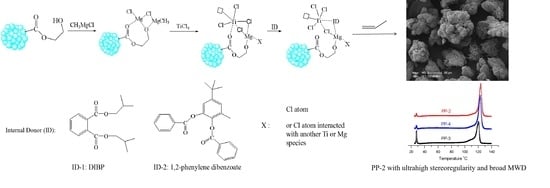
Porous Organic Polymers-Supported Zeigler-Natta Catalysts for Preparing Highly Isotactic Polypropylene with Broad Molecular Weight Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of POP Supports and POP-Based Ziegler–Natta Catalysts
2.3. Propylene Polymerization
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of POP Supports
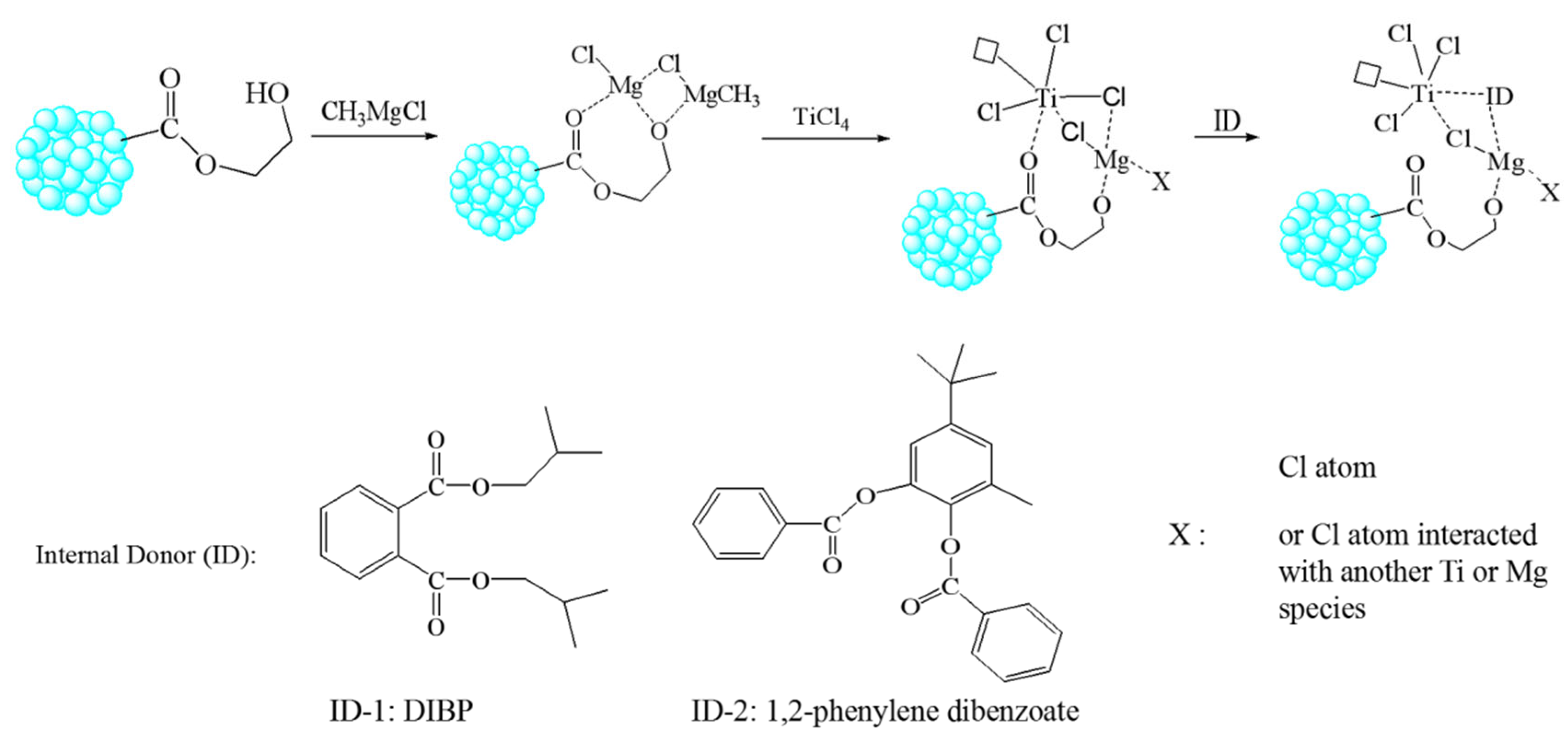
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of POP-Based Ziegler–Natta Catalyst
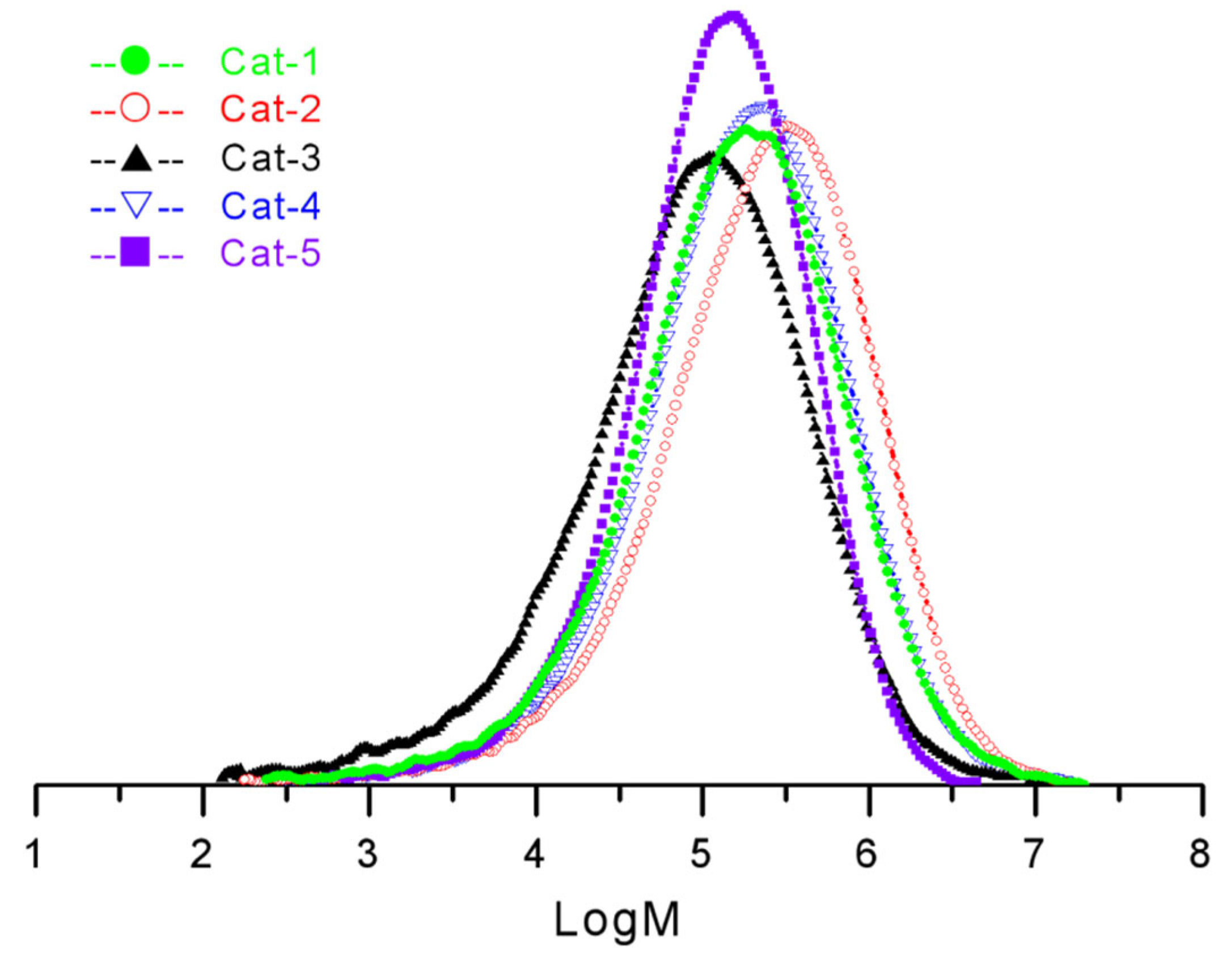
3.3. Propylene Polymerization by POP-Based Ziegler–Natta Catalysts
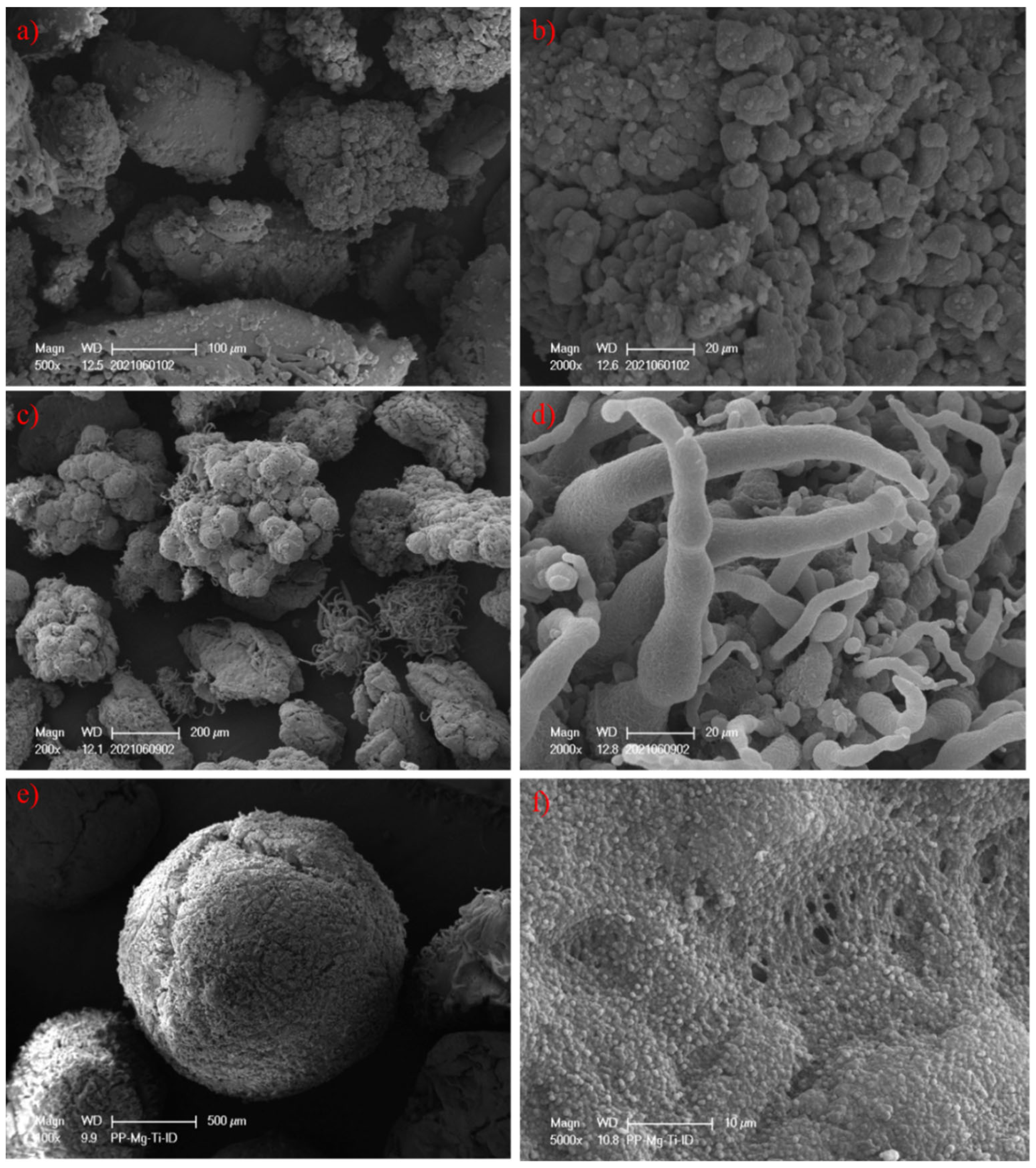
3.4. Surface Morphology of Prepared PP
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galli, P.; Vecellio, G. Polyolefins: The most promising large-volume materials for the 21st century. J. Polym. Sci. A. Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 396–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.M.; Gupta, V.K. Progress in MgCl2 supported Ziegler-Natta catalyzed polyolefin products and applications. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, P.; Vecellio, G. Technology: Driving force behind innovation and growth of polyolefins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1287–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covezzi, M.; Mei, G. The multizone circulating reactor technology. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 4059–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, P. The reactor granule technology: A revolutionary approach to polymer blends and alloys. Macromol. Symp. 1994, 78, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Kang, W.; Fan, J.; Han, X.; Xu, Y. Versatile Polypropylene Copolymers from a Pilot-Scale Spheripol II Process. Polymers 2020, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchin, G.; Morini, G.; Pelliconi, G. Polypropylene product innovation by reactor granule technology. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 173, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.Y.; Xu, R.W. Polypropylene-Polymerization and Characterization of Mechanical and Thermal Properties; Wang, W.Y., Zeng, Y.M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, G.; Xu, R. Toughened High-Flow Polypropylene with Polyolefin-Based Elastomers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paghadar, B.R.; Sainani, J.B.; Samith, K.M.; Bhagavath, P. Internal donors on supported Ziegler Natta catalysts for isotactic polypropylene: A brief tutorial review. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kaur, S.; Makwana, U.; Patankar, R.B.; Gupta, V.K. Influence of Internal Donors on the Performance and Structure of MgCl2 Supported Titanium Catalysts for Propylene Polymerization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwa, N. The Discovery and Progress of MgCl2-Supported TiCl4 Catalysts. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanakumar, E.S.; Thushara, K.S.; Gowda, R.R.; Raman, S.K.; Ajithkumar, T.G.; Rajamohanan, P.R.; Chakraborty, D.; Gopinath, C.S. MgCl2·6C6H11OH: A High Mileage Porous Support for Ziegler−Natta Catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2012, 116, 24115–24122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovano, A.; Wada, T.; Amodio, A.; Takasao, G.; Ikeda, T.; Zhu, D.; Terano, M.; Chammingkwan, P.; Groppo, E.; Taniike, T. Formation of Highly Active Ziegler−Natta Catalysts Clarified by a Multifaceted Characterization Approach. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 13782–13796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukalov, D.V.; Zakharov, V.A.; Potapov, A.G.; Bukatov, G.B. Supported Ziegler-Natta Catalysts for Propylene Polymerization. Study of Surface Species Formed at Interaction of Electron Donors and TiCl4 With Activated MgCl2. J. Catal. 2009, 266, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregonese, D.; Noto, V.D.; Peloso, A.; Bresadola, S. MgCl2-supported catalysts for the propylene polymerization: Effects of triethers as internal donors on the activity and stereoselectivity. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 2122–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y. Ziegler-Natta catalysts with novel internal electron donors for propylene polymerization. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Ji, M.; Yi, Q.; Niu, H.; Dong, J.-Y. Magnesium chloride supported Ziegler-Natta catalysts containing succinate internal electron donors for the polymerization of propylene. J. Appl. Polym Sci. 2010, 118, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Singh, S.C.; Gupta, V.K. Morphology Controlled Magnesium Ethoxide: Influence of Reaction Parameters and Magnesium Characteristics. Part. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2009, 27, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, K.; Shiono, T. Ziegler-Natta catalysts for olefin polymerizations. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1997, 22, 1503–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Xu, S.; Hao, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, A.; Zhang, Y. Surface effect of MgCl2 support in Zieger-Natta catalyst for ethylene polymerization: A computational study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 589, 153002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovano, A.; Groppo, E. Flexible ligands in heterogeneous catalysts for olefin polymerization: Insights from spectroscopy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 451, 214258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi-Dehaghani, Z.-A.; Arabi, H.; Thalheim, D.; Vidakovic, D.; Haghighi, M.N.; Veith, L.; Klapper, M. Organic Versus Inorganic Supports for Metallocenes: The Influence of Rigidity on the Homogeneity of the Polyolefin Microstructure and Properties. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 2667–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapper, M.; Joe, D.; Nietzel, S.; Krumpfer, J.W.; Müllen, K. Olefin polymerization with supported catalysts as an exercise in nanotechnology. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 802–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Riduan, S.N. Functional porous organic polymers for heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. Synthesis and characterization of functional porous organic polymers as efficient metallocene catalyst supports. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8324–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.-L.; Liu, W.-X.; Zhang, P.-S. Feasibility study on the design and synthesis of functional porous organic polymers with tunable pore structure as metallocene catalyst supports. Polymers 2018, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Han, X. Metal oxide as a template in the preparation of porous poly (2-hydroxyethylmethylacrylate-co-divinylbenzene) particles as a metallocene catalyst support. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 52464–52474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kang, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, P.; Jia, H.; Gao, D. Porous organic polymer/MMT hybrid supports for efficient metallocene catalysts. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 19253–19266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Hupp, J.T.; Nguyen, S.T. Porous organic polymers in catalysis: Opportunities and challenges. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Ren, F.; Xu, R.; Bai, Y. Porous organic polymers-supported metallocene catalysts for ethylene/1-hexene copolymerization. Catalysts 2018, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurtefeu, B.; Bouilhac, C.; Cloutet, É.; Taton, D.; Deffieux, A.; Cramail, H. Polymer support of ″single-site″ catalysts for heterogeneous olefin polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 89–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Han, Z.; Bai, Y. Highly tunable porous organic polymer (POP) supports for metallocene-based ethylene polymerization. Appl. Surface Sci. 2017, 420, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y. Sulfonated porous organic polymer supported Zeigler-Natta polypropylene catalysts with high stereoregularity and broad molecular weight distribution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 343, 112151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Zhou, G. Porous polyethylene spheres with nanofiber structure from Ziegler-Natta catalyst supported on porous polymer particles. Polymer 2011, 52, 602–605. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Hsu, C.C.; Bacon, D.W. Polymer-Supported Ziegler-Natta Catalysts. 1. A Preliminary Study of Catalyst Synthesis. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1994, 32, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Han, X.; Da, M. Ionic Liquid-Modified Porous Organic Polymers as Efficient Metallocene Catalyst Supports. Catalysts 2022, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kang, W.; Gao, L.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y. Highly flowable nano TiO2/porous organic polymer (POP) supports for efficient metallocene catalysts. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanidis, G.G.; Karayannis, N.M. Infrared Characterization of Supported Propylene Polymerization Catalysts-A Link to Catalyst Performance. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1990, 56, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, J.C.W.; Wu, J.-C.; Kuo, C. Magnesium Chloride Supported High-Mileage Catalysts for Olefin Polymerization. IV. FTIR and Quantitative Analysis of Modifiers in the Catalysts. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1983, 21, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thushara, K.S.; D’Amore, M.; Piovano, A.; Bordiga, S.; Groppo, E. The Influence of Alcohols in Driving the Morphology of MgCl2 Nanocrystals. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, T.; Takasao, G.; Piovano, A.; D’Amore, M.; Thakur, A.; Chammingkwan, P.; Bruzzes, P.C.; Terano, M.; Civalleri, B.; Bordiga, S.; et al. Revisiting the identity of d-MgCl2: Part I. Structural disorder studied by synchrotron X-ray total scattering. J. Catal. 2020, 385, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
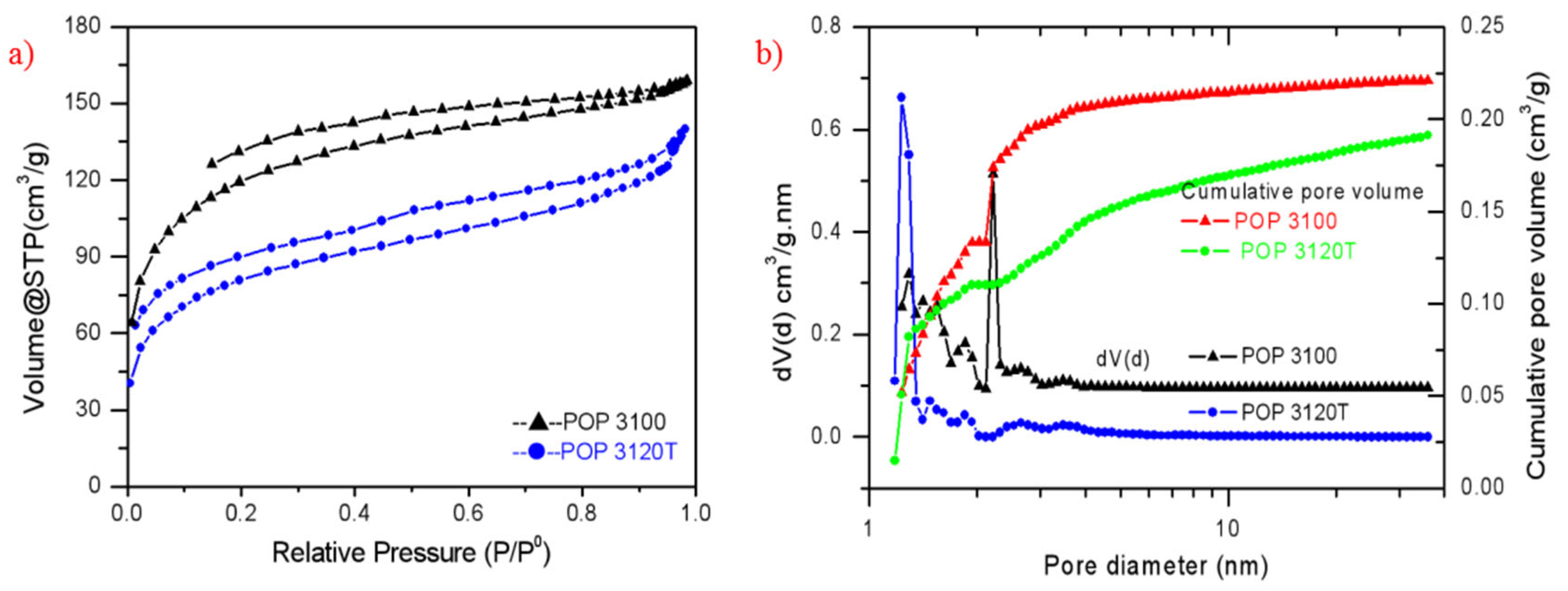



| Support | Specific Surface Area m2/g | Total Pore Volume cm3/g | Average Pore Diameter nm | Bulk Density g/cm3 | Particle Flowability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POP3120T | 272 | 0.216 | 3.172 | 0.28 | excellent |
| POP3100 | 397 | 0.246 | 2.478 | 0.14 | good |
| Catalyst No. | Support | Internal Electron Donor (ID) | Mg (wt%) | Ti Loading Amounts (wt%) | ID (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat-1 | POP3120T | ID-1 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.8 |
| Cat-2 | POP3120T | ID-2 | 4.2 | 3.5 | 4.2 |
| Cat-3 | POP3100 | No ID | 3.9 | 3.2 | - |
| Cat-4 | MgCl2 | ID-2 | 17.8 | 3.2 | 7.1 |
| Cat-5 | MgCl2 | ID-3 | 17.2 | 3.0 | 7.6 |
| Catalysts No. | Activity (×106 g·PP/mol·Ti·h) | Productivity (kg·pp/g·cat·h) | Bulk Density (g/mL) | Isotactic Index (%) | Mw | Mn | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat-1 | 10.5 | 8.8 | 0.33 | 97.5 | 39.40 | 3.47 | 11.4 |
| Cat-2 | 15.3 | 11.2 | 0.31 | 98.2 | 55.06 | 4.46 | 12.3 |
| Cat-3 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 0.24 | 91.5 | 23.45 | 1.44 | 16.3 |
| Cat-4 | 54.5 | 36.4 | 0.40 | 97.0 | 41.45 | 3.77 | 11.0 |
| Cat-5 | 39.1 | 24.5 | 0.38 | 98.4 | 22.91 | 4.33 | 5.3 |
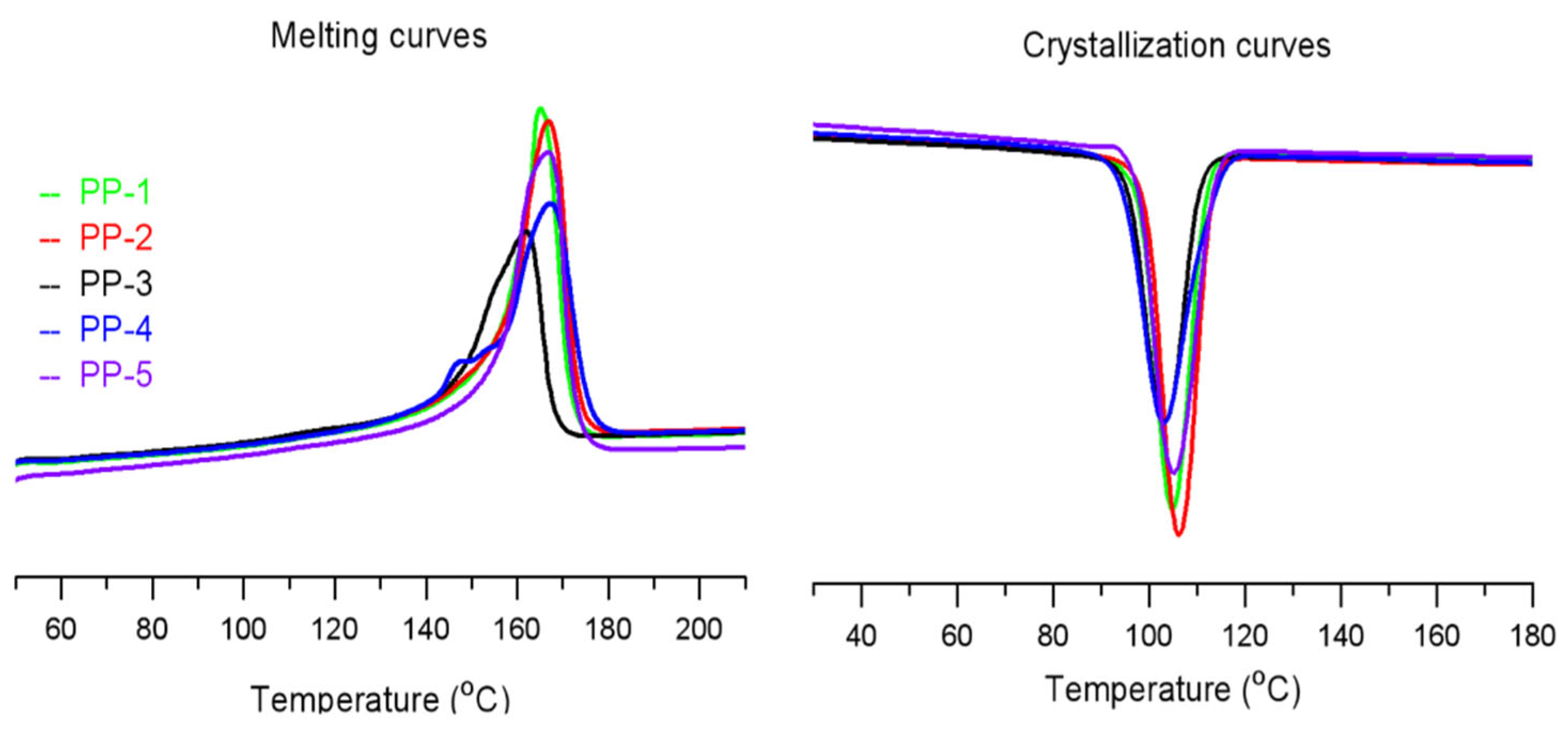
| Sample | Tc (Peak) °C | Tc (Onset) °C | Tm (Peak) °C | ΔHm J/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-1 | 104.9 | 111.9 | 165.0 | 105.3 |
| PP-2 | 106.3 | 113.0 | 166.8 | 110.8 |
| PP-3 | 103.3 | 110.5 | 161.9 | 86.1 |
| PP-4 | 103.0 | 113.3 | 167.2 | 103.0 |
| PP-5 | 105.2 | 113.6 | 166.5 | 113.9 |
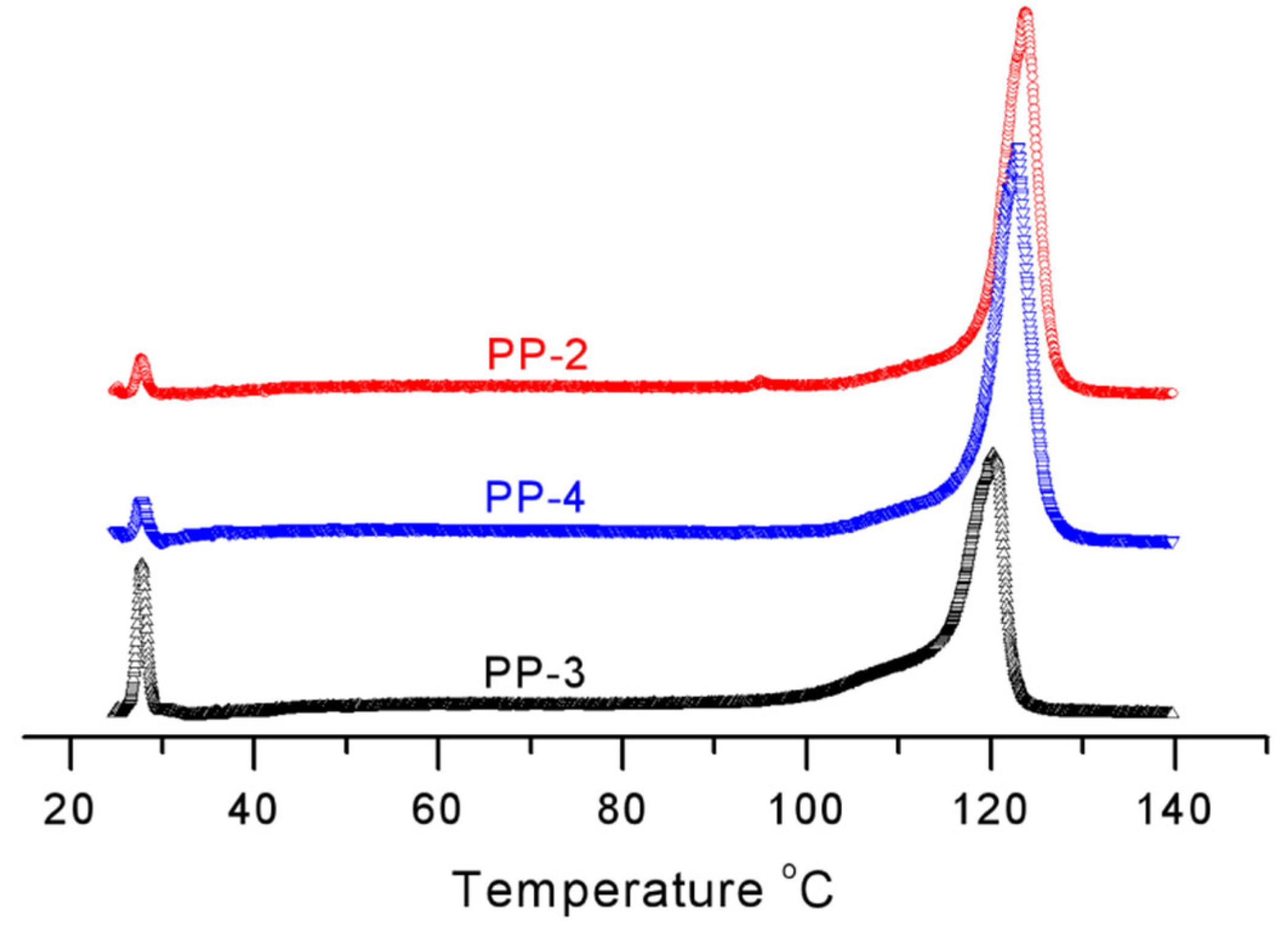
| Sample | Item | Soluble Fraction (SF) | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | Peak 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-1 | T/oC | 51.2 | 70 | 84.4 | 121.6 | |
| Area/% | 2.7 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 1.4 | 90.8 | |
| PP-2 | T/oC | 47.1 | 55.5 | 80.1 | 124.0 | |
| Area/% | 1.9 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 91.7 | |
| PP-3 | T/oC | 51.1 | 57.6 | 81.2 | 119.9 | |
| Area/% | 8.4 | 3.0 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 84 | |
| PP-4 | T/oC | 48.2 | 52.7 | 59 | 122.5 | |
| Area/% | 3.2 | 4.5 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 87.2 | |
| PP-5 | T/oC | 60.0 | 72.9 | 75.4 | 122.8 | |
| Area/% | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 94.0 |
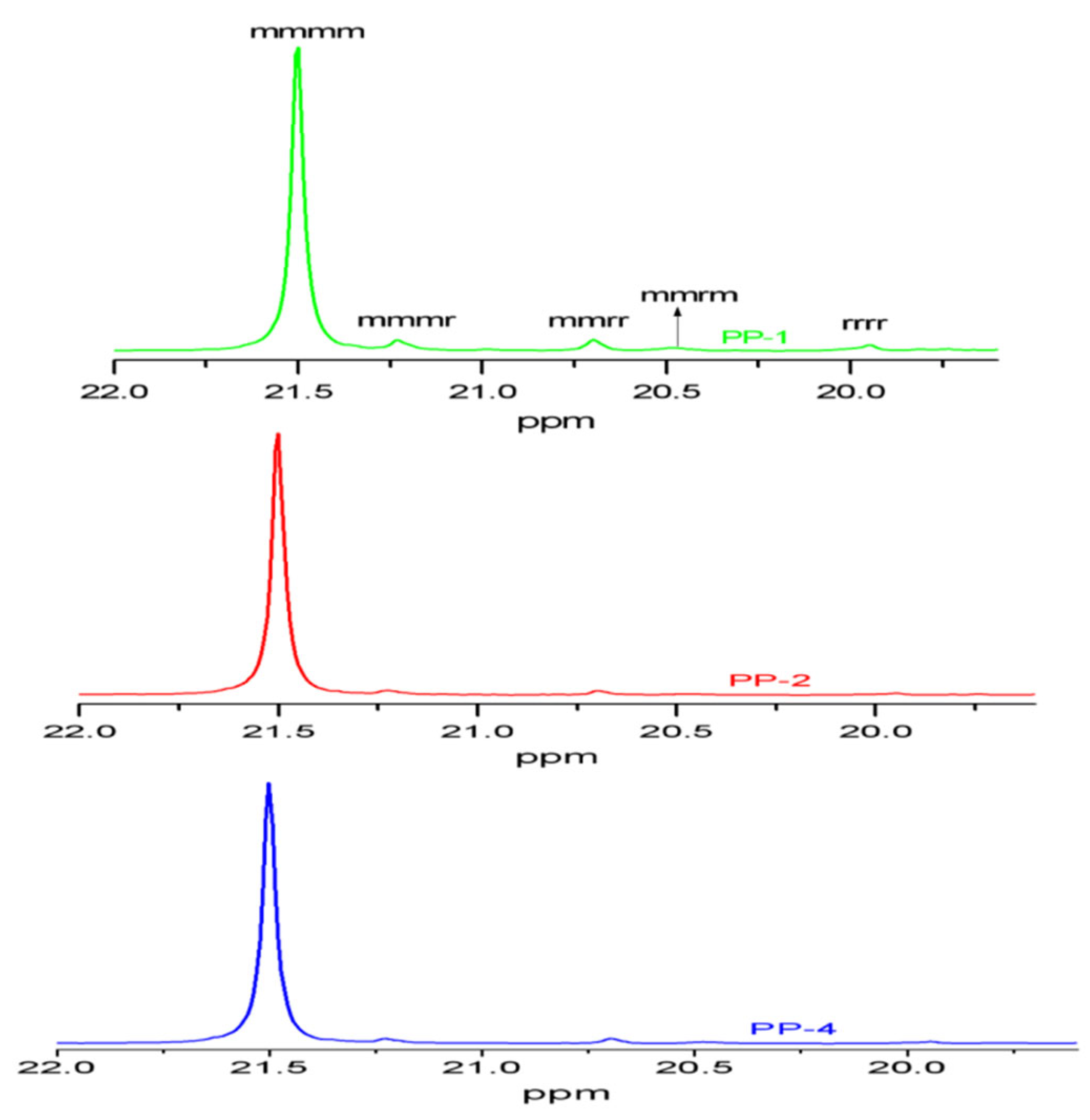
| Sample No. | Methyl Pentad Sequence Distribution (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmmm | mmmr | rmmr | mmrr | mrmm | mrmr | rrrr | rrrm | mrrm | |
| PP-1 | 87.3 | 4.68 | 0 | 3.81 | 1.83 | 0 | 2.38 | 0 | 0 |
| PP-2 | 93.0 | 3.17 | 0 | 1.96 | 0.83 | 0 | 1.04 | 0 | 0 |
| PP-4 | 92.5 | 3.07 | 0 | 2.19 | 1.13 | 0 | 1.11 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Mu, X.; Kang, W.; Li, G.; Huang, A.; Xie, Y. Porous Organic Polymers-Supported Zeigler-Natta Catalysts for Preparing Highly Isotactic Polypropylene with Broad Molecular Weight Distribution. Polymers 2023, 15, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030555
Wang X, Wu D, Mu X, Kang W, Li G, Huang A, Xie Y. Porous Organic Polymers-Supported Zeigler-Natta Catalysts for Preparing Highly Isotactic Polypropylene with Broad Molecular Weight Distribution. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030555
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiong, Dong Wu, Xuemei Mu, Wenqian Kang, Guangquan Li, Anping Huang, and Yuan Xie. 2023. "Porous Organic Polymers-Supported Zeigler-Natta Catalysts for Preparing Highly Isotactic Polypropylene with Broad Molecular Weight Distribution" Polymers 15, no. 3: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030555
APA StyleWang, X., Wu, D., Mu, X., Kang, W., Li, G., Huang, A., & Xie, Y. (2023). Porous Organic Polymers-Supported Zeigler-Natta Catalysts for Preparing Highly Isotactic Polypropylene with Broad Molecular Weight Distribution. Polymers, 15(3), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030555