Spinodal Decomposition of Filled Polymer Blends: The Role of the Osmotic Effect of Fillers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. The Condition of the Spinodal Decomposition of Filled Polymer Blends in Infinite Dilution Approximation
2.2. Osmotic Effect of Fillers on the Thermodynamics of a Polymer Blend
2.3. The Effect of Fillers on the Spinodal Decomposition of Polymer Blends
3. Discussion and Comparison with the Experiment
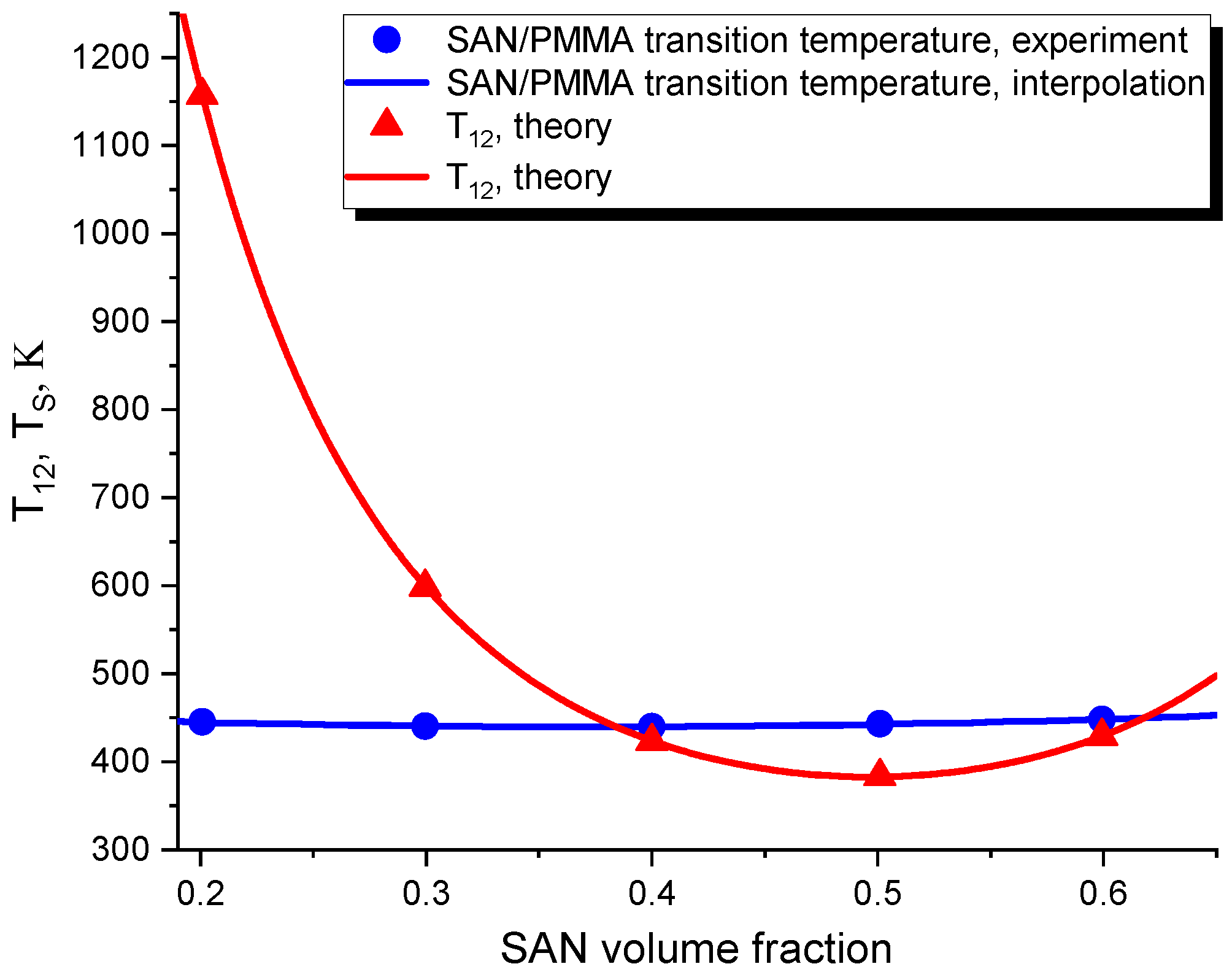
3.1. Determination of the Cross-Species Interaction Parameter of a Pure Blend
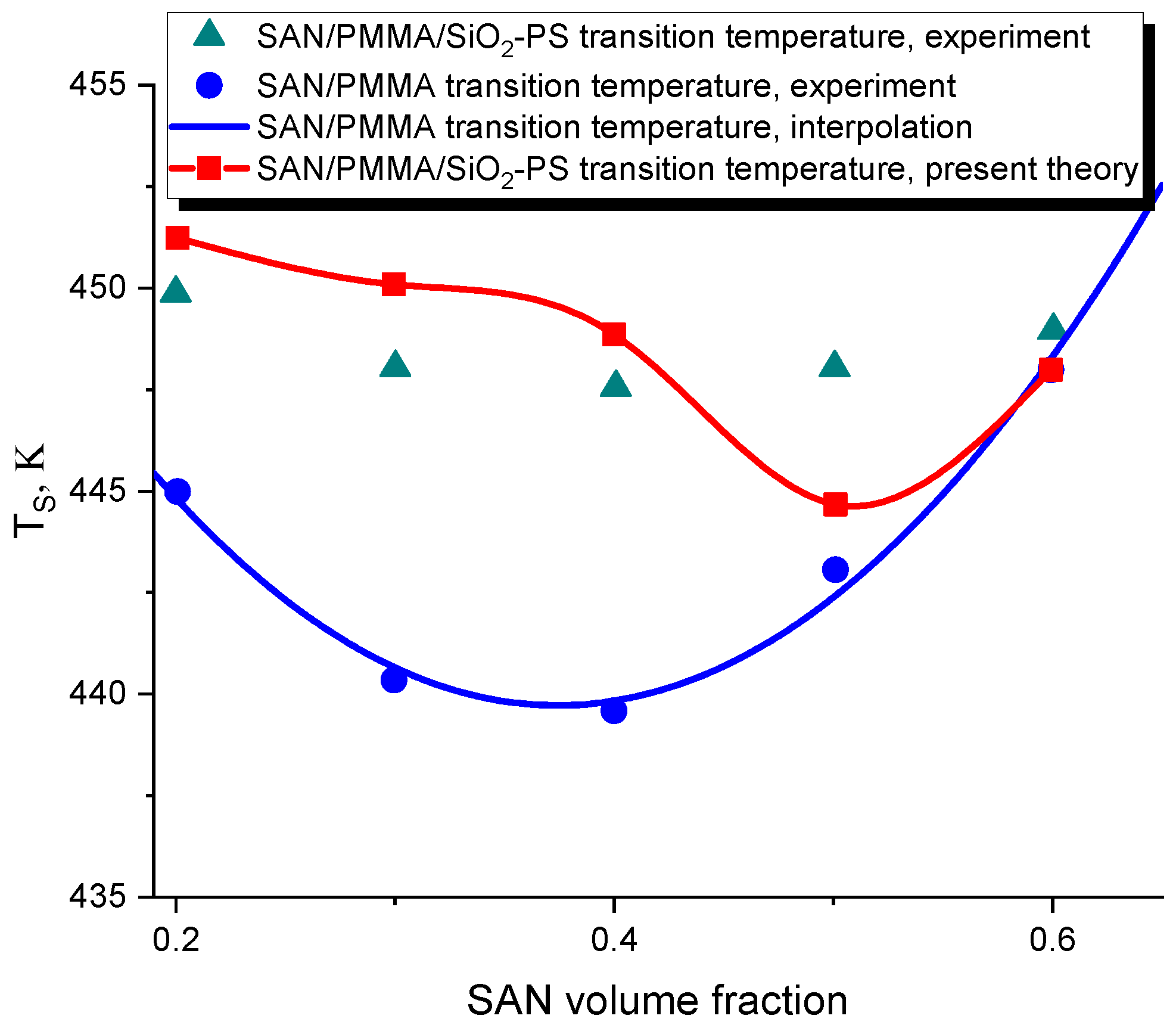
3.2. The Spinodal of a Filled Polymer Blend
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SL | Sanchez–Lacombe lattice theory |
| LCST | Low critical solution temperature |
| UCST | Upper critical solution temperature |
| r.(l.) h.s. | Right (left) hand side |
Appendix A
References
- Qi, X.D.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Z.W.; Kuehnert, I.; Poetschke, P.; Wang, Y. Selective localization of carbon nanotubes and its effect on the structure and properties of polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 123, 101471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.T.; Xie, X.M. Computational modeling and simulation of nanoparticle self-assembly in polymeric systems: Structures, properties and external field effects. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 369–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.; Zhou, C. Phase Separation of Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) Blends with Controlled Distribution of Silica Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8420–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, N.; Yu, W.; Zhou, C. Phase separation of poly (methyl methacrylate)/poly (styrene-co-acrylonitrile) blends in the presence of silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2012, 53, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.J.; Kim, J.; Ohno, K.; Composto, R.J. Controlling the Location of Nanoparticles in Polymer Blends by Tuning the Length and End Group of Polymer Brushes. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziri, A.A.; Ehsani, M.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Hemmati, F.; Jafari, S.H. Spherical nanoparticle effects on the lower critical solution temperature phase behavior of poly(e-caprolactone)/poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) blends: Separation of thermodynamic aspects from kinetics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzata, T.S.; Jagadeshvaran, P.L.; Bose, S. Nanoparticles influence miscibility in LCST polymer blends: From fundamental perspective to current applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 20167–20188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, P.; Rao, P.; Bose, S. Nanoparticle induced miscibility in LCST polymer blends: Critically assessing the enthalpic and entropic effects. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; l’Abee, R.M.A.; Goossens, J.G.P. The Control of Silica Nanoparticles on the Phase Separation of Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) Blends. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipatov, Y.S.; Nesterov, A.E.; Ignatova, T.D.; Nesterov, D.A. Effect of polymer-filler surface interactions on the phase separation in polymer blends. Polymer 2002, 43, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, A.E.; Lipatov, Y.S. Compatibilizing effect of a filler in binary polymer mixtures. Polymer 1999, 40, 1347–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.; Rzeczkowski, P.; Poetschke, P. Thermal Conductivity and Electrical Resistivity of Melt-Mixed Polypropylene Composites Containing Mixtures of Carbon-Based Fillers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeriyanov, F.F.; Chervanyov, A.I.; Jurk, R.; Subramaniam, K.; Koenig, S.; Roscher, M.; Das, A.; Stoeckelhuber, K.W.; Heinrich, G. Non-monotonic dependence of the conductivity of carbon nanotube-filled elastomers subjected to uniaxial compression/decompression. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 159901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushmita, K.; Formanek, P.; Krause, B.; Poetschke, P.; Bose, S. Distribution of Carbon Nanotubes in Polycarbonate-Based Blends for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvan, N.T.; Eshwaran, S.B.; Das, A.; Stoeckelhuber, K.W.; Wiessner, S.; Poetschke, P.; Nando, G.B.; Chervanyov, A.I.; Heinrich, G. Piezoresistive natural rubber-multiwall carbon nanotube nanocomposite for sensor applications. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2016, 239, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenbrinke, G.; Karasz, F.E. Lower critical solution temperature behavior in polymer blends-compressibility and directional-specific interactions. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nesterov, A.E.; Lipatov, Y.S.; Horichko, V.V.; Gritsenko, O.T. Filler effects on the compatibility and phase-separation kinetics of poly(vinyl acetate) poly(methyl methacrylate) mixtures. Polymer 1992, 33, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lv, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, G. The Molecular Mechanism of the Morphology Change in PS/PVME/Silica Blends Based on Rheology. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 8323–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Yang, S.H. 19-Hybrid materials based on polymer nanocomposites for environmental applications. In Polymer-Based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Jawaid, M., Khan, M.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 507–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, P. Phase behavior of a colloid plus binary polymer mixture: Theory. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4588–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkerkerker, H.N.W.; Poon, W.C.K.; Pusey, P.N.; Stroobants, A.; Warren, P.B. Phase-behavior of colloid plus polymer mixtures. Europhys. Lett. 1992, 20, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipatov, Y.S. Polymer blends and interpenetrating polymer networks at the interface with solids. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1721–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzburg, V.V. Influence of nanoparticles on miscibility of polymer blends. A simple theory. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Ginzburg, V.V.; Balazs, A.C. Determining the phase behavior of nanoparticle-filled binary blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B-Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 2389–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.; Ginzburg, V.V.; Balazs, A.C. Thermodynamic behavior of particle/diblock copolymer mixtures: Simulation and theory. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8085–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.B.; Ginzburg, V.V.; Matsen, M.W.; Balazs, A.C. Block copolymer-directed assembly of nanoparticles: Forming mesoscopically ordered hybrid materials. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, F.J.; Tang, H. A bulk perturbation in a grafted brush. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7953–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, I.C.; Balazs, A.C. Generalization of the lattice-fluid model for specific interactions. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, P.A.; Paul, D.R.; Barlow, J.W. Procedure For Predicting Lower Critical Solution Temperature Behavior In Binary Blends of Polymers. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 4101–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voutsas, E.C.; Pappa, G.D.; Boukouvalas, C.J.; Magoulas, K.; Tassios, D.P. Miscibility in binary polymer blends: Correlation and prediction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.A.; Lipson, J.E.G. LCST and UCST behavior in polymer solutions and blends. Polymer 2012, 53, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, I.C.; Lacombe, R.H. Statistical thermodynamics of polymer-solutions. Macromolecules 1978, 11, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, G.; Chen, D. Effect of fillers on the phase stability of binary polymer blends: A dynamic shear rheology study. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 5117–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharachorlou, A.; Goharpey, F. Rheologically determined phase behavior of LCST blends in the presence of spherical nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3276–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervanyov, A.I.; Heinrich, G. Immersion energy and polymer-mediated depletion interactions between nanocolloids as studied by analytic self-consistent field theory. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 021801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervanyov, A.I. Polymer-mediated interactions and their effect on the coagulation-fragmentation of nano-colloids: A self-consistent field theory approach. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 1038–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervanyov, A.I. Effective interaction between colloids immersed in a polymer blend and their effect on the equation of state of this blend. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 563, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervanyov, A.I. Conductivity of Insulating Diblock Copolymer System Filled with Conductive Particles Having Different Affinities for Dissimilar Copolymer Blocks. Polymers 2020, 12, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervanyov, A.I. Temperature dependence of the conductivity of filled diblock copolymers. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 052504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervanyov, A.I. Conductivity of diblock copolymer system filled with conducting nano-particles: Effect of copolymer morphology. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, E. Thermodynamics. An Advanced Treatment for Chemists and Physicists. Z. Für Naturforschung A 1950, 5, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlubek, G.; Piontech, J.; Kilburn, J. The structure of the free volume in poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) from positron lifetime and pressure volume temperature (PVT) experiments: 1. free volume from the Simha-Somcynsky analysis of PVT experiments. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Sun, Z.; Shi, T.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W.; An, L.; Li, B. Thermodynamics of PMMA/SAN blends: Application of the Sanchez-Lacombe lattice fluid theory. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 6291–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chervanyov, A.I. Spinodal Decomposition of Filled Polymer Blends: The Role of the Osmotic Effect of Fillers. Polymers 2024, 16, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010038
Chervanyov AI. Spinodal Decomposition of Filled Polymer Blends: The Role of the Osmotic Effect of Fillers. Polymers. 2024; 16(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleChervanyov, A. I. 2024. "Spinodal Decomposition of Filled Polymer Blends: The Role of the Osmotic Effect of Fillers" Polymers 16, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010038
APA StyleChervanyov, A. I. (2024). Spinodal Decomposition of Filled Polymer Blends: The Role of the Osmotic Effect of Fillers. Polymers, 16(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010038






