Thermal Degradation and Chemical Analysis of Flame-Retardant-Treated Jute Fabrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Fabric Preparation
2.4. Treatment for FR Finishing
2.5. Characterization of Fabric Surface
2.6. Analysis of Thermal Degradation Properties
2.7. Color Change Measurement Study
2.8. Durability Test
2.9. Free Formaldehyde Content Determination
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Assessment of Color Variation
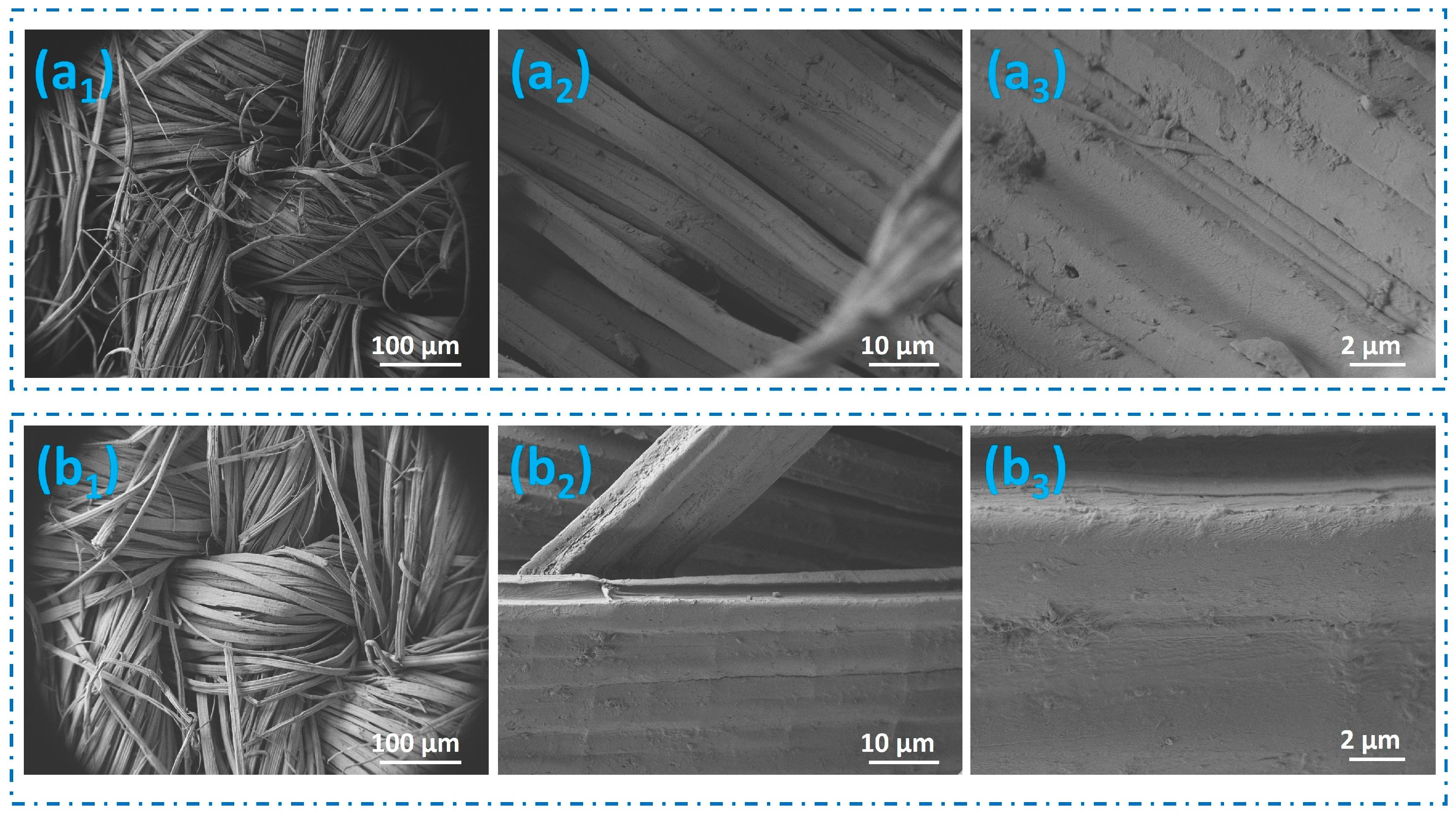
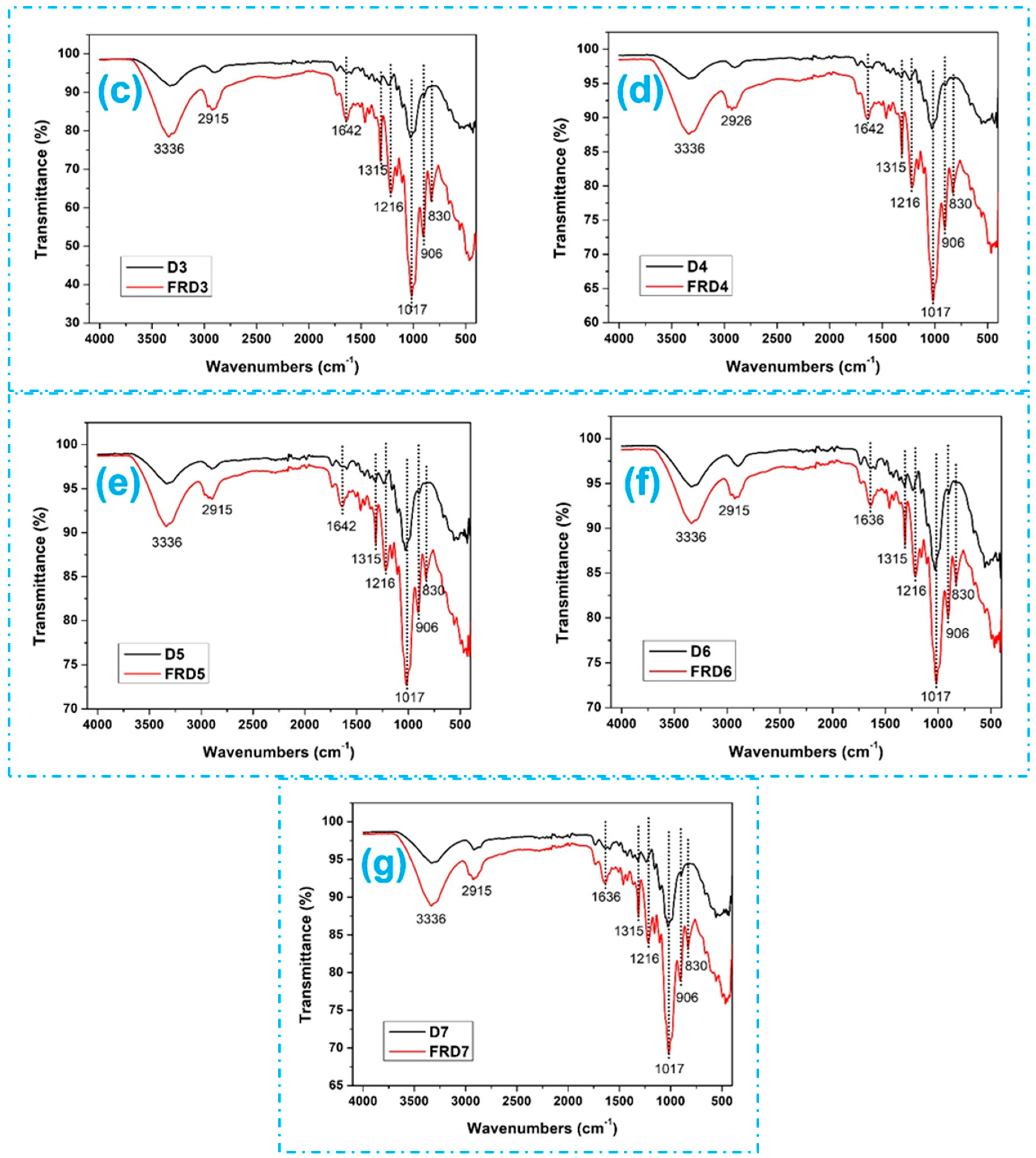
3.2. Analysis of Surface Morphology and Chemical Composition
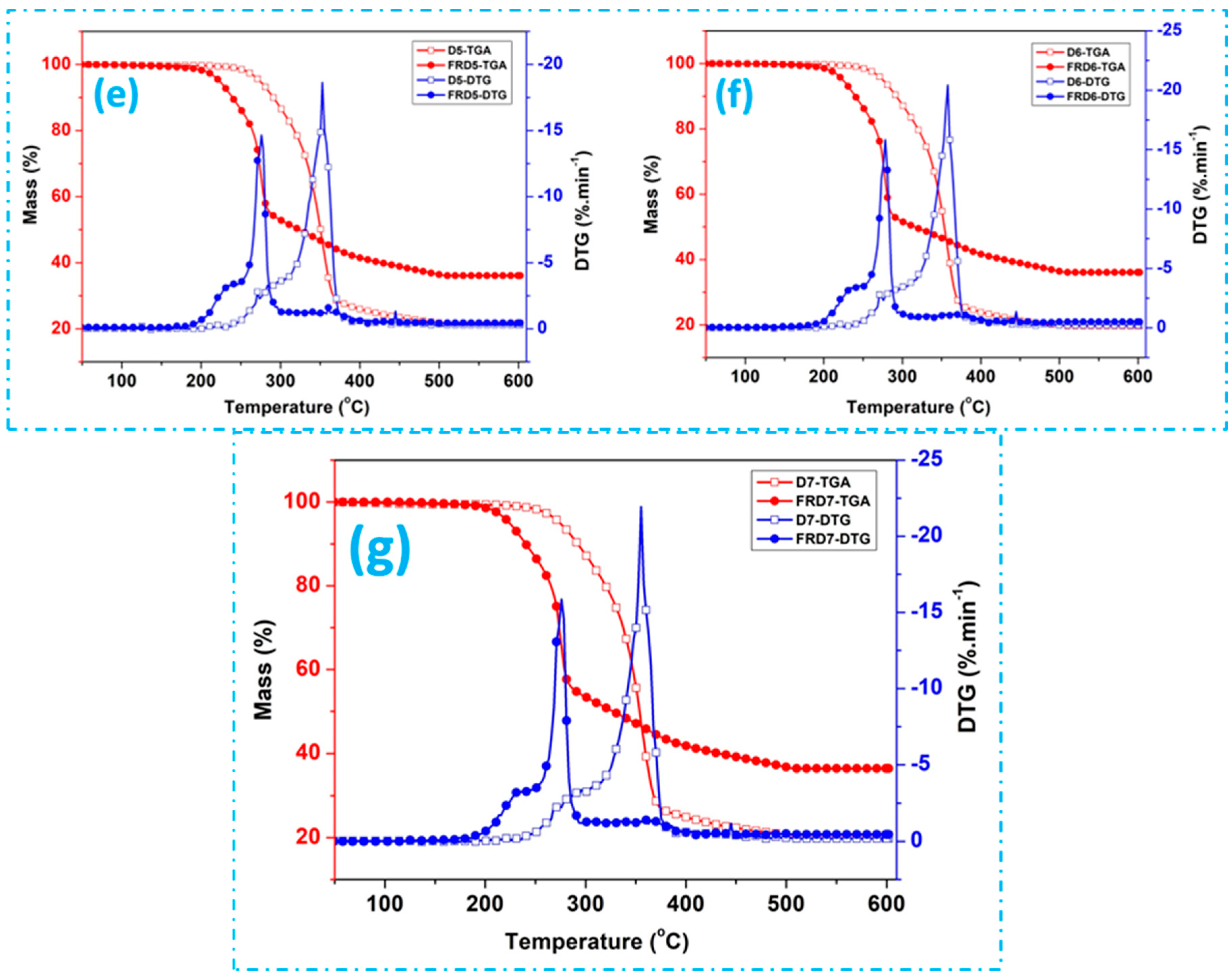
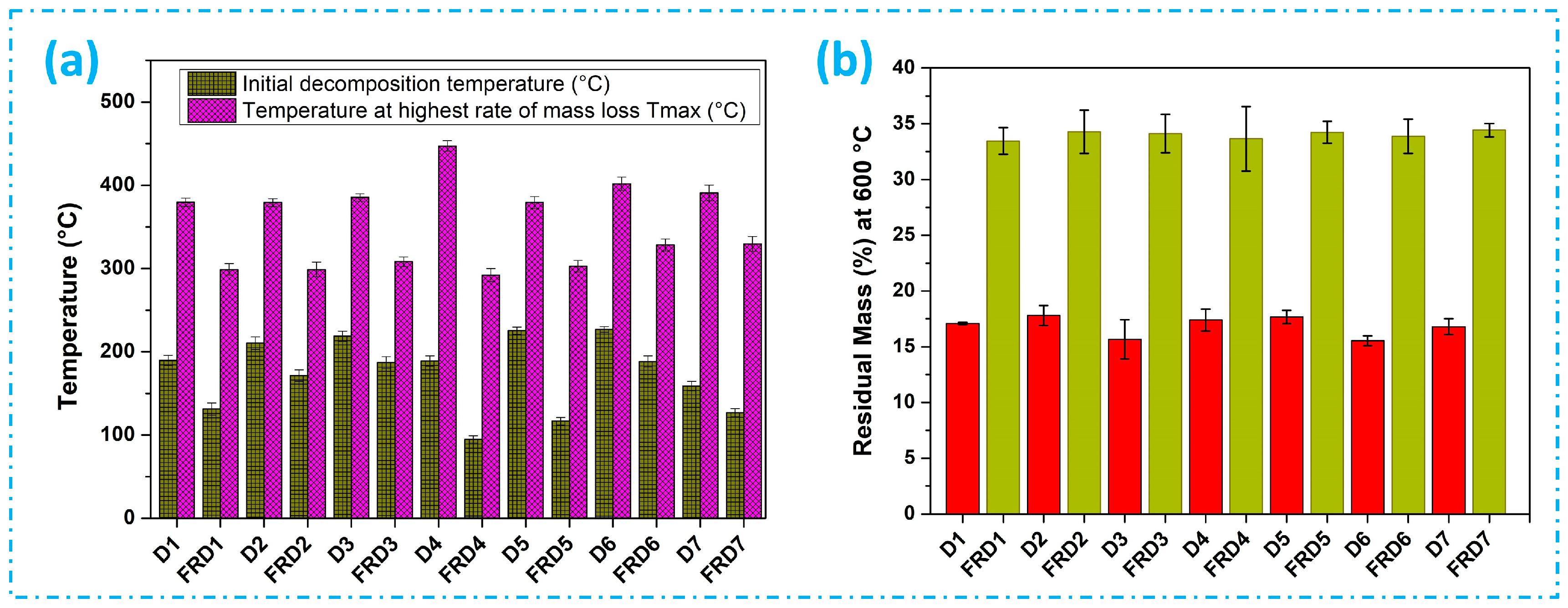
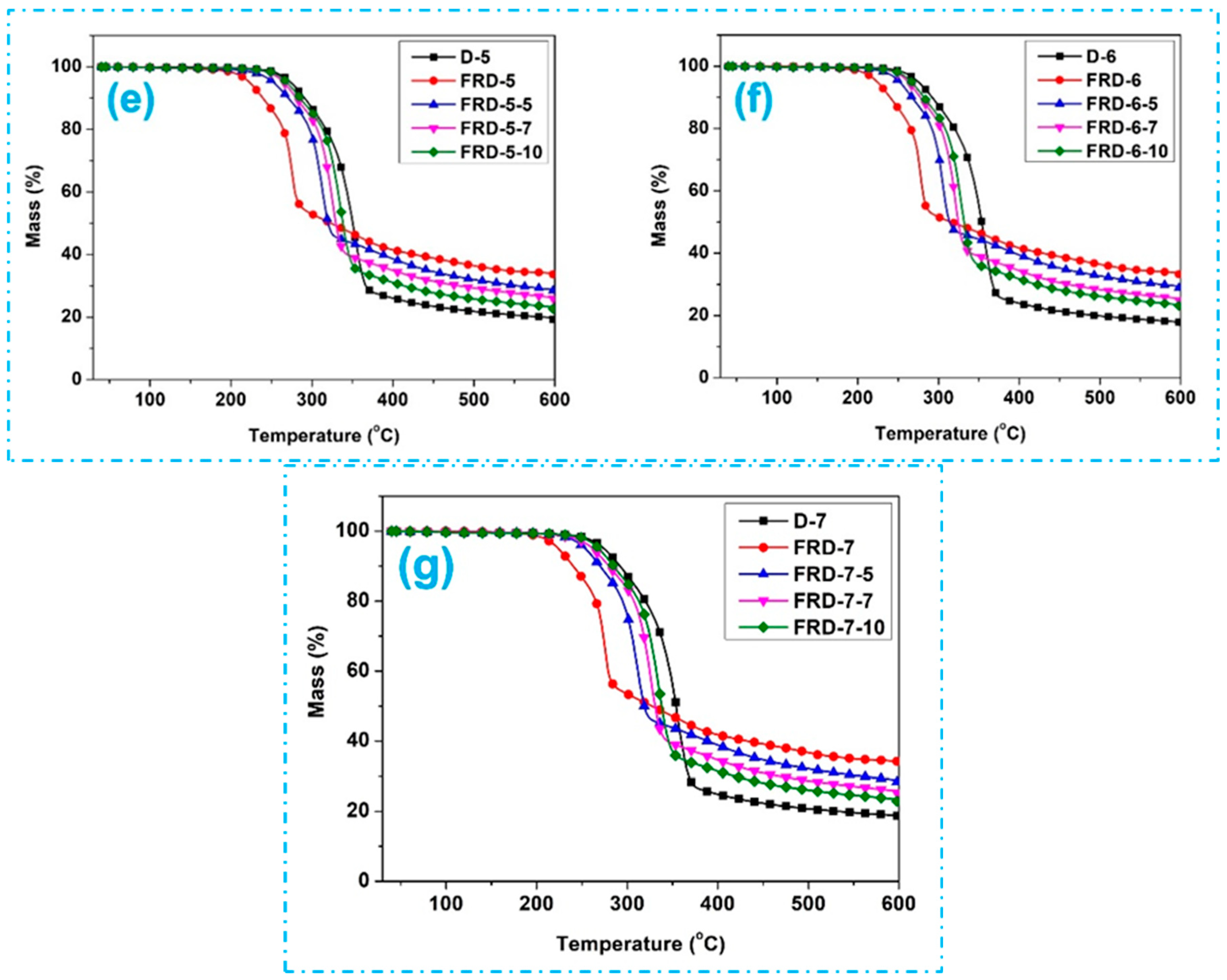
3.3. Thermal Properties Analysis
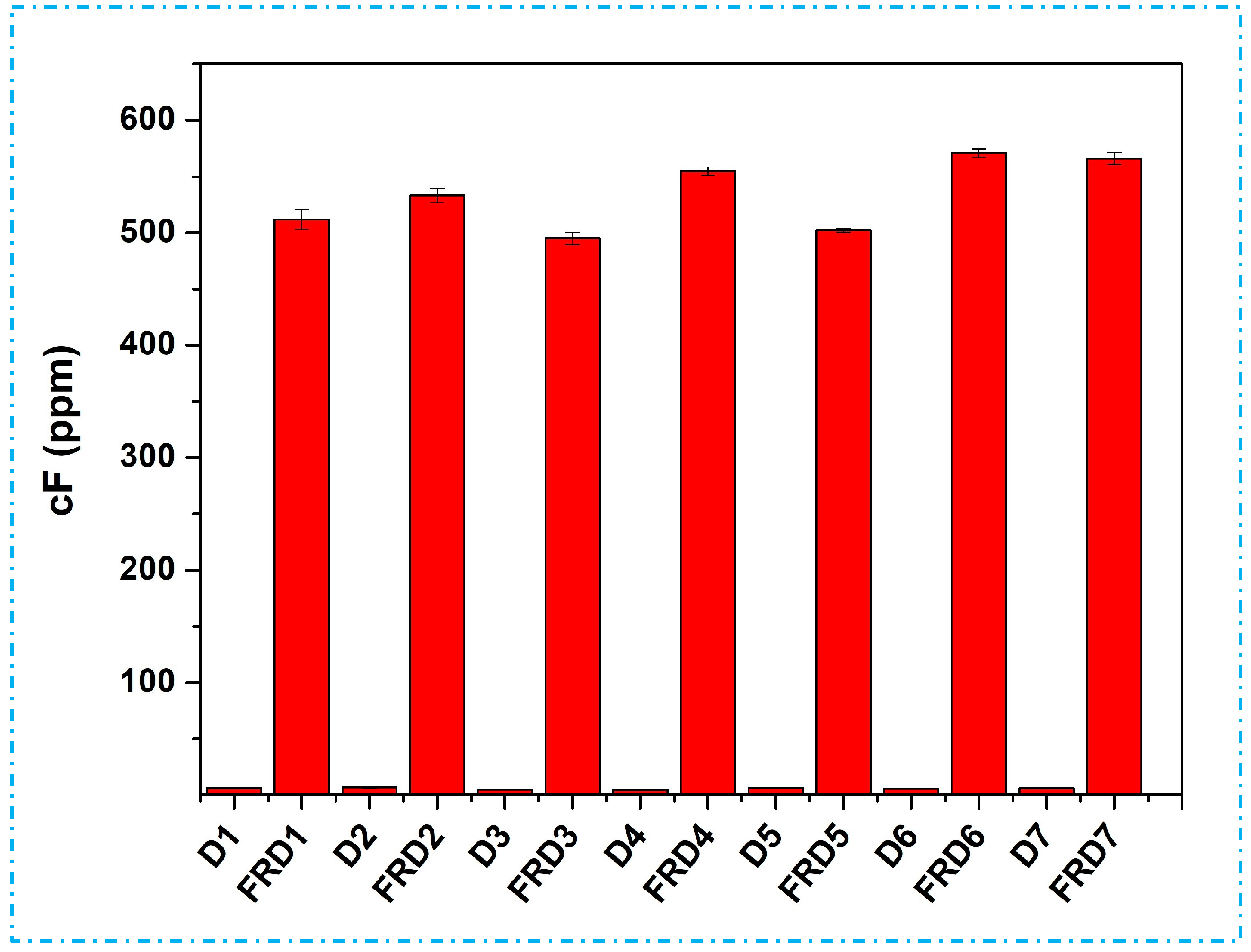
3.4. Free Formaldehyde Content Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basak, R.K.; Saha, S.G.; Sarkar, A.K.; Saha, M.; Das, N.N.; Mukherjee, A.K. Thermal Properties of Jute Constituents and Flame Retardant Jute Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 1993, 63, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K.; Biswas, S.K.; Bagchi, A.; Bhattacharjee, R. Semi-Durable Fire Retardant Finishing of Jute Fabric and Its Thermal Behaviour. J. Inst. Eng. 2011, 91, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, A.K.; Bagchi, A.; Biswas, S.K. Fire Retardant Finishing of Jute Fabric and Its Thermal Behaviour Using Phosphorous and Nitrogen Based Compound. J. Polym. Mater. 2011, 28, 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Weil, E.D.; Levchik, S.V. Flame Retardants in Commercial Use or Development for Textiles. J. Fire Sci. 2008, 26, 243–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K. Chemical Finishing of Jute and Jute Blended Textiles. Colourage 1995, 42, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, W.D.; Hauser, P.J.; Textile Institute. Chemical Finishing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 1855739054. [Google Scholar]
- Roy Choudhury, A.K. Flame- and Fire-Retardant Finishes. In Principles of Textile Finishing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 195–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wyld, O. Making or Preparing of Paper, Linen, Canvass and Such Like Substances, Which Will Neither Flame nor Retain Fire, and Which Hath Also a Property in It of Resisting Moisture and Damps. British Patent 551 17 March 1735. [Google Scholar]
- Gay-Lussac, J.L. Note on Properties of Salts for Making Fabrics Incombustible. Ann. Chim. 1821, 18, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.N.; Day, A.; Mathew, M.D. Thermal Analysis of Chemically Treated Jute Fibers. Text. Res. J. 1993, 63, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Butola, B.S. A Study on Durable Flame Retardancy of Jute. J. Nat. Fibers 2018, 15, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M. A Review on Flame Retardant Textile Finishing: Current and Future Trends. Curr. Smart Mater. 2018, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.D.; Mansurul Hoque, A.K.M. Flammability of Metal-Cation-Exchanged Jute Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 1982, 52, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorez, G.; Ferry, L.; Sonnier, R.; Taguet, A.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M. Effect of Cellulose, Hemicellulose and Lignin Contents on Pyrolysis and Combustion of Natural Fibers. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 107, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.M.; Feris, K.; Bell, J.; Wingett, D.G.; Hanley, C.; Punnoose, A. Selective Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles to Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 213902-1–213902-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, M.S.; Kader, A.; Milašius, R. Flame-Retardance Functionalization of Jute and Jute-Cotton Fabrics. Polymers 2023, 15, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.; Kader, A.; Milašius, R. The Effect of Flame-Retardant Finish on Jute and Jute-Cotton Fabrics. In Proceedings of the AUTEX 2022 Conference Proceedings (21st World Textile Conference), Lodz, Poland, 7–10 June 2022; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Samanta, K.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.K.; Das, S.; Narkar, R.; Dsouza, C.; Shaikh, A.H. Flame Retardant and Antimicrobial Jute Textile Using Sodium Metasilicate Nonahydrate. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2014, 16, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K.; Bhattacharya, K. Simultaneous Dyeing and Fire-Retardant Finishing of Jute Fabric Using an Acid Dye and Selective F-R Finishing Chemicals. Text. Light. Ind. Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repon, M.R.; Siddiquee, N.A.; Jalil, M.A.; Mikučionienė, D.; Karim, M.R.; Islam, T. Flame Retardancy Enhancement of Jute Fabric Using Chemical Treatment. Tekstilec 2021, 64, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Jose, S.; Basu, G.; Chowdhury, R. Fire Retardant Finish of Jute Fabric with Nano Zinc Oxide. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Tang, R.C.; Yu, C.B. Flame Retardant Treatment of Jute Fabric with Chitosan and Sodium Alginate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 196, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14184-1; Textiles—Determination of Formaldehyde—Part 1: Free and Hydrolysed Formaldehyde (Water Extraction Method). International Organization of Standarization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Ganguly, P.K.; Chanda, S. Dyeing of Jute: Effect of Progressive Removal of Hemicellulose and Lignin. Indian. J. Fibre Text. Res. 1994, 19, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, M.M. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF JUTE II: The Study of Chemically Treated Fibres. J. Text. Inst. Trans. 1953, 44, T44–T52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.B.; Mazumdar, A.K. Note on the Lignin and Hemicellulose of Jute. Text. Res. J. 1955, 25, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Tong, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Ingram, L. Isolation and Structural Characterization of Sugarcane Bagasse Lignin after Dilute Phosphoric Acid plus Steam Explosion Pretreatment and Its Effect on Cellulose Hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boundzanga, H.M.; Cagnon, B.; Roulet, M.; de Persis, S.; Vautrin-Ul, C.; Bonnamy, S. Contributions of Hemicellulose, Cellulose, and Lignin to the Mass and the Porous Characteristics of Activated Carbons Produced from Biomass Residues by Phosphoric Acid Activation. Biomass Convers. Biorefin 2022, 12, 3081–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xue, G.; Weng, L.; Guo, X. Pretreatment of moso bamboo with dilute phosphoric acid. BioResources 2012, 7, 4902–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Leman, Z.; Jawaid, M. A Review on the Characterisation of Natural Fibres and Their Composites after Alkali Treatment and Water Absorption. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2017, 46, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothibasu, S.; Mohanamurugan, S.; Vijay, R.; Lenin Singaravelu, D.; Vinod, A.; Sanjay, M.R. Investigation on the Mechanical Behavior of Areca Sheath Fibers/Jute Fibers/Glass Fabrics Reinforced Hybrid Composite for Light Weight Applications. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 49, 1036–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, M.C.; Ammar, I.; Campos, A.R.; Cheikh, R.B.; Cunha, A.M. Alfa Fibres: Mechanical, Morphological and Interfacial Characterization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommula, V.P.; Reddy, K.O.; Shukla, M.; Marwala, T.; Rajulu, A.V. Physico-Chemical, Tensile, and Thermal Characterization of Napier Grass (Native African) Fiber Strands. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2013, 18, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rosa, I.M.; Kenny, J.M.; Puglia, D.; Santulli, C.; Sarasini, F. Morphological, Thermal and Mechanical Characterization of Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus) Fibres as Potential Reinforcement in Polymer Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonia, A.; Priya Dasan, K. Chemical, Morphology and Thermal Evaluation of Cellulose Microfibers Obtained from Hibiscus Sabdariffa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y. Water-Solubility of Chitosan and Its Antimicrobial Activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmane, E.M.; Taourirte, M.; Eladlani, N.; Rhazi, M. Extraction and Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan from Parapenaeus Longirostris from Moroccan Local Sources. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2014, 19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.-P.M.; Kan, C.-W.; Fan, J.-T.; Tso, S.-L. Effect of Softener and Wetting Agent on Improving the Flammability, Comfort, and Mechanical Properties of Flame-Retardant Finished Cotton Fabric. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2619–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, C.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Daliani, I.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Polissiou, M. Comparison of Classical and Ultrasound-Assisted Isolation Procedures of Cellulose from Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) and Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus rodustrus Sm.). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2002, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ding, D.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G. A High Durable Polysaccharide Flame Retardant Based on Phosphorus Element for Cotton Fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 210, 110313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Wen, L.; Cen, K. Mechanism Study on Cellulose Pyrolysis Using Thermogravimetric Analysis Coupled with Infrared Spectroscopy. Front. Energy Power Eng. China 2007, 1, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hatakeyama, H. Vaporization of Bound Water Associated with Cellulose fibres. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 352–353, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hatakeyama, H. Determination of Bound Water Content in Polymers by DTA, DSC and TG. Thermochim. Acta 1988, 123, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Hatakeyama, T. Interaction between Water and Hydrophilic Polymers. Thermochim. Acta 1998, 308, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Sui, S.; Wang, B.; Sun, K.; Sun, G. A Study of Pyrolysis and Pyrolysis Products of Flame-Retardant Cotton Fabrics by DSC, TGA, and PY-GC-MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2004, 71, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Frendi, A.; Tewari, S.S.; Sibulkin, M. Combustion Properties of Pure and Fire-Retarded Cellulose. Combust. Flame 1991, 84, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessan, F.; Montazer, M.; Moghadam, M.B. A Novel Durable Flame-Retardant Cotton Fabric Using Sodium Hypophosphite, Nano TiO2 and Maleic Acid. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 520, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.A. Thermal Degradation of Organophosphorus Flame Retardants. Polymers 2022, 14, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özer, M.S.; Gaan, S. Recent Developments in Phosphorus Based Flame Retardant Coatings for Textiles: Synthesis, Applications and Performance. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 171, 107027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fei, B.; Wang, X.; Xin, J.H. A Novel Halogen-Free and Formaldehyde-Free Flame Retardant for Cotton Fabrics. Fire Mater. 2012, 36, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, B.K.; Horrocks, S.; Horrocks, A.R. Evidence of Interaction in Flame-Retardant Fibre-Intumescent Combinations by Thermal Analytical Techniques. Thermochim. Acta 1997, 294, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lei, D.; Fei, B.; Xin, J.H. A Durable Flame Retardant for Cellulosic Fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin, C.G. IARC Classifies Formaldehyde as Carcinogenic. Oncol. Times 2004, 26, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protano, C.; Buomprisco, G.; Cammalleri, V.; Pocino, R.N.; Marotta, D.; Simonazzi, S.; Cardoni, F.; Petyx, M.; Iavicoli, S.; Vitali, M. The Carcinogenic Effects of Formaldehyde Occupational Exposure: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheman, A.J.; Carroll, P.A.; Brown, K.H.; Osburn, A.H. Formaldehyde-Related Textile Allergy: An Update. Contact Dermat. 1998, 38, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.F., Jr.; Skinner, S.M.; Belsito, D.V. Allergic Contact Dermatitis from Formaldehyde Resins in Permanent Press Clothing: An Underdiagnosed Cause of Generalized Dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 27, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidney, B.L.; Reinhardt, R.M. What Do Formaldehyde Tests Measure? Text. Chem. Color. 1981, 13, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Katović, D.; Flinčec Grgac, S.; Bischof-Vukušić, S.; Katović, A. Formaldehyde Free Binding System for Flame Retardant Finishing of Cotton Fabrics. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2012, 20, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, M.; Ramzan, N.; Quatab, H.G.; Ahmad, S.W.; Sarwar, N. Synthesis of Halogen and Formaldehyde Free Bio Based Fire Retardant for Cotton. Ind. Textila 2017, 68, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Government Accountability Office. Formaldehyde in Textiles; United States Government Accountability Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Senaldi, C.; Summa, C.; Piccinini, P. European Survey on the Release of Formaldehyde from Textiles; Publications Office: Nashville, TN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Samanta, K.K.; Saxena, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.K.; Narkar, R.; Mahangade, R.; Hadge, G.B. Flame Resistant Cellulosic Substrate Using Banana Pseudostem Sap. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2015, 17, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Liao, W.; Deng, S.B.; Cao, Z.J.; Wang, Y.Z. Flame Retardation of Cellulose-Rich Fabrics via a Simplified Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Cheng, B.W.; Ren, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.G.; Ding, C. Durable Flame Retardant Cellulosic Fibers Modified with Novel, Facile and Efficient Phytic Acid-Based Finishing Agent. Cellulose 2018, 25, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, H.; Kong, D.; Lu, Z. Durable Flame Retardant Cotton Fabrics Modified with a Novel Silicon–Phosphorus–Nitrogen Synergistic Flame Retardant. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9027–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaan, S.; Sun, G. Effect of Nitrogen Additives on Thermal Decomposition of Cotton. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 84, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample ID | Weave Structure |
|---|---|
| D1 | Warp Rib: 2/2 |
| D2 | Weft Rib: 2/2 |
| D3 | Basket weave (Matt): 4/4 |
| D4 | Twill 3/1 |
| D5 | Twill 2/2 |
| D6 | Plain 1/1 |
| D7 | 4 ends Irregular Satin |
| Chemicals | Commercial Name of the Chemicals | Amount in the Recipe (g/L) |
|---|---|---|
| FR chemical | ITOFLAM CPN | 400 |
| Crosslinking Agent | KNITTEX CHN | 50 |
| Catalyst | Phosphoric Acid (80%) | 20 |
| Pick-up % | 75 |
| Sample ID | Color Difference (ΔE) | |
|---|---|---|
 |  | 6.16 |
| 6.28 | ||
| 6.28 | ||
| 4.24 | ||
| 3.92 | ||
| 5.35 | ||
| 5.90 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Begum, M.S.; Hummel, M.; Mandal, S.; Mahmood, S.; Repon, M.R.; Milašius, R. Thermal Degradation and Chemical Analysis of Flame-Retardant-Treated Jute Fabrics. Polymers 2024, 16, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142049
Begum MS, Hummel M, Mandal S, Mahmood S, Repon MR, Milašius R. Thermal Degradation and Chemical Analysis of Flame-Retardant-Treated Jute Fabrics. Polymers. 2024; 16(14):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142049
Chicago/Turabian StyleBegum, Most. Setara, Michael Hummel, Sumit Mandal, Shahriare Mahmood, Md. Reazuddin Repon, and Rimvydas Milašius. 2024. "Thermal Degradation and Chemical Analysis of Flame-Retardant-Treated Jute Fabrics" Polymers 16, no. 14: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142049
APA StyleBegum, M. S., Hummel, M., Mandal, S., Mahmood, S., Repon, M. R., & Milašius, R. (2024). Thermal Degradation and Chemical Analysis of Flame-Retardant-Treated Jute Fabrics. Polymers, 16(14), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142049











