Influence of Montmorillonite Organoclay Fillers on Hygrothermal Response of Pultruded E-Glass/Vinylester Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
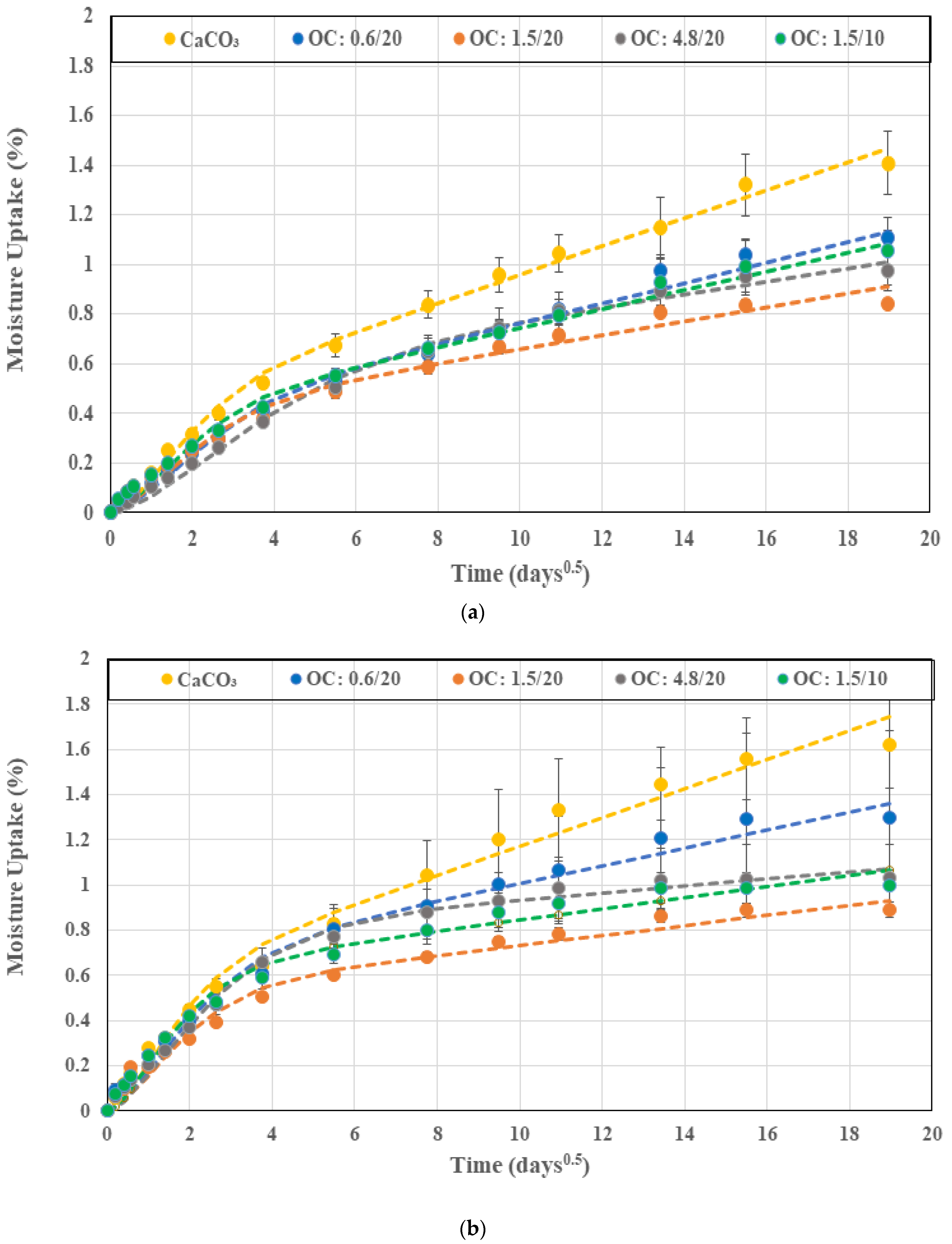
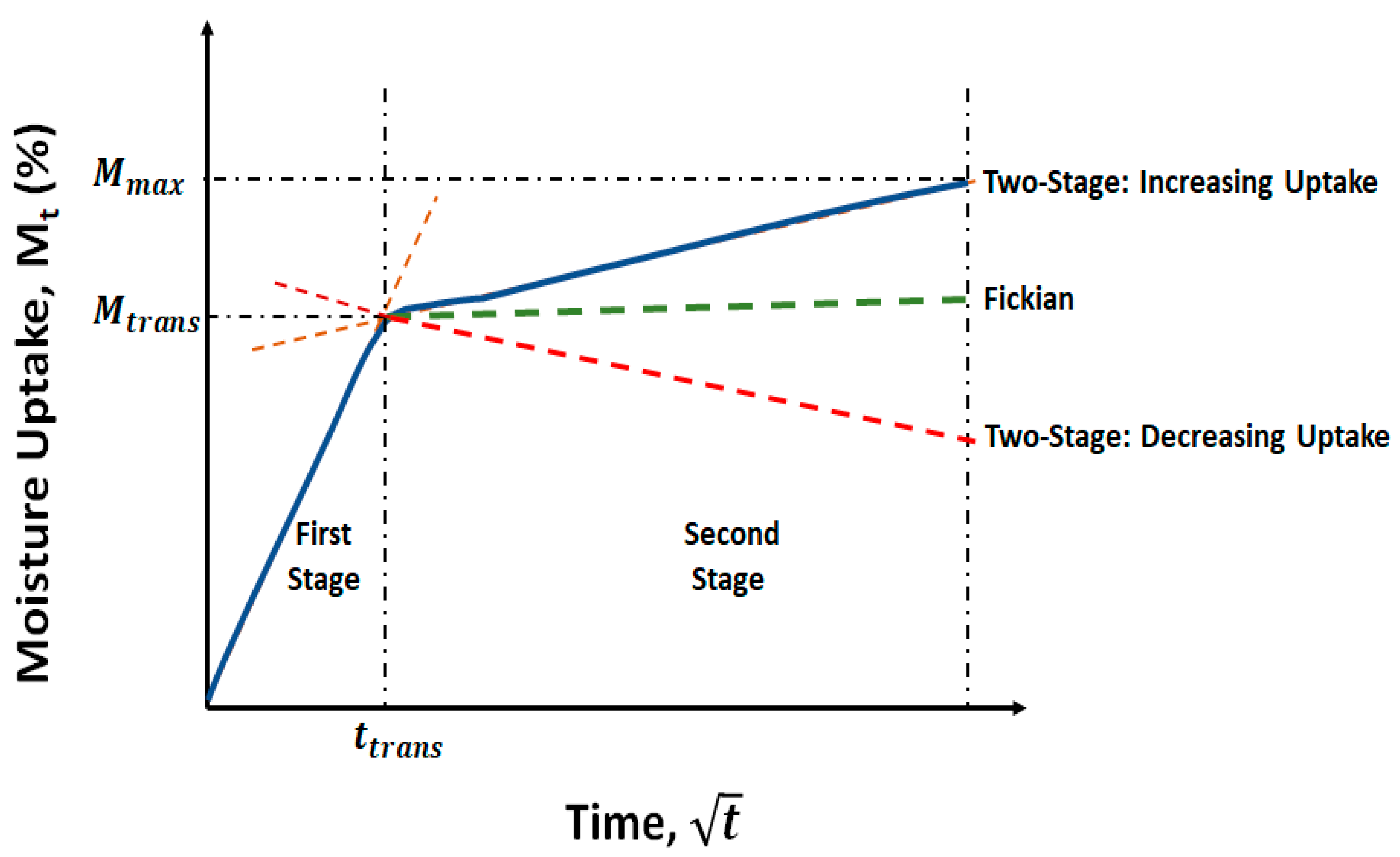
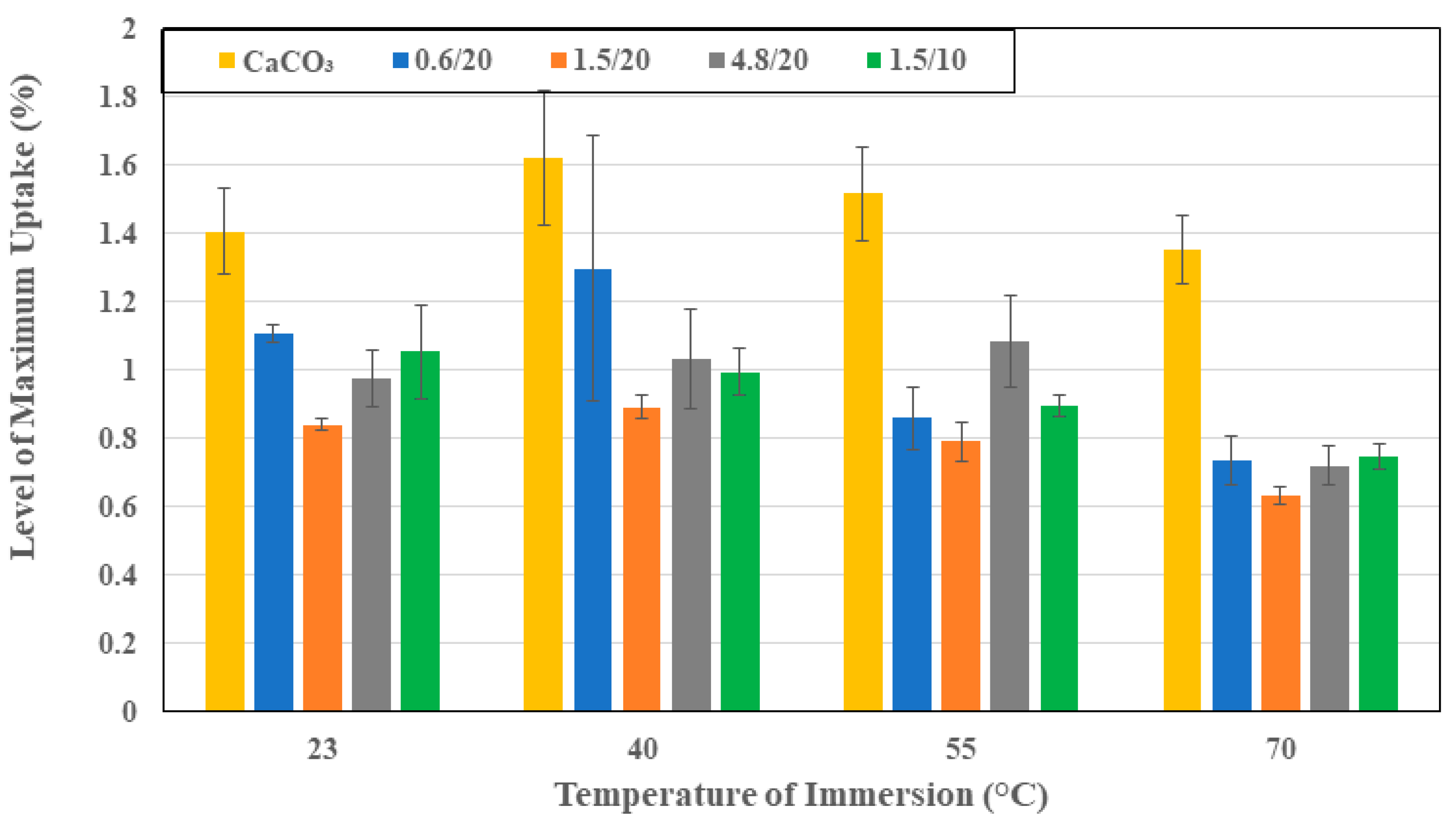
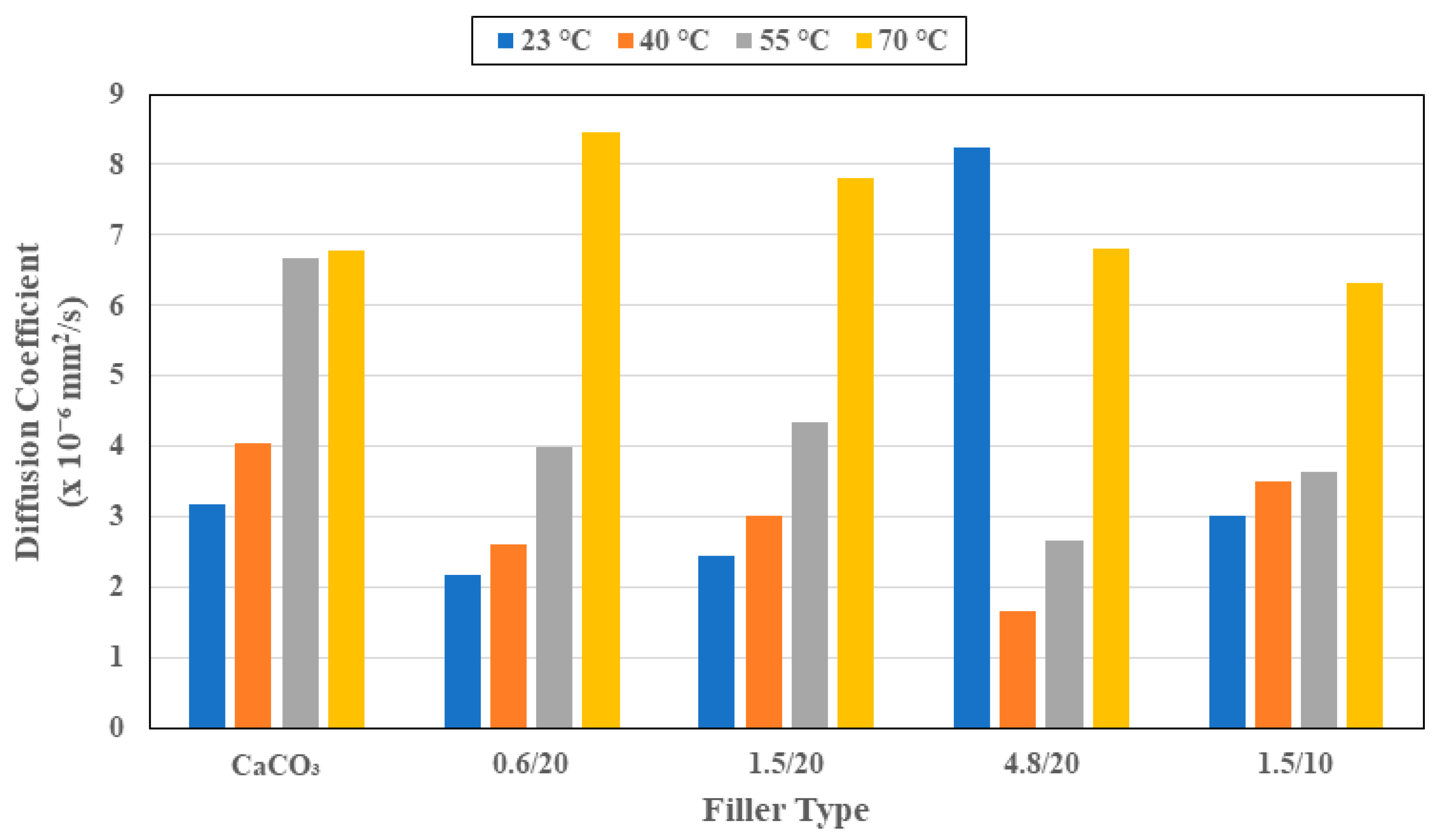
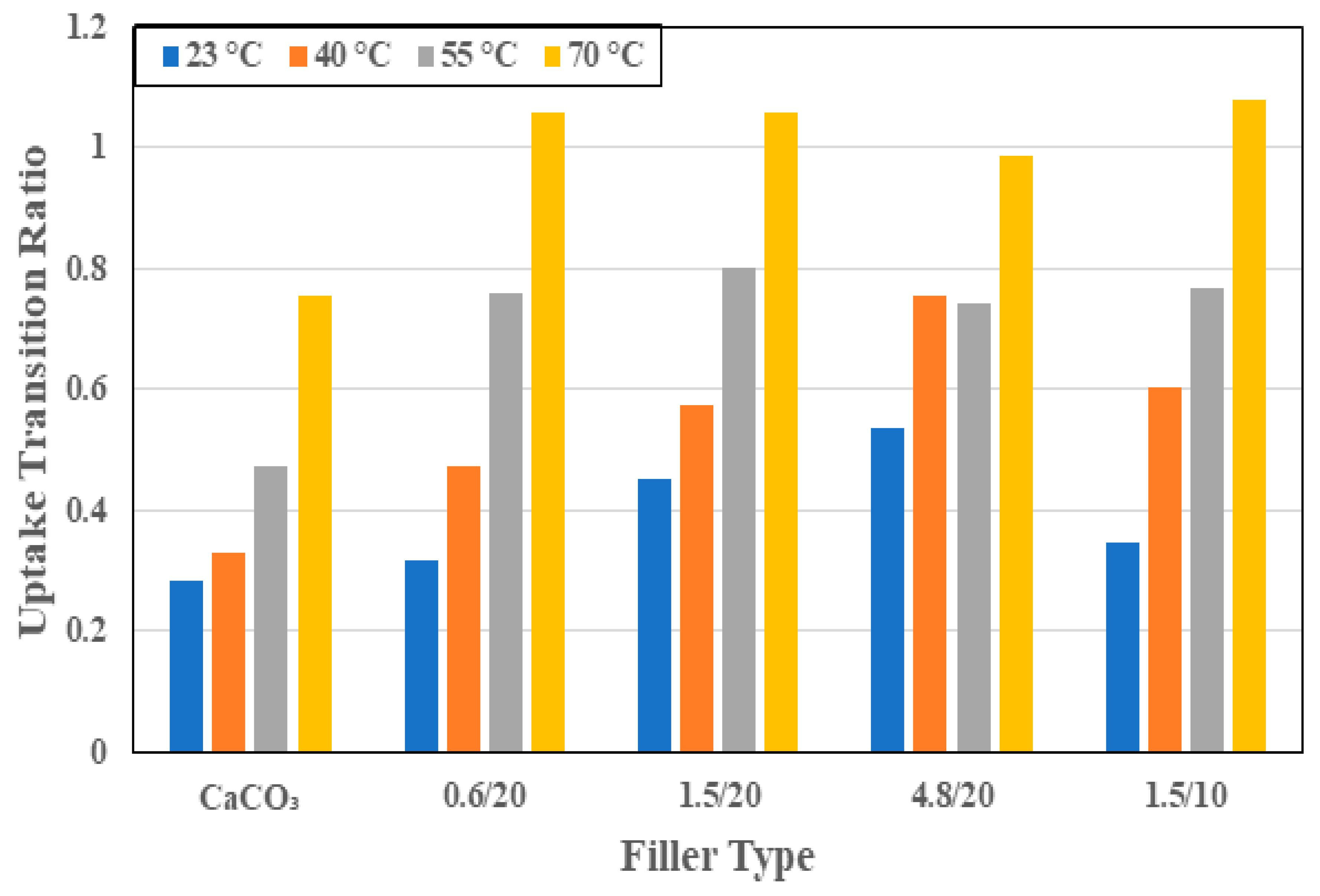
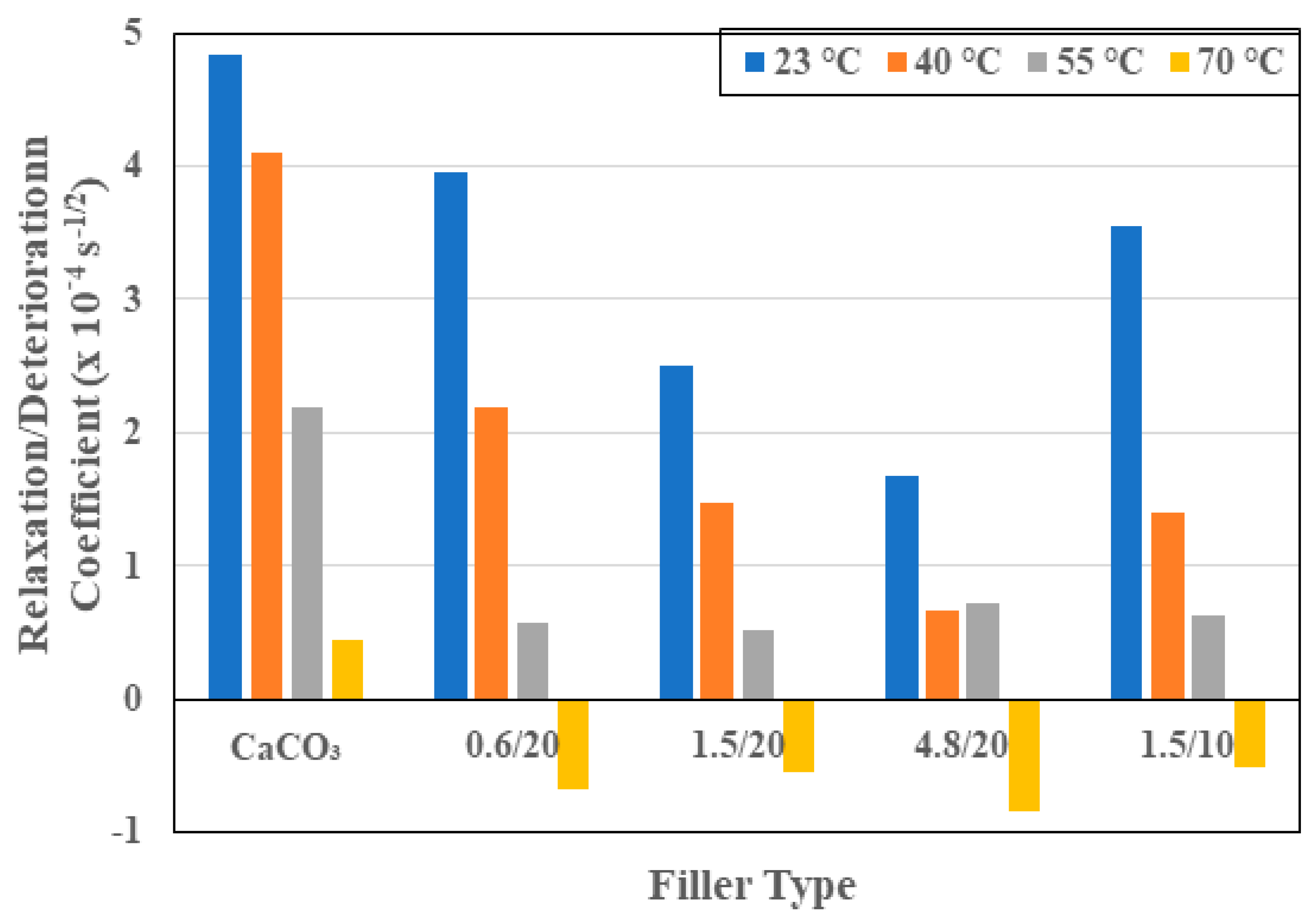
3.1. Moisture Kinetics
3.2. Mechanical Characterization
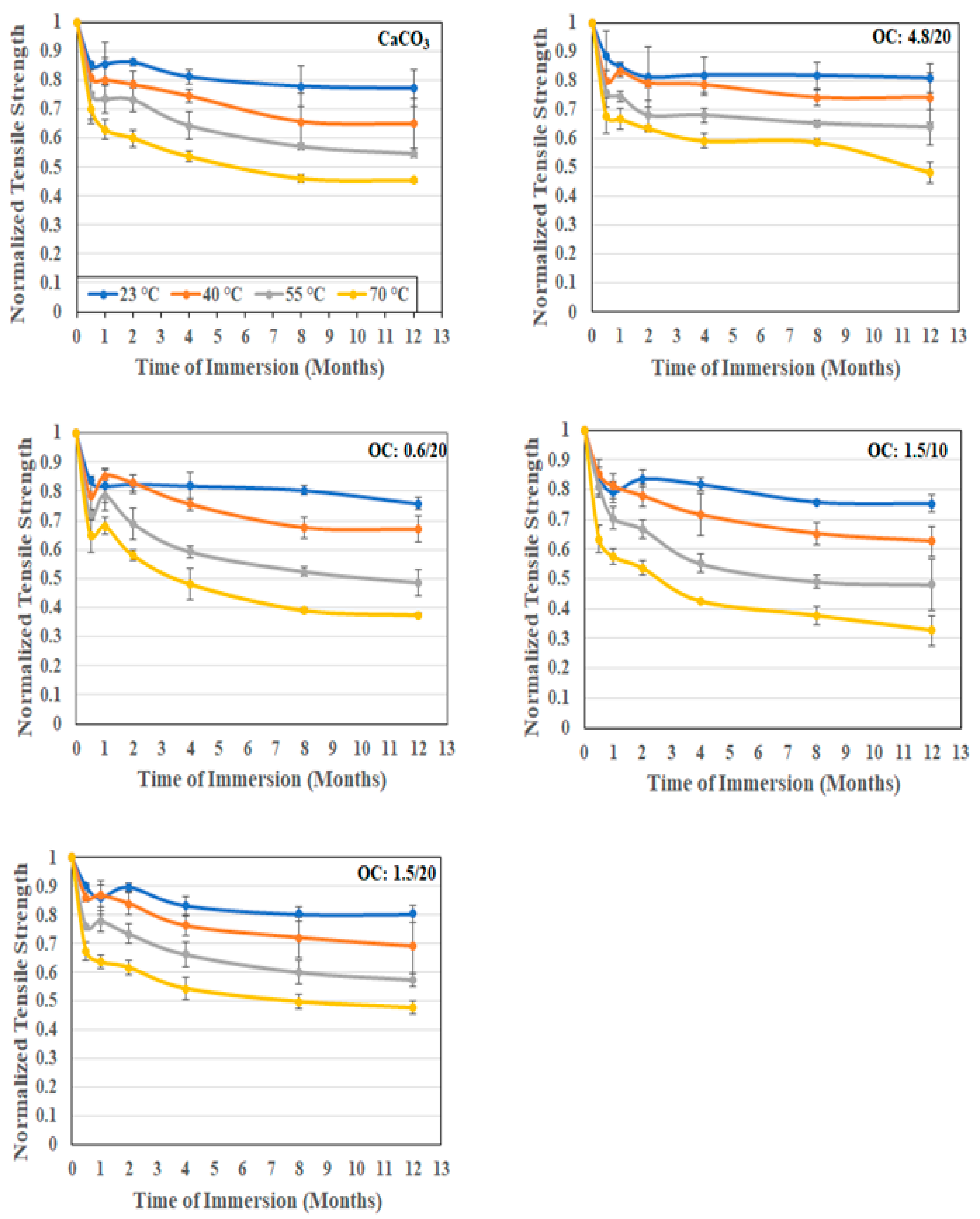
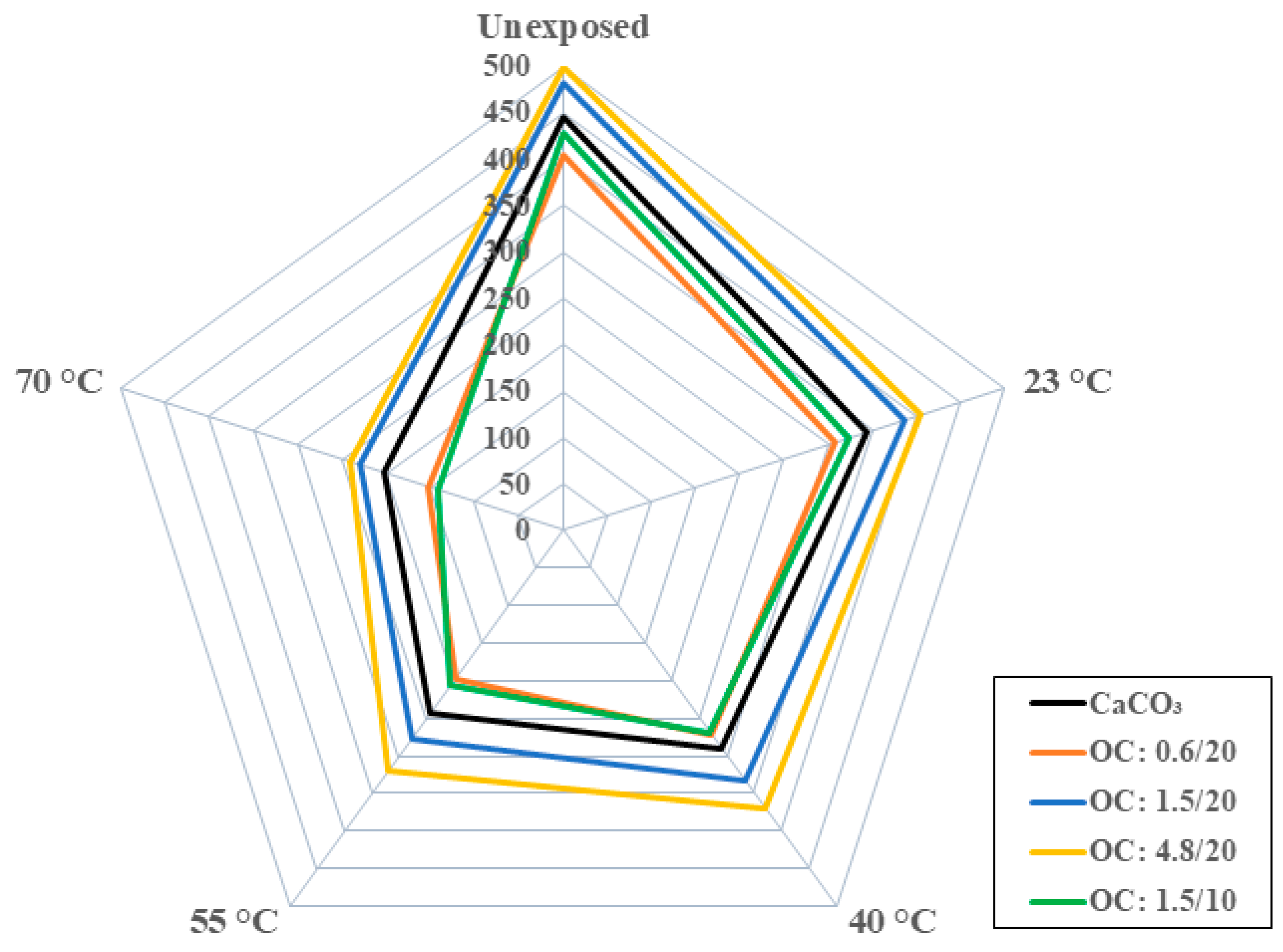
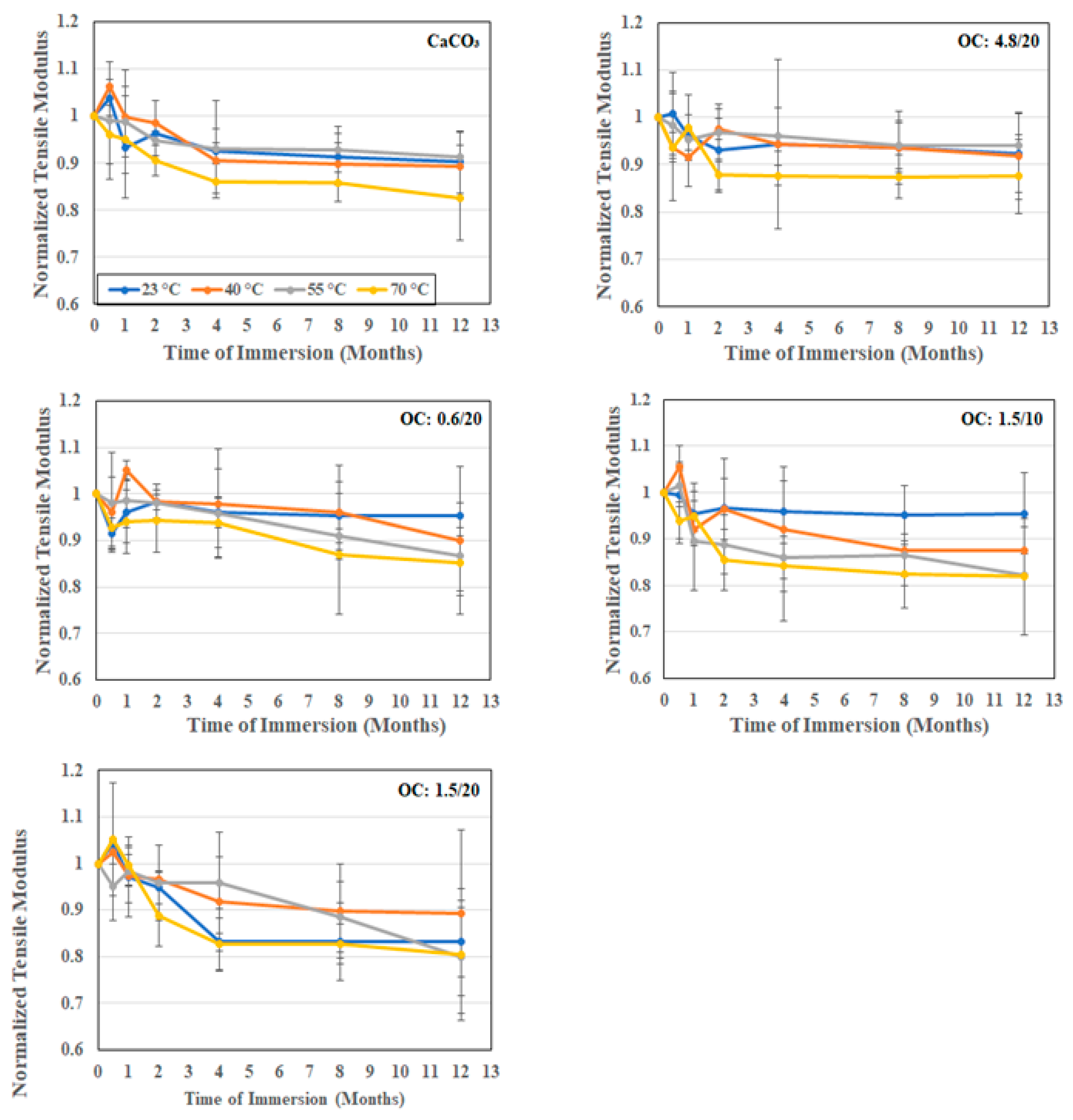
3.2.1. Tensile Characterization
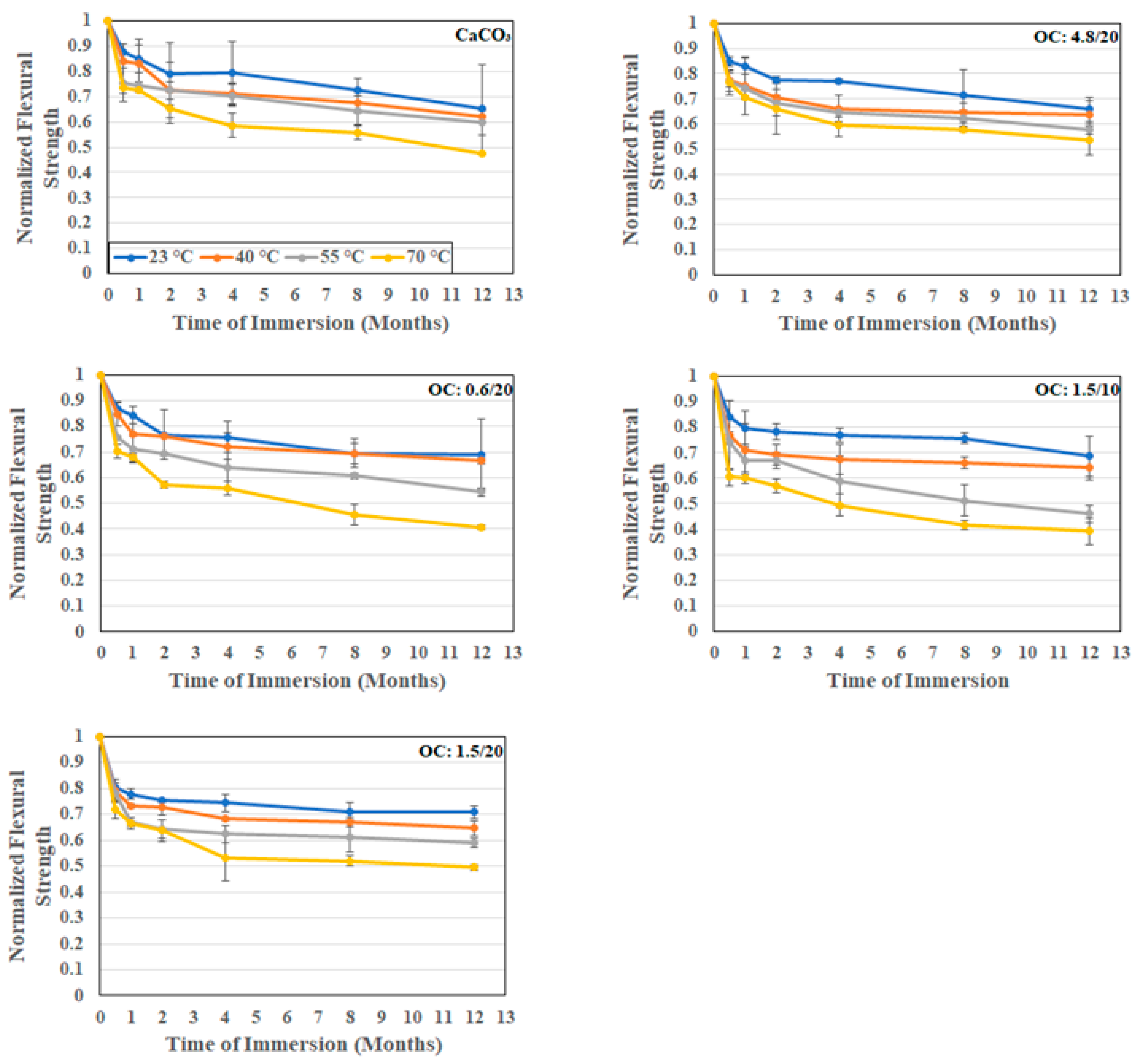
3.2.2. Flexural Response
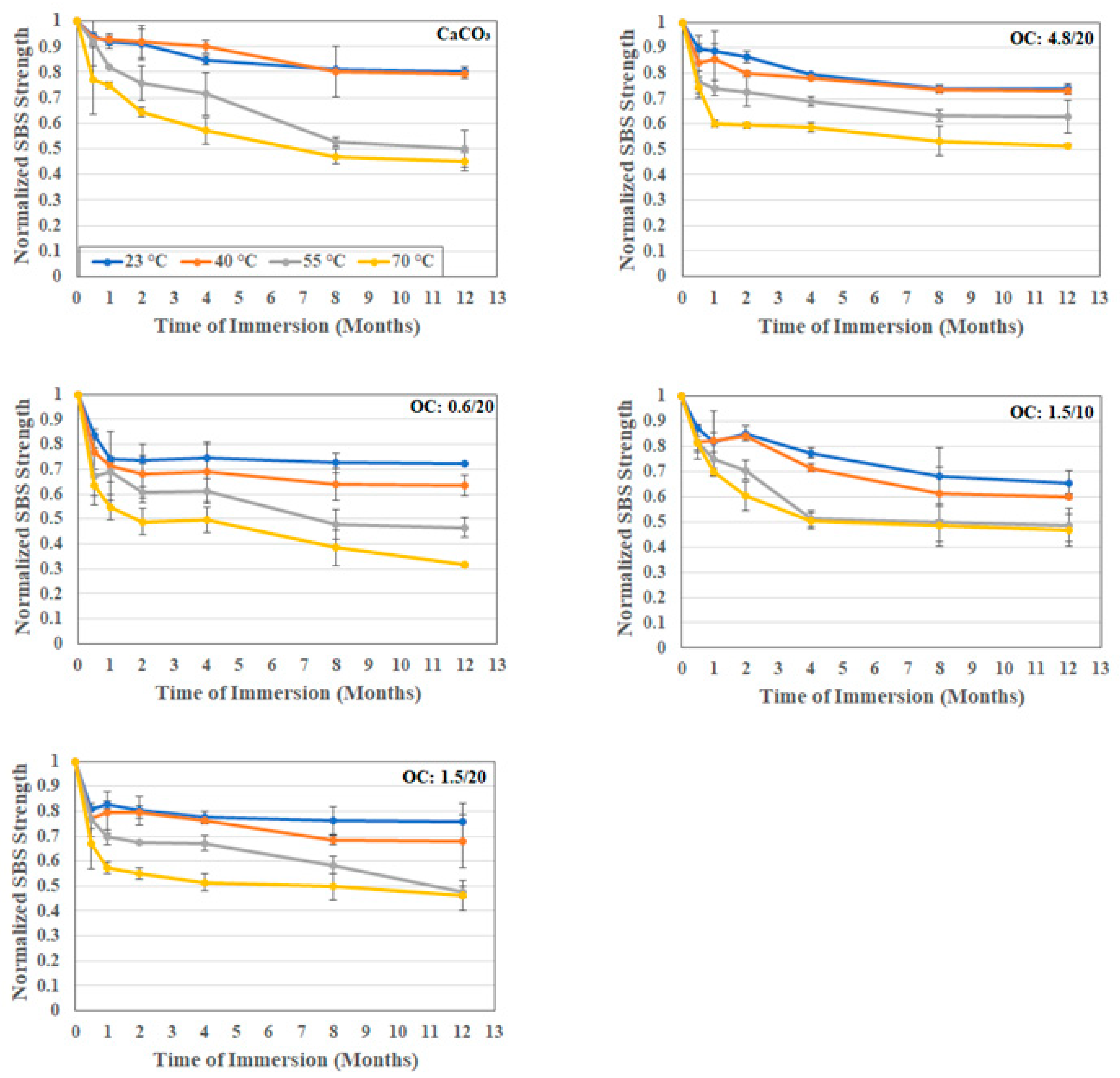
3.2.3. Interfacial Strength
4. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vedernikov, A.; Safonov, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P.; Akhator, I. Pultruded materials and structures: A review. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 5426, 4081–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Yuksel, O.; Baran, I.; Hattel, J.H.; Spagenberg, J.; Sandberg, M. Cost-efficient, automated, and sustainable composite profile manufacture: A review of the state-of-the-art, innovations, and future of pultrusion technologies. Compos. B 2022, 246, 110135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fascetti, A.; Feo, L.; Abbaszadeh, H. A critical review of numerical methods for the simulation of pultruded fiber-reinforced structural elements. Compos. Struct. 2021, 273, 114284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Mosch, W. High Voltage and Electrical Insulation Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Syamsir, A.; Ean, L.-W.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Supian, A.B.M.; Madenci, E.; Ozkilic, Y.O.; Akseylu, C. Recent advances of GFRP cross arms and energy transmission tower: A short review on design improvements in mechanical properties. Materials 2023, 16, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, I.; Tatum, C.C.; Hattel, J.M. The internal stress evaluation of the pultruded blades for a Darrieus wind turbine. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 554–577, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, B.L.; Das, S.; Norris, R.E. Economic competitiveness of protruded fiber composites for wind turbine applications. Compos. B 2023, 265, 110960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elchalakani, M.; Higgoda, T.M.; Kimiaei, M.; Yang, B. Pultruded FRP tubular section members, connections and frames: A review of experimental studies. Structures 2023, 56, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Li, S.; Cao, Z.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Ko, T.J. Carbon fiber composites for large-scale wind turbine blades: Applicability study and comprehensive evaluation in China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumerak, J.E.; Martin, J.D. Pultrusion. In ASM Handbook Volume 21: Composites; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2001; pp. 550–564. [Google Scholar]
- Boukhili, R.; Boukehili, H.; Ben Daly, H.; Gasmi, A. Physical and mechanical properties of pultruded composites containing fillers and low profile additives. Polym. Compos. 2006, 27, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhili, R.; Boukehili, H.; Gauvin, R.; Ben Daly, H.; Gasmi, A. Effect of fillers and low profile additives on the bending of pultruded composites. In High Performance Structures and Materials II; Brebbia, C.A., DeWilde, W.P., Eds.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2004; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.Y.; Zureick, A.-H. Effect of filler and void content on mechanical properties of pultruded composite materials under shear loading. Polym. Compos. 2005, 26, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Lee, N. Shape effect of platelet clay filler on mechanical behaviors of pultruded polymer composites under shear loading. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2007, 26, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, M.; Renukappa, N.M.; Suresh, B. Influence of micro and nanofillers on mechanical properties of pultruded unidirectional glass fiber reinforced epoxy composite systems. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 50, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, K. Compressive properties of nano-calcium carbonate/epoxy and its fibre composites. Compos. B 2013, 45, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, H.; Walia, R.S. Effect of fillers on tensile strength of pultruded glass fiber reinforced polymer composite. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2015, 22, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, M.D.; Govindaraju, H.K.; Jayaraju, T.; Kumar, N. Review- Effect of fillers and mechanical properties of polymer matrix composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 22421–22424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Xian, G. Thermomechanical characterization of organo-clay epoxy nanocomposites for use in civil infrastructure. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2022, 61, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, L.B.; De Santis, H.; Vasquez, A. Influence of the addition of montmorillonite to the matrix of unidirectional glass fibre/epoxy composites on the mechanical and water absorption properties. Compos. A 2008, 39, 1726–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.T.; Zhou, C.H.; Kabwe, F.K.; Wu, Q.Q.; Li, C.S.; Zhang, J.R. Exfoliation of montmorillonite and related properties of clay/polymer nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 169, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swearingen, C.; Macha, S.; Fitch, A. Leashed ferrocenes at clay surfaces: Potential applications for environmental catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 199, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelis, E.P. Polymer layered silicate nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 1996, 8, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Baron, P.; Wang, Z.; Pinnavaia, J.T. Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: An overview. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 15, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.D.; Wu, M.D. Organoclay effects on mechanical responses of glass/epoxy nanocomposite. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 42, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, A.K.; Sun, C.T. Enhancing compressive strength of unidirectional polymer composites using nanoclay. Compos. A 2006, 37, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.N.; Thakur, R.K.; Singh, K.K. Influence of nanoclay filler on mechanical properties of CFRP composites. Mater. Proc. 2022, 66, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, X.; Rees, M.; Thomann, Y.; Necola, A.; Barbezat, M.; Thomann, R. Epoxy-layered silicate nanocomposite as matrix in glass fibre-reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, H.; Jurek, R.J.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Biobased epoxy/clay nanocomposites as a new matrix for CFRP. Compos. A 2006, 37, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, C.N.; Claure, G.; Alvarez, J.; Nanni, A. Evaluation of fiber content in GFRP bars using digital image processing. Compos. B 2020, 200, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlaczek, P.; Sinn, G.; Peter, P.; Wan-Wendner, R.; Lichtenegger, H.C. Characterization of moisture uptake and diffusion mechanisms in particle-filled composites. Polymer 2022, 249, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliem, M.; Hogsberg, J.; Wang, Q.; Dannemann, M. Characterization of clay-modified thermoset polymers under various environmental conditions for the use in high voltage power pylons. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017698890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM D790-17; Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM D2344; Standard Test Method for Short-Beam-Shear Strength of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials and Their Laminates. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Morii, T.; Tanimoto, T.; Hamada, H.; Maekawa, Z.-I.; Hirano, T.; Kiyosumi, K. Weight changes of randomly oriented GRP panel in hot water. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1993, 49, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanilla, M.A.; Li, Y.; Karbhari, V.M. Durability characterization of wet layup graphite/epoxy composites used in external strengthening. Compos. B 2006, 37, 2101–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-R.; Yee, A.F.; Lee, C.Y.-C. Moisture absorption and hydrothermal aging in a bismaleimide resin. Polymer 2001, 42, 7327–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Hong, S.K. Effect of sequential thermal aging and water immersion and moisture kinetics and SBS strength of wet layup carbon epoxy composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, E.; Long, F.A. Two-stage sorption and desorption of organic vapors in cellulose acetate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Long-term hydrothermal aging of carbon-epoxy materials for rehabilitation of civil infrastructure. Compos. A 2022, 153, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Springer, G.S. Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, K.; Kiekens, P. Chemical resistance of pultruded E-glass reinforced polyester composites. In Recent Developments in Durability Analysis of Composite Systems; Cardon, A.H., Fukuda, H., Reifsnider, K.L., Verchery, G., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Grammatikos, S.A.; Zafari, B.; Evernden, M.C.; Mottram, J.T.; Mitchels, J.M. Moisture uptake characteristics of a pultruded fiber reinforced polymer flat sheet subjected to hot/wet aging. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, B.; Karbhari, V.M. Moisture and glass transition temperature kinetics of ambient-cured carbon/epoxy composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2003, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, O.; Varley, R.J.; Simon, G.P. Thermal stability and water update performance of epoxy layered silicate nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Hu, C.; Woo, R.S.C.; Sham, M.-L. Moisture barrier characteristics of organoclay-epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmono, M.; Wildan, M.W.; Ishak, Z.A.M. Preparation and properties of clay reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2013, 690675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanbabaei, G.; Aalaie, J.; Rahmatpour, A.; Khoshniyat, A.; Gharabadian, M.A. Preparation and properties of epoxy-clay nanocomposites. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2007, 46, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.P.; Gupta, R.K.; Gangarao, H.V.S. Moisture diffusion through vinyl/ester nanocomposites made with montmorillonite clay. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, J.E.; Sims, G.D.; Maxwell, A.S.; Frenz, S.; Ogin, S.L.; Foreman, C.; Dorey, R.A. On the relationship between moisture uptake and mechanical property changes in a carbon fibre/epoxy composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Acharya, R.; Hong, S.K. Sea water effects on thermally aged ambient cured carbon/epoxy composites: Moisture kinetics and uptake characteristics. Polymers 2023, 15, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.G.; Unal, H.; Mimaroglu, A. Study of the strength and erosive behavior of CaCO3/glass fiber reinforced polyester composite. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafillidis, C.S.; Lebaron, P.C.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Thermoset epoxy-clay nanocomposites: The dual role of a,w -diamines as clay surface modifiers and polymer curing agents. J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 167, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, X.; Lindberg, H.; Berglund, L.A. Synthesis of epoxy-clay nanocomposites. Influence of the nature of the curing agent on structure. Polymer 2001, 42, 4493–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jana, S. Adverse effects of thermal disassociation of alkyl ammonium ions on nanoclay exfoliation in epoxy-clay systems. Polymer 2004, 45, 7673–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.S.; Nguyen, V.H.; Manouche-Chergui, S.; Carbonnier, B.; Naili, S. Estimation of effective elastic properties of polymer/clay nanocomposites: A parametric study. Compos. B 2018, 152, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M.; Alothman, Z. Mechanical, thermal and microstructural characteristics of cellulose fiber reinforced epoxy/organoclay nanocomposites. Compos. B 2012, 43, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.L. The interface region in glass fibre-reinforced epoxy resin composites II: Water absorption, voids, and the interface. Composites 1995, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. E-glass/vinylester composites in aqueous environments: Effects on short beam shear strength. ASCE J. Compos. Constr. 2004, 8, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Units | Filler Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3 | OC: 0.6/20 | OC: 1.5/20 | OC: 4.8/20 | OC: 1.5/10 | ||
| Tensile Strength | MPa | 445.26 [9.93] | 412.03 [19.51] | 480.98 [23.30] | 499.66 [14.92] | 428.51 [17.79] |
| Tensile Modulus | GPa | 30.97 [2.00] | 30.88 [1.01] | 31.15 [1.89] | 31.62 [1.85] | 30.69 [1.31] |
| Flexural Strength | MPa | 460.71 [50.14] | 470.29 [40.69] | 486.81 [22.78] | 488.42 [38.51] | 482.28 [29.04] |
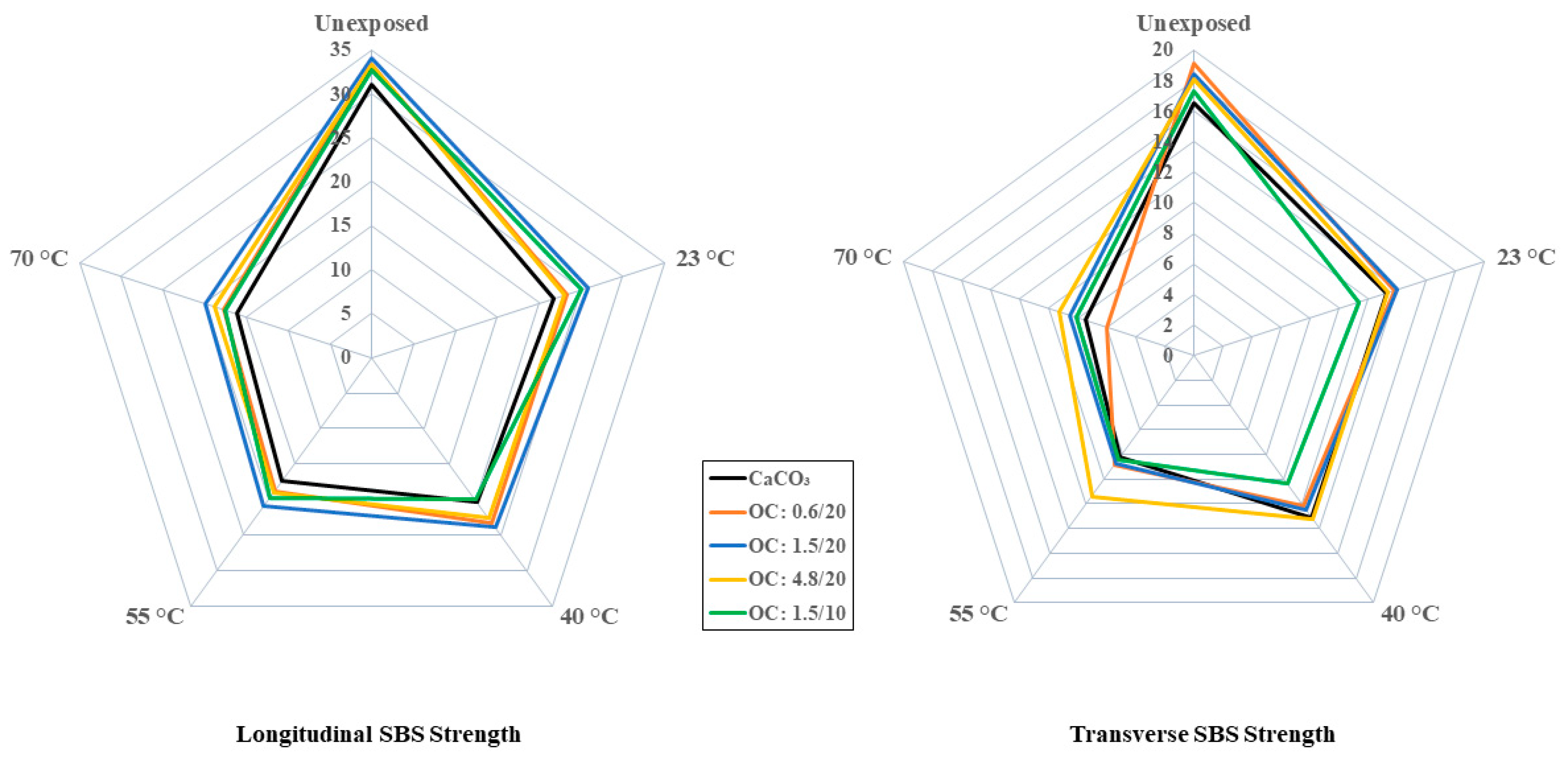
| Longitudinal SBS Strength | MPa | 31.04 [4.94] | 33.28 [1.83] | 34.04 [2.75] | 33.33 [1.72] | 32.73 [3.37] |
| Transverse SBS Strength | MPa | 16.53 [1.90] | 19.12 [0.30] | 18.44 [1.10] | 18.11 [0.98] | 17.26 [1.17] |
| Temperature of Immersion (°C) | Performance Characteristic | Filler Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3 | OC: 0.6/20 | OC: 1.5/20 | OC: 4.8/20 | OC: 1.5/10 | ||
| 70 | Tensile Strength | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| Tensile Modulus | 3 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| Flexural Strength | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 5 | |
| SBS Strength (L) | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| SBS Strength (T) | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karbhari, V.M. Influence of Montmorillonite Organoclay Fillers on Hygrothermal Response of Pultruded E-Glass/Vinylester Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152157
Karbhari VM. Influence of Montmorillonite Organoclay Fillers on Hygrothermal Response of Pultruded E-Glass/Vinylester Composites. Polymers. 2024; 16(15):2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152157
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarbhari, Vistasp M. 2024. "Influence of Montmorillonite Organoclay Fillers on Hygrothermal Response of Pultruded E-Glass/Vinylester Composites" Polymers 16, no. 15: 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152157
APA StyleKarbhari, V. M. (2024). Influence of Montmorillonite Organoclay Fillers on Hygrothermal Response of Pultruded E-Glass/Vinylester Composites. Polymers, 16(15), 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152157








