Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panels after Fatigue in Hygrothermal Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Specimen and Experimental Setup
2.1. Specimen
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.2.1. Hygrothermal Aging Test
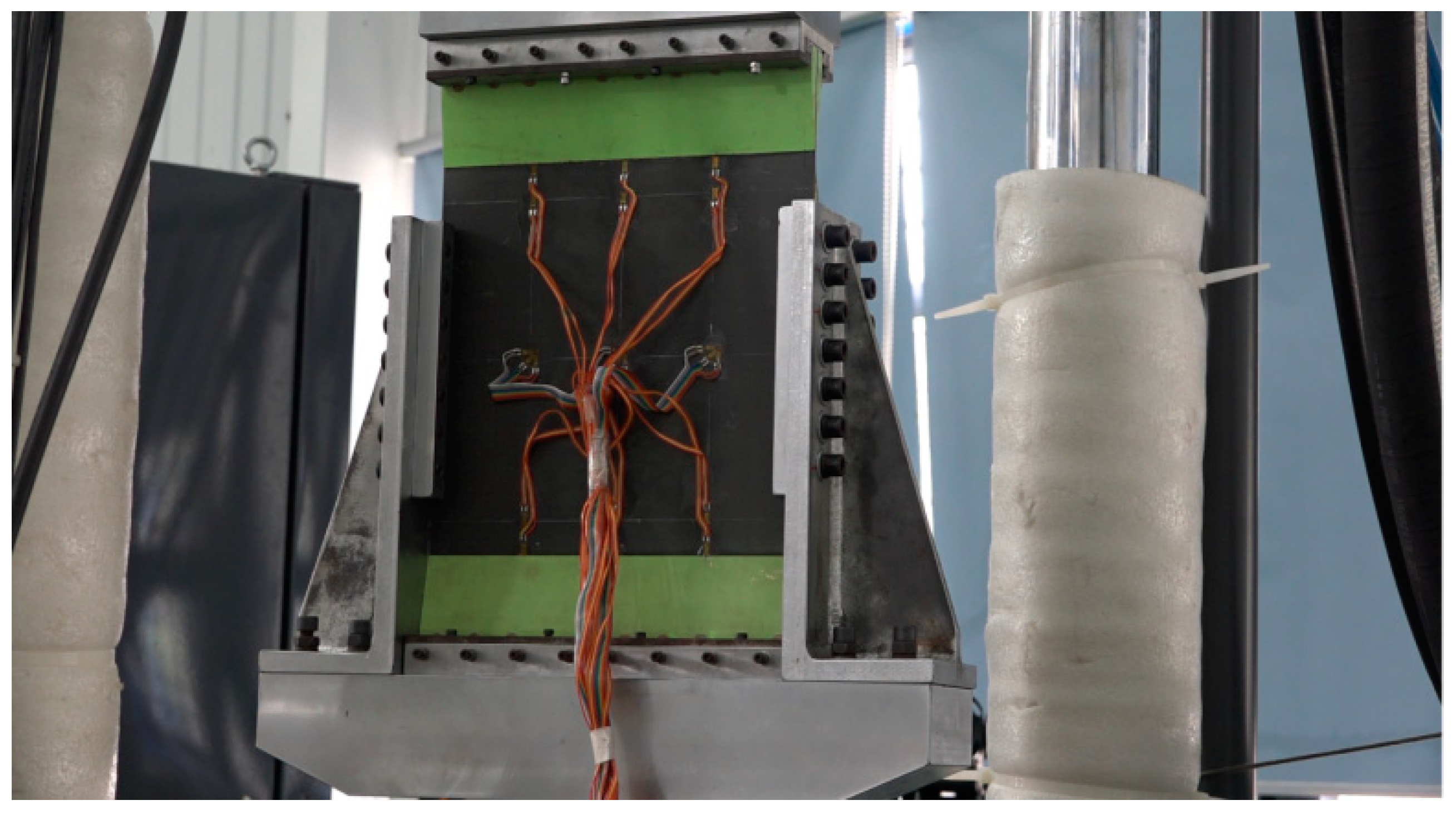
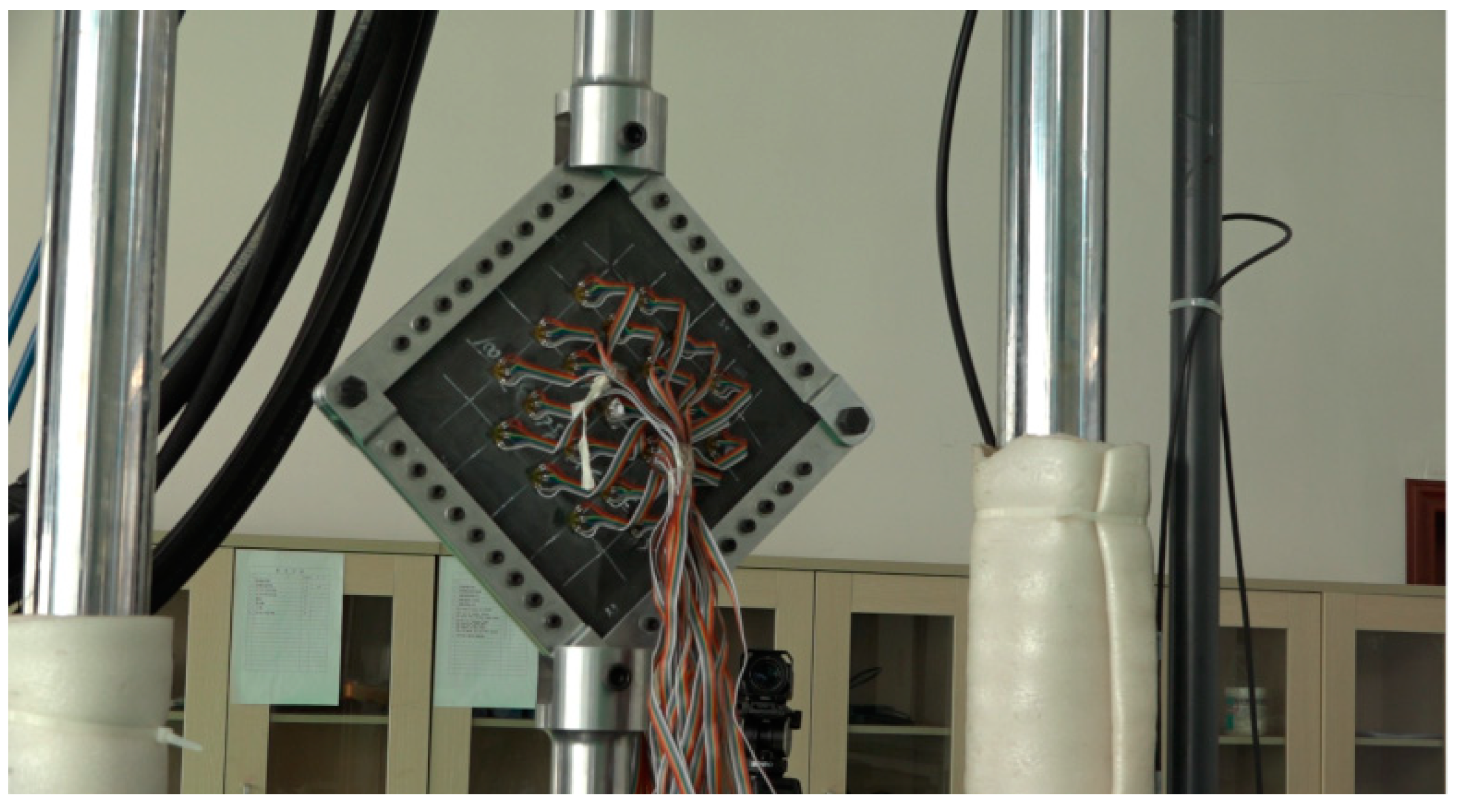
2.2.2. Compression Test
2.2.3. Shearing Test
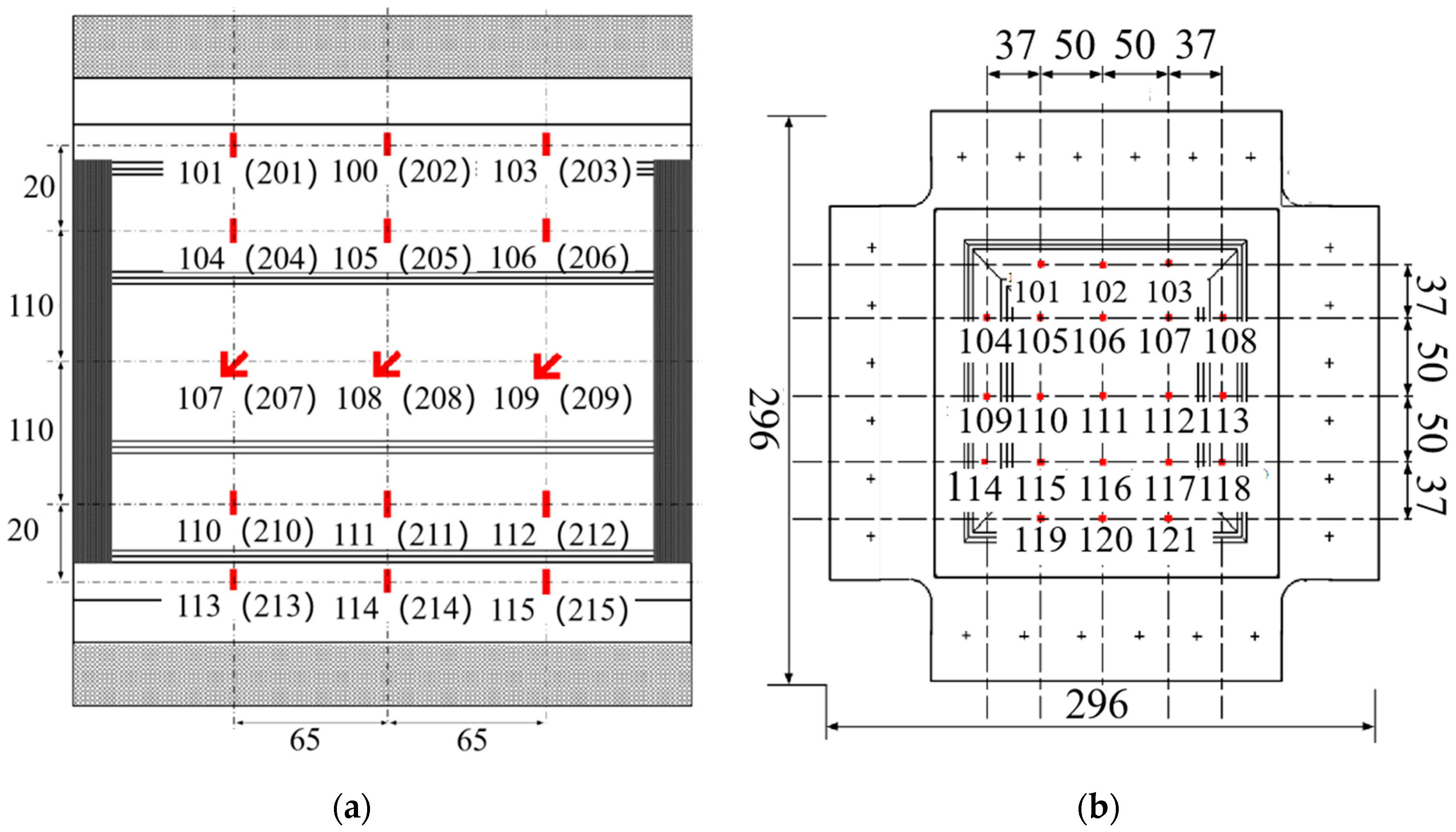
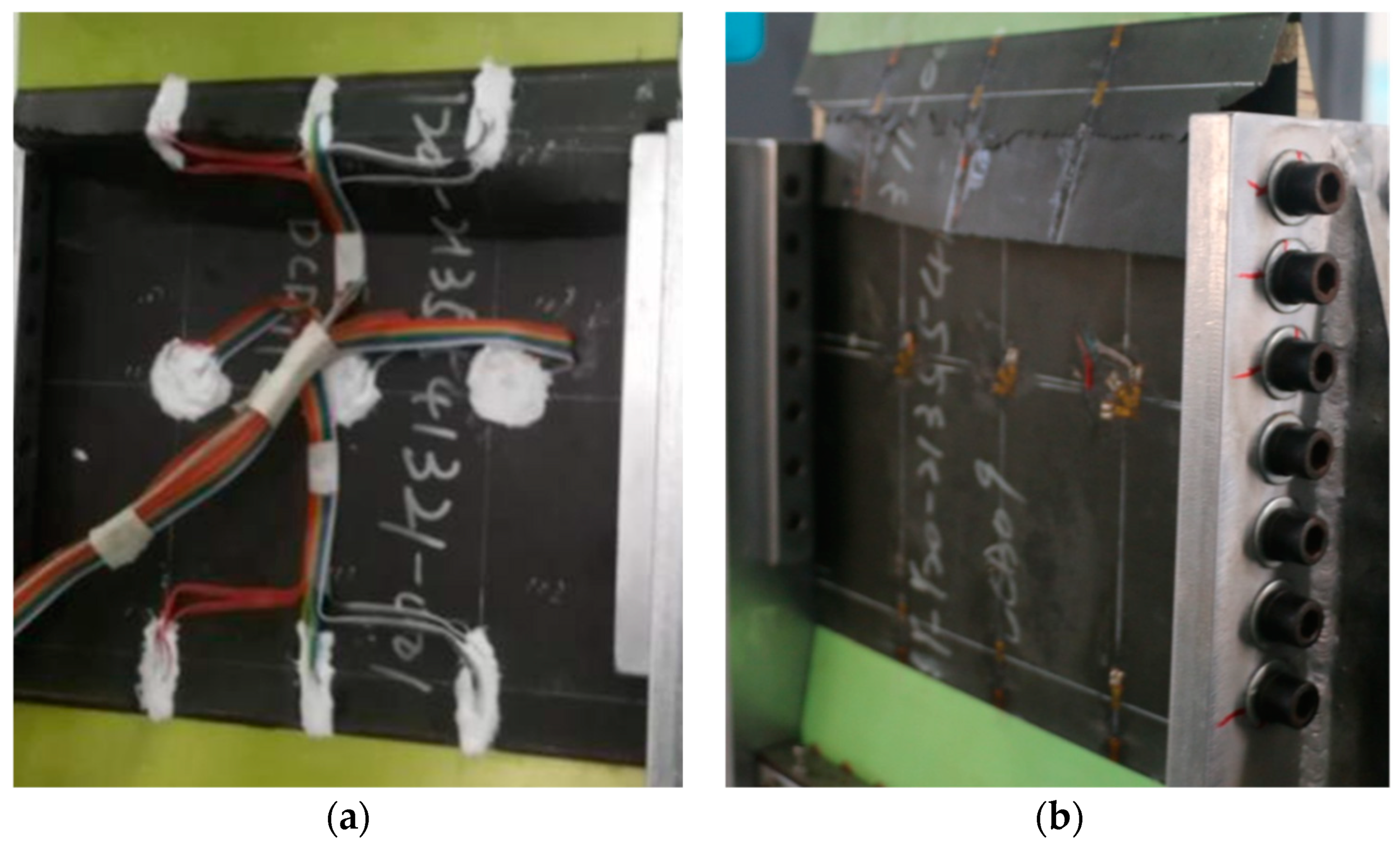
2.3. Measurement Programme
3. Experiment Results
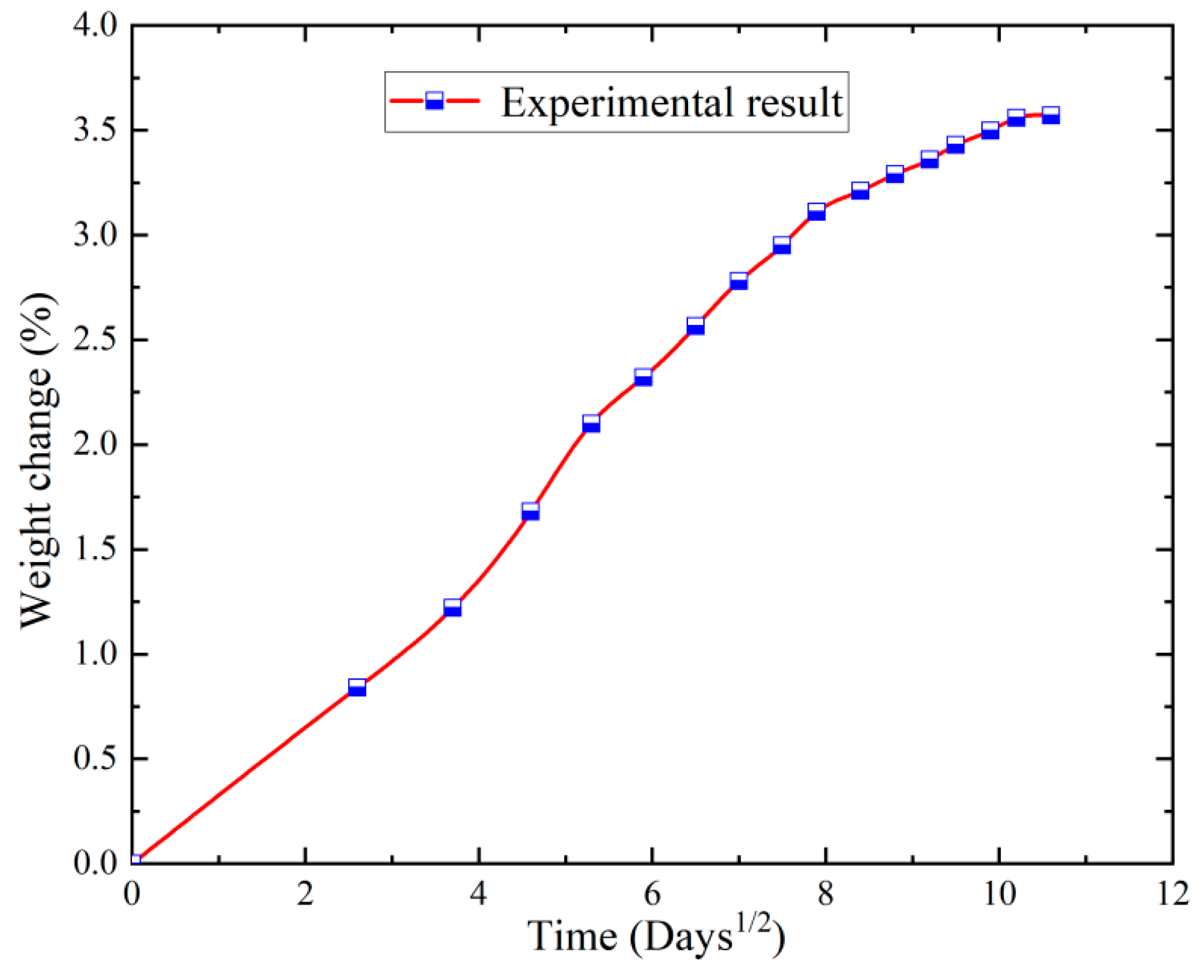
3.1. Moisture Absorption Characterization
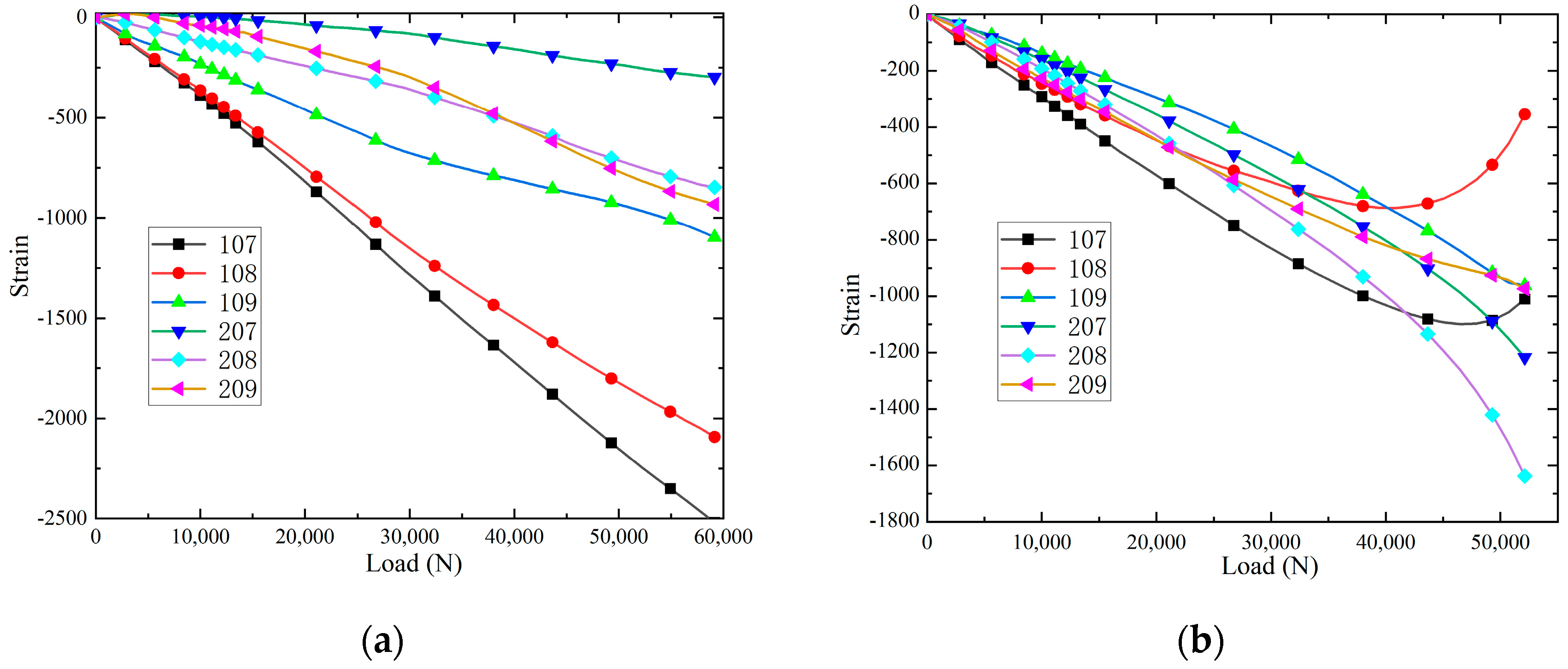
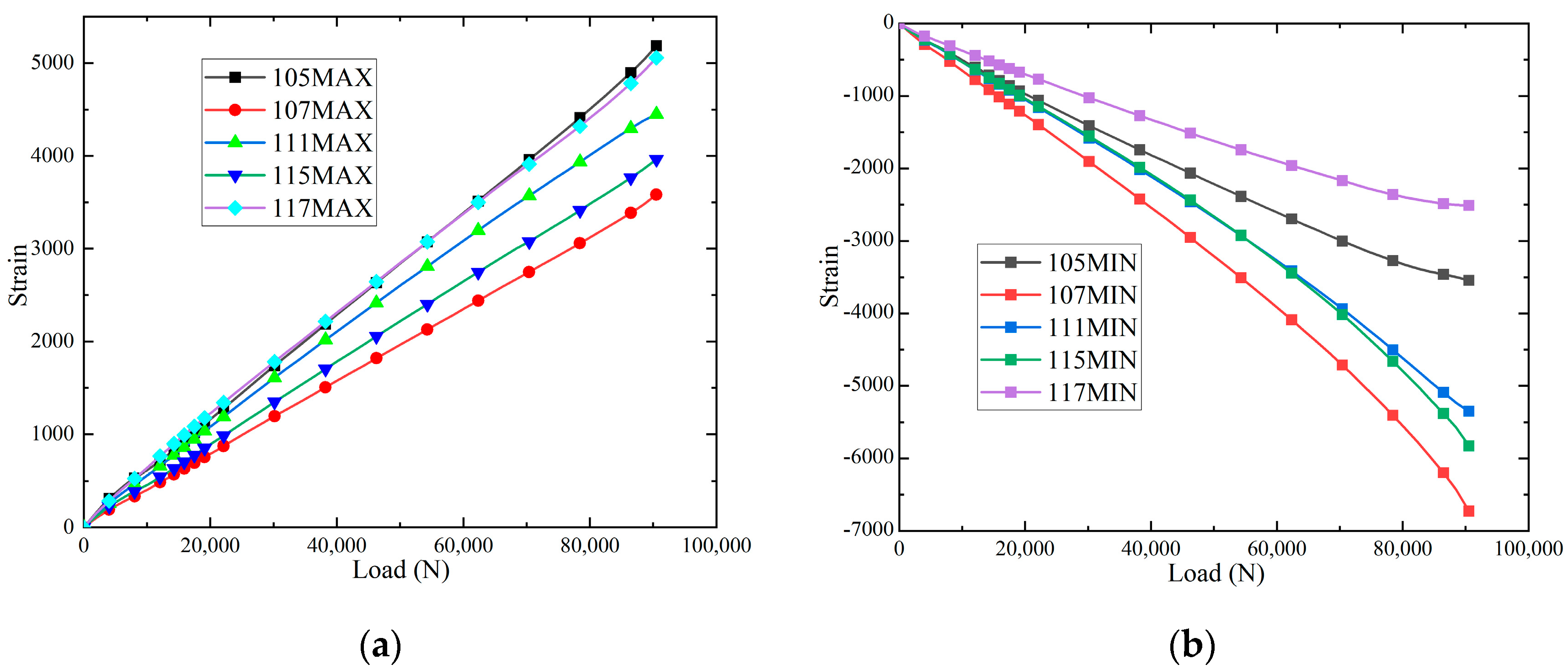
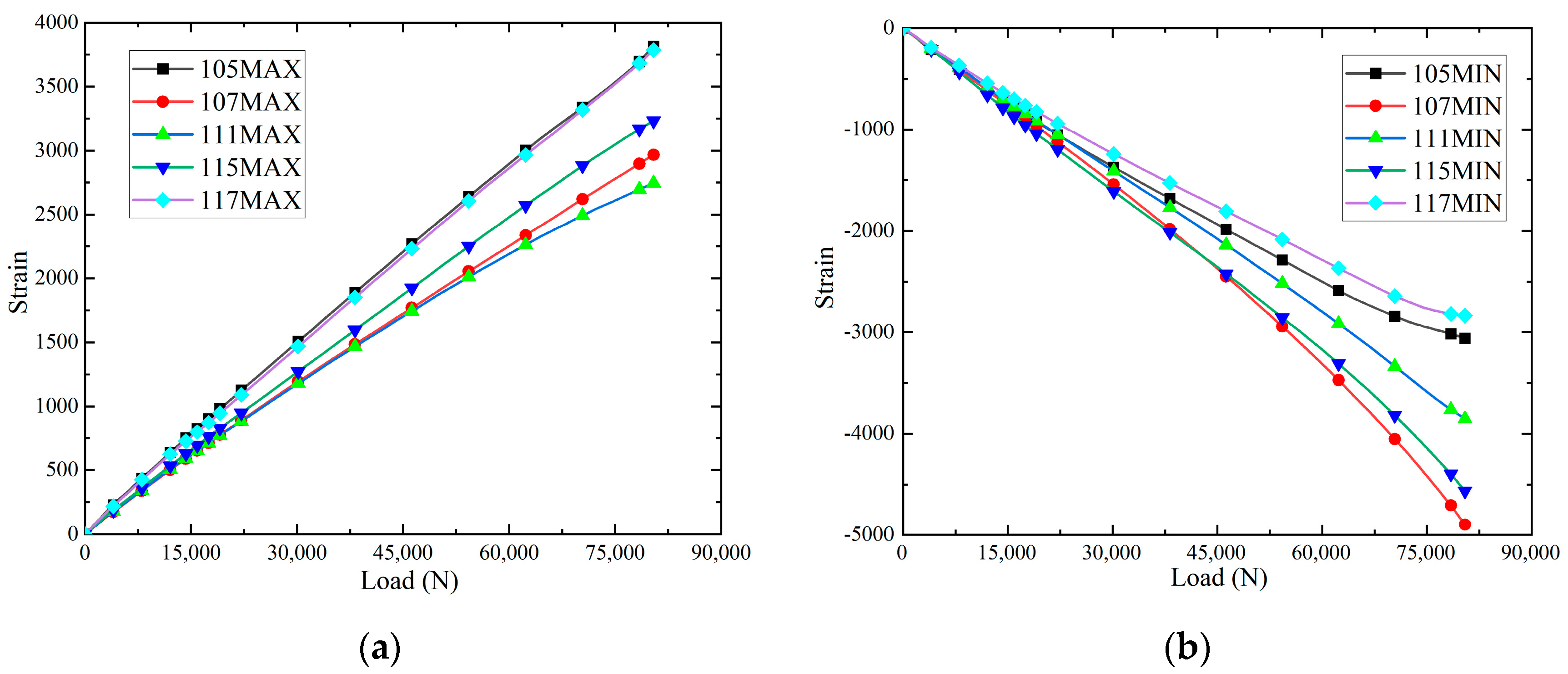
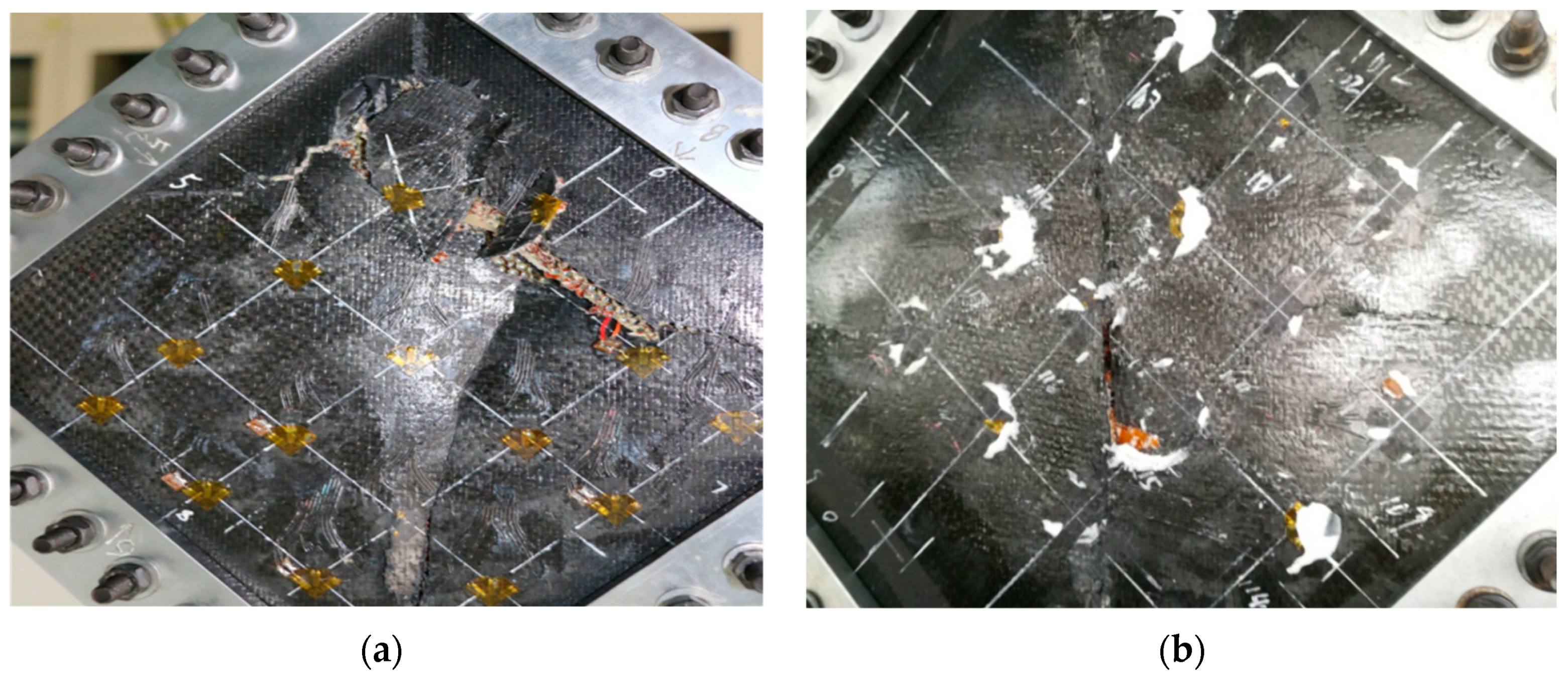
3.2. Compression Test Results
3.3. Shearing Test Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, I.; Kim, J.G.; Seo, I.S. Radar absorbing sandwich construction composed of CNT, PMI foam and carbon/epoxy composite. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3002–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.C.; Chin, W.S.; Seo, I.S. EM characteristics of the RAS composed of E-glass/epoxy composite and single dipole FSS element. Compos. Struct. 2006, 75, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinker, M.; John, M.; Zahlen, P.C.; Schäuble, R. Face sheet debonding in CFRP/PMI sandwich structures under quasi-static and fatigue loading considering residual thermal stress. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2011, 78, 2835–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, P.; Huang, C.; Fu, L.; Song, C.; Hou, H.; Chang, J. Hydrothermal synthesis, structure characterization and luminescence property of three porous coordination polymers using a flexible tripodal amide containing linker. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2012, 15, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granville, D.M. Moisture effects of polymethacrylimide foam and honeycomb core in sandwich/skin structures. In Proceedings of the AHS, 43rd Annual Forum, Saint Louis, MO, USA, 18–20 May 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Gibson, R.F.; Ayorinde, E.O. Fatigue of foam and honeycomb core composite sandwich structures: A tutorial. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2006, 8, 263–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sokolinsky, V.S.; Rajaram, S.; Nutt, S.R. Assessment of sandwich models for the prediction of sound transmission loss in unidirectional sandwich panels. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosveld, F.W.; Mixson, J.S. Noise transmission through an acoustically treated and honeycomb-stiffened aircraft sidewall. J. Aircr. 1985, 22, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuure, A.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, I. Mechanical properties of composite panels based on woven sandwich-fabric preforms. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2000, 31, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.; Reghunadhan Nair, C.; Mathew, D.; Ninan, K.N. Foam sandwich composites with cyanate ester based syntactic foam as core and carbon-cyanate ester as skin: Processing and properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzuca, P.; Firmo, J.P.; Correia, J.R.; Castilho, E. Mechanical be-haviour in shear and compression at elevated temperature of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 42, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzuca, P. Flexural be-haviour of GFRP sandwich panels with eco-friendly PET foam core for the rehabilitation of building floors. Structures 2024, 60, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, R.; Sankaran, S. Gradient syntactic foams: Tensile strength, modulus and fractographic features. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 412, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mamalis, A.; Papapostolou, D. Experimental investigation of strain rate effects on the crushing characteristics of composite sandwich panels. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2010, 15, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgarva, L.; Åström, B. Experimental investigation of compression moulding of glass/PA12-PMI foam core sandwich components. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, R.; Patel, S. Efficient design of composite honeycomb sandwich panels under blast loading. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusri, M.; Zuhri, M.; Ishak, M.; Azman, M.A. The Capabilities of Honeycomb Core Structures Made of Kenaf/Polylactic Acid Composite under Compression Loading. Polymers 2023, 15, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanarasu, M.; Vm, S. Structural response of sandwich structures with CFRP face sheets under quasi-static indentation and high velocity impact: An experimental and numerical study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2023, 237, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fatlawi, A.; Jármai, K.; Kovács, G. Optimization of a totally fiber-reinforced plastic composite sandwich construction of helicopter floor for weight saving, fuel saving and higher safety. Polymers 2021, 13, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Thayamballi, A.K.; Kim, G.S. The strength characteristics of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels. Thin-Walled Struct. 1999, 35, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakke, V.; Carlsson, L.A. Experimental investigation of compression failure of sandwich specimens with face/core debond. Compos. Part B Eng. 2004, 35, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gdoutos, E.E.; Daniel, I.M.; Wang, K.A. Compression facing wrinkling of composite sandwich structures. Mech. Mater. 2003, 35, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Yoon, S.; Sistare, P. Compressive failure of carbon-foam sandwich composites with holes and/or partial delamination. Compos. Struct. 1997, 38, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grediac, M. A finite element study of the transverse shear in honeycomb cores. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1993, 30, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoushahi, H.; Goodarzian, F. Dynamic and buckling analysis of composite laminated plates with and without strip delamination under hygrothermal effects using finite strip method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 131, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Meng, M.; Zhu, T.; He, Z.; Xiao, S. On crashworthiness and energy-absorbing mechanisms of hygrothermal-aged CFRP structures subjected to quasi-static loads. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghad, A.; Mabrouk, K.E. Exploring the impact of void content and hygrothermal aging on the performance of carbon/epoxy composite laminates: A comprehensive study. Iran. Polym. J. 2024, 33, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaschetti, M.P.; Scafé, M.; Zavatta, N.; Troiani, E. Hygrothermal ageing influence on bvi-damaged carbon/epoxy coupons under compression load. Polymers 2021, 13, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Xie, L.; Wu, Z.; Ning, W.; Du, J.; Zhang, M. Effects of Hygrothermal Aging and Cyclic Compressive Loading on the Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Conductive Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, J. Study of Hygrothermal Aging for Basalt Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composites Modified with CeCl3. Polymers 2024, 16, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Fang, J.; Xuan, S.; Zhou, J.; Tian, W. Investigation on interlayer debonding behavior of unidirectional composite laminates under cyclical hygrothermal aging duration effects. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 6830–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veazie, D.R.; Robinson, K.R.; Shivakumar, K. Effects of the marine environment on the interfacial fracture toughness of PVC core sandwich composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2004, 35, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manujesh, B.; Rao, V.; Aan, M.S. Moisture absorption and mechanical degradation studies of polyurethane foam cored E-glass-reinforced vinyl-ester sandwich composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzman, H.A.; Castaneda, R.M.; Lee, H.S. Moisture diffusion in composite sandwich structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Hussain, M.M. Hydrothermal ageing effects on flexural properties of GFRP composite laminates. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2013, 20, 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- Azadi, M.; Bahrololoom, M.E.; Heidari, F. Enhancing the mechanical properties of an epoxy coating with rice husk ash, a green product. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2011, 8, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
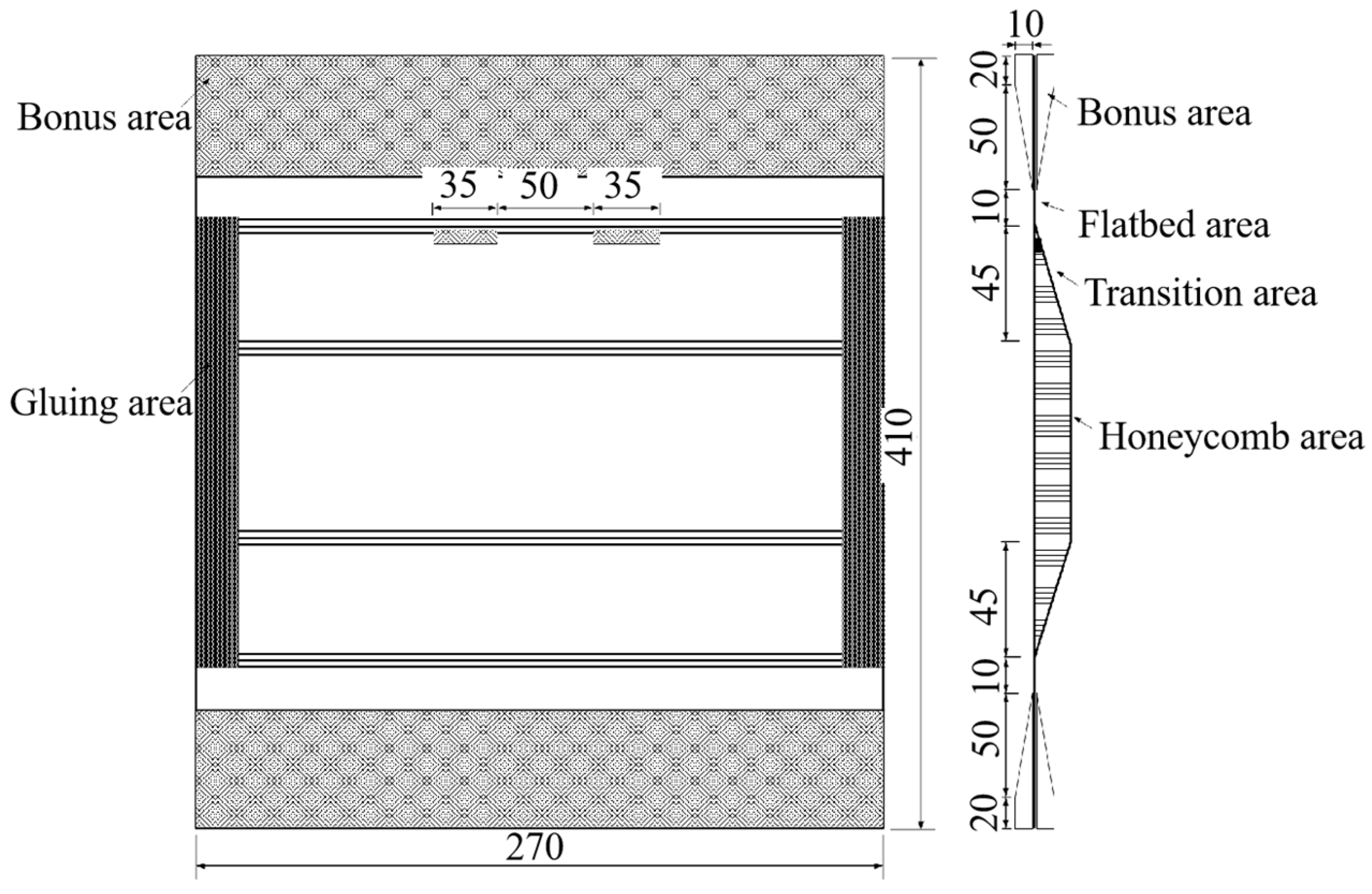
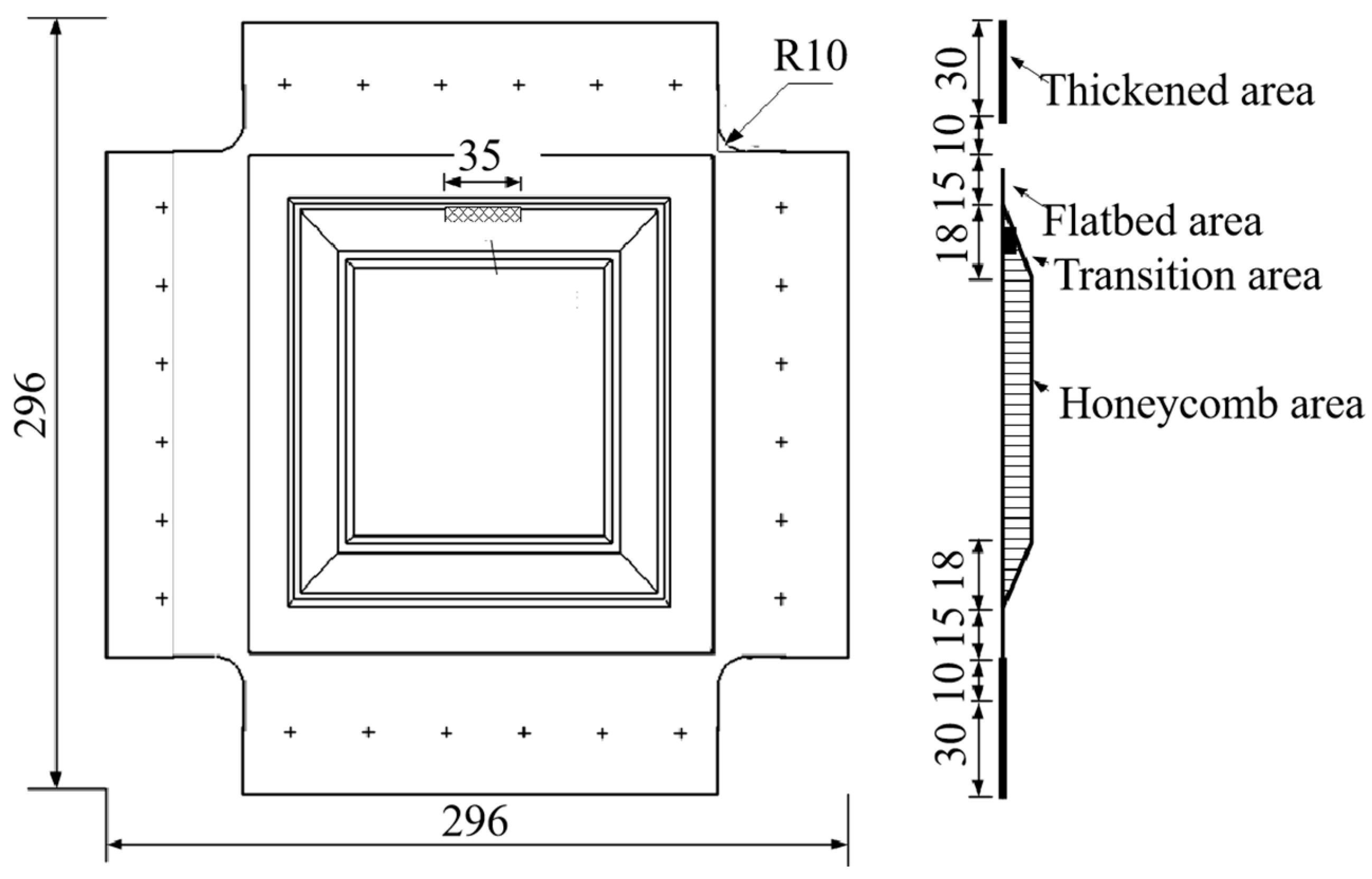

| Position | Thickness/mm | Stacking Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Flatbed area | 2.67 | [(±45)/0/(±45)/0/0/+45/90/−45/0]s |
| Transition area | 0.835 + 15.0 + 1.085 | [(±45)/0/(±45)/0/0/NRH-2.0-48-δ15/90/+45/0/0/(±45)/0/(±45)] |
| Honeycomb area | 0.585 + 15.0 + 0.46 | [(±45)/0/(±45)/NRH-2.0-48-δ15/(±45)/(±45)] |
| Position | Thickness/mm | Stacking Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Thickened area | 3.59 | [(±45)/0/(±45)/90/(±45)/0/(±45)/0/45/90/−45]s |
| Flatbed area | 2.17 | [(±45)/0/(±45)/0/45/90/−45]s |
| Transition area | 0.835 + 6.0 + 1.335 | [(±45)/0/(±45)/0/45/NRH-2.0-48-δ6/90/−45/−45/90/45/0/(±45)/0/(±45)] |
| Honeycomb area | 0.585 + 6.0 + 0.585 | [(±45)/0/(±45)/NRH-2.0-48-δ6/(±45)/0/(±45)] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Jin, H.; Yun, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, W. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panels after Fatigue in Hygrothermal Environments. Polymers 2024, 16, 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172497
Zhao M, Jin H, Yun Z, Meng Z, Zhang W. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panels after Fatigue in Hygrothermal Environments. Polymers. 2024; 16(17):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172497
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ming, Haibo Jin, Zhaoxin Yun, Zhengwei Meng, and Wei Zhang. 2024. "Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panels after Fatigue in Hygrothermal Environments" Polymers 16, no. 17: 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172497
APA StyleZhao, M., Jin, H., Yun, Z., Meng, Z., & Zhang, W. (2024). Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Panels after Fatigue in Hygrothermal Environments. Polymers, 16(17), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172497






