Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Fabrication of P-CPCS
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
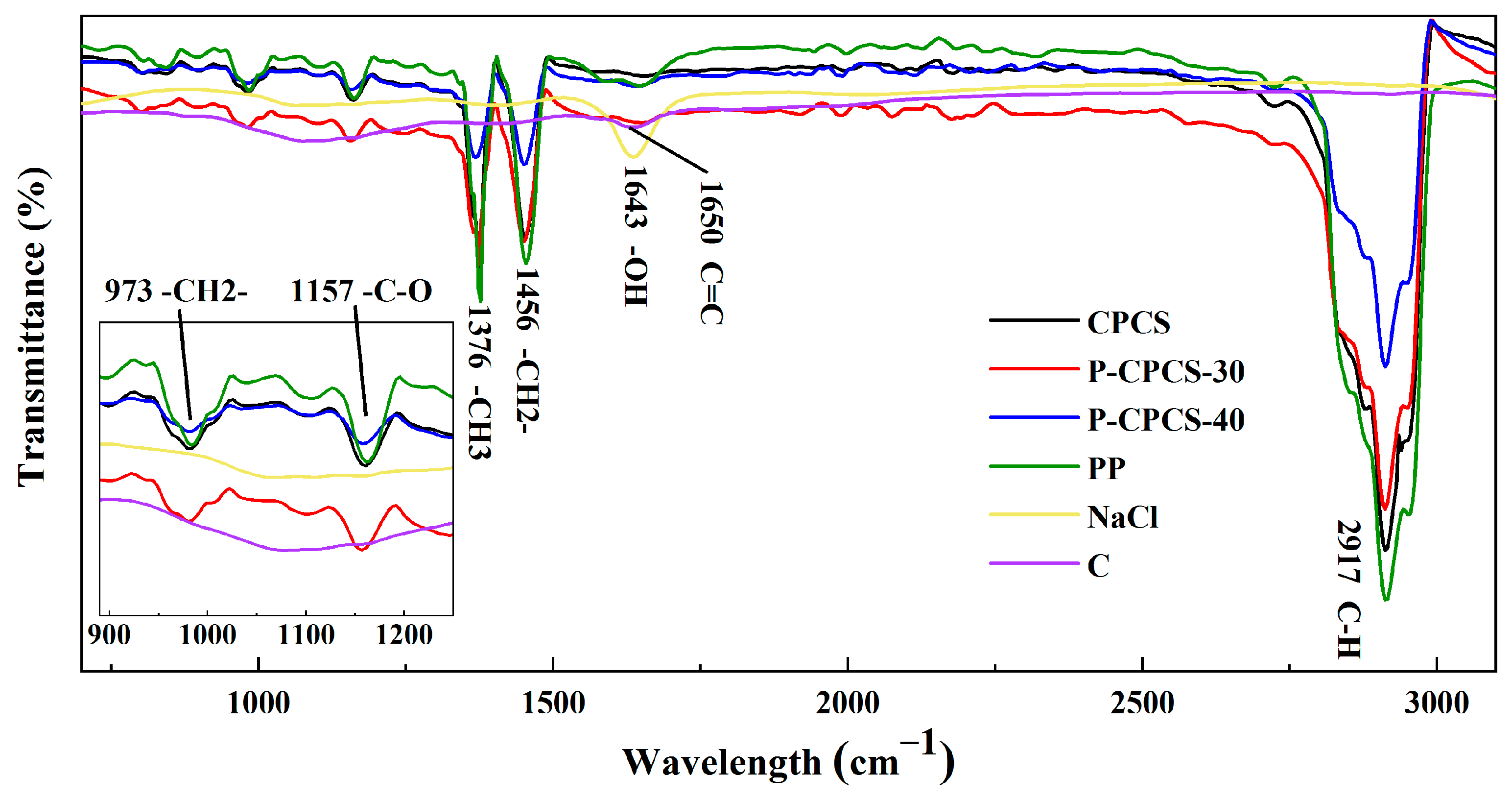
3.1. Formability and Characterization of P-CPCS
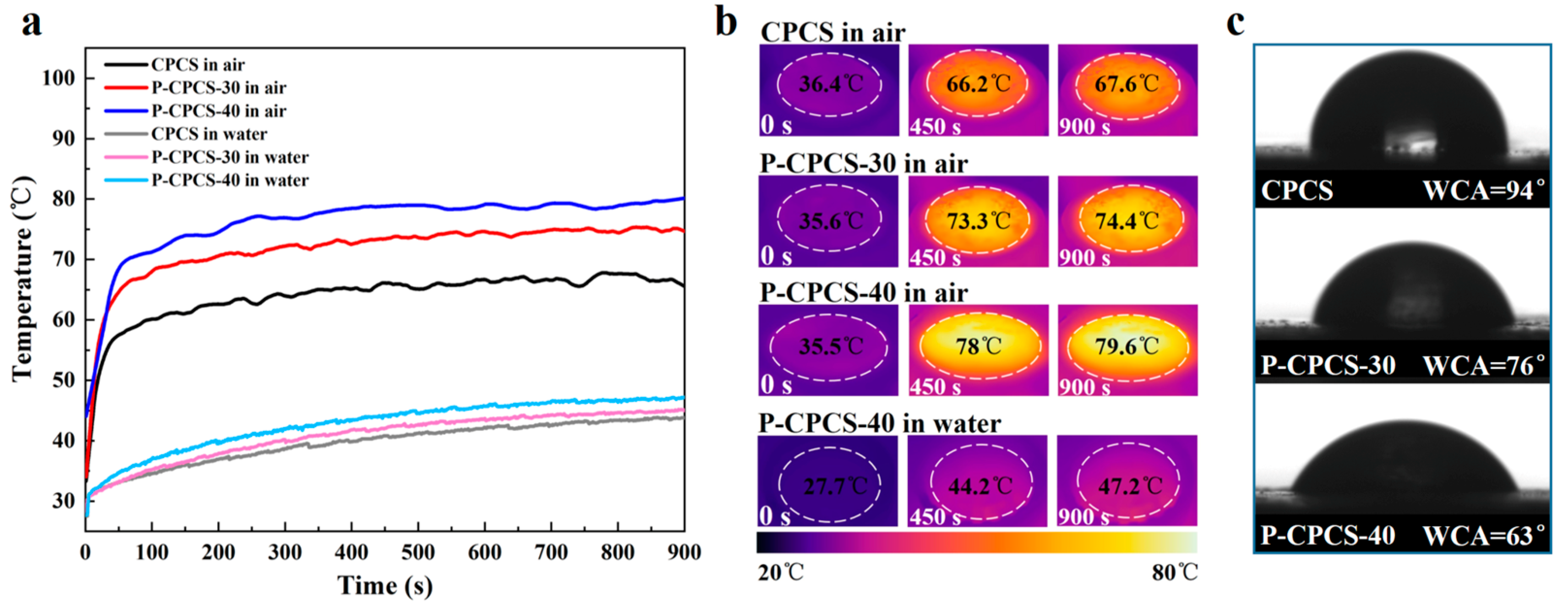
3.2. Photothermal Conversion by P-CPCS
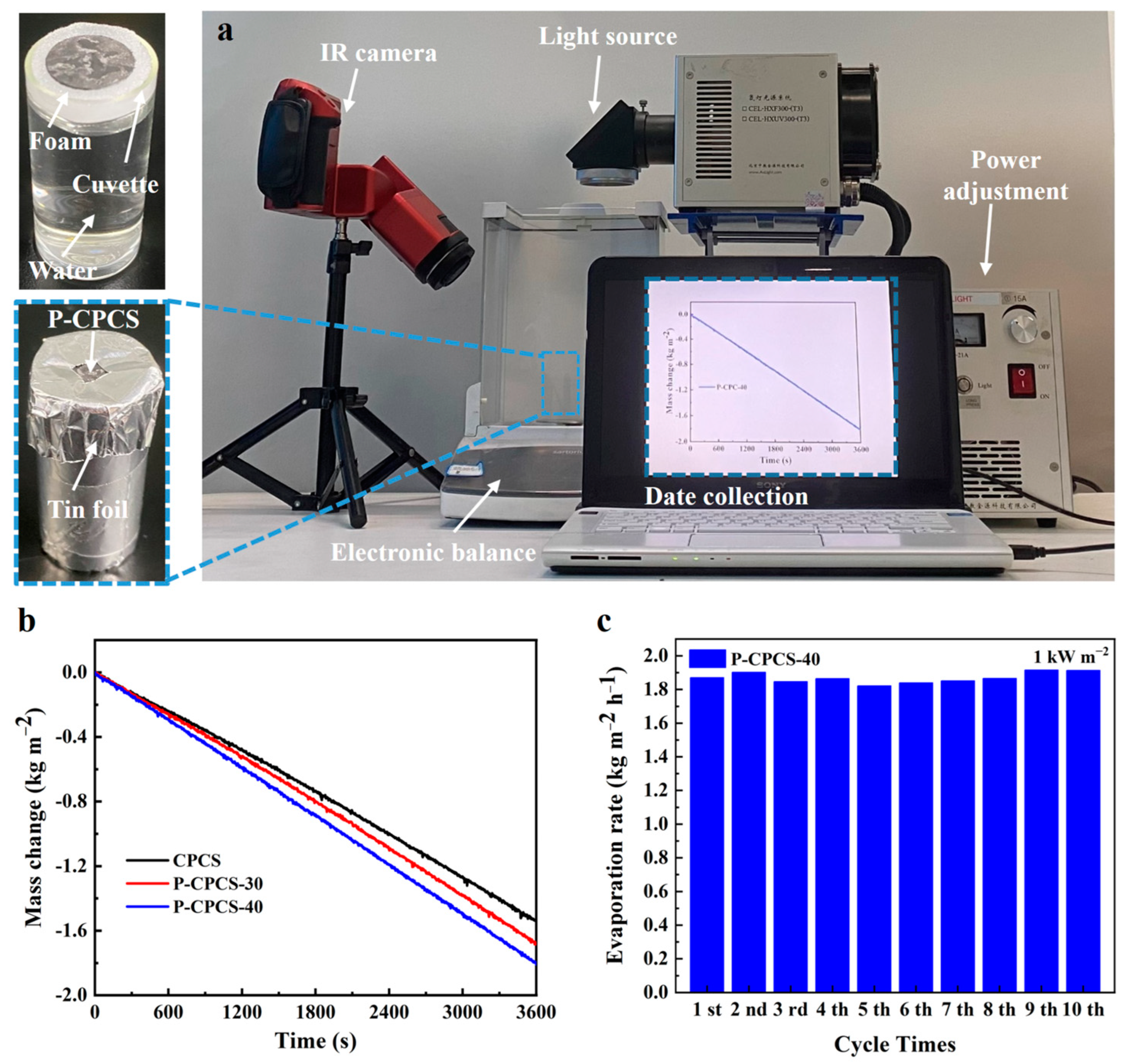
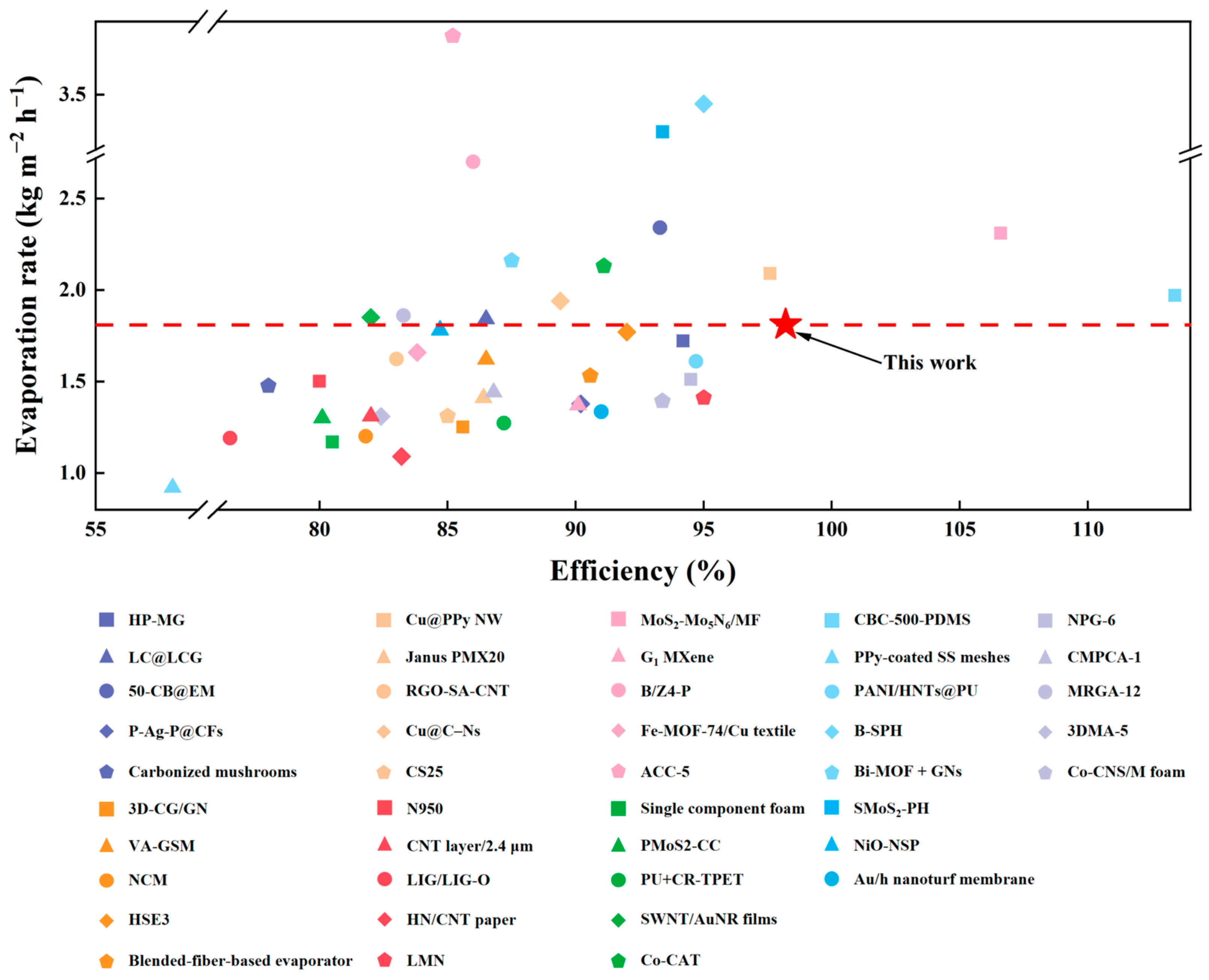
3.3. Evaporation Performance of P-CPCS
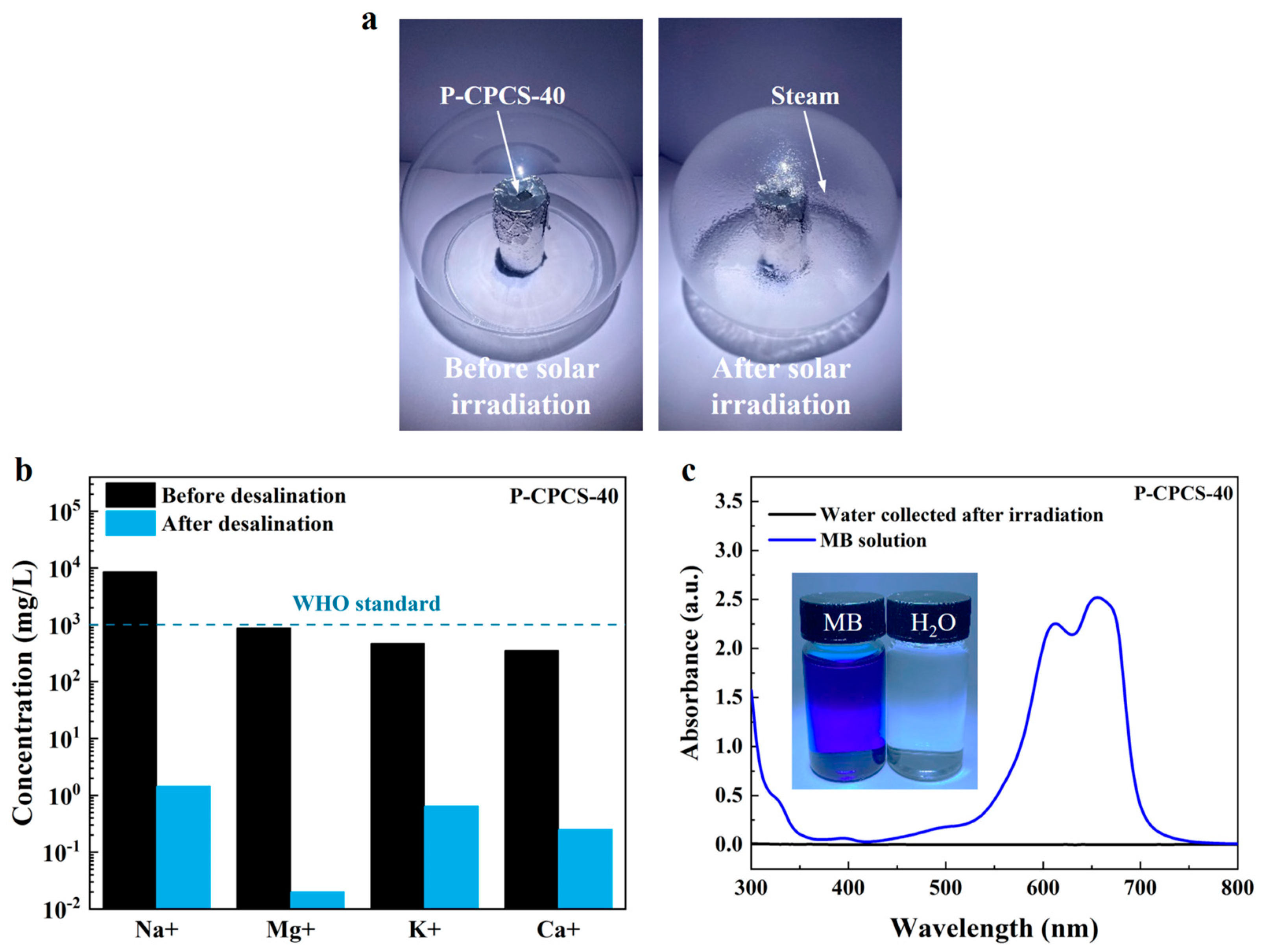
3.4. Desalination and Sewage Treatment
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The P-CPCS samples have sufficient strength when prepared with NaCl volume ratios as high as 40%. P-CPCS has a well-distributed porous structure with internal and external connected water paths. The CPCS, P-CPCS-30, and P-CPCS-40 mainly show differences in porosity within the pore size range of 10 nm to 10 μm. Differences in light reflectance properties are primarily attributed to this difference in porosity. In the visible-NIR wavelength region, P-CPCS-40 has a low reflectance of nearly 10%.
- (2)
- P-CPCS has an enhanced porous structure, leading to significantly better photothermal properties compared to CPCS. The P-CPCS-40 sample rapidly reaches a temperature of 128 °C at a heating rate of 12.4 °C/s when irradiated at 1.2 W/cm2 with an 808 nm laser.
- (3)
- P-CPCS-40 achieves an evaporation rate as high as 1.81 kg m−2 h−1 and evaporation efficiency of 98.2% under 1 sun irradiation. Compared to previously reported absorbers, P-CPCS-40 ranks among the top in terms of evaporation efficiency.
- (4)
- Desalination and sewage treatment experiments were performed, confirming the potential of P-CPCS for practical applications. We believe that the application of P-CPCS is not only limited to these fields. Due to its promising performance, P-CPCS could potentially be applied in fields such as rehabilitative physiotherapy, photocatalysis, and photothermal imaging.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, M.; You, S.; Xia, J.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Li, X.; Li, B. An optimized Monte Carlo ray tracing optical simulation model and its applications to line-focus concentrating solar collectors. Appl. Energy 2018, 225, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, H.; Wald, S.; Semiat, R. Challenges and solutions for global water scarcity. Membranes 2023, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, P.; Li, X.; He, Y.; An, L.; Qu, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Self-cleaning solar water evaporation device based on polyaniline/TiO2/natural cellulose fibers for contaminant water. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, F. Full biomass-derived solar stills for robust and stable evaporation to collect clean water from various water-bearing media. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10672–10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhuo, S.; Zhang, C.; Aldrees, Y.; Aleid, S.; Wang, P. Multi-functional 3D honeycomb ceramic plate for clean water production by heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction and solar-driven water evaporation. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Brajpuriya, R.; Gupta, R. Solar steam generation using hybrid nanomaterials to address global environmental pollution and water shortage crisis. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 21, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Cai, Z. Efficient solar water vapor generation enabled by water-absorbing polypyrrole coated cotton fabric with enhanced heat localization. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 141, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, T.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Luo, W.; Song, J.; Hitz, E.; Jia, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B. 3D-printed, all-in-one evaporator for high-efficiency solar steam generation under 1 sun illumination. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhu, L.; Peh, C.K.; Ho, G.W. Solar absorber material and system designs for photothermal water vaporization towards clean water and energy production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 841–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Hsiung, C.E.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Fratalocchi, A. High-performance large-scale solar steam generation with nanolayers of reusable biomimetic nanoparticles. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2017, 1, 1600013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Duan, H.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Quan, X.; Tao, P.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.; Song, C. Enhancing localized evaporation through separated light absorbing centers and scattering centers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, M.S.; Choi, J.W.; La Grange, T.; Modestino, M.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Pu, Y.; Birkhold, S.; Hubbell, J.A.; Psaltis, D. Hollow mesoporous plasmonic nanoshells for enhanced solar vapor generation. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Gu, J.; Yang, L.; Pantelic, D.; Jelenkovic, B.; Zhang, D. 3D interconnected gyroid Au–CuS materials for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34837–34847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.; Seo, D.H.; McDonagh, A.M.; Shon, H.K.; Tijing, L. Semiconductor photothermal materials enabling efficient solar steam generation toward desalination and wastewater treatment. Desalination 2021, 500, 114853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Song, Y.; Deng, K.; Lin, S.; Bi, Y.; Scarpa, F.; Crouse, D. High solar desalination efficiency achieved with 3D Cu2ZnSnS4 nanosheet-assembled membranes. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2017, 1, 1700064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, S.L.; Vasquez, L.; Paul, U.C.; Campagnolo, L.; Athanassiou, A.; Fragouli, D. Solar-driven freshwater generation from seawater and atmospheric moisture enabled by a hydrophilic photothermal foam. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10307–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Anilkumar, P.; Cao, L.; Kong, C.Y.; Meziani, M.J.; Qian, H.; Veca, L.M.; Thorne, T.J.; Tackett, K.N.; Edwards, T. Graphene oxides dispersing and hosting graphene sheets for unique nanocomposite materials. Acs Nano 2011, 5, 3052–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhvalov, D.W.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Son, Y.W. Origin of anomalous water permeation through graphene oxide membrane. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3930–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Lv, L.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L. Vertically aligned graphene sheets membrane for highly efficient solar thermal generation of clean water. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5087–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Tao, P.; Song, C.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.; Deng, T. Efficient solar-thermal energy harvest driven by interfacial plasmonic heating-assisted evaporation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23412–23418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Liu, Y.; Quan, X.; Tao, P.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.; Song, C.; Deng, T. The impact of surface chemistry on the performance of localized solar-driven evaporation system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Lee, C.S.; Zhang, X.H. From materials to devices: Rationally designing solar steam system for advanced applications. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2200835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Wei, N.; Weng, Y.; Dong, S.; Qi, D.; Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, T. High-performance photothermal conversion of narrow-bandgap Ti2O3 nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Albolkany, M.K.; Wu, N.; Wang, M.; Yang, L. Efficient solar evaporation by [Ni (phen)3][V14O34Cl] Cl hybrid semiconductor confined in mesoporous glass. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 2945–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ai, L.; Chen, M.; Jiang, J. Broadband nickel sulfide/nickel foam-based solar evaporator for highly efficient water purification and electricity generation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10833–10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Fang, H.; Wang, D.; Sun, J. Spray-coated commercial PtFe membrane from mos2/laf3/pdms ink as solar absorber for efficient solar steam generation. Solar RRL 2020, 4, 2000126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Hitz, E.; Jia, C.; Gong, A.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.Y. Highly flexible and efficient solar steam generation device. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Tanabe, Y.; Han, J.; Fujita, T.; Tanigaki, K.; Chen, M. Multifunctional porous graphene for high-efficiency steam generation by heat localization. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4302–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Yang, P.; Li, J.; Ding, T.; Duan, J.; Qi, B.; Zhou, J. Robust and low-cost flame-treated wood for high-performance solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15052–15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Qiao, W.; Long, D.; Ling, L. Macroscopic and mechanically robust hollow carbon spheres with superior oil adsorption and light-to-heat evaporation properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5368–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, L.; Xie, H. 3D graphene nanofluids with high photothermal conversion and thermal transportation properties. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2020, 4, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, F.K.; Tung, T.T.; Dao, V.D.; Huyen, N.K.; Nine, M.J.; Hassan, K.; Ma, J.; Losic, D. Graphene-based multifunctional surface and structure gradients engineered by atmospheric plasma. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 27, 101486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, B.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Wang, P. Hydrophobic light-to-heat conversion membranes with self-healing ability for interfacial solar heating. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4889–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, M.; Tian, K.; Fu, Q.; Deng, H. Dendritic structure-inspired coating strategy for stable and efficient solar evaporation of salinity brine. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3882–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, O.R.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Adly, M.S.; Samra, S.E.; Ouf, A.M.A.; El-Hakam, S.A.; Ahmed, A.I. Solar-driven seawater desalination via plasmonic hybrid MOF/polymer and its antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 18525–18537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Highly Salt-Resistant interfacial solar evaporators based on Melamine@ Silicone nanoparticles for stable Long-Term desalination and water harvesting. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2023, 646, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Jia, F.; Li, Y.; Song, S. Facile preparation of three-dimensional MoS2 aerogels for highly efficient solar desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 32673–32680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerty, C.; Zhang, L.; Sedlak, D.L.; Nelson, K.L.; Mi, B. Synthetic graphene oxide leaf for solar desalination with zero liquid discharge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11701–11709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Qu, L. High rate production of clean water based on the combined photo-electro-thermal effect of graphene architecture. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Peng, H.; Wu, W.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation of the viscoelastic heating mechanism in ultrasonic plasticizing of amorphous polymers for micro injection molding. Polymers 2016, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janer, M.; Planta, X.; Riera, D. Ultrasonic moulding: Current state of the technology. Ultrasonics 2020, 102, 106038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Peng, H.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, B. Characteristics and mechanisms of polymer interfacial friction heating in ultrasonic plasticization for micro injection molding. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Lin, J.; Zou, H. Preparation and properties of eutectic salt-ceramic composite phase change material. J. Funct. Mater. 2021, 52, 6019–6025, 6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimassi, S.N.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Daly Yahia, M.N.; Ahmad, M.I.; Sayadi, S.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Insights into the Degradation Mechanism of PET and PP under Marine Conditions Using FTIR. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 447, 130796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ţucureanu, V.; Matei, A.; Avram, A.M. FTIR Spectroscopy for Carbon Family Study. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.J.; Huang, H.X.; Xie, H. Rapid fabrication of antireflective pyramid structure on polystyrene film used as protective layer of solar cell. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2017, 171, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Robson, M.E.; Phelps, J.L.; Tan, J.S.; Shao, B.; Owens, G.; Xu, H. A flexible photothermal cotton-CuS nanocage-agarose aerogel towards portable solar steam generation. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, M.N.A.S.; Saleque, A.M.; Ahmed, S.; Cheng, P.K.; Qiao, J.; Alam, T.I.; Tsang, Y.H. Waste egg tray and toner-derived highly efficient 3D solar evaporator for freshwater generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7936–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Wu, S.; Xu, B.; Ma, J.; Du, J.; Lei, J. Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation. Polymers 2024, 16, 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192813
Xu S, Wu S, Xu B, Ma J, Du J, Lei J. Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation. Polymers. 2024; 16(19):2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192813
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shuqing, Shiyun Wu, Bin Xu, Jiang Ma, Jianjun Du, and Jianguo Lei. 2024. "Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation" Polymers 16, no. 19: 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192813
APA StyleXu, S., Wu, S., Xu, B., Ma, J., Du, J., & Lei, J. (2024). Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation. Polymers, 16(19), 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192813








