In Vitro Hemostatic Activity of Novel Fish Gelatin–Alginate Sponge (FGAS) Prototype
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
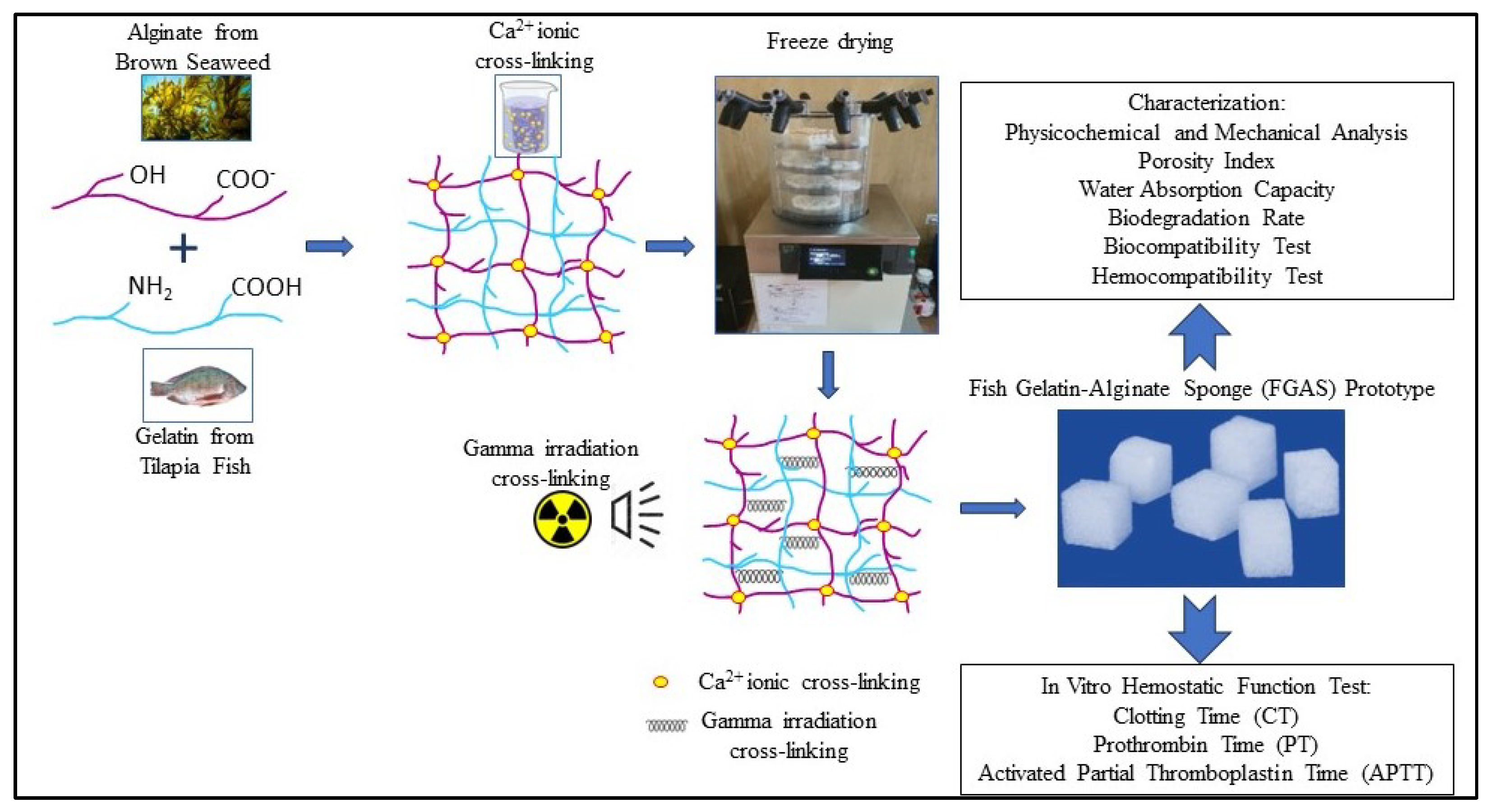
2.2.1. Synthesis of the Fish Gelatin–Alginate Sponge (FGAS) Prototype
2.2.2. Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization
2.2.3. Porosity Index Analysis
2.2.4. Water Absorption Capacity
2.2.5. Biodegradation Rate
2.2.6. Biocompatibility (Cytotoxicity Test)
2.2.7. Hemocompatibility (Hemolysis Test)
2.2.8. Clotting Time (CT)
2.2.9. Prothrombin Time (PT)
2.2.10. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
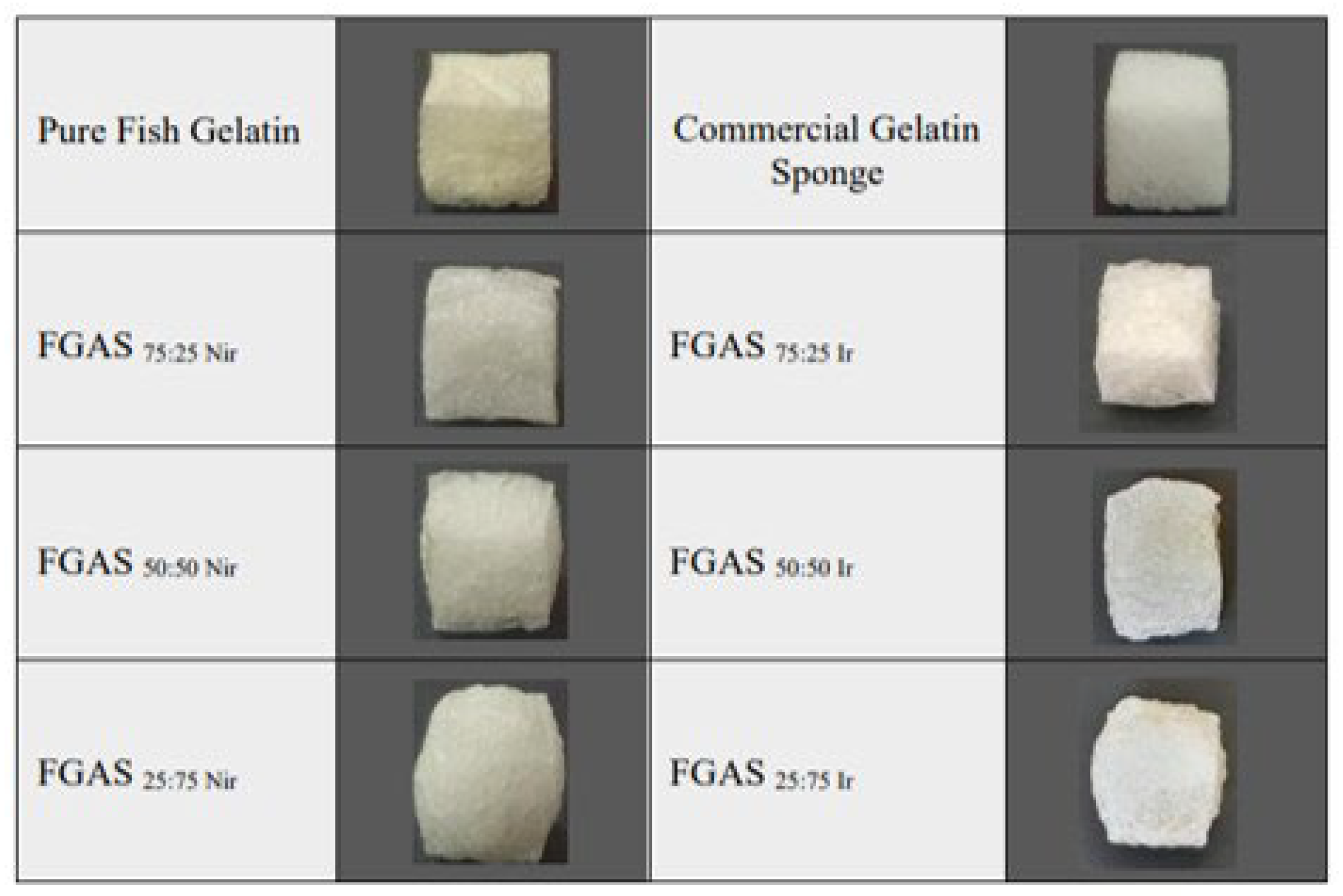
3.1. Synthesis of the Fish Gelatin–Alginate Sponge (FGAS) Prototype
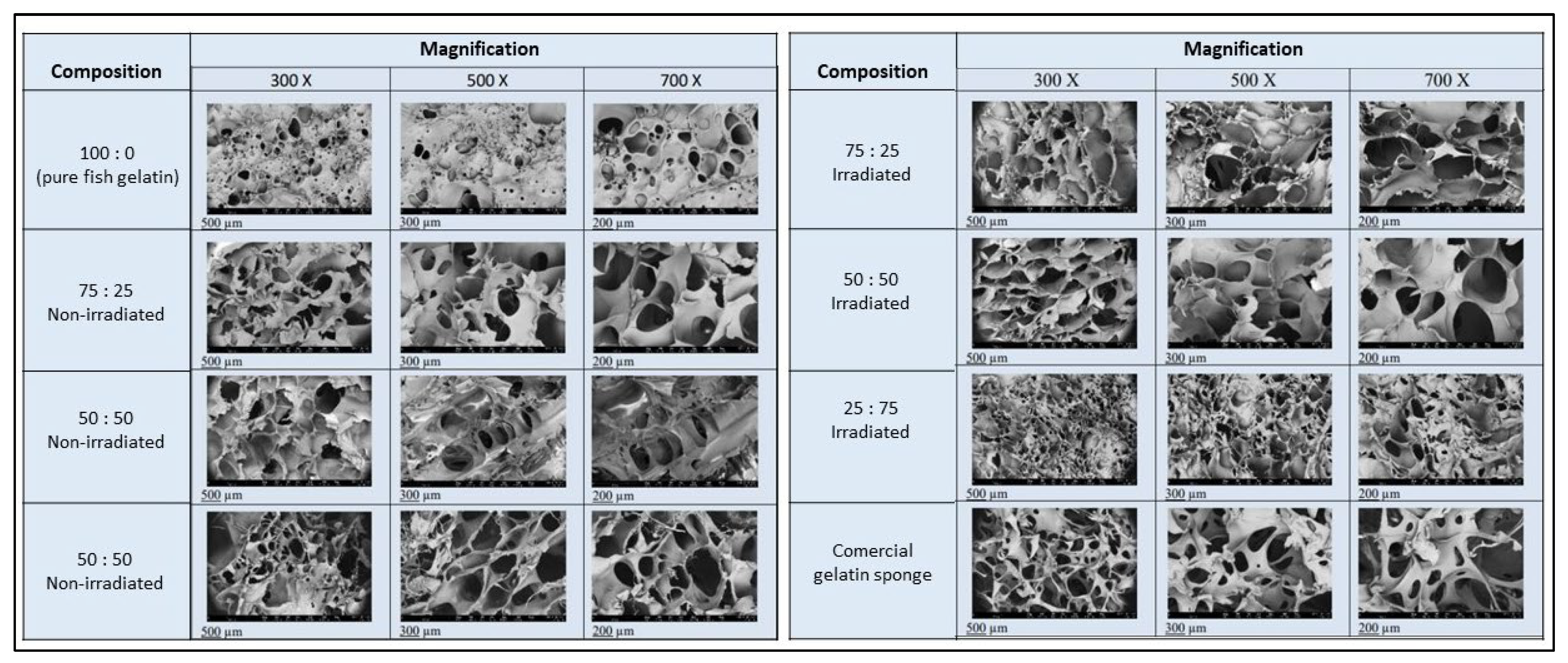
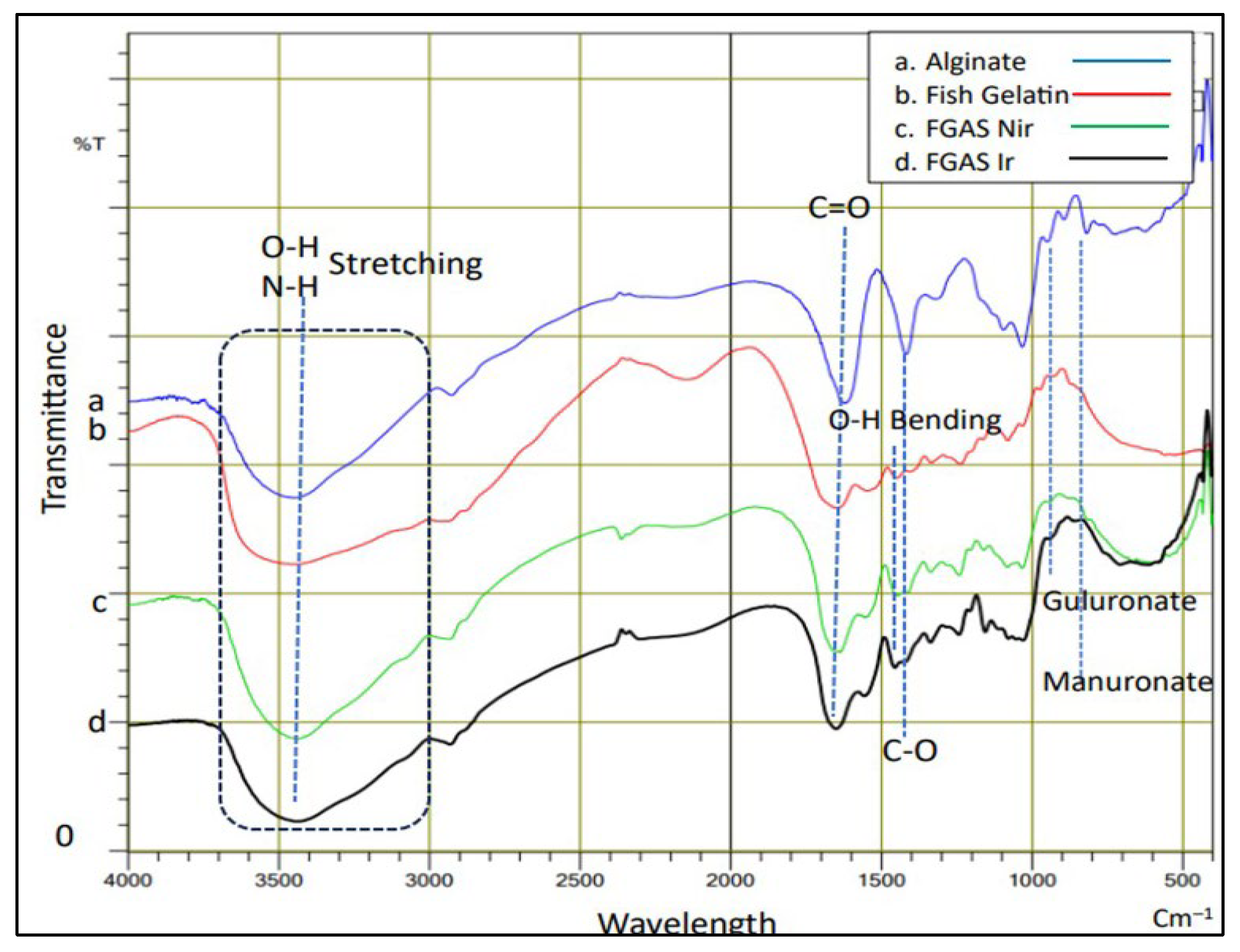
3.2. Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization
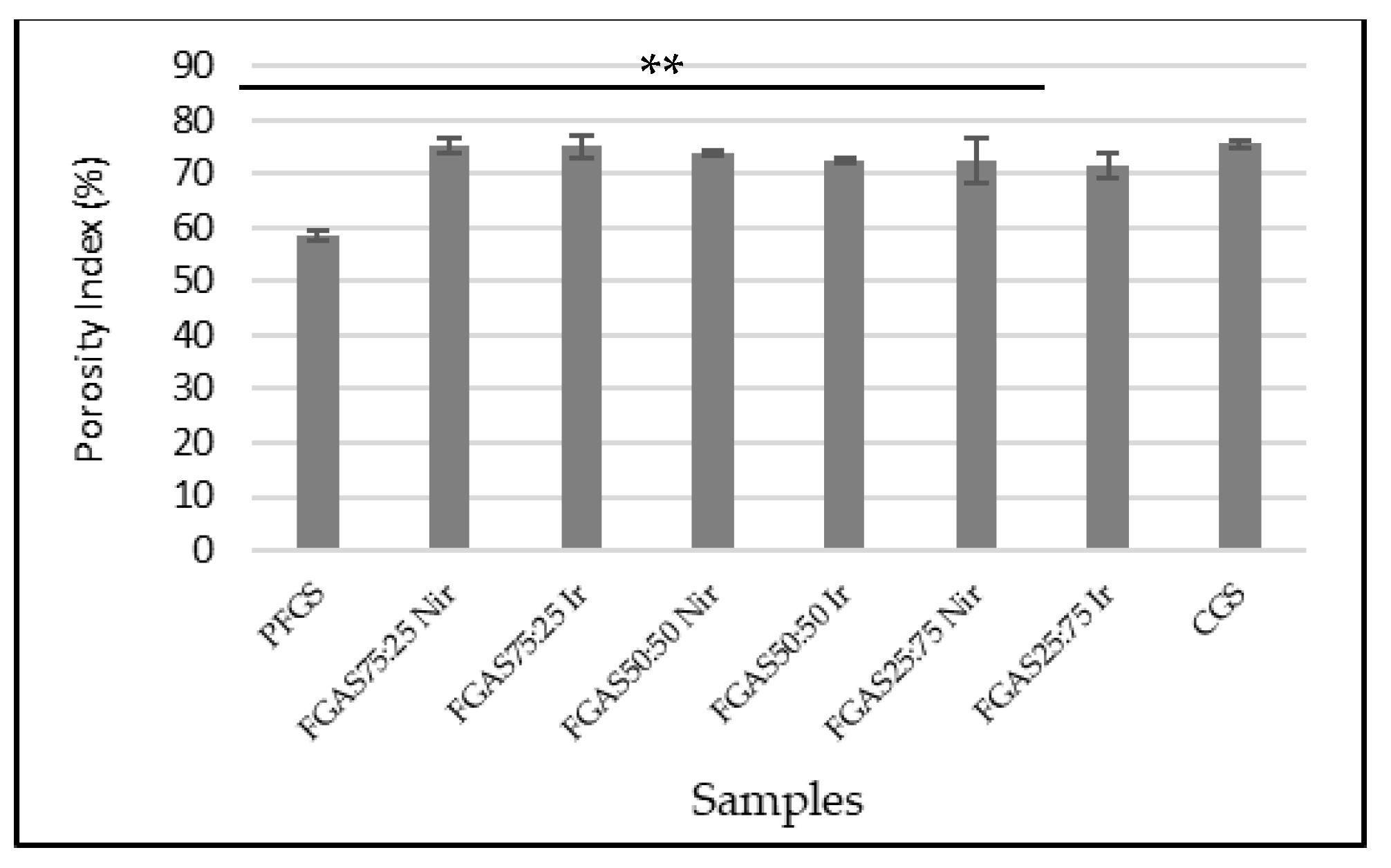
3.3. Porosity Index Analysis
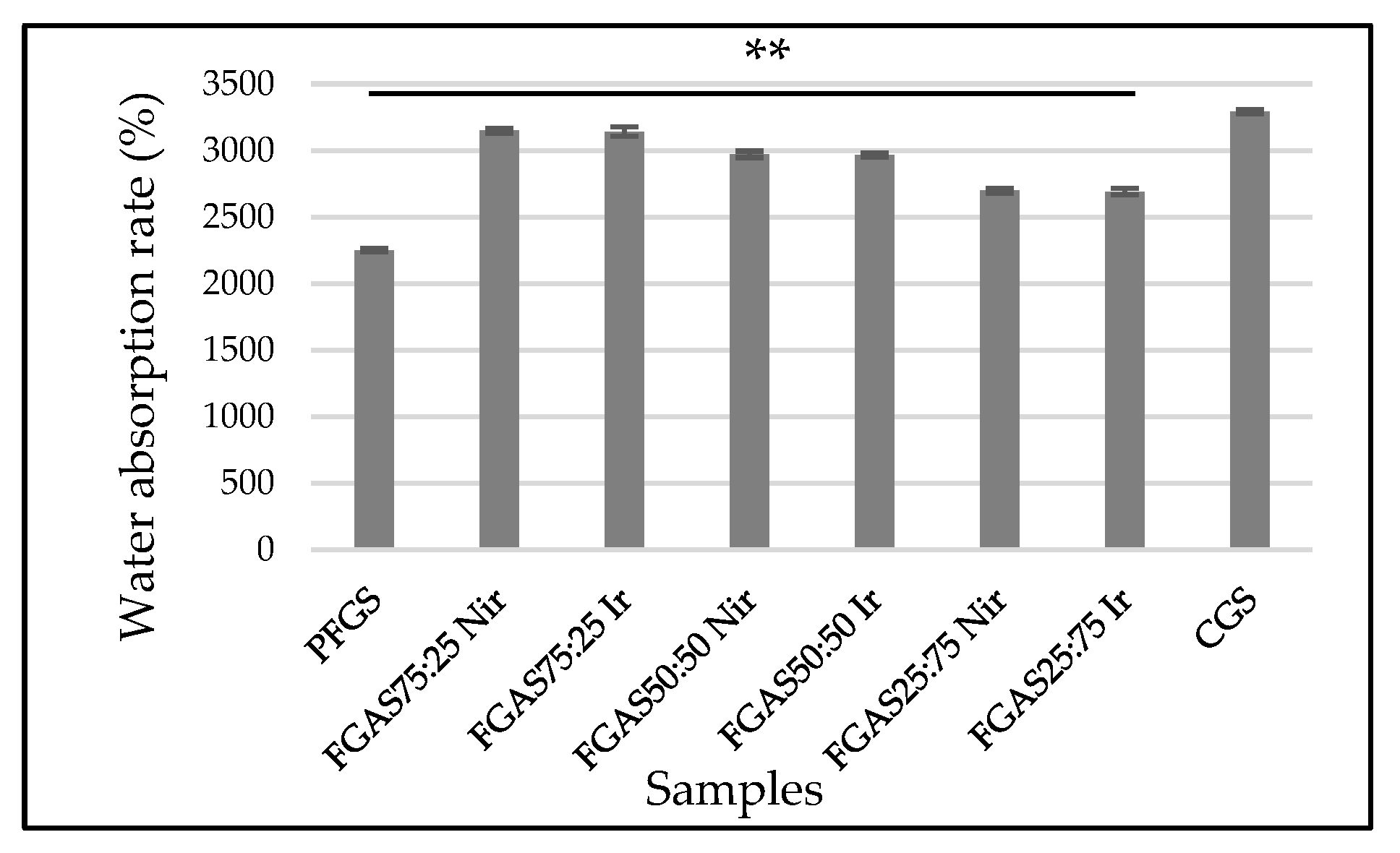
3.4. Water Absorption Capacity
3.5. Biodegradation Rate
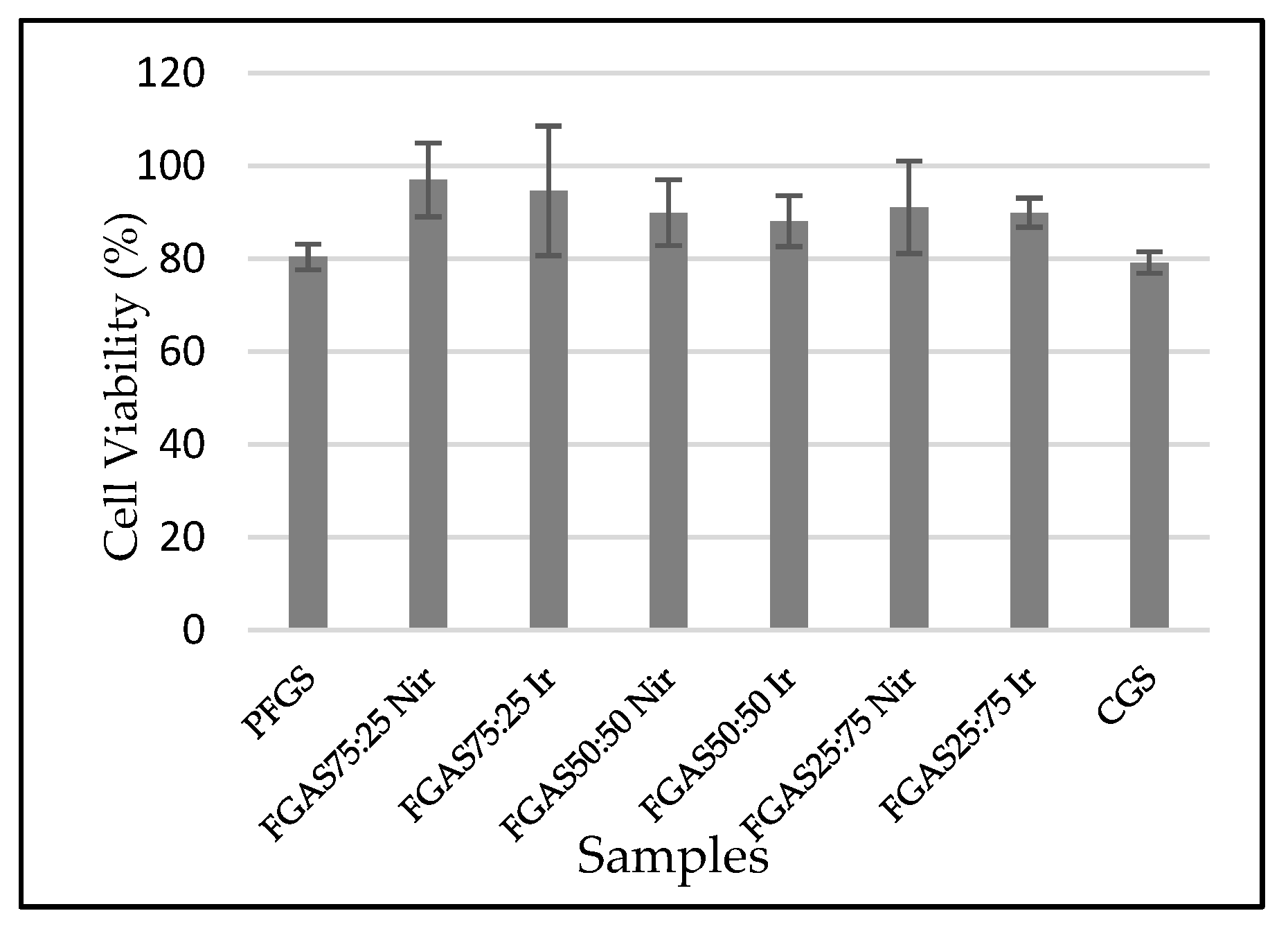
3.6. Biocompatibility (Cytotoxicity Test)
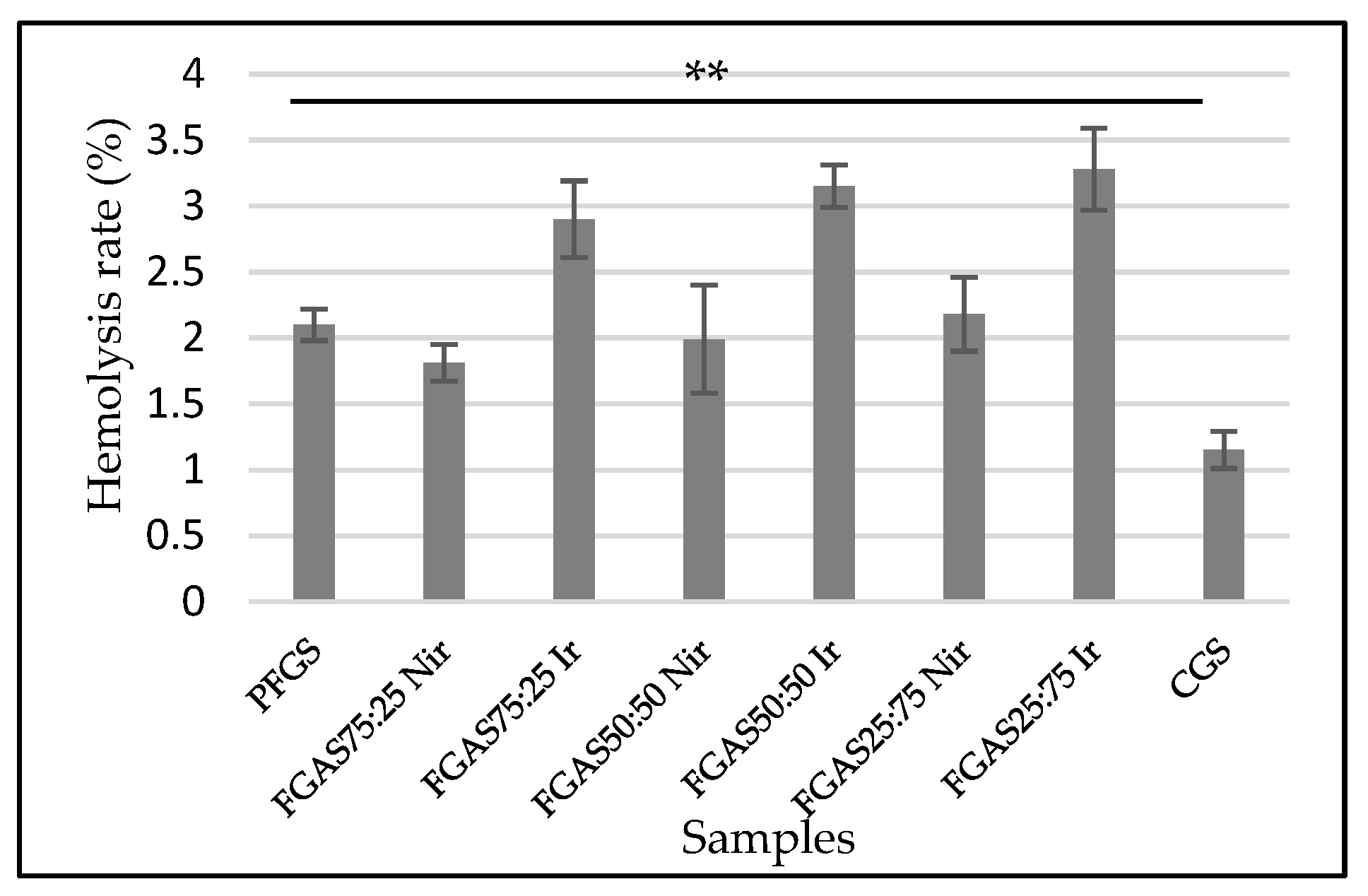
3.7. Hemolysis Test
3.8. Hemostatic Activity Test
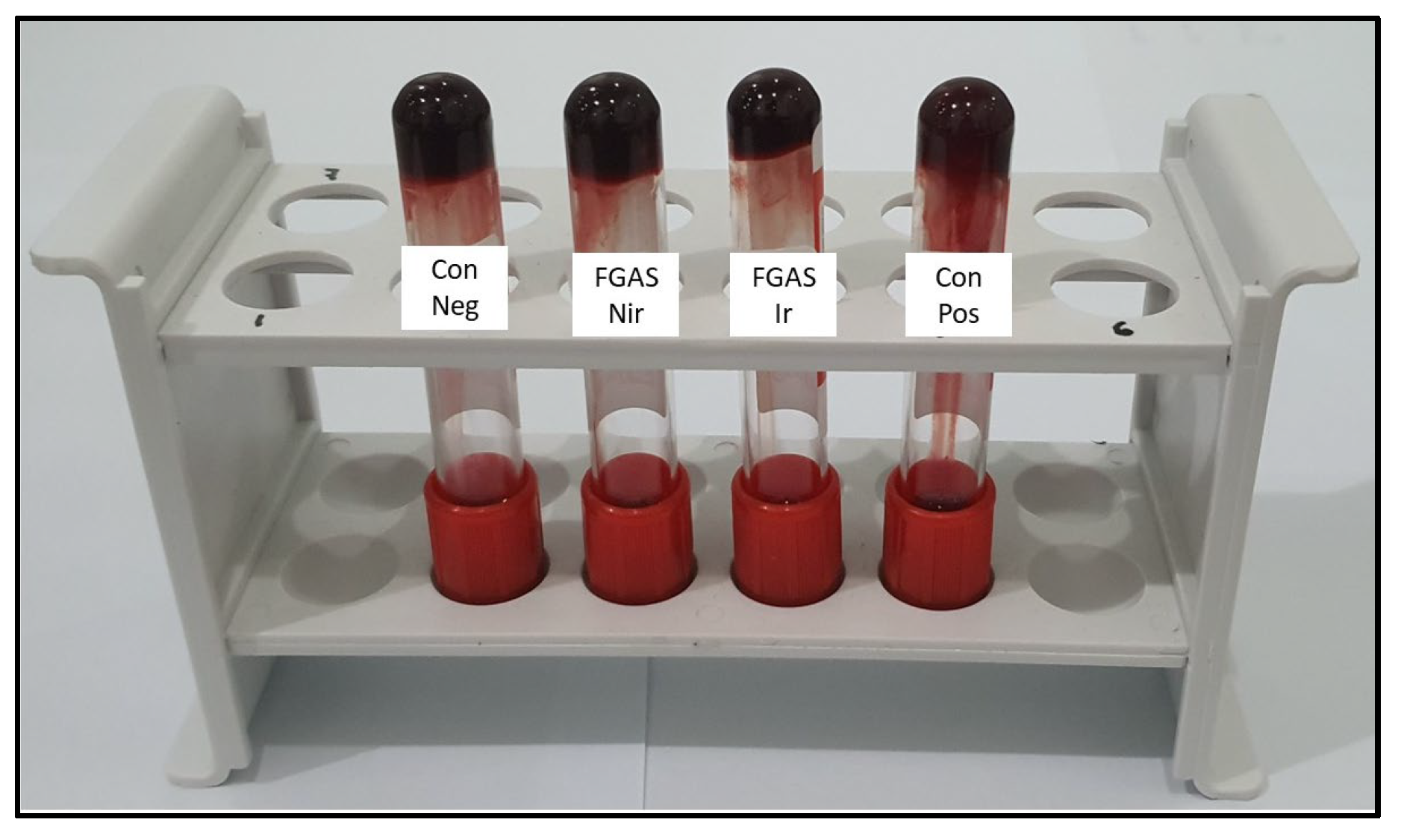
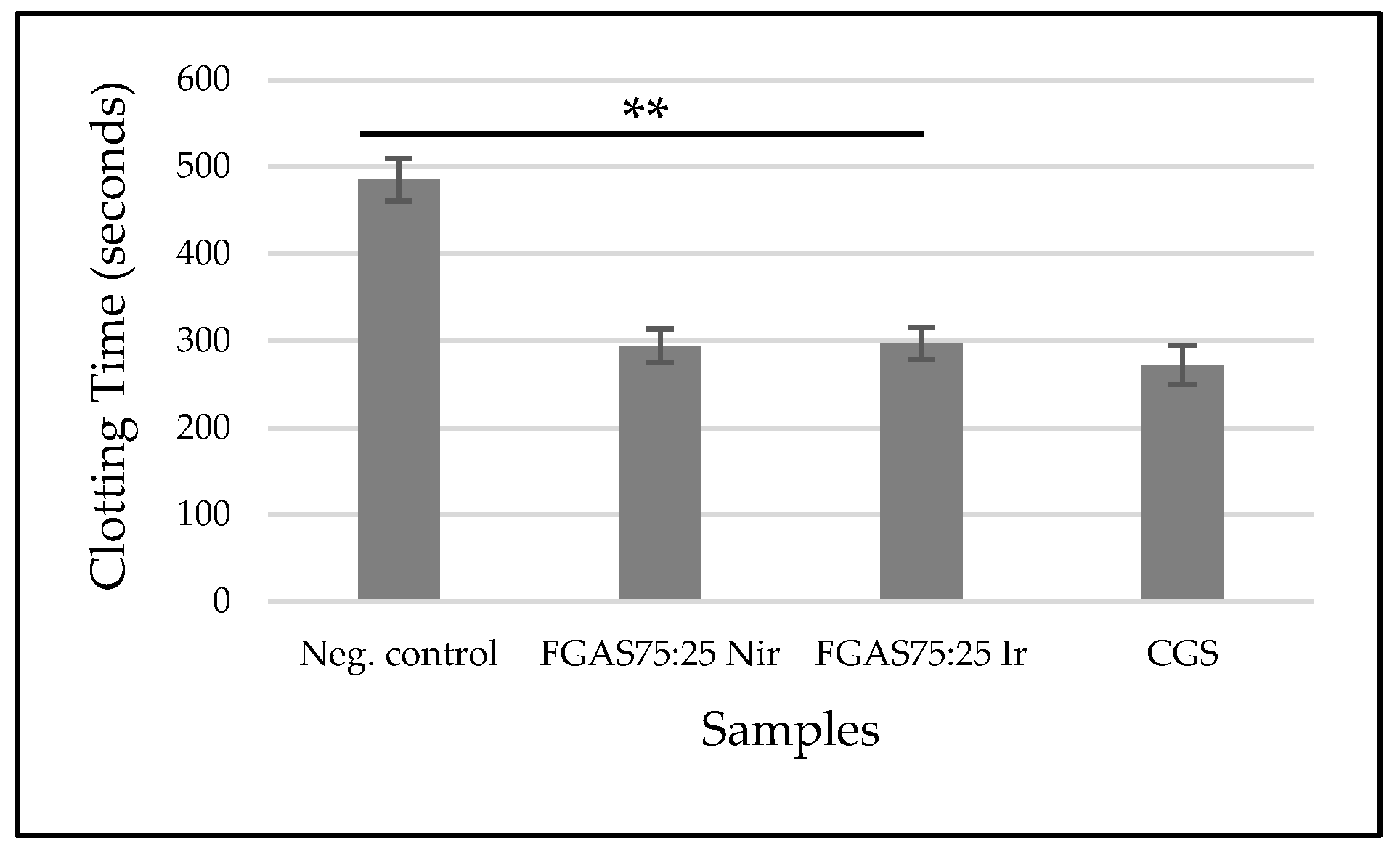
3.8.1. Clotting Time (CT)
3.8.2. Prothrombin Time (PT)
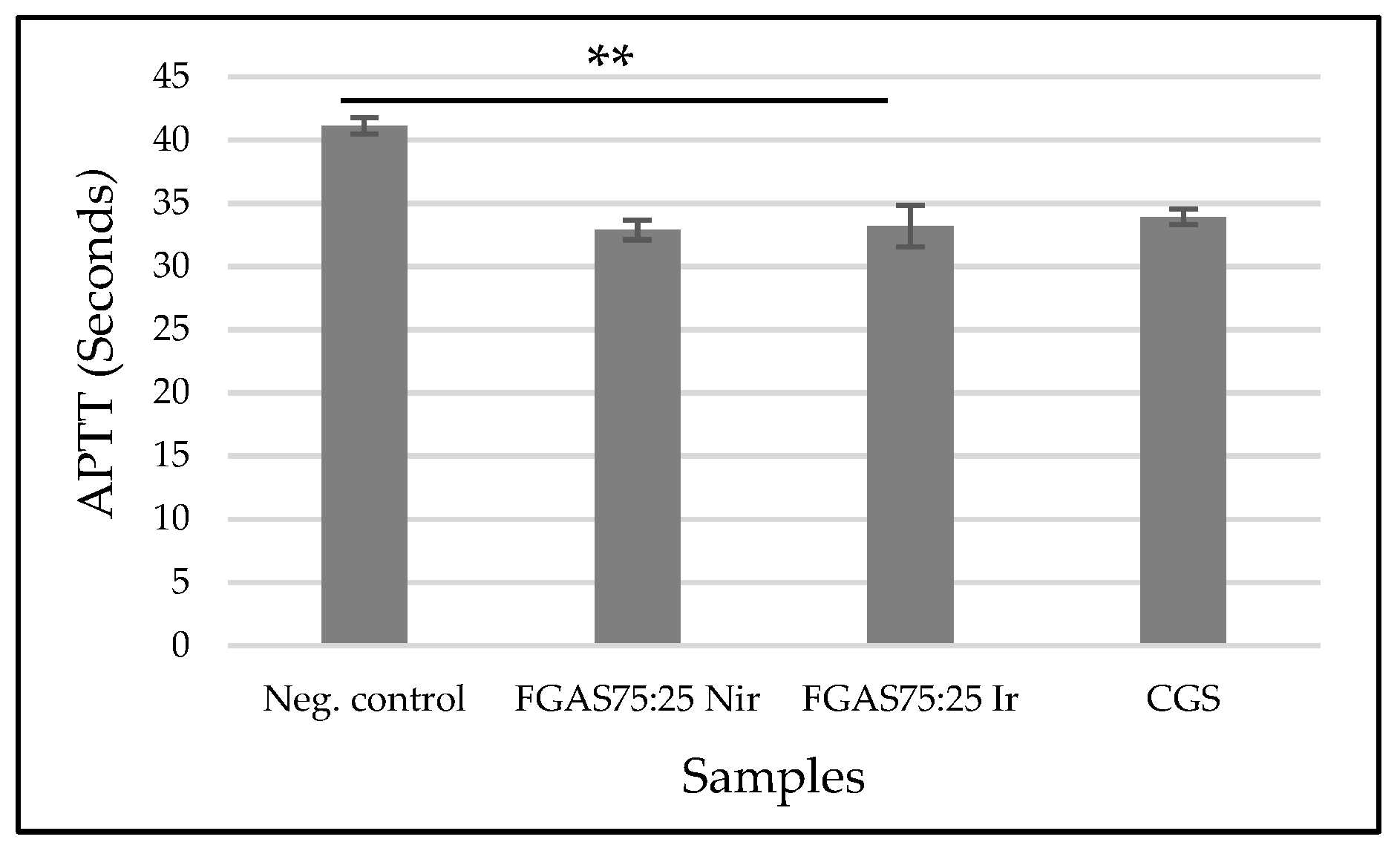
3.8.3. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordy, S.D.; Rhee, P.; Schreiber, M.A. Military applications of novel hemostatic devices. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2011, 8, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Rehman, F.U.; Shah, K.U.; Naz, S.S.; Qaisar, S. Hemostatic strategies for uncontrolled bleeding: A comprehensive update. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.; Todkar, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, Y.; Rehan, M.; Rizvi, Q. Assessment of knowledge, importance and management of uncontrolled bleeding in dental surgical procedures among dental professionals. Int. J. Appl. Dent. Sci. 2021, 7, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos, N.; Furlaneto, F.; Buischi, Y.D.P. Bleeding in dental surgery. In Contemporary Applications of Biologic Hemostatic Agents across Surgical Specialties; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chiara, O.; Cimbanassi, S.; Bellanova, G.; Chiarugi, M.; Mingoli, A.; Olivero, G.; Ribaldi, S.; Tugnoli, G.; Basilicò, S.; Bindi, F.; et al. A systematic review on the use of topical hemostats in trauma and emergency surgery. BMC Surg. 2018, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, N.I.; Mohd Zubir, A.Z.; Suwandi, A.; Haris, M.S.; Jaswir, I.; Lestari, W. Gelatin-based hemostatic agents for medical and dental application at a glance: A narrative literature review. Saudi Dent. J. 2022, 34, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herliana, H.; Yusuf, H.Y.; Laviana, A.; Wandawa, G.; Cahyanto, A. Characterization and Analysis of Chitosan-Gelatin Composite-Based Biomaterial Effectivity as Local Hemostatic Agent: A Systematic Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, J.A.; Akhter, N.; Ashraf, Q.S.; Mir, S.A.; Makroo, H.A.; Majid, D.; Barba, F.J.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Dar, B.N. A comprehensive review on gelatin: Understanding impact of the sources, extraction methods, and modifications on potential packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Mohd Pu’ad, N.A.S.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialisation. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurilmala, M.; Suryamarevita, H.; Husein Hizbullah, H.; Jacoeb, A.M.; Ochiai, Y. Fish skin as a biomaterial for halal collagen and gelatin. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Al-Kahtani, H.A.; Jaswir, I.; AbuTarboush, H.; Ismail, E.A. Extraction and characterization of gelatin from camel skin (potential halal gelatin) and production of gelatin nanoparticles. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.; Shangguan, X.; Sha, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bansal, N. Fish gelatin modifications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, A.; Stobel Christy, E.J.; Pius, A. Biopolymer blends and composites: Processing technologies and their properties for industrial applications. Biopolym. Their Ind. Appl. 2021, 105–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, H.W.; Toong, D.W.Y.; Ng, J.C.K.; Ow, V.; Lu, S.; Tan, L.P.; Wong, P.E.H.; Venkatraman, S.; Huang, Y.; Ang, H.Y. Polymer blends and polymer composites for cardiovascular implants. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocolloids 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Choi, J.B.; Jang, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Bae, T.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, J.M.; Lee, M.H. Mammalian and fish gelatin methacryloyl–alginate interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels for tissue engineering. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17433–17441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.W.; Huang, M.S.; Chang, C.Y.; Lu, C.T.; Chen, W.C.; Lin, J.H. Preliminary study in cross-linked gelatin/alginate sponges. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 184–185, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.; Mehdipour, A.; Salmanipour, S.; Alipour, N.; Salehi, R. Highly Porous Alginate/Gelatin Sponge for Hemostasis of Severe Femoral Bleeding in Rats. Stud. Med. Sci. 2023, 33, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, L.; Deng, L. Radiation cross-linked gelatin/sodium alginate/carboxymethylcellulose sodium hydrogel for the application as debridement glue paste. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyanti Erizal Apriyani, R.Z.; Perkasa, D.P.; Lestari, I.; Rahmi, H. Synthesis of Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)-Gelatin Hydrogel from White Snapper (Lates calcarifer, Bloch) with Gamma Irradiation and Its Characterizations. Atom. Indones. 2023, 49, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Butler, J.A.; Britten, N.S.; Venkatraman, P.D.; Rahatekar, S.S. Natural antimicrobial nano composite fibres manufactured from a combination of alginate and oregano essential oil. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin compared to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ouyang, Q.Q.; Cheng, Y.; Hong, P.Z.; Liao, M.N.; Chen, F.J.; Li, S.D. Optimization of preparation process and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate hemostatic sponge. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 213, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Jo, C.; Lee, N.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Byun, M.W. A combination of gamma irradiation and CaCl2 immersion for a pectin-based biodegradable film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Z.K.; Lai, P.L.; Toh, E.K.W.; Weng, C.H.; Tseng, H.W.; Chang, P.Z.; Chen, C.C.; Cheng, C.M. Osteogenic differentiation of preosteoblasts on a hemostatic gelatin sponge. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Włodarczyk-Biegun, M.K. Faithful scanning electron microscopic (SEM) visualization of 3D printed alginate-based scaffolds. Bioprinting 2020, 20, e00098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Zhuang, Q.; Huang, G.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X. Infrared Spectrum Characteristics and Quantification of OH Groups in Coal. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 17064–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Quan, K.; Liang, Y.; Li, T.; Yuan, Q.; Tao, L.; Xie, Q.; Wang, X. Graphene-Montmorillonite Composite Sponge for Safe and Effective Hemostasis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 35071–35080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojat, N.; Gentile, P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Šiller, L. Automatic pore size measurements from scanning electron microscopy images of porous scaffolds. J. Porous Mater. 2023, 30, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasya, A.Y.; Kusumawati, D.H. Karakteristik Porositas Wound Dressing Nanofiber PVA-Ekstrak Daun Nangka. J. Inov. Fis Indones. 2023, 12, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, P. Alginate/gelatin blended hydrogel fibers cross-linked by Ca 2+ and oxidized starch: Preparation and properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Pan, H.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; Ji, D.; Yun, K.; Su, Y.; Liu, D.; Pan, W. A novel alginate/gelatin sponge combined with curcumin-loaded electrospun fibers for postoperative rapid hemostasis and prevention of tumor recurrence. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, S.; Maleki Dizaj, S.; Ahmadian, E.; Karimpour, A.; Maleki, A.; Memar, M.Y.; Ghavimi, M.A.; Dalir Abdolahinia, E.; Goh, K.W. A Biodegradable Flexible Micro/Nano-Structured Porous Hemostatic Dental Sponge. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahadat Hossain, M.; Shaikh, M.A.A.; Jahan, S.A.; Mahmud, M.; Bin Mobarak, M.; Rahaman, M.S.; Uddin, M.N.; Ahmed, S. Exploring the biomedical competency of gamma-radiation aided hydroxyapatite and its composite fabricated with nano-cellulose and chitosan. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 9654–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, Y.L. Coagulation. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2014, 44, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulat, M.; Ozukaya, D. Preparation and Characterization of Na-Alginate Hydrogel Beads. Eurasia Proc. Sci. Technol. Eng. Math. (EPSTEM) 2019, 6, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, N.; Singh, B.; Sharma, S. Hydrogels for potential food application: Effect of sodium alginate and calcium chloride on physical and morphological properties. Pharma Innov. J. 2018, 7, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xia, F. Role of a high calcium ion content in extending the properties of alginate dual-crosslinked hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25390–25401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, A.; Tran, H.D.N.; Nguyen, N.T.; Ta, H.T. Advances in haemostatic sponges: Characteristics and the underlying mechanisms for rapid haemostasis. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 27, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, M. Porosity parameters in biomaterial science: Definition, impact, and challenges in tissue engineering. Front. Mater. Sci. 2021, 15, 352–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheraslani, M.; Gardeniers, H. High-Resolution SEM and EDX Characterization of Deposits Formed by CH4+Ar DBD Plasma Processing in a Packed Bed Reactor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkasa, D.P.; Erizal, E.; Darmawan, D.; Rasyid, A. Effect of gamma irradiation on mechanical and thermal properties of fish gelatin film isolated from Lates calcarifer scales. Indones. J. Chem. 2013, 13, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I.; Kolotova, D.S.; Kuchina, Y.A. Interactions between gelatin and sodium alginate: UV and FTIR studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Huang, Z.; McCarthy, A.; Huang, Y.; Pan, J.; Chen, S.; Wan, W. Super-Elastic Carbonized Mushroom Aerogel for Management of Uncontrolled Hemorrhage. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Yates, K.; Vogt, C.; Qian, Z.; Frost, M.C.; Zhao, F. Increasing mechanical strength of gelatin hydrogels by divalent metal ion removal. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atma, Y. Synthesis and application of fish gelatin for hydrogels/composite hydrogels: A review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 3966–3976. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Cheng, K.; Wang, Y.; Yi, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Liang, K.; Zhang, M. Dual green hemostatic sponges constructed by collagen fibers disintegrated from Halocynthia roretzi by a shortcut method. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 24, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afjoul, H.; Shamloo, A.; Kamali, A. Freeze-gelled alginate/gelatin scaffolds for wound healing applications: An in vitro, in vivo study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarai, A.; Kasparkova, V.; Sedlacek, T.; Saha, P. A comparative study of crosslinked sodium alginate/gelatin hydrogels for wound dressing. In Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS international conference on Energy and development-environment-biomedicine EMESEG’11, Corfu Island, Greece, 14–16 July 2011; pp. 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nimry, S.; Dayah, A.A.; Hasan, I.; Daghmash, R. Cosmetic, Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications of Fish Gelatin/Hydrolysates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Long, H.; Ma, K.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J. Assessment of the characteristics and biocompatibility of gelatin sponge scaffolds prepared by various crosslinking methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junkyu, S. Evaluation of Calcium Alginate Microparticles Prepared Using a Novel Nebulized Aerosol Mediated Interfacial Crosslinking Method. Master’s Thesis, University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Foox, M.; Ben-Tzur, M.; Koifman, N.; Zilberman, M. Effect of gamma radiation on novel gelatin alginate-based bioadhesives. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.; Azam, N.; Moni, N.; Gobetti, A.; Ramorino, G. Advances in Modulating Mechanical Properties of Gelatin-Based Hydrogel in Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, S.; Nickel, A. Toxic or not toxic? The specifications of the standard ISO 10993-5 are not explicit enough to yield comparable results in the cytotoxicity assessment of an identical medical device. Front. Med. Technol. 2023, 5, 1195529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallapalli, S.; Liman, A.M.; Guhathakurta, S. Hemocompatibility and surface properties of bovine pericardial patches: Effects of gamma sterilization. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2016, 6, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalezinková, M. In vitro hemocompatibility testing of medical devices. Thromb. Res. 2020, 195, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Li, M.; Gong, J.; Meng, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, J. Silk fibroin/gelatin/calcium alginate composite materials: Preparation, pore characteristics, comprehensive hemostasis in vitro. Mater. Des. 2022, 216, 110577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Gao, P.; He, F.; Zhang, C. Application of Alginate-Based Hydrogels in Hemostasis. Gels 2022, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Qin, S. Three polymers from the sea: Unique structures, directional modifications, and medical applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Luan, S.; Yin, J.; Li, X.; Shi, H. Surface-Adaptive and On-Demand Antibacterial Sponge for Synergistic Rapid Hemostasis and Wound Disinfection. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sah, D.K.; Khanna, K.; Rai, Y.; Yadav, A.K.; Ansari, M.S.; Bhatt, A.N. A calcium and zinc composite alginate hydrogel for pre-hospital hemostasis and wound care. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Composition | Chemical Elements (wt%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | Nitrogen (N) | Oxygen (O) | Calcium (Ca) | ||
| 1 | PFGS | 22.478 | 21.578 | 16.583 | - |
| 2 | FGAS75:25 Nir | 5.506 | 12.613 | 10.711 | 30.030 |
| 3 | FGAS50:50 Nir | 6.300 | 4.600 | 9.800 | 25.600 |
| 4 | FGAS25:75 Nir | 1.800 | 1.900 | 5.300 | 18.700 |
| 5 | FGAS75:25 Ir | 20.500 | 27.000 | 8.900 | 22.000 |
| 6 | FGAS50:50 Ir | 18.418 | 15.516 | 14.715 | 19.119 |
| 7 | FGAS25:75 Ir | 17.700 | 6.900 | 16.700 | 17.700 |
| 8 | CGS | 35.200 | 33.900 | 30.900 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herliana, H.; Yusuf, H.Y.; Laviana, A.; Wandawa, G.; Abbas, B. In Vitro Hemostatic Activity of Novel Fish Gelatin–Alginate Sponge (FGAS) Prototype. Polymers 2024, 16, 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142047
Herliana H, Yusuf HY, Laviana A, Wandawa G, Abbas B. In Vitro Hemostatic Activity of Novel Fish Gelatin–Alginate Sponge (FGAS) Prototype. Polymers. 2024; 16(14):2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142047
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerliana, Heri, Harmas Yazid Yusuf, Avi Laviana, Ganesha Wandawa, and Basril Abbas. 2024. "In Vitro Hemostatic Activity of Novel Fish Gelatin–Alginate Sponge (FGAS) Prototype" Polymers 16, no. 14: 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142047
APA StyleHerliana, H., Yusuf, H. Y., Laviana, A., Wandawa, G., & Abbas, B. (2024). In Vitro Hemostatic Activity of Novel Fish Gelatin–Alginate Sponge (FGAS) Prototype. Polymers, 16(14), 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16142047







