Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Rapid Multi-Channel Detection of Tetracycline Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Coated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Synthesis of GQDs@PAD
2.4. Synthesis of MIPs@GQDs@PAD
2.5. Fluorescence Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Fabrication and Sensing Mechanism of MIPs@GQDs@PAD
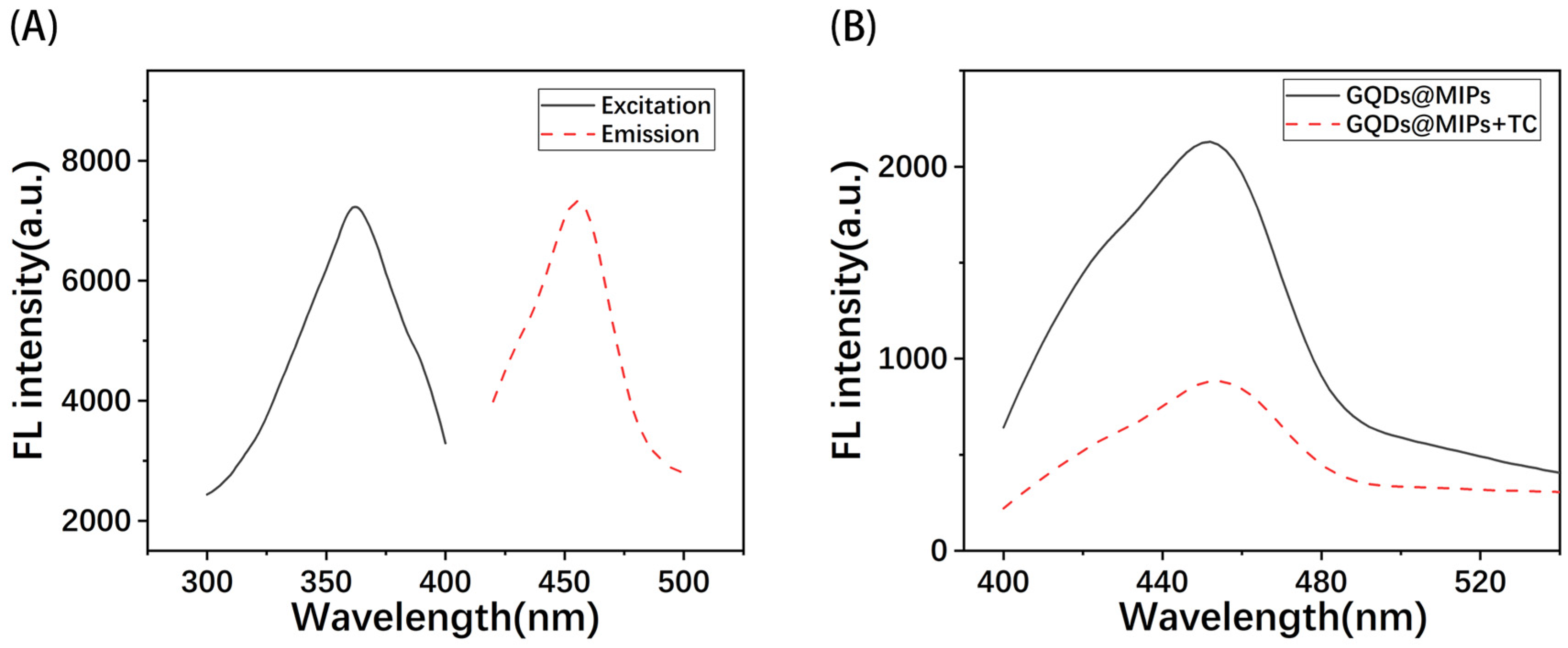
3.2. Optical Characterization
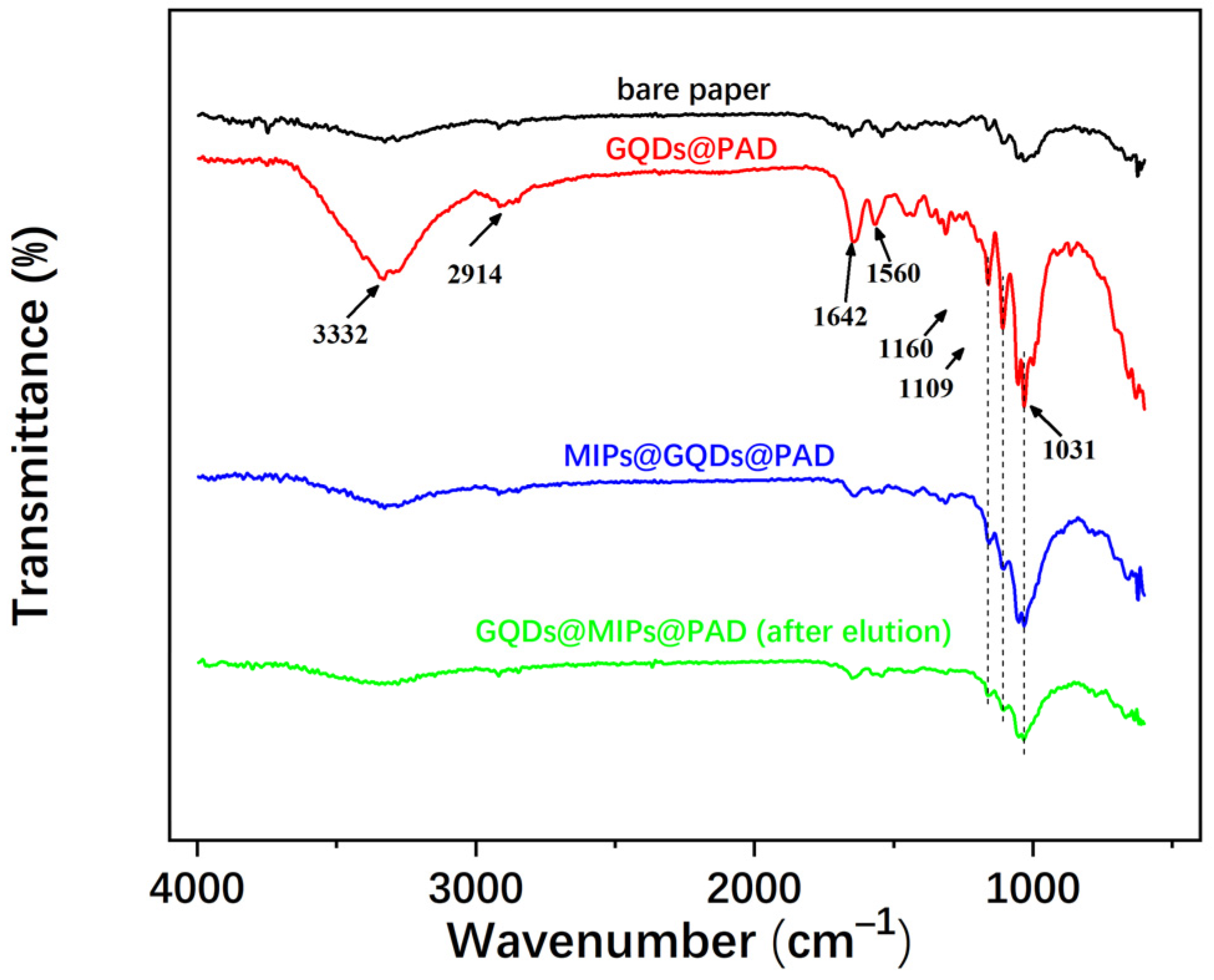
3.3. SEM and FT-IR Characterization
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.4.1. Effect of Grafting Time and Amount of GQDs
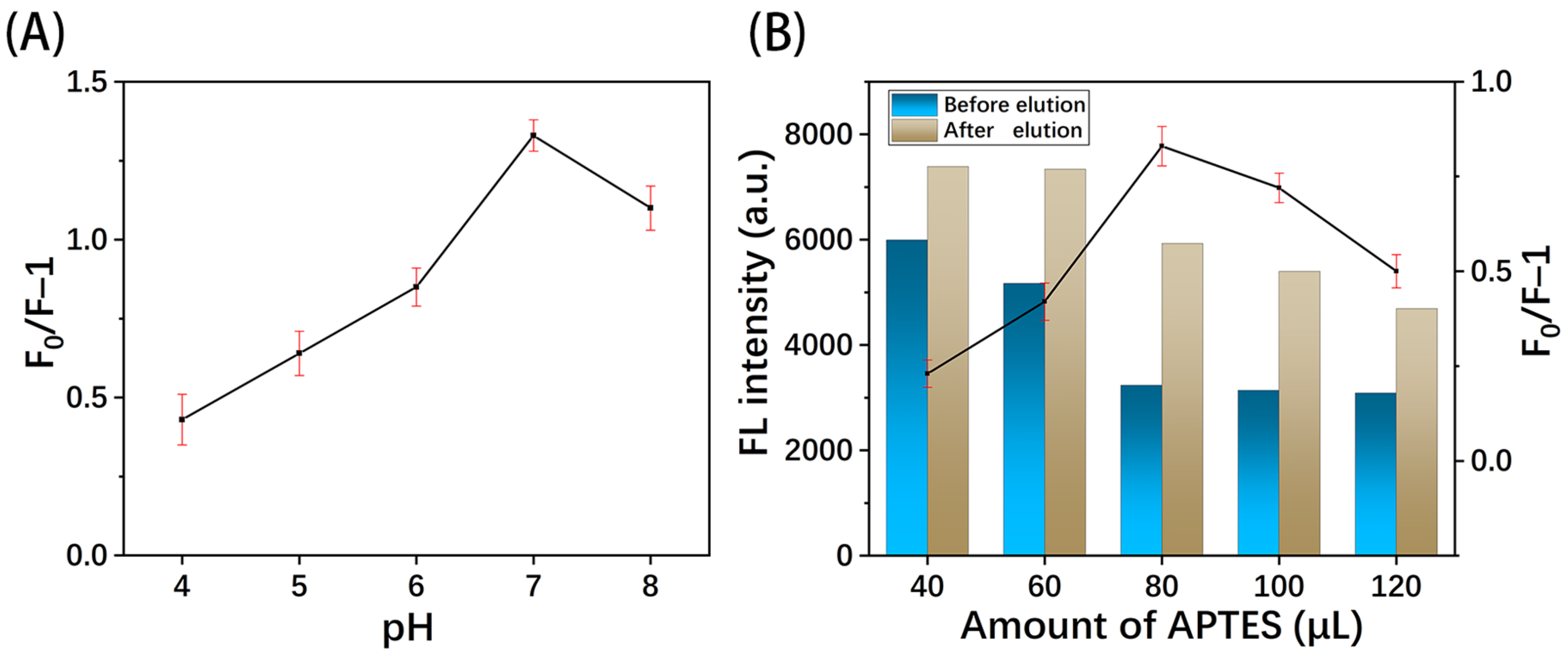
3.4.2. Effect of pH
3.4.3. Effect of Amount of Functional Monomer
3.4.4. Effect of Eluent and Elution Times
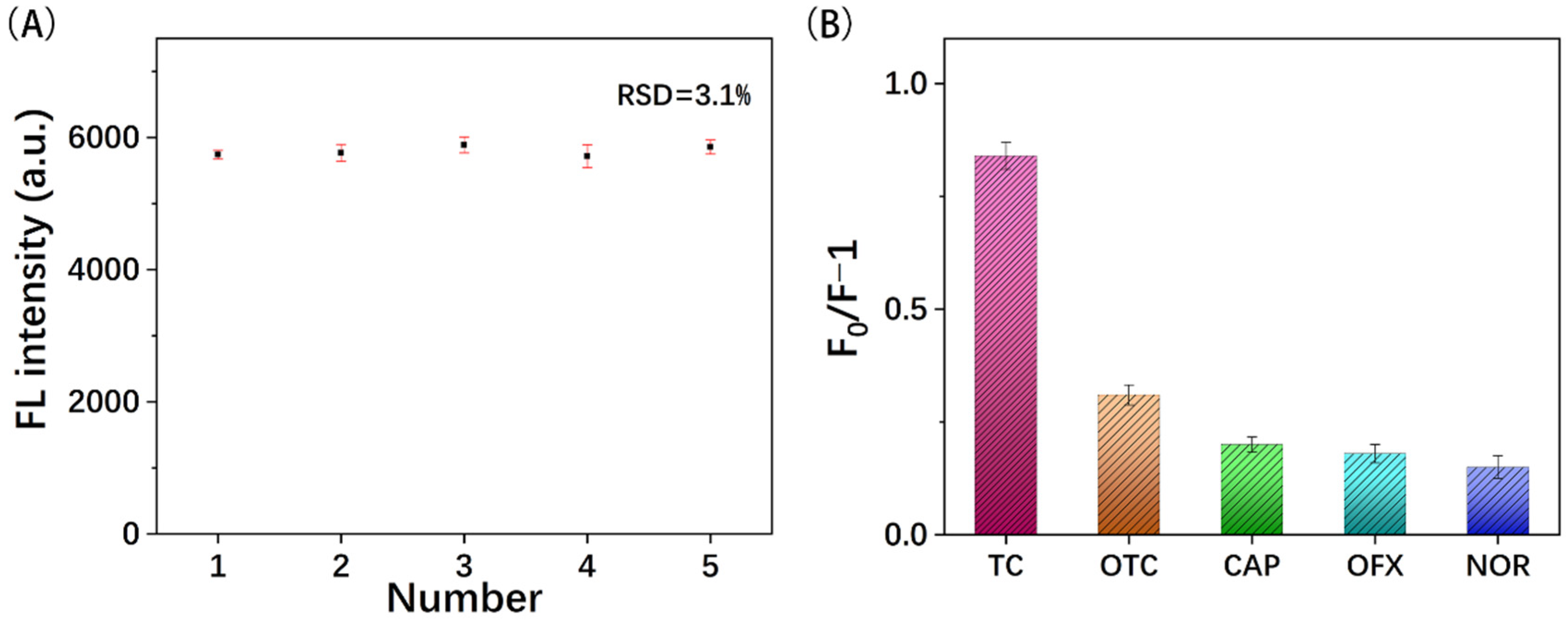
3.5. Analytical Performance of MIPs@GQDs@PAD
3.6. Application of MIPs@GQDs@PAD for TC Detection in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, T.; Halder, A.; Sun, Y. Fluorescent Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coated on Graphene Quantum Dots for Fast Detection of Antibiotics. Biosensors 2018, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adsetts, J.R.; Hoesterey, S.; Gao, C.; Love, D.A.; Ding, Z. Electrochemiluminescence and Photoluminescence of Carbon Quantum Dots Controlled by Aggregation-Induced Emission, Aggregation-Caused Quenching, and Interfacial Reactions. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14432–14442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majoul, N.; Aouida, S.; Bessais, B. Progress of porous silicon APTES-functionalization by FTIR investigations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 331, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-Castro, F.d.J.; Aguilar-García, D.G.; Gómez-Balderas, R.; Galván-García, E.A.; Miranda-Soto, V.; Tirado-Guízar, A.; Ochoa Terán, A.; Pina Luis, G.E. Computational and spectroscopic study of the prepolymerization complex formation in the tetracycline-based imprinted polymer synthesis. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1289, 135869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Mei, X.; Peng, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. A paper-based microfluidic sensor array combining molecular imprinting technology and carbon quantum dots for the discrimination of nitrophenol isomers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Zheng, X.; Guo, Q. A fluorescence labelling and switchable nanosensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2022, 45, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.-R.; Hu, C.-W.; Chen, J.-L. Comparative syntheses of tetracycline-imprinted polymeric silicate and acrylate on CdTe quantum dots as fluorescent sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Fu, H.; Tan, L.; Wang, J. CdTe quantum dots coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer for fluorometric determination of norfloxacin in seawater. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadnejad, P.; Hosseini, S.M.M.; Sohrabi, B. The graphene quantum dots encased in the molecularly imprinted polymer as a new fluorescent nanosensor for the detection of biotin. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2024, 7, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Mei, X.; Peng, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. A rotating paper-based microfluidic sensor array combining Michael acceptors and carbon quantum dots for discrimination of biothiols. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yi, M.; Xin, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zou, Y. Reduced Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diodes Fabricated Using an Ultraviolet Light Emitting Diode Photolithography Technique. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 48976–48985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, S.; Lee, J.; Mehta, A.; Kumar, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Basu, S.; Rawat, M. Highly fluorescent carbon dots derived from Mangifera indica leaves for selective detection of metal ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z. Paper-Based Molecular-Imprinting Technology and Its Application. Biosensors 2022, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, H. Ratiometric fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor based on dual-emission quantum dots hybrid for determination of tetracycline. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5809–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, W. Preparation of molecularly imprinted fluorescence sensor based on carbon quantum dots via precipitation polymerization for fluorescence detection of tetracycline. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Sun, Y. A multifunctional molecularly imprinted polymer-based biosensor for direct detection of doxycycline in food samples. Talanta 2018, 182, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Lu, K.; Yan, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymers-captivity ZnO nanorods for sensitive and selective detecting environmental pollutant. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 228, 117785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Fluorescence Sensors | Linear Ranges (µmol/L) | Limit of Detections (µmol/L) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP–g/r-QD | 10–160 | 0.35 | [14] |
| MIPs-AA/CQDs | 1–60 | 0.17 | [15] |
| FeOx@SiO2-FMIPs | 0.2–6 | 0.117 | [16] |
| MIPs-ZnO NRs | 5–120 | 1.02 | [17] |
| MIPs@GQDs@PAD | 0–40 | 0.87 | This work |
| Sample | Add (μmol/L) | Found (μmol/L) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 0 | - | - | - |
| 5 | 5.47 | 109.4% | 5.3% | |
| 10 | 10.81 | 108.1% | 4.8% | |
| River water | 0 | - | - | - |
| 5 | 5.36 | 107.2% | 6.4% | |
| 10 | 10.33 | 103.3% | 4.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Wei, W.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhang, C.; Fu, F. Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Rapid Multi-Channel Detection of Tetracycline Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Coated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Polymers 2024, 16, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172540
Wang L, Hu J, Wei W, Song Y, Li Y, Gao G, Zhang C, Fu F. Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Rapid Multi-Channel Detection of Tetracycline Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Coated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Polymers. 2024; 16(17):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172540
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Linzhe, Jingfang Hu, Wensong Wei, Yu Song, Yansheng Li, Guowei Gao, Chunhui Zhang, and Fangting Fu. 2024. "Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Rapid Multi-Channel Detection of Tetracycline Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Coated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer" Polymers 16, no. 17: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172540
APA StyleWang, L., Hu, J., Wei, W., Song, Y., Li, Y., Gao, G., Zhang, C., & Fu, F. (2024). Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Rapid Multi-Channel Detection of Tetracycline Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Coated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Polymers, 16(17), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172540





