Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Gluten-Konjac glucomannan Conjugates Prepared by Maillard Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Degree of Graft (DG)
2.4. Color Measurement
2.5. Particle Size and Turbidity Determination
2.6. Secondary Structure
2.7. Measurement of Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectra
2.8. Determination of Electric Potential
2.9. Determination of Surface Hydrophobicity
2.10. Foaming Capacity and Stability
2.11. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsifying Stability Index (ESI)
2.12. Rheological Properties
2.13. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. DG Analysis
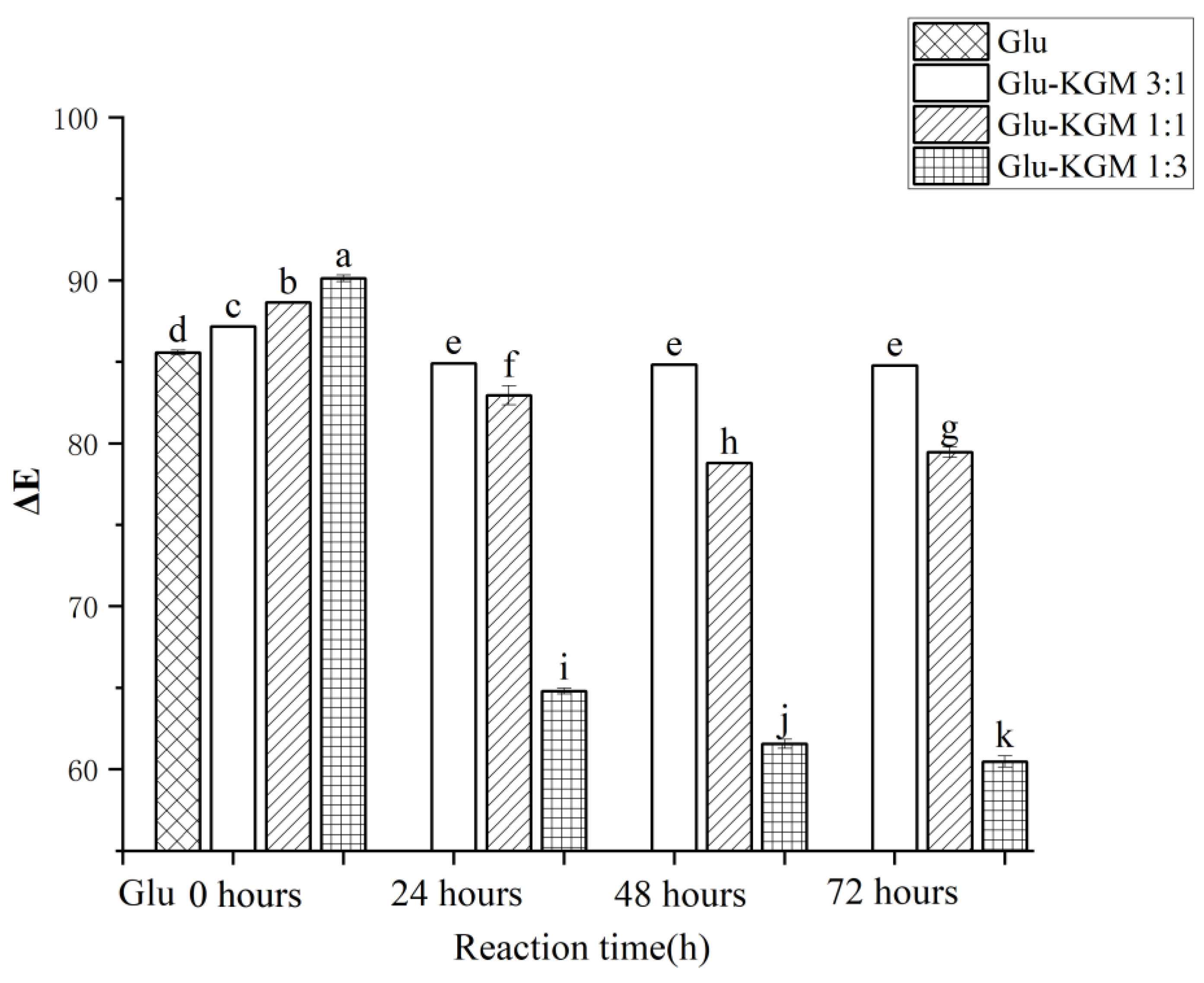
3.2. Color Change
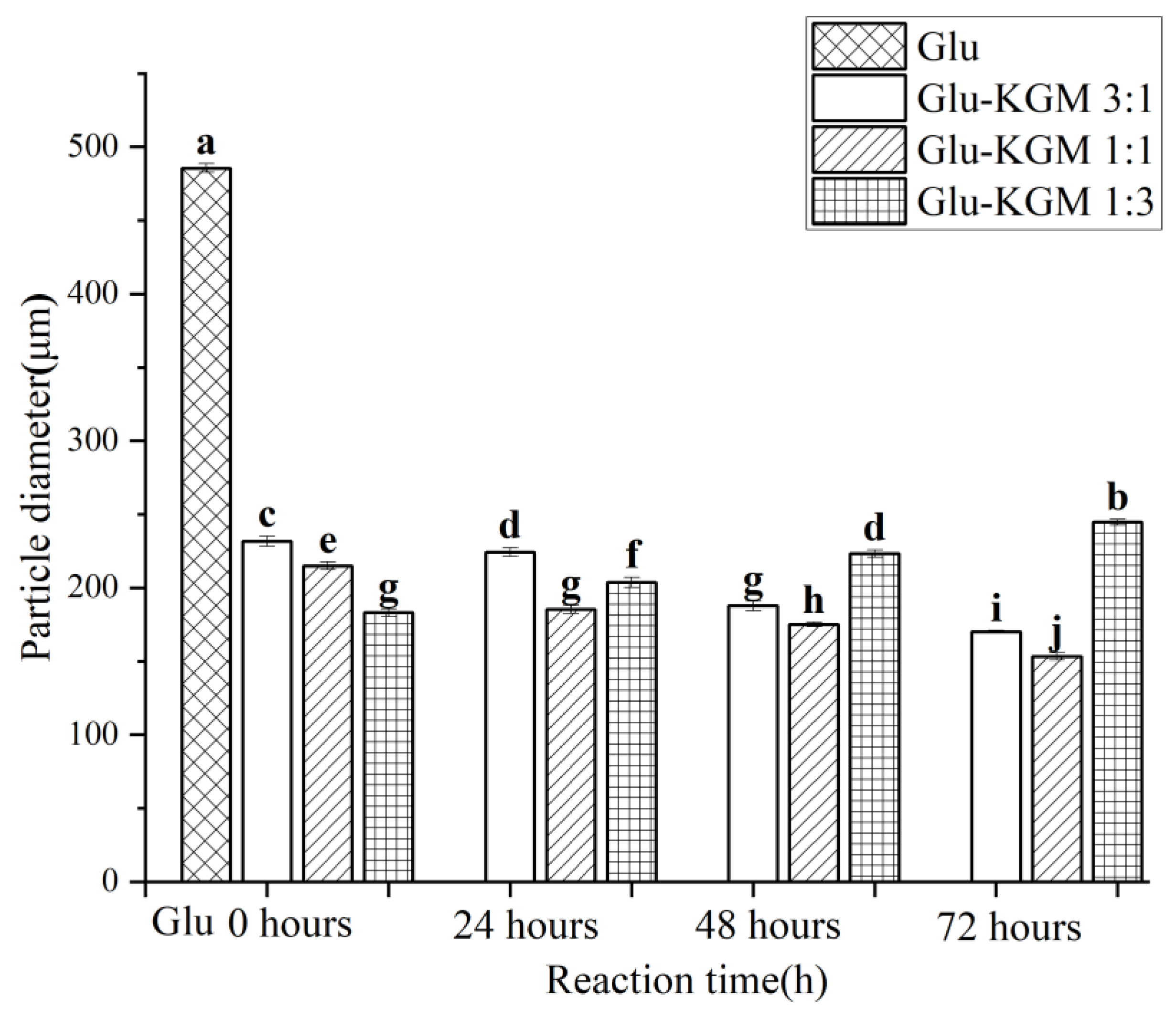
3.3. Particle Size and Turbidity
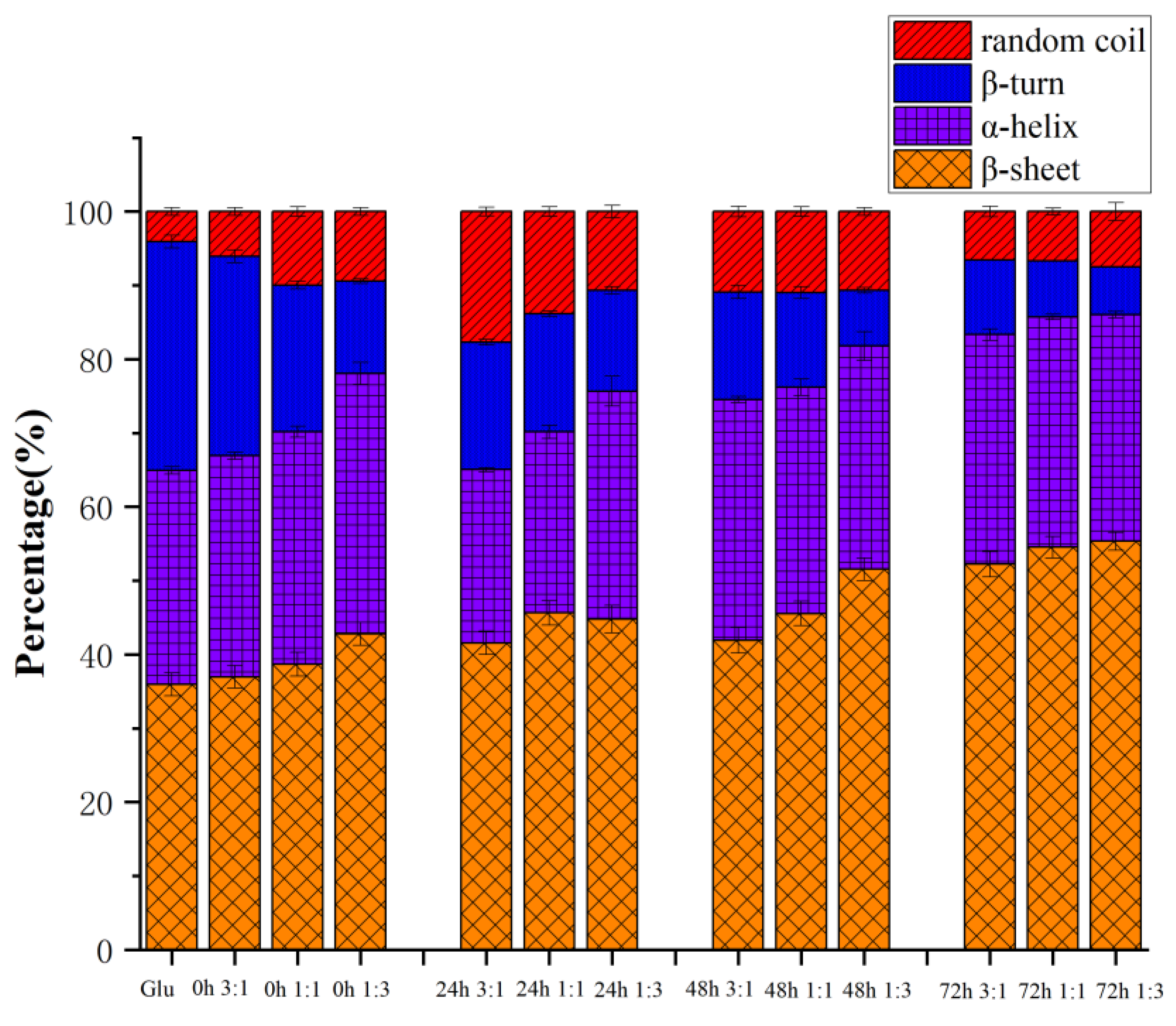
3.4. Secondary Structure
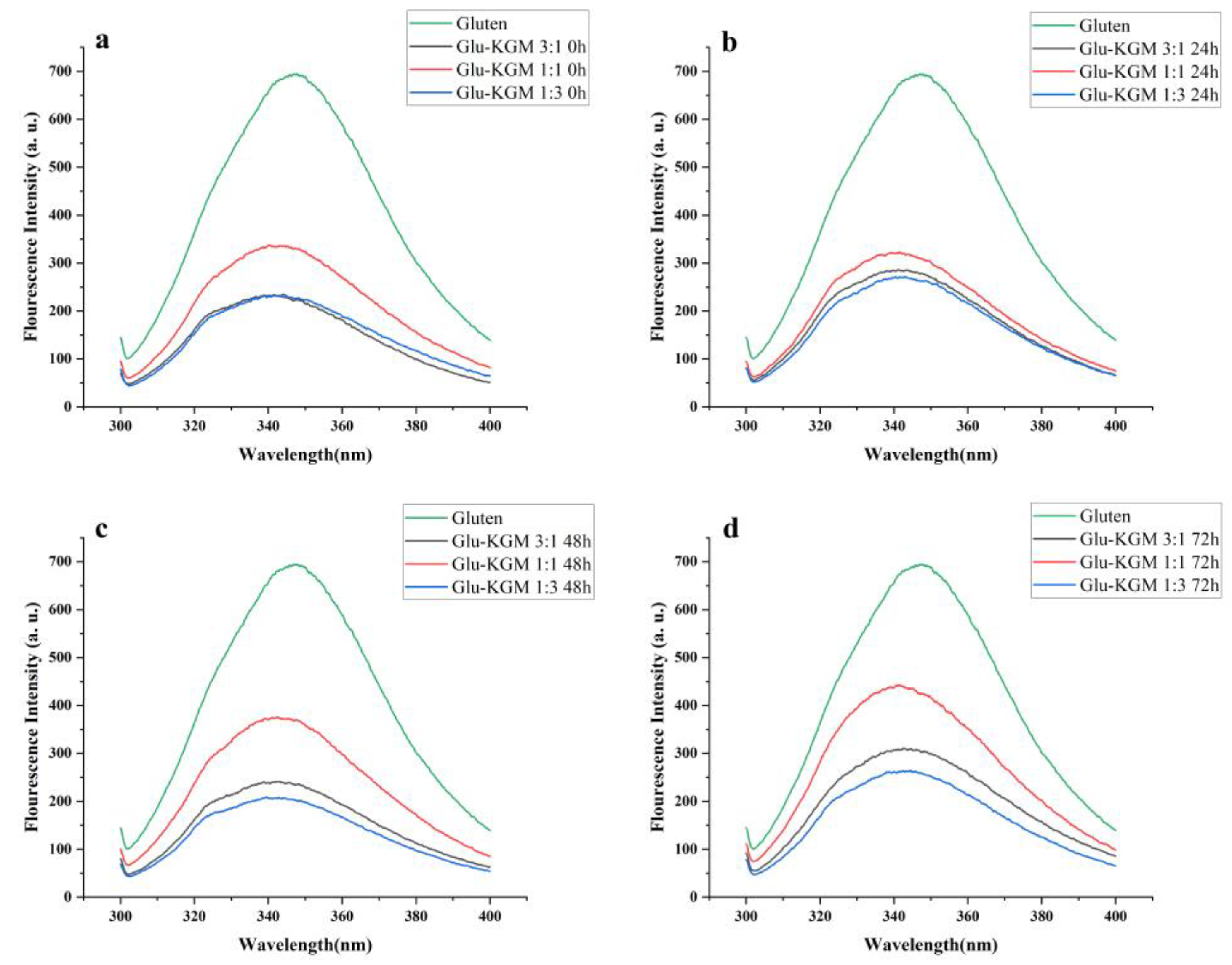
3.5. Intrinsic Fluorescence Intensity
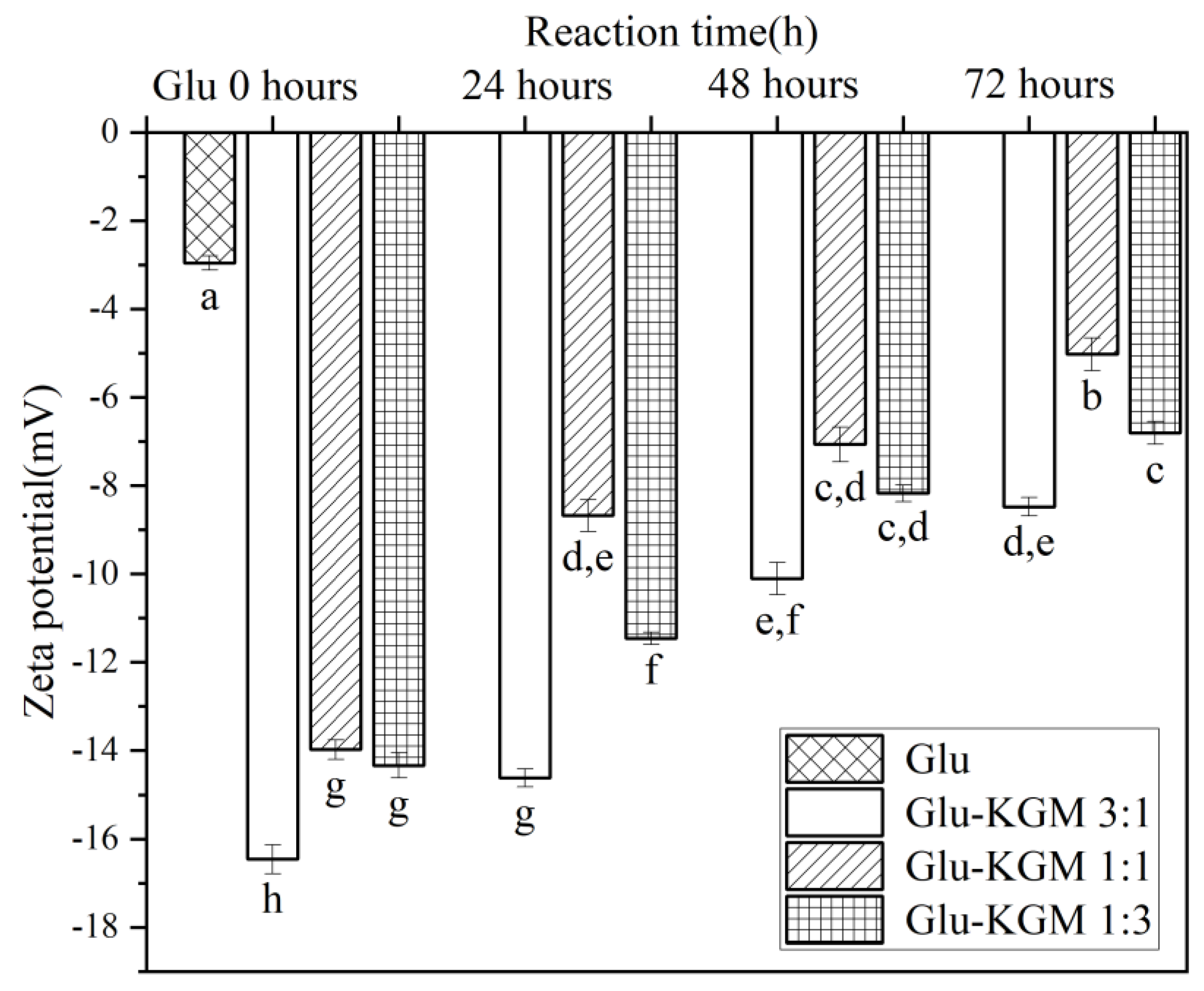
3.6. Zeta Potential
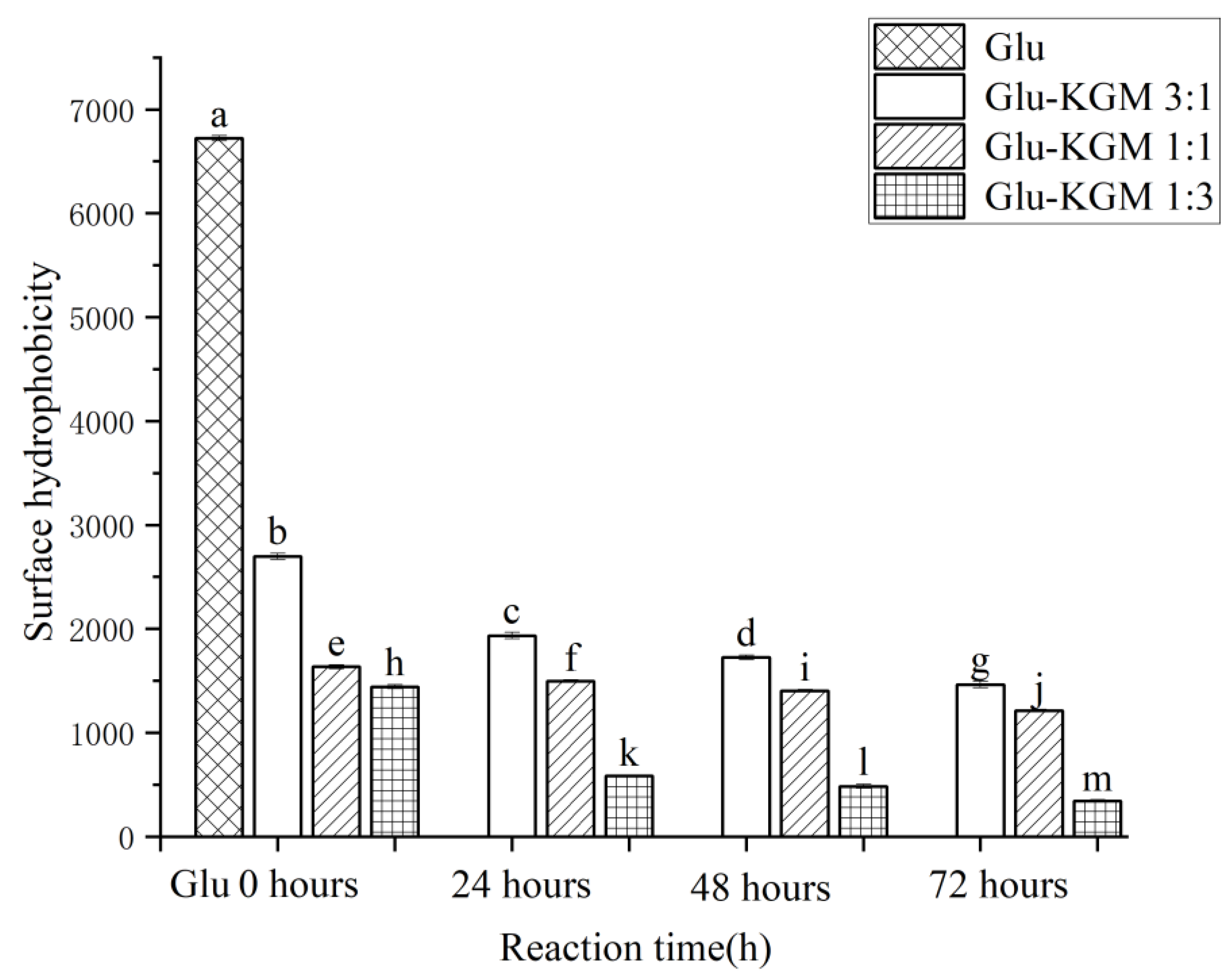
3.7. Surface Hydrophobicity(H0)
3.8. Foaming Capacity and Stability
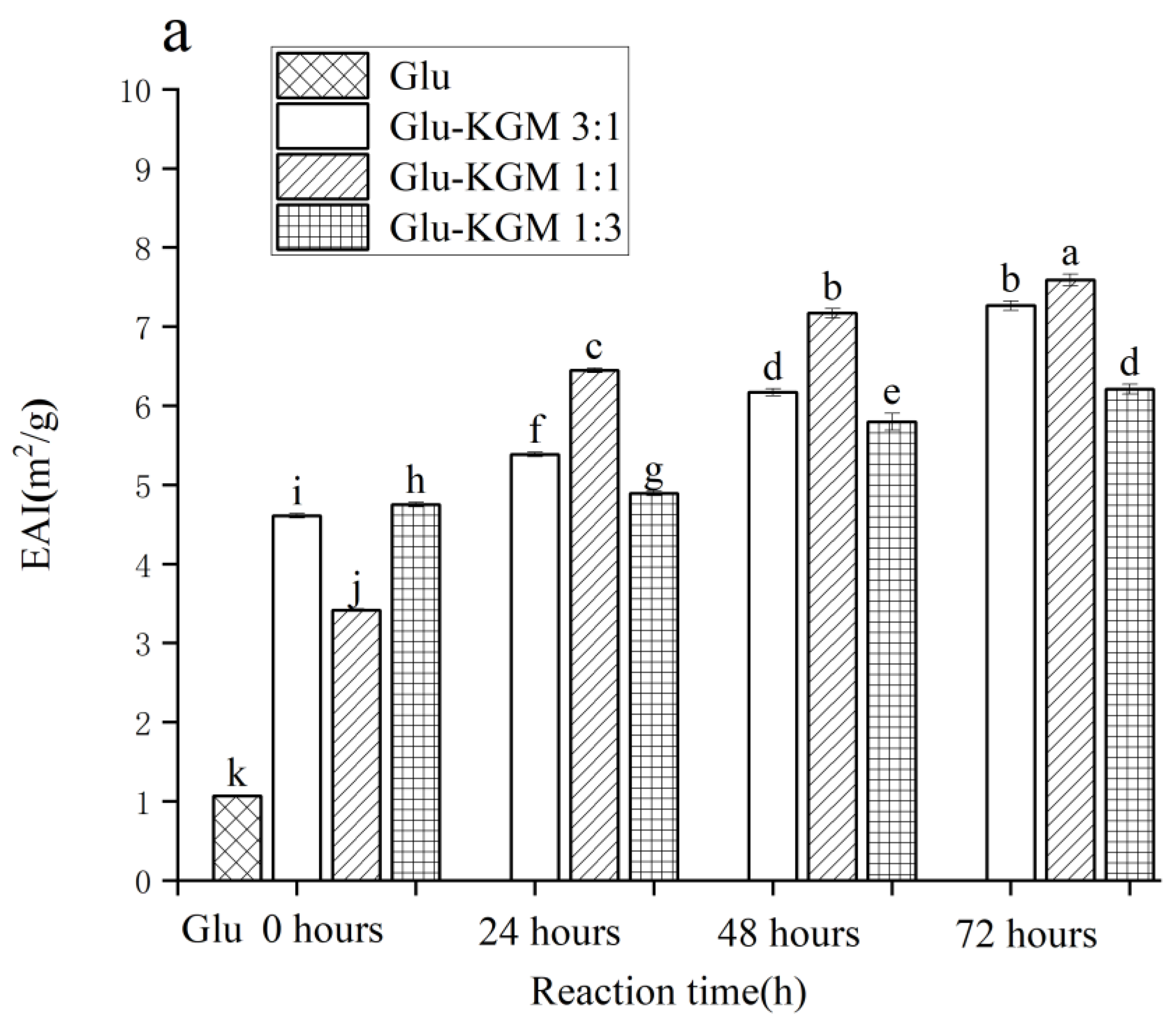
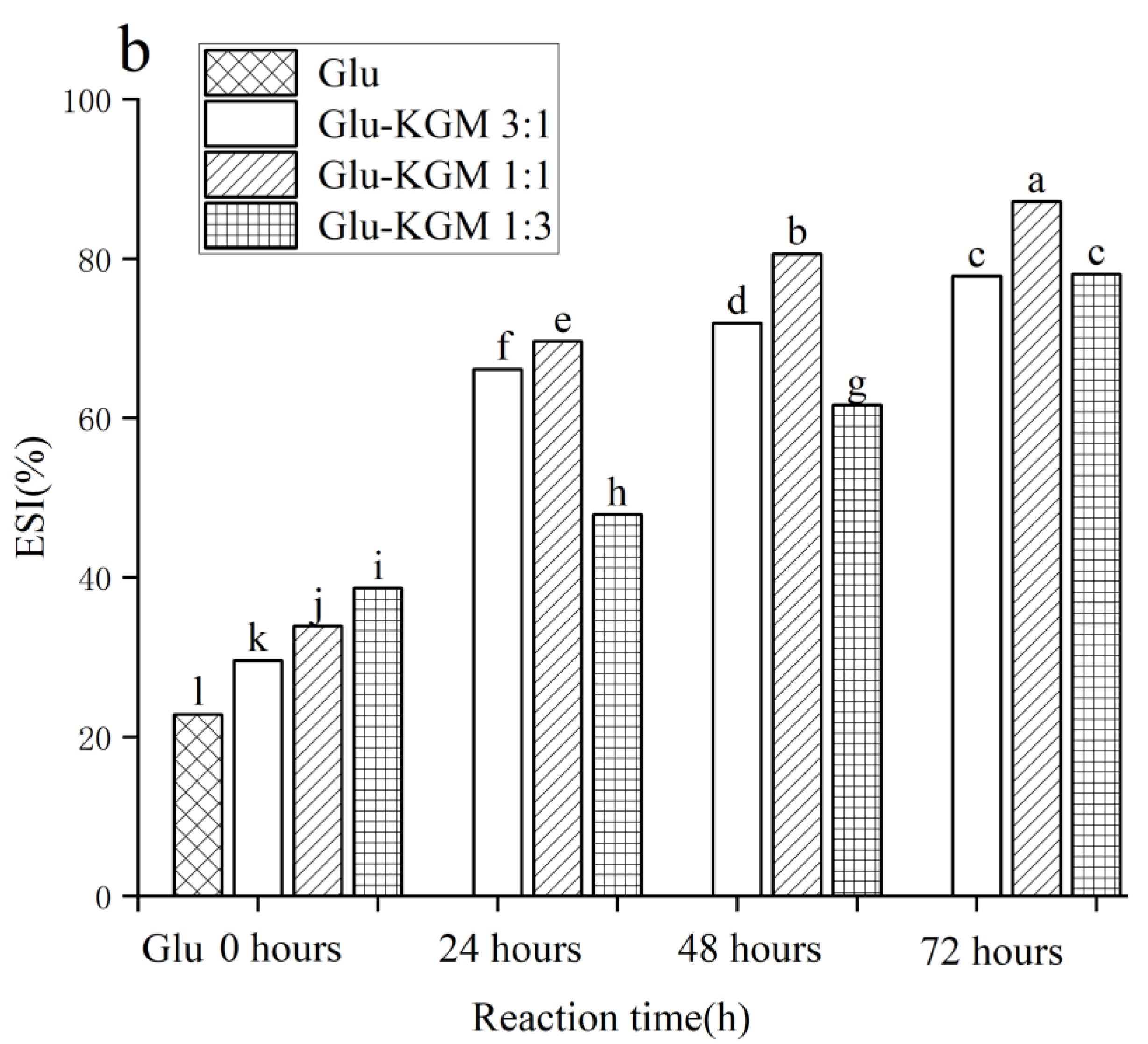
3.9. EAI and ESI
3.10. Rheological Properties
3.11. Microscopic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Nirasawa, S.; Tatsumi, E.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y. Effects of konjac glucomannan on heat-induced changes of wheat gluten structure. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, S.; Saari, N.; Ghazali, H.M.; Abdulkarim, S.M.; Hamid, A.A.; Anwar, F. Gluten proteins: Enzymatic modification, functional and therapeutic properties. J. Proteom. 2022, 251, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, N. Relationship of polymeric proteins and empirical dough rheology with dynamic rheology of dough and gluten from different wheat varieties. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamone, G.; Addeo, F.; Chianese, L.; Di Luccia, A.; De Martino, A.; Nappo, A.; Formisano, A.; De Vivo, P.; Ferranti, P. Characterization of wheat gliadin proteins by combined two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.; Baldwin, T.C.; Hocking, T.J.; Chan, K. Traditional uses and potential health benefits of Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch ex N.E.Br. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, J.; Ren, G.; Cui, G.; Han, S.; Liu, J. Effects of konjac glucomannan on the water distribution of frozen dough and corresponding steamed bread quality. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, P. Effect of konjac glucomannan on gelatinization, retrogradation, and gelling properties of frozen wheat starch. Starch-Starke 2020, 73, 2000025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Luo, D.; Xiang, J.; Sun, J. Influence of konjac glucomannan on thermal and microscopic properties of frozen wheat gluten, glutenin and gliadin. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 102866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, F.; Gan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Hao, J. Effects of Konjac glucomannan with different viscosities on the rheological and microstructural properties of dough and the performance of steamed bread. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.R.; Wang, Y.; Selomulya, C. Improvements of plant protein functionalities by Maillard conjugation and Maillard reaction products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7036–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arogundade, L.A.; Mu, T.H.; Zhang, M.; Khan, N.M. Impact of dextran conjugation on physicochemical and gelling properties of sweet potato protein through Maillard reaction. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, L.; Chang, C.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Molecular forces and gelling properties of heat-induced gel from egg white protein glycated with isomalto-oligosaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, L.; Tan, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Duan, X. Phosvitin-wheat gluten complex catalyzed by transglutaminase in the presence of Na2SO3: Formation, cross-link behavior and emulsifying properties. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xiong, H.; Selomulya, C.; Chen, X.D.; Huang, S.; Ruan, X.; Sun, W. Effects of spray drying and freeze drying on the properties of protein isolate from rice dreg protein. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Mu, M.; Jia, F.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J. Aggregative and structural properties of wheat gluten induced by pectin. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 100, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Xie, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, X. Prevention of frozen-dough from deterioration with incorporation of glutenin-polyphenols conjugates prepared by ultrasound. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, Y. Drying methods affect physicochemical and functional properties of quinoa protein isolate. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, X.Y.; Qi, J.R.; Yin, S.W.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhu, J.H.; Huang, L.X. Formation of soy protein isolate-dextran conjugates by moderate Maillard reaction in macromolecular crowding conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, J.; Ma, W.; Pu, H.; Huang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Control of wheat starch rheological properties and gel structure through modulating granule structure change by reconstituted gluten fractions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193 Pt B, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G.; Tatham, A.S. High molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin. J. Cereal Sci. 1992, 15, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, C.E.; Tsiami, A.A.; Schofield, J.D.; Dobraszczyk, B.J. Effect of heat on rheology, surface hydrophobicity and molecular weight distribution of glutens extracted from flours with different bread-making quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steertegem, B.; Pareyt, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. The role of gluten proteins in production and quality of a yeast leavened sugar and fat rich wheat based food model system. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zou, M.; Gu, Z.; Yang, R. Heat-induced polymerization behavior variation of frozen-stored gluten. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Feng, Y.; Li, X. Influence of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit composition at Glu-B1 locus on secondary and micro structures of gluten in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Food Chem. 2016, 197 Pt B, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Q.; Luo, S.Z.; Zhong, X.Y.; Cai, J.; Jiang, S.T.; Zheng, Z. Changes in chemical interactions and protein conformation during heat-induced wheat gluten gel formation. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Pang, J. Comparative studies on physicochemical properties of bovine serum albumin-glucose and bovine serum albumin-mannose conjugates formed via Maillard reaction. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirestani, S.; Nasirpour, A.; Keramat, J.; Desobry, S. Preparation of chemically modified canola protein isolate with gum Arabic by means of Maillard reaction under wet-heating conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, T.; Vasiljevic, T.; Ramchandran, L. Shear, heat and pH induced conformational changes of wheat gluten—Impact on antigenicity. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihi, M.L.; Mession, J.L.; Sok, N.; Saurel, R. Heat-induced soluble protein aggregates from mixed pea globulins and β-lactoglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2780–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghribi, A.M.; Gafsi, I.M.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Besbes, S. Effect of drying methods on physicochemical and functional properties of chickpea protein concentrates. J. Food Eng. 2015, 165, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Rana, J.C.; Kaur, A. Relationship between physicochemical and functional properties of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) protein isolates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gan, J.; Li, Y.; Nirasawa, S.; Cheng, Y. Conformation and emulsifying properties of deamidated wheat gluten-maltodextrin/citrus pectin conjugates and their abilities to stabilize β-carotene emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Adhikari, B.; Aldred, P.; Panozzo, J.F.; Kasapis, S.; Barrow, C.J. Interfacial and emulsifying properties of lentil protein isolate. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xi, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, M. Effect of glycosylation with apple pectin, citrus pectin, mango pectin and sugar beet pectin on the physicochemical, interfacial and emulsifying properties of coconut protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Hu, M.; Du, X.; Liao, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhang, S.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Correlating structure and emulsification of soybean protein isolate: Synergism between low-pH-shifting treatment and ultrasonication improves emulsifying properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 646, 128963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wu, M.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Xu, W.; Qiu, S. Synergistic effect of pH shifting and mild heating in improving heat induced gel properties of peanut protein isolate. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Xue, F. Effects of conjugation between proteins and polysaccharides on the physical properties of emulsion-based edible films. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Liang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Nirasawa, S. Effects of dough mixing time before adding konjac glucomannan on the quality of noodles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3837–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironeasa, S.; Iuga, M.; Zaharia, D.; Mironeasa, C. Rheological analysis of wheat flour dough as influenced by grape peels of different particle sizes and addition levels. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbo, M.G.; Fadda, C.; Marceddu, S.; Conte, P.; Del Caro, A.; Piga, A. Improving the quality of dough obtained with old durum wheat using hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Li, C.; Wang, S. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound treatment on physiochemical properties of caseins-cyanidin-3-galactoside conjugates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3378–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, R.; Wu, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M. Soluble dietary fiber fractions in wheat bran and their interactions with wheat gluten have impacts on dough properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8735–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lei, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ming, J. Carboxymethylcellulose-induced changes in rheological properties and microstructure of wheat gluten proteins under different pH conditions. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Huang, D.; Guo, W.; Gao, Y.; Xue, F.; Xiong, X.; Li, C. Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Gluten-Konjac glucomannan Conjugates Prepared by Maillard Reaction. Polymers 2023, 15, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030631
Song Y, Huang D, Guo W, Gao Y, Xue F, Xiong X, Li C. Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Gluten-Konjac glucomannan Conjugates Prepared by Maillard Reaction. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030631
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yukang, Danping Huang, Wanchun Guo, Yiqing Gao, Feng Xue, Xiaohui Xiong, and Chen Li. 2023. "Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Gluten-Konjac glucomannan Conjugates Prepared by Maillard Reaction" Polymers 15, no. 3: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030631
APA StyleSong, Y., Huang, D., Guo, W., Gao, Y., Xue, F., Xiong, X., & Li, C. (2023). Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Gluten-Konjac glucomannan Conjugates Prepared by Maillard Reaction. Polymers, 15(3), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030631






