Comparative Study of the Dehydrothermal Crosslinking of Electrospun Collagen Nanofibers: The Effects of Vacuum Conditions and Subsequent Chemical Crosslinking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Electrospinning Solution
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Crosslinking
2.4. Mechanical Testing
2.5. Model for the Stress–Strain Relationship
2.6. Degradation and Swelling
2.7. Material Shrinkage
2.8. SEM Image Analysis
2.9. Infrared Spectroscopy
2.10. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
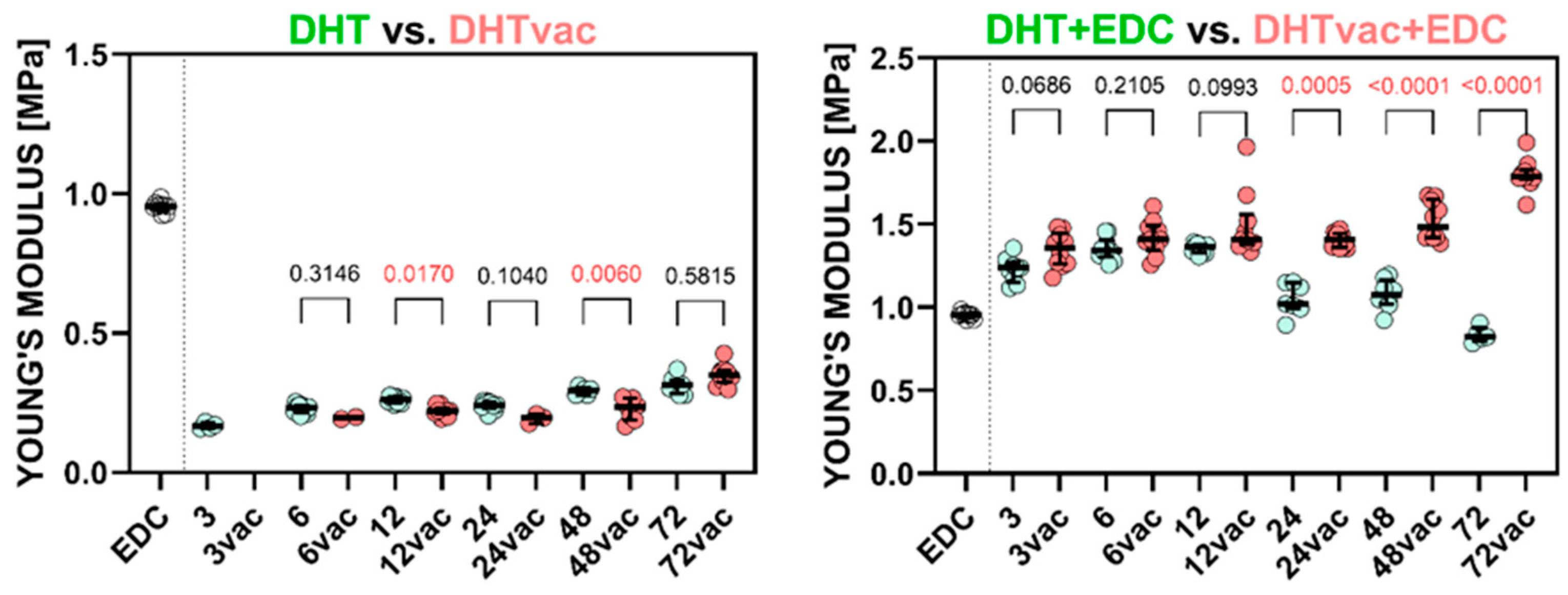
3.1. Mechanical Testing
3.2. Model
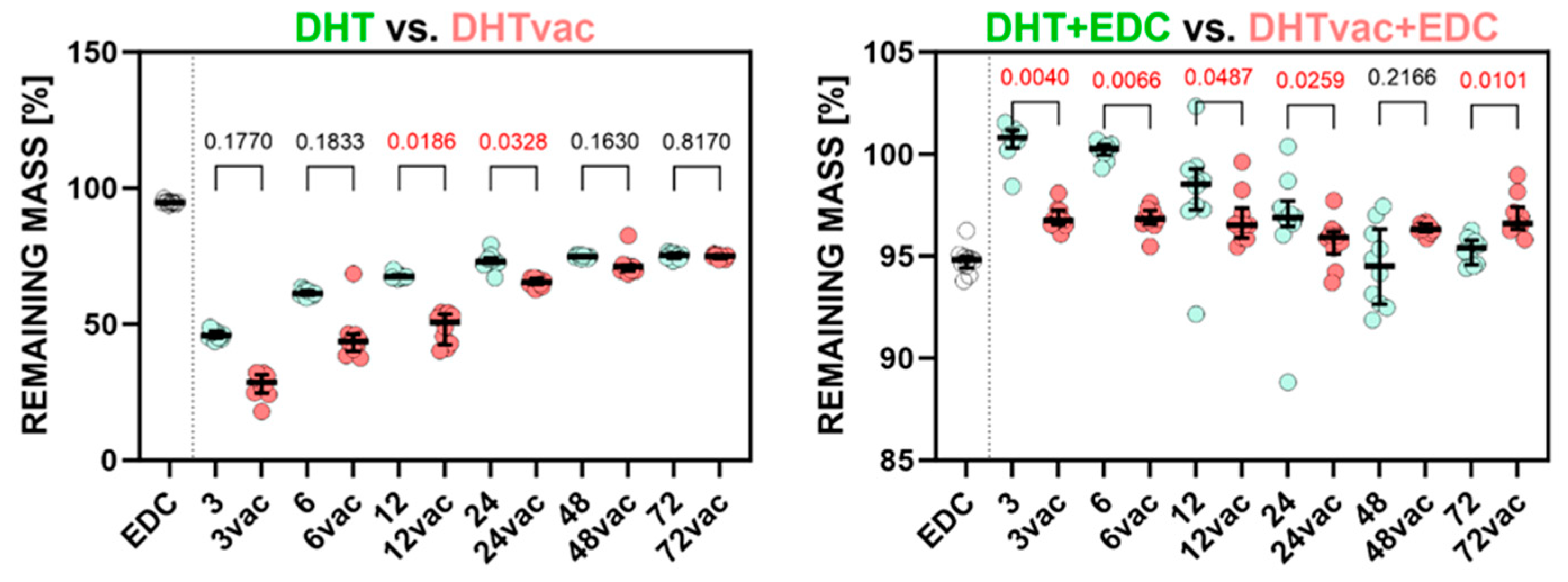
3.3. Degradation Test
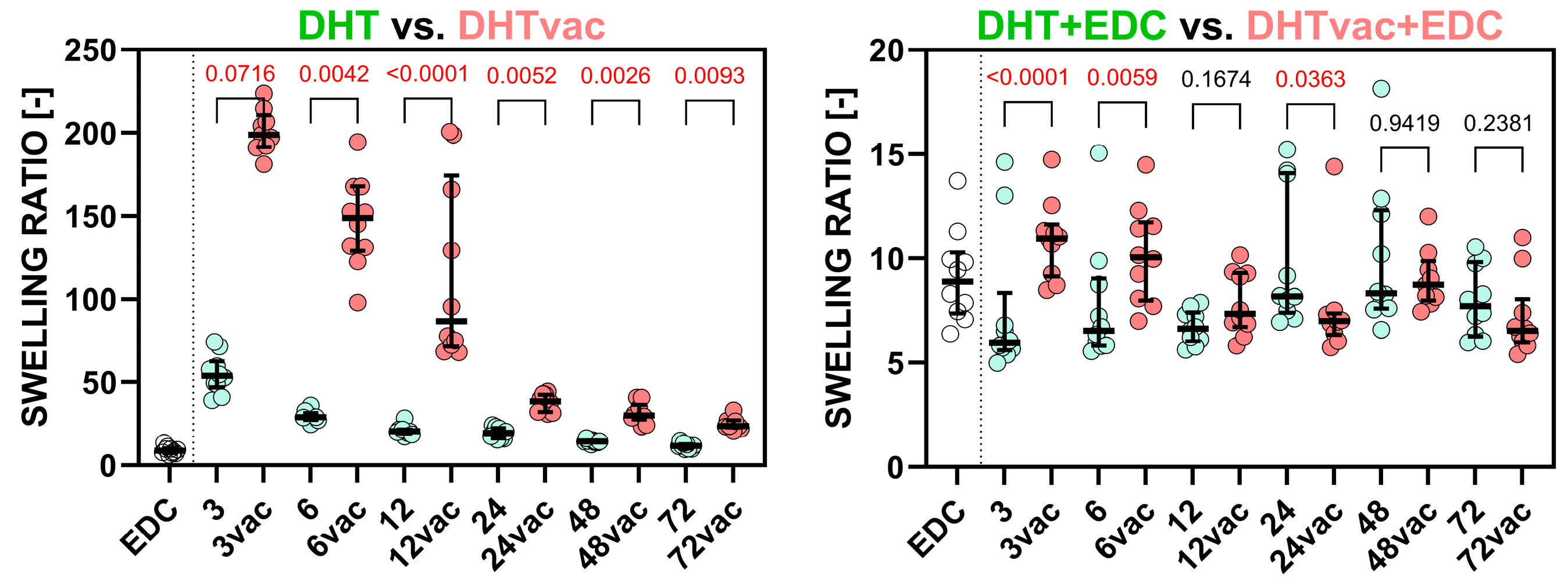
3.4. Swelling Test
3.5. Shrinkage of the Material
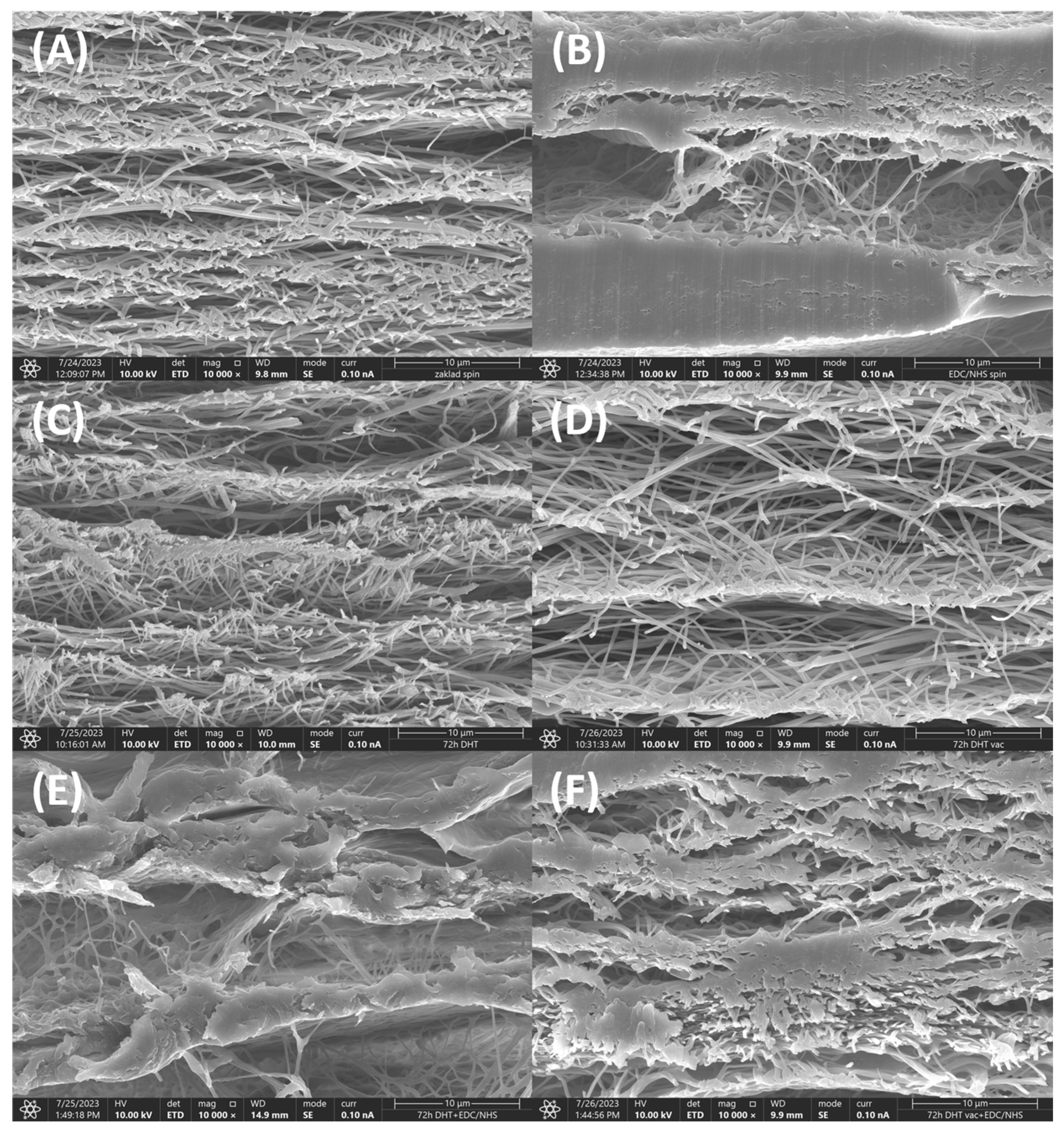
3.6. SEM Morphology Analysis
3.7. Infrared Spectrometry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, C.; Lv, Y. Application of collagen scaffold in tissue engineering: Recent advances and new perspectives. Polymers 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchý, T. Collagen in Bone Tissue Regeneration: Focusing on the Mechanical and Structural Constraints. 2020. Available online: https://dspace.cvut.cz/handle/10467/106899 (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Cen, L.; Liu, W.; Cui, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Y. Collagen tissue engineering: Development of novel biomaterials and applications. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehy, E.; Cunniffe, G.; O’Brien, F. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue regeneration and repair. In Peptides and Proteins as Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration and Repair; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2018; pp. 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Blackstone, B.N.; Gallentine, S.C.; Powell, H.M. Collagen-based electrospun materials for tissue engineering: A systematic review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.; Araújo, J.V.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Electrospun nanostructured scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atala, A.; Lanza, R.; Lanza, R.P. Methods of Tissue Engineering; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Buttafoco, L.; Kolkman, N.; Engbers-Buijtenhuijs, P.; Poot, A.; Dijkstra, P.; Vermes, I.; Feijen, J. Electrospinning of collagen and elastin for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahria, H. Electrospinning of collagen: Formation of biomedical scaffold. Adv. Res. Text. Eng. 2017, 2, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Arnoult, O.; Smith, M.; Wnek, G.E. Electrospinning of in situ crosslinked collagen nanofibers. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19412–19417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchý, T.; Šupová, M.; Sauerová, P.; Verdanova, M.; Sucharda, Z.; Rýglová, S.; Žaloudková, M.; Sedláček, R.; Kalbacova, M.H. The effects of different cross-linking conditions on collagen-based nanocomposite scaffolds—An in vitro evaluation using mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 065008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, H.-E.; Kim, H.-W. Electrospun fibrous web of collagen–apatite precipitated nanocomposite for bone regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Lou, Y.-Y.; Li, T.-H.; Liu, B.-Z.; Chen, K.; Zhang, D.; Li, T. Cross-linking methods of type I collagen-based scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 1146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Zou, Y.; Lu, G.; Ronca, A.; D’amora, U.; Liang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y. Advanced application of collagen-based biomaterials in tissue repair and restoration. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2022, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yu, Z.-L.; Li, S.; Xu, C.-Z.; Hou, Y.-J.; Liao, L.-X.; Xu, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-T.; Wei, B.-M.; Wen, W.; et al. Recent Advances on Collagen Biomaterial: From Extraction, Cross-Linking to Tissue Regeneration. Polym. Rev. 2024, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.W.; Powell, H.M. Dehydrothermal crosslinking of electrospun collagen. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2011, 17, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, S.D.; Light, N.D.; Diamond, A.M.; Willins, M.J.; Bailey, A.J.; Wess, T.J.; Leslie, N.J. Effect of chemical modifications on the susceptibility of collagen to proteolysis. II. Dehydrothermal crosslinking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1992, 14, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weadock, K.; Olson, R.M.; Silver, F.H. Evaluation of collagen crosslinking techniques. Biomater. Med. Devices Artif. Organs 1983, 11, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damink, L.H.H.O.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Van Luyn, M.J.A.; Van Wachem, P.B.; Nieuwenhuis, P.; Feijen, J. Glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent for collagen-based biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.P.; Shanmugasundaram, S.; Masih, P.; Pandya, D.; Amara, S.; Collins, G.; Arinzeh, T.L. An investigation of common crosslinking agents on the stability of electrospun collagen scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, D.R.; Wu, J.-J. Collagen cross-links. In Collagen: Primer in Structure, Processing and Assembly; Spinger: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 207–229. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.-J. Cross-linking agents for electrospinning-based bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scialla, S.; Gullotta, F.; Izzo, D.; Palazzo, B.; Scalera, F.; Martin, I.; Sannino, A.; Gervaso, F. Genipin-crosslinked collagen scaffolds inducing chondrogenesis: A mechanical and biological characterization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2022, 110, 1372–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, D.V.; Shepherd, J.H.; Ghose, S.; Kew, S.J.; Cameron, R.E.; Best, S.M. The process of EDC-NHS cross-linking of reconstituted collagen fibres increases collagen fibrillar order and alignment. APL Mater. 2015, 3, 014902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhail, M.; Wong, K.K.H.; Padavan, D.T.; Wu, Y.; O’Gorman, D.B.; Wan, W. Genipin-cross-linked electrospun collagen fibers. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2011, 22, 2241–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiak, K.; Sionkowska, A. Current methods of collagen cross-linking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weadock, K.S.; Miller, E.J.; Bellincampi, L.D.; Zawadsky, J.P.; Dunn, M.G. Physical crosslinking of collagen fibers: Comparison of ultraviolet irradiation and dehydrothermal treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tihăuan, B.-M.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Bucos, M.A.; Marinaș, I.C.; Nicoară, A.-C.; Măruțescu, L.; Oprea, O.; Matei, E.; Maier, S.S. Crosslinked collagenic scaffold behavior evaluation by physico-chemical, mechanical and biological assessments in an in vitro microenvironment. Polymers 2022, 14, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, M.G.; Jaasma, M.J.; O’Brien, F.J. The effect of dehydrothermal treatment on the mechanical and structural properties of collagen-GAG scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2009, 89, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchý, T.; Vištejnová, L.; Šupová, M.; Klein, P.; Bartoš, M.; Kolinko, Y.; Blassová, T.; Tonar, Z.; Pokorný, M.; Sucharda, Z.; et al. Vancomycin-loaded collagen/hydroxyapatite layers electrospun on 3D printed titanium implants prevent bone destruction associated with S. epidermidis infection and enhance osseointegration. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchý, T.; Šupová, M.; Sauerová, P.; Kalbáčová, M.H.; Klapková, E.; Pokorný, M.; Horný, L.; Závora, J.; Ballay, R.; Denk, F.; et al. Evaluation of collagen/hydroxyapatite electrospun layers loaded with vancomycin, gentamicin and their combination: Comparison of release kinetics, antimicrobial activity and cytocompatibility. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 140, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchý, T.; Šupová, M.; Klapková, E.; Adamková, V.; Závora, J.; Žaloudková, M.; Rýglová, Š.; Ballay, R.; Denk, F.; Pokorný, M.; et al. The release kinetics, antimicrobial activity and cytocompatibility of differently prepared collagen/hydroxyapatite/vancomycin layers: Microstructure vs. nanostructure. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 100, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, M.; Suchý, T.; Kotzianová, A.; Klemeš, J.; Denk, F.; Šupová, M.; Sucharda, Z.; Sedláček, R.; Horný, L.; Králík, V.; et al. Surface treatment of acetabular cups with a direct deposition of a composite nanostructured layer using a high electrostatic field. Molecules 2020, 25, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rýglová, Š.; Braun, M.; Suchý, T. Collagen and Its Modifications—Crucial Aspects with Concern to Its Processing and Analysis. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Calò, E.; Bonfrate, V.; Pedone, D.; Gallo, N.; Natali, M.L.; Sannino, A.; Madaghiele, M. Exploring the effects of the crosslink density on the physicochemical properties of collagen-based scaffolds. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, T.; Zeeshan, R.; Zarif, F.; Ilyas, K.; Muhammad, N.; Safi, S.Z.; Rahim, A.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; Rehman, I.U. FTIR analysis of natural and synthetic collagen. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2018, 53, 703–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Choo, L.-P.; Watson, P.H.; Halliday, W.C.; Mantsch, H.H. Beware of connective tissue proteins: Assignment and implications of collagen absorptions in infrared spectra of human tissues. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 1995, 1270, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabotyagova, O.S.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Collagen structural hierarchy and susceptibility to degradation by ultraviolet radiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski Herman, A. Infrared Band Hand-Book; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, UK, 2000.
- Vrandečić, N.S.; Erceg, M.; Jakić, M.; Klarić, I. Kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of poly (ethylene glycol) and poly (ethylene oxide) s of different molecular weight. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 498, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prystupa, D.; Donald, A. Infrared study of gelatin conformations in the gel and sol states. Polym. Gels Netw. 1996, 4, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, K.; Veis, A. Fourier transform IR spectroscopy of collagen and gelatin solutions: Deconvolution of the amide I band for conformational studies. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 1988, 27, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Huang, X.; Wei, S.; Zhai, M. Structural study and preliminary biological evaluation on the collagen hydrogel crosslinked by γ-irradiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 2960–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Gawron, M.; Kozlowska, J.; Planecka, A. Chemical and thermal cross-linking of collagen and elastin hydrolysates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Dederko-Kantowicz, P.; Staroszczyk, H.; Sommer, S.; Michalec, M. Enzymatic and chemical cross-linking of bacterial cellulose/fish collagen composites—A comparative study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.P.; Sell, S.A.; Boland, E.D.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Nanofiber technology: Designing the next generation of tissue engineering scaffolds. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kužma, J.S.T.; Horný, L. Effect of Cross-Linking Agent Concentration on Mechanical Properties of Collagen-CaP Nanostructured Composite. In Studentská Tvůrčí Činnost 2017; ČVUT v Praze—Fakulta Strojní: Praha, Czech Republic, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kužma, J.; Horný, L.; Suchý, T.; Šupová, M.; Sucharda, Z. Electrospun Collagen Variability Characterized by Tensile Testing. In Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fathima, N.N. Hydration and Shrinkage Phenomena in Native and Crosslinked Collagen. Proc. Indian Natn Sci. Acad. 2011, 77, 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Kume, M.; Hirano, A.; Ochiai, B.; Endo, T. Copolymers containing a spiro orthoester moiety that undergo no shrinkage during cationic crosslinking. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 3666–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, L.; Xu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Shinoda, M.; Kishimoto, M.; Tanaka, T.; Yamane, H. Effect of the Application of a Dehydrothermal Treatment on the Structure and the Mechanical Properties of Collagen Film. Materials 2020, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. Water-stability and biological behavior of electrospun collagen/PEO fibers by environmental friendly crosslinking. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Mingche, W.; Pins, G.D.; Silver, F.H. Collagen fibres with improved strength for the repair of soft tissue injuries. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaar, J.; Naffa, R.; Brimble, M. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic crosslinks found in collagen and elastin and their chemical synthesis. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 2789–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, J.; Brodsky, B.; Berman, H.M. Hydration structure of a collagen peptide. Structure 1995, 3, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchotkina, N. Aspects of Lyophilization of Cardiac Bioimplant. Innov. Biosyst. Bioeng. 2021, 5, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrilaka, C.; Karipidou, N.; Petrou, N.; Manglaris, C.; Katrilakas, G.; Tzavellas, A.N.; Pitou, M.; Tsiridis, E.E.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Aggeli, A. Freeze-Drying Process for the Fabrication of Collagen-Based Sponges as Medical Devices in Biomedical Engineering. Materials 2023, 16, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Group | Type of Control/Crosslinking Procedure: |
|---|---|
| OR (control) | Original collagen material |
| ES (control) | Electrospun, not crosslinked |
| EDC/NHS (control) | Electrospun, EDC/NHS crosslinked |
| DHT | DHT in air |
| DHTvac | DHT under vacuum conditions |
| DHT+EDC | DHT in air and subsequent EDC/NHS crosslinking |
| DHTvac+EDC | DHT under vacuum conditions and subsequent EDC/NHS crosslinking |
| Group | μ (MPa) | ±CI μ 95% | α (−) | ±CI α 95% | R2 | E (MPa) | SD | UTS (MPa) | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDC | 0.352 | 0.001 | 3.582 | 0.022 | 0.998 | 0.954 | 0.019 | 0.859 | 0.223 | |
| DHT | 3 h | 0.063 | 0.001 | 1.575 | 0.073 | 0.976 | 0.168 | 0.011 | 0.159 | 0.062 |
| 6 h | 0.088 | 0.001 | 2.841 | 0.043 | 0.978 | 0.229 | 0.016 | 0.360 | 0.107 | |
| 12 h | 0.111 | 0.000 | 2.198 | 0.014 | 0.989 | 0.261 | 0.011 | 0.285 | 0.084 | |
| 24 h | 0.099 | 0.001 | 1.733 | 0.021 | 0.976 | 0.239 | 0.016 | 0.265 | 0.117 | |
| 48 h | 0.117 | 0.001 | 1.902 | 0.024 | 0.985 | 0.293 | 0.014 | 0.263 | 0.017 | |
| 72 h | 0.123 | 0.001 | 1.715 | 0.024 | 0.978 | 0.313 | 0.031 | 0.269 | 0.100 | |
| DHTvac | 6 h | 0.075 | 0.001 | 4.342 | 0.079 | 0.996 | 0.195 | 0.006 | 0.191 | 0.052 |
| 12 h | 0.087 | 0.000 | 3.379 | 0.056 | 0.975 | 0.220 | 0.017 | 0.157 | 0.037 | |
| 24 h | 0.072 | 0.001 | 3.717 | 0.417 | 0.976 | 0.194 | 0.017 | 0.124 | 0.057 | |
| 48 h | 0.083 | 0.001 | 1.262 | 0.318 | 0.940 | 0.224 | 0.040 | 0.329 | 0.248 | |
| 72 h | 0.135 | 0.001 | 3.444 | 0.110 | 0.966 | 0.350 | 0.036 | 0.779 | 0.059 | |
| DHT+EDC | 3 h | 0.431 | 0.004 | 6.982 | 0.247 | 0.989 | 1.224 | 0.076 | 0.330 | 0.132 |
| 6 h | 0.498 | 0.003 | 4.083 | 0.084 | 0.989 | 1.353 | 0.066 | 0.691 | 0.221 | |
| 12 h | 0.489 | 0.002 | 4.133 | 0.044 | 0.997 | 1.356 | 0.029 | 0.675 | 0.117 | |
| 24 h | 0.392 | 0.002 | 2.391 | 0.031 | 0.989 | 1.049 | 0.096 | 0.682 | 0.266 | |
| 48 h | 0.392 | 0.004 | 2.777 | 0.107 | 0.981 | 1.077 | 0.090 | 0.478 | 0.163 | |
| 72 h | 0.300 | 0.003 | 3.087 | 0.154 | 0.990 | 0.835 | 0.046 | 0.302 | 0.087 | |
| DHTvac+EDC | 3 h | 0.494 | 0.006 | 7.099 | 0.306 | 0.979 | 1.348 | 0.105 | 0.877 | 0.086 |
| 6 h | 0.512 | 0.005 | 7.076 | 0.229 | 0.984 | 1.421 | 0.105 | 0.928 | 0.212 | |
| 12 h | 0.503 | 0.005 | 5.475 | 0.157 | 0.983 | 1.490 | 0.194 | 1.456 | 0.230 | |
| 24 h | 0.527 | 0.003 | 3.987 | 0.073 | 0.990 | 1.407 | 0.046 | 1.568 | 0.248 | |
| 48 h | 0.552 | 0.004 | 3.934 | 0.062 | 0.988 | 1.519 | 0.117 | 1.742 | 0.388 | |
| 72 h | 0.703 | 0.006 | 2.772 | 0.088 | 0.978 | 1.798 | 0.093 | 1.677 | 0.387 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kužma, J.; Suchý, T.; Horný, L.; Šupová, M.; Sucharda, Z. Comparative Study of the Dehydrothermal Crosslinking of Electrospun Collagen Nanofibers: The Effects of Vacuum Conditions and Subsequent Chemical Crosslinking. Polymers 2024, 16, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172453
Kužma J, Suchý T, Horný L, Šupová M, Sucharda Z. Comparative Study of the Dehydrothermal Crosslinking of Electrospun Collagen Nanofibers: The Effects of Vacuum Conditions and Subsequent Chemical Crosslinking. Polymers. 2024; 16(17):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172453
Chicago/Turabian StyleKužma, Ján, Tomáš Suchý, Lukáš Horný, Monika Šupová, and Zbyněk Sucharda. 2024. "Comparative Study of the Dehydrothermal Crosslinking of Electrospun Collagen Nanofibers: The Effects of Vacuum Conditions and Subsequent Chemical Crosslinking" Polymers 16, no. 17: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172453
APA StyleKužma, J., Suchý, T., Horný, L., Šupová, M., & Sucharda, Z. (2024). Comparative Study of the Dehydrothermal Crosslinking of Electrospun Collagen Nanofibers: The Effects of Vacuum Conditions and Subsequent Chemical Crosslinking. Polymers, 16(17), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172453






