Effects of pH and Crosslinking Agent in the Evaluation of Hydrogels as Potential Nitrate-Controlled Release Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Polymeric Systems
Structural Characterization of the Polymeric Systems
2.3. Effect of pH on Swelling Kinetics
2.4. Effect of pH on Nitrate Ion Release Kinetics
2.5. Diffusion Mechanisms
2.6. Study of Nitrate Ion Release in Dynamic Regime
- T-0 test
- T-1 test
- T-2 test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization of the Polymeric Systems
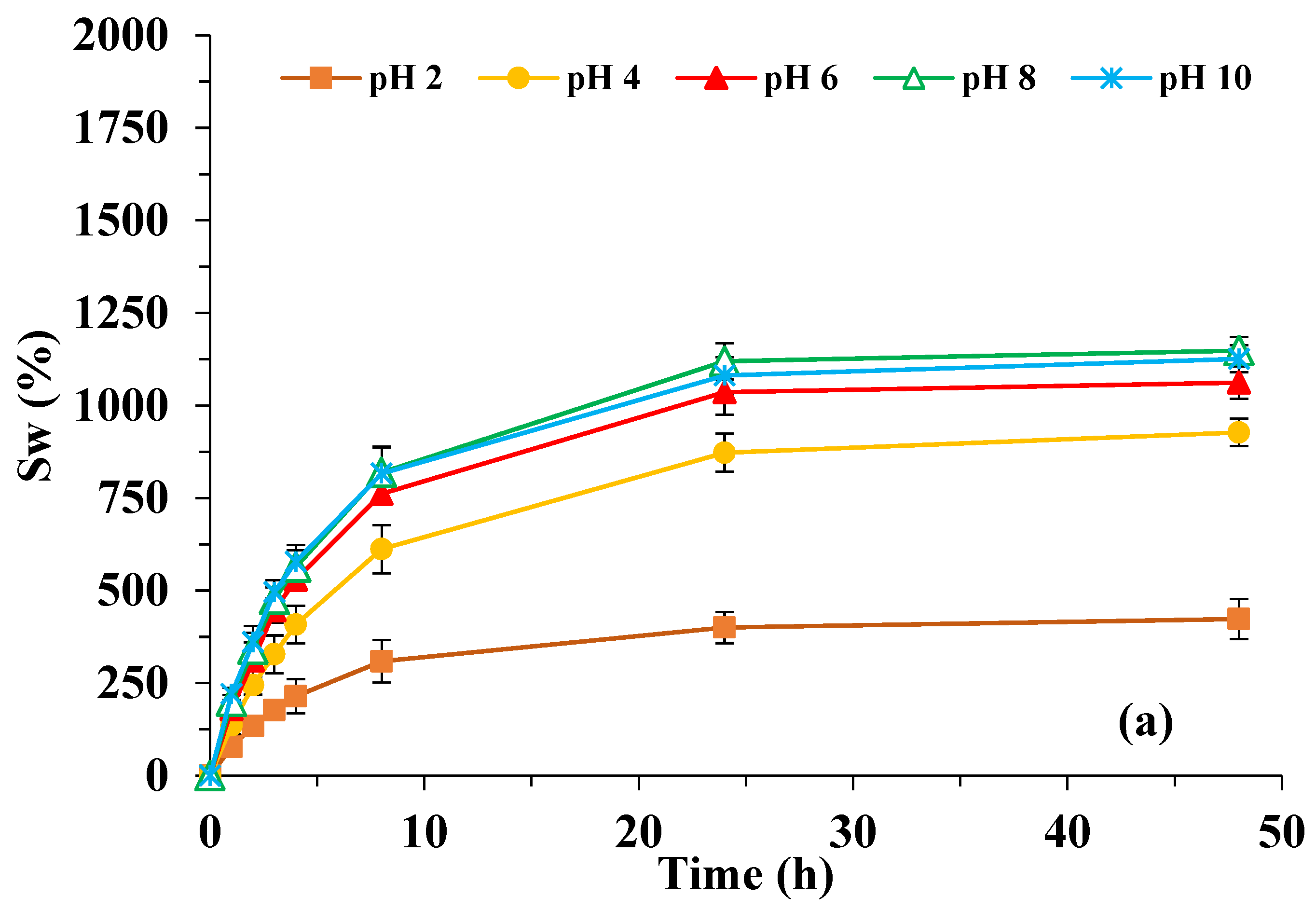
3.2. Effect of pH on Swelling Kinetics
3.2.1. H-Systems
3.2.2. SLC Systems
3.3. Effect of pH on Nitrate Ion Release Kinetics
3.4. Diffusion Mechanisms
Release Kinetic
3.5. Behavior of Polymeric Systems in Dynamic Regime
- T-0 Test
- T-1 Test
- T-2 Test
4. Conclusions
5. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Transforming Food and Agriculture to Achieve the SDGs, 2nd ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Sustainable Food and Agriculture. 5 Key Principles of Sustainability for Food and Agriculture. Available online: http://www.fao.org/sustainability/background/en (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Moddassir, A.; Muhammad, R.; Zahid, M.; Nasir, A.S. Excessive use of nitrogenous fertilizers: An unawareness causing serious threats to environment and human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26983–26987. [Google Scholar]
- Rütting, T.; Aronsson, H.; Delin, S. Efficient use of nitrogen in agriculture. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 110, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullyot, G.E.; Ullyot, B.H.; Slater, L.B. The metamorphosis of smithkline & French laboratories to Smith kline beecham: 1925–1998. Bull. Hist. Chem. 2000, 25, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, A.S. The origins and evolution of “controlled” drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-based medicines: A review of FDA-approved materials and clinical trials to date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewu, F.B.; Volova, T.; Thomas, S.; Rakhimol, K.R. Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture, 1st ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo, J.; Mendizábal, E.; Rentería, M.; Katime, I. Caracterización de hidrogeles con base de ácido itacónico para la liberación de ciclosporina. Rev. Iberoam. Polímeros 2013, 14, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow- and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers. An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Efficiency in Agriculture, 2nd ed.; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, C.T.; Lee, D.S. Controlled Release. In Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials; Kobayashi, S., Müllen, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, P.; França, D.; Gambaro Balieiro, A.; Faez, R. Polymers and its applications in agriculture. Polímeros 2017, 27, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Lin, X.; Khan, F.; Bennett, A.E.; Winter, J.O. Translating controlled release systems from biomedicine to agriculture. Front. Front. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 1, 1011877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjuik, T.A.; Nokes, S.E.; Montross, M.D.; Wendroth, O. The Impacts of Bio-Based and Synthetic Hydrogels on Soil Hydraulic Properties: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, K.; Mohd, A.; Mohd, H.; Shahid, K.; Mohd Shoeb, K.; Shahid, S.; Nami, S.A. Synthesis, classification, and properties of hydrogels: Their applications in drug delivery and agriculture. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 170–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A.; Muhammad, Y.; Ahmad, D.A.; Vidhya, S.; Faridah, S.; Cheyma, N.A. pH sensitive hydrogels in drug delivery: Brief history, properties, swelling and release mechanism, material selection and applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasution, H.; Harahap, H.; Dalimunthe, N.F.; Ginting, M.H.; Jaafar, M.; Tan, O.O.; Aruan, H.K.; Herfananda, A.L. Hydrogel and effects of crosslinking agent on cellulose-based hydrogels: A review. Gels 2022, 8, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Gao, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, M. Superabsorbent poly(acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogel microspheres: Preparation, characterization and absorbency. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2014, 56, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas de Gáscue, B.; Ramírez, M.; García, A.; Aguilera, R.; Gabriela de Souza, M.; Prin, J.L.; Rojas de Astudillo, L.; Murillo, M.; Astudillo, H.; Muñoz, F.; et al. Efecto de diferentes variables en la síntesis de hidrogeles copolímeros de poli(acrilamida-co-ácido maleico) y poli(acrilamida-co-ácido itacónico) sobre su capacidad de absorción. Rev. Iberoam. Polímeros 2016, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, M.A.; Al-Sweasy, O.; Sadek, M.A.; Elazab, H.A. Investigating the agricultural applications of acryl amide-based hydrogel. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, S.; Wesołowska-Piętak, A.; Konefał, R.; Świergosz, T. Persulfate initiated free-radical polymerization of itaconic acid: Kinetics, end-groups and side products. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 106, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulat, M.; Eksi, H. Determination of swelling behavior and morphological properties of poly(acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) and poly(acrylic acid-co-itaconic acid) copolymeric hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 5994–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco Guareño, E.; Hernández, S.L.; Gómez Salazar, S.; Mendizábal, E.; Katime, I. Estudio de hinchamiento de hidrogeles acrílicos terpoliméricos en agua y en soluciones acuosas de ión plumboso. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 2011, 10, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, N.C. Water uptake kinetics and control release of agrochemical fertilizers from nanoclay-assisted semi-interpenetrating sodium acrylate-based hydrogel. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 744–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Su, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. A biodegradable biomass-based polymeric composite for slow release and water retention. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, B.; Gao, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Poly(maleic anhydride-CO-acrylic acid)/Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels with pH- and ionic-strength- responses. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 28, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak, D.; Mikula, K.; Izydorczyk, G.; Dawiec-Lisniewska, A.; Moustakas, K.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. New directions for agricultural wastes valorization as hidrogel biocomposite fertilizers. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos Nascimento, C.D.; Simmons, R.W.; Pessoa de Andrade Feitosa, J.; Tadeu dos Santos Dias, C.; Gomes Costa, M.C. Potential of superabsorbent hydrogels to improve agriculture under abiotic stresses. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 189, 104496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano Juan, M.M.; Socias Viciana, M.M.; Ureña Amate, M.D. Evaluation of nitrate controlled release systems based on (acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 141, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prin, J.L.; González, N.; Villarroel, H.; Ramírez, M.; Rojas de Gáscue, B. El secado de punto crítico (SPC) como técnica aplicada en la preparación de geles de poli(acrilamida-co-ácido acrílico) por microscopía electrónica de barrido. Rev. Latinoam. Metal. Y Mater. 2012, S5, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- González, N.; Contreras, J.; López Carrasquero, F.; El Halah, A.; Torres, C.; Prin, J.L.; Benítez, J.; Rojas de Gáscue, B. Estudio de la síntesis y caracterización de hidrogeles semi-ipn obtenidos a partir de poliacrilamida y el biopolímero poli(hidroxibutirato-co-hidroxivalerato). Interciencia 2013, 38, 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-Fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modelling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, V.; Kosmidis, K.; Vlachou, M.; Macheras, P. On the use of the Weibull function for the discernment of drug release mechanisms. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 309, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierszewska-Druzyńska, M.; Ostrowska-Czubenko, J. Mechanism of water diffusion into noncrosslinked and ionically crosslinked chitosan membranes. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Its Deriv. 2012, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- González, N.; Prin, J.L.; Benítez, J.L.; Ramírez, A.; García, A.; Ramírez Sabino, M.; Rojas de Gáscue, M.B. Estudio de la cinética de difusión en hidrogeles sintetizados a partir de acrilamida-co-ácido acrílico con turba y almidón vía calentamiento convencional y bajo radiación microondas. Rev. Latinoam. Metal. Mater. 2012, 32, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Han, H.; Li, T.; Li, L.; Guo, X. Chitosan cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels: Drug release control and mechanism. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, J.L.; García, D.M.; Zaldivar, D.; Katime, I. Hidrogeles. Principales características en el diseño de sistemas de liberación controlada de fármacos. Rev. Iberoam. De Polímeros 2002, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Mathematical modelling of drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, H. Swelling kinetics of polymers. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 1992, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, H. Kinetics of swelling of polymers and their gels. J. Pharm. Sci. 1992, 81, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katime Amashta, I.A.; Katime Trabanca, D.; Trabanca Katime, Ó. Los Materiales Inteligentes de este Milenio: Los Hidrogeles Macromoleculares. Síntesis, Propiedades y Aplicaciones; Universidad del País Vasco: Bilbao, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- El Hamshary, H. Synthesis and water sorption studies of pH sensitive poly(acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4830–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Nitrate adsorption using poly(dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride)/polyacrylamide hydrogel. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3494–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kumar, M.; Suresh, K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Influence of organically modified Ni-Al layered double hydroxide (LDH) loading on the rheological properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)/LDH blend solution. Powder Technol. 2014, 256, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallés, E.; Durando, D.; Katime, I.; Mendizábal, E.; Puig, J.E. Equilibrium swelling and mechanical properties of hydrogels of acrylamide and itaconic acid or its esters. Polym. Bull. 2000, 44, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidzadeh, A.; Olad, A. Slow-released NPK fertilizer encapsulated by NaAlg-g-poly(AA-co-AAm)/MMT superabsorbent nanocomposite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasques Bueno, V.; Bentini, R.; Catalani, L.H.; Siqueira Petri, D.F. Synthesis and swelling behavior of xanthan-based hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-d’Arlas, B. Series liotrópicas en la Química Macromolecular. An. De Química 2016, 112, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.C.; Evans, R.Y.; Paul, J.L. Fertilizer salts reduce hydration of polyacrylamide gels and affect physical properties of gel-amended container media. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1990, 115, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarbary, A.M.; Ghobashy, M.M. Controlled release fertilizers using superabsorbent hydrogel prepared by gamma radiation. Radiochim. Acta 2017, 105, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, J.L.; Lárez Velásquez, C.; Rojas de Gáscue, B. Cinética de absorción y transporte del agua en hidrogeles sintetizados a partir de acrilamida y anhídrido maleico. Rev. Latinoam. De Metal. Y Mater. 2015, 35, 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Vázquez, N.; Antonio-Cruz, R.d.C.; Álvarez-Castillo, A.; Mendoza-Martinez, A.M.; Morales-Cepeda, A.B. Swelling kinetic of hydrogels from methyl cellulose and poly(acrylamide). Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2007, 6, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Bocourt Povea, M.; Cruz Rigñack, J.; Bada Rivero, N.; Peniche Covas, C. Síntesis y caracterización de hidrogeles biocompatibles interpenetrados de quitosana y poliacrilamida. Rev. CENIC Cienc. Químicas 2008, 39, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Barón Cortés, A.; Barrera Ramírez, I.X.; Boada Eslava, L.F.; Rodríguez Niño, G. Evaluación de hidrogeles para aplicaciones agroforestales. Ing. E Investig. 2007, 27, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, P.A.; Baena, Y.; Aragón, M.; Rosas, J.E.; Ponce D’León, L.F. Mecanismos generales de cesión de principios activos a partir de matrices monolíticas hidrofílicas preparadas con éteres de celulosa. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Químico Farm. 2008, 37, 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, B.; Liu, M.; Lü, S. Multifunctional slow-release urea fertilizer from ethylcellulose and superabsorbent coated formulations. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrestarazu Gavilán, M. Manual Práctico del Cultivo sin suelo e Hidroponía; Ediciones Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Louf, J.F.; Lu, N.B.; O’Connell, M.G.; Cho, H.J.; Datta, S.S. Under pressure: Hydrogel swelling in a granular medium. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vence, L.B.; Valenzuela, O.R.; Svartz, H.A.; Conti, M.E. Elección del substrato y manejo del riego utilizando como herramienta las curvas de retención de agua. Ciencia del Suelo 2013, 31, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sarıyer, O.S.; Sergey Panyukov, A.R.; Rubinstein, M.; Kumacheva, E. Universal behavior of hydrogels confined to narrow capillaries. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, T.; Peixinho, J.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; MacMinn, C.W. Dynamics of Swelling and Drying in a Spherical Gel. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 6, 064010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, C.; Nakamatsu, J. Matrices poliméricas para la liberación controlada de sustancias activas. Rev. Química 2002, 16, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B. Preparation and properties of new non-loading and superhigh ammonium nitrate loading hydrogels. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| n | Diffusion Mechanism |
|---|---|
| n < 0.5 | Almost Fickian |
| n = 0.5 | Fickian |
| 0.5 < n < 1 | Non-Fickian or Anomalous |
| n = 1 | Case II |
| n > 1 | Supercase II |
| Polymeric System | pH | Sw (%) | Vi (h−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-NMBA | 2 | 423 | 0.45 | 99.15 |
| 4 | 927 | 0.9 | 99.46 | |
| 6 | 1062 | 1.18 | 98.95 | |
| 8 | 1148 | 1.22 | 98.95 | |
| 10 | 1126 | 1.21 | 98.74 | |
| H-EGDMA | 2 | 1052 | 0.71 | 99.97 |
| 4 | 2672 | 1.67 | 99.96 | |
| 6 | 3550 | 2.36 | 99.68 | |
| 8 | 4142 | 2.46 | 99.82 | |
| 10 | --- | 2.76 | 99.95 |
| Polymeric System | pH | Sw (%) | Vi (h−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC-NMBA | 6 | 1017 | 0.94 | 99.73 |
| 8 | 1078 | 0.99 | 99.69 | |
| 10 | 1185 | 1.04 | 99.72 | |
| SLC-EGDMA | 6 | 1809 | 1.54 | 99.55 |
| 8 | 2236 | 1.59 | 99.62 | |
| 10 | --- | 1.79 | 99.83 |
| Polymeric System | pH | RN 1 h (%) | RN 2 h (%) | RN 48 h (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC-NMBA | 6 | 61.9 | 77.2 | 88.8 |
| 8 | 64.9 | 78.0 | 85.6 | |
| 10 | 60.2 | 82.6 | 85.8 | |
| SLC-EGDMA | 6 | 71.3 | 91.0 | 97.6 |
| 8 | 67.1 | 91.0 | 94.9 | |
| 10 | 65.8 | 88.0 | ----- |
| Fick Model | Authors Model | Schott Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric System | pH | n | k | R2 (%) | D (cm2/s) | R2 (%) | Swe (%) | Kap (h−1) | R2 (%) |
| H-NMBA | 6 | 0.79 | 0.34 | 99.74 | 0.09 | 99.48 | 1190 | 2.36 | 99.80 |
| 8 | 0.76 | 0.36 | 99.80 | 0.08 | 99.61 | 1285 | 2.58 | 99.82 | |
| 10 | 0.71 | 0.38 | 99.77 | 0.07 | 99.56 | 1242 | 2.78 | 99.93 | |
| SLC-NMBA | 6 | 0.70 | 0.38 | 99.68 | 0.09 | 99.72 | 1160 | 1.91 | 99.83 |
| 8 | 0.66 | 0.40 | 99.56 | 0.08 | 99.63 | 1220 | 2.14 | 99.84 | |
| 10 | 0.70 | 0.38 | 99.76 | 0.09 | 99.78 | 1355 | 1.98 | 99.96 | |
| H-EGDMA | 6 | 0.97 | 0.27 | 99.82 | 0.13 | 99.74 | 4808 | 2.87 | 99.82 |
| 8 | 0.90 | 0.29 | 99.96 | 0.12 | 99.95 | 5682 | 3.12 | 99.93 | |
| 10 | 0.91 | 0.28 | 100 | 0.12 | 100 | ----- | ----- | ----- | |
| SLC-EGDMA | 6 | 0.77 | 0.34 | 99.92 | 0.14 | 99.93 | 2123 | 2.70 | 99.94 |
| 8 | 0.74 | 0.36 | 99.94 | 0.13 | 99.94 | 2681 | 2.69 | 99.88 | |
| 10 | 0.75 | 0.35 | 99.94 | 0.13 | 99.89 | ----- | ----- | ----- | |
| Fick Model | Authors Model | Schott Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric System | pH | n | k | R2 (%) | D (cm2/s) | R2 (%) | RN (%) | Kap (h−1) | R2 (%) |
| SLC-NMBA | 6 | 0.28 | 0.70 | 96.46 | 4.69 × 10−3 | 95.30 | 88.74 | 4.09 | 99.97 |
| 8 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 93.68 | 1.12 × 10−3 | 92.15 | 85.72 | 6.10 | 99.99 | |
| 10 | 0.30 | 0.70 | 89.26 | 6.26 × 10−3 | 86.66 | 85.90 | 35.71 | 99.99 | |
| SLC-EGDMA | 6 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 88.64 | 1.51 × 10−3 | 86.96 | 97.16 | 3.44 | 99.92 |
| 8 | 0.28 | 0.71 | 89.77 | 5.99 × 10−3 | 87.84 | 94.76 | 7.18 | 99.97 | |
| 10 | 0.26 | 0.73 | 88.82 | 4.08 × 10−3 | 86.91 | 90.97* | 16.21 * | 99.96 * | |
| Physico-Chemical Property | |
|---|---|
| Total pore space (%) | 96.30 |
| Aeration capacity (% vol) | 32 |
| Apparent Density (g/cm3) | 0.06 |
| Real Density (g/cm3) | 1.52 |
| Water retention capacity (mL/L) | 523 |
| pH | 5.98 |
| Electric Conductivity (dS/m) | 3.52 |
| Organic mass (%) | 92.07 |
| Polymeric System | H (%) | Swe (%) |
|---|---|---|
| H-NMBA | 2646 | 1190 |
| SLC-NMBA | 1931 | 1160 |
| Leachate | KNO3 | SLC-NMBA |
|---|---|---|
| RN (%) | RN (%) | |
| 1 | 92.42 | 28.67 |
| 2 | 12.38 | 55.86 |
| 3 | 0 | 3.37 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 104.8 | 87.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ureña-Amate, M.D.; Socias-Viciana, M.d.M.; Urbano-Juan, M.d.M.; García-Alcaraz, M.d.C. Effects of pH and Crosslinking Agent in the Evaluation of Hydrogels as Potential Nitrate-Controlled Release Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051246
Ureña-Amate MD, Socias-Viciana MdM, Urbano-Juan MdM, García-Alcaraz MdC. Effects of pH and Crosslinking Agent in the Evaluation of Hydrogels as Potential Nitrate-Controlled Release Systems. Polymers. 2023; 15(5):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051246
Chicago/Turabian StyleUreña-Amate, María Dolores, María del Mar Socias-Viciana, María del Mar Urbano-Juan, and María del Carmen García-Alcaraz. 2023. "Effects of pH and Crosslinking Agent in the Evaluation of Hydrogels as Potential Nitrate-Controlled Release Systems" Polymers 15, no. 5: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051246
APA StyleUreña-Amate, M. D., Socias-Viciana, M. d. M., Urbano-Juan, M. d. M., & García-Alcaraz, M. d. C. (2023). Effects of pH and Crosslinking Agent in the Evaluation of Hydrogels as Potential Nitrate-Controlled Release Systems. Polymers, 15(5), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051246







