Study on Properties and Micro-Mechanism of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Asphalt
2.2. SBS
2.3. RHB
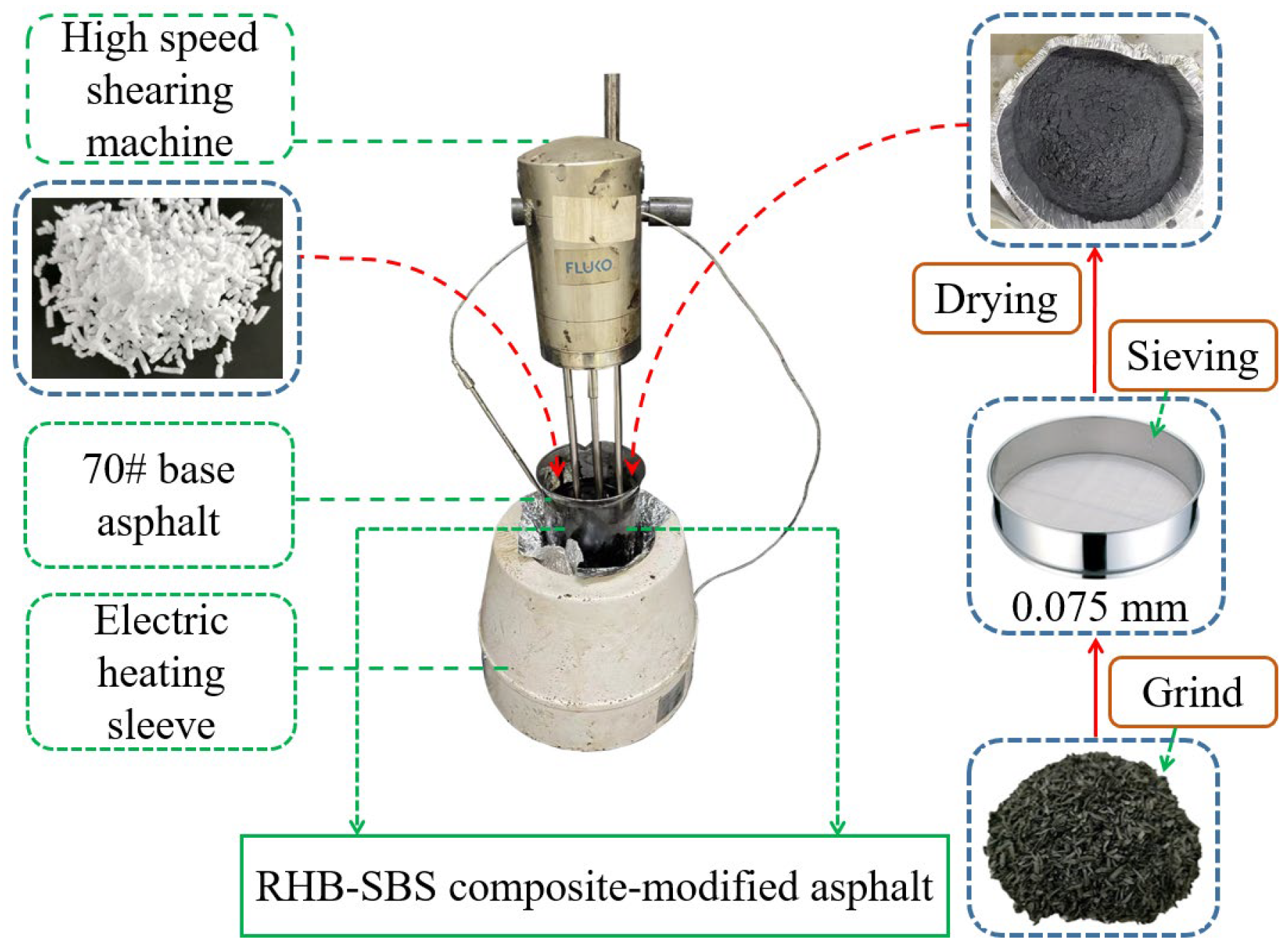
2.4. Sample Preparation Method
2.5. Experimental Method
2.5.1. Conventional Physical Performance Experiments
2.5.2. Rheological Property Experiments
2.5.3. Microscopic Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Conventional Properties of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt
3.1.1. Penetration Experiment
3.1.2. Softening Point Experiment
3.1.3. Ductility Experiment
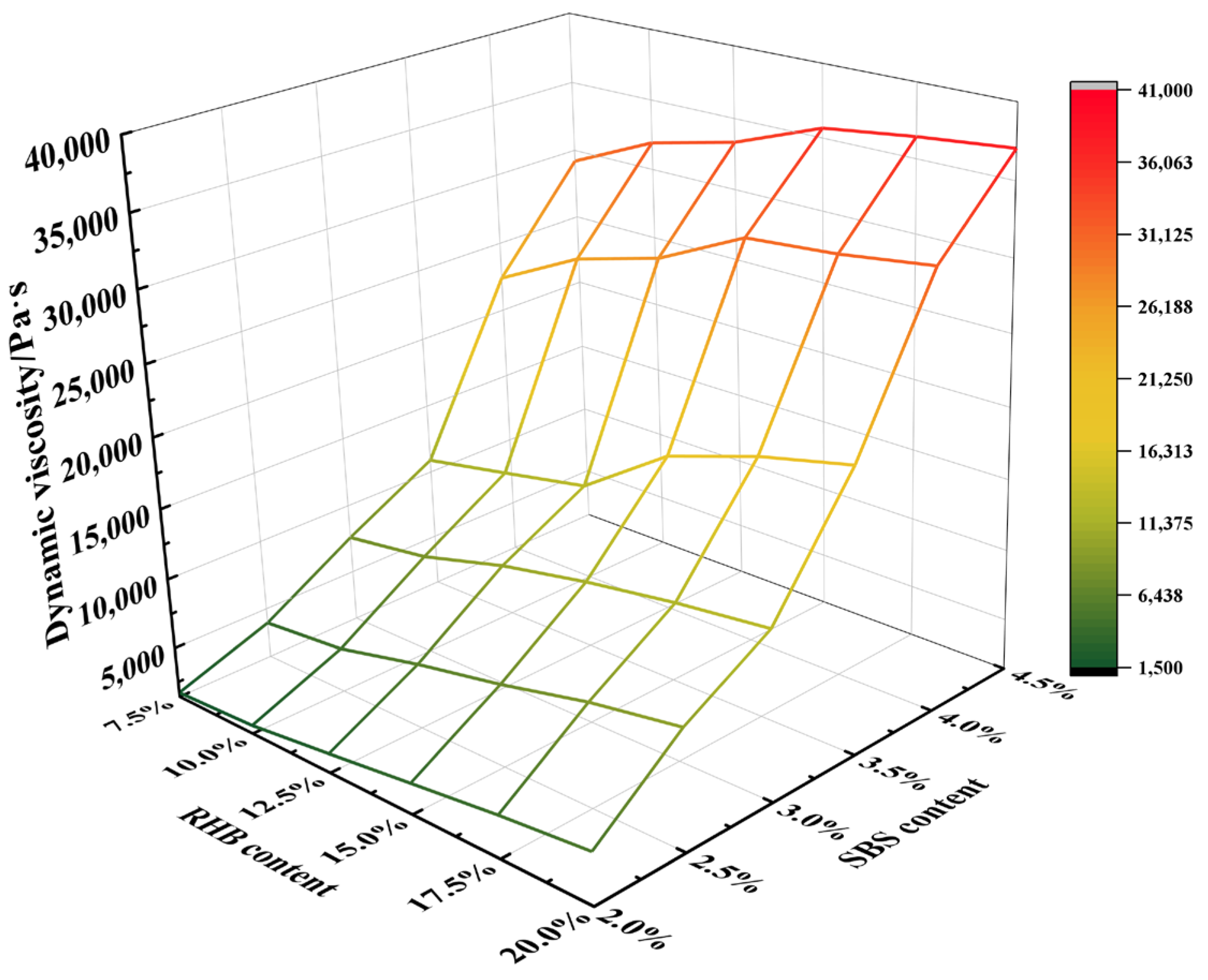
3.1.4. Dynamic Viscosity Experiment
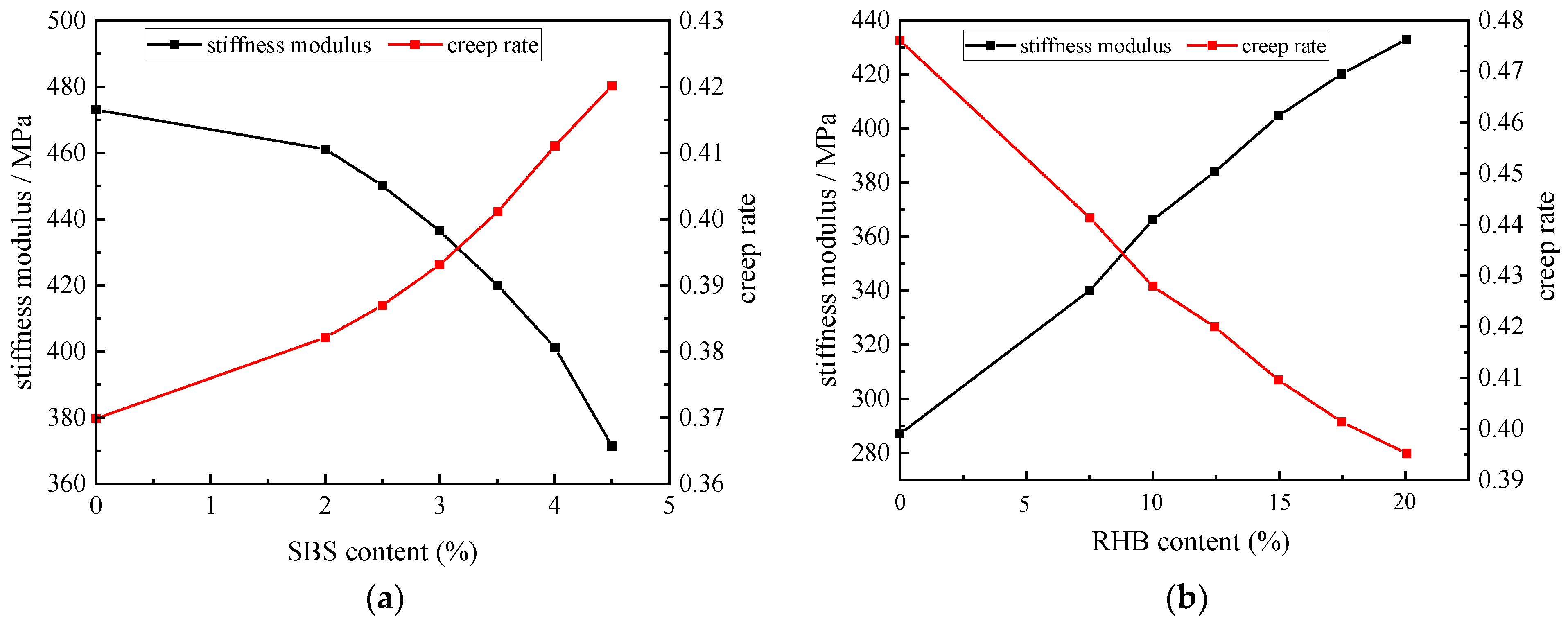
3.2. Rheological Properties of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt
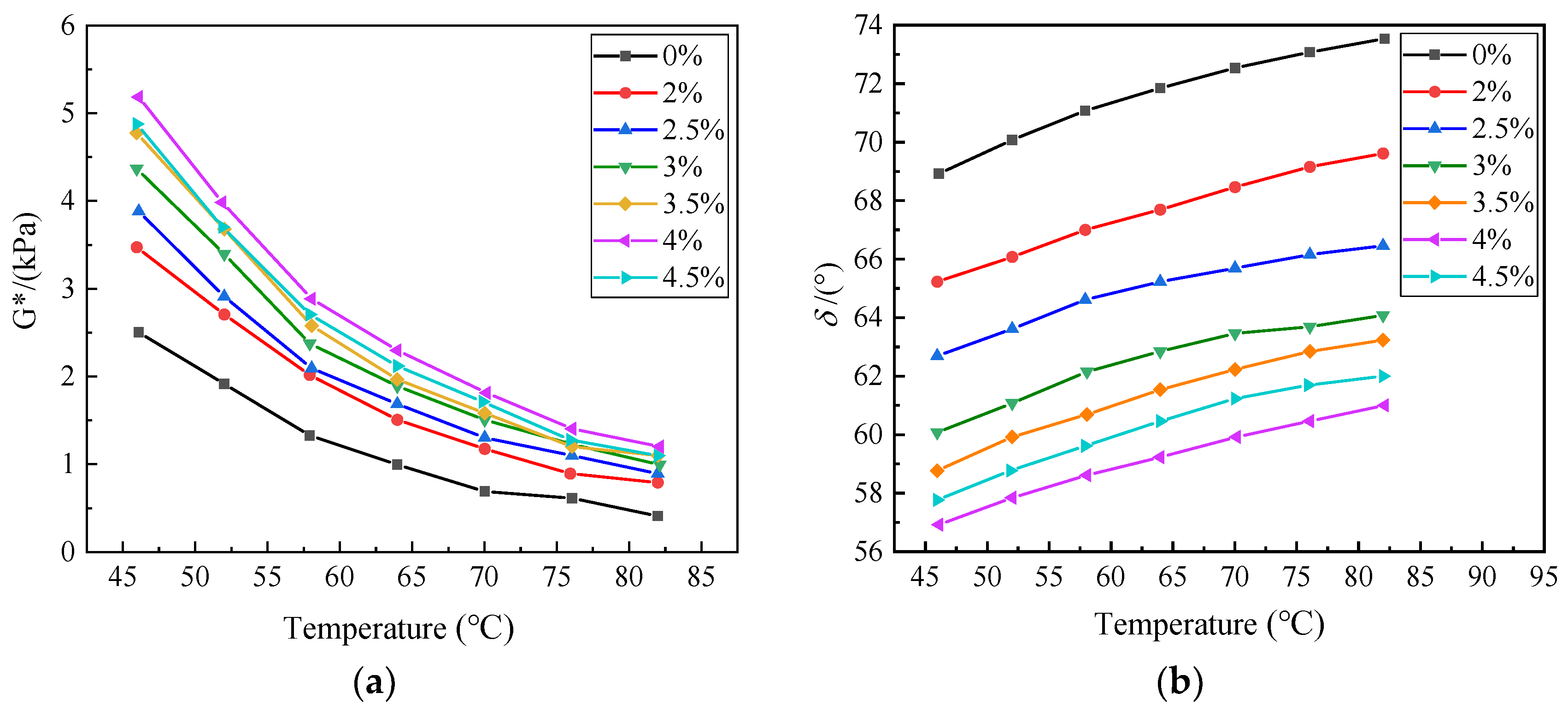
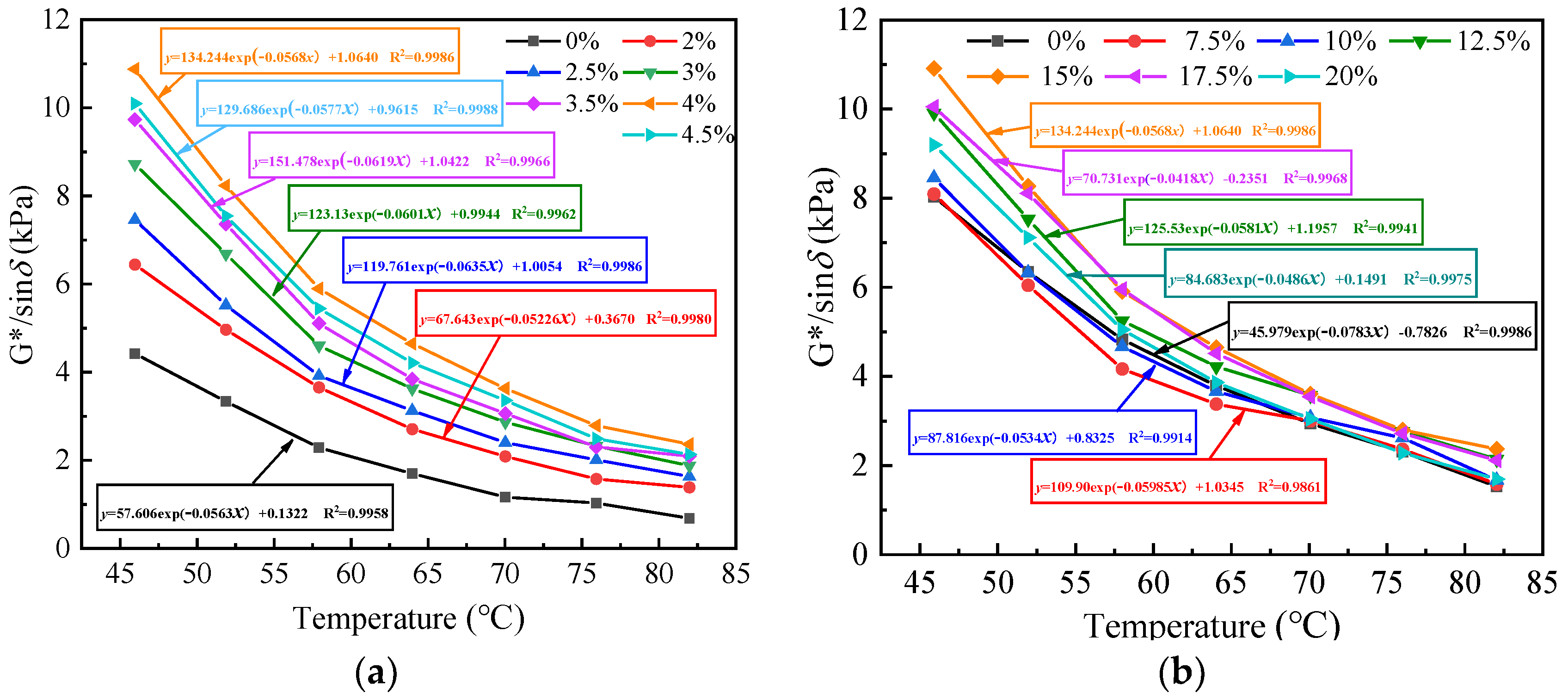
3.2.1. Temperature Sweep Experiment
3.2.2. BBR
3.3. Microscopic Analysis of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt
3.3.1. Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy Test
3.3.2. Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy Test
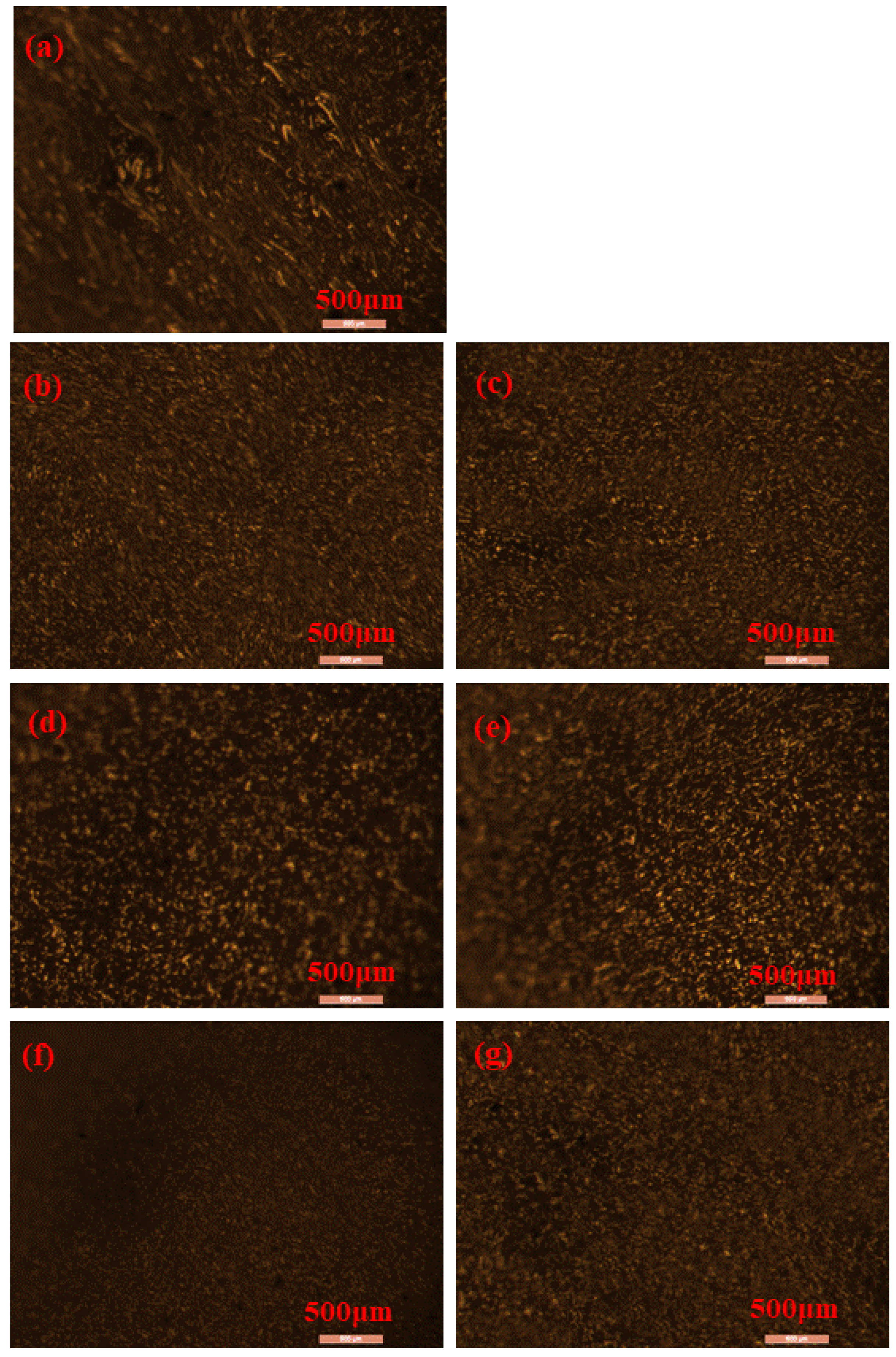
3.3.3. Leica Fluorescence Electron Microscopy Test
3.4. Road Performance of Different Types of Asphalt Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, F.; Dai, J.; Fu, Z.; Liu, J.; Dong, W.; Huang, Z. A new type of crumb rubber asphalt mixture: A dry process design and performance evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Fan, W.; Wei, J. Effect of shear time and the crumb rubber percentage on the properties of composite modified asphalt. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 848, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, C. The research for structural characteristics and modification mechanism of crumb rubber compound modified asphalts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Gao, J. Laboratory study on cr/sbs modified asphalt: Preparation and performance characterization. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, X.; Kundwa, M.J.; Li, Z.; Wei, D. Evaluation of the adhesion characteristics of material composition for polyphosphoric acid and SBS modified bitumen based on surface free energy theory. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F. Improving the low-temperature performance of RET modified asphalt mixture with different modifiers. Coatings 2020, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shuang, E.; Liu, L. Analysis of pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of sweet sorghum bagasse and cotton stalk. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Lu, S. Pyrolysis temperature affects pore characteristics of rice straw and canola stalk biochars and biochar-amended soils. Geoderma 2021, 397, 115097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.; Jagadevan, S. Effect of pyrolysis of rice husk–derived biochar on the fuel characteristics and adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 14, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwapinski, W.; Byrne, C.M.; Kryachko, E.; Wolfram, P.; Adley, C.; Leahy, J.J.; Novotny, E.H. Biochar from biomass and waste. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2010, 1, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Al Mamun, M.A.; Alyousef, R.; Mohammadhosseini, H. State-of-the-art-review on rice husk ash: A supplementary cementitious material in concrete. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 33, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fapohunda, C.; Akinbile, B.; Shittu, A. Structure and properties of mortar and concrete with rice husk ash as partial replacement of ordinary Portland cement—A review. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 675–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wu, S.; Cai, J.; Zhou, M.; Zha, J. Effects of two biomass ashes on asphalt binder: Dynamic shear rheological characteristic analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Sha, A.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zou, X.; Yuan, D. Study on the optimum rice husk ash content added in asphalt binder and its modification with bio-oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Sha, A.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Studying the properties of SBS/rice husk ash-modified asphalt binder and mixture. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4545063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Test Rules for Asphalt and Asphalt Mixture in Highway Engineering. Ministry of Communications of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- AASHTO T315; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- AASHTO T313; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Flexural Creep Stiffness of Asphalt Binder Using the Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Zhong, K.; Cao, D.W.; Luo, S. Determination the modifier content in SBS modified asphalt based on infrared spectroscopy technique. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2010, 34, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, A.M.; Keppel, E.; Speck, A.K. Absorption and reflection infrared spectra of MgO and other diatomic compounds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 345, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timischl, F.; Date, M.; Nemoto, S. A statistical model of signal–noise in scanning electron microscopy. Scanning 2012, 34, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Scanning electron microscopy: Principle and applications in nanomaterials characterization. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 13–145. [Google Scholar]
- Arabani, M.; Tahami, S.A. Assessment of mechanical properties of rice husk ash modified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Dai, J.; Fu, Z.; Li, C.; Wen, Y.; Jia, M.; Wang, Y.; Shi, K. Biochar for asphalt modification: A case of high-temperature properties improvement. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Feng, J.; Zhou, N. Hydrochar from corn stalk used as bio-asphalt modifier: High-temperature performance improvement. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Lv, S.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, F. Applications of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy technologies on asphalt materials. Measurement 2018, 121, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, W.; Feng, H.; Cao, K. High and low temperature performance and fatigue properties of silica fume/SBS compound modified asphalt. Materials 2020, 13, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yue, M.; Xiong, Y.; Yue, J. Experimental study on mechanism, aging, rheology and fatigue performance of carbon nanomaterial/SBS-modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; You, Z.; Mills-Beale, J. Asphalt binders blended with a high percentage of biobinders: Aging mechanism using FTIR and rheology. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 4014157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Lv, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, C. Performance and mechanism of asphalt modified by buton-rock asphalt and different types of styrene-butadiene-rubber. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Fan, X.; Yao, H.; You, L.; You, Z.; Fan, G. Analysis of performance and mechanism of Buton rock asphalt modified asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 46903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.; Remya, N. Influence of operating parameters on the microwave pyrolysis of rice husk: Biochar yield, energy yield, and property of biochar. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 12, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo EY, L.; Muniandy, L.; Ng, E.P.; Adam, F.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jose, R.; Chong, K.F. High surface area activated carbon from rice husk as a high performance supercapacitor electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 192, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yi, J.; Feng, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, D. Analysis of adhesive characteristics of asphalt based on atomic force microscopy and molecular dynamics simulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12393–12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakurt, C. Microstructure properties of waste tire rubber composites: An overview. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qiu, L.; Liu, J.; Hu, K.; Zou, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, F.; Zang, J. Modification mechanism of C9 petroleum resin and its influence on SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifan, C.; Hui, W.; Yao, Z. Research on the performance of rice husk charcoal-SBS composite modified asphalt and mixes. Build. Technol. 2022, 5, 129–132. [Google Scholar]







| Technical Indicators | Test Results | Technical Requirements | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s) (0.1 mm) | 64.3 | 60~80 | T0604-2011 |
| Penetration (30 °C, 100 g, 5 s) (0.1 mm) | 106.1 | -- | T0604-2011 |
| Penetration (15 °C, 100 g, 5 s) (0.1 mm) | 25.3 | -- | T0604-2011 |
| Softening point (°C) | 47.2 | ≥43 | T0606-2011 |
| Ductility (5 cm/min, 10 °C) (cm) | 39.8 | ≥20 | T0605-2011 |
| Dynamic viscosity (60 °C) (Pa·s) | 218.3 | ≥160 | T0620-2000 |
| Density (15 °C) (g/cm3) | 0.97 | -- | T0603-2011 |
| Sample | S/B | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Stress at Definite Elongation (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Permanent Deformation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YH-791-H SBS | 30/70 | ≥18 | ≥1.9 | ≥700 | ≤45 |
| Sample | Elemental Analysis/% | Component Analysis/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | Moisture | Ash Content | Volatile Component | Fixed Carbon | |
| RHB | 51.68 | 1.77 | 45.72 | 0.64 | 0.19 | 5.60 | 38.13 | 9.65 | 53.34 |
| Sample | pH | Water Content (%) | Carbon Content (%) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Bulk Specific Weight (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHB | >7 | <10 | >50 | >400 | <450 |
| Type of mixture | Dynamic Stability/Time·mm−1 | Maximum Flexural Strain/με | Immersion Residual Stability Ratio/% | Freeze-Thaw Split Intensity Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base asphalt mixture | 1796 | 2159 | 61.2 | 66.8 |
| RHB asphalt mixture | 3691 | 1068 | 63.5 | 68.7 |
| SBS asphalt mixture | 6592 | 3805 | 86.3 | 87.8 |
| RHB-SBS composite-modified asphalt mixture | 7715 | 3224 | 82.9 | 87.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Lei, T.; Duan, P.; Cao, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, H. Study on Properties and Micro-Mechanism of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2023, 15, 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071718
Yi Y, Chen Y, Shi S, Zhao Y, Wang D, Lei T, Duan P, Cao W, Wang Q, Li H. Study on Properties and Micro-Mechanism of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071718
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Youqiu, Yifan Chen, Shuo Shi, Yao Zhao, Daming Wang, Tao Lei, Pengpeng Duan, Weiwei Cao, Qiang Wang, and Haitao Li. 2023. "Study on Properties and Micro-Mechanism of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071718
APA StyleYi, Y., Chen, Y., Shi, S., Zhao, Y., Wang, D., Lei, T., Duan, P., Cao, W., Wang, Q., & Li, H. (2023). Study on Properties and Micro-Mechanism of RHB-SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt. Polymers, 15(7), 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071718







