Superhydrophobic, Magnetic Aerogels Based on Nanocellulose Fibers Derived from Harakeke for Oily Wastewater Remediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
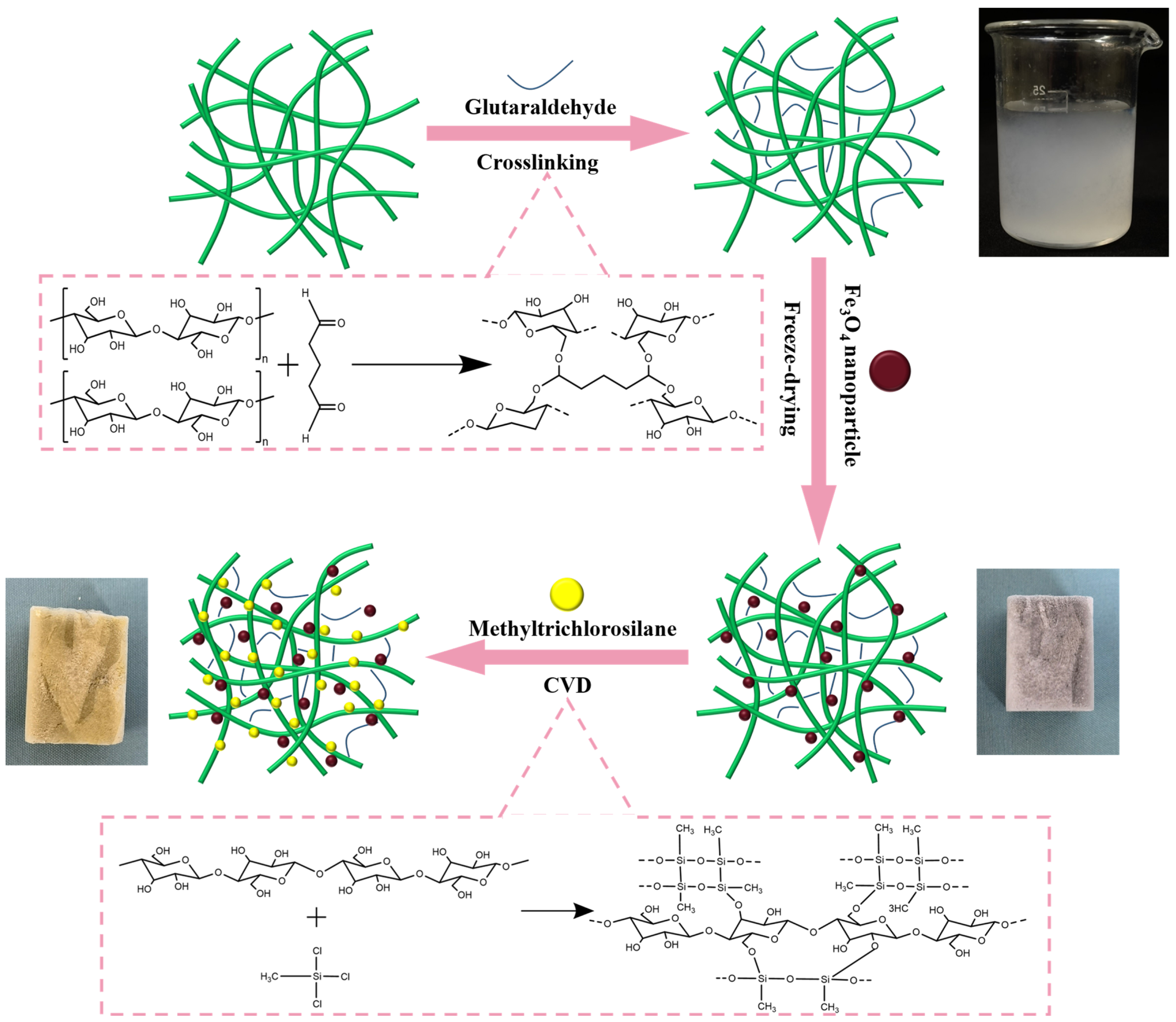
2.2. Synthesis of Pristine Cellulose Aerogel (CA)
2.3. Preparation of Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticle-Coated Cellulose Aerogels (MCA)
2.4. Preparation of Super-Hydrophobic Magnetic Cellulose Aerogels (HMCA)
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
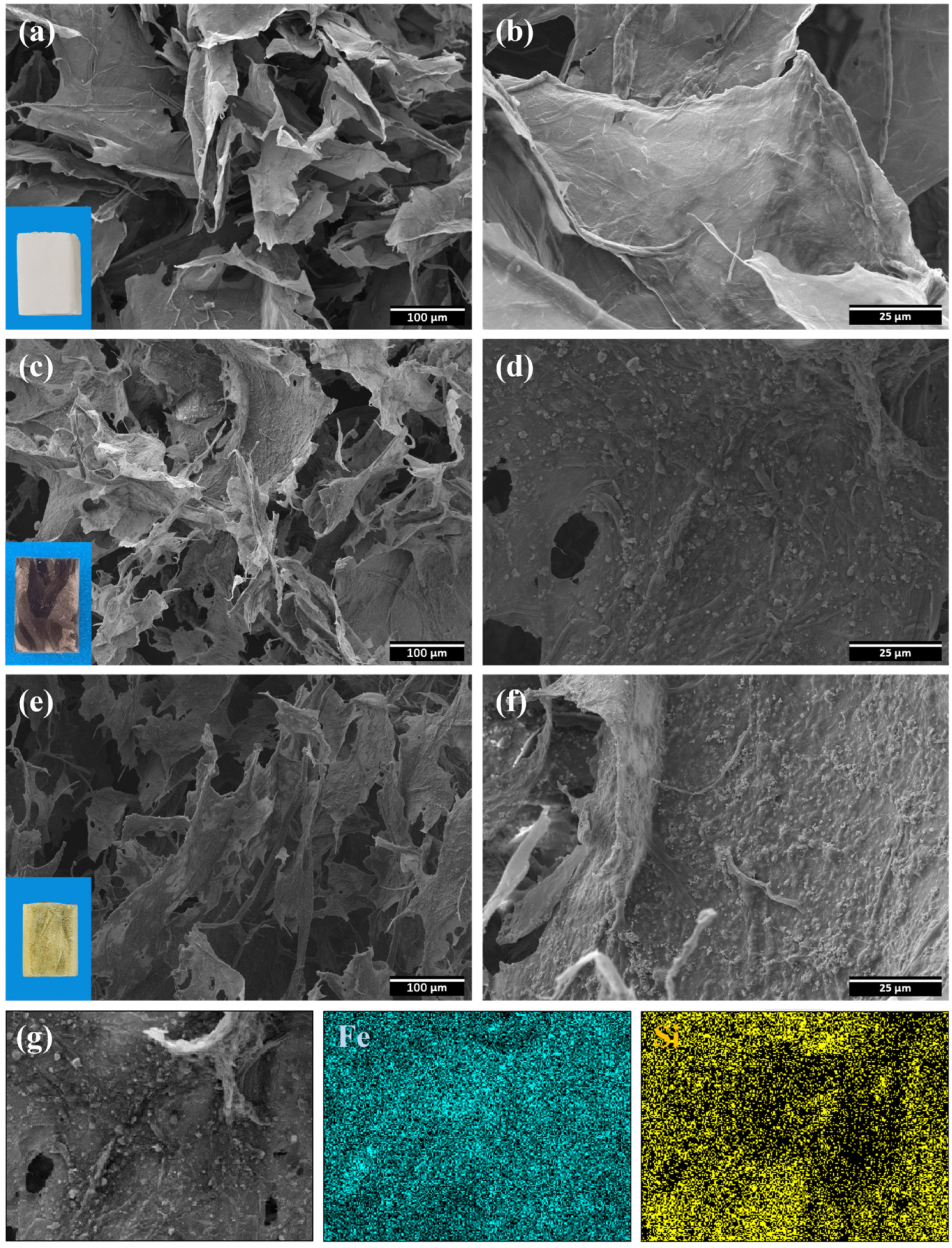
3.1. Fabrication and Structural Characterization of CA, MCA, and HMCA
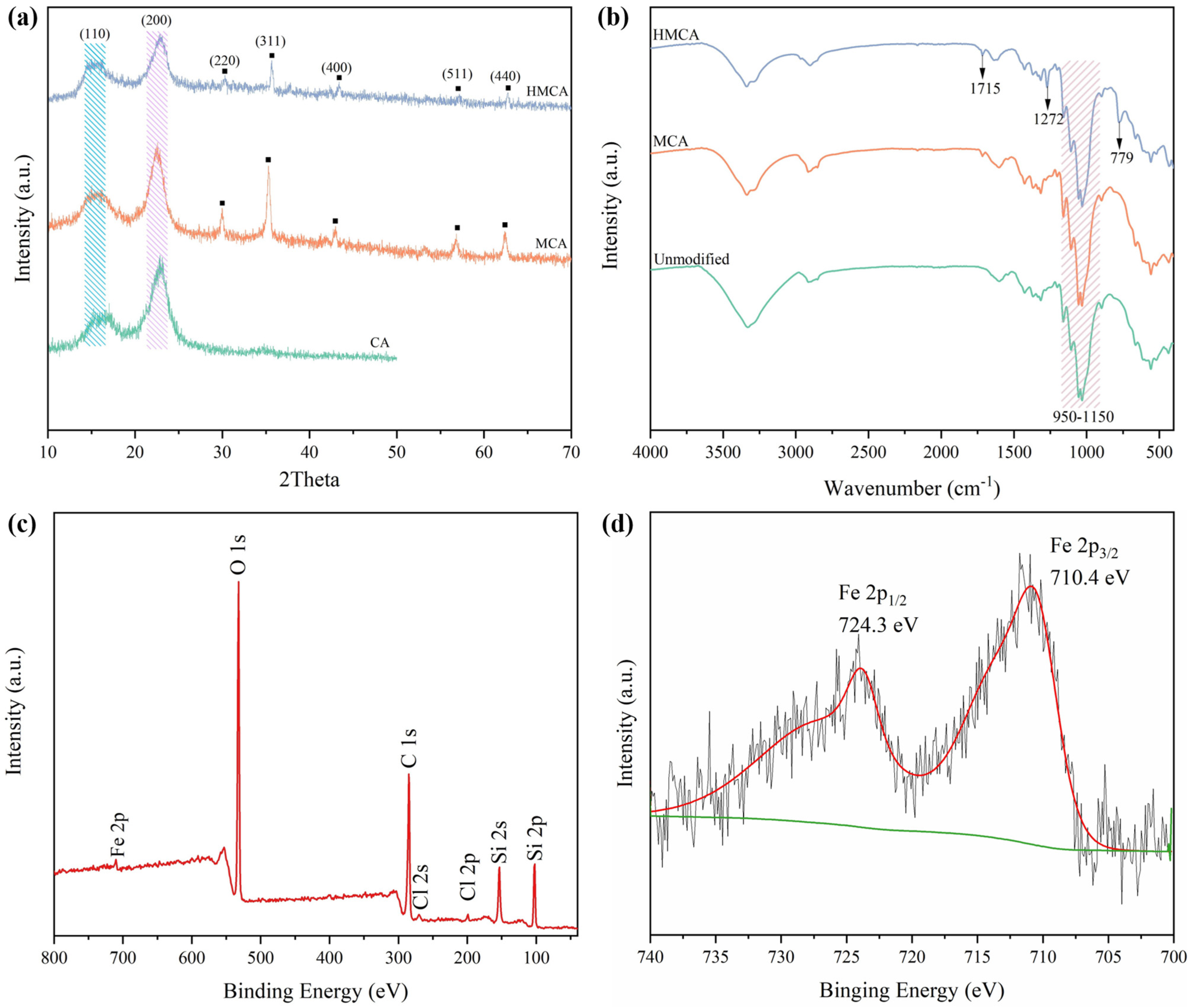
3.2. Characterization of CA, MCA, and HMCA
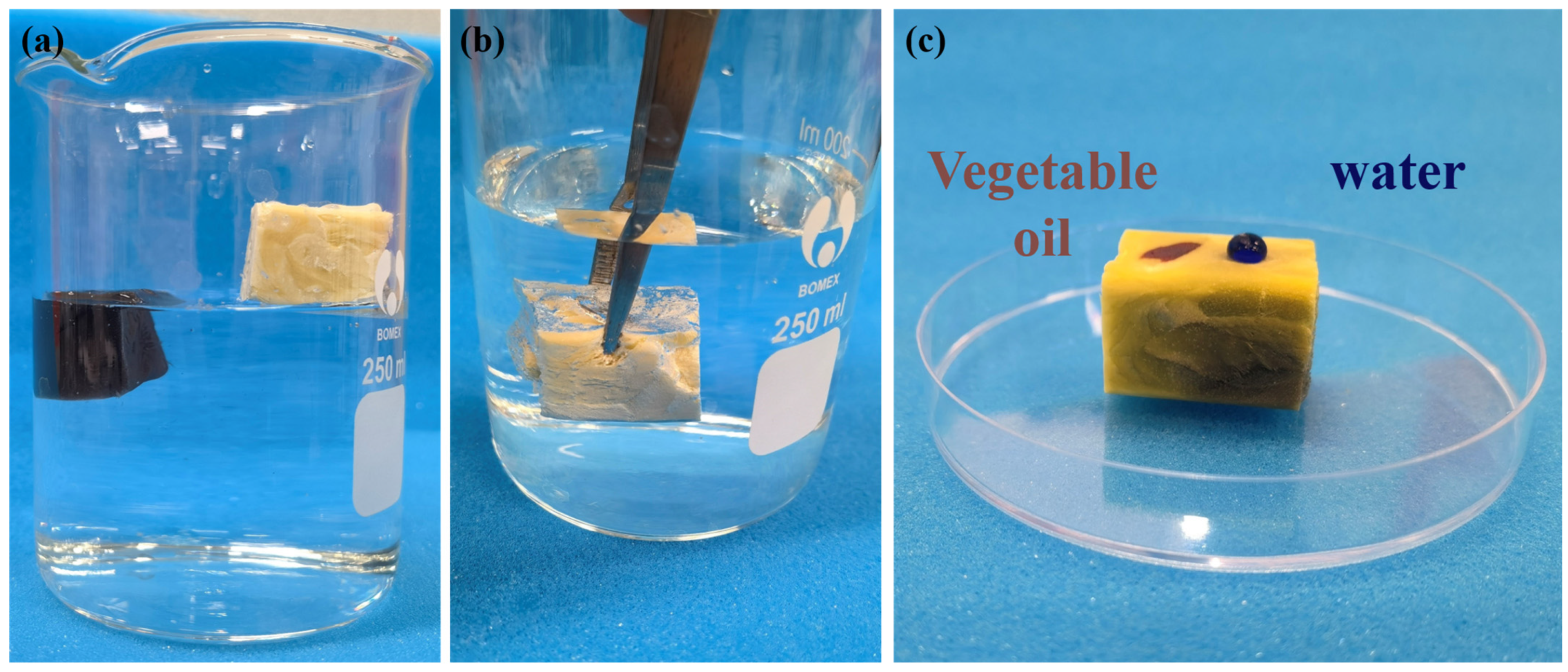
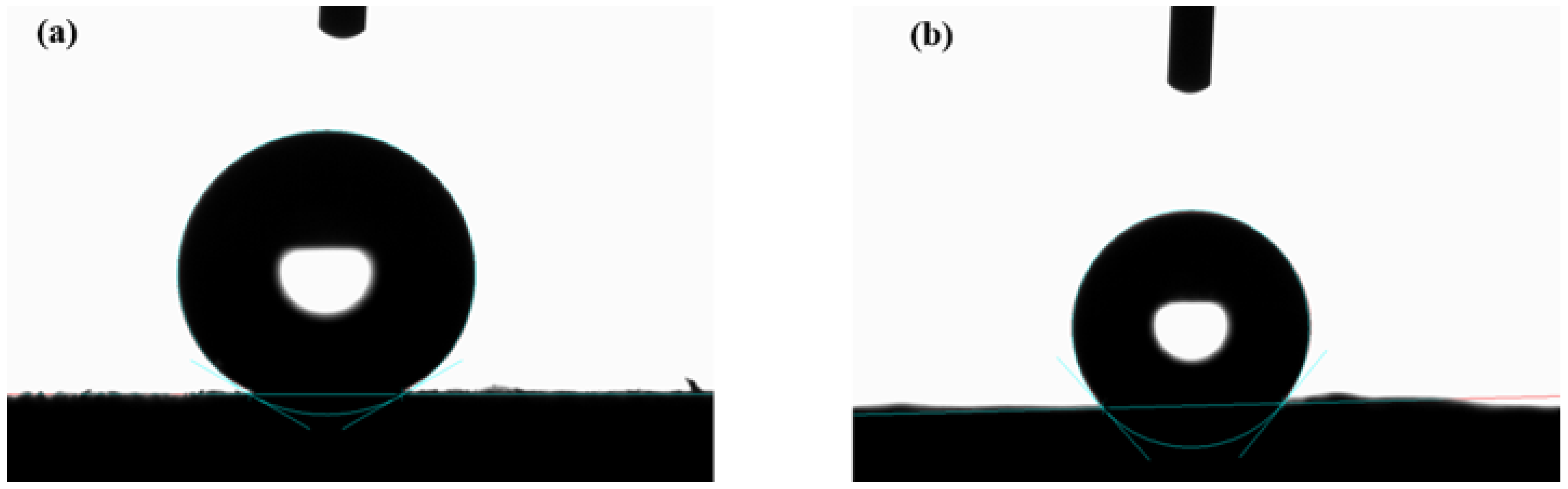
3.3. Surface Wettability
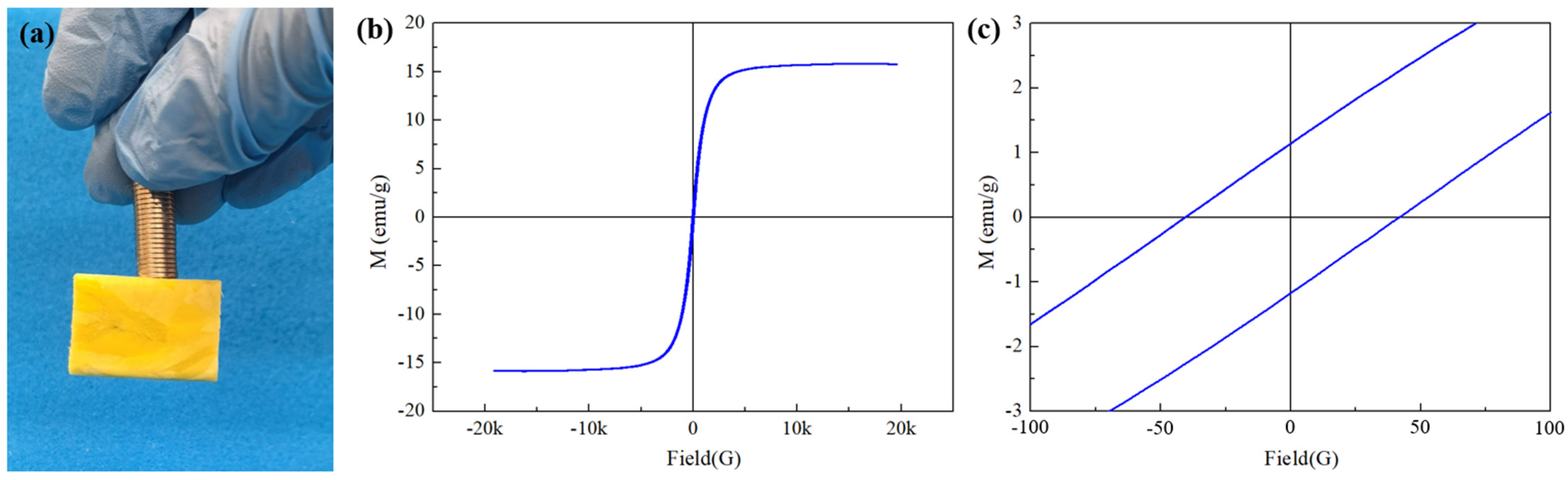
3.4. Magnetic Property of HMCA
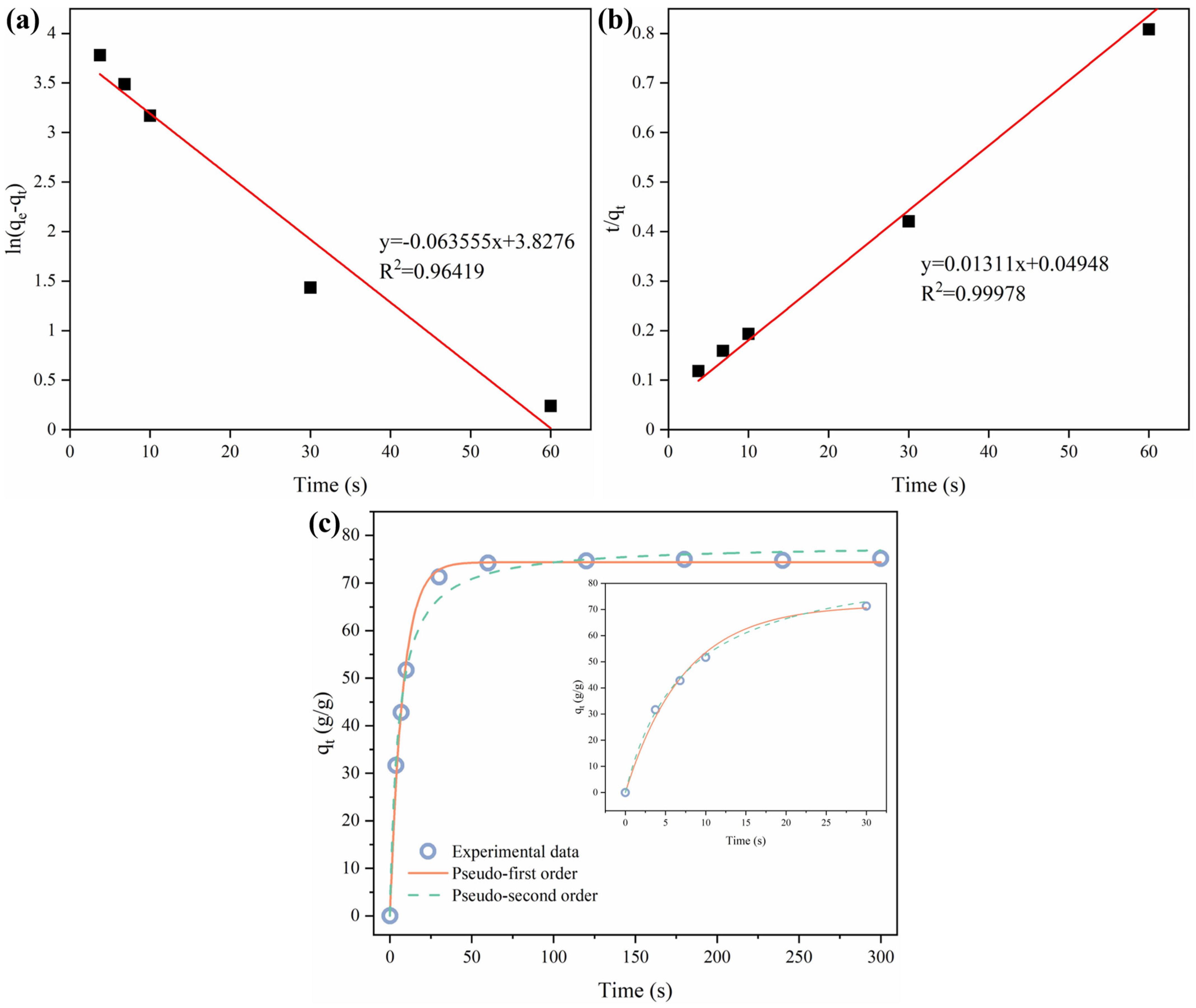
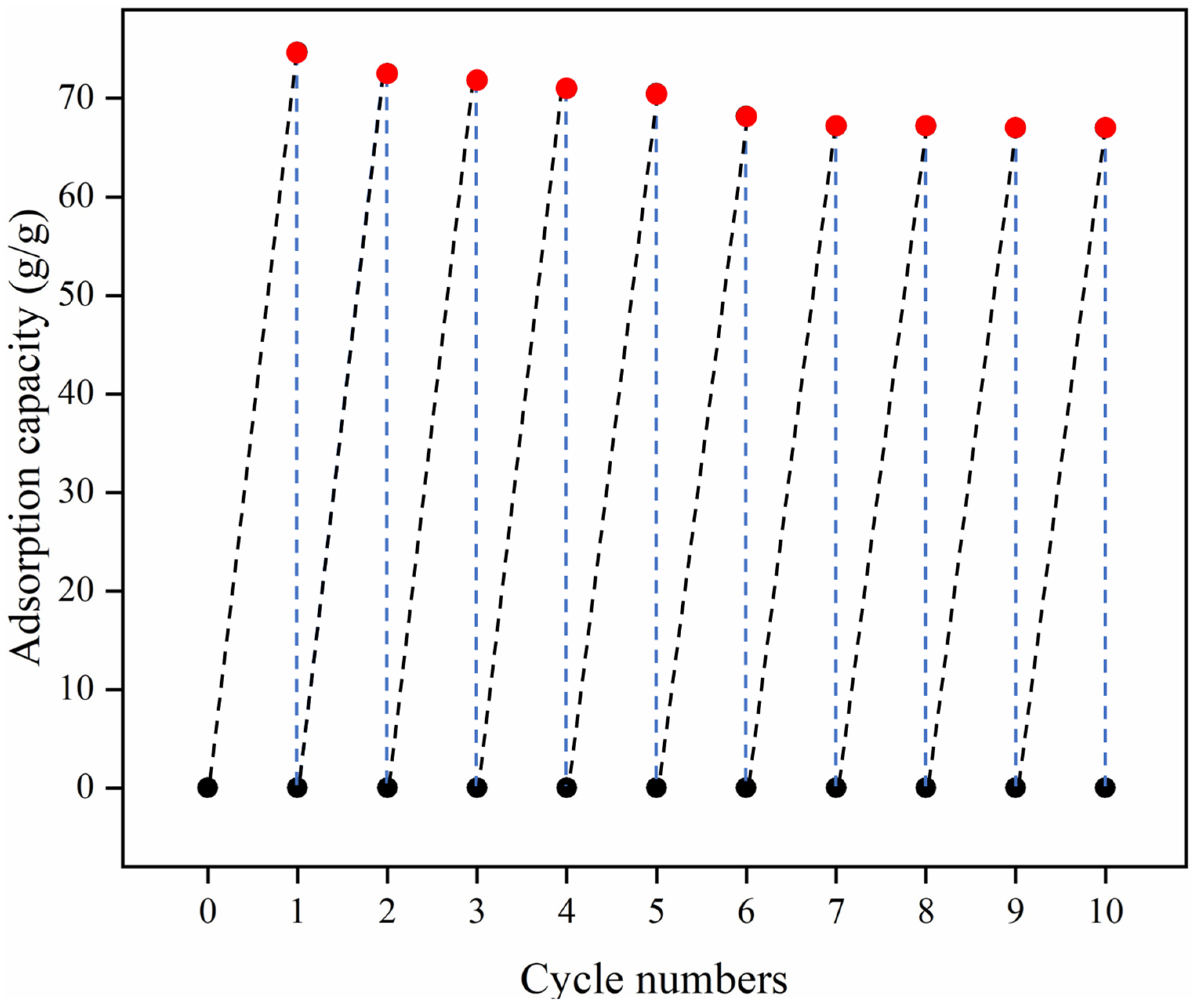
3.5. Adsorption Capacity and Adsorption Kinetics of HMCA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Biomimetic, Highly Reusable and Hydrophobic Graphene/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogels as Oil-Removing Absorbents. Polymers 2022, 14, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekperusi, A.O.; Onyena, A.P.; Akpudo, M.Y.; Peter, C.C.; Akpoduado, C.O.; Ekperusi, O.H. In-situ burning as an oil spill control measure and its effect on the environment. In Proceedings of the SPE Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, Lagos, Nigeria, 5–7 August 2019; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saththasivam, J.; Loganathan, K.; Sarp, S. An overview of oil–water separation using gas flotation systems. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Han, X.; Huang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J. Characterization and migration of oil and solids in oily sludge during centrifugation. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintella, C.M.; Mata, A.M.; Lima, L.C. Overview of bioremediation with technology assessment and emphasis on fungal bioremediation of oil contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailan, S.M.; Ponnamma, D.; Krupa, I. The separation of oil/water mixtures by modified melamine and polyurethane foams: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruthapandi, M.; Saravanan, A.; Manoj, S.; Luong, J.H.; Gedanken, A. Facile ultrasonic preparation of a polypyrrole membrane as an absorbent for efficient oil-water separation and as an antimicrobial agent. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 78, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Jing, X.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, P.-Y.; He, P.; Liu, Y. Superhydrophobic cellulose nanofibril/silica fiber/Fe3O4 nanocomposite aerogel for magnetically driven selective oil absorption. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8909–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, G.; Liu, R.; Yan, Z.; Yin, Y. Fatigue resistant aerogel/hydrogel nanostructured hybrid for highly sensitive and ultrabroad pressure sensing. Small 2022, 18, 2104706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.; Li, D.-D.; Chen, L.; Ma, M.-G. Collaboration of two-star nanomaterials: The applications of nanocellulose-based metal organic frameworks composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchtová, N.; Budtova, T. Cellulose aero-, cryo- and xerogels: Towards understanding of morphology control. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2585–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, S.S. Coherent expanded aerogels and jellies. Nature 1931, 127, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budtova, T. Cellulose II aerogels: A review. Cellulose 2019, 26, 81–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigacci, A.; Budtova, T.; Smirnova, I. Aerogels: A fascinating class of materials with a wide potential of application fields. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olalekan, A.P.; Dada, A.O.; Adesina, O.A. Silica aerogel as a viable absorbent for oil spill remediation. J. Encapsulation Adsorpt. Sci. 2014, 4, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lü, X.; Cui, Z.; Wei, W.; Xie, J.; Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, J. Constructing polyurethane sponge modified with silica/graphene oxide nanohybrids as a ternary sorbent. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 284, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Zhang, F.; Yu, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y. Hydrothermal formation of graphene aerogel for oil sorption: The role of reducing agent, reaction time and temperature. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3040–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhuo, Q.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Z.; Fan, H. Hydrophobic silica aerogel reinforced with carbon nanotube for oils removal. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Gu, B.; Pennefather, M.P.; Nguyen, T.X.; Phan-Thien, N.; Duong, H.M. Cotton aerogels and cotton-cellulose aerogels from environmental waste for oil spillage cleanup. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, H. Ultralight, hydrophobic, sustainable, cost-effective and floating kapok/microfibrillated cellulose aerogels as speedy and recyclable oil superabsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, C.; Yu, D.; Wu, M. A facile method to prepare superhydrophobic nanocellulose-based aerogel with high thermal insulation performance via a two-step impregnation process. Cellulose 2022, 29, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Yuan, X.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H. Superhydrophobic cellulose-based aerogel derived from Phormium tenax (harakeke) for efficient oil sorption. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 202, 116981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Shi, S.; Guo, H.; Xie, L.; Chai, X.; Xu, K.; Du, G.; Zhang, L. Self-crosslinking of metal-organic framework (MOF-801) in nanocellulose aerogel for efficient adsorption of Cr (VI) in water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, T.; Jiang, T.; Wang, C.; Luan, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z. Preparation and adsorption properties of magnetic hydrophobic cellulose aerogels based on refined fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilamian, M.; Noroozi, B. Rice straw agri-waste for water pollutant adsorption: Relevant mesoporous super hydrophobic cellulose aerogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Scalable fabrication of efficient and recycling wood residue-derived sponge for crude oil adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qi, G.; Kenny, J.M.; Puglia, D.; Ma, P. Effect of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Lignin Nanoparticles on Mechanical, Antioxidant and Water Vapour Barrier Properties of Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked PVA Films. Polymers 2020, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wang, M.; Wu, T.; Guo, L.; Han, W. Covalent Crosslinking Cellulose/Graphene Aerogels with High Elasticity and Adsorbability for Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption. Polymers 2023, 15, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Hu, L.; Liu, C.; Ren, X.; Zhou, Y. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Cross-Linked Nanocellulose Aerogels for Oil–Water Separation. Polymers 2021, 13, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Gao, R.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. Fabrication and characterization of nanofibrillated cellulose and its aerogels from natural pine needles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 119, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Guo, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.-F.; Feng, Y.; He, M.; Yao, J. Glutaraldehyde and polyvinyl alcohol crosslinked cellulose membranes for efficient methyl orange and Congo red removal. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5065–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.G.; Kim, H.C.; Palem, R.R.; Kim, J.; Kang, T.J. Cross-linking of cellulose nanofiber films with glutaraldehyde for improved mechanical properties. Mater. Lett. 2019, 250, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, J.; Yang, Q.; Tian, H.; Shi, Z.; Yao, J.; et al. Facile fabrication of Fe3O4 nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber aerogel from Fe-ion cross-linked cellulose nanofibrils as anode for lithium-ion battery with superhigh capacity. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 829, 154541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, S.; Cassie, A.B.D. 8—The Water Repellency of Fabrics and a New Water Repellency Test. J. Text. Inst. 1945, 36, T67–T90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieian, F.; Hosseini, M.; Jonoobi, M.; Yu, Q. Development of hydrophobic nanocellulose-based aerogel via chemical vapor deposition for oil separation for water treatment. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4695–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z. Coir fiber-reinforced PVA aerogels for oil adsorption. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 16265–16268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Kwon, T.-H.; Im, H.; Moon, D.-I.; Baek, D.J.; Seol, M.-L.; Duarte, J.P.; Choi, Y.-K. A polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sponge for the selective absorption of oil from water. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4552–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Ji, B.; Jiang, R.; Cui, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhou, M.; Li, Z. Polydimethylsiloxane/carbonized bacterial cellulose sponge for oil/water separation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Kettunen, M.; Ras, R.H.A.; Ikkala, O. Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivito, F.; Algieri, V.; Jiritano, A.; Tallarida, M.A.; Costanzo, P.; Maiuolo, L.; De Nino, A. Bio-Based Polyurethane Foams for the Removal of Petroleum-Derived Pollutants: Sorption in Batch and in Continuous-Flow. Polymers 2023, 15, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaquera, A.L.M.; Herrera, M.U.; Manalo, R.D.; Maguyon-Detras, M.C.; Futalan, C.C.M.; Balela, M.D.L. Oil Adsorption Kinetics of Calcium Stearate-Coated Kapok Fibers. Polymers 2023, 15, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Lu, B.; Gao, J.; Jin, X.; Sun, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Qu, L. Reconstruction of Inherent Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystals for Large-Scale Fabrication of Structure-Intact Graphene Aerogel Bulk toward Practical Applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11407–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.V.; Tri, N.; Tran, B.A.; Dao Duy, T.; Nguyen, S.T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Phan, A.N.; Mai Thanh, P.; Huynh, H.K.P. Synthesis, Characteristics, Oil Adsorption, and Thermal Insulation Performance of Cellulosic Aerogel Derived from Water Hyacinth. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 26130–26139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Hu, L.; Bo, C.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y. Bio-inspired castor oil modified cellulose aerogels for oil recovery and emulsion separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 636, 128043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fu, Q.; Liu, H.; Gu, H.; Guo, Z. Solvent-free nanoalumina loaded nanocellulose aerogel for efficient oil and organic solvent adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, D.; Gangawane, K.M. Superhydrophobic hybrid silica-cellulose aerogel for enhanced thermal, acoustic, and oil absorption characteristics. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 13385–13402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z. Preparation of antifouling and highly hydrophobic cellulose nanofibers/alginate aerogels by bidirectional freeze-drying for water-oil separation in the ocean environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Fan, Z.; Duong, H.M. Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 270, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CA | MCA | HMCA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (mg/cm3) | 9.47 | 14.63 | 18.25 |
| Porosity (%) | 99.38 | 99.04 | 98.80 |
| Material | Adsorption Capacity (g/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulosic aerogel from water hyacinth | 40.40–43.3 | [43] |
| TiO2-coated nanocellulose aerogels | 20–40 | [39] |
| Cellulose/tannic acid/castor oil aerogels | 53.2–113.8 | [44] |
| Nanoalumina-loaded nanocellulose aerogel | 64.83–117.64 | [45] |
| Hybrid silica–cellulose aerogel | 24.8 | [46] |
| Cellulose nanofibers/alginate aerogels | 88.91 | [47] |
| HMCA | 61.56–113.49 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Y.; Yuan, X. Superhydrophobic, Magnetic Aerogels Based on Nanocellulose Fibers Derived from Harakeke for Oily Wastewater Remediation. Polymers 2023, 15, 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193941
Zhai Y, Yuan X. Superhydrophobic, Magnetic Aerogels Based on Nanocellulose Fibers Derived from Harakeke for Oily Wastewater Remediation. Polymers. 2023; 15(19):3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193941
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Yitong, and Xiaowen Yuan. 2023. "Superhydrophobic, Magnetic Aerogels Based on Nanocellulose Fibers Derived from Harakeke for Oily Wastewater Remediation" Polymers 15, no. 19: 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193941
APA StyleZhai, Y., & Yuan, X. (2023). Superhydrophobic, Magnetic Aerogels Based on Nanocellulose Fibers Derived from Harakeke for Oily Wastewater Remediation. Polymers, 15(19), 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193941






