Ecotoxicity Assessment of α-Amino Acid-Derived Polyamidoamines Using Zebrafish as a Vertebrate Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
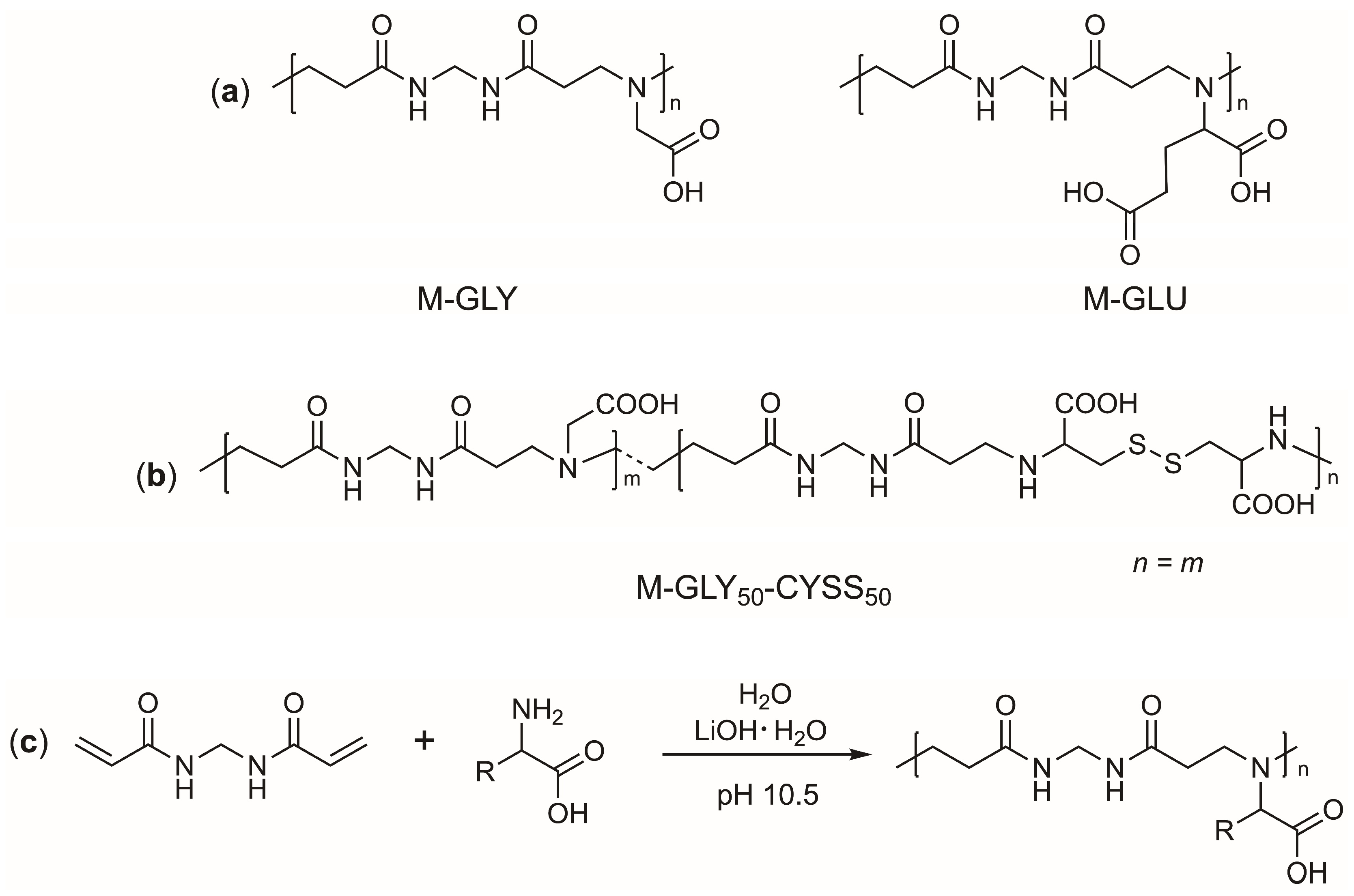
2.2. Synthesis of PAAs
2.3. Biological Experiments
2.3.1. Ethics Statement
2.3.2. Zebrafish Maintenance and Egg Collection
2.3.3. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test
2.3.4. Transgenic Tg(fli1:EGFP) Zebrafish Embryos for Angiogenesis Assessment
2.3.5. Transgenic Tg(Bmp:EGFP) Zebrafish Embryos for Somite Segmentation Assessment
2.3.6. Locomotor Behavior Assessment with the Light/Dark Locomotion Test
2.3.7. Touch-Evoked Response Test
2.3.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polyamidoamines (PAAs): Synthesis and Ionic Species Distribution
3.2. Timeline of the Experiments Carried Out on Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to PAAs
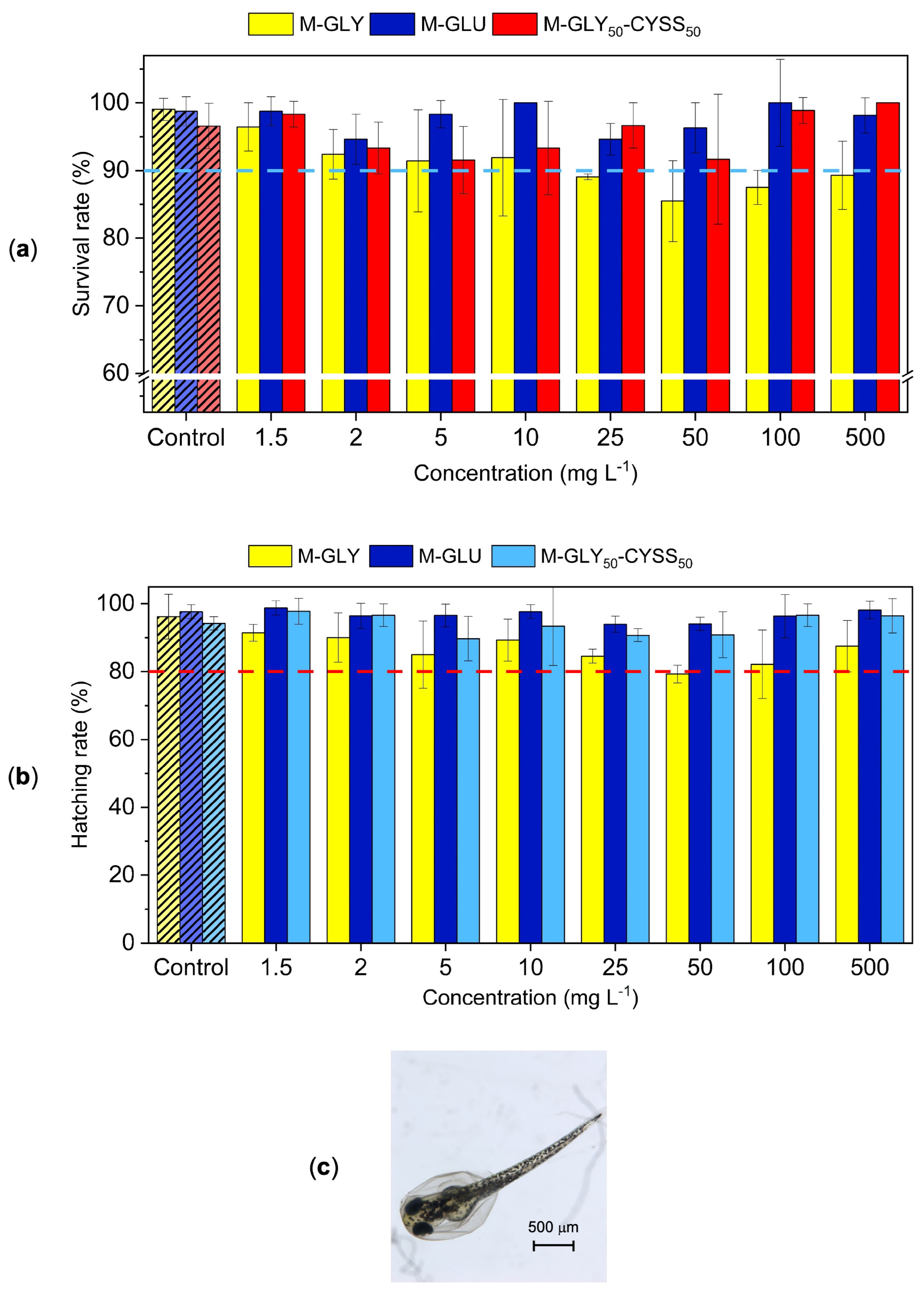
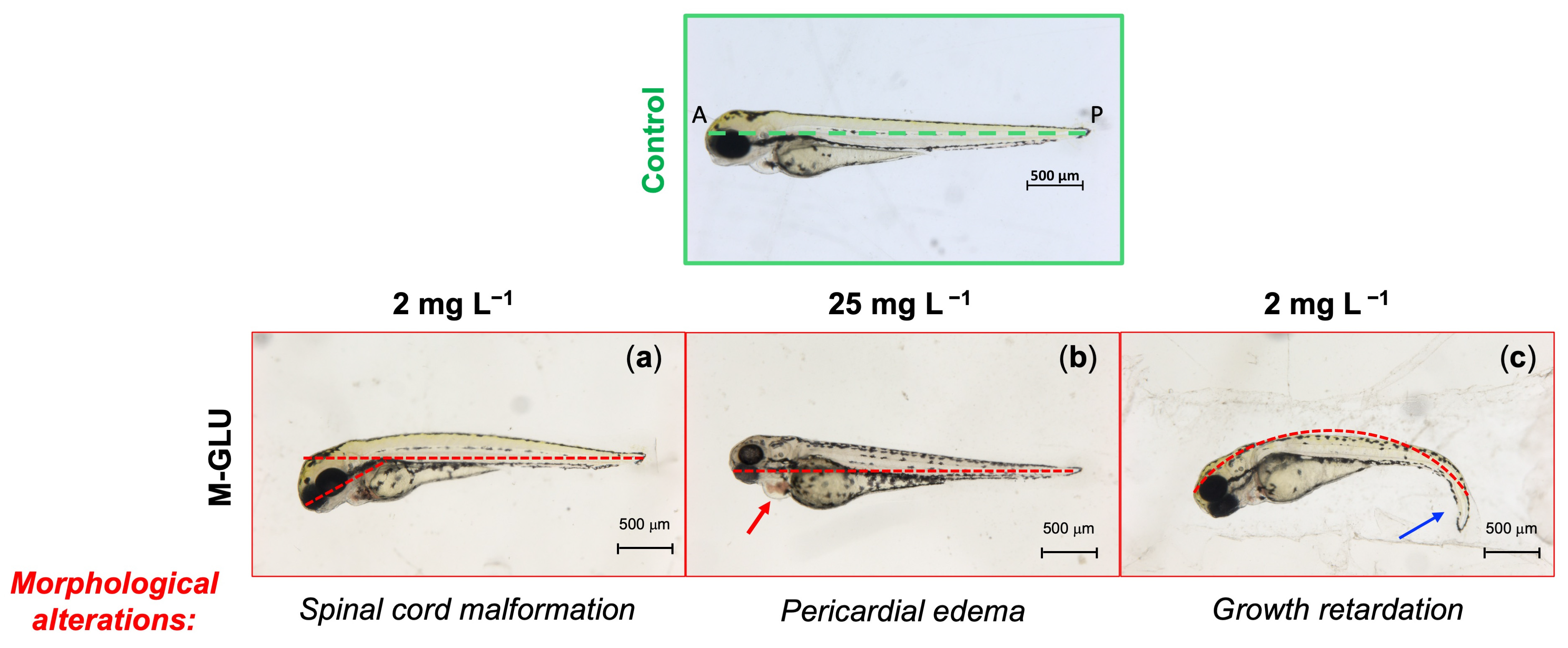
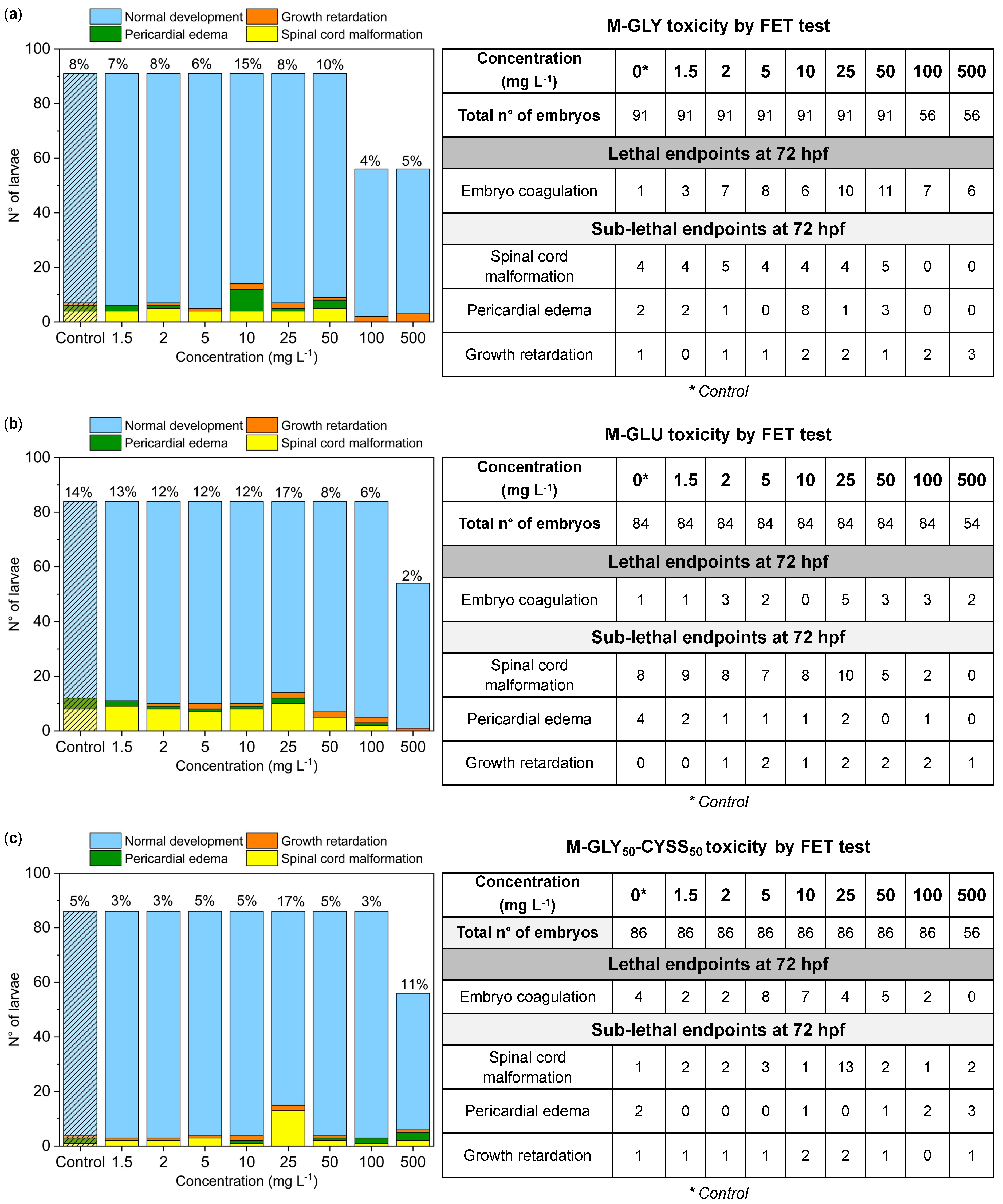
3.3. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test
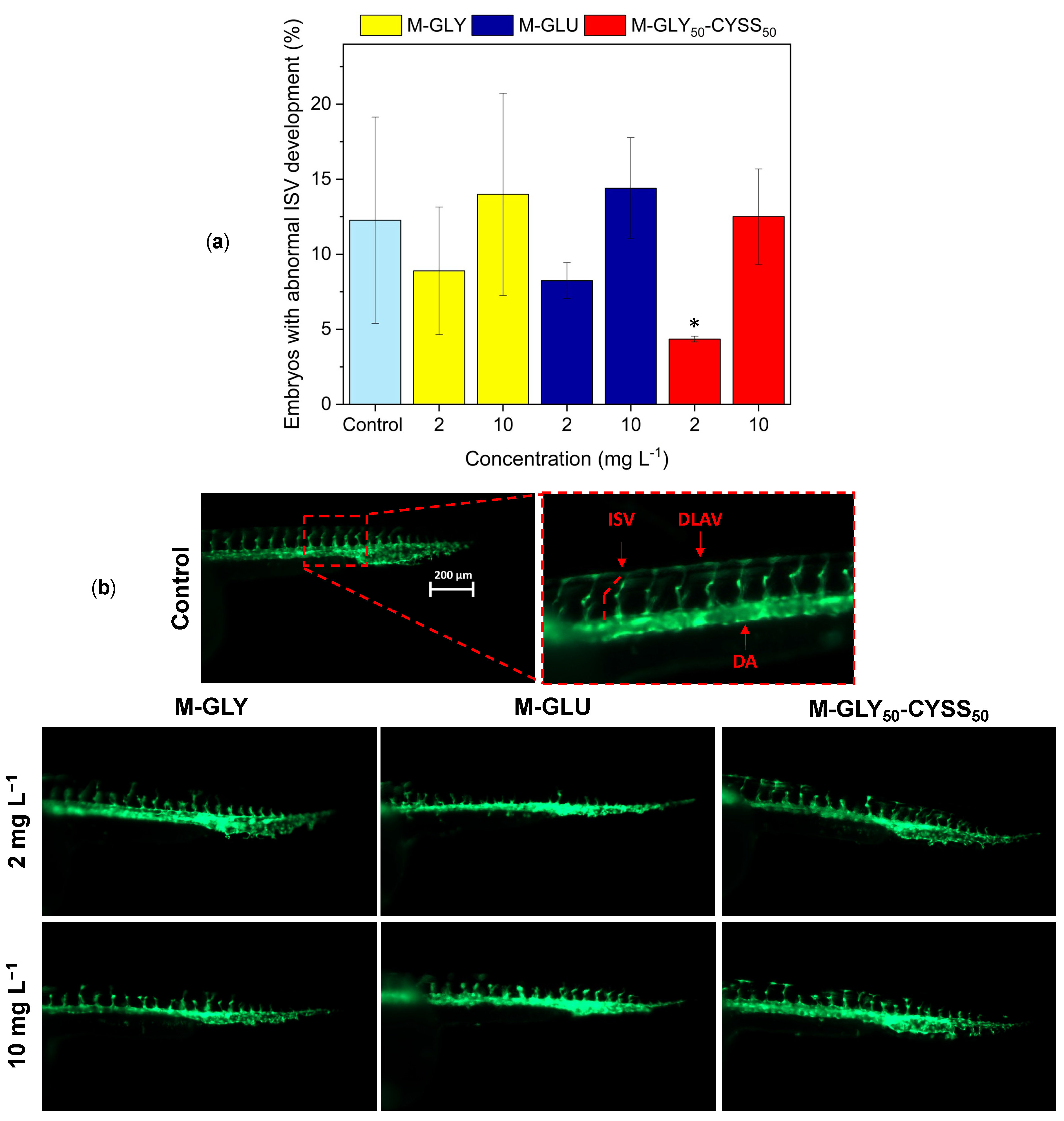
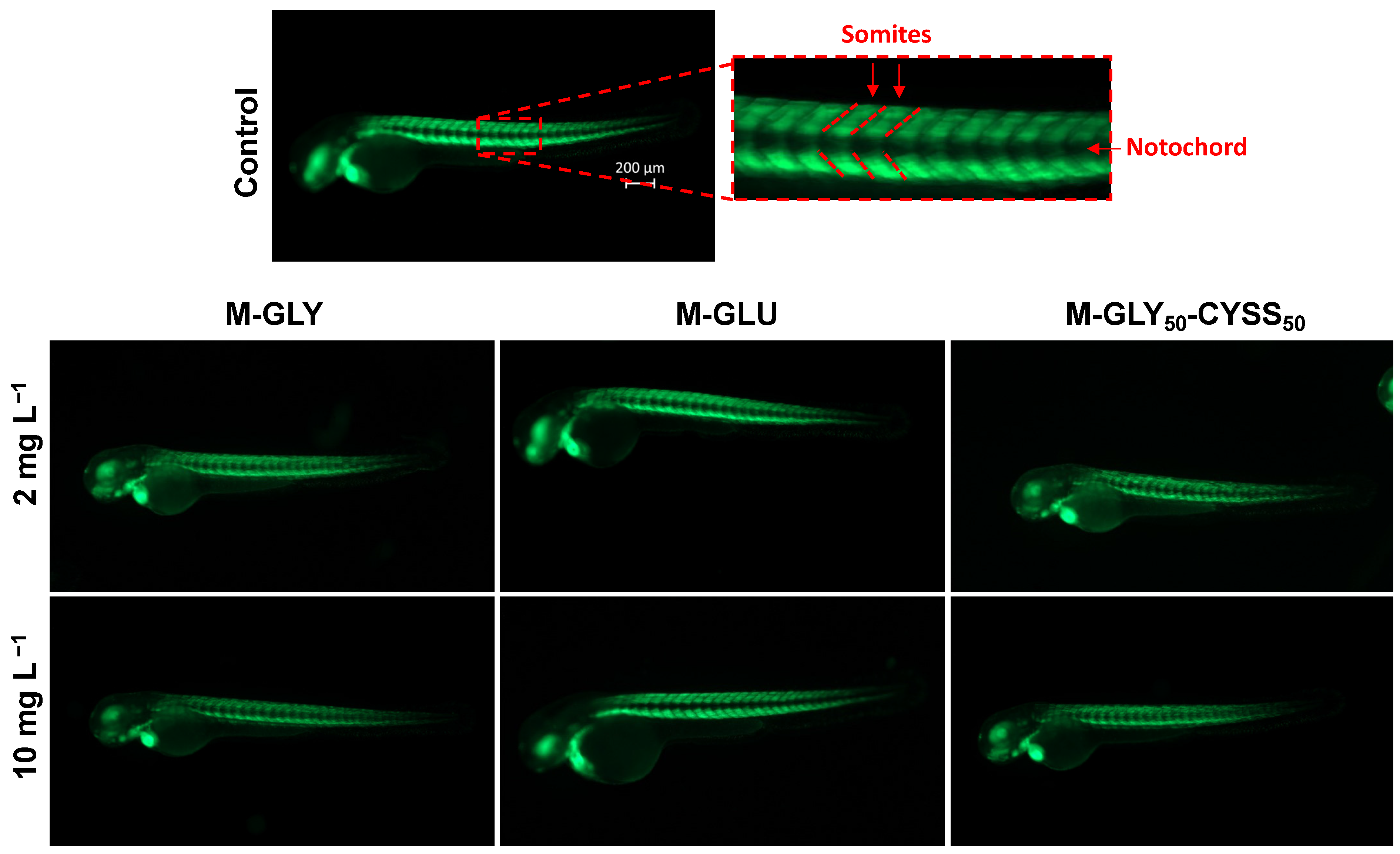
3.4. Analysis of Microscopic Malformations Using Transgenic Zebrafish Lines
3.4.1. Fluorescent Tg(fli1:EGFP) Zebrafish Lines for the Assessment of the Angiogenesis Process during Embryonic Development
3.4.2. Fluorescent Tg(Bmp:EGFP) Zebrafish Lines for the Assessment of Somite Segmentation
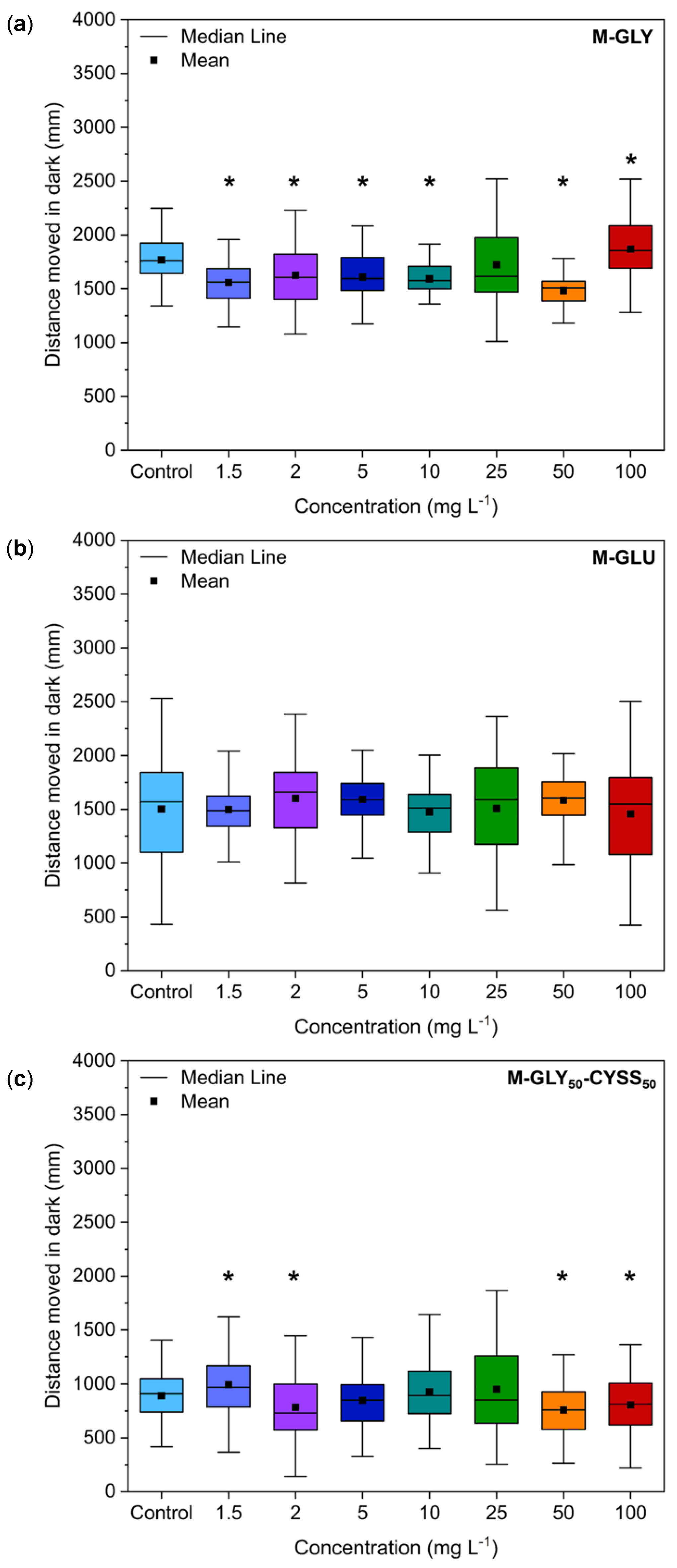
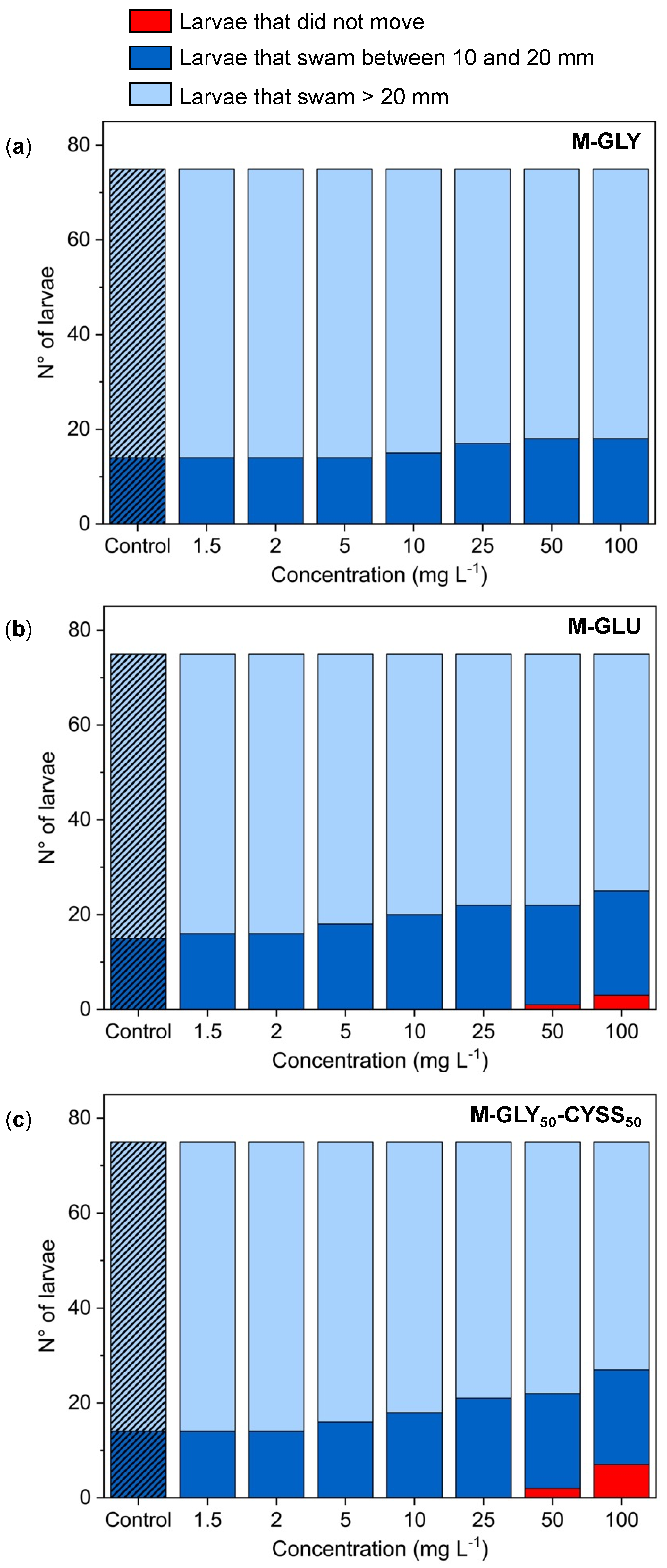
3.5. Sensory–Motor Tests
3.5.1. Locomotor Behavior Assessment Using the Light/Dark Locomotion Test
3.5.2. Touch-Evoked Response Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| PAA | Polyamidoamine. |
| REACH | Regulation, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals. |
| M | N,N′-Methylenebisacrylamide. |
| M-GLY | M-glycine-derived polyamidoamine. |
| M-CYSS | M-cystine-derived polyamidoamine. |
| M-GLY50-CYSS50 | M-glycine-cystine-derived polyamidoamine. |
| M-GLU | M-glutamic acid-derived polyamidoamine. |
| EGFP | Enhanced green fluorescent protein. |
| Bmp | Bone morphogenetic protein. |
| Fli1 | Friend leukemia integration 1 transcription factor. |
| Tg(fli1:EGFP) | Transgenic zebrafish line with the endothelial marker fli1 driving EGFP. |
| Tg(Bmp:EGFP) | Transgenic zebrafish line with the bmp marker driving EGFP. |
| Hpf | Hours post-fertilization. |
| OECD | Organization for economic co-operation and development. |
| LC50 | 50% lethal concentration. |
| FET | Fish embryo acute toxicity. |
| ISV | Intersegmental vessel. |
| DLAV | Dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel. |
| DA | Dorsal aorta. |
References
- Ferruti, P. Poly(Amidoamine)s: Past, Present, and Perspectives. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 2319–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arioli, M.; Manfredi, A.; Alongi, J.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E. Highlight on the Mechanism of Linear Polyamidoamine Degradation in Water. Polymers 2020, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, N.; Chiellini, F.; Bartoli, C.; Gazzarri, M.; Laus, M.; Antonioli, D.; Griffiths, P.; Manfredi, A.; Ranucci, E.; Ferruti, P. RGD-Mimic Polyamidoamine–Montmorillonite Composites with Tunable Stiffness as Scaffolds for Bone Tissue-Engineering Applications. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Primo, L.; Sessa, R.; Chiaverina, G.; di Blasio, L.; Alongi, J.; Manfredi, A.; Ranucci, E.; Ferruti, P. The AGMA1 Polyamidoamine Mediates the Efficient Delivery of SiRNA. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruti, P.; Alongi, J.; Barabani, E.; Manfredi, A.; Ranucci, E. Silk/Polyamidoamine Membranes for Removing Chromium VI from Water. Polymers 2023, 15, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Ferruti, P.; Manfredi, A.; Carosio, F.; Feng, Z.; Hakkarainen, M.; Ranucci, E. Superior Flame Retardancy of Cotton by Synergetic Effect of Cellulose-Derived Nano-Graphene Oxide Carbon Dots and Disulphide-Containing Polyamidoamines. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2019, 169, 108993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Carosio, F.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E.; Alongi, J. Linear Polyamidoamines as Novel Biocompatible Phosphorus-Free Surface-Confined Intumescent Flame Retardants for Cotton Fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2018, 151, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, C.; Alongi, J.; Beduini, A.; Borsacchi, S.; Calucci, L.; Carosio, F.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E. The Thermo-Oxidative Behavior of Cotton Coated with an Intumescent Flame Retardant Glycine-Derived Polyamidoamine: A Multi-Technique Study. Polymers 2021, 13, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadajji, V.G.; Betageri, G.V. Water Soluble Polymers for Pharmaceutical Applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1972–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julinová, M.; Vaňharová, L.; Jurča, M. Water-Soluble Polymeric Xenobiotics—Polyvinyl Alcohol and Polyvinylpyrrolidon—And Potential Solutions to Environmental Issues: A Brief Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission; Bougas, K.; Corden, C.; Crookes, M.; Federici, G.; Fisk, P. Scientific and Technical Support for the Development of Criteria to Identify and Group Polymers for Registration/Evaluation under REACH and Their Impact Assessment: Final Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020; ISBN 9789276207795. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, G.J.; Miller, W.P. Polyacrylamide Adsorption and Aggregate Stability. Soil Tillage Res. 1999, 51, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argillier, J.F.; Audibert, A.; Lecourtier, J.; Moan, M.; Rousseau, L. Solution and Adsorption Properties of Hydrophobically Associating Water-Soluble Polyacrylamides. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 113, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, K.J.; Arp, H.P.H.; MacLeod, M.; Wang, Z. Assessing and Managing Environmental Hazards of Polymers: Historical Development, Science Advances and Policy Options. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 25, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Research Progress of Zebrafish Model in Aquatic Ecotoxicology. Water 2023, 15, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, S.; Otten, C.; Abdelilah-Seyfried, S. Asymmetric Involution of the Myocardial Field Drives Heart Tube Formation in Zebrafish. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-N.; van Eeden, F.; Warren, K.S.; Chin, A.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C.; Haffter, P.; Fishman, M.C. Left-right pattern of cardiac BMP4 may drive asymmetry of the heart in zebrafish. Development 1997, 4382, 4373–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bressan, M.; Hassel, D.; Huisken, J.; Staudt, D.; Kikuchi, K.; Poss, K.D.; Mikawa, T.; Stainier, D.Y.R. A Dual Role for ErbB2 Signaling in Cardiac Trabeculation. Development 2010, 137, 3867–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, L.; Hawkey, A.B.; Wells, C.N.; Drastal, M.; Odamah, K.A.; Behl, M.; Levin, E.D. Developmental Exposure to Low Concentrations of Organophosphate Flame Retardants Causes Life-Long Behavioral Alterations in Zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 165, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usenko, C.Y.; Abel, E.L.; Hopkins, A.; Martinez, G.; Tijerina, J.; Kudela, M.; Norris, N.; Joudeh, L.; Bruce, E.D. Evaluation of Common Use Brominated Flame Retardant (BFR) Toxicity Using a Zebrafish Embryo Model. Toxics 2016, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Shi, X.; Luo, C.; Huang, W.; Lin, H.; Peng, J.; Tan, W.; Wu, K. Neurodevelopmental Toxicity of Organophosphate Flame Retardant Triphenyl Phosphate (TPhP) on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) at Different Life Stages. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Nigro, L.; Sbarberi, R.; Della Torre, C.; Magni, S. To Be or Not to Be Plastics? Protein Modulation and Biochemical Effects in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Three Water-Soluble Polymers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beduini, A.; Carosio, F.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E.; Alongi, J. Polyamidoamines Derived from Natural α-Amino Acids as Effective Flame Retardants for Cotton. Polymers 2021, 13, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, N.D.; Weinstein, B.M. In Vivo Imaging of Embryonic Vascular Development Using Transgenic Zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2002, 248, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, S.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Developmental Toxicity of Fipronil in Early Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Larvae: Disrupted Vascular Formation with Angiogenic Failure and Inhibited Neurogenesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collery, R.F.; Link, B.A. Dynamic Smad-Mediated BMP Signaling Revealed through Transgenic Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 2011, 240, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, E.; Vettori, A.; Porazzi, P.; Schiavone, M.; Rampazzo, E.; Casari, A.; Ek, O.; Facchinello, N.; Astone, M.; Zancan, I.; et al. Generation and Application of Signaling Pathway Reporter Lines in Zebrafish. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2013, 288, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizioli, D.; Zanella, I.; Mignani, L.; Degli Antoni, M.; Castelli, F.; Quiros-Roldan, E. Cabotegravir Exposure of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos Impacts on Neurodevelopment and Behavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Organization for economic co-operation and development Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Guidel. Test. Chem. 2004, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zizioli, D.; Ferretti, S.; Mignani, L.; Castelli, F.; Tiecco, G.; Zanella, I.; Quiros-Roldan, E. Developmental Safety of Nirmatrelvir in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Birth Defects Res. 2023, 115, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsignorio, D.; Perego, L.; Del Giacco, L.; Cotelli, F. Structure and Macromolecular Composition of the Zebrafish Egg Chorion. Zygote 1996, 4, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodewein, L.; Schmelter, F.; Di Fiore, S.; Hollert, H.; Fischer, R.; Fenske, M. Differences in Toxicity of Anionic and Cationic PAMAM and PPI Dendrimers in Zebrafish Embryos and Cancer Cell Lines. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 305, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busquet, F.; Strecker, R.; Rawlings, J.M.; Belanger, S.E.; Braunbeck, T.; Carr, G.J.; Cenijn, P.; Fochtman, P.; Gourmelon, A.; Hübler, N.; et al. OECD Validation Study to Assess Intra- and Inter-Laboratory Reproducibility of the Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test for Acute Aquatic Toxicity Testing. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelka, K.E.; Henn, K.; Keck, A.; Sapel, B.; Braunbeck, T. Size Does Matter—Determination of the Critical Molecular Size for the Uptake of Chemicals across the Chorion of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 185, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobanska, M.; Scholz, S.; Nyman, A.M.; Cesnaitis, R.; Gutierrez Alonso, S.; Klüver, N.; Kühne, R.; Tyle, H.; de Knecht, J.; Dang, Z.; et al. Applicability of the Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test (OECD 236) in the Regulatory Context of Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 5th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Basnet, R.M.; Zizioli, D.; Taweedet, S.; Finazzi, D.; Memo, M. Zebrafish Larvae as a Behavioral Model in Neuropharmacology. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walz, W. Zebrafish Protocols for Neurobehavioral Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; ISBN 9781607618829. [Google Scholar]
- Beduini, A.; Carosio, F.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E.; Alongi, J. Sulfur-Based Copolymeric Polyamidoamines as Efficient Flame-Retardants for Cotton. Polymers 2019, 11, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beduini, A.; Carosio, F.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E.; Alongi, J. Synergism between α-Amino Acid-Derived Polyamidoamines and Sodium Montmorillonite for Enhancing the Flame Retardancy of Cotton Fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2024, 225, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilitri, E.; Ferruti, P.; Annunziata, R.; Ranucci, E.; Rossi, M.; Falciola, L.; Mussini, P.; Chiellini, F.; Bartoli, C. Novel Amphoteric Cystine-Based Poly(Amidoamine)s Responsive to Redox Stimuli. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 4785–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hellfeld, R.; Brotzmann, K.; Baumann, L.; Strecker, R.; Braunbeck, T. Adverse Effects in the Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test: A Catalogue of Unspecific Morphological Changes versus More Specific Effects in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahardehi, A.M.; Arsad, H.; Lim, V. Zebrafish as a Successful Animal Model for Screening Toxicity of Medicinal Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisenden, B.D.; Paulson, D.C.; Orr, M. Zebrafish Embryos Hatch Early in Response to Chemical and Mechanical Indicators of Predation Risk, Resulting in Underdeveloped Swimming Ability of Hatchling Larvae. Biol. Open 2022, 11, bio059229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, C.P.; Choi, S.Y.; Kee, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.C.; Ro, H. Transgenic Fluorescent Zebrafish Lines That Have Revolutionized Biomedical Research. Lab. Anim. Res. 2021, 37, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Brito, R.; Canedo, A.; Farias, D.; Rocha, T.L. Transgenic Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as an Emerging Model System in Ecotoxicology and Toxicology: Historical Review, Recent Advances, and Trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzicka, L.; Howe, D.G.; Ramachandran, S.; Toro, S.; Van Slyke, C.E.; Bradford, Y.M.; Eagle, A.; Fashena, D.; Frazer, K.; Kalita, P.; et al. The Zebrafish Information Network: New Support for Non-Coding Genes, Richer Gene Ontology Annotations and the Alliance of Genome Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D867–D873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, F.; Manfredi, A.; Alongi, J.; Mendichi, R.; Ganazzoli, F.; Raffaini, G.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E. Self-Structuring in Water of Polyamidoamino Acids with Hydrophobic Side Chains Deriving from Natural α-Amino Acids. Polymers 2018, 10, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, A.; Mauro, N.; Terenzi, A.; Alongi, J.; Lazzari, F.; Ganazzoli, F.; Raffaini, G.; Ranucci, E.; Ferruti, P. Self-Ordering Secondary Structure of D- And L-Arginine-Derived Polyamidoamino Acids. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, F.; Manfredi, A.; Alongi, J.; Ganazzoli, F.; Vasile, F.; Raffaini, G.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E. Hydrogen Bonding in a L-Glutamine-Based Polyamidoamino Acid and Its PH-Dependent Self-Ordered Coil Conformation. Polymers 2020, 12, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, D.M.; Zhang, T.; Kalicharan, D.; Jongebloed, W.L. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy Studies of the Chorion, Plasma Membrane and Syncytial Layers of the Gastrula-Stage Embryo of the Zebrafish Brachydanio Rerio: A Consideration of the Structural and Functional. Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schier, A.F.; Talbot, W.S. Molecular Genetics of Axis Formation in Zebrafish. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 561–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, D.; Zizioli, D.; Tiso, N.; Facchinello, N.; Vezzoli, S.; Gianoncelli, A.; Memo, M.; Monti, E.; Borsani, G.; Finazzi, D. Down-Regulation of Coasy, the Gene Associated with NBIA-VI, Reduces Bmp Signaling, Perturbs Dorso-Ventral Patterning and Alters Neuronal Development in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganathan, S.R.; Oates, A.C. Patterning and Mechanics of Somite Boundaries in Zebrafish Embryos. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 107, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.S.H.; Cheng, S.H. Cadmium Affects Muscle Type Development and Axon Growth in Zebrafish Embryonic Somitogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 73, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetcho, J.R.; McLean, D.L. Startle Response. Encycl. Neurosci. 2009, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, T.D.; MacPhail, R.C.; Hunter, D.L.; Padilla, S. Acute Neuroactive Drug Exposures Alter Locomotor Activity in Larval Zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colwill, R.M.; Creton, R. Locomotor Behaviors in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Larvae. Behav. Process. 2011, 86, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, L.; Magni, S.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Gazzotti, S.; Signorini, S.G.; Sbarberi, R.; Della Torre, C.; Binelli, A. Assessment of Behavioural Effects of Three Water-Soluble Polymers in Zebrafish Embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.Q.; Xu, M.Q.; He, L.; Li, S.; Guo, N. Differential Behavioral Responses of Zebrafish Larvae to Yohimbine Treatment. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwill, R.M.; Creton, R. Imaging Escape and Avoidance Behavior in Zebrafish Larvae. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 22, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Costentin, C.; Stubbe, J.; Nocera, D.G. Disulfide Radical Anion as a Super-Reductant in Biology and Photoredox Chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 6876–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PAA | pKa Values | IP (a) | Net Charge at pH 7 | Positive/Negative Charge (b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-GLY [7] | pKa-COOH = 1.9 pKa-NR3 = 7.7 | 4.8 | −0.39 | 0.61 |
| M-GLU [41] | pKa-COOH,1 = 2.32 pKa-COOH,2 = 4.28 pKa-NR3 = 7.78 | 3.3 | −1.14 | 0.43 |
| M-GLY50-CYSS50 (c) | - | 4.9 | −0.35 | 0.72 |
| M-CYSS [42] | pKa-NR3,1 = 2.4 pKa-NR3,2 = 4.0 pKa-COOH,1 = 8.2 pKa-COOH,2 = 12.7 | 5.0 | −0.31 | 0.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Treccani, S.; Ferruti, P.; Alongi, J.; Monti, E.; Zizioli, D.; Ranucci, E. Ecotoxicity Assessment of α-Amino Acid-Derived Polyamidoamines Using Zebrafish as a Vertebrate Model. Polymers 2024, 16, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142087
Treccani S, Ferruti P, Alongi J, Monti E, Zizioli D, Ranucci E. Ecotoxicity Assessment of α-Amino Acid-Derived Polyamidoamines Using Zebrafish as a Vertebrate Model. Polymers. 2024; 16(14):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142087
Chicago/Turabian StyleTreccani, Sofia, Paolo Ferruti, Jenny Alongi, Eugenio Monti, Daniela Zizioli, and Elisabetta Ranucci. 2024. "Ecotoxicity Assessment of α-Amino Acid-Derived Polyamidoamines Using Zebrafish as a Vertebrate Model" Polymers 16, no. 14: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142087
APA StyleTreccani, S., Ferruti, P., Alongi, J., Monti, E., Zizioli, D., & Ranucci, E. (2024). Ecotoxicity Assessment of α-Amino Acid-Derived Polyamidoamines Using Zebrafish as a Vertebrate Model. Polymers, 16(14), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142087










