Degradation of Polymer Films of Sodium Alginate during Prolonged Irradiation with X-ray under Ultra-High Vacuum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
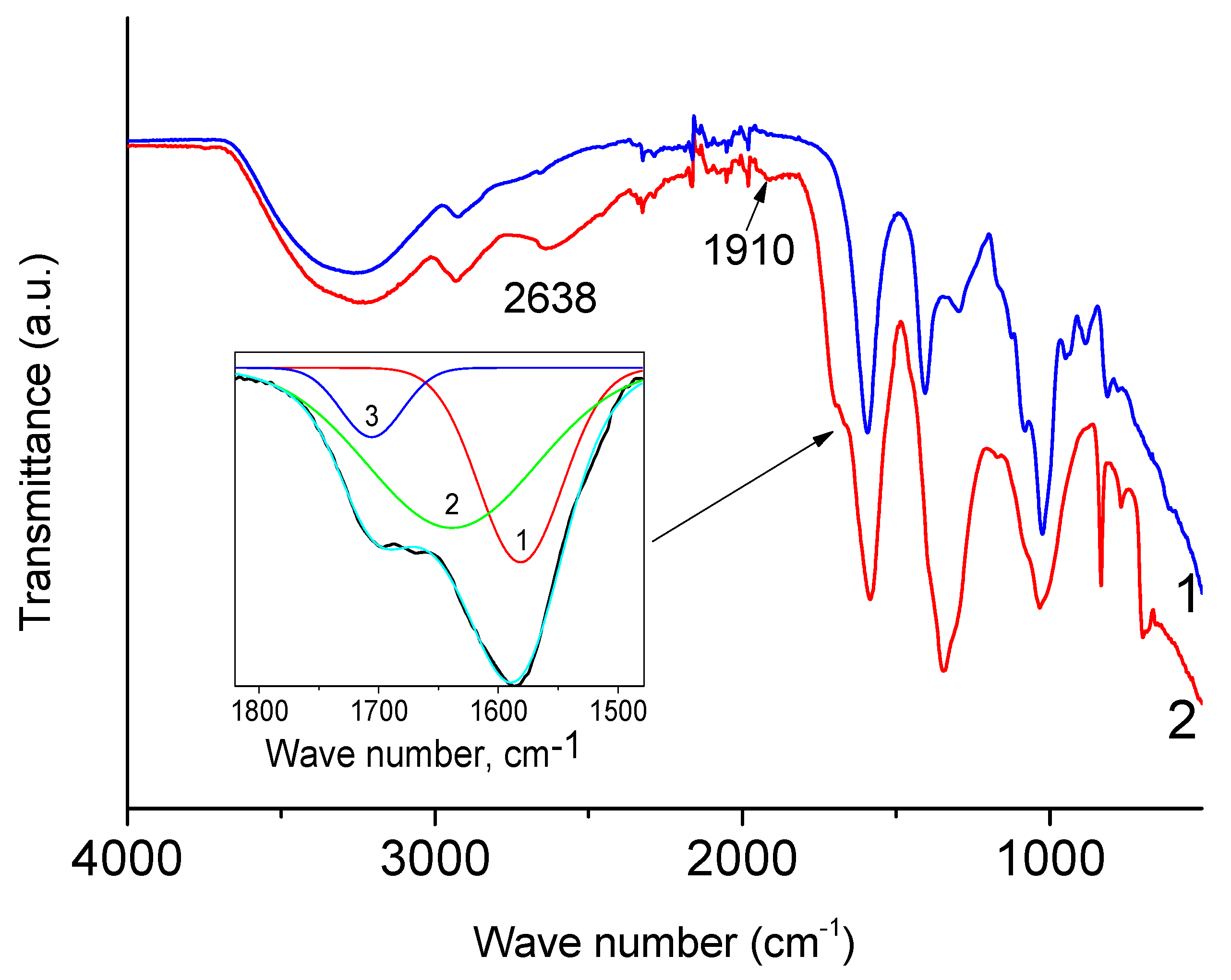
3.1. IR Spectra of NaAlg
3.2. XPS Spectra of NaAlg—Dependence on the Choice of Anode
3.3. Dependence of Spectra on Sample Preparation Method
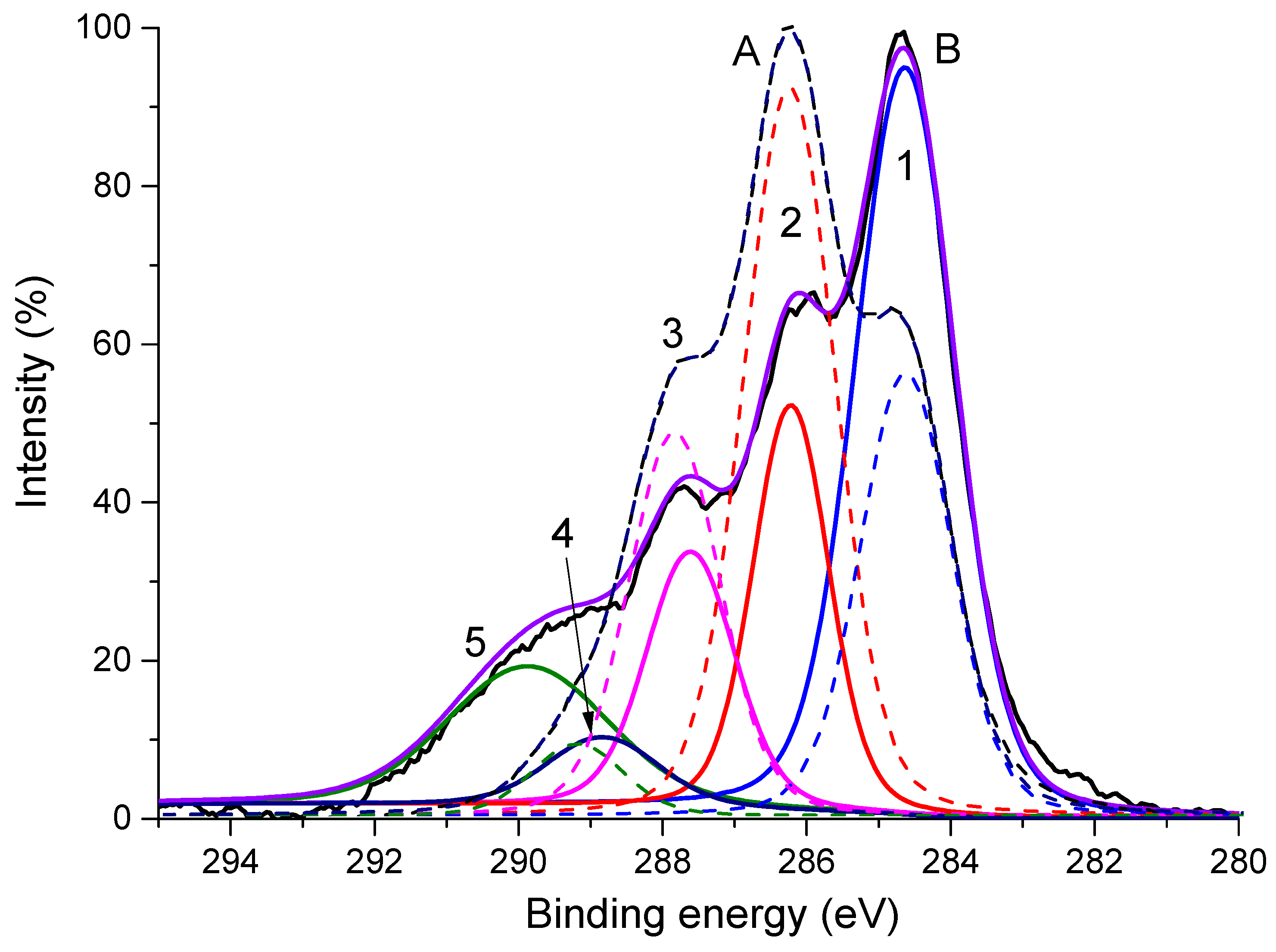
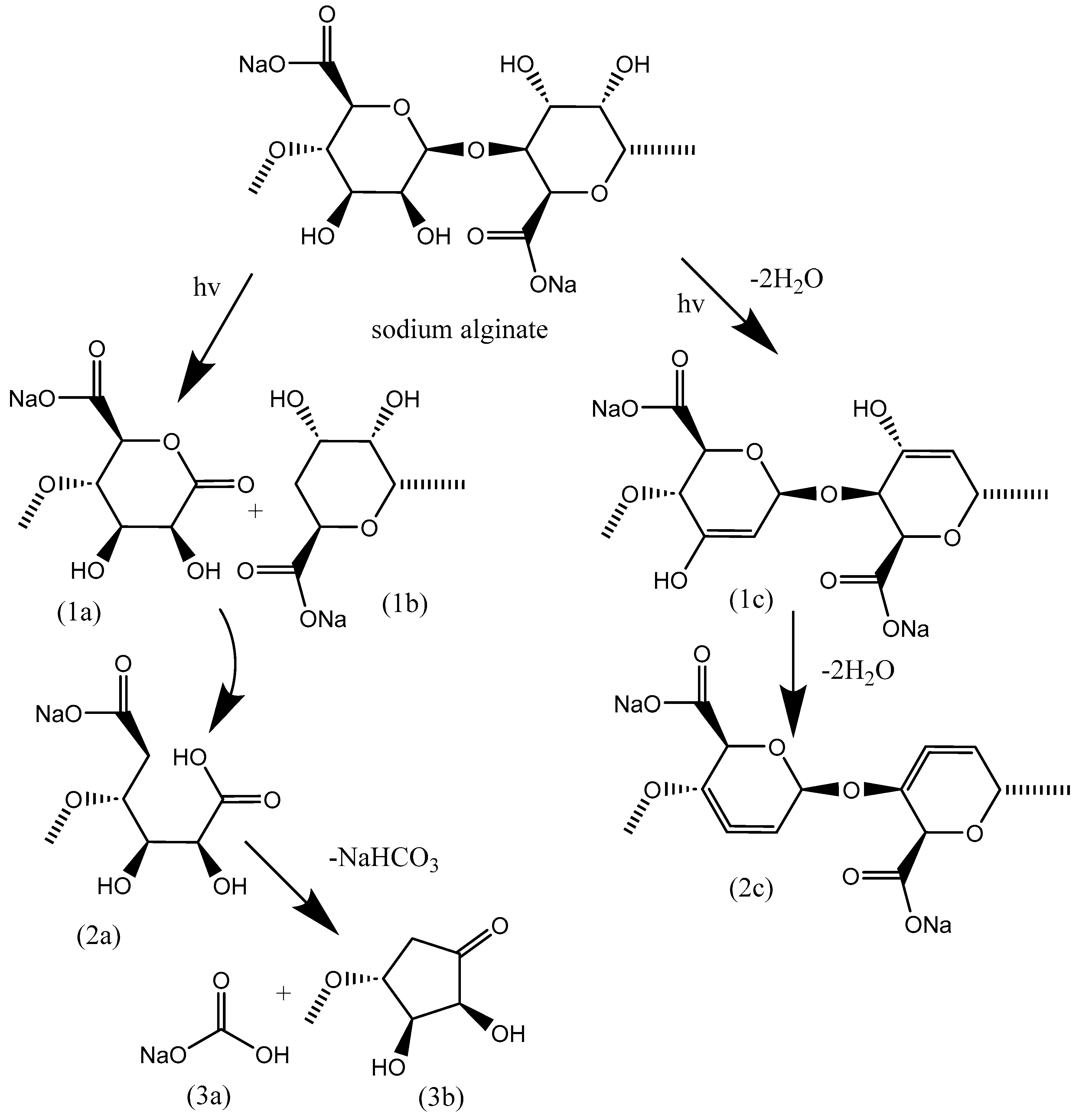
3.4. Degradation of NaAlg Films
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Degradation is accompanied by a change in the color of NaAlg from light to yellow-brown;
- (2)
- NaAlg is amorphized as a result of irradiation;
- (3)
- When irradiated, the average molecular weight of alginates decreases;
- (4)
- It has been established that during the process of radiation degradation, the formation of both carbonyl groups and double bonds occurs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draget, K.I.; Skjåk Bræk, G.; Smidsrød, O. Alginic acid gels: The effect of alginate chemical composition and molecular weight. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draget, K.I.; Skjåk-Bræek, G.; Smidsrød, O. Alginate based new materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1997, 21, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draget, K.I.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Stokke, B.T. Similarities and differences between alginic acid gels and ionically crosslinked alginate gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Iskandar, L.; Deb, S. Green synthetic routes to alginate-graphene oxide composite hydrogels with enhanced physical properties for bioengineering applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 103, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Chen, J.; Gao, B. Alginate-based composites for environmental applications: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutirman, Z.A.; Sanagi, M.M.; Wan Aini, W.I. Alginate-based adsorbents for removal of metal ions and radionuclides from aqueous solutions: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 174, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Kanikireddy, V.; Toro, C.; Sadiku, E.R. Alginate-based composite materials for wound dressing application: A mini review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-González, A.C.; Téllez-Jurado, L.; Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.M. Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Mishra, V.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Alginate: Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Feng, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, H. The role of sodium alginate in the flotation separation of apatite and dolomite. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, G.; Keen, I.; Drew, B.; Chandler-Temple, A.; Rintoul, L.; Fredericks, P.; Grondahl, L. Interactions between alginate and chitosan biopolymers characterized using ftir and xps. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.G.; Wang, Z.Q. Preparation of composite aerogels based on sodium alginate, and its in removal of Pb2+ and Cu2+ from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Huang, R. Efficient removal of lead, copper and cadmium ions from water by a porous calcium alginate/graphene oxide composite aerogel. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. A Study on the Correlation between the Oxidation Degree of Oxidized Sodium Alginate on Its Degradability and Gelation. Polymers 2022, 14, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriamanantoanina, H.; Rinaudo, M. Characterization of the alginates from five madagascan brown algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fertah, M.; Belfkira, A.; Dahmane, E.M.; Taourirte, M.; Brouillette, F. Extraction and characterization of sodium alginate from Moroccan Laminaria digitata brown seaweed. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3707–S3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari-Chmayssem, N.; Taha, S.; Mawlawi, H.; Guégan, J.P.; Jeftić, J.; Benvegnu, T. Extracted and depolymerized alginates from brown algae Sargassum vulgare of Lebanese origin: Chemical, rheological, and antioxidant properties. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Han, J.; Han, G.; French, A.D.; Qi, Y.; Wu, Q. Cellulose nanofibers reinforced sodium alginate-polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels: Core-shell structure formation and property characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Xie, H.; Lu, L. Surface modification of sphalerite with sodium alginate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 274, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Jiang, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Mao, X. Characteristics and applications of alginate lyases: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1304–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, N.; Mitomo, M.; Yoshii, F.; Kume, T. Radiation-induced degradation of sodium alginate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 69, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Choi, W.S.; Byun, M.W.; Park, H.J.; Yu, Y.-M.; Lee, C.M. Effect of γ-Irradiation on Degradation of Alginate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4819–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Mohdy, H.L. Radiation-induced degradation of sodium alginate and its plant growth promotion effect. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S431–S438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14976:1998; Surface Chemical Analysis—Data Transfer Format. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Shi, T.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M. Highly efficient and selective adsorption of heavy metal ions by hydrazide-modified sodium alginate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakugawa, K.; Ikeda, A.; Takemura, A.; Ono, H. Simplified method for estimation of composition of alginates by FTIR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurikar, A.; Seow, X.T.; Lawrie, G.; Martin, D.; Jayakrishnan, A.; Grondahl, L. Degradable alginate hydrogels crosslinked by the macromolecular crosslinker alginate dialdehyde. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9751–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamson, G.; Briggs, D. High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers: The Scienta ESCA300 Database; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, D.J.; Uthayasekaran, S. Revisiting degradation in the XPS analysis of polymers Surface and Interface Analysis. Surf. Interface Anal. 2023, 55, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.L. Applied Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals, Techniques, and Analytical Problem-Solving; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, L.Q.; Nagasawa, N.; Ha, V.T.T.; Nakanishi, T.M. A study of degradation mechanism of alginate by gamma-irradiation. Radioisotopes 2009, 58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
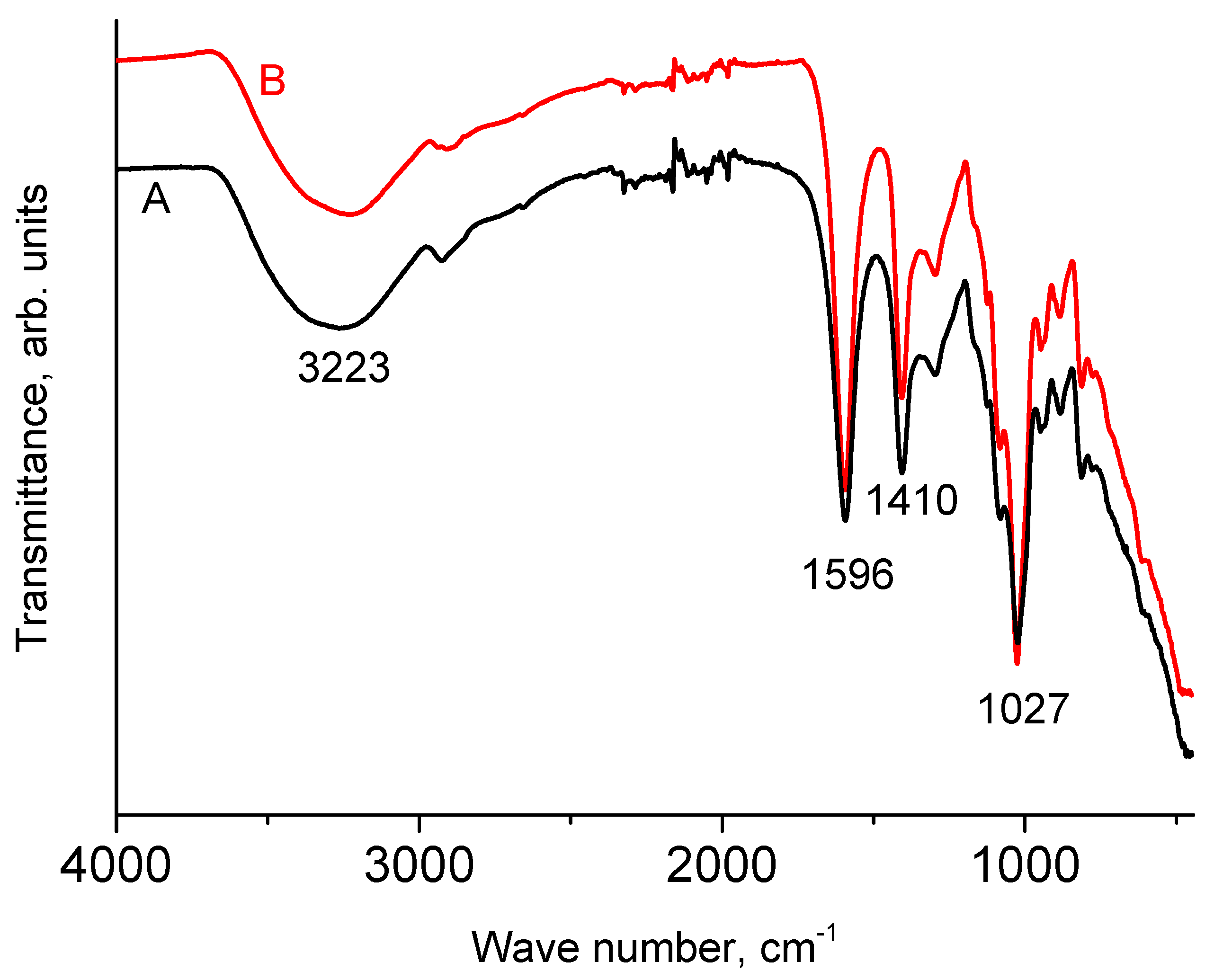
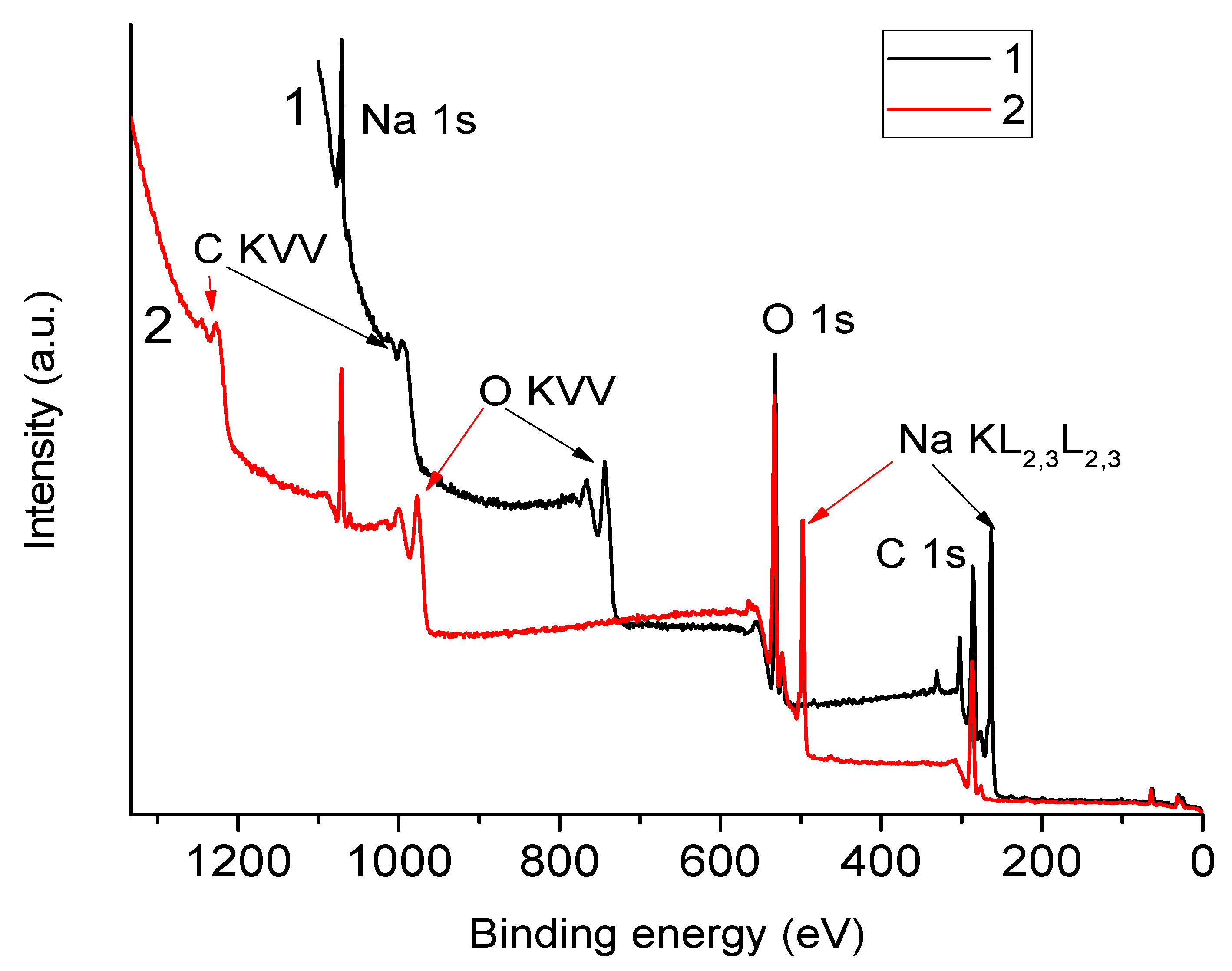
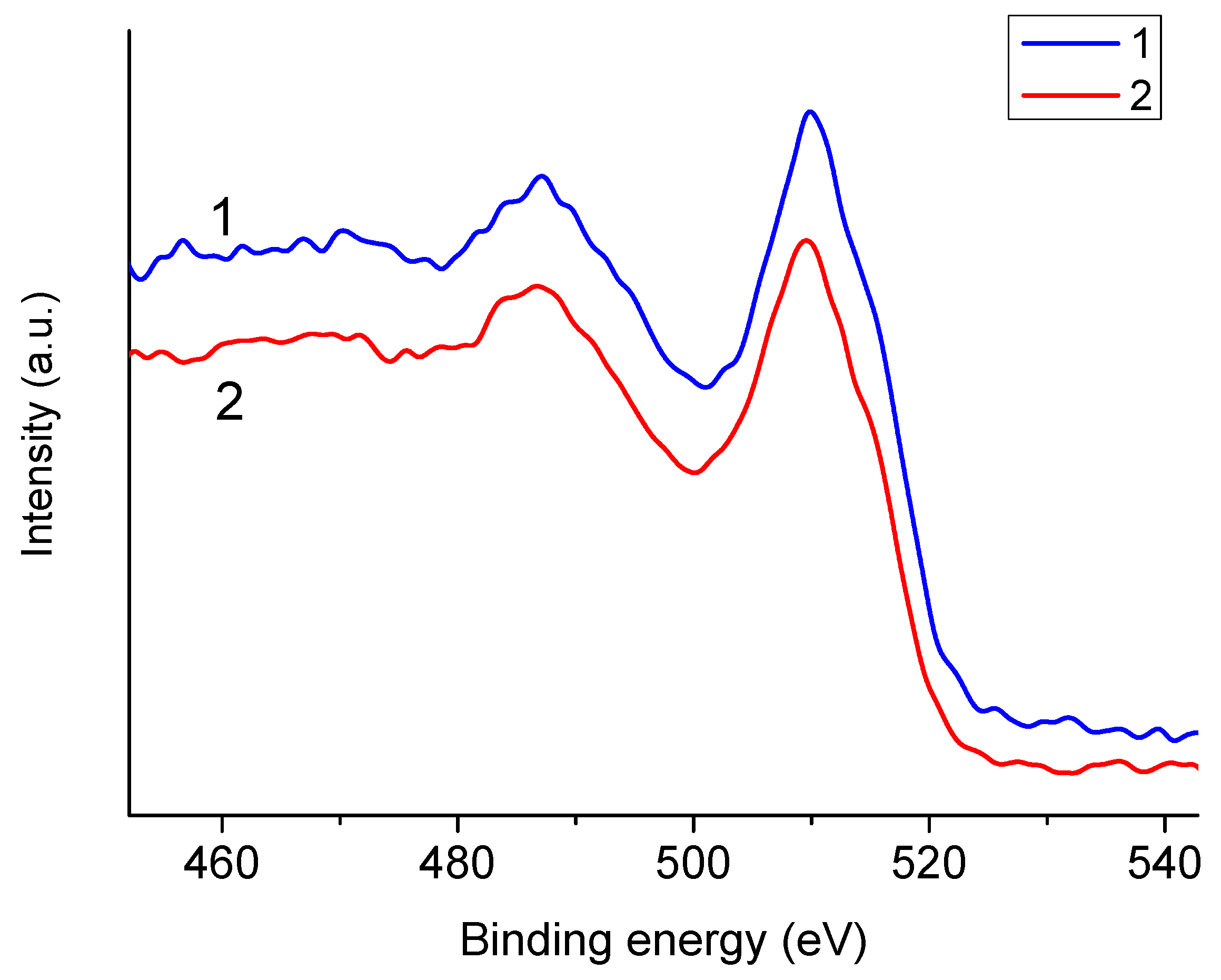
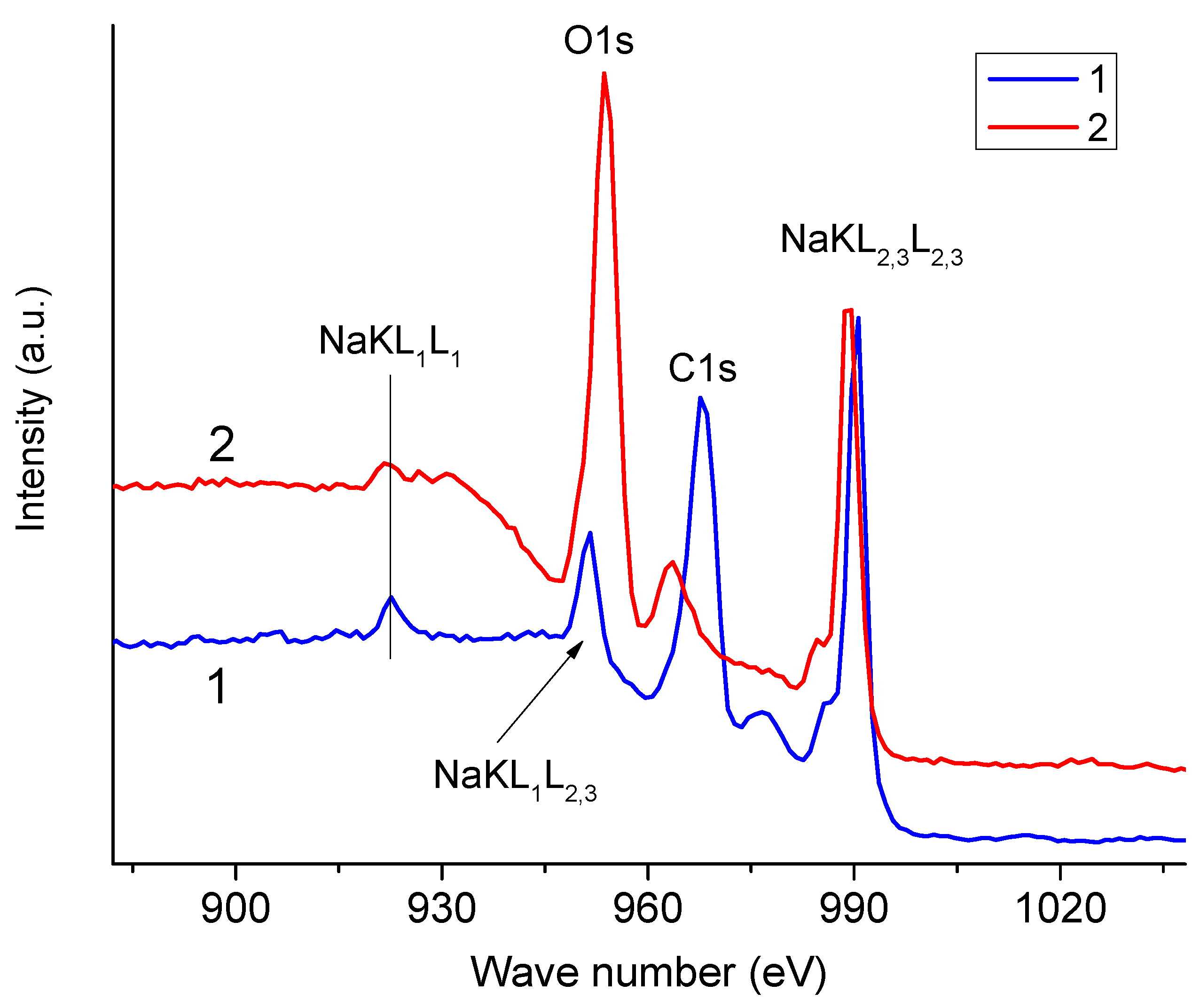
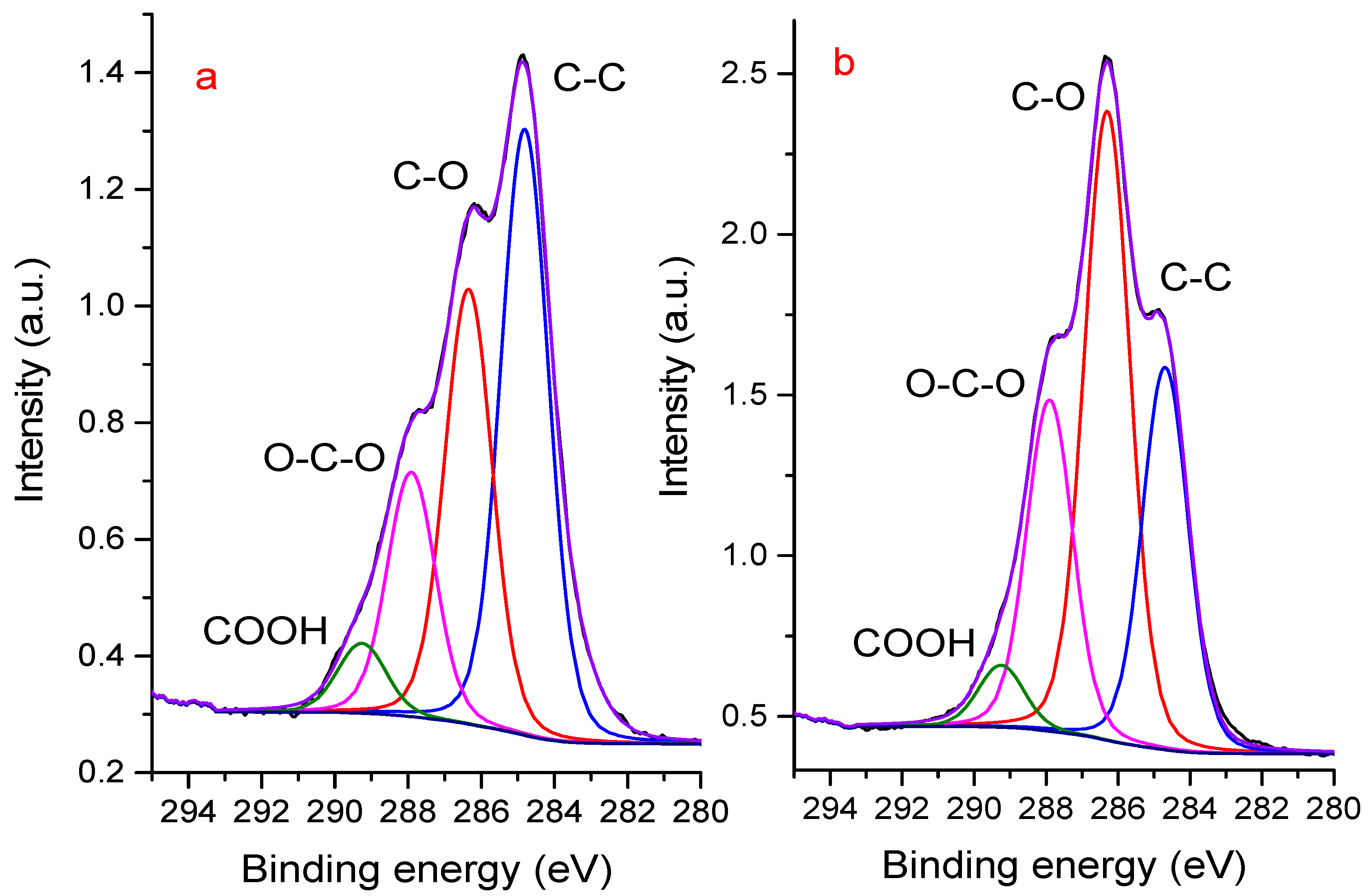



| Anode | O1s | C1s | Na1s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 2.93 | 1 | 8.52 |
| Mg | 2.85 | 1 | 7.99 |
| Anode | Peak | Binding Energy, eV | FWHM, eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Na1s | 1071 | 3 |
| O1s | 533 | 3.9 | |
| C1s | 287 | 4.5 | |
| Mg | Na1s | 1071 | 2.5 |
| O1s | 532 | 3.3 | |
| C1s | 286 | 4.4 |
| Peak Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assignment | C-C | C-O | O-C-O/C=O | COOH | CO32− |
| Spectrum A, eV (%) | 284.9 (47.27) | 286.5 (14.29) | 287.9 (19.39) | 289.2 (4.85) | 290.2 (14.2) |
| Spectrum B, eV (%) | 284.7 (32.69) | 286.3 (36.06) | 287.9 (20.8) | 289.2 (10.44) | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabachkov, E.N.; Baskakov, S.A.; Shulga, Y.M. Degradation of Polymer Films of Sodium Alginate during Prolonged Irradiation with X-ray under Ultra-High Vacuum. Polymers 2024, 16, 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142072
Kabachkov EN, Baskakov SA, Shulga YM. Degradation of Polymer Films of Sodium Alginate during Prolonged Irradiation with X-ray under Ultra-High Vacuum. Polymers. 2024; 16(14):2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142072
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabachkov, Eugene N., Sergey A. Baskakov, and Yury M. Shulga. 2024. "Degradation of Polymer Films of Sodium Alginate during Prolonged Irradiation with X-ray under Ultra-High Vacuum" Polymers 16, no. 14: 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142072
APA StyleKabachkov, E. N., Baskakov, S. A., & Shulga, Y. M. (2024). Degradation of Polymer Films of Sodium Alginate during Prolonged Irradiation with X-ray under Ultra-High Vacuum. Polymers, 16(14), 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142072








