Influence of Delamination Size and Depth on the Compression Fatigue Behaviour of a Stiffened Aerospace Composite Panel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
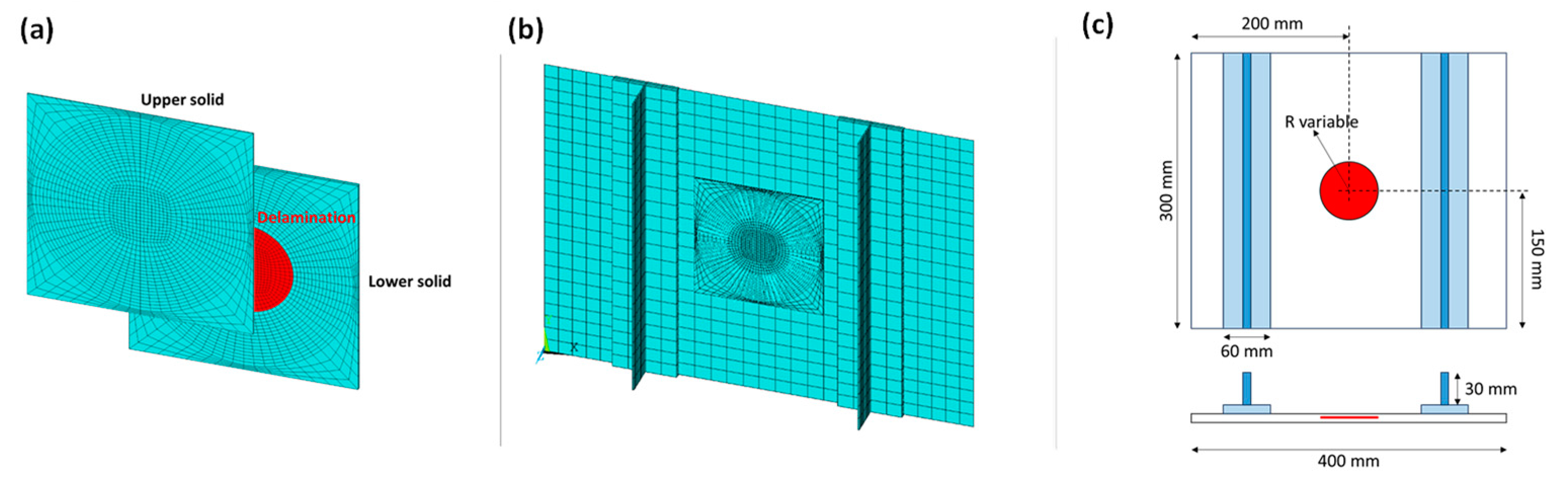
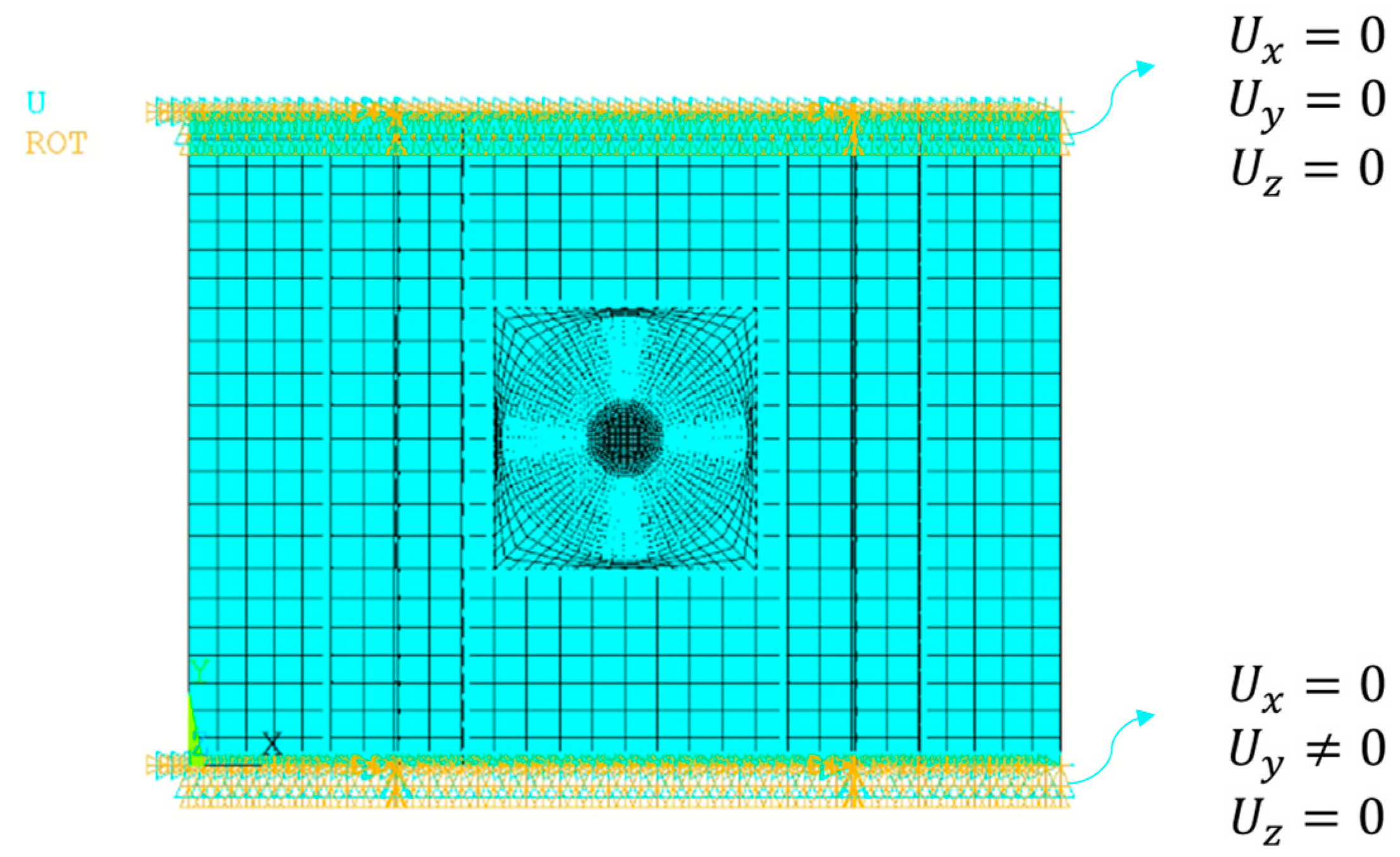
2. Numerical Model Description
2.1. FT-SMXB Approach
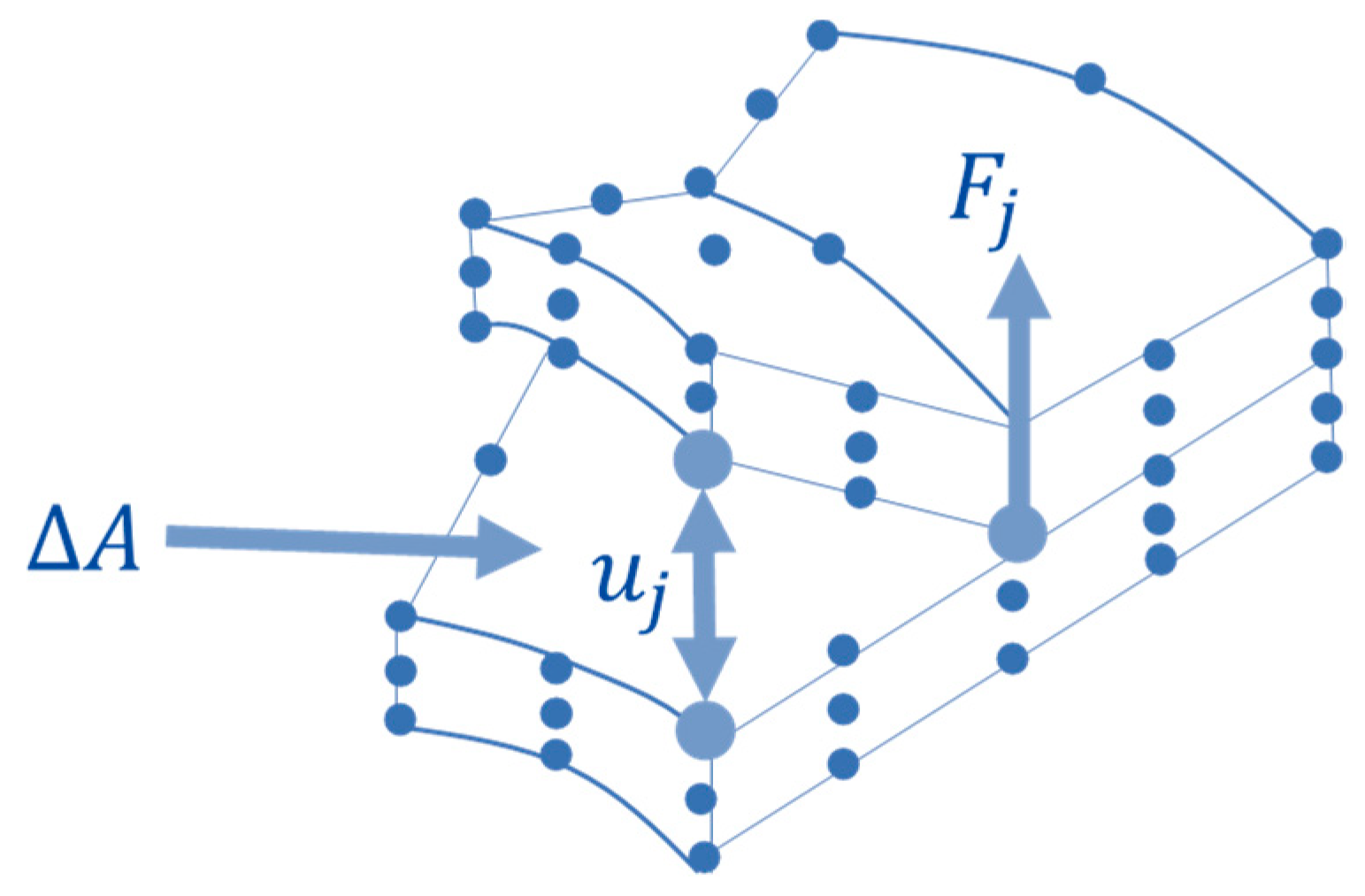
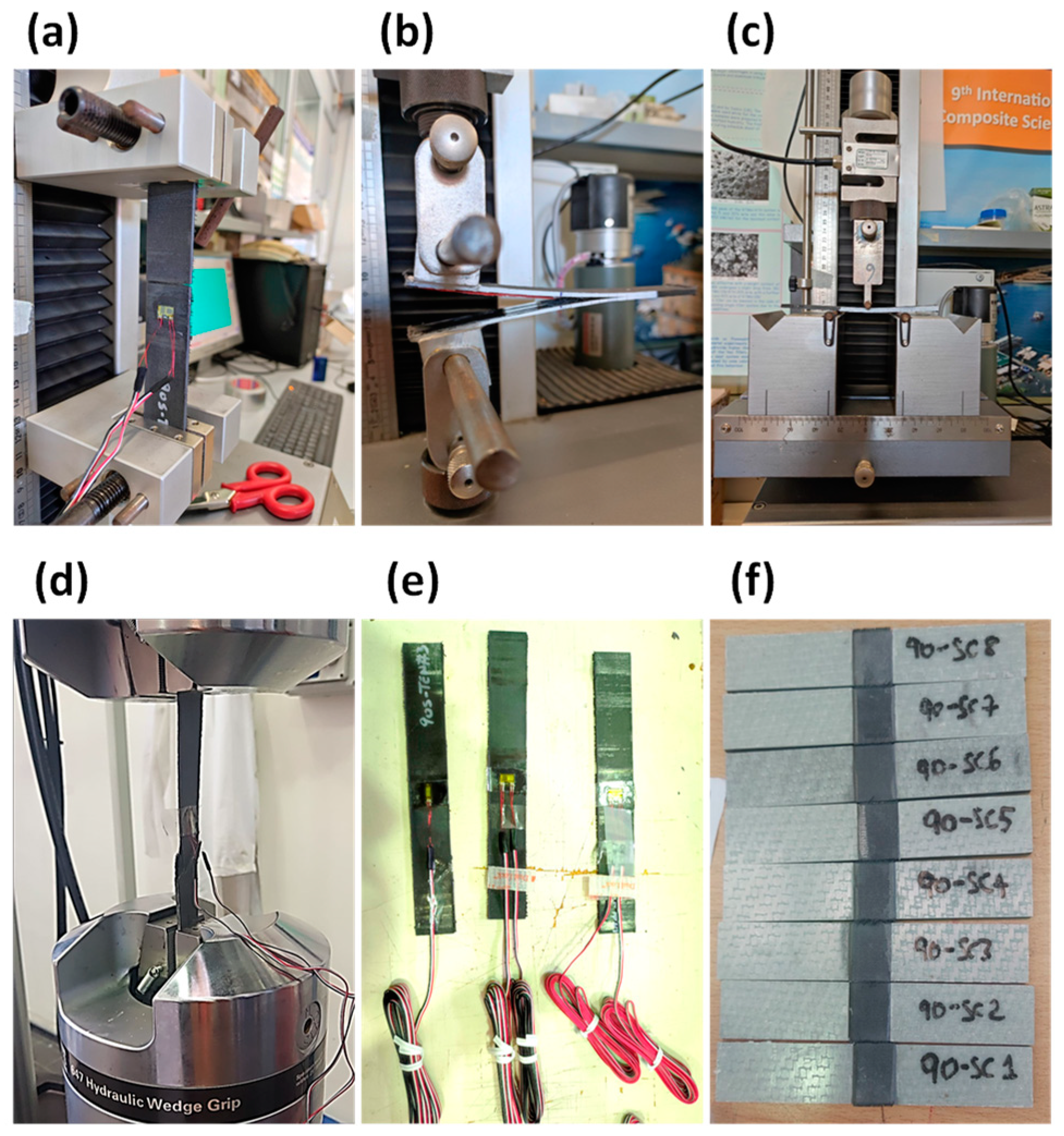
2.2. Preliminary Static Analysis
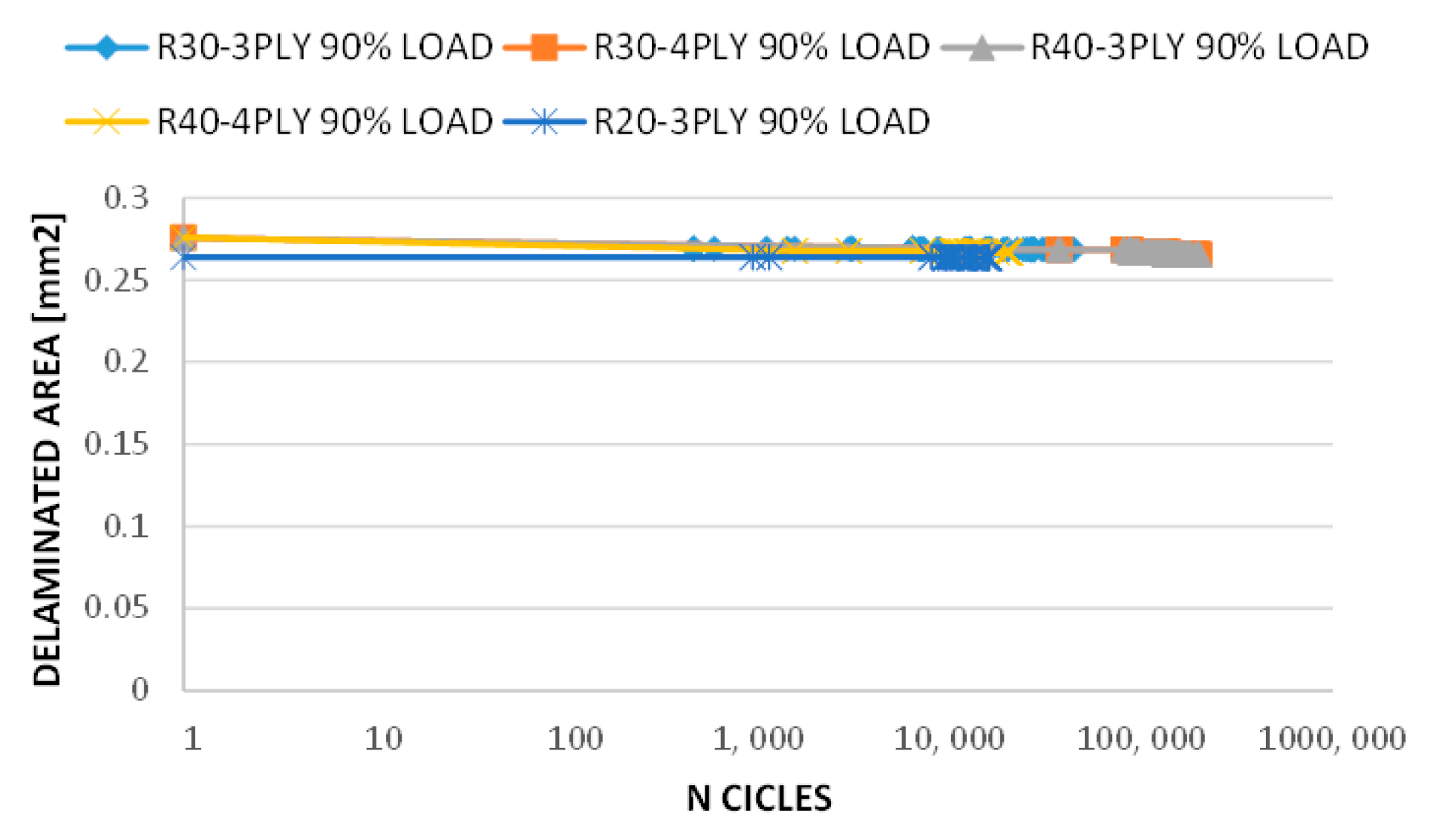
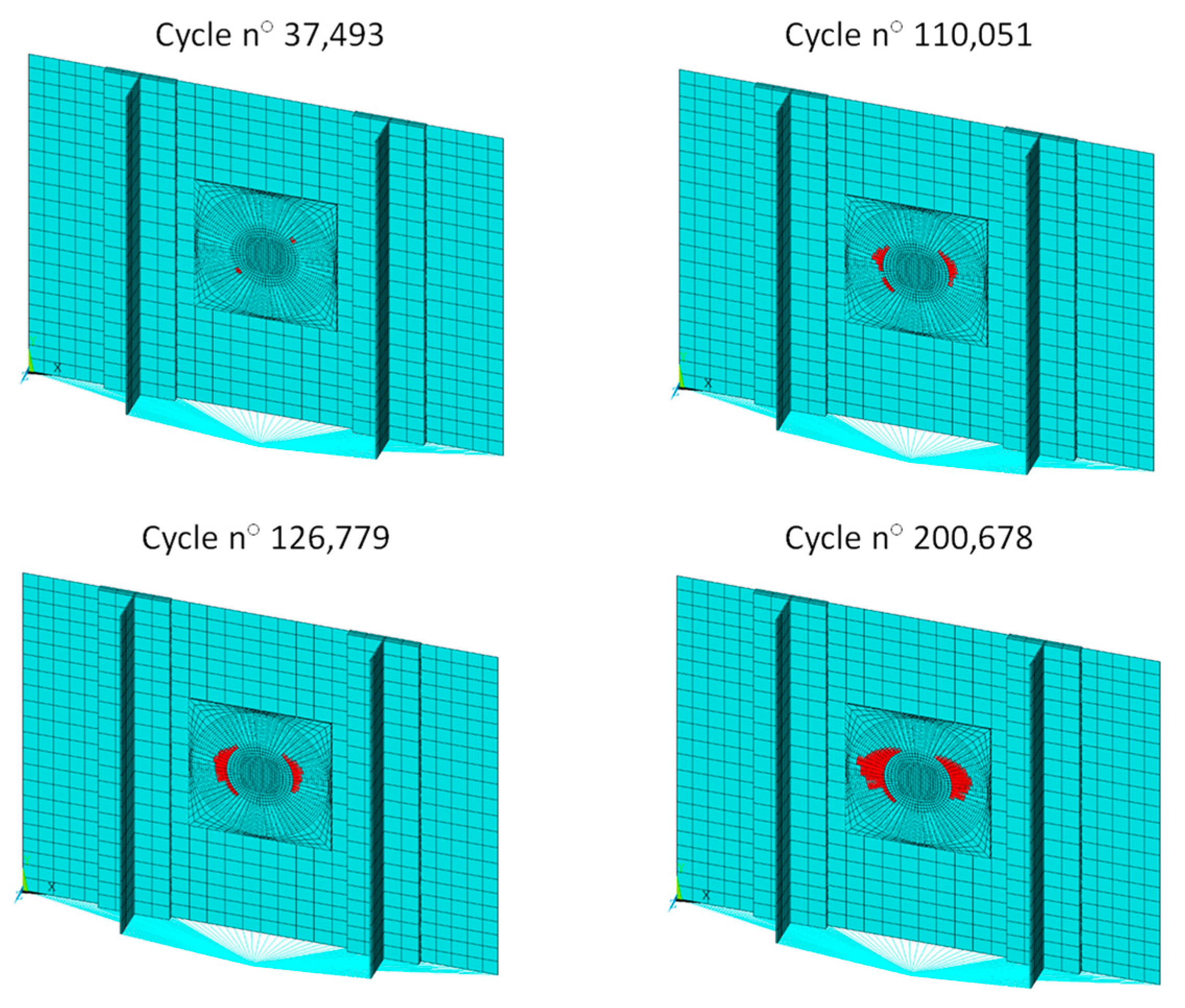
3. Results and Discussion
4. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, A.A. Composite Materials for Aircraft Structures; AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Irving, P.E.A.C.S. Polymer Composites in the Aerospace Industry; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rikards, R. Interlaminar Fracture Behaviour of Laminated Composites; Computers & Structures: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Christoforou, A.P.A.A.S.Y. Scaling of low-velocity impact response in composite structures. Compos. Struct. 2009, 91, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, F.E.A. Numerical study for the structural analysis of composite laminates subjected to low velocity impact. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 67, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, L.E.A. Simulation of low velocity impact on composite laminates with progressive failure analysis. Compos. Struct. 2013, 103, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriani, M.J.; Rapi, H.Z.; Ilyas, R.A.; Petrů, M.; Sapuan, S.M. Delamination and manufacturing defects in natural fiber-reinforced hybrid composite: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fox, B.L. Manufacturing influence on the delamination fracture behavior of the T800H/3900-2 carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2007, 22, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Alderliesten, R.C.; Zhao, M.; Benedictus, R. Discussion on the use of the strain energy release rate for fatigue delamination characterization. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 66, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanulia, V.; Wang, J.; Pearce, G.M.; Baker, A.; David, M.; Prusty, B.G. A procedure to assess disbond growth and determine fatigue life of bonded joints and patch repairs for primary airframe structures. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 137, 105664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarve, E.V.; Gurvich, M.R.; Mollenhauer, D.H.; Rose, C.A.; Dávila, C.G. Mesh-independent matrix cracking and delamination modeling in laminated composites. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2011, 88, 749–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnom, M.R. The role of delamination in failure of fibre-reinforced composites. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2012, 370, 1850–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessi, S.; Pitarresi, G.; Spadaro, G. Effect of hydrothermal ageing on the thermal and delamination fracture behaviour of CFRP composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 67, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Yao, X.; Zhang, X. Delamination prediction in composite laminates under low-velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Hou, S.J.; Chu, J.K.; Hu, X.Y.; Zhou, C.L.; Liu, Y.L.; Zheng, J.Y.; Zhao, A.; Yan, L. Finite element analysis of postbuckling and delamination of composite laminates using virtual crack closure technique. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, A.; Goyal, V.K. Durability of Buckled Composites Using Virtual Crack Closure Technique Fatigue R-Curve Implementation. AIAA J. 2023, 61, 3644–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalcová, L.; Rechcígel, L.; Blský, P.; Kucharský, P. Fatigue disbonding analysis of wide composite panels by means of Lamb waves. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2018, 10599, 105991E. [Google Scholar]
- Šedková, L.; Vlk, V.; Šedek, J. Delamination/disbond propagation analysis in adhesively bonded composite joints using guided waves. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2022, 7, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.F.; Toso-Pentecôte, N.; Schueler, D. Numerical modelling of impact and damage tolerance in aerospace composite structures. Numer. Model. Fail. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2015, 479–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.H.; Karuppanan, S.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S.M.; Sajid, Z. Impact resistance and damage tolerance of fiber reinforced composites: A review. Compos. Struct. 2019, 217, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R. Fatigue crack growth and damage tolerance. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2014, 37, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, F. Damage tolerance of a stitched carbon/epoxy laminate. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1997, 28, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müzel, S.D.; Bonhin, E.P.; Guimarães, N.M.; Guidi, E.S. Application of the finite element method in the analysis of composite materials: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.Q.; Elder, D.J.; Bayandor, J.; Thomson, R.S.; Scott, M.L. A review of explicit finite element software for composite impact analysis. J. Compos. Mater. 2005, 39, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyad, A.S.; Ghugal, Y.M. Bending, buckling and free vibration of laminated composite and sandwich beams: A critical review of literature. Compos. Struct. 2017, 171, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.S.; Awruch, A.M. Design optimization of composite laminated structures using genetic algorithms and finite element analysis. Compos. Struct. 2009, 88, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muc, A.; Gurba, W. Genetic algorithms and finite element analysis in optimization of composite structures. Compos. Struct. 2001, 54, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, S.-C.; Liang, Y.-C. The finite element analysis of composite laminates and shell structures subjected to low velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 2004, 66, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guynn, E.G.; Ochoa, O.O.; Bradley, W.L. A Parametric Study of Variables That Affect Fiber Microbuckling Initiation in Composite Laminates: Part 1-Analyses. J. Compos. Mater. 1992, 26, 1594–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zona, A.; Barbato, M.; Conte, J.P. Finite element response sensitivity analysis of steel-concrete composite beams with deformable shear connection. J. Eng. Mech. 2005, 131, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegorin, F.; Pingkarawat, K.; Daynes, S.; Mouritz, A.P. Influence of z-pin length on the delamination fracture toughness and fatigue resistance of pinned composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 78, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ridha, M.; Chen, B.Y.; Tan, V.B.C.; Tay, T.E. On cohesive element parameters and delamination modelling. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 206, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blal, N.; Daridon, L.; Monerie, Y.; Pagano, S. On Mesh Size to Cohesive Zone Parameters Relationships; ACOMEN: Liège, Belgium, 2011; p. Cd–Rom. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, A.; Riccio, A.; Palumbo, C.; Sellitto, A. Fatigue driven delamination in composite structures: Definition and assessment of a novel fracture mechanics based computational tool. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 166, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Riccio, A.; Sellitto, A. A robust cumulative damage approach for the simulation of delamination under cyclic loading conditions. Compos. Struct. 2022, 281, 114998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, A.; Castaldo, R.; Palumbo, C.; Russo, A. Delamination Effect on the Buckling Behaviour of Carbon–Epoxy Composite Typical Aeronautical Panels. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039/D3039M-00; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000.
- ASTM D3410; Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Unidirectional or Cross-ply Fiber-Resin Composites. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1987; pp. 132–139.
- ASTM D3518/D3518M-94; Standard Test Method for in-Plane Shear Response of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials by Tensile Test of a ±45° Laminate. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001.
- ASTM D5528; Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1994.
- ASTM Standard D6115; Mode I Fatigue Delamination Growth Onset of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM D 7905/D7905M-14; ASTM Int. Standard Test Method for Determination of the Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, L. Study on the effect of delamination defects on the mechanical properties of CFRP composites. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 153, 107576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, A.A.; Woo, K.; Kang, M.; Kim, I.-G. Effects of Size and Location of Initial Delamination on Post-buckling and Delamination Propagation Behavior of Laminated Composites. Int. J. Aeronaut Space Sci. 2020, 21, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

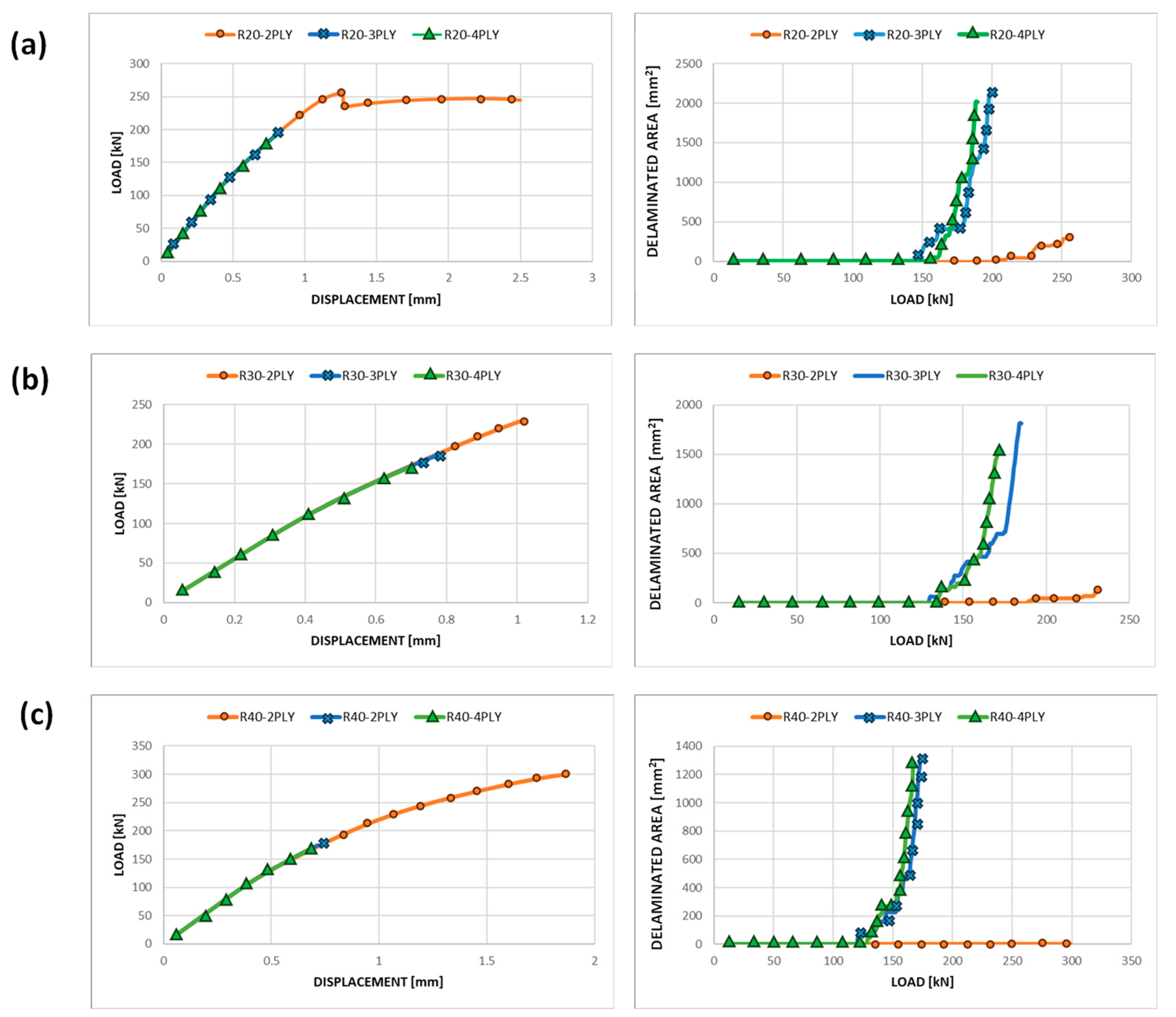
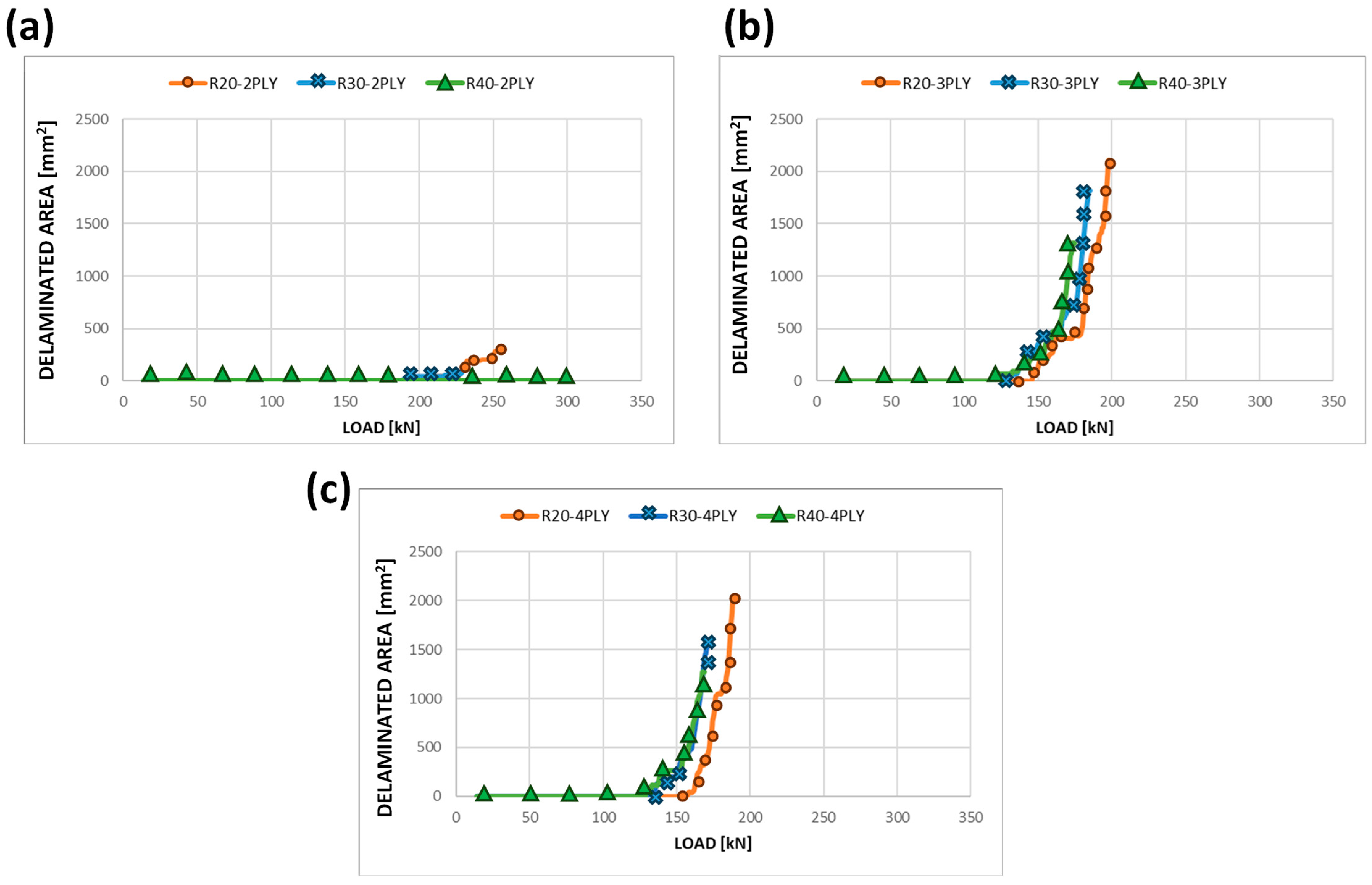
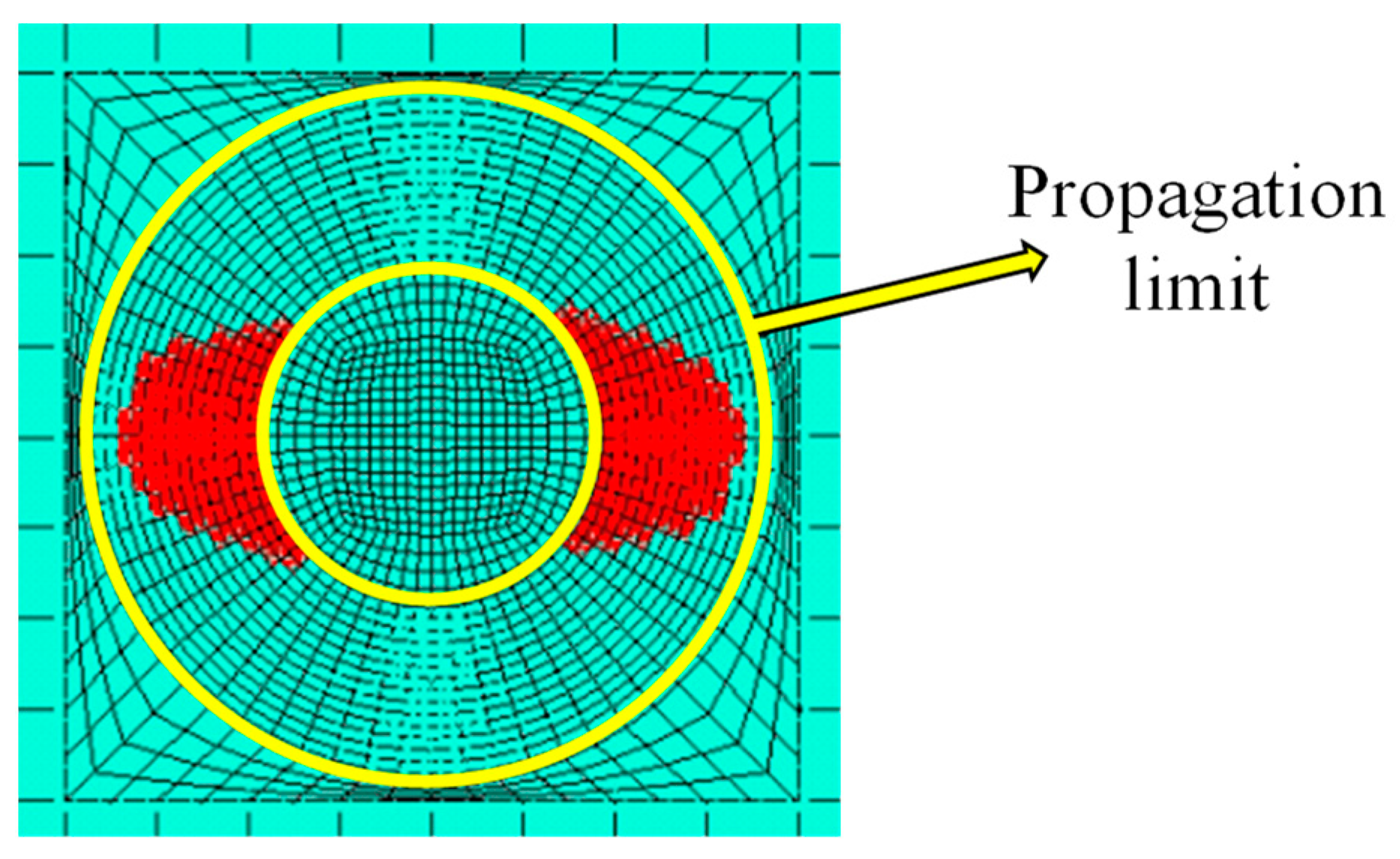

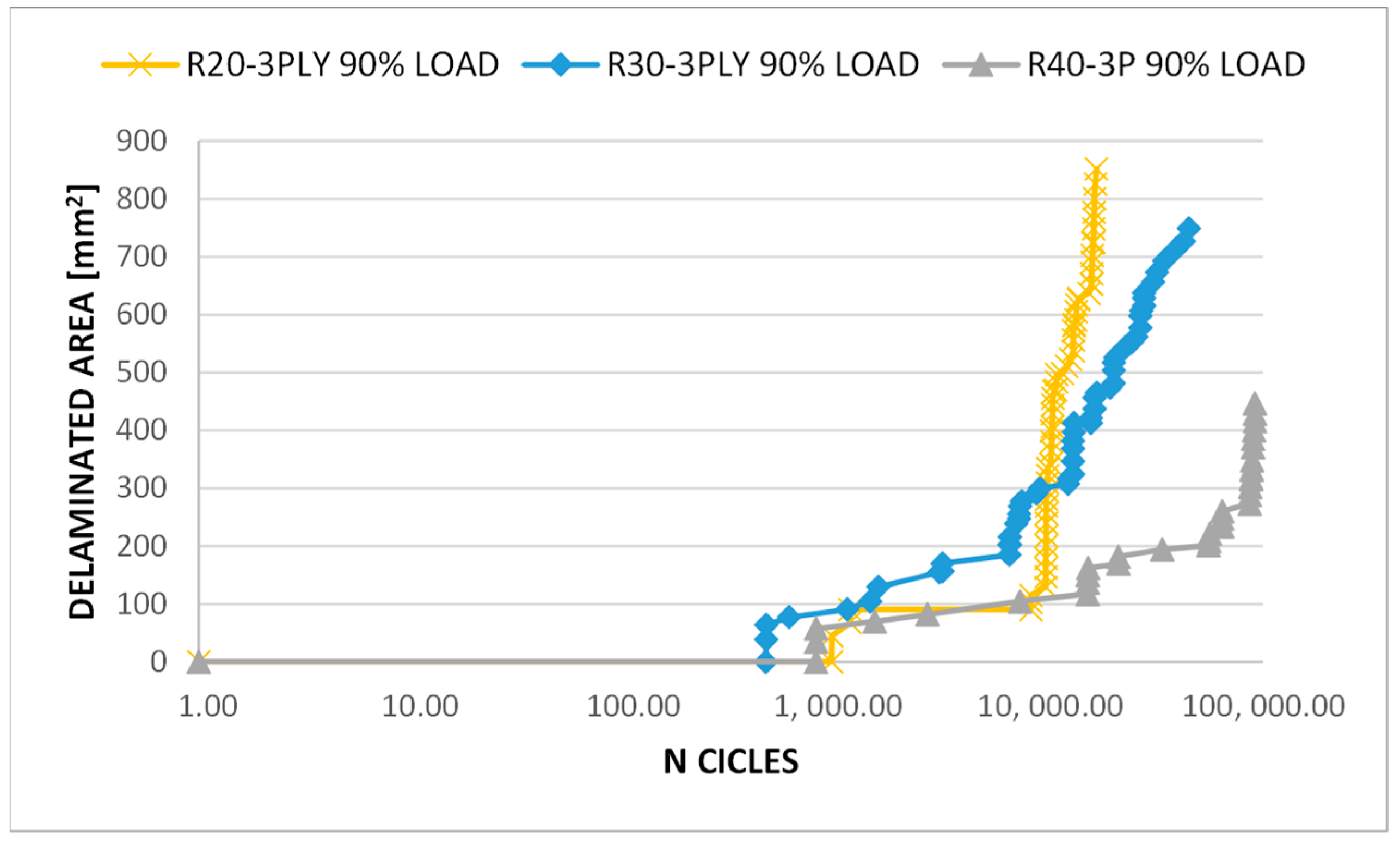

| Component | Number of Plies | Layup | Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin panel | 16 | [45,90,0,−45]2s | 2.64 mm |
| Foot stringer | 24 | [(0,90,90,0)s(45,90,0,−45)2s] | 3.96 mm |
| Web stringer | 8 | [0,90,90,0]s | 1.32 mm |
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus in the fibre’s direction | ||
| Young’s modulus in the transverse direction | ||
| Shear modulus in the 1–2 and 1–3 planes | ||
| Shear modulus in the 2–3 plane | ||
| Poisson’s ratio in the 1–2 and 1–3 planes | ||
| Poisson’s ratio in the 2–3 plane | ||
| GIc | 180 J/m2 | Mode I critical energy release rate |
| GIic = GIIIc | 1900 J/m2 | Mode II and Mode III critical strain energy release rate |
| c1 | 0.7188 | Mode I Paris constant |
| n1 | 8 | Mode I Paris exponent |
| c2 | 6.5938 | Mode II Paris constant |
| n2 | 6 | Mode II Paris exponent |
| Id Configuration | Delamination Radius | Delamination Depth |
|---|---|---|
| R20-2PLY | 20 mm | 0.33 mm |
| R20-3PLY | 20 mm | 0.495 mm |
| R20-4PLY | 20 mm | 0.66 mm |
| R30-2PLY | 30 mm | 0.33 mm |
| R30-3PLY | 30 mm | 0.495 mm |
| R30-4PLY | 30 mm | 0.66 mm |
| R40-2PLY | 40 mm | 0.33 mm |
| R40-3PLY | 40 mm | 0.495 mm |
| R40-4PLY | 40 mm | 0.66 mm |
| Id Configuration | Static Delamination Onset Load | Fatigue Loads | Onset Cycle | Failure Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R20-3PLY | 147 kN | 80% 90% | 113,593 939 | >1 × 106 16,459 |
| R20-4PLY | 158 kN | 80% 90% | >1 × 106 >1 × 106 | - |
| R30-3PLY | 130 kN | 80% 90% | 50,507 461 | 672,364 44,866 |
| R30-4PLY | 135 kN | 80% 90% | >1 × 106 37,493 | - 200,678 |
| R40-3PLY | 121 kN | 80% 90% | 15,049 792 | >1 × 106 91,584 |
| R40-4PLY | 130 kN | 80% 90% | 170,487 1562 | >1 × 106 20,665 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, A.; Castaldo, R.; Palumbo, C.; Riccio, A. Influence of Delamination Size and Depth on the Compression Fatigue Behaviour of a Stiffened Aerospace Composite Panel. Polymers 2023, 15, 4559. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234559
Russo A, Castaldo R, Palumbo C, Riccio A. Influence of Delamination Size and Depth on the Compression Fatigue Behaviour of a Stiffened Aerospace Composite Panel. Polymers. 2023; 15(23):4559. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234559
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Angela, Rossana Castaldo, Concetta Palumbo, and Aniello Riccio. 2023. "Influence of Delamination Size and Depth on the Compression Fatigue Behaviour of a Stiffened Aerospace Composite Panel" Polymers 15, no. 23: 4559. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234559
APA StyleRusso, A., Castaldo, R., Palumbo, C., & Riccio, A. (2023). Influence of Delamination Size and Depth on the Compression Fatigue Behaviour of a Stiffened Aerospace Composite Panel. Polymers, 15(23), 4559. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234559









