Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silk Fibroin/Ag-NPs Composite Nanofibers as a Substrate for MG-63 Cells’ Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fibroin Extraction
2.3. Ag-NPs’ Synthesis
2.4. Preparation of Electrospinning Solutions
2.5. Preparation of Nanofiber Scaffolds
2.6. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs)
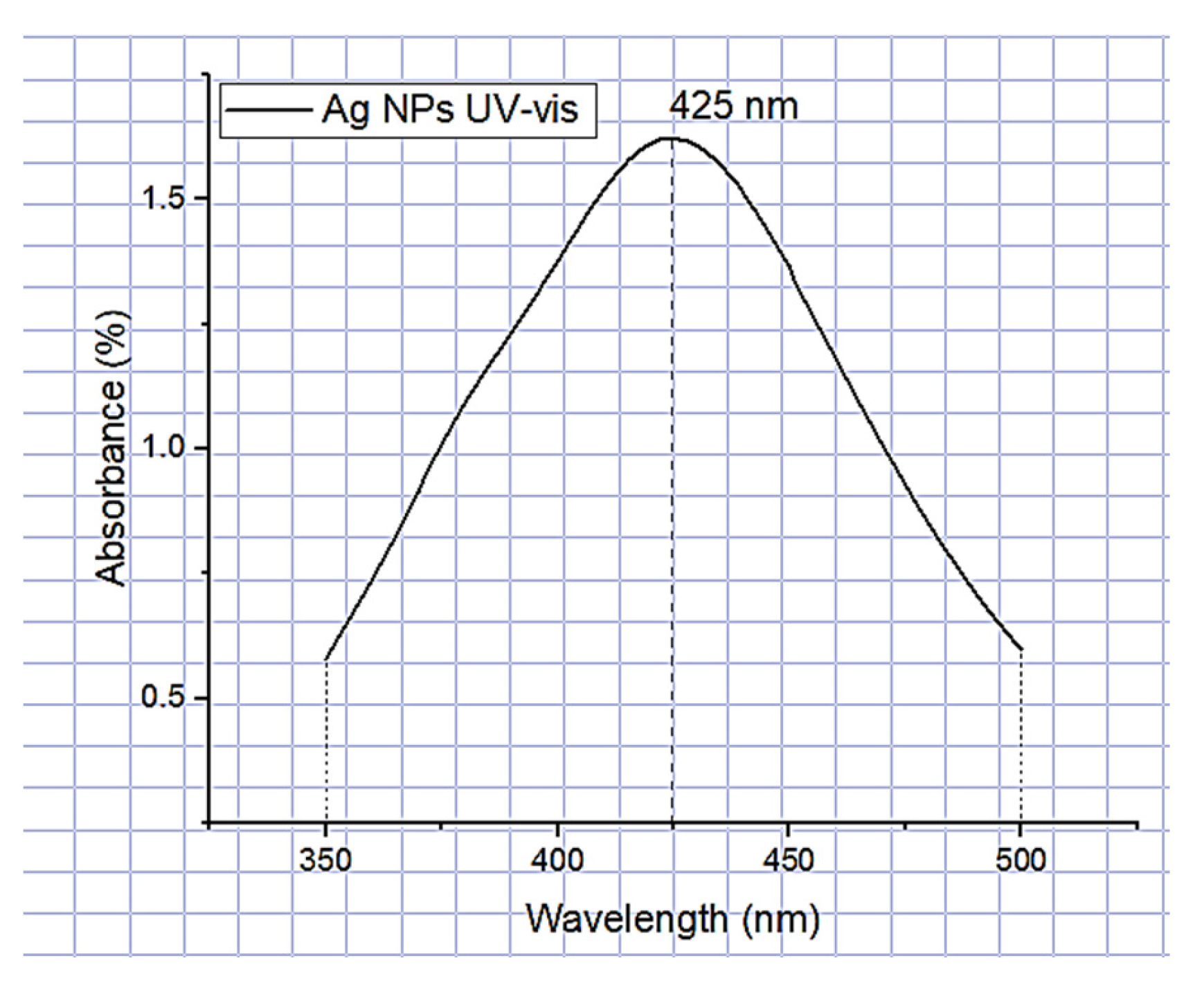
2.6.1. Formation of Ag-NPs (UV-Vis) Spectrometry
2.6.2. Average Ag-NPs’ Size (DLS)
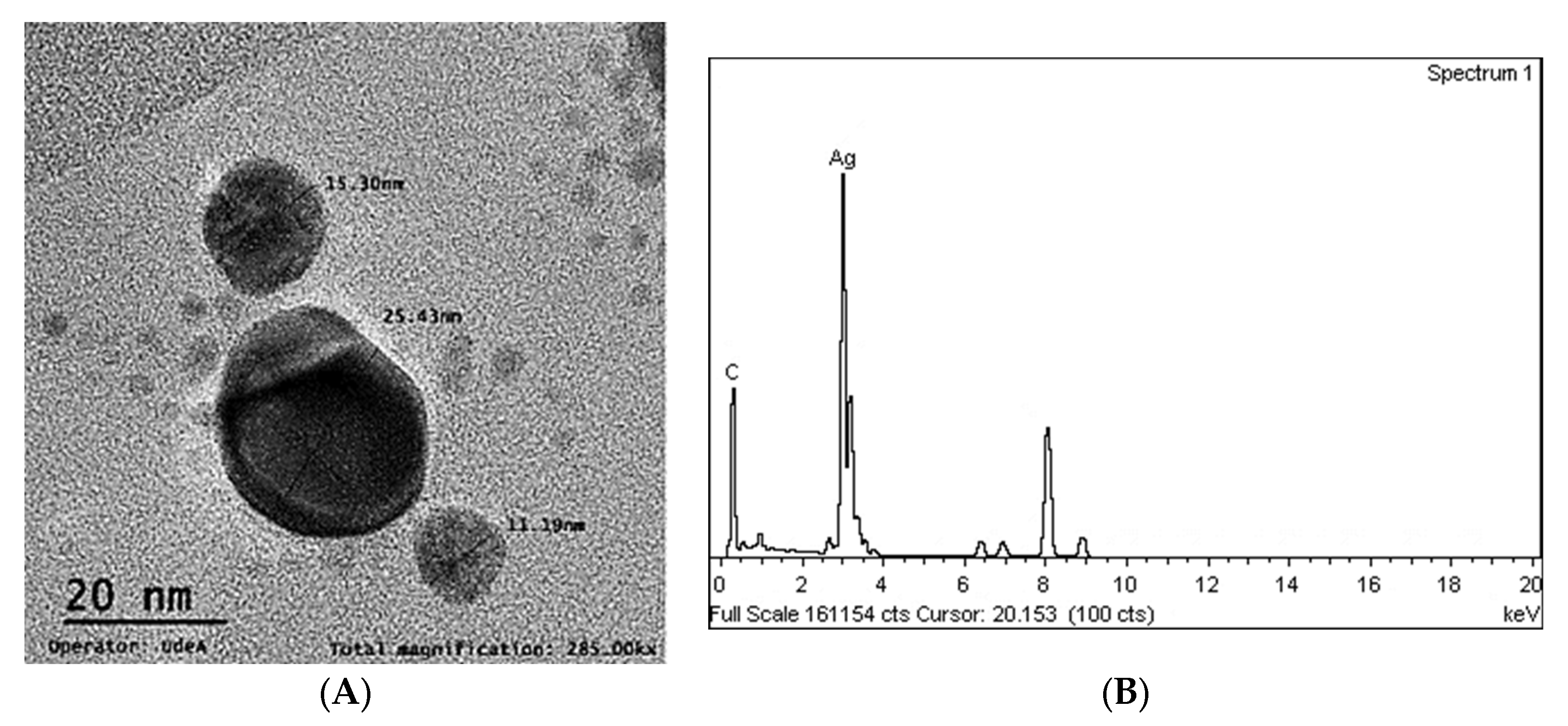
2.6.3. Morphology and Size of Ag-NPs (TEM)
2.7. Characterization of Nanofibers’ Scaffolds
2.7.1. Morphology of Electrospun Fibers (FE-SEM)
2.7.2. Average Pore Diameter
2.7.3. Stiffness (AFM)
2.7.4. Thermal Degradation
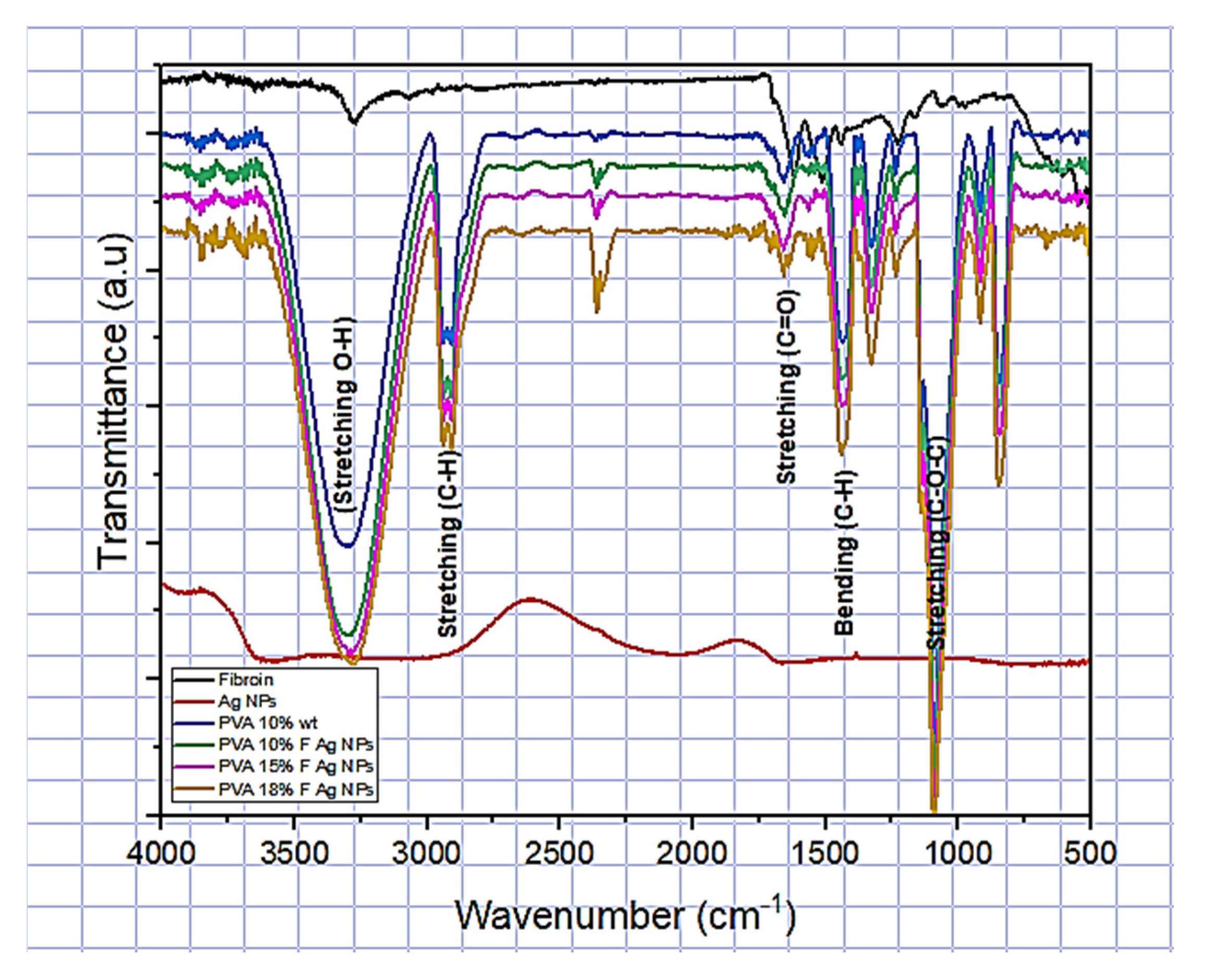
2.7.5. Chemical Interaction (FTIR)
2.7.6. Wettability
2.8. In Vitro Test
2.8.1. MG-63 Cell Viability
2.8.2. Alizarin Red (ARS)
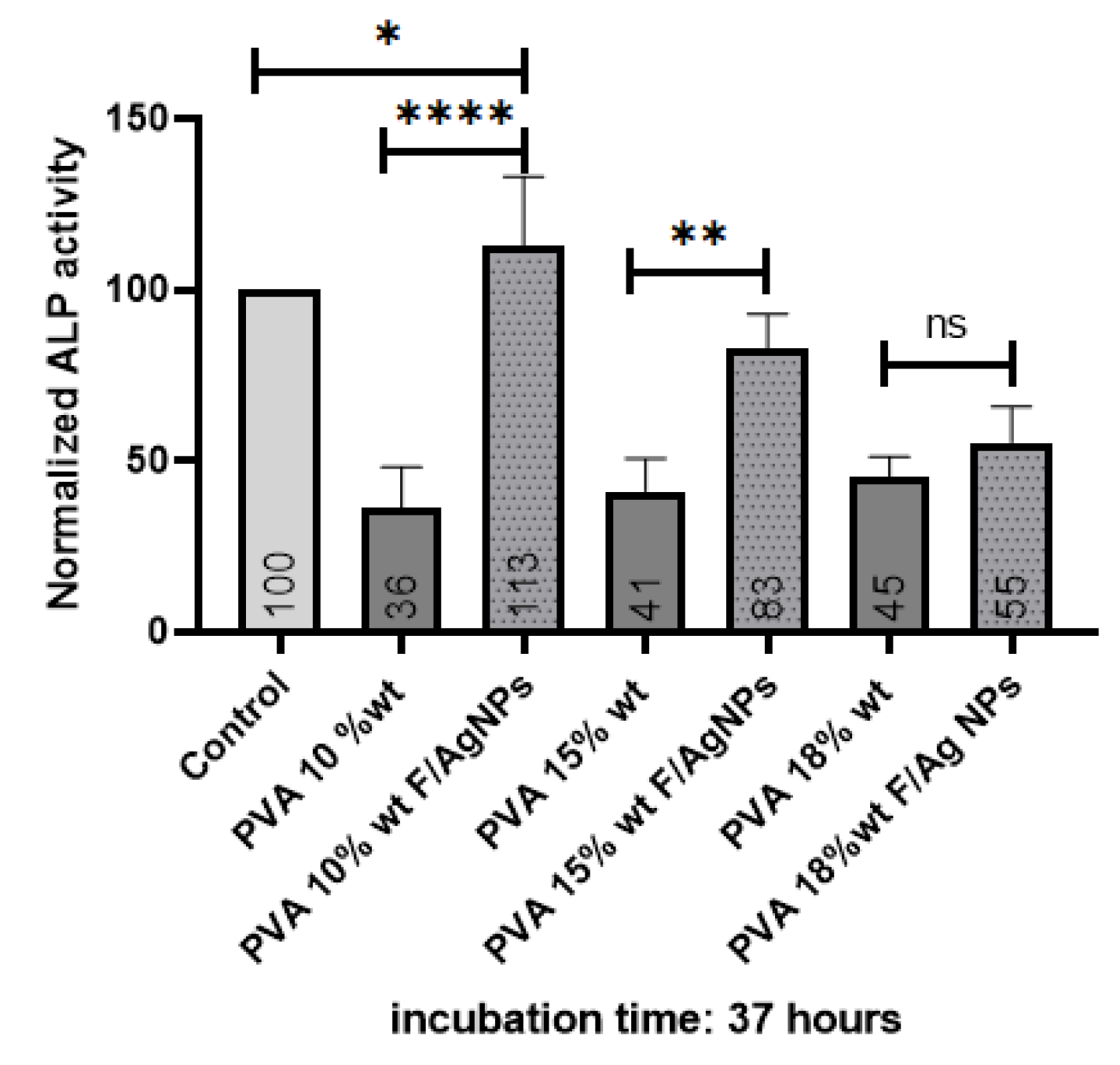
2.8.3. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
2.8.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs)
3.1.1. Formation of Ag-NPs (UV-Vis) Spectrometry
3.1.2. Average Ag-NPs’ Size (DLS)
3.1.3. Morphology and Size of Ag-NPs (TEM)
3.2. Characterization of Nanofiber Scaffolds
3.2.1. Morphology of the Electrospun Nanofibers
3.2.2. Average Pore Diameter
3.2.3. Stiffness (AFM)
3.2.4. Thermal Degradation
Mass Loss (TGA)
Thermal Behavior (DSC)
3.2.5. Chemical Interaction (FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.2.6. Wettability
3.3. In Vitro Test
3.3.1. MG-63 Cell Viability
3.3.2. Alizarin Red (ARS)
3.3.3. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalani, M.M.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Negahdari, B.; Rahimi, A.; Sell, S.A. Electrospun core-sheath poly(vinyl alcohol)/silk fibroin nanofibers with Rosuvastatin release functionality for enhancing osteogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama, M.; Vijayalakshmi, U. Influence of silk fibroin on the preparation of nanofibrous scaffolds for the effective use in osteoregenerative applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 61, 102182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, M.S.; Behzad, T.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Rafienia, M.; Bagheri, R.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Kolbuk, D.; Pahlevanneshan, Z.; Bonakdar, S.H. Development of electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol)-based bionanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 106, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shao, W.; Qian, W.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, K.; Wang, L.; Cui, S.; Wang, R. Biomineralized poly (l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-tussah silk fibroin nanofiber fabric with hierarchical architecture as a scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 84, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.N.; Pramanik, K. Generation of bioactive nano-composite scaffold of nanobioglass/silk fibroin/carboxymethyl cellulose for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 2011–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Pal, K.; Rahier, H.; Uludag, H.; Kim, I.S.; Bechelany, M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanni, R.; Wibowo, U.A.; Judawisastra, H.; Barlian, A. Growth of Human Dermal Fibroblasts on Polyvinyl Alcohol-Silk Fibroin Nanofiber Scaffold. J. Math. Fundam. Sci. 2019, 51, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, C.M.; Purwar, R.; Gupta, A.P. Enhanced potential of biomimetic, silver nanoparticles functionalized Antheraea mylitta (tasar) silk fibroin nanofibrous mats for skin tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, M.M.; Mousa, H.M.; El-Aassar, M.; El-Deeb, N.M.; Ghazaly, N.M.; Dewidar, M.M.; Abdal-Hay, A. Enhancing mechanical and biodegradation properties of polyvinyl alcohol/silk fibroin nanofibers composite patches for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Mater. Lett. 2019, 255, 126510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanha, N.R.; Nouri, M. An experimental study on the coaxial electrospinning of silk fibroin/poly(vinyl alcohol)–salicylic acid core-shell nanofibers and process optimization using response surface methodology. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 48, 884–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, J.; Hadidi, M.; Nazarpak, M.H.; Mansouri, M.; Hasannasab, M. Physicochemical and Antibacterial Characterization of Nanofibrous Wound Dressing from Silk Fibroin-polyvinyl Alcohol- Elaeagnus Angustifolia Extract. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.-C.; Liau, J.-J. Cell culture and characterization of cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol)-g-starch 3D scaffold for tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheradvar, S.A.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Tabesh, H.; Bagheri, B. Starch nanoparticle as a vitamin E-TPGS carrier loaded in silk fibroin-poly(vinyl alcohol)-Aloe vera nanofibrous dressing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 166, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Markel, D.C.; Wang, S.; Shi, T.; Mao, G.; Ren, W. Electrospun polyvinyl alcohol–collagen–hydroxyapatite nanofibers: A biomimetic extracellular matrix for osteoblastic cells. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, D.; Ghosh, A.K.; Mandal, M.; Das, P.; Nandi, S.K.; Kundu, S.C. Dual growth factor loaded nonmulberry silk fibroin/carbon nanofiber composite 3D scaffolds for in vitro and in vivo bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2017, 136, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Advanced Nanofibrous Materials Manufacture Technology Based on Electrospinning; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchaiyaphum, P.; Punyodom, W.; Watanesk, S.; Watanesk, R. Composition optimization of polyvinyl alcohol/rice starch/silk fibroin-blended films for improving its eco-friendly packaging properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2614–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Dai, L.X. Improvement of Morphology, Structure, and Thermal Properties of Electrospun PVA/RSF Fiber Mats by SiO2. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 184–185, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, M.M.; Gopinathan, J.; Indumathi, B.; Manjoosha, Y.R.; Sahanand, K.S.; Rai, B.K.D.; Selvakumar, R.; Bhattacharyya, A. Silk–PVA Hybrid Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Enhanced Primary Human Meniscal Cell Proliferation. J. Membr. Biol. 2016, 249, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urena-Saborio, H.; Rodríguez, G.; Madrigal-Carballo, S.; Gunasekaran, S. Characterization and applications of silver nanoparticles-decorated electrospun nanofibers loaded with polyphenolic extract from rambutan (Nepelium lappaceum). Materialia 2020, 11, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, C.A.; Correa, D.S.; Zucolotto, V. Polycaprolactone nanofiber mats decorated with photoresponsive nanogels and silver nanoparticles: Slow release for antibacterial control. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 107, 110334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Kundu, B.; Naskar, D.; Maiti, T.K.; Bhattacharya, D.; Kundu, S.C. Nanofibrous nonmulberry silk/PVA scaffold for osteoinduction and osseointegration. Biopolymers 2015, 103, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, M.L.; Moncada, M.E. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silk Fibroin/Ag NPs composite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Mexico City, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Echeverri-Correa, E.; Grajales-Lopera, D.O.; Gutiérrez-Restrepo, S.; Ossa-Orozco, C.P. Effective sericin-fibroin separation from Bombyx mori silkworms fibers and low-cost salt removal from fibroin solution. Rev. Fac. Ing. 2019, 94, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo-Osorio, G.A.; Escobar-Jaramillo, M.; Ossa-Orozco, C.P. Diseño factorial 2k para la optimización de la síntesis de nanopartículas de plata para su aplicación en biomaterials 2k factorial design to optimize the synthesis of silver nanoparticles for application in biomaterials Projeto fatorial 2k para a otim. Rev. ION 2020, 33, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Singh, N. Antibacterial silk fibroin scaffolds with green synthesized silver nanoparticles for osteoblast proliferation and human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 176, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Ferraz, M.P.; Monteiro, F.J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Beppu, M.M.; Mantione, D.; Sardon, H. Antibacterial silk fibroin/nanohydroxyapatite hydrogels with silver and gold nanoparticles for bone regeneration. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yu, X.; Markel, D.C.; Shi, T.; Ren, W. Coaxial PCL/PVA electrospun nanofibers: Osseointegration enhancer and controlled drug release device. Biofabrication 2013, 5, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.B.; Eğri, S.; Eğri, Ö.; Caglayan, M.O. Nanomechanical characterization of electrospun biodegradable vascular scaffolds. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; Hocking, D.M.; O’Connor, A.J. In situ formation of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles and the impregnation of hydrophobic polycaprolactone matrix for antimicrobial medical device applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 47, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Xu, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, F. Fabrication of silver nanoparticle/polyvinyl alcohol/polycaprolactone hybrid nanofibers nonwovens by two-nozzle electrospinning for wound dressing. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Giraldo, J.; Mena, P.; Galeano, B.; Escobar, N.; Mejía, M.L.; Ortiz, I.C.; Cuesta, D.; Botero, L.E.; Hoyos-Palacio, L.M. Characterization of silver nanoparticles for potential use as antimicrobial agent. In Proceedings of the VII Latin American Congress on Biomedical Engineering CLAIB 2016, Bucaramanga, Colombia, 26–28 October 2016; Volume 60, pp. 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Ramana, E. Patents on Magnetoelectric Multiferroics and their Processing by Electrophoretic Deposition. Recent Pat. Mater. Sci. 2014, 7, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.P.G.; Orozco, C.P.O. Fabricación y caracterización de nanopartículas de plata con potencial uso en el tratamiento del cáncer de piel. Ing. Desarro. 2022, 37, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhao, H.; Sun, D. Fabrication and durable antibacterial properties of 3D porous wet electrospun RCSC/PCL nanofibrous scaffold with silver nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.-J.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Youk, J.H. A study on the preparation of poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles. Synth. Met. 2007, 157, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgic, A.D.; Atila, D.; Karatas, A.; Tezcaner, A.; Keskin, D. Diatom shell incorporated PHBV/PCL-pullulan co-electrospun scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Salcedo, S.; Nieto, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Hydroxyapatite/β-tricalcium phosphate/agarose macroporous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Hussain, F.S.J.; Kumar, A.; Rasad, M.S.B.A.; Yusoff, M.M. Fabrication, characterization and in vitro biocompatibility of electrospun hydroxyethyl cellulose/poly (vinyl) alcohol nanofibrous composite biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 144, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Naskar, D.; Kim, H.-W.; Maiti, T.K.; Bhattacharya, D.; Kundu, S.C. Non-mulberry silk fibroin grafted PCL nanofibrous scaffold: Promising ECM for bone tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 71, 490–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, A.; Sadrnezhaad, S.; Johari, N. The prominent role of fully-controlled surface co-modification procedure using titanium nanotubes and silk fibroin nanofibers in the performance enhancement of Ti6Al4V implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 412, 127001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, I.; Sadeghi, A. Investigating the Mechanical Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofibers Based on Aligned and Random Orientations. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 12479–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, M.S.; Behzad, T.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Bagheri, R.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Pierini, F. Theoretical and experimental study of the stiffness of electrospun composites of poly(vinyl alcohol), cellulose nanofibers, and nanohydroxy apatite. Cellulose 2017, 25, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lim, J.; Teoh, S.-H. Review: Development of clinically relevant scaffolds for vascularised bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 688–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Pramanik, K. Development of novel silk fibroin/polyvinyl alcohol/sol–gel bioactive glass composite matrix by modified layer by layer electrospinning method for bone tissue construct generation. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 015028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Yeum, J.H. Electrospun pullulan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/silver hybrid nanofibers: Preparation and property characterization for antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Thirugnanam, A. Effect of Porous Activated Charcoal Reinforcement on Mechanical and In-Vitro Biological Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naebe, M.; Lin, T.; Tian, W.; Dai, L.; Wang, X. Effects of MWNT nanofillers on structures and properties of PVA electrospun nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 225605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Kim, H.-Y.; Gong, J.; Ding, B.; Lee, D.-R.; Park, S.-J. Fiber mats of poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica composite via electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Baek, D.H.; Ki, C.S.; Park, Y.H. Preparation and characterization of wet spun silk fibroin/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend filaments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 41, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Shmueli, S.; Shur, I.; Benayahu, D.; Aronov, D.; Rosenman, G. The effect of surface treatment on the surface texture and contact angle of electrochemically deposited hydroxyapatite coating and on its interaction with bone-forming cells. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3178–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, P.A.L. Aceleración de la Consolidación de la Fractura ósea Empleando Láser. Ph.D. Thesis, National Polytechnic Institute, Mexico City, Mexico, 2004. Available online: http://tesis.ipn.mx/handle/123456789/2512 (accessed on 27 January 2023).








| Solution | PVA | Fibroin | Ag-NPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA 10% wt | 10% wt | -- | -- |
| PVA10/SF/Ag-NPs | 10% wt | 2% wt | 0.5% wt |
| PVA 15% wt | 15% wt | -- | -- |
| PVA15/SF/Ag-NPs | 15% wt | 2% wt | 0.5% wt |
| PVA 18% wt | 18% wt | -- | -- |
| PVA18/SF/Ag-NPs | 18% wt | 2% wt | 0.5% wt |
| PVA 10% wt | PVA 15% wt | PVA 18% wt |
 |  |  |
| PVA10/SF/Ag-NPs | PVA15/SF/Ag-NPs | PVA18/SF/Ag-NPs |
 |  |  |
| Time | PVA 10% wt | PVA10/SF/Ag-NPs | PVA 15% wt | PVA15/SF/Ag-NPs | PVA 18% wt | PVA18/SF/Ag-NPs | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| 24 h |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| 36 h |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| PVA 15% wt | PVA 15% F Ag-NPs | Control |
 |  |  |
| PVA 18% wt | PVA 18% F Ag-NPs | |
 |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mejía Suaza, M.L.; Leos Rivera, J.C.; Rodríguez Padilla, M.C.; Moncada Acevedo, M.E.; Ossa Orozco, C.P.; Zarate Triviño, D.G. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silk Fibroin/Ag-NPs Composite Nanofibers as a Substrate for MG-63 Cells’ Growth. Polymers 2023, 15, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081838
Mejía Suaza ML, Leos Rivera JC, Rodríguez Padilla MC, Moncada Acevedo ME, Ossa Orozco CP, Zarate Triviño DG. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silk Fibroin/Ag-NPs Composite Nanofibers as a Substrate for MG-63 Cells’ Growth. Polymers. 2023; 15(8):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081838
Chicago/Turabian StyleMejía Suaza, Monica L., Jennifer C. Leos Rivera, Maria C. Rodríguez Padilla, Maria E. Moncada Acevedo, Claudia P. Ossa Orozco, and Diana G. Zarate Triviño. 2023. "Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silk Fibroin/Ag-NPs Composite Nanofibers as a Substrate for MG-63 Cells’ Growth" Polymers 15, no. 8: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081838
APA StyleMejía Suaza, M. L., Leos Rivera, J. C., Rodríguez Padilla, M. C., Moncada Acevedo, M. E., Ossa Orozco, C. P., & Zarate Triviño, D. G. (2023). Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silk Fibroin/Ag-NPs Composite Nanofibers as a Substrate for MG-63 Cells’ Growth. Polymers, 15(8), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081838








