The Interplay of Protein Hydrolysis and Ammonia in the Stability of Hevea Rubber Latex during Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
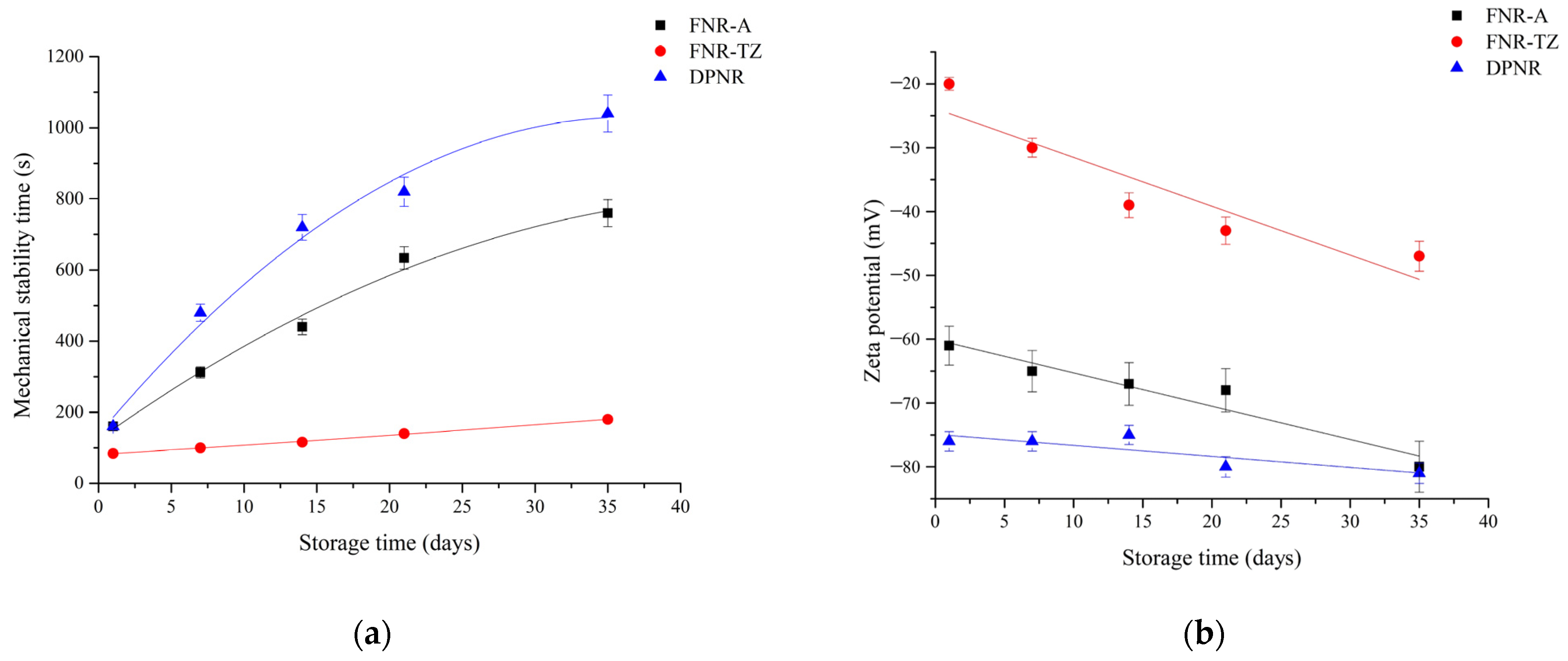
2.2. Determination of Zeta Potential
2.3. Determination of Mechanical Stability Time (MST)
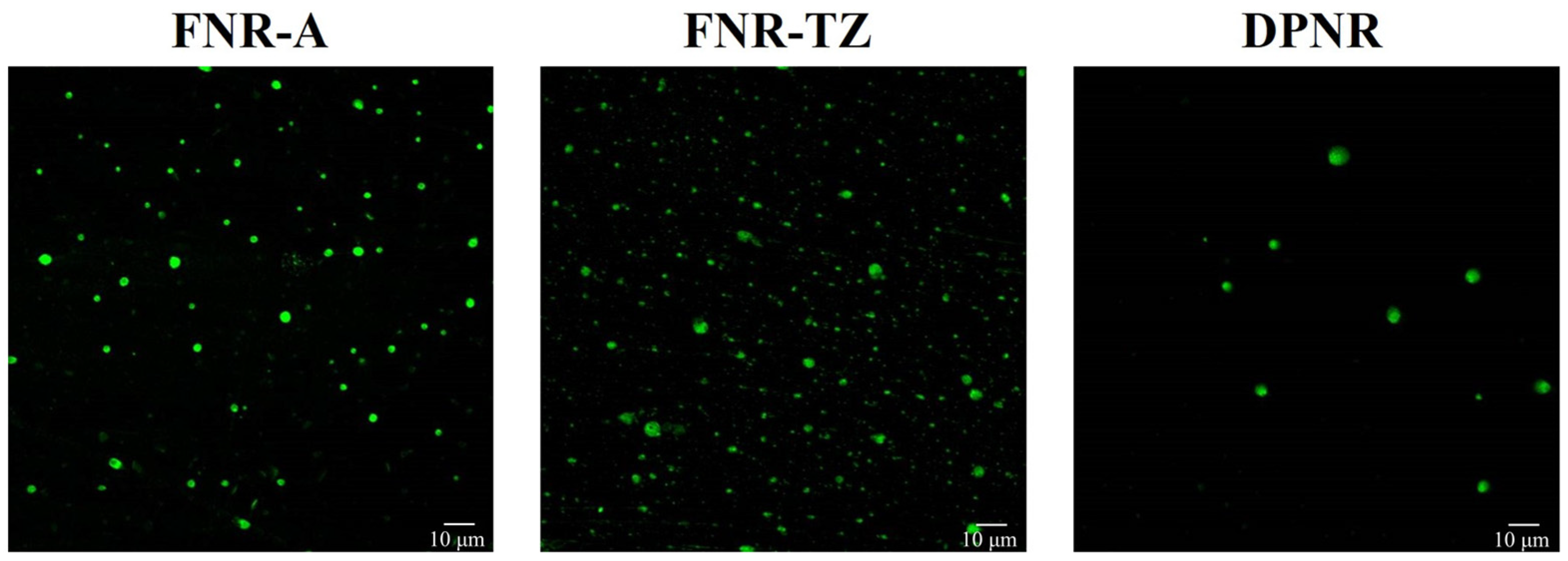
2.4. Fluorescence Labeling and Analysis of NR Particles Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
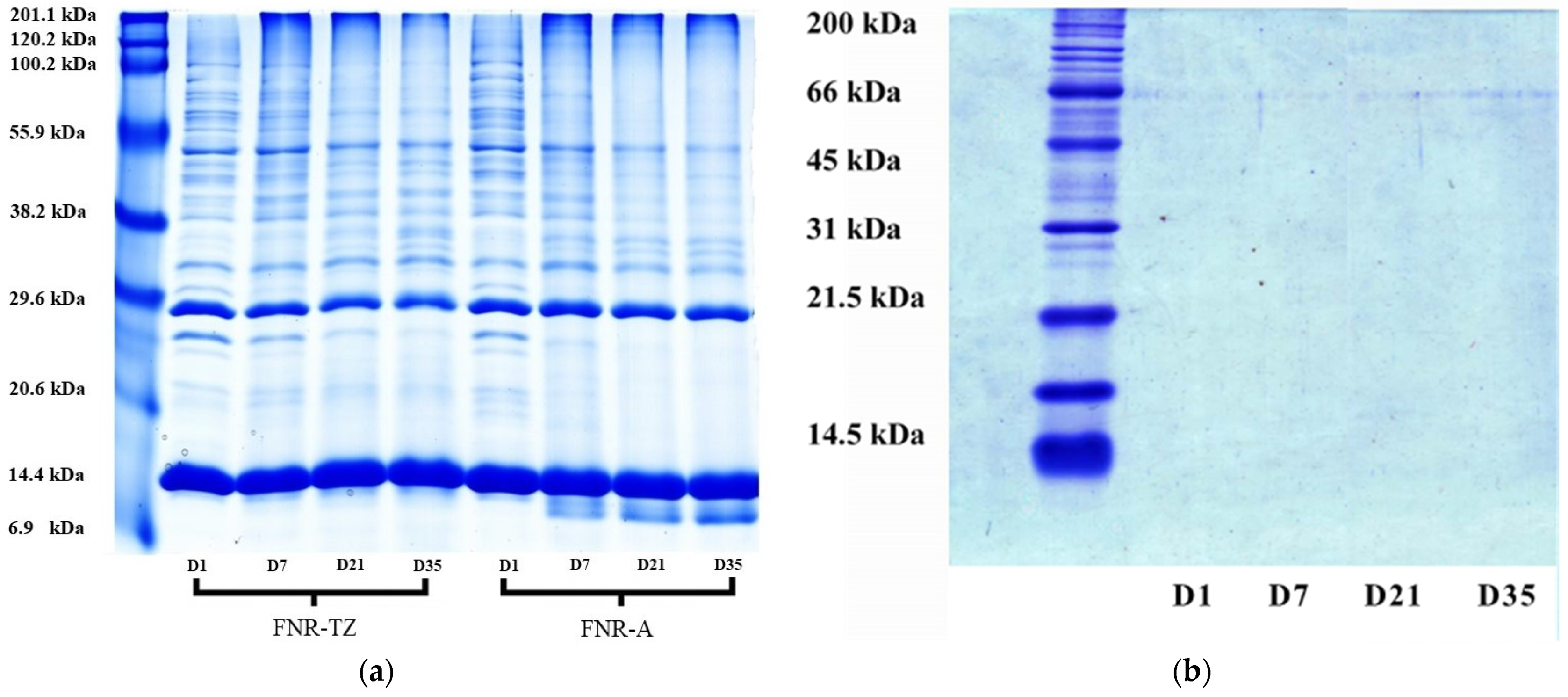
2.5. Determination of Proteins
2.6. Characterization of Surface Morphology
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Latexes
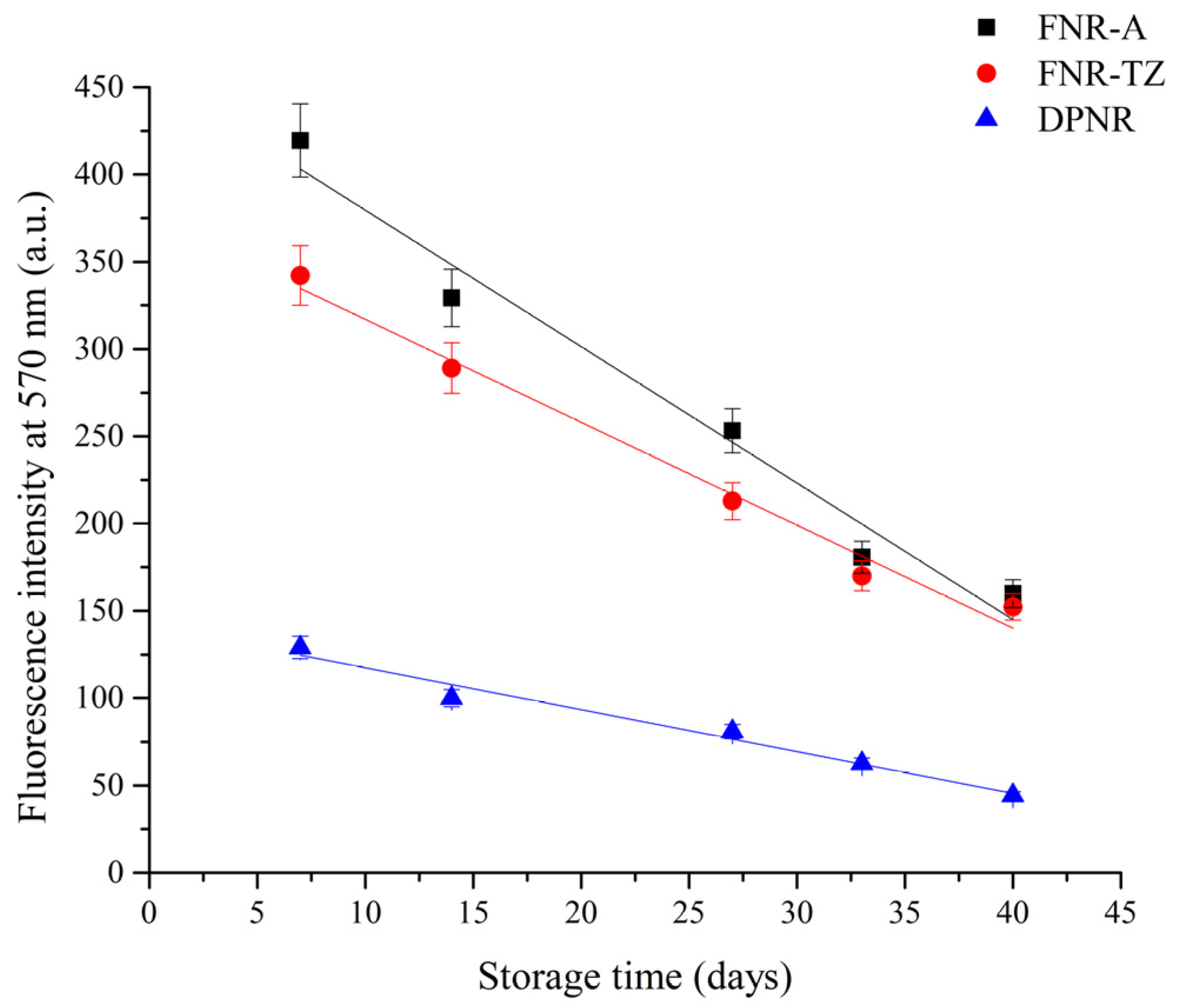
3.2. Latex Stability
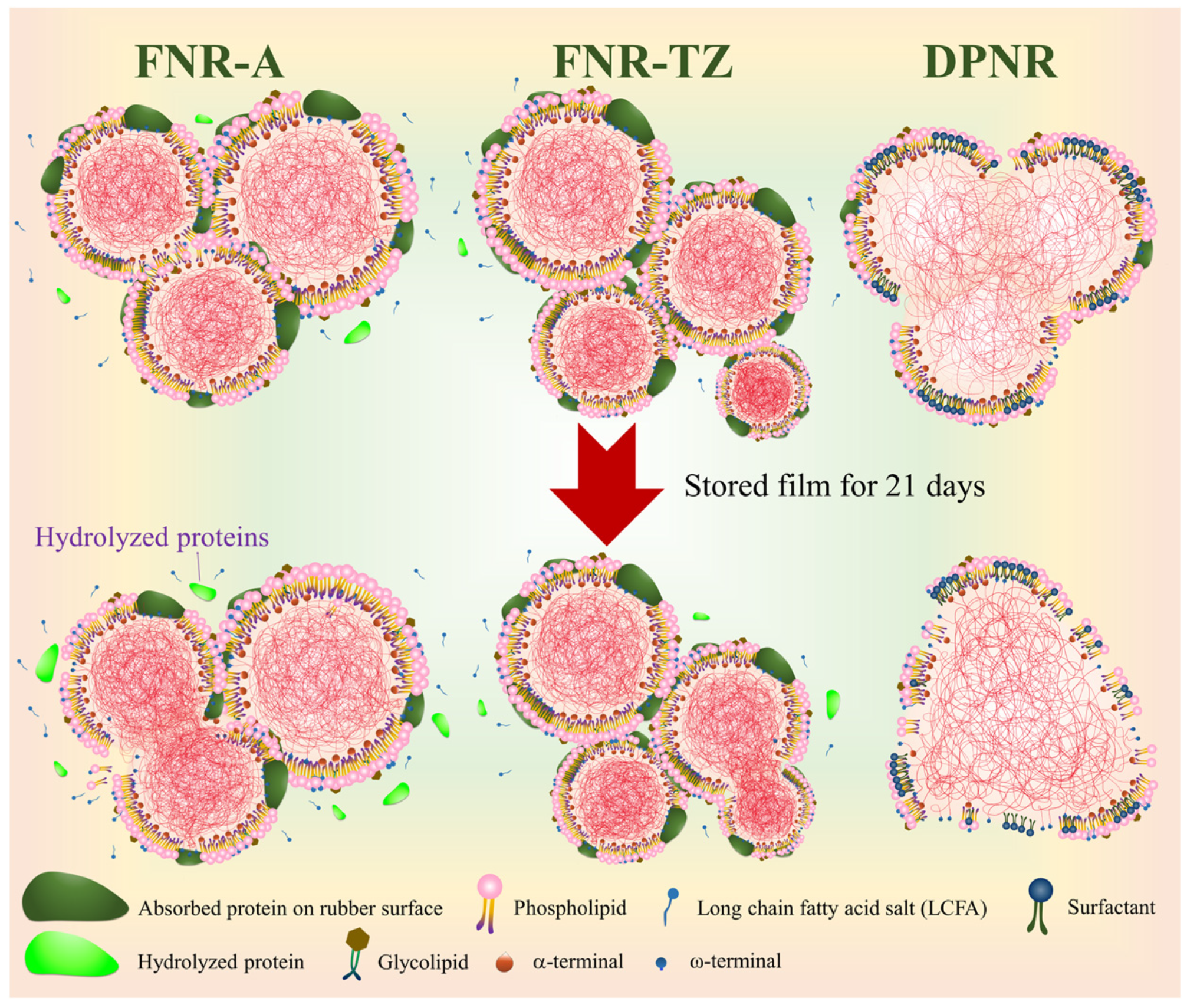
3.3. Proteins Hydrolysis
3.4. Effects of Ammonia on the Latex Film Morphology Arising from Storage Duration and Hydrolysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, Q.; Xia, K.; Dai, L.; Kang, G.; Li, Y.; Nie, Z.; Duan, C.; Zeng, R. Proteome analysis of the large and the small rubber particles of Hevea brasiliensis using 2D-DIGE. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 60, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuampoemsab, S.; Nimpaiboon, A.; Sakdapipanich, J.T. Quantitative Analysis of Isoprene Units in Natural Rubber and Synthetic Polyisoprene using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy with an Internal Standard. Polym. Test. 2015, 43, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansatsadeekul, J.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Rojruthai, P. Characterization of Associated Proteins and Phospholipids in Natural Rubber Latex. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, K.; Wood, D.F.; Windle, J.J.J.P. Rubber particles from four different species, examined by transmission electron microscopy and electron-paramagnetic-resonance spin labeling, are found to consist of a homogeneous rubber core enclosed by a contiguous, monolayer biomembrane. Planta 1999, 210, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, K. Biochemistry of natural rubber, a vital raw material, emphasizing biosynthetic rate, molecular weight and compartmentalization, in evolutionarily divergent plant species. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.F.; Cornish, K. Microstructure of Purified Rubber Particles. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2000, 161, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarachiwin, L.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Ute, K.; Kitayama, T.; Tanaka, Y. Structural Characterization of α-Terminal Group of Natural Rubber. 2. Decomposition of Branch-Points by Phospholipase and Chemical Treatments. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkriengkrai, D.; Sakdapipanich, J.T.; Tanaka, Y. Structural Characterization of Terminal Groups in Natural Rubber: Origin of Nitrogenous Groups. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2006, 79, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Huang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Characterizing the naturally occurring sacrificial bond within natural rubber. Polymer 2019, 161, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, G.; Huang, C.; Luo, M.-C.; Zheng, J. Study of molecular weight and chain branching architectures of natural rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Tang, Z.; Lin, T.; Guo, B.; Huang, G. New evidence disclosed for networking in natural rubber by dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Waki, T.; Aoki, Y.; Mizuno, M.; Yanbe, F.; Ishii, T.; Funaki, A.; Tozawa, Y.; Miyagi-Inoue, Y.; et al. Identification and reconstitution of the rubber biosynthetic machinery on rubber particles from Hevea brasiliensis. eLife 2016, 5, e19022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthelot, K.; Lecomte, S.; Estevez, Y.; Zhendre, V.; Henry, S.; Thévenot, J.; Dufourc, E.J.; Alves, I.D.; Peruch, F. Rubber particle proteins, HbREF and HbSRPP, show different interactions with model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oouchi, M.; Ukawa, J.; Ishii, Y.; Maeda, H. Structural Analysis of the Terminal Groups in Commercial Hevea Natural Rubber by 2D-NMR with DOSY Filters and Multiple-WET Methods Using Ultrahigh-Field NMR. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, J.S. Formation of volatile fatty acids in ammonia preserved natural latex concentrate. Trans. Instn. Rubb. Ind. 1959, 35, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- McGavack, J. Proper Preservation and Storage of Latex. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1947, 20, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackley, D.C. Polymer Latices, 2nd ed.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kumarn, S.; Churinthorn, N.; Nimpaiboon, A.; Sriring, M.; Ho, C.-C.; Takahara, A.; Sakdapipanich, J. Investigating the Mechanistic and Structural Role of Lipid Hydrolysis in the Stabilization of Ammonia-Preserved Hevea Rubber Latex. Langmuir 2018, 34, 12730–12738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-F.; Ng, C.-S. The Natural Higher Fatty Acid Soaps in Natural Rubber Latex and Their Effect on the Mechanical Stability of the Latex. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1984, 57, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasma, H. Lipids associated with rubber particles and their possible role in mechanical stability of latex concentrates. J. Nat. Rubber Res. 1991, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.-X.; He, M.-F.; Luo, M.-C.; Wei, Y.-C.; Liao, S. The role of natural rubber endogenous proteins in promoting the formation of vulcanization networks. e-Polymers 2022, 22, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hehir, R.E.; Sutherland, M.F.; Drew, A.C.; Rolland, J.M. Latex Allergy. In Allergy and Allergic Diseases; Blackwells: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 1164–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, G.L.; Beezhold, D.H.; Kurup, V.P. Allergens and natural rubber proteins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, S33–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.L.; Podjasek, J.O.; Dimitropoulos, V.A.; Brown, C.W. Natural rubber latex allergy. Dis. Mon. 2016, 62, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, T.W.; Saunders, M.E. 28—Allergy and Hypersensitivity. In The Immune Response; Mak, T.W., Saunders, M.E., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 923–962. [Google Scholar]
- Yeang, H.Y.; Arif, S.A.M.; Yusof, F.; Sunderasan, E. Allergenic proteins of natural rubber latex. Methods 2002, 27, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.C.; Kondo, T.; Muramatsu, N.; Ohshima, H. Surface Structure of Natural Rubber Latex Particles from Electrophoretic Mobility Data. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1996, 178, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qu, W.; Huang, G.; Wang, S.; Huang, C.; Liu, H. Super-Resolution Fluorescence Imaging of Spatial Organization of Proteins and Lipids in Natural Rubber. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipithakul, T.; Watthanachote, L.; Kalapat, N. Preliminary study of extractable protein binding using maleic anhydride copolymer. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 30, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, S.; Hamid, S.; Cardosa, M.J.; Yeang, H.Y. Allergenic Proteins of Hevea brasiliensis Latex Fractions. J. Rubber Res. 1994, 9, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Cremer, R.; Posch, A.; Raulf-Heimsoth, M.; Rihs, H.-P.; Baur, X. On the allergenicity of Hev b 1 among health care workers and patients with spina bifida allergic to natural rubber latex. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.J.; Kurup, V.P.; Hoffman, D.R.; Kelly, K.J.; Murali, P.S.; Fink, J.N. Characterization of a major latex allergen associated with hypersensitivity in spina bifida patients. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeang, H.Y.; Cheong, K.F.; Sunderasan, E.; Hamzah, S.; Chew, N.P.; Hamid, S.; Hamilton, R.G.; Cardosa, M.J. The 14.6 kd rubber elongation factor (Hev b 1) and 24 kd (Hev b 3) rubber particle proteins are recognized by IgE from patients with spina bifida and latex allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.S.; Light, D.R. Rubber elongation factor from Hevea brasiliensis: Identification, characterization, and role in rubber biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 18608–18617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthelot, K.; Lecomte, S.; Estevez, Y.; Coulary-Salin, B.; Bentaleb, A.; Cullin, C.; Deffieux, A.; Peruch, F. Rubber elongation factor (REF), a major allergen component in Hevea brasiliensis latex has amyloid properties. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.-C.; Xia, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, T.-T.; Liao, S. Influence of non-rubber components on film formation behavior of natural rubber latex. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

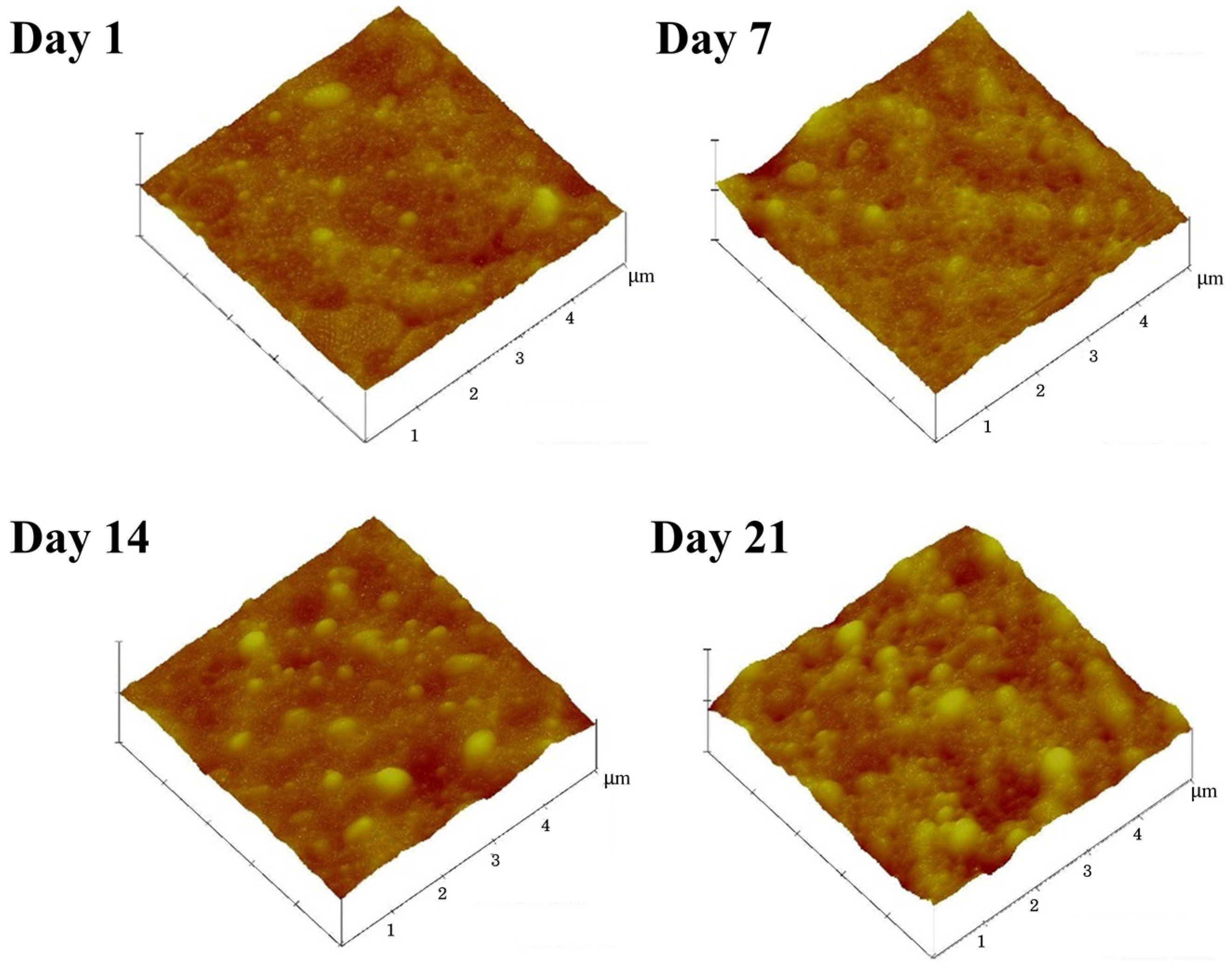
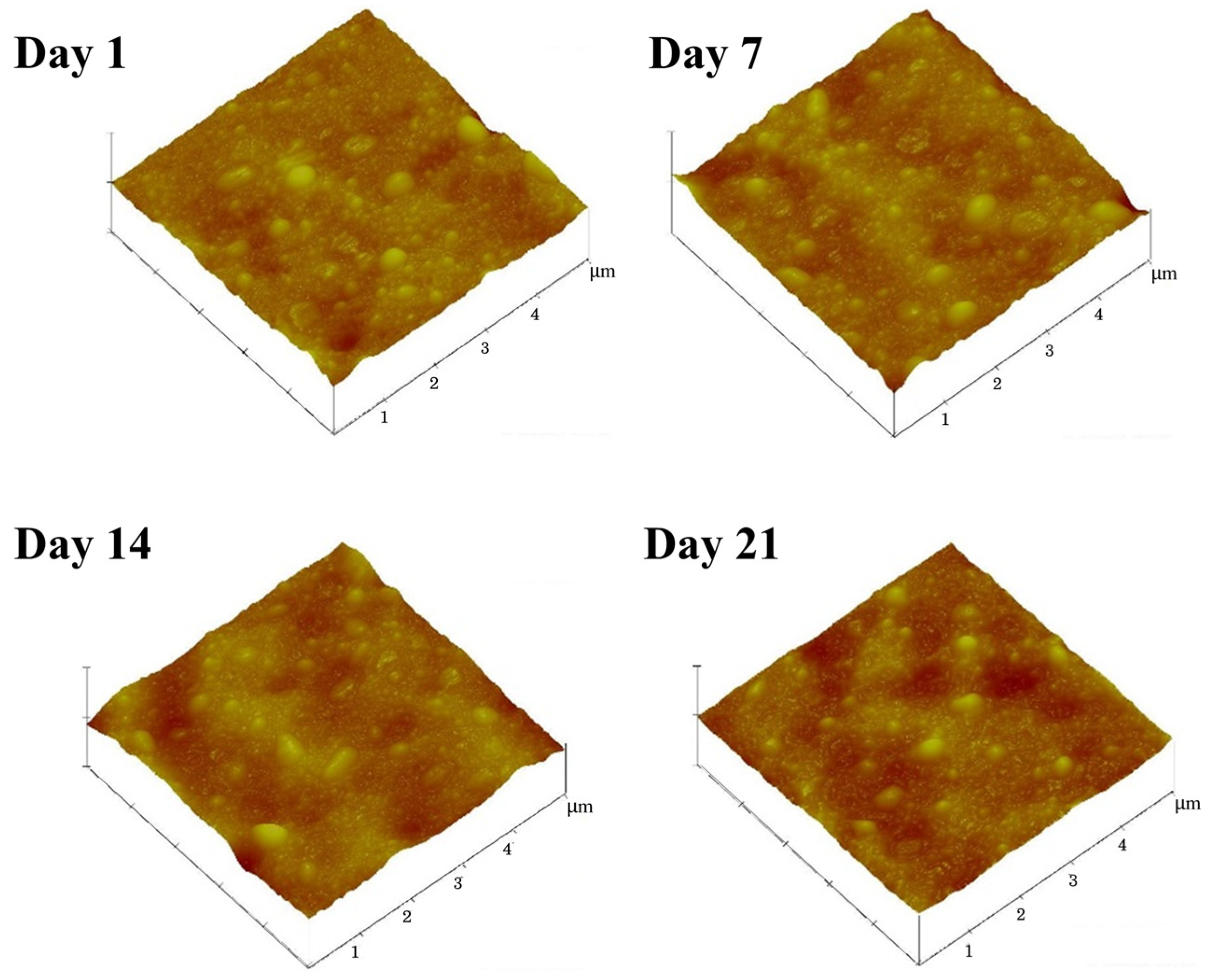
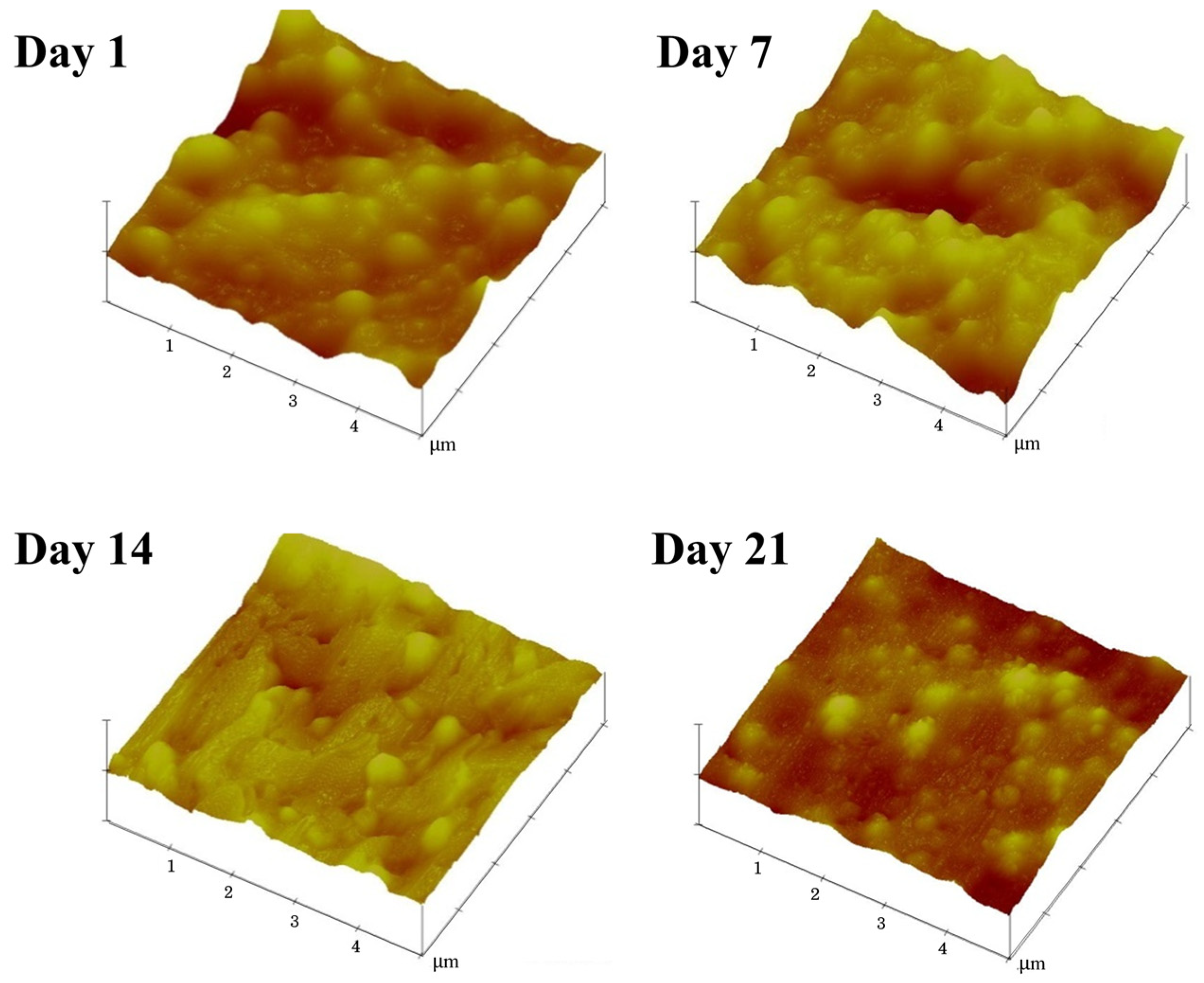

| Samples | Mean Diameter (nm) | Protein Content (wt.%) | Ester Content (mmol/kg Rubber) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FNR-A | 636 ± 2 | 4.30 ± 0.02 | 28.1 ± 0.2 |
| FNR-TZ | 635 ± 1 | 4.63 ± 0.03 | 28.5 ± 0.5 |
| DPNR | 664 ± 3 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 25.9 ± 0.7 |
| Storage Time (Days) | Color Intensity | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FNR-A | FNR-TZ | |||||||
| 100–50 kDa | 36–10 kDa | 29.6 kDa (Hev b3) | 14.4 kDa (Hev b1) | 100–50 kDa | 36–10 kDa | 29.6 kDa (Hev b3) | 14.4 kDa (Hev b1) | |
| 1 | 45.996 | 11.077 | 151.412 | 180.345 | 38.056 | 6.911 | 156.813 | 181.712 |
| 35 | 37.402 | 59.008 | 147.836 | 177.424 | 39.763 | 17.325 | 131.313 | 178.529 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Payungwong, N.; Sakdapipanich, J.; Wu, J.; Ho, C.-C. The Interplay of Protein Hydrolysis and Ammonia in the Stability of Hevea Rubber Latex during Storage. Polymers 2023, 15, 4636. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244636
Payungwong N, Sakdapipanich J, Wu J, Ho C-C. The Interplay of Protein Hydrolysis and Ammonia in the Stability of Hevea Rubber Latex during Storage. Polymers. 2023; 15(24):4636. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244636
Chicago/Turabian StylePayungwong, Narueporn, Jitladda Sakdapipanich, Jinrong Wu, and Chee-Cheong Ho. 2023. "The Interplay of Protein Hydrolysis and Ammonia in the Stability of Hevea Rubber Latex during Storage" Polymers 15, no. 24: 4636. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244636
APA StylePayungwong, N., Sakdapipanich, J., Wu, J., & Ho, C.-C. (2023). The Interplay of Protein Hydrolysis and Ammonia in the Stability of Hevea Rubber Latex during Storage. Polymers, 15(24), 4636. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244636









