Mass Spectrometry of Collagen-Containing Allogeneic Human Bone Tissue Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Sources and Materials
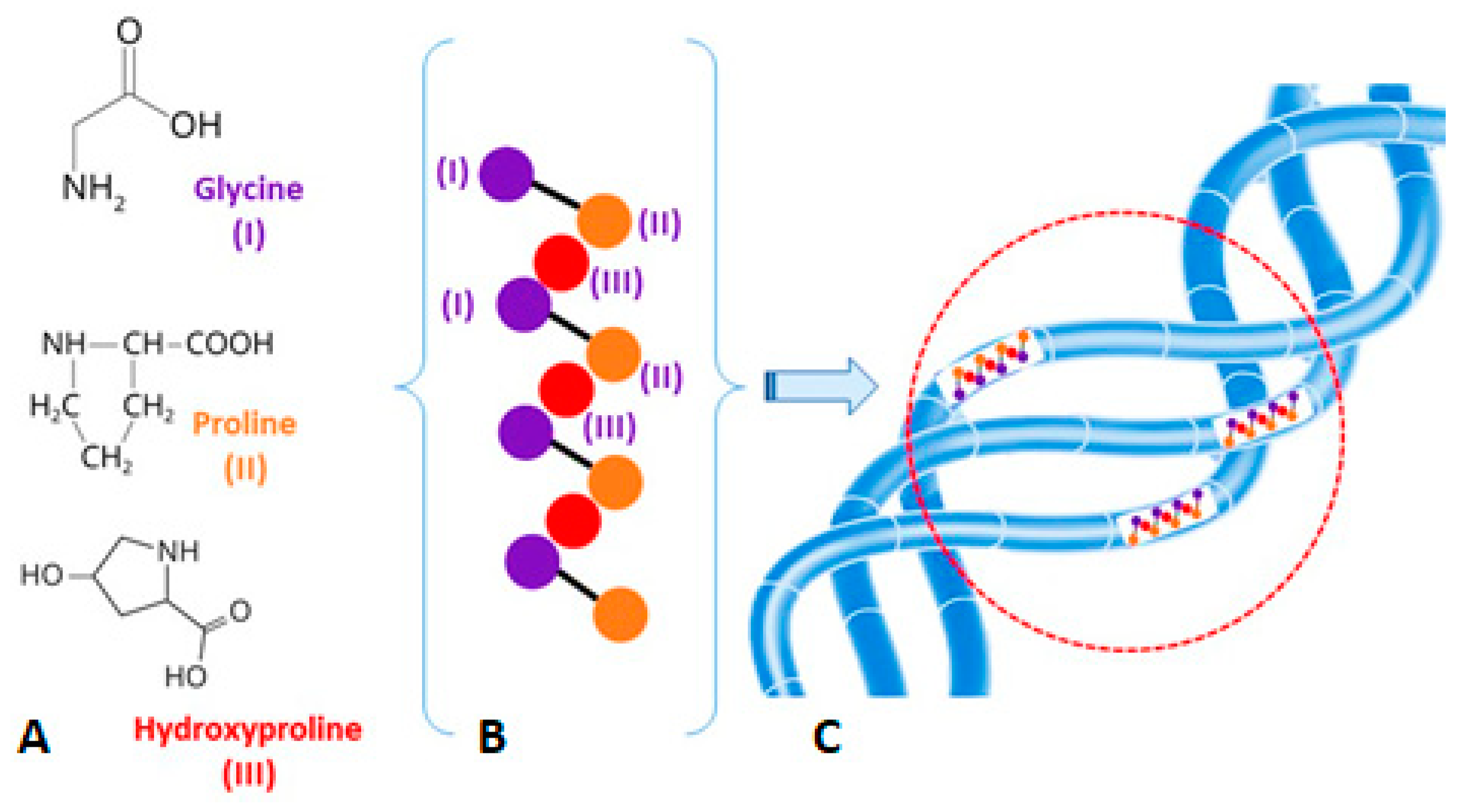
2.2. Studying Object
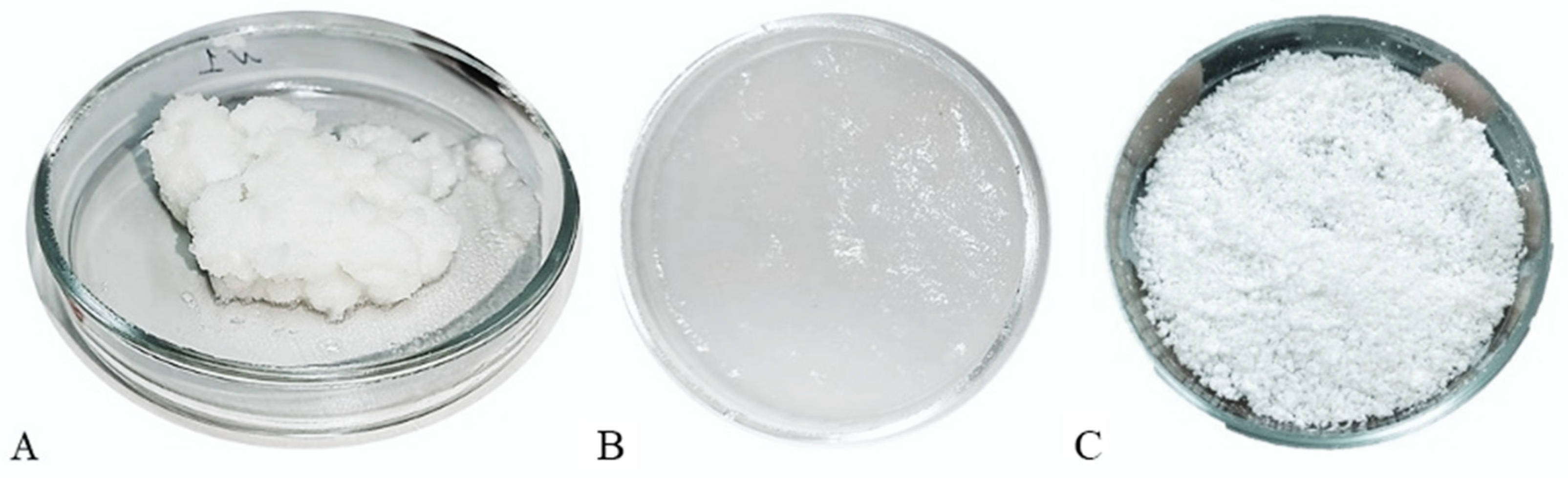
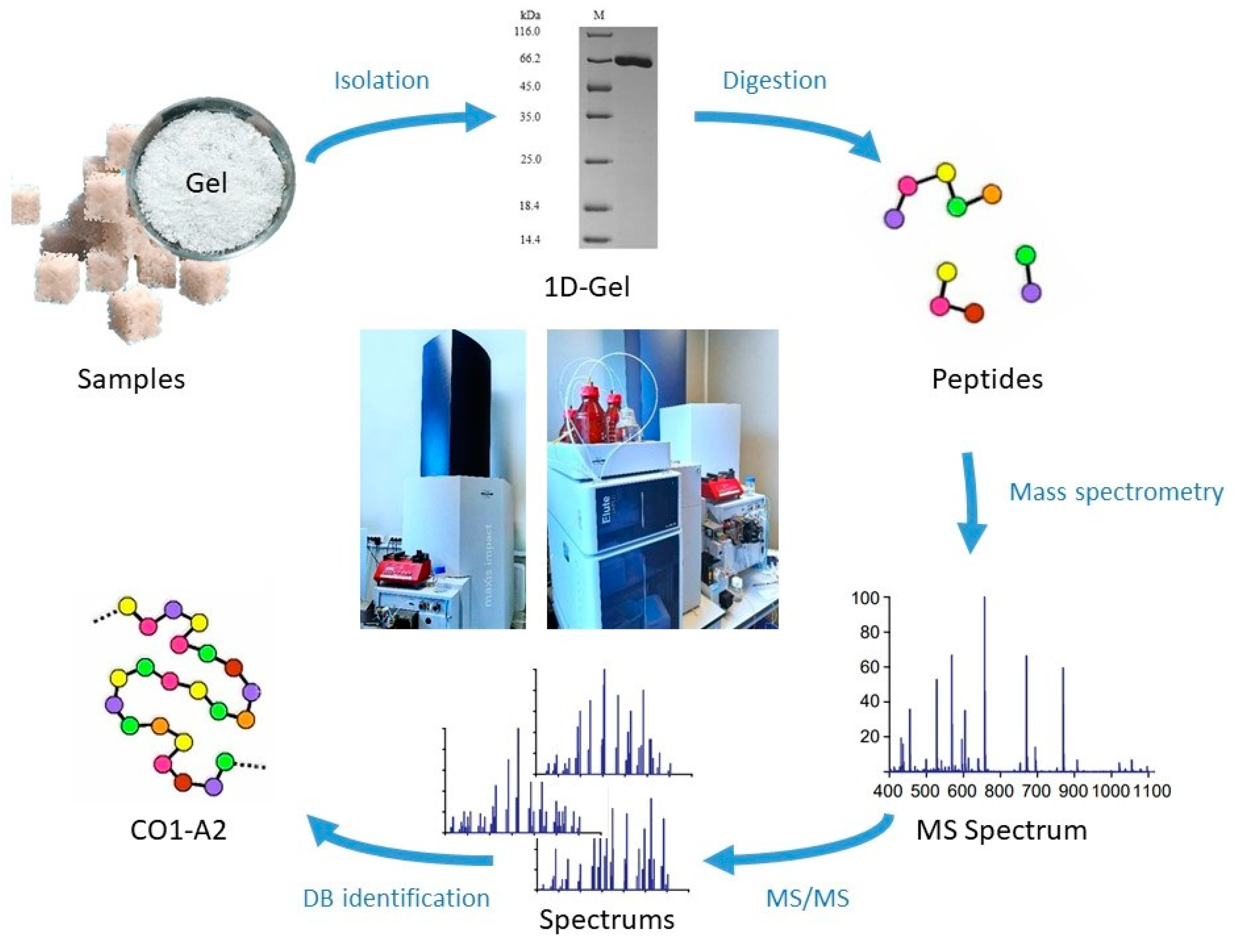
2.3. Sample Preparation
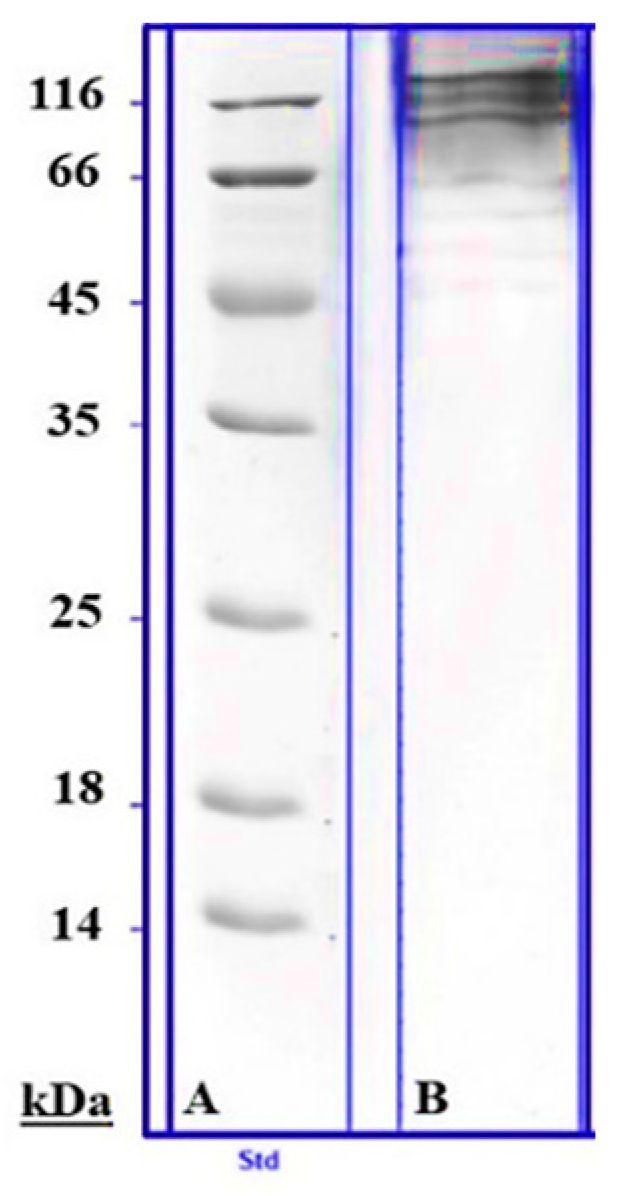
2.4. Mass Spectrometry (Proteomic Assay)
3. Results and Discussion
- fibril-forming collagen type I;
- cartilaginous tissue-specific collagen type II;
- collagen type IV, the main structural component of basal membranes;
- collagen type IX, a hyaline cartilage component;
- collagen type XXVII, the protein essential for cartilage calcification and cartilage-bone transformation;
- collagen type XXVIII, cell-binding protein.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| AARS2 | Alanine-tRNA-ligase |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| AHNAK | Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein |
| Ala-AMP | Alanine-adenosine monophosphate |
| AREs | Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BMAL1/2 | Brain and muscle arnt-like 1/2, or Arntl |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A |
| CLOCK | Clock Circadian Regulator |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain |
| COL1A2 | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain |
| COL27A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XXVII) chain |
| COL28A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XXVIII) chain |
| COL2A1 | Collagen alpha-1(II) chain |
| COL4A2 | Collagen alpha-2(IV) chain |
| COL9A2 | Collagen alpha-2(IX) chain |
| CRY1 | Cryptochrome-1 |
| CRY1 (2) | Cryptochrome Circadian Regulator 1 (2) |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| ELAVL3 | ELAV Like RNA Binding Protein 3 |
| ITGA10 | Integrin alpha-10 |
| JARID2 | Jumonji protein |
| JMJD5 | Jumonji-C (JmjC) domain-containing protein 5 |
| KDM8 | Lysine Demethylase 8 |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| NPAS2 | Neuronal PAS Domain Protein 2 |
| NR1D1 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group D Member 1 |
| PER1/2/3 | Period Circadian Regulator 1/2/3 |
| PRC2 | Polycomb repressive complex 2 |
| RORA/B/G | Related Orphan Receptor A/B/G |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel |
| SPTBN2 | Spectrin beta chain non-erythrocytic 2 |
| TTFL | Transcription/translation feedback loop |
| UPLC | ultra-high performance liquid chromatography |
| UPLC-MS | Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography—mass spectrometry |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| ZNF267 | Zinc finger protein 267 |
| ZNF394 | Zinc finger protein 394 |
| ZNF585 A | Zinc finger protein 585 A |
| H1/2/3/4 | Histones 1/2/3/4 |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Qing, L.; Luo, G.; Ahmadpoor, X.; Li, X.; Wu, P.; Tang, J. Variations in deep iliac circumflex artery perforator chimeric flap design for single-stage customized-reconstruction of composite bone and soft-tissue defect. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2023, 87, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ni, S.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Chu, H.Y.; Zhang, N.; Sun, M.; Li, N.; Ren, Q.; et al. Targeting loop3 of sclerostin preserves its cardiovascular protective action and promotes bone formation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhai, W.; Cheng, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Unraveling of Advances in 3D-Printed Polymer-Based Bone Scaffolds. Polymers 2022, 14, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Y.; Yin, Y.; Guan, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, J. Rational Design of Bioactive Materials for Bone Hemostasis and Defect Repair. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2023, 4, 0058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiklin, I.L.; Pugachev, E.I.; Kolsanov, A.V.; Timchenko, E.V.; Boltovskaya, V.V.; Timchenko, P.E.; Volova, L.T. Biopolymer Material from Human Spongiosa for Regenerative Medicine Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.R.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E. Advanced Strategies for Tissue Engineering in Regenerative Medicine: A Biofabrication and Biopolymer Perspective. Molecules 2021, 26, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. On the Mechanisms of Biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokoshkin, S.; Pustov, Y.; Zhukova, Y.; Kadirov, P.; Karavaeva, M.; Prosviryakov, A.; Dubinskiy, S. Effect of Thermomechanical Treatment on Structure and Functional Fatigue Characteristics of Biodegradable Fe-30mn-5si (Wt %) Shape Memory Alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, M.; Doi, Y.; Hellwich, K.H.; Hess, M.; Hodge, P.; Kubisa, P.; Rinaudo, M.; Schué, F. Terminology for Biorelated Polymers and Applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 377–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications of Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, S.; Layland, S.L.; Schenke-Layland, K. ECM and ECM-like Materials—Biomaterials for Applications in Regenerative Medicine and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Collagen for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelse, K. Collagens—Structure, Function, and Biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.; Kajave, N.; Cai, H.H.; Gu, L.; Albanna, M.; Kishore, V. In Vitro Characterization of Xeno-Free Clinically Relevant Human Collagen and Its Applicability in Cell-Laden 3D Bioprinting. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 35, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowacki, J.; Mizuno, S. Collagen Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, M.; Bieri, O.; Miska, M.; Wiewiorski, M.; Hainc, N.; Valderrabano, V.; Studler, U. Characterization of the Collagen Component of Cartilage Repair Tissue of the Talus with Quantitative MRI: Comparison of T2 Relaxation Time Measurements with a Diffusion-Weighted Double-Echo Steady-State Sequence (DwDESS). Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Taniguchi, T.; Goda, Y.; Kosaka, H.; Higashino, K.; Sakai, T.; Katoh, S.; Yasui, N.; Sairyo, K.; Taniguchi, H. Proteomic Analysis of Human Tendon and Ligament: Solubilization and Analysis of Insoluble Extracellular Matrix in Connective Tissues. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 4709–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammi, M.J.; Häyrinen, J.; Mahonen, A. Proteomic Analysis of Cartilage- and Bone-associated Samples. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 2687–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.R. Mass Spectrometry of Proteins and Peptides; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; p. 539. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, J.R.; Ruse, C.I.; Nakorchevsky, A. Proteomics by Mass Spectrometry: Approaches, Advances, and Applications. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 11, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addona, T.A.; Shi, X.; Keshishian, H.; Mani, D.R.; Burgess, M.; Gillette, M.A.; Clauser, K.R.; Shen, D.; Lewis, G.D.; Farrell, L.A.; et al. A Pipeline That Integrates the Discovery and Verification of Plasma Protein Biomarkers Reveals Candidate Markers for Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naba, A.; Pearce, O.M.T.; Del Rosario, A.; Ma, D.; Ding, H.; Rajeeve, V.; Cutillas, P.R.; Balkwill, F.R.; Hynes, R.O. Characterization of the Extracellular Matrix of Normal and Diseased Tissues Using Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Ciborowski, M.; Kisluk, J.; Kretowski, A.; Barbas, C. Mass Spectrometry Based Proteomics and Metabolomics in Personalized Oncology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, S.P.; Dubey, P.K.; Rachana, R.; Mani, S.; Yadav, D.; Agarwal, M.; Agarwal, S.; Agarwal, V.; Kaur, H. Advent of Proteomic Tools for Diagnostic Biomarker Analysis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 13485:2016; Medical Devices—Quality Management Systems—Requirements for Regulatory Purposes. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 9001:2015; Quality Management Systems—Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Timchenko, P.E.; Timchenko, E.V.; Volova, L.T.; Zybin, M.A.; Frolov, O.O.; Dolgushov, G.G. Optical Assessment of Dentin Materials. Opt. Mem. Neural Netw. 2020, 29, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, L.T. Method for Manufacturing Large-Block Lyophilized Bone Implants. Russian Federation Patent No. 2366173 C1, 15 May 2008. IPC A01N 1/00. No. 2008119004/14: Application. 05/15/2008: Publ. 09/10/2009. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.H.; Sponseller, P.; Mims, B.; Child, A.; Milewicz, D.M.; Blanton, S.H. Genetic Analysis of Structural Elastic Fiber and Collagen Genes in Familial Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Orthop. Res. 1996, 14, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Rest, M.; Garrone, R. Collagen Family of Proteins. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Center for Biotechnology Information Advances Science and Health by Providing Access to Biomedical and Genomic Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- White, D. The Collagen Receptor Subfamily of the Integrins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camper, L.; Holmvall, K.; Wangnerud, C.; Aszodi, A.; Lundgren-Akerlund, E. Distribution of the collagenbinding integrin alpha10beta1 during mouse development. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 306, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiger, C.F.; Fougerousse, F.; Grundström, G.; Velling, T.; Gullberg, D. A11β1 Integrin Is a Receptor for Interstitial Collagens Involved in Cell Migration and Collagen Reorganization on Mesenchymal Nonmuscle Cells. Dev. Biol. 2001, 237, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, J. The Collagen Receptor Integrins Have Distinct Ligand Recognition and Signaling Functions. Matrix Biol. 2000, 19, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnert, K.; Ni, J.; Leung, E.; Gough, S.; Morris, C.M.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.X.; Langley, R.; Krissansen, G.W. The integrin alpha10 subunit: Expression pattern, partial gene structure, and chromosomal localization. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1999, 87, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, U.; Purfürst, B.; Schöwel, V.; Morano, I.; Spuler, S.; Haase, H. Ahnak1 Abnormally Localizes in Muscular Dystrophies and Contributes to Muscle Vesicle Release. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2011, 32, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Laval, S.H.; Remoortere, A.; Baudier, J.; Benaud, C.; Anderson, L.V.B.; Straub, V.; Deelder, A.; Frants, R.R.; Dunnen, J.T.; et al. AHNAK a Novel Component of the Dysferlin Protein Complex, Redistributes to the Cytoplasm with Dysferlin during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, E.A.; Staknis, D.; Weitz, C.J. Light-Independent Role of CRY1 and CRY2 in the Mammalian Circadian Clock. Science 1999, 286, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, T.; Noshiro, M.; Sato, F.; Maemura, K.; Takeda, N.; Nagai, R.; Iwata, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Furukawa, M.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. A Novel Autofeedback Loop of Dec1 Transcription Involved in Circadian Rhythm Regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 313, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamia, K.A.; Papp, S.J.; Yu, R.T.; Barish, G.D.; Uhlenhaut, N.H.; Jonker, J.W.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. Cryptochromes Mediate Rhythmic Repression of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Nature 2011, 480, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.-G.; Shin, J.-Y.; Na, W.; Jeong, H.; Lee, J.-W.; Cho, S.; Kim, W.-S.; Ju, B.-G. Role of Type II Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in the Regulation of Circadian Per1 Gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita Rendón, O.; Fredrickson, E.K.; Howard, C.J.; Van Vranken, J.; Fogarty, S.; Tolley, N.D.; Kalia, R.; Osuna, B.A.; Shen, P.S.; Hill, C.P.; et al. Vms1p Is a Release Factor for the Ribosome-Associated Quality Control Complex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, A.; Garzia, A.; Kigoshi-Tansho, Y.; Patil, P.R.; Umbaugh, C.S.; Dallinger, T.; Liu, J.; Kreger, S.; Patrizi, A.; Cox, G.A.; et al. Convergence of Mammalian RQC and C-End Rule Proteolytic Pathways via Alanine Tailing. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 2112–2122.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youmans, D.T.; Gooding, A.R.; Dowell, R.D.; Cech, T.R. Competition between PRC2.1 and 2.2 Subcomplexes Regulates PRC2 Chromatin Occupancy in Human Stem Cells. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 488–501.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Rocha, S.T.; Boeva, V.; Escamilla-Del-Arenal, M.; Ancelin, K.; Granier, C.; Matias, N.R.; Sanulli, S.; Chow, J.; Schulz, E.; Picard, C.; et al. Jarid2 Is Implicated in the Initial Xist-Induced Targeting of PRC2 to the Inactive X Chromosome. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasini, D.; Cloos, P.A.C.; Walfridsson, J.; Olsson, L.; Bukowski, J.-P.; Johansen, J.V.; Bak, M.; Tommerup, N.; Rappsilber, J.; Helin, K. JARID2 Regulates Binding of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 to Target Genes in ES Cells. Nature 2010, 464, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. BMP2 Induces PANC-1 Cell Invasion by MMP-2 Overexpression through ROS and ERK. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, A.J.; Menet, J.S. Regulation of Circadian Clock Transcriptional Output by CLOCK:BMAL1. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, T.; Zhao, Z.; Lee, C.C. Interactive Organization of the Circadian Core Regulators PER2, BMAL1, CLOCK and PML. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabl, B.; Czech, B.; Valletta, D.; Weiss, T.S.; Kirovski, G.; Hellerbrand, C. Increased Expression of Zinc Finger Protein 267 in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 4, 661–666. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Becker, M.; John, S.; Parekh, B.S.; Huang, S.; Hendarwanto, A.; Martinez, E.D.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; et al. HDAC1 Acetylation Is Linked to Progressive Modulation of Steroid Receptor-Induced Gene Transcription. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, S.; Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Ding, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; et al. Class I Histone Deacetylases Are Major Histone Decrotonylases: Evidence for Critical and Broad Function of Histone Crotonylation in Transcription. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 898–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guezennec, X.; Vermeulen, M.; Brinkman, A.B.; Hoeijmakers, W.A.M.; Cohen, A.; Lasonder, E.; Stunnenberg, H.G. MBD2/NuRD and MBD3/NuRD, Two Distinct Complexes with Different Biochemical and Functional Properties. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubers, L.; Valderrama-Carvajal, H.; Laframboise, J.; Timbers, J.; Sanchez, G.; Côté, J. HuD Interacts with Survival Motor Neuron Protein and Can Rescue Spinal Muscular Atrophy-like Neuronal Defects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 553–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ref. No. | Protein | Encoding Gene | Functions | Molecular Weight, kDa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain | COL1A2 | Participates in collagen fibril arrangement, provides a structural component of the ECM [12,13,31,32] | 129.2 |
| 2. | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain | COL1A1 | Participates in collagen fibril arrangement, provides a structural component of the ECM [14,16,33] | 138.9 |
| 3. | Collagen alpha-1(II) chain | COL2A1 | Structural component of the ECM, confers tensile properties, binds metal ions, proteoglycans and platelet-derived growth factor, provides protein homodimerization activity [12,13,33] | 141.7 |
| 4. | Collagen alpha-2(IV) chain | COL4A2 | Structural component of basal membranes. Has both anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities. Inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and migration, decreases mitochondrial membrane potential and induces apoptosis [14,33] | 167.4 |
| 5. | Collagen alpha-2(IX) chain | COL9A2 | Structural component of hyaline cartilage, the main structural component of basal membranes [33] | 65.1 |
| 6 | Collagen alpha-1(XXVII) chain | COL27A1 | Participates in the cartilage calcification and cartilage-bone transformation [33] | 186.8 |
| 7. | Collagen alpha-1(XXVIII) chain | COL28A1 | Participates in the cell binding (a cell-binding protein) [33] | 116.6 |
| 8. | Integrin alpha-10 | ITGA10 | Collagen’s membrane receptor, integral transmembrane glycoprotein consisting of non-covalently bound alpha and beta chains. Participates in the cell adhesion as well as in the cell surface-mediated signaling. Differential pattern of integrin’s expression is mediated by growth and differentiation factors and may indicate participation of integrin in bone and cartilage metabolism [33,34,35,36,37,38] | 127.5 |
| 9. | Spectrin beta chain, non-erythrocytic 2 (SPTBN2) and Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein (AHNAK) | SPTBN2 AHNAK | Cell membrane formation. Neurogenesis (proliferation and differentiation of nervous system cells) [5,33,39,40]. | 271.2 |
| 10. | Cryptochrome-1 | CRY1 | Transcription repressor, the main component of circadian clock. Transcription and translation of the main clock components (CLOCK, NPAS2, BMAL1, BMAL2, PER1, PER2, PER3, CRY1, and CRY2) [33,41,42,43,44] | 66.4 |
| 11. | Alanine-tRNA ligase, mitochondrial | AARS2 | Catalyst of amino acid activation (aminoacylation/tRNA charging) [33,45,46] | 107.6 |
| 12. | Jumonji protein | JARID2 | Regulator of histone-methyltransferase complexes. Participates in the stem cell differentiation and normal embryogenesis including heart, neural tube development and haematopoiesis [33,47,48,49] | 138.3 |
| 13. | ELAV-like protein 3 | ELAVL3 | RNA-binding protein, stabilizes mRNA. Participates in the cell differentiation and nervous system development [33,50] | 39.5 |
| 14. | Bifunctional peptidase (KDM8) and arginyl hydroxylase (JMJD5) | KDM8 JMJD5 | Cleaves peptide bonds via hydrolysis reactions [33,51,52] | 47.2 |
| 15. | Zinc finger protein 394, Zinc finger protein 267, Zinc finger protein 585 A | ZNF394 ZNF267 ZNF585 A | DNA-binding transcription factors [33,53] | 64.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryabov, N.A.; Volova, L.T.; Alekseev, D.G.; Kovaleva, S.A.; Medvedeva, T.N.; Vlasov, M.Y. Mass Spectrometry of Collagen-Containing Allogeneic Human Bone Tissue Material. Polymers 2024, 16, 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131895
Ryabov NA, Volova LT, Alekseev DG, Kovaleva SA, Medvedeva TN, Vlasov MY. Mass Spectrometry of Collagen-Containing Allogeneic Human Bone Tissue Material. Polymers. 2024; 16(13):1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131895
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyabov, Nikolay A., Larisa T. Volova, Denis G. Alekseev, Svetlana A. Kovaleva, Tatyana N. Medvedeva, and Mikhail Yu. Vlasov. 2024. "Mass Spectrometry of Collagen-Containing Allogeneic Human Bone Tissue Material" Polymers 16, no. 13: 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131895
APA StyleRyabov, N. A., Volova, L. T., Alekseev, D. G., Kovaleva, S. A., Medvedeva, T. N., & Vlasov, M. Y. (2024). Mass Spectrometry of Collagen-Containing Allogeneic Human Bone Tissue Material. Polymers, 16(13), 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131895






