fatigue Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mangalgiri, P.D. Composite materials for aerospace applications. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1999, 22, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, G.V.; Aher, V.S. Composite material: A review over current development and automotive application. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine application of fiber reinforced composites: A review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safri, S.N.A.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Yidris, N.; Mustapha, F. Low velocity and high velocity impact test on composite materials–a review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2014, 3, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Talreja, R.; Phan, N. Assessment of damage tolerance approaches for composite aircraft with focus on barely visible impact damage. Compos. Struct. 2019, 219, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.H.; Karuppanan, S.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S.M.; Sajid, Z. Impact resistance and damage tolerance of fiber reinforced composites: A review. Compos. Struct. 2019, 217, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunith, B.L.; Kumar, K.P.; JayaChristiyan, K.G. Studies on factors influencing Low Velocity Impact of Composite Materials–A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1126, 012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, C.; Shivamurthy, B.; Mohan, M.; Mourad, A.H.I.; Selvam, R.; Thimmappa, B.H.S. Low velocity impact behavior of fabric reinforced polymer composites–A review. Eng. Sci. 2022, 18, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaware, K.; Kotambkar, M. Low velocity impact response and influence of parameters to improve the damage resistance of composite structures/materials: A critical review. Int. J. Crashworthines 2022, 27, 1232–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubham, S.K.; Purohit, R.; Yadav, P.S.; Rana, R.S. Study of nano-fillers embedded in polymer matrix composites to enhance its properties–A review. Mater. Today-Proc. 2020, 26, 3024–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmakuri, A.; Palevicius, A.; Vilkauskas, A.; Janusas, G. Review of hybrid fiber based composites with nano particles—Material properties and applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Nurazzi, N.; Asyraf, M.M.; Khalina, A.; Abdullah, N.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Kamarudin, S.H.; Ahmad, S.B.; Mahat, A.M.; Lee, C.L.; Aisyah, H.A.; et al. Fabrication, functionalization, and application of carbon nanotube-reinforced polymer composite: An overview. Polymers 2021, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Tan, C.Y.; Shen, X.; Ramesh, S.; Zarei, M.S.; Kolahchi, R.; Hajmohammad, M.H. The effects of nano-additives on the mechanical, impact, vibration, and buckling/post-buckling properties of composites: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 7570–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cicco, D.; Asaee, Z.; Taheri, F. Use of nanoparticles for enhancing the interlaminar properties of fiber-reinforced composites and adhesively bonded joints—A review. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saghafi, H.; Fotouhi, M.; Minak, G. Improvement of the impact properties of composite laminates by means of nano-modification of the matrix—A review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, R.; Tian, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.H. A review of the electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanofiller-reinforced polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1036–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Mai, Y.W.; Zhou, X.P. Dispersion and alignment of carbon nanotubes in polymer matrix: A review. Mat. Sci. Eng. R. 2005, 49, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboki, T.; Jar, P.Y.; Forest, T.W. Influence of interlaminar fracture toughness on impact resistance of glass fibre reinforced polymers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulos, V.; Baltopoulos, A.; Karapappas, P.; Vavouliotis, A.; Paipetis, A. Impact and after-impact properties of carbon fibre reinforced composites enhanced with multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatanarayanan, P.S.; Stanley, A.J. Intermediate velocity bullet impact response of laminated glass fiber reinforced hybrid (HEP) resin carbon nano composite. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2012, 21, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.; Boroujeni, A.Y.; Hartman, T.B.; Haugh, T.P.; Case, S.W.; Al-Haik, M.S. Mechanical characterization and impact damage assessment of a woven carbon fiber reinforced carbon nanotube–epoxy composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 75, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Hei, Y.; Zhang, B.; Bao, J.; Chen, X. Improving compression-after-impact performance of carbon–fiber composites by CNTs/thermoplastic hybrid film interlayer. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 95, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hosur, M.; Hsiao, K.T.; Wallace, L.; Jeelani, S. Low velocity impact properties of carbon nanofibers integrated carbon fiber/epoxy hybrid composites manufactured by OOA–VBO process. Compos. Struct. 2015, 120, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Singh, K.K. Damage tolerance of carbon fiber woven composite doped with MWCNTs under low-velocity impact. Procedia Eng. 2017, 173, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, T.H.; Islam, M.E.; Hosur, M.V.; Jeelani, S. Low-velocity impact performance of carbon fiber-reinforced plastics modified with carbon nanotube, nanoclay and hybrid nanoparticles. J. Reinf. Plast. Comp. 2017, 36, 696–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Kırıcı, M.; Tatar, A.C.; Avcı, A. Impact behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy composite tubes reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes at cryogenic environment. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2018, 145, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, K.I.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shah, A.U.M.; Jawaid, M.; Safri, S.N.A. Low velocity impact and compression after impact properties of hybrid bio-composites modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 163, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, A.F.M.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Jawaid, M.; Azmi, A.M.R.; Shah, A.U.M. Analysing impact properties of CNT filled bamboo/glass hybrid nanocomposites through drop-weight impact testing, UWPI and compression-after-impact behaviour. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 168, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, M.; Feli, S. Mechanical and low-velocity impact properties of epoxy-composite beams reinforced by MWCNTs. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, Ö.; Kadıoğlu, K.; Çolak, P.; Günaydın, E.; Doğu, M.; Topalömer, N.; Eskizeybek, V. Compression after impact and Charpy impact characterizations of glass fiber/epoxy/MWCNT composites. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Bavasso, I.; Sbardella, F.; Lampani, L.; De Rosa, I.M. Impact and post-impact properties of multiscale carbon fiber composites interleaved with carbon nanotube sheets. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 183, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, F.; Tatar, A.C.; Eskizeybek, V.; Avcı, A.; Aydın, M. Impact response of nanoparticle reinforced 3D woven spacer/epoxy composites at cryogenic temperatures. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 4231–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praneeth, H.R.; Patil, S.; Budavi, P.; Srinivas, G.S.; Usman, M.; Pasha, S. Study of Effect of Carbon nanotube on Tensile, Impact and Flexural properties of Carbon fibre/epoxy reinforcement polymer. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1248, 012088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.; Khashaba, E.U. Impact and mechanical properties of different composite systems modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 234, 4087–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, C.; Ierardo, N.; Lampani, L.; Calzolari, A.; Valente, T.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J. Low-velocity impact response of MWCNTs toughened CFRP composites: Stacking sequence and temperature effects. Thin Wall. Struct. 2022, 175, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amooyi Dizaji, R.; Yazdani, M.; Aligholizadeh, E.; Rashed, A. Effect of 3D-woven glass fabric and nanoparticles incorporation on impact energy absorption of GLARE composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 3528–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domun, N.; Kaboglu, C.; Paton, K.R.; Dear, J.P.; Liu, J.; Blackman, B.R.; Liaghat, G.; Hadavinia, H. Ballistic impact behaviour of glass fibre reinforced polymer composite with 1D/2D nanomodified epoxy matrices. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 167, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmarakbi, A.; Ciardiello, R.; Tridello, A.; Innocente, F.; Martorana, B.; Bertocchi, F.; Cristiano, F.; Elmarakbi, M.; Belingardi, G. Effect of graphene nanoplatelets on the impact response of a carbon fibre reinforced composite. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaadi, M.; Younus, B.; Erklig, A.; Bulut, M.; Bozkurt, O.; Sulaiman, B. Effect of graphene nano-platelets on mechanical and impact characteristics of carbon/Kevlar reinforced epoxy hybrid nanocomposites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 7139–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D7136/D7136M-15; Standard Test Method for Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d7136_d7136m-15.html (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- Munoz, V.; Vales, B.; Perrin, M.; Pastor, M.L.; Welemane, H.; Cantarel, A.; Karama, M. Damage detection in CFRP by coupling acoustic emission and infrared thermography. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2016, 85, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Tao, S.J. Low-velocity impact damage characterization of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) using infrared thermography. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, B.; Montero, J.; Buzaglo, M.; Regev, O.; Marques, E.F. Comparative trends and molecular analysis on the surfactant-assisted dispersibility of 1D and 2D carbon materials: Multiwalled nanotubes vs graphene nanoplatelets. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, P.; Sokolova, A.; Salim, N.; Juodkazis, S.; Fuss, F.K.; Fox, B.; Hameed, N. Distribution states of graphene in polymer nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 226, 109353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrieh, M.M.; Esmkhani, M.; Shahverdi, H.R.; Vahedi, F. Effect of graphene nanosheets (GNS) and graphite nanoplatelets (GNP) on the mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2013, 5, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
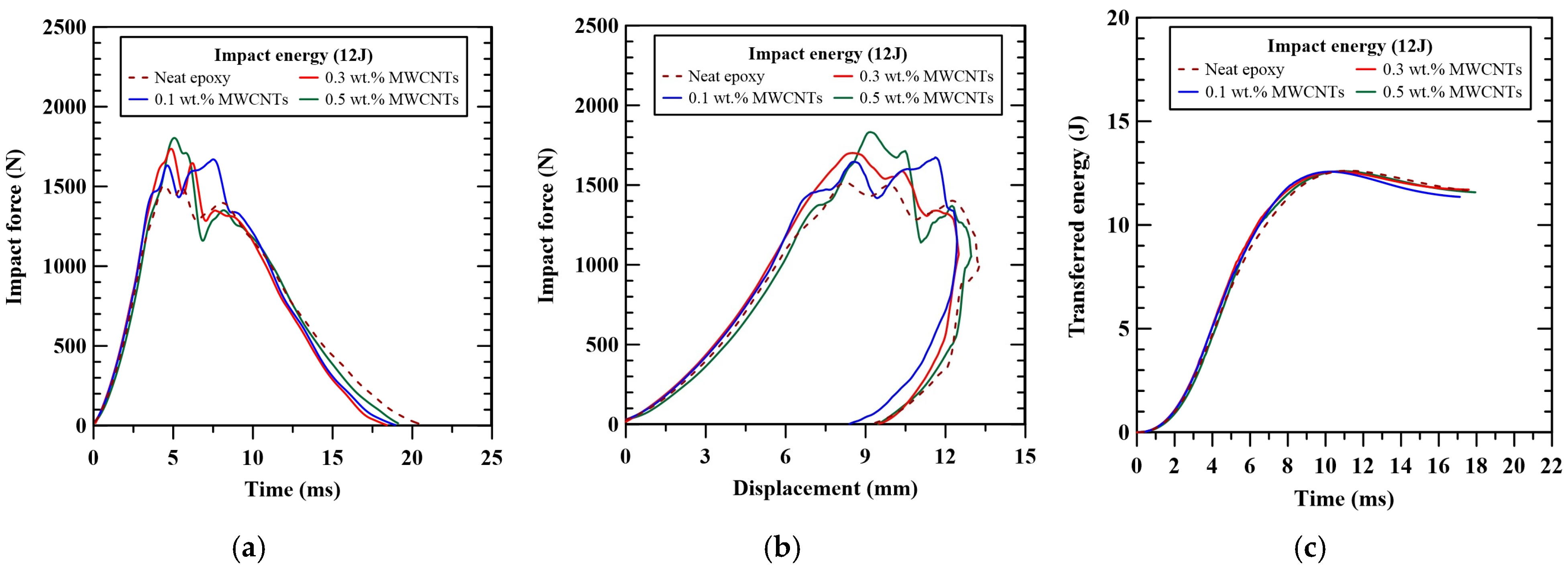

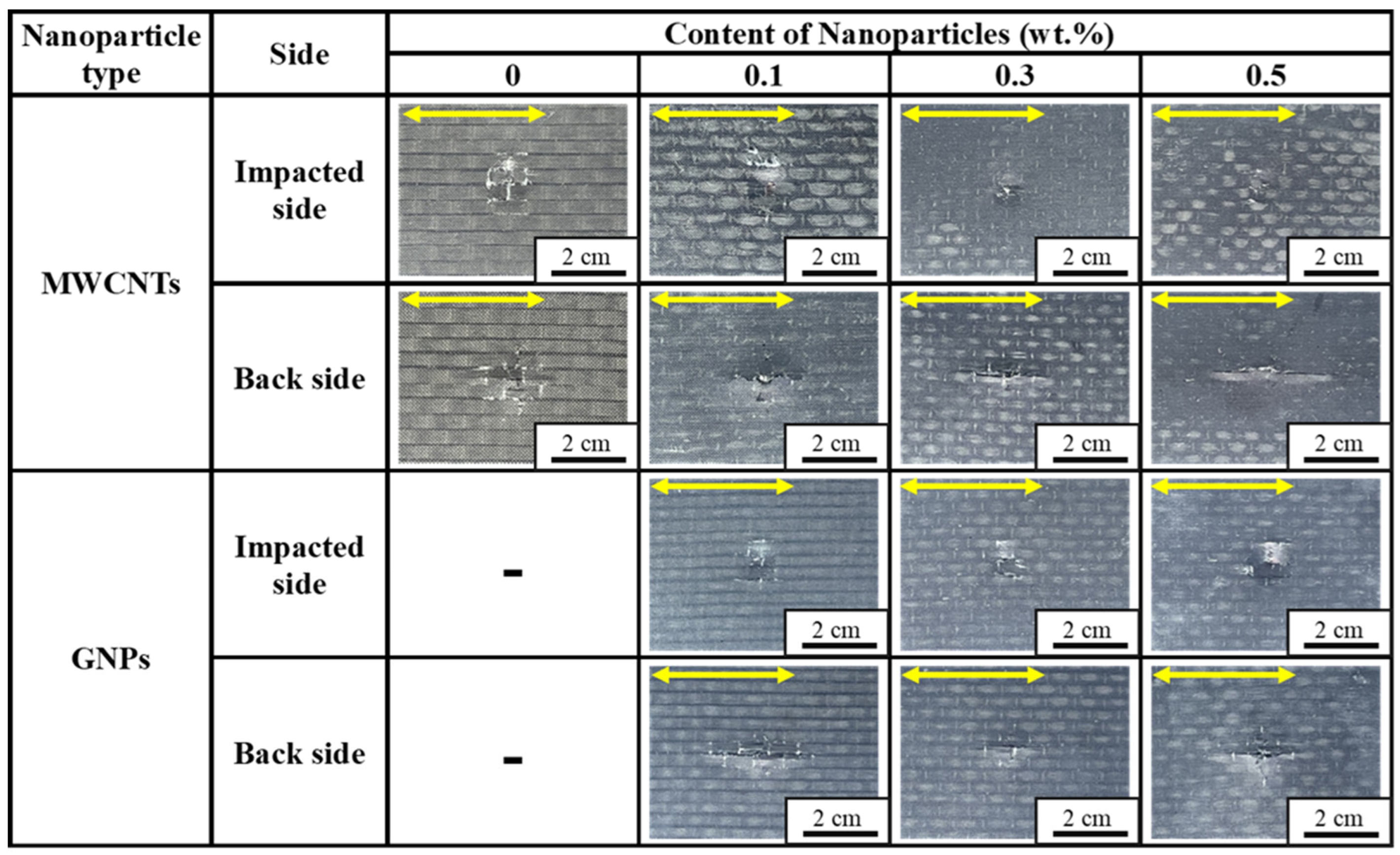

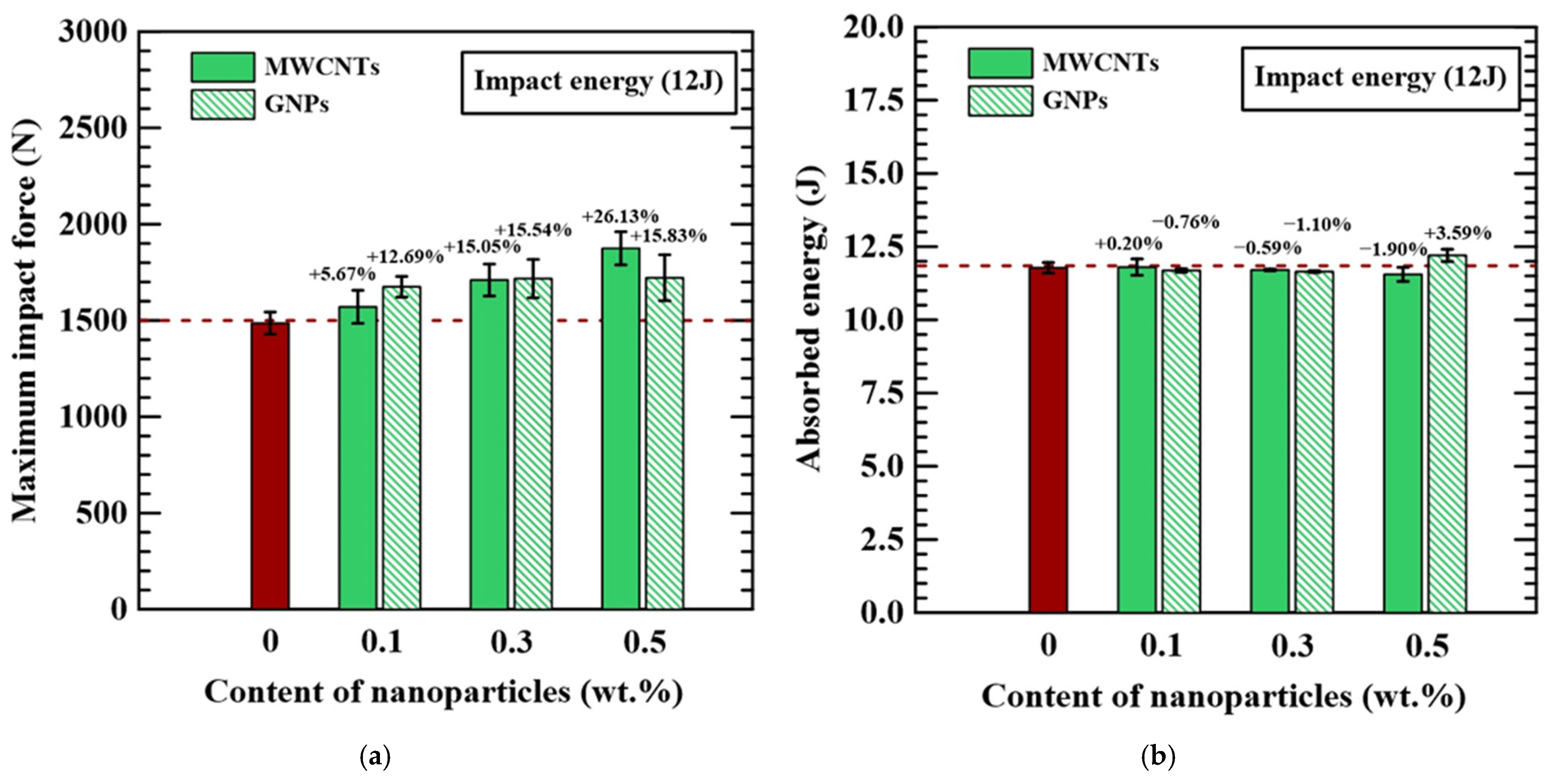





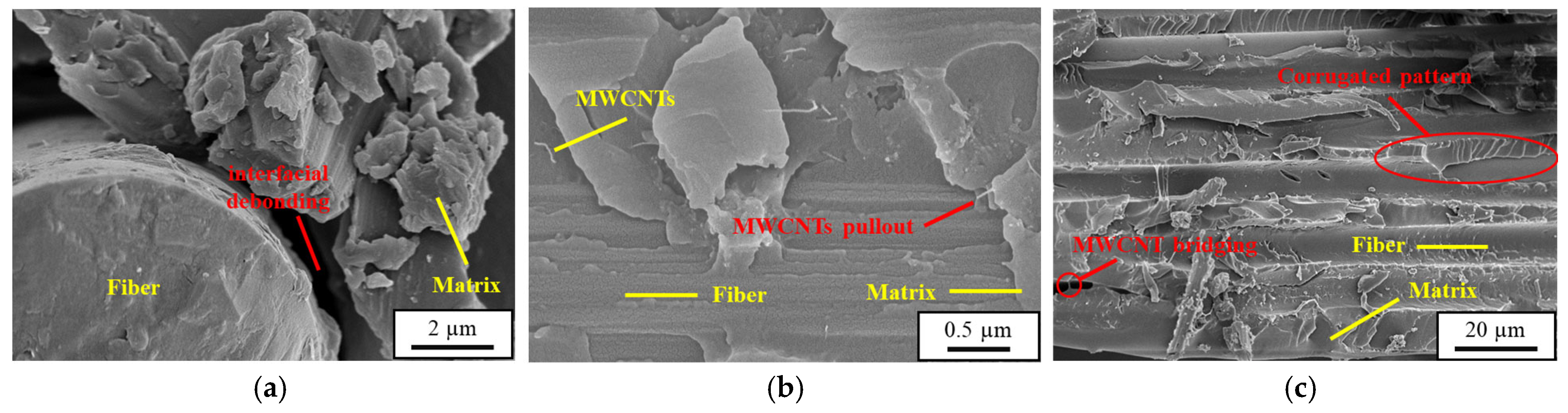
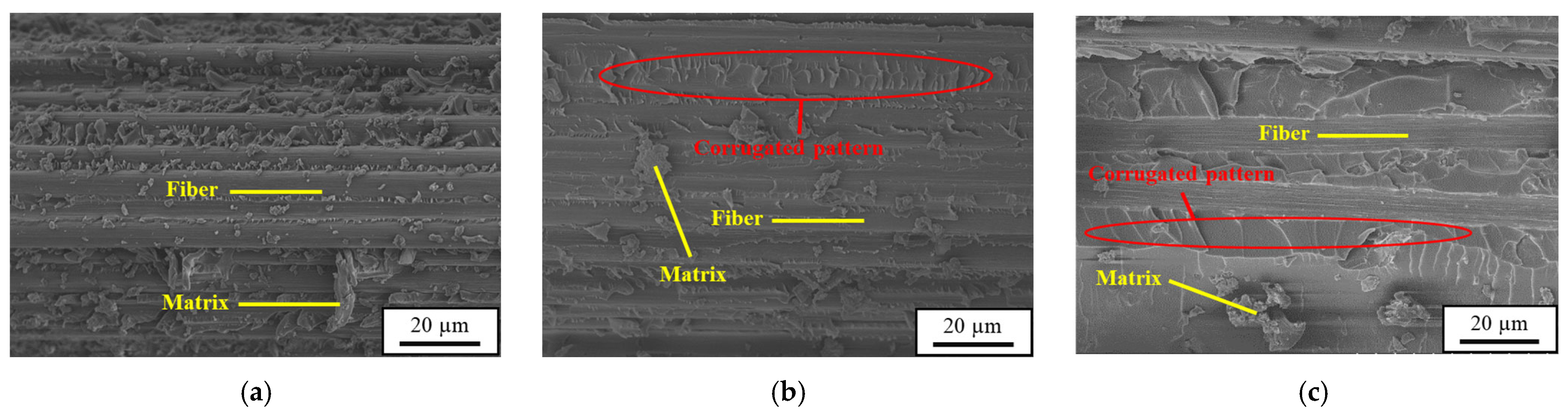
| Nanoparticle Type | Nanoparticle Concentration (wt.%) | Maximum Impact Force (N) | Absorbed Energy (J) | Damage Area (mm2) | Dent Depth (N) | Tensile Strength After Impact σTAI (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat epoxy | 0 | 1486.33 ± 57.63 | 11.77 ± 0.18 | 177.00 ± 43.82 | 1.04 ± 0.089 | 214.55 ± 0.54 |
| MWCNTs | 0.1 | 1570.66 ± 85.76 | 11.80 ± 0.28 | 161.33 ± 1.62 | 0.72 ± 0.091 | 225.31 ± 1.94 |
| 0.3 | 1710.00 ± 83.14 | 11.70 ± 0.03 | 130.00 ± 16.77 | 0.69 ± 0.046 | 242.32 ± 1.40 | |
| 0.5 | 1874.66 ± 86.26 | 11.55 ± 0.24 | 129.00 ± 8.83 | 0.68 ± 0.057 | 259.18 ± 3.79 | |
| GNPs | 0.1 | 1675.00 ± 53.88 | 11.68 ± 0.06 | 163.00 ± 12.24 | 0.84 ± 0.081 | 220.44 ± 0.25 |
| 0.3 | 1717.33 ± 99.60 | 11.64 ± 0.03 | 142.33 ± 16.99 | 0.83 ± 0.012 | 228.00 ± 1.48 | |
| 0.5 | 1721.66 ± 119.33 | 12.20 ± 0.21 | 120.67 ± 7.48 | 0.81 ± 0.030 | 231.65 ± 7.95 |
| Nanoparticle Type | Nanoparticle Concentration (wt.%) | Load Level (%) | Fatigue Life Nf (Cycles) | Fatigue Life Average and Standard Deviation (Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat epoxy | 0 | 80 | >90,000, >90,000, >90,000 | - |
| 90 | 14,692, 15,198, 12,153 | 14,014 ± 1322 | ||
| MWCNTs | 0.1 | 80 | >90,000, >90,000, >90,000 | - |
| 90 | 34,698, 29,572, 27,809 | 30,693 ± 2921 | ||
| 0.3 | 80 | >90,000, >90,000, >90,000 | - | |
| 90 | 32,485, 30,127, 38,464 | 33,692 ± 3508 | ||
| 0.5 | 80 | >90,000, >90,000, >90,000 | - | |
| 90 | 32,203, 37,541, 36,566 | 35,436 ± 2320 | ||
| GNPs | 0.1 | 80 | >90,000, >90,000, >90,000 | - |
| 90 | 14,305, 24,648, 18,055 | 19,002 ± 4275 | ||
| 0.3 | 80 | >90,000, >90,000, >90,000 | - | |
| 90 | 25,945, 19,986, 21,089 | 22,340 ± 2588 | ||
| 0.5 | 80 | >90,000, >90,000, >90,000 | - | |
| 90 | 39,137, 41,199, 39,545 | 39,960 ± 891 |
| Nanoparticle Type | Nanoparticle Concentration (wt.%) | Damage Area Growth Rate, dA/dN (10−3 mm2/Cycle) | Coefficient of Determination R-Squared | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80% Load Level | 90% Load Level | 80% Load Level | 90% Load Level | ||
| Neat epoxy | 0 | 2.22 | 8.65 | 0.98 | 0.92 |
| MWCNTs | 0.1 0.3 0.5 | 2.01 1.87 1.69 | 6.12 5.68 4.54 | 0.86 0.83 0.93 | 0.92 0.92 0.89 |
| GNPs | 0.1 0.3 0.5 | 2.07 1.65 1.80 | 5.40 5.10 5.62 | 0.94 0.86 0.99 | 0.96 0.84 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jen, Y.-M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Yu, T.-H. Improving the Impact Resistance and Post-Impact Tensile Fatigue Damage Tolerance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites by Embedding the Carbon Nanoparticles in Matrix. Polymers 2024, 16, 3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243589
Jen Y-M, Chen Y-J, Yu T-H. Improving the Impact Resistance and Post-Impact Tensile Fatigue Damage Tolerance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites by Embedding the Carbon Nanoparticles in Matrix. Polymers. 2024; 16(24):3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243589
Chicago/Turabian StyleJen, Yi-Ming, Yu-Jen Chen, and Tzung-Han Yu. 2024. "Improving the Impact Resistance and Post-Impact Tensile Fatigue Damage Tolerance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites by Embedding the Carbon Nanoparticles in Matrix" Polymers 16, no. 24: 3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243589
APA StyleJen, Y.-M., Chen, Y.-J., & Yu, T.-H. (2024). Improving the Impact Resistance and Post-Impact Tensile Fatigue Damage Tolerance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites by Embedding the Carbon Nanoparticles in Matrix. Polymers, 16(24), 3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243589







