Effects of Polyethylene Terephthalate Particle Size on the Performance of Engineered Cementitious Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials and Mix Proportion
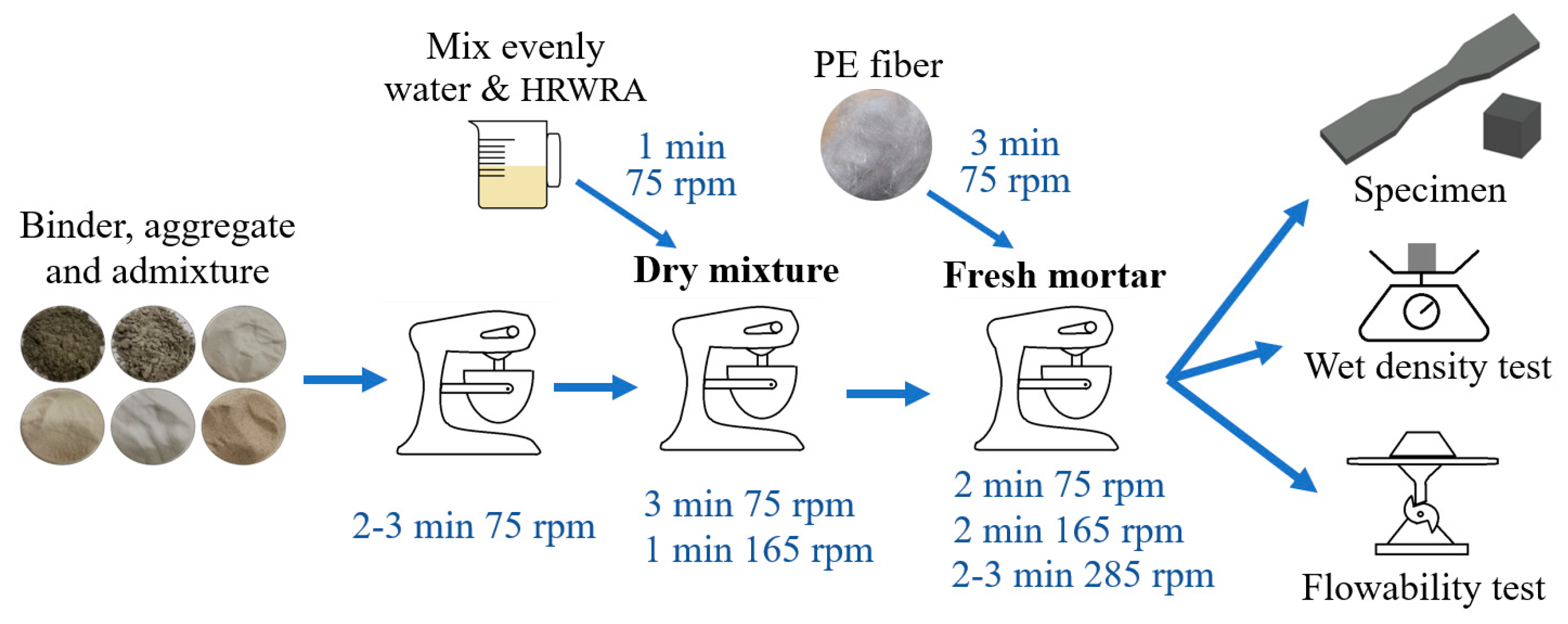
2.2. Mixing Process
3. Experimental Setup and Procedure
3.1. Flowability Test
3.2. Density Test
3.3. Compression Test
3.4. Tensile Test
3.5. SEM and EDS
4. Results and Discussion
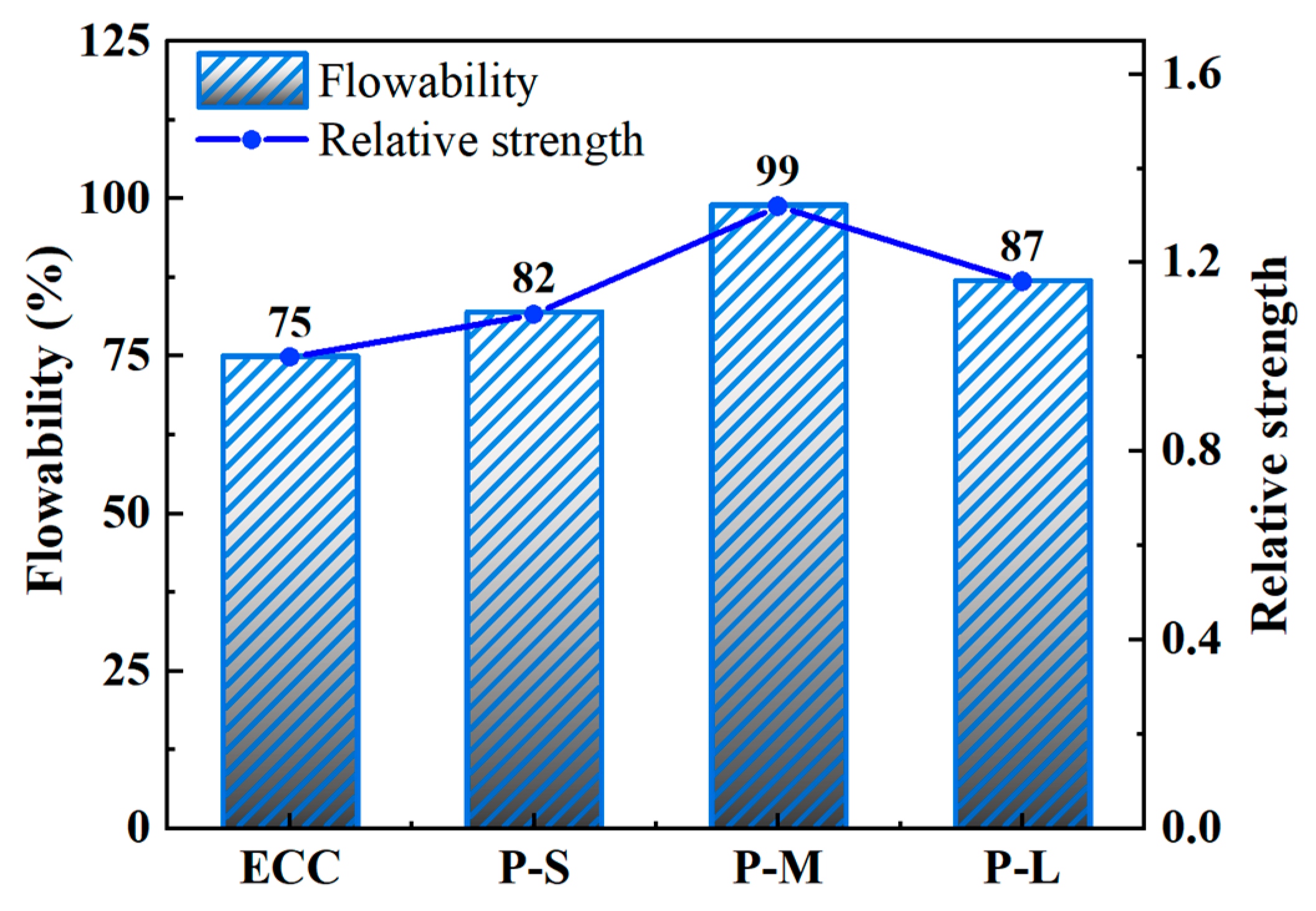
4.1. Flowability
4.2. Density
4.3. Compressive Behavior
4.3.1. Failure Mode
4.3.2. Compressive Strength
4.4. Tensile Behavior
4.4.1. Failure Mode
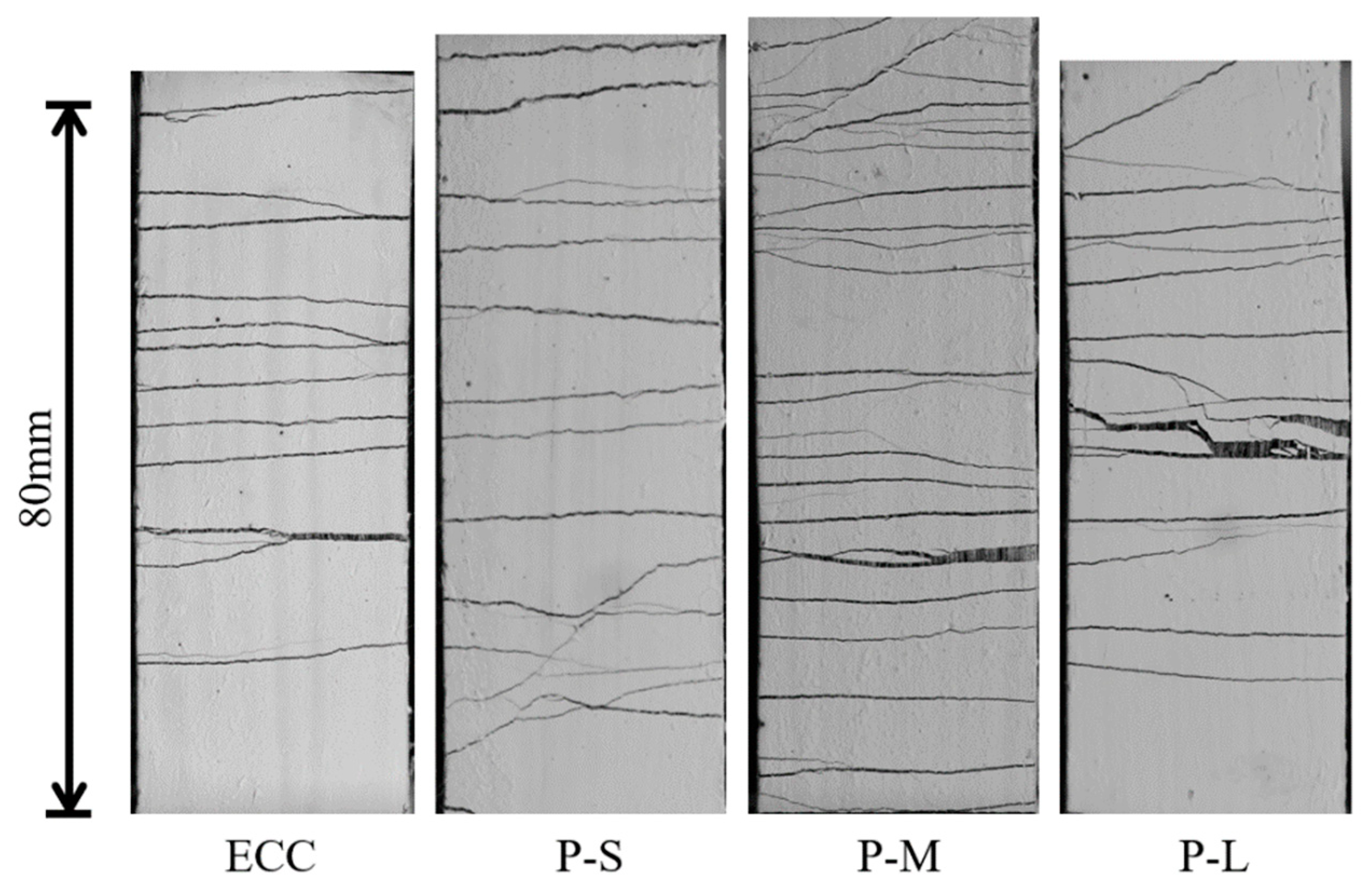
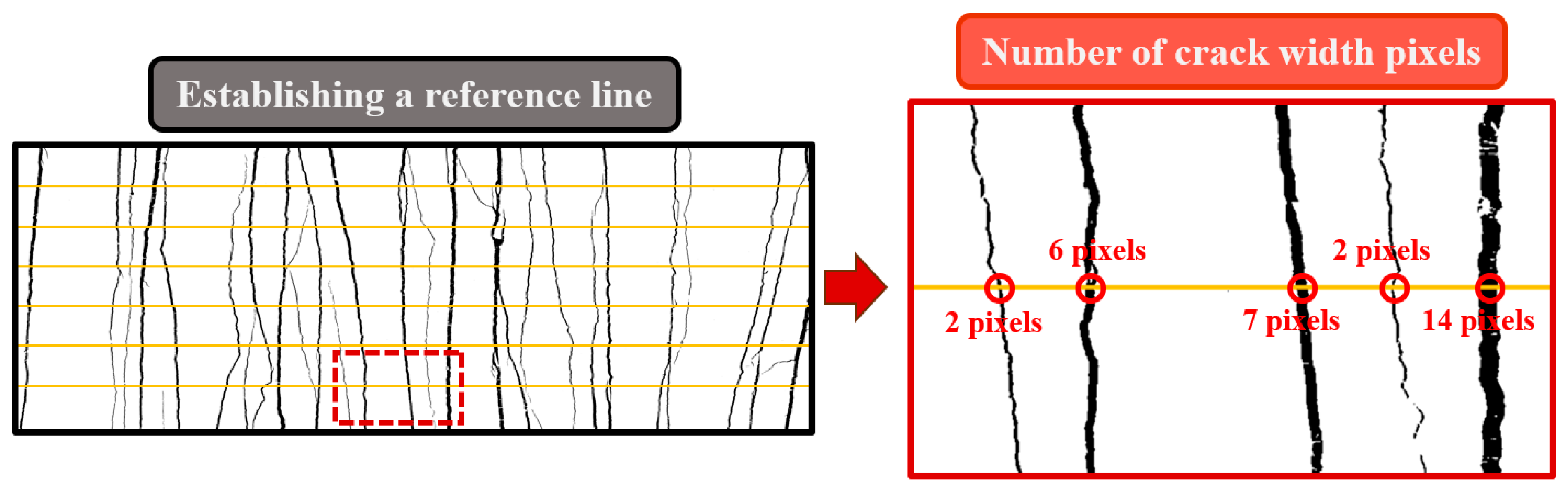
4.4.2. Crack Parameters
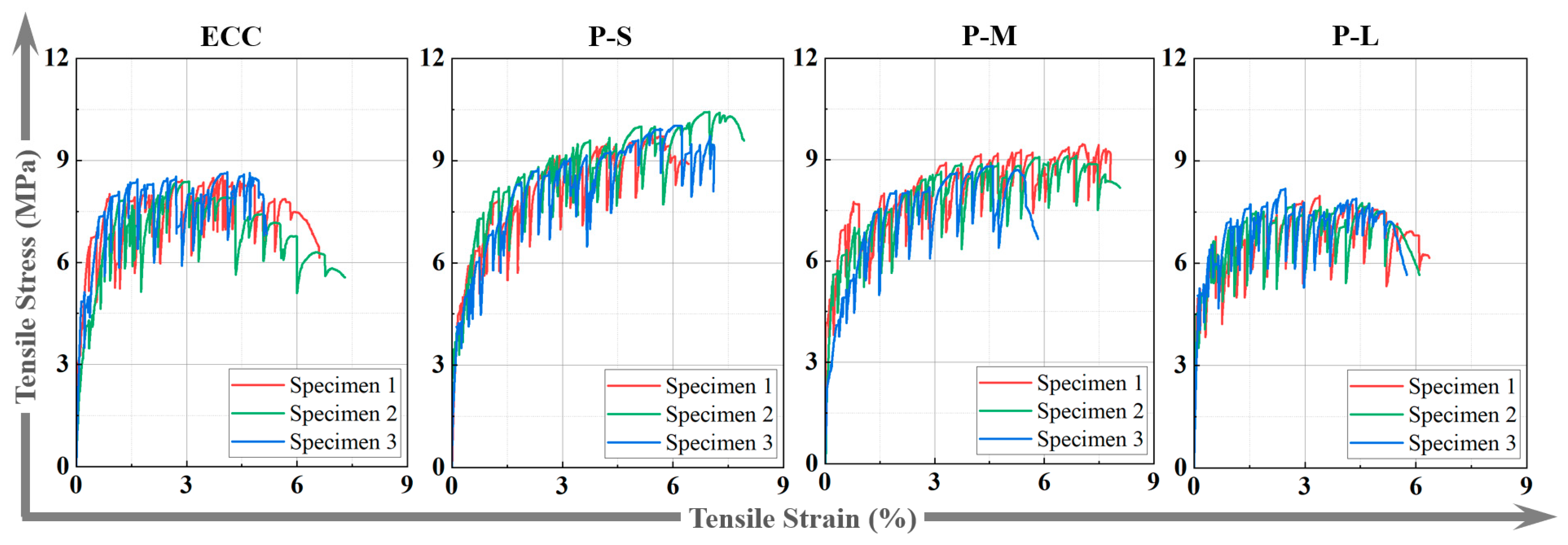
4.4.3. Tensile Stress–Strain Curves
4.4.4. Tensile Characteristic Parameters
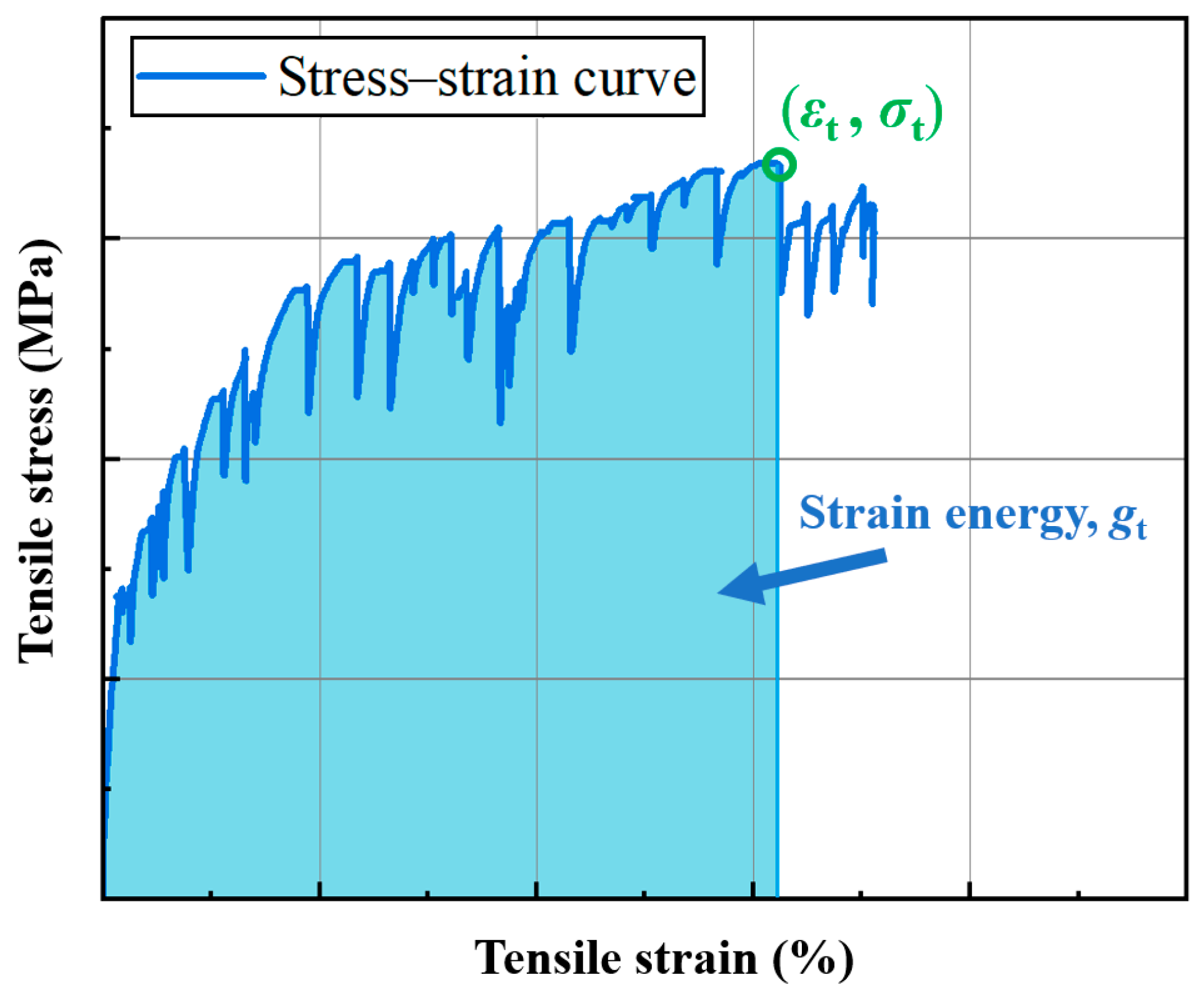
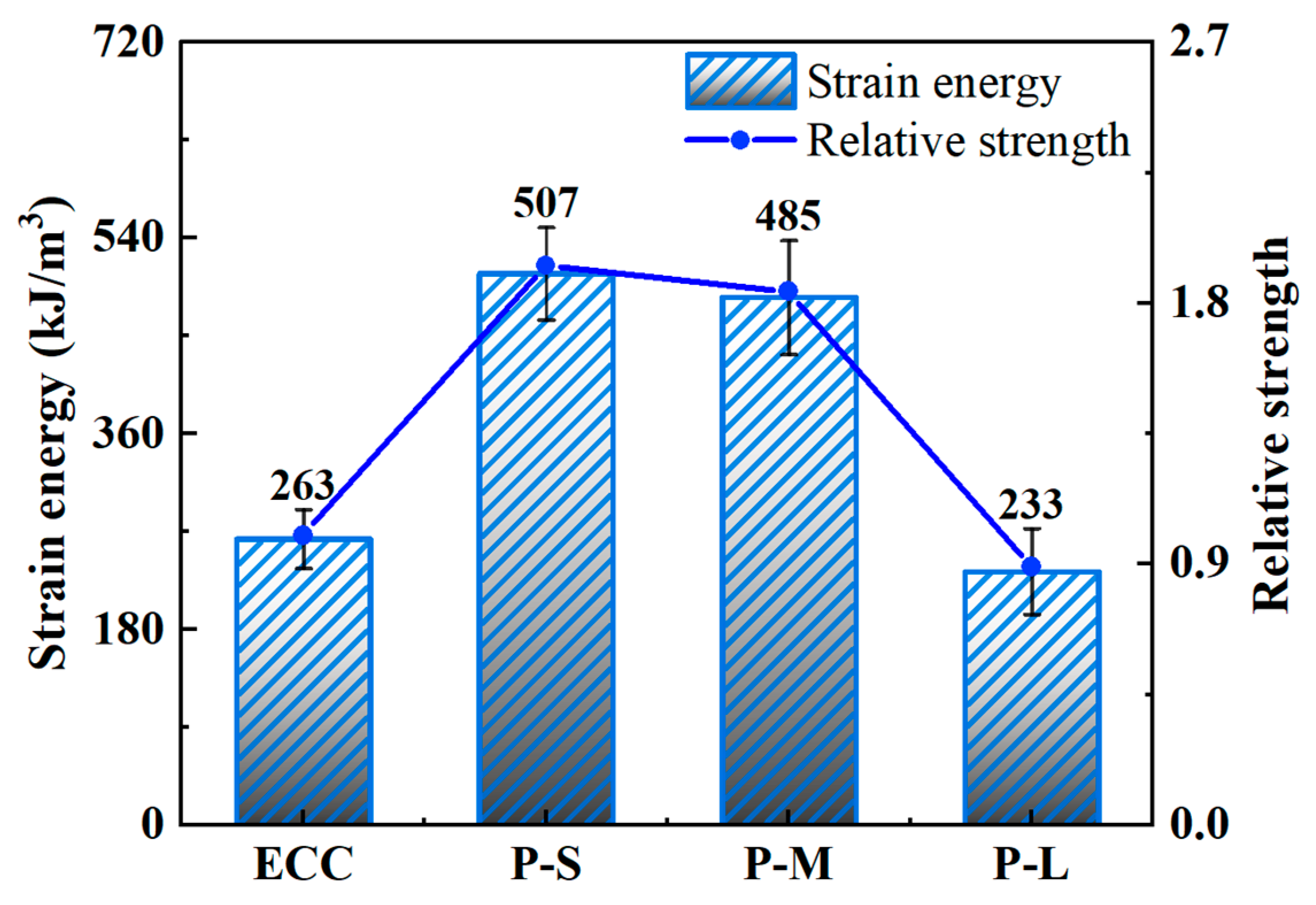
4.4.5. Strain Energy
4.5. Microstructure Analysis
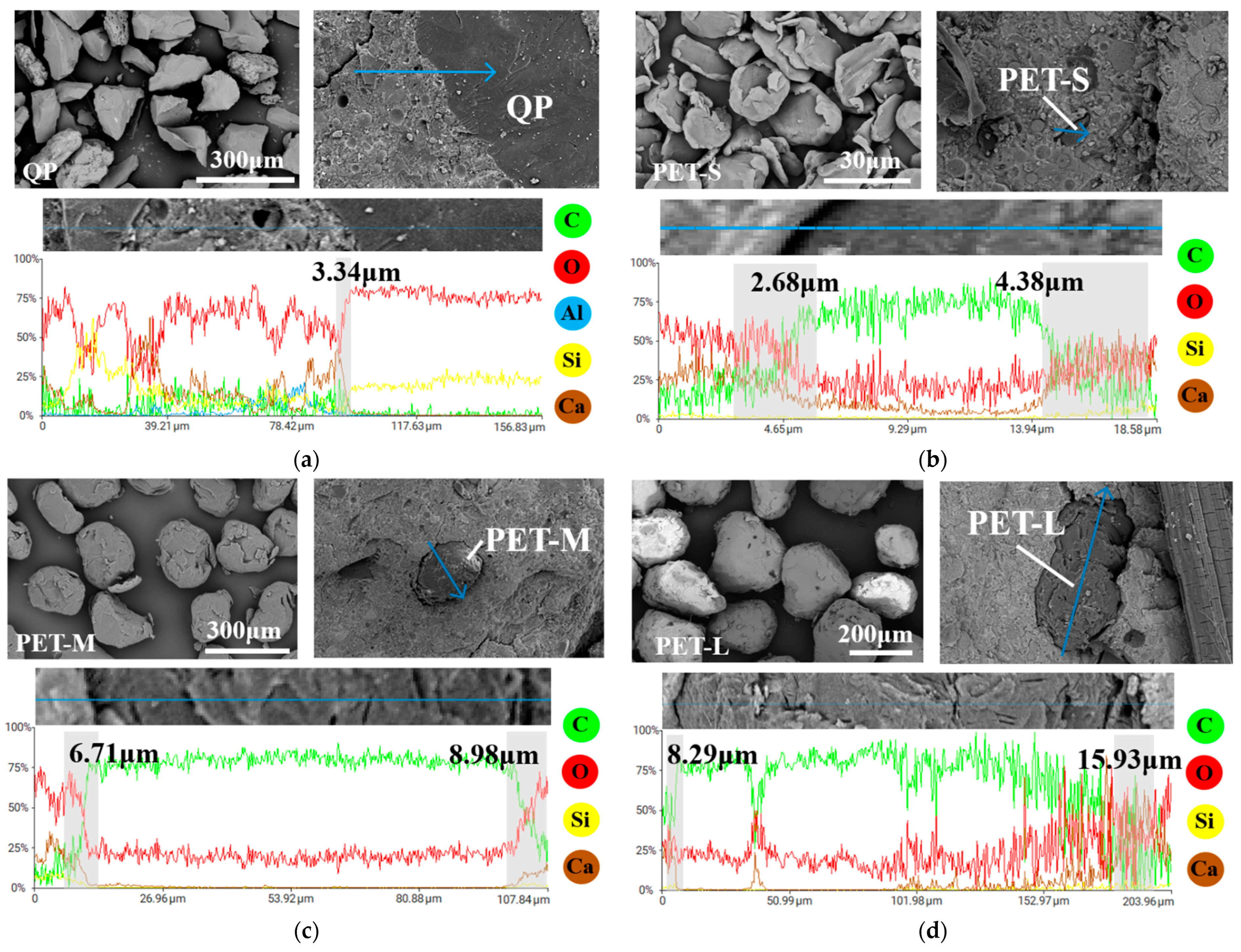
4.5.1. Interface Transition Zone Characterization
4.5.2. Microstructure
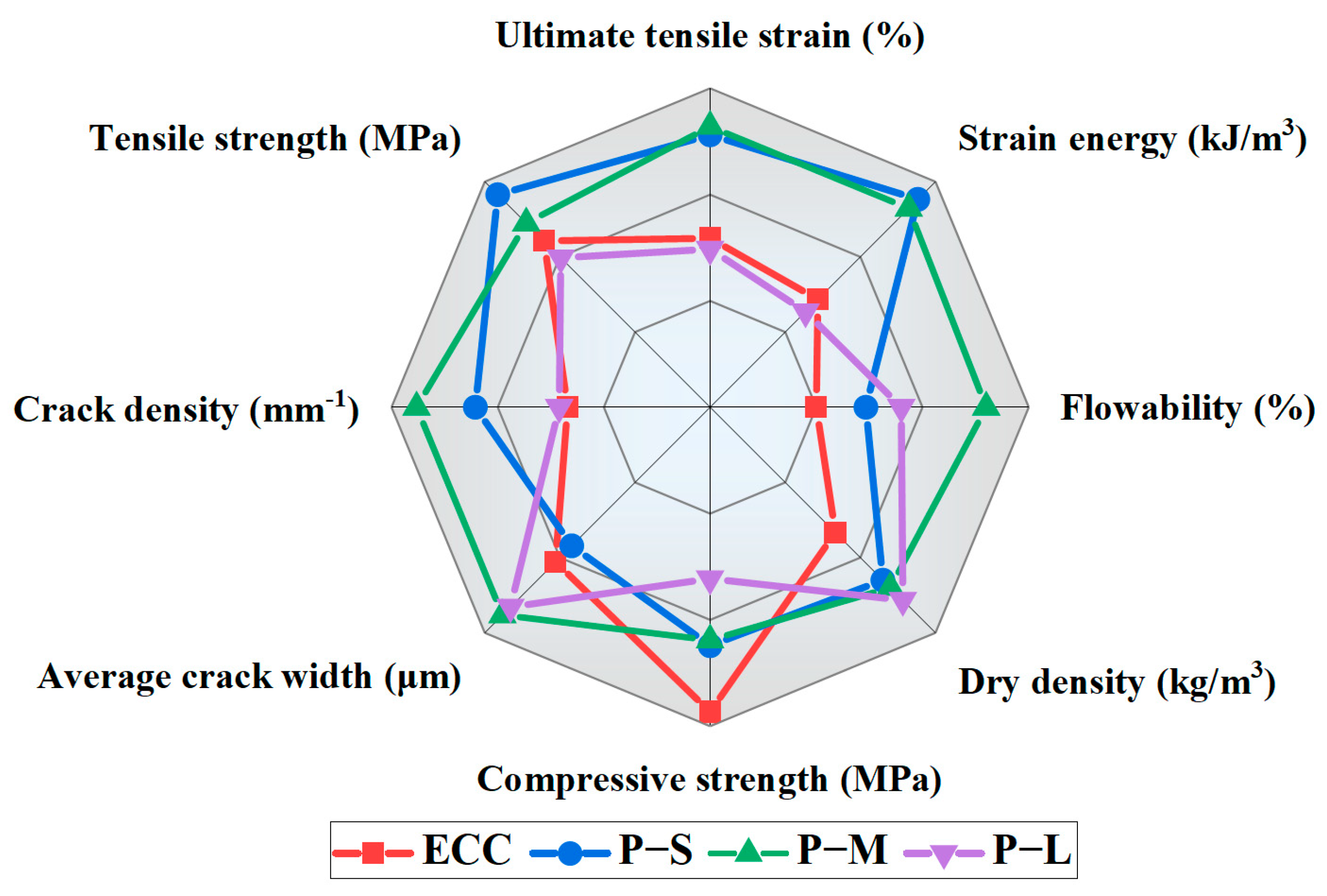
4.6. Comprehensive Performance Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The use of PET aggregates positively impacts the workability of ECC fresh paste, improving its processability and fiber dispersion. As the PET aggregate particle size increases, workability initially improves and then decreases. Among the samples, P-M showed the highest increase in workability, improving by 28.6% compared to the control group.
- (2)
- An appropriate increase in PET aggregate particle size enhances P-ECC’s crack control ability, resulting in reduced crack width and increased crack density. Compared to P-S, the P-M samples showed a 20.1% reduction in average crack width and a 10.7% increase in crack density. However, when the PET aggregate particle size is too large (P-L), the crack control ability weakens due to stress concentration.
- (3)
- Compared to ordinary ECC, the P-S and P-M samples showed improvements in tensile strength, ultimate tensile strain, and strain energy. P-S exhibited the highest increase in tensile strength and strain energy, with improvements of 18.1% and 92.8%, respectively. P-M contributed the highest increase in ultimate tensile strain, improving by 66.0%. In contrast, the P-L sample showed a significant decrease in tensile performance compared to the others.
- (4)
- On the micro level, the ITZ between PET aggregates and the cement matrix is wider than that of traditional quartz powder, and the ITZ widens as the PET aggregate particle size increases. This characteristic introduces defects into the ECC, where appropriately sized defects enhance the tensile strain capacity of P-S and P-M, while excessively large defects significantly reduce the performance of P-L.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; Huang, B.; Li, V.C.; Dai, J. High-strength high-ductility engineered/strain-hardening cementitious composites (ECC/SHCC) incorporating geopolymer fine aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C.; Bos, F.P.; Yu, K.; Mcgee, W.; Ng, T.Y.; Figueiredo, S.C.; Nefs, K.; Mechtcherine, V.; Nerella, V.N.; Pan, J.; et al. On the emergence of 3d printable engineered, strain hardening cementitious composites (ECC/SHCC). Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 132, 106038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C. Tailoring ecc for special attributes: A review. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2012, 6, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Luo, R.; Su, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, W. Coarse synthetic fibers (PP and POM) as a replacement to steel fibers in uhpc: Tensile behavior, environmental and economic assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C. Introduction to engineered cementitious composites (ECC). In Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC): Bendable Concrete for Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Zheng, D.; Pan, H.; Yang, J.; Lin, J.; Lai, H.; Wu, P.-Z.; Zhu, H.-Y. Strain hardening geopolymer composites with hybrid POM and UHMWPE fibers: Analysis of static mechanical properties, economic benefits, and environmental impact. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Liu, T.; Lu, D.; Han, X.; Sun, H.; Huang, J.; Ye, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y. Dynamic tensile properties of steel fiber reinforced polyethylene fiber-engineered/strain-hardening cementitious composites (PE-ECC/SHCC) at high strain rate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 143, 105234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yu, J.; Dong, F.; Ye, J. Effect of polyethylene fiber content on physical and mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Zhuo, K.; Chen, Z.; Guo, Y. High-strength and high-toughness alkali-activated composite materials: Optimizing mechanical properties through synergistic utilization of steel slag, ground granulated blast furnace slag, and fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 422, 135811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Song, Y.; Xie, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, B.; Zeng, J.; Wei, X. Static and dynamic mechanical behavior of engineered cementitious composites with PP and PVA fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xiong, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Su, Y. Effect of expansion agent and glass fiber on the dynamic splitting tensile properties of seawater–sea-sand concrete. Bulidings 2024, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H. Axial behavior of pre-damaged RC columns strengthened with CFRP textile grid-reinforced ECC matrix composites. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Ding, C.; Guo, L.; Chen, B.; Wang, A. Basic performances and potential research problems of strain hardening geopolymer composites: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 287, 123030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, C.; Li, S.; Lu, Y. Compressive performance and analytical modeling of early strength seawater sea sand engineered cementitious composites. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 90, 109282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.F.; Xia, L.P. Investigation of the behaviour of flexible and ductile ECC link slab reinforced with FRP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, J.; Ma, H.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, W.; Du, Y.; Huang, W.; Sun, C.; Zhu, Z. Investigation on interface fracture properties and nonlinear fracture model between ecc and concrete subjected to salt freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 119785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Pan, H.; Jiang, Z.; Lv, J.; Ruan, G.; Lai, H.; Lin, J.-X. Pseudo strain-hardening alkali-activated composites with up to 100 % rubber aggregate: Static mechanical properties analysis and constitutive model development. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 439, 137338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zheng, D.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Lao, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.-B.; Lan, X.-W. Development of high performance geopolymer concrete with waste rubber and recycle steel fiber: A study on compressive behavior, carbon emissions and economical performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 131988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, G.; Chen, G.M.; Xie, Z.H. Fracture behaviors of a new steel fiber reinforced recycled aggregate concrete with crumb rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, Q.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L. Static and fatigue performance of reinforced concrete beam strengthened with strain-hardening fiber-reinforced cementitious composite. Eng. Struct. 2019, 199, 109576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C.; Leung, C.K.Y. Steady-state and multiple cracking of short random fiber composites. J. Eng. Mech. 1992, 118, 2246–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, B.; Dai, J. Development of engineered cementitious composites (ECC) using artificial fine aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Shi, L.; Sun, D. Coral aggregate concrete: Numerical description of physical, chemical and morphological properties of coral aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 100, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pan, H.; Zhuo, K.; Su, J.; Xie, B.; Lin, J.; Guo, Y. Dynamic compressive behavior of environmentally friendly high-strength concrete: Experimental investigation and modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 427, 136259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Du, H. Efficient utilization of waste marine clay for fine aggregate to develop sustainable and cost-effective strain-hardening cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gong, G.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Huang, D.; Chen, Z.; Guo, M. Feasibility of incorporating recycled fine aggregate in high performance green lightweight engineered cementitious composites. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 280, 124445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, C.R.N. GDR. Engineered cementitious composites (ECC) with manufactured sand (M-sand) for pavement applications. Compos. Commun. 2023, 41, 101657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Chen, R.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, J. Relationship between fractal dimension and properties of engineered cementitious composites with different aggregates. Materials 2022, 15, 7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Ou, J. An economical ultra-high ductile engineered cementitious composite with large amount of coarse river sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Liu, H. The effects of particle sizes of expanded perlite on the mechanical properties and chloride penetration resistance of ECCS. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hesp, S.A.M. Effect of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fiber on the fracture resistance of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaoui, H.; Trabelsi, A.; Kammoun, Z.; Aouicha, B. Mechanical, physical, blast waves and ballistic impact resistance properties of a concrete incorporating thermally treated pet inclusions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.T.I.; Widiastuti, N.; Kusumawati, Y.; Jaafar, J. Utilization of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic bottle waste as membrane with several modifications for the removal of chromium ions in wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 74, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Fang, C.; Wang, D. A facile, alternative and sustainable feedstock for transparent polyurethane elastomers from chemical recycling waste pet in high-efficient way. Waste Manag. 2023, 155, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zuo, Z.; Tian, Q.; Xue, S.; Qiu, F.; Peng, X.; Zhang, T. Waste to treasure: A superwetting fiber membrane from waste pet plastic for water-in-oil emulsion separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, D.M.; Mendes, V.F.; Carvalho, V.R.; Nogueira, M.A.; de Carvalho, J.M.F.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Coating mortars produced with recycled pet aggregates: A technical, environmental, and socioeconomic approach applied to Brazilian social housing. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 83, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeshal, I.; Tayeh, B.A.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Mustafa Mohamed, A.; Alaskar, A. Use of recycled plastic as fine aggregate in cementitious composites: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Lyu, Q.; Zong, M.; Zhu, P. Effect of waste plastic fibers on the printability and mechanical properties of 3d-printed cement mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 83, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, N.; de Brito, J. Mechanical properties and abrasion behaviour of concrete containing shredded PET bottle waste as a partial substitution of natural aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçaözoğlu, S.; Atiş, C.D.; Akçaözoğlu, K. An investigation on the use of shredded waste pet bottles as aggregate in lightweight concrete. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.; Zinchenko, A. Design and synthesis of functional materials by chemical recycling of waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic: Opportunities and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 433, 139828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, F.K.; Ghataora, G.; Dirar, S.; Khan, M.I.; Zafar, I. Experimental study to investigate the engineering and durability performance of concrete using synthetic aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod Kumar, R.; Rupesh Kumar, D.D. Recycled plastic (HDPE) coarse aggregate manufacturing method and performance in concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 92, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigione, M. Recycling of pet bottles as fine aggregate in concrete. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangavar, M.E.; Lokuge, W.; Manalo, A.; Karunasena, W.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Development of sustainable concrete using recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) granules as fine aggregate. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 15, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, H.; Xiong, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zou, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, D.; Liu, F.; Ji, Y. Early mechanical performance of glass fibre-reinforced manufactured sand concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 83, 108440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Zhu, H.; Guo, M.; Shao, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Modeling for predicting triaxial mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete considering the recycled aggregate replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Sun, D. The durability of alkali-activated materials in comparison with ordinary portland cements and concretes: A review. Engineering 2020, 6, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobiszewska, M.; Bagcal, O.; Beycioğlu, A.; Goulias, D.; Köksal, F.; Płomiński, B.; Ürünveren, H. Utilization of rock dust as cement replacement in cement composites: An alternative approach to sustainable mortar and concrete productions. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lyu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, K.; Guo, L.; Sun, D. A gentle acid-wash and pre-coating treatment of coral aggregate to manufacture high-strength geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhan, P.; Narayana, H.; Darshan, N. Compressive strength studies of concrete with partial replacement of cement and fine aggregate with incinerated solid waste and recycled plastic waste. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, A.; Rawat, S.; Thakkar, S.; Dave, U.; Joshi, T. Influence on compressive strength of concrete by partial replacement of river sand with fly ash geopolymer sand. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J. A review on the influence of recycled plastic aggregate on the engineering properties of concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 79, 107787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.M.L.; Carneiro, E.P. Evaluation of pet waste aggregates in polymer mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbin, I.M.; Dezhampanah, S.; Charkhtab, S.; Mehdipour, S.; Shahvareh, I.; Ebrahimi, M.; Pournasir, A.; Pourghorban, H. Life cycle assessment and mechanical properties of high strength steel fiber reinforced concrete containing waste pet bottle. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 337, 127553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.Y.; Dheilly, R.M.; Queneudec, M. Valorization of post-consumer waste plastic in cementitious concrete composites. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhruddin Irmawaty, R.; Djamaluddin, R. Flexural behavior of monolith and hybrid concrete beams produced through the partial replacement of coarse aggregate with pet waste. Structures 2022, 43, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangavar, M.E.; Lokuge, W.; Manalo, A.; Karunasena, W.; Frigione, M. Investigation on the properties of concrete with recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) granules as fine aggregate replacement. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.F. Assessment of waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as sand in sustainable geopolymer concrete: Non-destructive tests investigation. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Civil Engineering, Da Nang, Vietnam, 7–9 December 2024; Springer: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, G.; Pavia, S. Physical properties and microstructure of plastic aggregate mortars made with acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), polycarbonate (PC), polyoxymethylene (POM) and ABS/PC blend waste. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1437-20; Standard Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM C138/C138M-23; Density (Unit Weight), Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- ASTM C109/C109M-21; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (using 2-in. Or [50 mm] Cube Specimens). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Yokota, H.; Rokugo, K.; Sakata, N. JSCE Recommendations for design and construction of high performance fiber reinforced cement composite with multiple fine cracks. In High Performance Fiber Reinforced Cement Composites; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, V.C. Processing of engineered cementitious composites (ECC). In Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC): Bendable Concrete for Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, N.; de Brito, J. Use of plastic waste as aggregate in cement mortar and concrete preparation: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.G.; Babu, D.S. Behaviour of lightweight expanded polystyrene concrete containing silica fume. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ/T12-2019; Technical Standard for Application of Lightweight Aggregate Concrete. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Kunthawatwong, R.; Sylisomchanh, L.; Pangdaeng, S.; Wongsa, A.; Sata, V.; Sukontasukkul, P.; Chindaprasirt, P. Recycled non-biodegradable polyethylene terephthalate waste as fine aggregate in fly ash geopolymer and cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C. Mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites (ECC). In Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC): Bendable Concrete for Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]









| Cementitious Materials | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | SO3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | TiO2 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 67.8 | 16.5 | 3.94 | 4.55 | 4.51 | 1.04 | 0.26 | 1.4 |
| FA | 4.88 | 51.9 | 31.1 | 1.07 | 4.97 | 0.85 | 1.38 | 3.85 |
| Length (mm) | Diameter (μm) | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Strength (MPa) | Density (g/cm3) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 24 | 116 | 3000 | 0.97 | 3 |
| Aggregate Type | D50 (μm) | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Density (g/cm3) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QP | 120 | 76 | 2.68 | - |
| PET-S | 21 | 4 | 1.38 | 9.5 |
| PET-M | 107 | |||
| PET-L | 244 |
| Group | Cement | FA | QP | PET Aggregate | Water | HRWRA | PE | VMA | DF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECC | 937 | 401 | 401 | 0 | 335 | 5.4 | 19.4 | 0.21 | 1.61 |
| P-S | 341 | 31.4 | |||||||
| P-M | |||||||||
| P-L |
| Group | Wet Density (kg/m3) | Dry Density (kg/m3) | Density Difference (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECC | 2118 | 1940 | 178 |
| P-S | 2096 | 1921 | 175 |
| P-M | 2097 | 1918 | 179 |
| P-L | 2097 | 1913 | 184 |
| Group | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Standard Deviation (MPa) | Relative Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECC | 98.2 | 2.0 | 1.00 |
| P-S | 89.9 | 1.7 | 0.92 |
| P-M | 89.2 | 0.9 | 0.91 |
| P-L | 81.5 | 1.3 | 0.83 |
| Group | Average Crack Width (μm) | Crack Density (mm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| ECC | 204 (11) | 0.17 (0.02) |
| P-S | 214 (7) | 0.28 (0.03) |
| P-M | 171 (4) | 0.35 (0.04) |
| P-L | 176 (9) | 0.18 (0.02) |
| Group | Cracking Strength σtc (MPa) | Cracking Strain εtc (%) | Tensile Strength σt (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strain εt (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECC | 5.29 (1.16) a | 0.24 (0.10) b | 8.53 (0.12) c | 3.71 (0.40) b |
| P-S | 4.10 (0.64) ab | 0.15 (0.08) b | 10.07 (0.37) a | 5.98 (0.63) a |
| P-M | 3.37 (1.04) b | 0.11 (0.06) b | 9.12 (0.32) b | 6.16 (0.88) a |
| P-L | 3.42 (0.34) c | 0.15 (0.02) a | 7.97 (0.21) d | 3.47 (1.07) b |
| Group | Strain Energy, gt (kJ/m3) | Standard Deviation (kJ/m3) | Relative Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECC | 263 | 54 | 1.00 |
| P-S | 507 | 85 | 1.93 |
| P-M | 485 | 105 | 1.84 |
| P-L | 233 | 79 | 0.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Lin, J. Effects of Polyethylene Terephthalate Particle Size on the Performance of Engineered Cementitious Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152143
Chen S, Liu R, Liu L, Huang X, Lin J. Effects of Polyethylene Terephthalate Particle Size on the Performance of Engineered Cementitious Composites. Polymers. 2024; 16(15):2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152143
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shijia, Runan Liu, Liuyi Liu, Xinying Huang, and Jiaxiang Lin. 2024. "Effects of Polyethylene Terephthalate Particle Size on the Performance of Engineered Cementitious Composites" Polymers 16, no. 15: 2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152143
APA StyleChen, S., Liu, R., Liu, L., Huang, X., & Lin, J. (2024). Effects of Polyethylene Terephthalate Particle Size on the Performance of Engineered Cementitious Composites. Polymers, 16(15), 2143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152143







