Multifunctional Nanoparticles with Superparamagnetic Mn(II) Ferrite and Luminescent Gold Nanoclusters for Multimodal Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of (3-Mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane Stabilized AuNCs (MPTS-AuNCs)
2.3. One-Pot Synthesis of MPTS-AuNCs in MSNs (MPTS-AuNCs@MSN)
2.4. Preparation of MnFe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles (MnFe2O4 NPs)
2.5. Silica Coating of MnFe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles (MnFe2O4@SiO2)
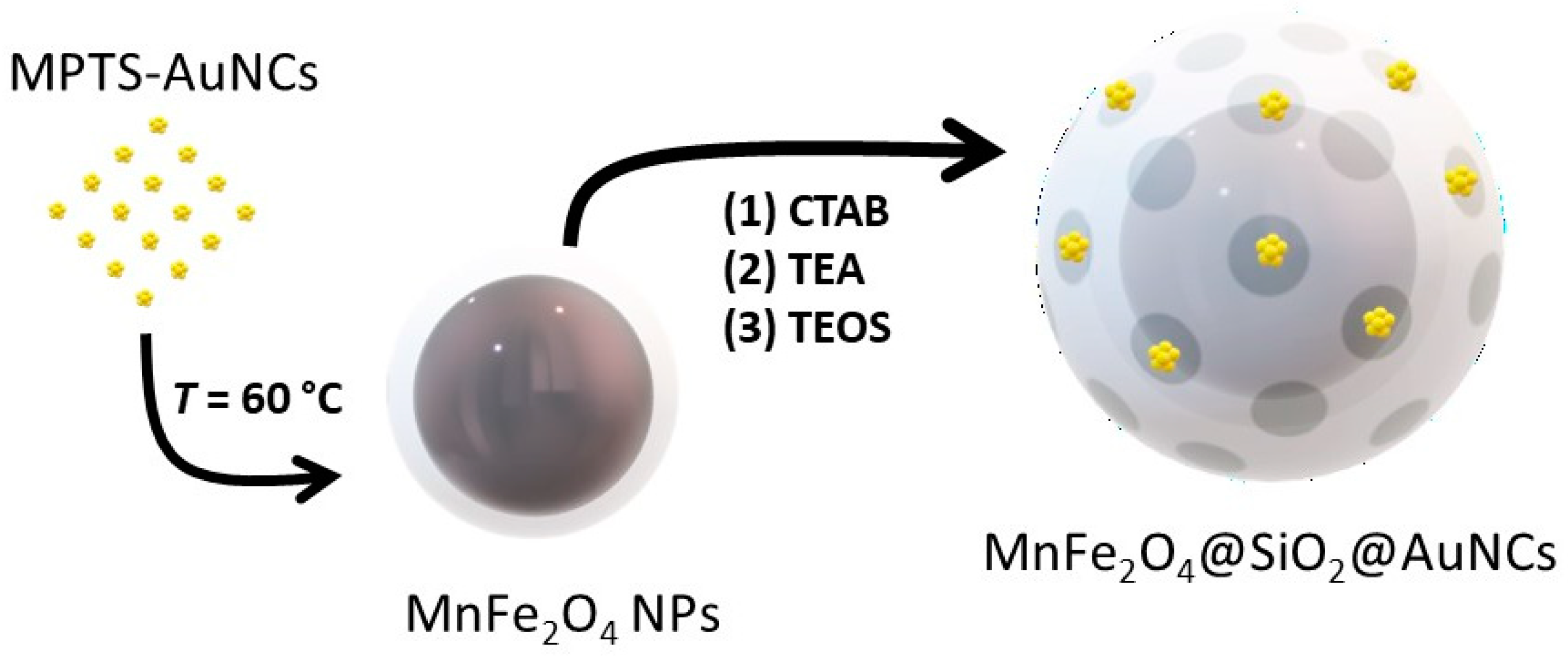
2.6. Hybrid Nanocomposite Conjugating MnFe2O4@SiO2 and MPTS-AuNCs (MnFe2O4@SiO2@AuNCs)
2.7. Characterization of the Materials
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AuNCs Stabilized with MPTS
3.2. One-Pot Synthesis of AuNC in MSN (AuNCs@MSN)
3.3. Incorporation of AuNCs and MnFe2O4 in MSNs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piñeiro, Y.; Rivas, J.; López-Quintela, M.A. Chapter 4—The Emergence of Quantum Confinement in Atomic Quantum Clusters. In Colloidal Foundations of Nanoscience; Berti, D., Palazzo, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 81–105. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Simultaneous RGB Emitting Au Nanoclusters in Chitosan Nanoparticles for Anticancer Gene Theranostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Luo, Z.; Li, N.; Lee, J.Y.; Xie, J.; Lu, J. Amphiphilic Polymeric Nanocarriers with Luminescent Gold Nanoclusters for Concurrent Bioimaging and Controlled Drug Release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4324–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, T.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, B.; Lin, Q. Polycation-functionalized gold nanodots with tunable near-infrared fluorescence for simultaneous gene delivery and cell imaging. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, X. Near-Infrared Emitting Gold Cluster–Poly(acrylic acid) Hybrid Nanogels. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-A.J.; Yang, T.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Huang, S.H.; Sperling, R.A.; Zanella, M.; Li, J.K.; Shen, J.-L.; Wang, H.-H.; Yeh, H.-I.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Bioconjugation of Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters toward Biological Labeling Applications. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, C.; Liao, S.; Li, L.; Wang, T.; Su, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Sui, C.; Lin, J. Silica-Encapsulated Gd3+-Aggregated Gold Nanoclusters for In Vitro and In Vivo Multimodal Cancer Imaging. Chem. A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 8876–8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.T.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, C.G.; Su, Z.M. Multifunctional spherical gold nanocluster aggregate@polyacrylic acid@mesoporous silica nanoparticles for combined cancer dual-modal imaging and chemo-therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2421–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hembury, M.; Chiappini, C.; Bertazzo, S.; Kalber, T.L.; Drisko, G.L.; Ogunlade, O.; Walker-Samuel, S.; Krishna, K.S.; Jumeaux, C.; Beard, P.; et al. Gold-silica quantum rattles for multimodal imaging and therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.-H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Cheon, J. Recent advances in magnetic nanoparticle-based multi-modal imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4501–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI Contrast Agents: Current Challenges and New Frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 957–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.-D.; Paudel, R.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhou, S.-K. MRI contrast agents: Classification and application (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, M.; Fernandes, C.; Pereira, C.; Rebelo, S.L.H.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freire, C. Gold-supported magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts: A sustainable solution for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol in water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5131–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Rocha, M.; Freire, C.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C. Architectured design of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for application as MRI contrast agents: Mastering size and magnetism for enhanced relaxivity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6261–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.; Pereira, C.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.P.; Pereira, A.M.; Guedes, A.; Fernandez-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, A.; Ibarra, M.R.; Araujo, J.P.; Freire, C. Tailored design of CoxMn1-xFe2O4 nanoferrites: A new route for dual control of size and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 5818–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, M.; Velumani, S. Manganese ferrite nanocubes as an MRI contrast agent. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 016107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Haque, M.; Kumar, A.; Hoq, A.; Hyder, F.; Hoque, S.M. Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles (MnFe2O4@): Size Dependence for Hyperthermia and Negative/Positive Contrast Enhancement in MRI. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgizadeh, M.; Behzadpour, N.; Salehi, F.; Daneshvar, F.; Vais, R.D.; Nazari-Vanani, R.; Azarpira, N.; Lotfi, M.; Sattarahmady, N. A MnFe2O4@/C nanocomposite as a novel theranostic agent in MRI, sonodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy of a melanoma cancer model. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Dong, Y.-L.; Chen, X.-J.; Zhang, H.-J.; Zheng, J.-M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.-G. A highly efficient catalyst: In situ growth of Au nanoparticles on graphene oxide–Fe3O4 nanocomposite support. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Bian, G.; Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Synthesis of monodisperse magnetic sandwiched gold nanoparticle as an easily recyclable catalyst with a protective polymer shell. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saire-Saire, S.; Barbosa, E.C.M.; Garcia, D.; Andrade, L.H.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Camargo, P.H.C.; Alarcon, H. Green synthesis of Au decorated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and dimethylphenylsilane oxidation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 22116–22123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, A.; Mondini, S.; Marelli, M.; Pifferi, V.; Falciola, L.; Ponti, A.; Ferretti, A.M.; Polito, L. Synthesis of Water Dispersible and Catalytically Active Gold-Decorated Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 7117–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Li, B.; Ren, X.; Tan, L.; Huang, Z.; Tang, F. One-pot gradient solvothermal synthesis of Au–Fe3O4 hybrid nanoparticles for magnetically recyclable catalytic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10513–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzing, A.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Carley, A.F.; Landon, P.; Hutchings, G.J. Identification of Active Gold Nanoclusters on Iron Oxide Supports for CO Oxidation. Science 2008, 321, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratila, R.M.; Mitchell, S.G.; del Pino, P.; Grazu, V.; de la Fuente, J.M. Strategies for the Biofunctionalization of Gold and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15057–15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Park, S.; Stojanović, Z.; Han, H.-S.; Lee, J.; Seok, H.K.; Uskoković, D.; Lee, K.H. Facile Solvothermal Preparation of Monodisperse Gold Nanoparticles and Their Engineered Assembly of Ferritin–Gold Nanoclusters. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15698–15703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Wei, Z.; Hu, F.; Wang, J.; Ge, G.; Hu, Z.; Shao, M.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, J. Fast assembling microarrays of superparamagnetic Fe3O4@Au nanoparticle clusters as reproducible substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13427–13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikova, S.; Pavlikov, A.; Trofimova, T.; Mikhlin, Y.; Karpov, D.; Asanova, A.; Grigoriev, Y.; Volochaev, M.; Samoilo, A.; Zharkov, S.; et al. Hybrid Nanoparticles Based on Cobalt Ferrite and Gold: Preparation and Characterization. Metals 2021, 11, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binaymotlagh, R.; Hajareh Haghighi, F.; Aboutalebi, F.; Mirahmadi-Zare, S.Z.; Hadadzadeh, H.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.-H. Selective chemotherapy and imaging of colorectal and breast cancer cells by a modified MUC-1 aptamer conjugated to a poly(ethylene glycol)-dimethacrylate coated Fe3O4–AuNCs nanocomposite. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guével, X.; Prinz, E.-M.; Müller, R.; Hempelmann, R.; Schneider, M. Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic nanoparticles coated with fluorescent gold nanoclusters. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Hsieh, W.-J.; Lin, C.-W.; Yang, H.-W.; Wang, C.-K. Multifunctional liposomal drug delivery with dual probes of magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 12442–12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, W.; Tai, F.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B.; Wong, W.-Y. An inorganic magnetic fluorescent nanoprobe with favorable biocompatibility for dual-modality bioimaging and drug delivery. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 192, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yao, Y.; Song, Q. Gold nanoclusters decorated with magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for potential multimodal optical/magnetic resonance imaging. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5910–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Palchoudhury, S.; Qin, Y.; Macher, T.; Bao, Y. Make Conjugation Simple: A Facile Approach to Integrated Nanostructures. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8767–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Rao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fluorescence and magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4@SiO2@Au MNPs as peroxidase mimetics for glucose detection. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 538, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, B. Fluorescence detection of bisphenol A in aqueous solution using magnetite core-shell material with gold nanoclusters prepared by molecular imprinting technique. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Calderon, S.; Fidalgo, A.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; André, V.; Teresa Duarte, M.; Ferreira, P.J.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Baleizão, C. Silica nanocarriers with user-defined precise diameters by controlled template self-assembly. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon V, S.; Ribeiro, T.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Baleizão, C.; Ferreira, P.J. On the Structure of Amorphous Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Aberration-Corrected STEM. Small 2018, 14, 1802180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florensa, M.; Llenas, M.; Medina-Gutiérrez, E.; Sandoval, S.; Tobías-Rossell, G. Key Parameters for the Rational Design, Synthesis, and Functionalization of Biocompatible Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.; Coutinho, E.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Hybrid mesoporous silica nanocarriers with thermovalve-regulated controlled release. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13485–13494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, S.; Rajput, S.J. Composite smart mesoporous silica nanoparticles as promising therapeutic and diagnostic candidates: Recent trends and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, E.-B. Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Crucho, C.I.C.; Alves, S.P.C.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Hybrid Mesoporous Nanoparticles for pH-Actuated Controlled Release. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Hybrid smart mesoporous silica nanoparticles for theranostics. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2311–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, N.B.; Nayak, Y.; Garg, S.; Nayak, U.Y. Multifunctional engineered mesoporous silica/inorganic material hybrid nanoparticles: Theranostic perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 478, 214977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, S.; Gao, X. Preparation of core–shell structured Au@SiO2 nanocomposite catalyst with Au core size below 2 nm without high-temperature calcination procedure. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 8086–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Chen, B.; Mahurin, S.M.; Hagaman, E.W.; Dai, S.; Overbury, S.H. Surface Sol−Gel Modification of Mesoporous Silica Materials with TiO2 for the Assembly of Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2793–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tsunoyama, H.; Akita, T.; Tsukuda, T. Preparation of ∼1 nm Gold Clusters Confined within Mesoporous Silica and Microwave-Assisted Catalytic Application for Alcohol Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 13457–13461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteleiro, B.; Martinho, J.M.G.; Farinha, J.P.S. Encapsulation of gold nanoclusters: Stabilization and more. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 17199–17217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yang, G.; Yang, P.; Yu, Y.; Lv, R.; Li, C.; Dai, Y.; Gai, S.; Lin, J. A New Single 808 nm NIR Light-Induced Imaging-Guided Multifunctional Cancer Therapy Platform. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3966–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Fernandes, C.; Rocha, M.; Mendes, R.; Fernández-García, M.P.; Guedes, A.; Tavares, P.B.; Grenèche, J.-M.; Araújo, J.P.; et al. Superparamagnetic MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) Nanoparticles: Tuning the Particle Size and Magnetic Properties through a Novel One-Step Coprecipitation Route. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, P.G.; Gouterman, M. Porphyrins: XIII: Fluorescence spectra and quantum yields. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1969, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, M.; Walker, M.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Whyman, R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two-phase Liquid-Liquid system. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Lanni, E.; Garg, N.; Bier, M.E.; Jin, R. Kinetically Controlled, High-Yield Synthesis of Au25 Clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1138–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Murray, R.W. Visible luminescence of water-soluble monolayer- protected gold clusters. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 12498–12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-W.; Yuan, Z.; Chang, H.-T. Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters: Recent Advances in Sensing and Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casteleiro, B.; Ribeiro, T.; Mariz, I.; Martinho, J.M.G.; Farinha, J.P.S. Encapsulation of gold nanoclusters by photo-initiated miniemulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Singh, T.; Hussain, J.I.; Hashmi, A.A. Au(III)–CTAB reduction by ascorbic acid: Preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 104, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, S.; Kosuge, K. Salt-Induced Formation of Uniform Fiberlike SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica Particles and Application to Toluene Adsorption. Langmuir 2007, 23, 11761–11768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Quaresma, P.; Tavares, P.B.; Pereira, E.; Araújo, J.P.; Freire, C. Superparamagnetic γ-Fe2O3@SiO2 nanoparticles: A novel support for the immobilization of [VO(acac)2]. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 2842–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidalgo, A.; Ilharco, L.M. The defect structure of sol–gel-derived silica/polytetrahydrofuran hybrid films by FTIR. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 283, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, R.; Pellenq, R.; Champenois, J.-B.; Poulesquen, A. Dissociation Mechanisms of Dissolved Alkali Silicates in Sodium Hydroxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 8288–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.H.; Hasan, H.; Anees, M.; Hussain, Z. FOLIC acid-conjugated doxorubicin-loaded photosensitizing manganese ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity against human cervical carcinoma cell line (hela). Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 9, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Félix, L.; Chaker, J.; Parise, M.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; De Los Santos Valladares, L.; Bustamante, A.; Garg, V.K.; Oliveira, A.C.; Morais, P.C. Synthesis and characterization of uncoated and gold-coated magnetite nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 2014, 224, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Raja, S.O.; Sardar, M.; Gayathri, N.; Ghosh, B.; Dasgupta, A. Iron oxide nanoparticles coated with gold: Enhanced magnetic moment due to interfacial effects. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Park, H.-Y.; Lim, S.I.I.; Schadt, M.J.; Mott, D.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Zhong, C.-J. Core@shell nanomaterials: Gold-coated magnetic oxide nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.G.; Sarkar, D.; Singh, A.K.; Mandal, K. Enhanced band gap emission and ferromagnetism of Au nanoparticle decorated α-Fe2O3 nanowires due to surface plasmon and interfacial effects. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrachev, M.; Antonello, S.; Dainese, T.; Ruzzi, M.; Zoleo, A.; Aprà, E.; Govind, N.; Fortunelli, A.; Sementa, L.; Maran, F. Magnetic Ordering in Gold Nanoclusters. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuboltsev, V.; Savin, A.; Pirojenko, A.; Räisänen, J. Magnetism in Nanocrystalline Gold. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6691–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.S.; Tarakeshwar, P.; Mujica, V.; Kumar, C.S.S.R. Chemically Induced Magnetism in Atomically Precise Gold Clusters. Small 2014, 10, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.M.; Pereira, C.; Silva, A.S.; Schmool, D.S.; Freire, C.; Grenèche, J.-M.; Araújo, J.P. Unravelling the effect of interparticle interactions and surface spin canting in γ-Fe2O3@SiO2 superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 114319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tang, T. Assembly of Magnetic Nano-Fe3O4@GSH-Au NCs Core–Shell Microspheres for the Visualization of Latent Fingerprints. Nano 2018, 13, 1850128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yang, H.; Jiang, P.; Chen, Z.; Ji, C.; Nie, L. Multi-Functional Fe3O4@mSiO2-AuNCs Composite Nanoparticles Used as Drug Delivery System. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



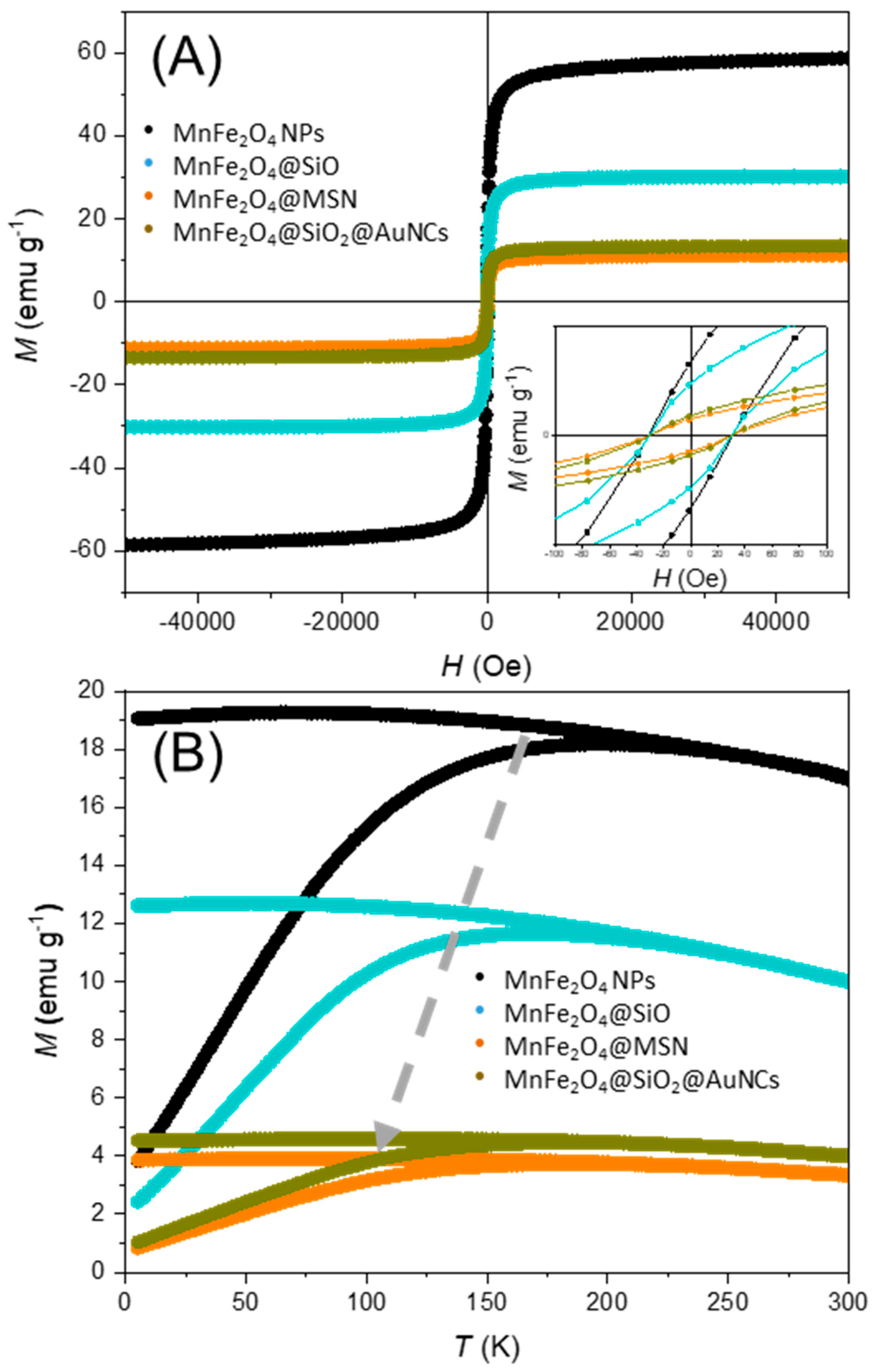
| Nanomaterial | MS @ 5 K (emu g−1) | MS @ 300 K (emu g−1) | HC @ 300 K (Oe) | Trev (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnFe2O4 | 85.4 | 58.7 | 31.0 | 253 |
| MnFe2O4@SiO2 | 44.7 | 30.1 | 30.3 | 245 |
| MnFe2O4@SiO2@MSN | 17.3 | 11.2 | 30.3 | 217 |
| MnFe2O4@SiO2@AuNCs | 19.0 | 13.4 | 30.2 | 241 |
| Nanocomposite | PL Wavelengths (nm) | MS (emu g−1) | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Fe3O4@Au@β-CD). Iron oxide-gold nanoclusters with the surface decorated with β-cyclodextrins | 600–700 | 2.832 | Bioimaging Drug Delivery | [32] |
| Fe3O4@AuNCs. Gold nanoclusters decorated with iron oxide NPs | 650 | 13.0 | PL Imaging MRI | [33] |
| Fe3O4@GSH-AuNCs. Core (iron oxide)—shell (glutathione gold nanoclusters) | 468 543 | 29.2 | Fingerprints visualization | [72] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@AuNCs-MIP. Core (iron oxide)—shell (silica decorated with covalently bonded GSH-AuNCs) plus a molecular imprinted polymer (MIP) layer | 562 | 9.87 | Detection of Bisphenol A | [36] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-AuNCs. Iron oxide NPs coated with a mesoporous silica shell decorated with covalently bond AuNCs | 630 | 24 | Drug delivery | [73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casteleiro, B.; Rocha, M.; Sousa, A.R.; Pereira, A.M.; Martinho, J.M.G.; Pereira, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Multifunctional Nanoparticles with Superparamagnetic Mn(II) Ferrite and Luminescent Gold Nanoclusters for Multimodal Imaging. Polymers 2023, 15, 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224392
Casteleiro B, Rocha M, Sousa AR, Pereira AM, Martinho JMG, Pereira C, Farinha JPS. Multifunctional Nanoparticles with Superparamagnetic Mn(II) Ferrite and Luminescent Gold Nanoclusters for Multimodal Imaging. Polymers. 2023; 15(22):4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224392
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasteleiro, Bárbara, Mariana Rocha, Ana R. Sousa, André M. Pereira, José M. G. Martinho, Clara Pereira, and José P. S. Farinha. 2023. "Multifunctional Nanoparticles with Superparamagnetic Mn(II) Ferrite and Luminescent Gold Nanoclusters for Multimodal Imaging" Polymers 15, no. 22: 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224392
APA StyleCasteleiro, B., Rocha, M., Sousa, A. R., Pereira, A. M., Martinho, J. M. G., Pereira, C., & Farinha, J. P. S. (2023). Multifunctional Nanoparticles with Superparamagnetic Mn(II) Ferrite and Luminescent Gold Nanoclusters for Multimodal Imaging. Polymers, 15(22), 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224392









