Brief Analysis on the Degradation of Sugar-Based Copolyesters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Synthesis
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Synthesis
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Hydrolysis Degradation Test
2.2.2. Degradation Test in Natural Water
2.2.3. Simulated Natural Environment Test
2.2.4. Viscosity Average Molecular Weights of Copolyesters
2.2.5. Determination of Carboxyl End Group Content
2.2.6. Crystallization Melting Enthalpy Test
2.2.7. Mechanical Strength Testing
2.2.8. Morphology Testing
3. Results
3.1. Hydrolytic Behavior in Water
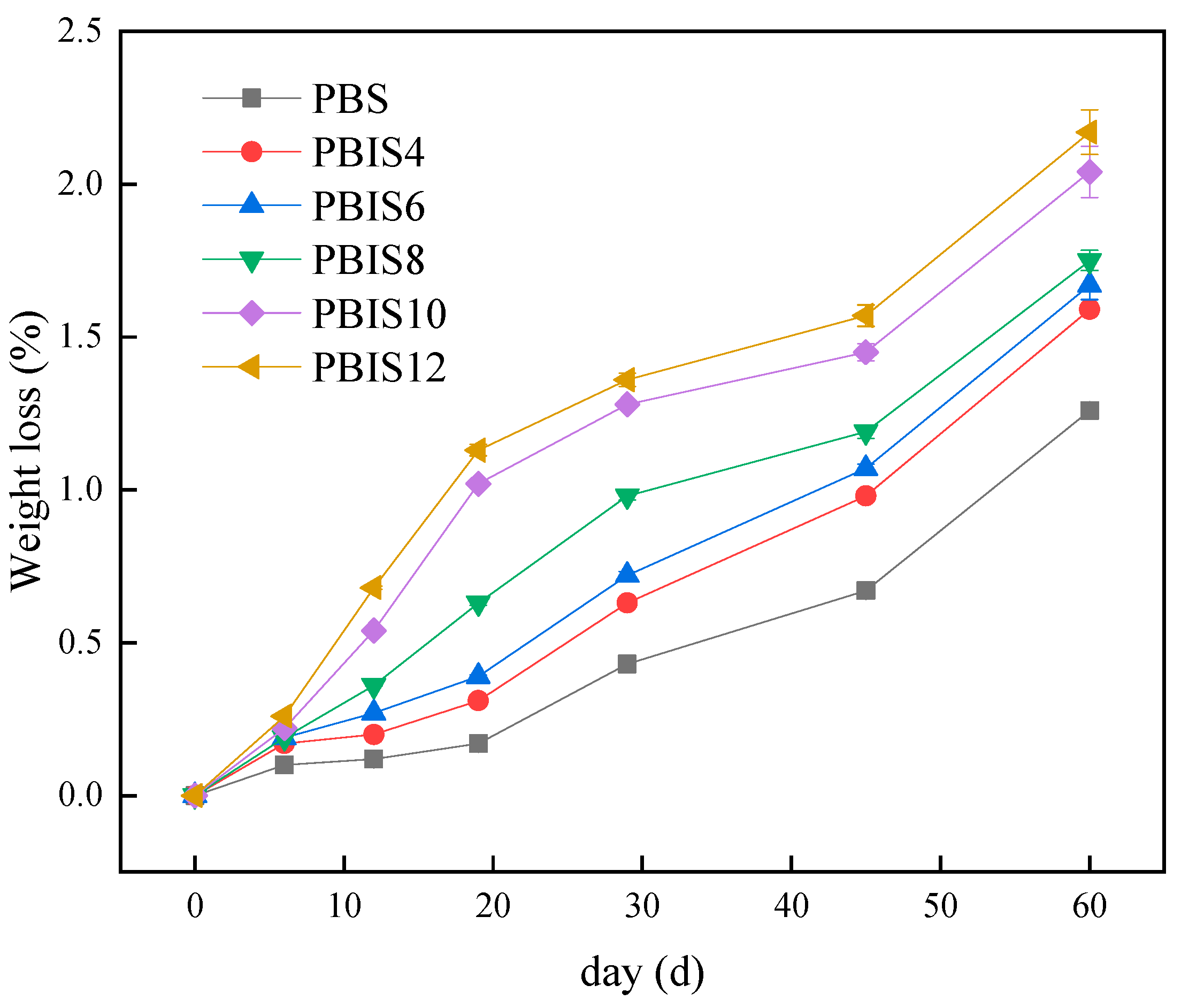
3.1.1. Weight Loss Rates of Copolyesters
3.1.2. Viscosity Average Molecular Weights of Copolyesters
3.1.3. Carboxyl End-Group Content of Copolyesters
3.1.4. Crystallization Melting Enthalpy of Polyester
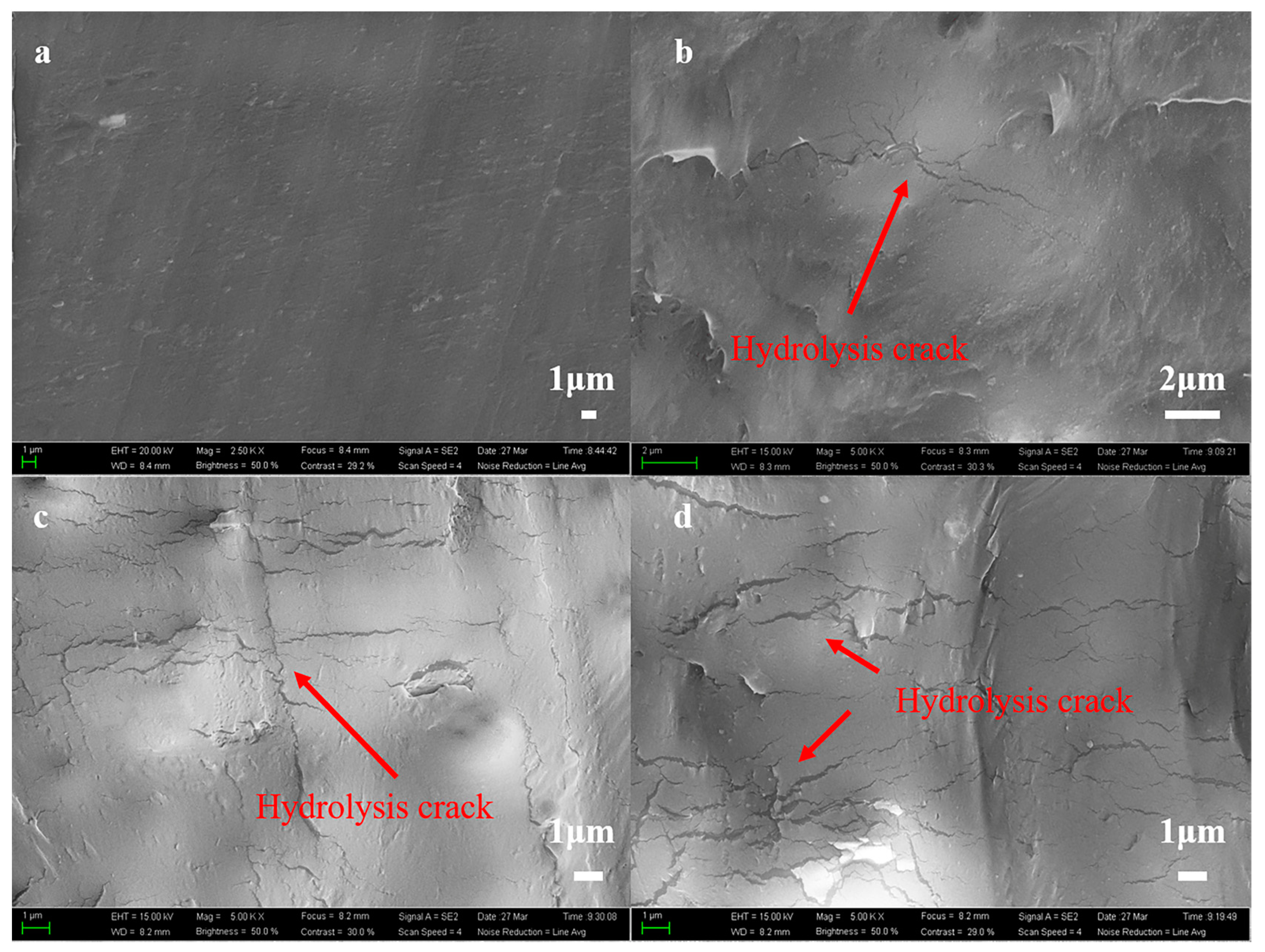
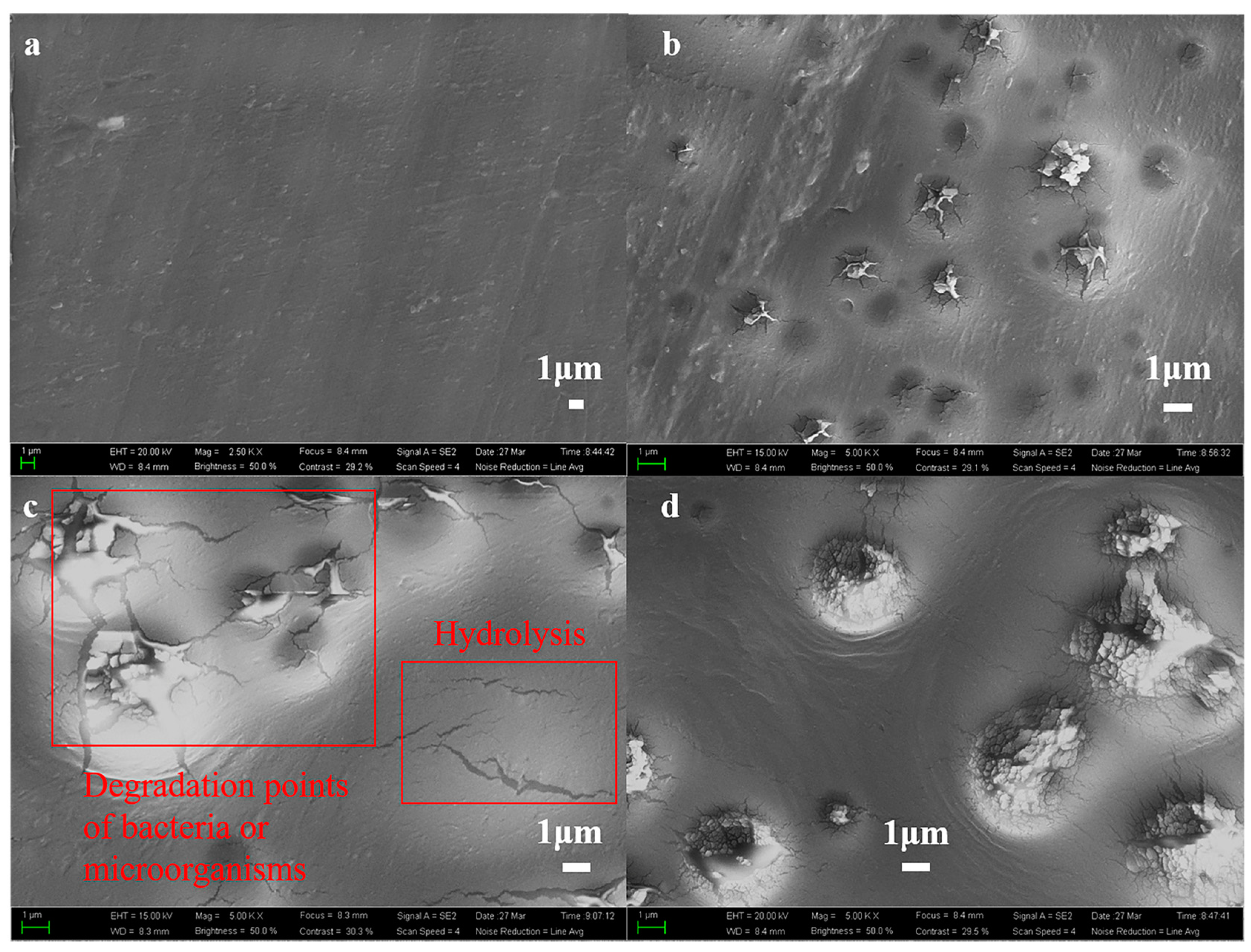
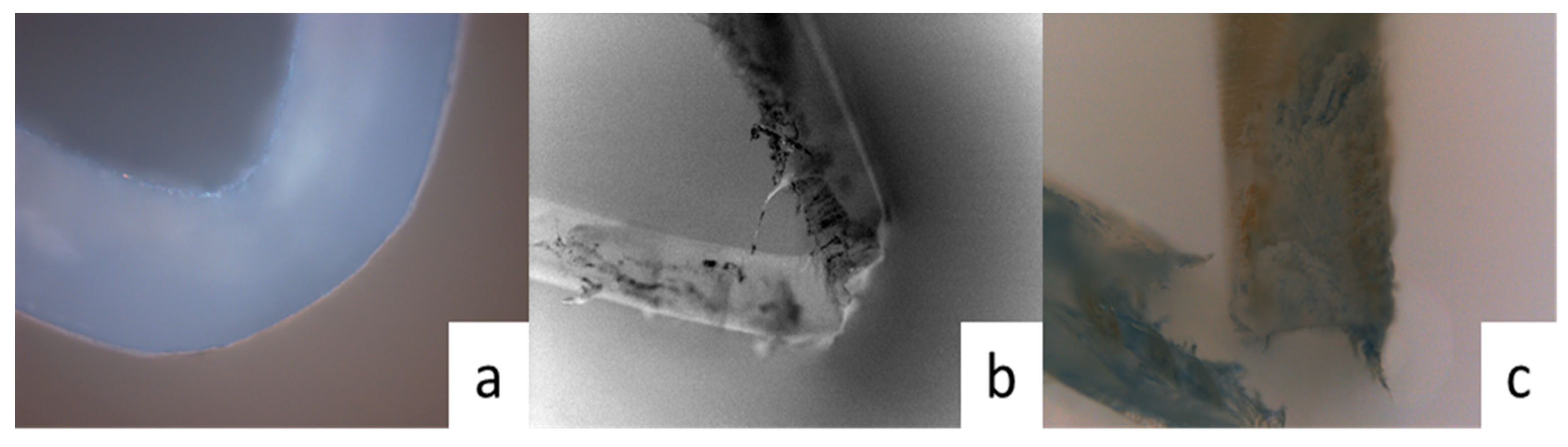
3.1.5. Surface Morphology of Polyester
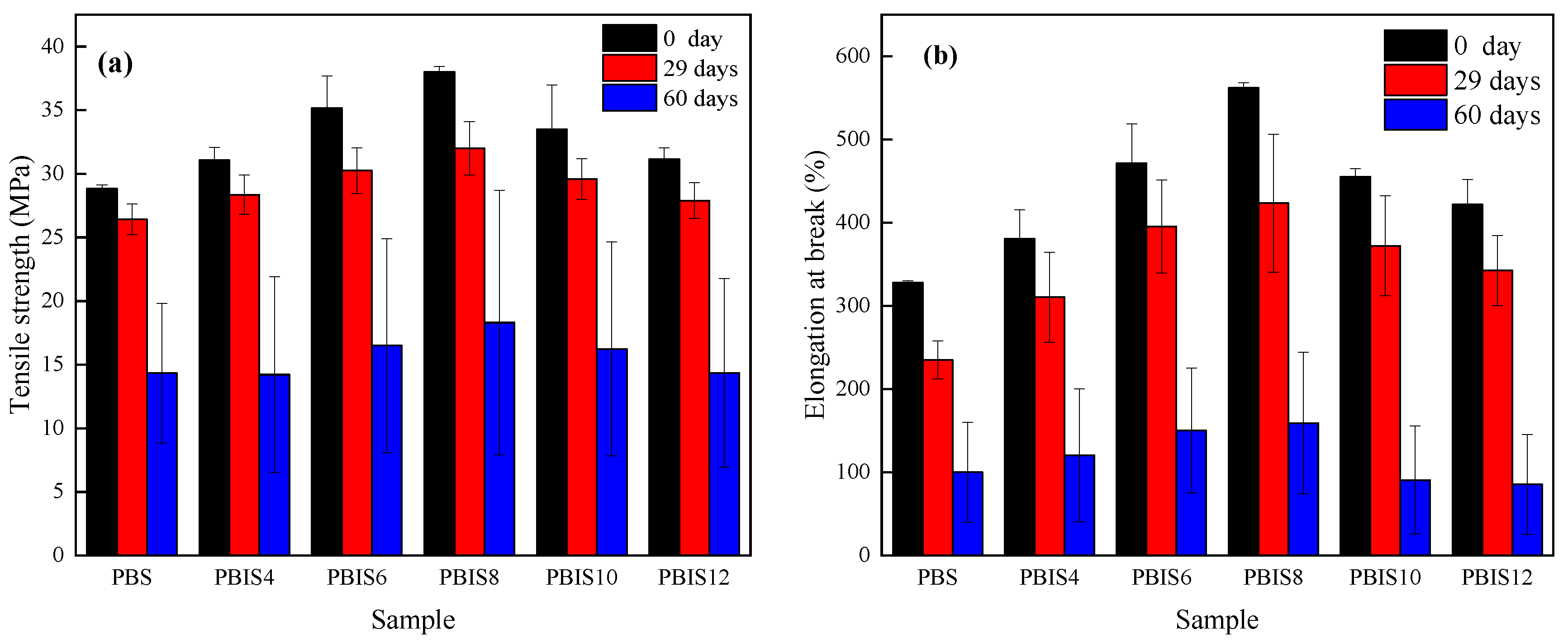
3.1.6. Mechanical Properties of Copolyesters
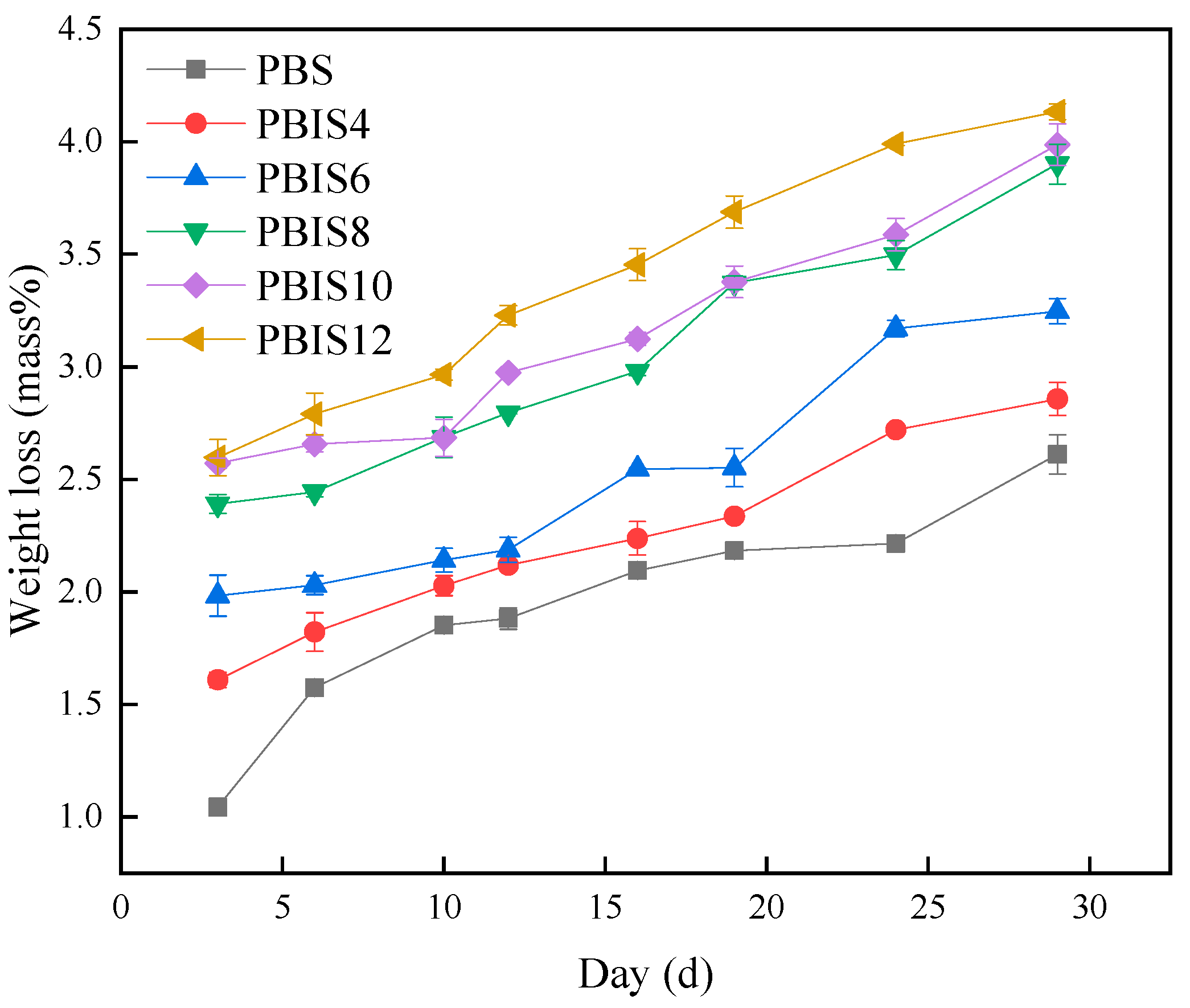
3.2. Degradation Performance of Copolyesters in Simulated Natural Environments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iqbal, N.; Khan, A.; Asif, A. Recent Concepts in Biodegradable Polymers for Tissue Engineering Paradigms: A Critical Review. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 91–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavitehrani, I.; Fathi, A.; Badr, H. Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polyesters. Polymers 2016, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckachan, G.; Pillai, C. Biodegradable Polymers—A Review on Recent Trends and Emerging Perspectives. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 637–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, T.; Völker, C.; Kramm, J. Plastics of the Future? The Impact of Biodegradable Polymers on the Environment and on Society. Angew. Chem. 2019, 58, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göpferich, A. Mechanisms of Polymer Degradation and Erosion. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadian, S.; Onay, T.; Demirel, B. Biodegradation of Bioplastics in Natural Environments. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigli, M.; Fabbri, M.; Lotti, N. Poly (Butylene Succinate)-Based Polyesters for Biomedical Applications: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 431–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ekenstein, G.; Woortman, A. Fully Biobased Unsaturated Aliphatic Polyesters from Renewable Resources: Enzymatic Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2014, 215, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitakumi, E.; Yoshikawa, K.; Nakano, K. Biodegradation of Poly(tetramethylene succinate-co-tetramethylene adipate) and poly Poly(tetramethylene succinate) through water-soluble products. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 941–946. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Su, T. Effect of hydroxyl monomers on the enzymatic degradation of poly(ethylene succinate), poly(butylene succinate), and poly(hexylene succinate). Polymers 2018, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayase, N.; Yano, H.; Kudoh, E. Isolation and characterization of poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate)-degrading microorganism. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 97, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Yamagata, Y.; Abe, K. Purification and characterization of a biodegradable plastic-degrading enzyme from aspergillus oryzae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, K.; Jin, H. Biodegradability of ethyl and n-octyl branched poly(ethylene adipate) and poly(butylene succinate). Eur. Polym. J. 2001, 37, 1843–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, B.; Lee, S. Enhanced interfacial adhesion, mechanical and thermal properties of natural flour-filled biodegradable polymer bio-composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Wang, L.; Sun, S.; Gao, H.; Bai, Y.; Ding, L. Mechanical Properties of Poly(Butylene-co-Isosorbide Succinate) after Blown Film Extrusion. Green Mater. 2020, 8, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Gao, H.; Wang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Li, N. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of bio-based poly(butylene-co-isosorbide succinate)(PBIS). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 139, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, E.; Ilarduya, A.; León, S.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Sugar-based bicyclic monomers for aliphatic polyesters: A comparative appraisal of acetalized alditols and isosorbide. Des. Monomers Polym. 2017, 20, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavilla, C.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Biodegradation and hydrolytic degradation of poly(butylene terephthalate) copolyesters containing cyclic sugar units. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.; Edge, M.; Mohammadian, M. Physicochemical Aspects of the Environmental Degradation of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1994, 43, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G154-07; Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PN, USA, 2017.
- Liu, X. Study on the Synthesis and Properties of Poly(Butylene Succinate). Master’s Thesis, Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology, Beijing, China, December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D638-14; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PN, USA, 2014.
- Deng, X.; Xiong, C.; Cheng, L. Studies on the Block Copolymerization of D, L-Lactide and Poly (Ethyle Glycol) with Aluminium Complex Catalyst. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 55, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserki, V.; Matzinos, P.; Pavlidou, E.; Biodegradable Aliphatic Polyesters Part, I.I. Synthesis and Characterization of Chain Extended Poly (Butylene Succinate-co-Butylene Adipate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Day/d | Viscosity Average Molecular Weight/g·mol−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | PBIS4 | PBIS6 | PBIS8 | PBIS10 | PBIS12 | ||
| 0 | 159,600 (200) | 158,300 (700) | 160,300 (400) | 159,400 (400) | 161,200 (800) | 157,500 (1000) | |
| Distilled Water | 19 | 145,600 (1000) | 141,500 (700) | 143,200 (800) | 139,800 (2000) | 142,500 (1200) | 132,400 (1200) |
| 29 | 132,600 (2400) | 135,300 (1100) | 129,500 (1200) | 113,500 (1600) | 125,800 (1100) | 113,500 (700) | |
| 45 | 123,000 (2700) | 115,000 (2100) | 105,300 (1800) | 108,500 (2900) | 112,500 (1600) | 94,300 (3000) | |
| 60 | 102,300 (3500) | 103,500 (3700) | 97,500 (3400) | 96,500 (4000) | 92,000 (4600) | 89,500 (3600) | |
| Natural Water | 19 | 121,600 (1300) | 121,900 (2400) | 117,500 (1700) | 113,000 (2500) | 107,500 (1500) | 102,400 (1300) |
| 29 | 89,500 (5100) | 87,200 (6000) | 88,700 (6200) | 82,600 (7200) | 73,700 (4800) | 73,200 (6000) | |
| Degradation Time/d | Carboxyl End Group/mol·t−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | PBIS4 | PBIS6 | PBIS8 | PBIS10 | PBIS12 | ||
| 0 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 2.1 | |
| Distilled Water | 29 | 245.2 (37.6) | 269.4 (35.3) | 273.8 (25.3) | 271.6 (41.0) | 288.3 (20.3) | 296.5 (26.1) |
| 60 | 475.7 (97.8) | 504.3 (58.6) | 517.5 (58.8) | 531.4 (75.5) | 540.2 (59.2) | 548.7 (58.1) | |
| Natural Water | 19 | 186.6 (21.1) | 207.4 (35.9) | 218.6 (14.1) | 249.0 (28.0) | 275.4 (14.6) | 290.2 (40.5) |
| 29 | 510.8 (124.8) | 533.3 (92.8) | 536.1 (119.8) | 586.6 (86.6) | 628.4 (62.0) | 653.9 (142.8) | |
| Degradation Time/Days | Crystallization Melting Enthalpy/J·g−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | PBIS4 | PBIS6 | PBIS8 | PBIS10 | PBIS12 | ||
| 0 | 67.22 | 64.52 | 62.46 | 54.15 | 52.11 | 50.49 | |
| Distilled Water | 12 | 67.72 | 64.80 | 62.89 | 54.57 | 52.85 | 50.91 |
| 29 | 68.37 | 65.45 | 63.28 | 54.97 | 53.17 | 51.43 | |
| 45 | 68.83 | 66.01 | 63.94 | 55.41 | 53.78 | 51.96 | |
| 60 | 69.66 | 66.52 | 64.76 | 56.01 | 54.67 | 52.54 | |
| Natural Water | 6 | 68.24 | 65.26 | 63.64 | 54.86 | 53.26 | 52.03 |
| 12 | 69.02 | 65.91 | 64.84 | 55.80 | 64.32 | 52.73 | |
| 19 | 69.97 | 66.49 | 65.27 | 56.62 | 55.14 | 53.47 | |
| 29 | 70.42 | 67.87 | 66.49 | 57.86 | 56.15 | 54.59 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, D.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y. Brief Analysis on the Degradation of Sugar-Based Copolyesters. Polymers 2023, 15, 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224372
Qu D, Yang Z, Zhang J, Wang S, Lu Y. Brief Analysis on the Degradation of Sugar-Based Copolyesters. Polymers. 2023; 15(22):4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224372
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Dezhi, Ziheng Yang, Jinyu Zhang, Shuyu Wang, and Yao Lu. 2023. "Brief Analysis on the Degradation of Sugar-Based Copolyesters" Polymers 15, no. 22: 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224372
APA StyleQu, D., Yang, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, S., & Lu, Y. (2023). Brief Analysis on the Degradation of Sugar-Based Copolyesters. Polymers, 15(22), 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15224372







