Biological Macromolecule Hydrogel Based on Recombinant Type I Collagen/Chitosan Scaffold to Accelerate Full-Thickness Healing of Skin Wounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The Synthesis of CS/rCol/Cu/DMA Hydrogels
2.2. Rheology of CS/rCol/Cu/DMA Hydrogels
2.3. Compression Test of CS/rCol/Cu/DMA Hydrogels
2.4. In Vitro Contact Antibacterial Activity of CS/rCol/Cu/DMA Hydrogels
2.5. ROS Scavenging Ability and Angiogenesis Capacity
2.6. In Vivo Full-Thickness Wound-Healing Test
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
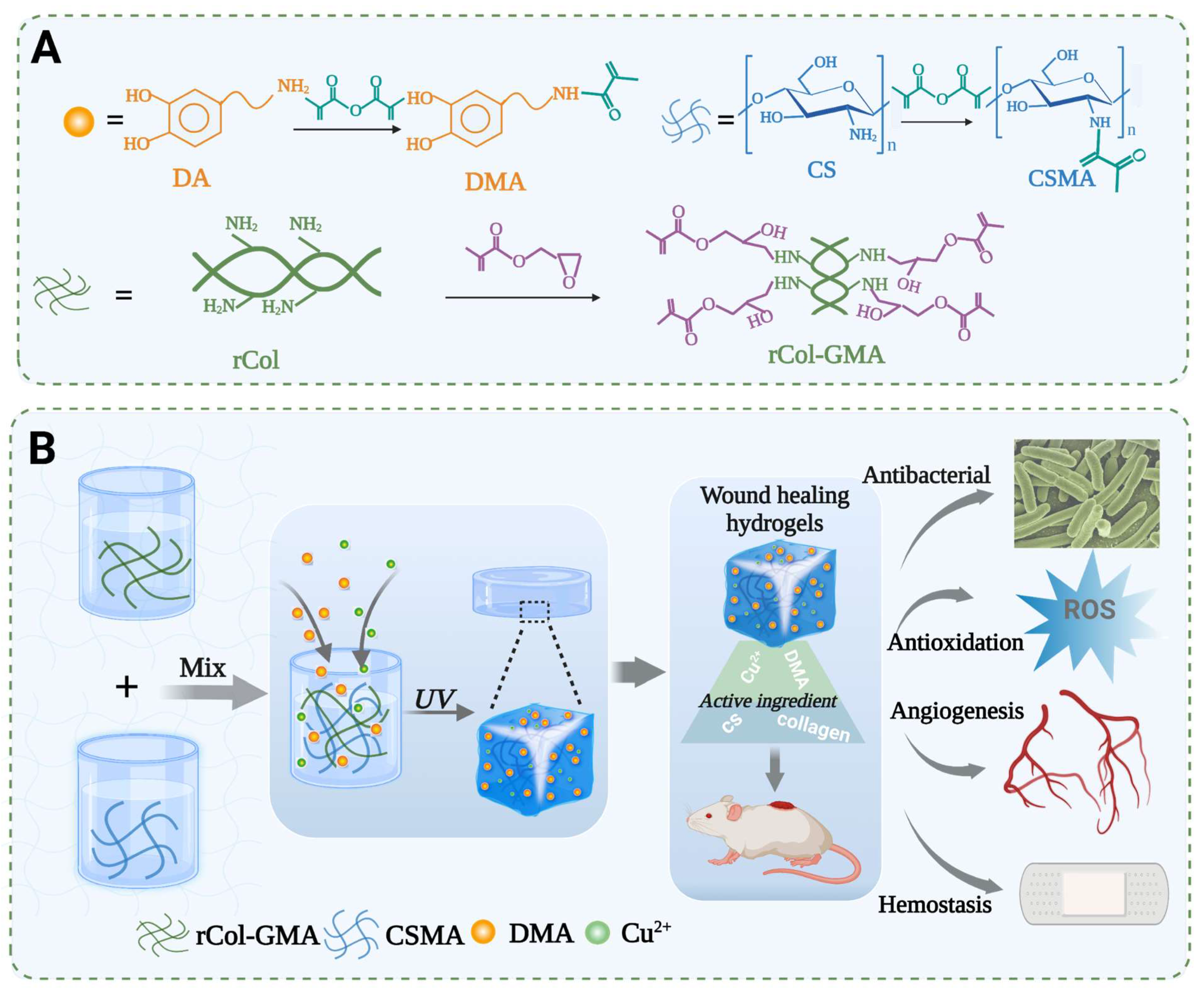
3.1. Acquisition of Recombinant Type I Collagen
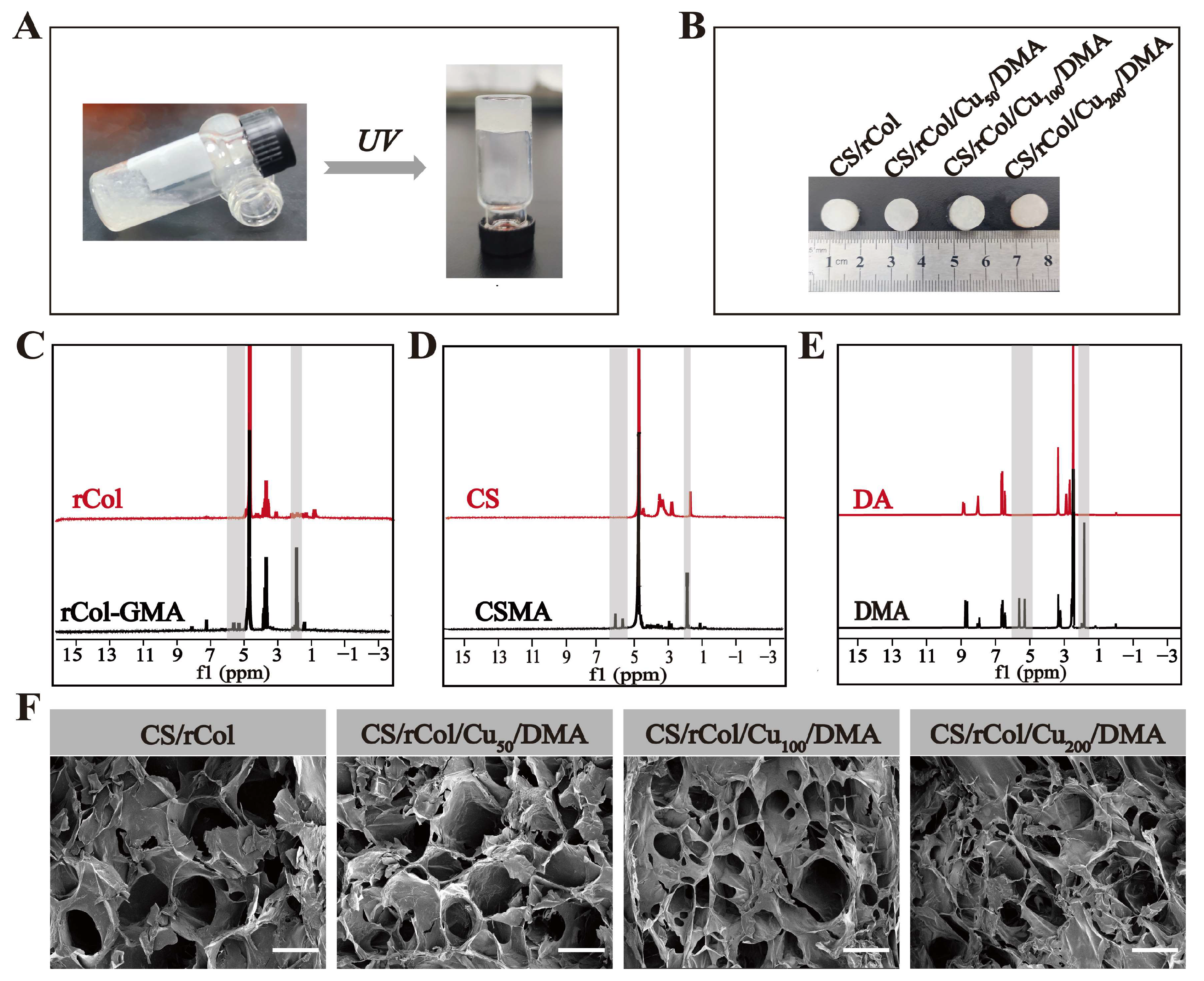
3.2. Preparation of CS/rCol/Cu/DMA Hydrogels
3.3. Characterization of CS/rCol/Cu/DMA Hydrogels
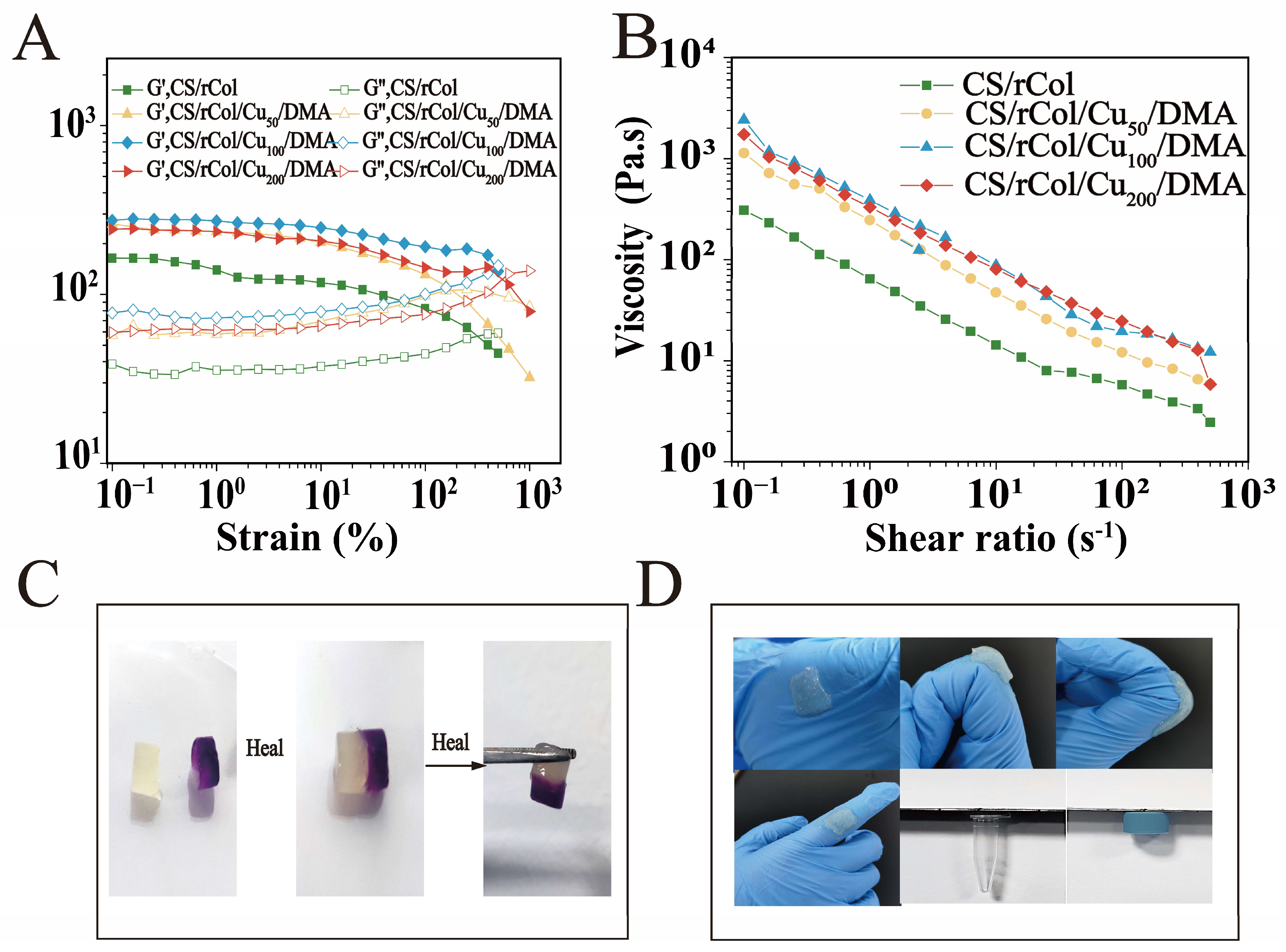
3.4. Rheological, Shear-Thinning, and Self-Healing Property Tests
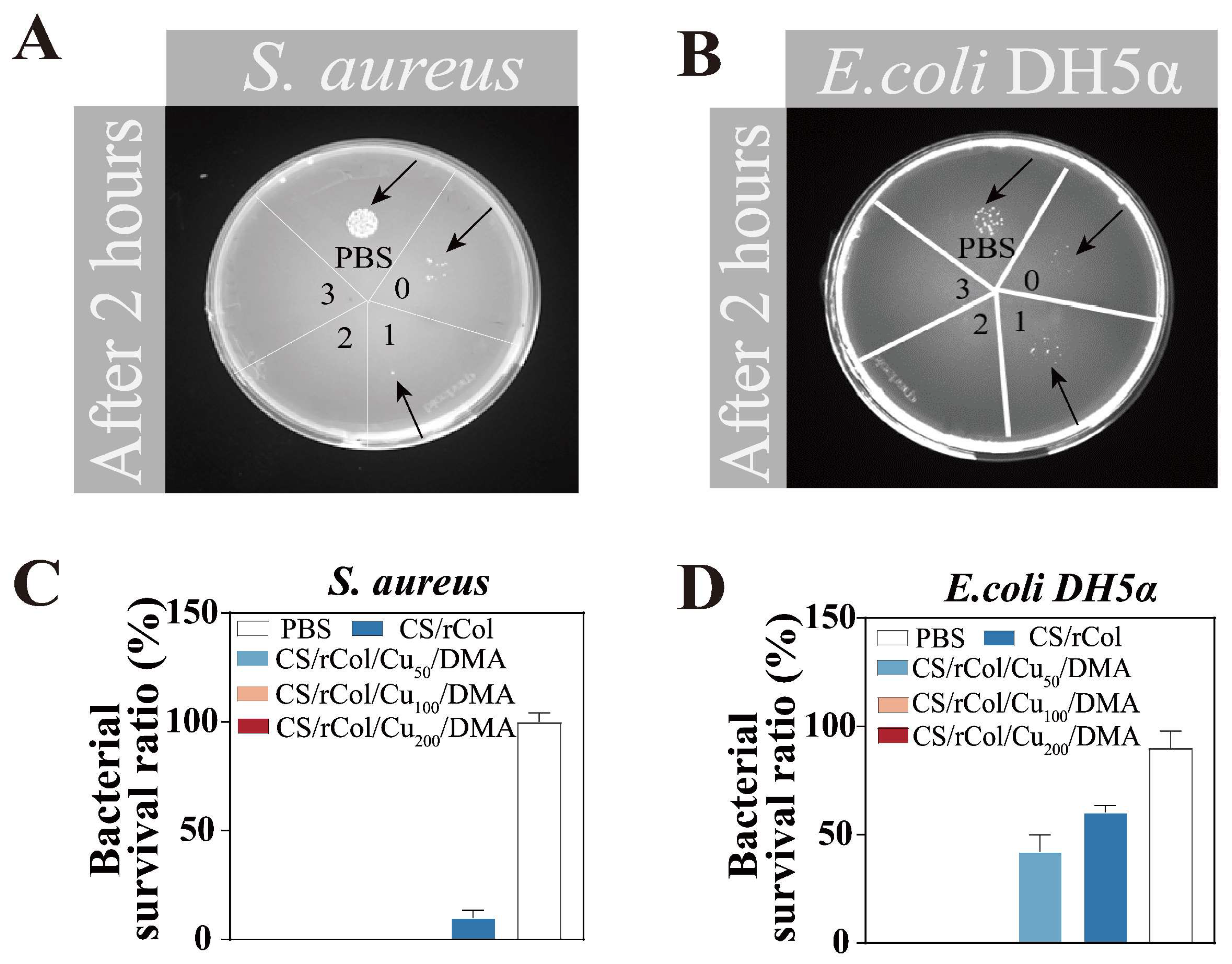
3.5. Contact Antibacterial Activity of the Hydrogel
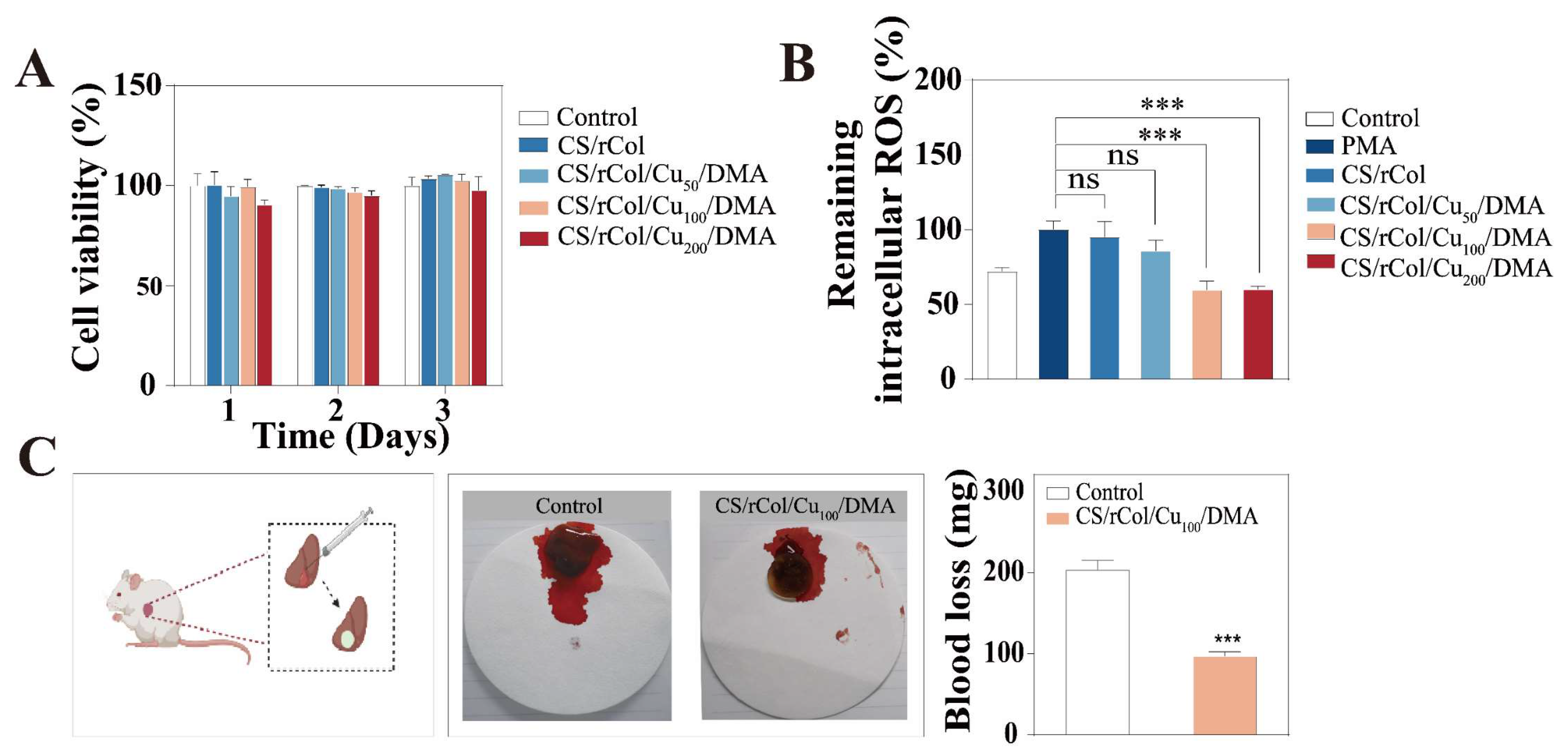
3.6. In Vitro Biocompatibility, Angiogenesis, and ROS Scavenging Ability
3.7. Hemostasis Performance of Hydrogels
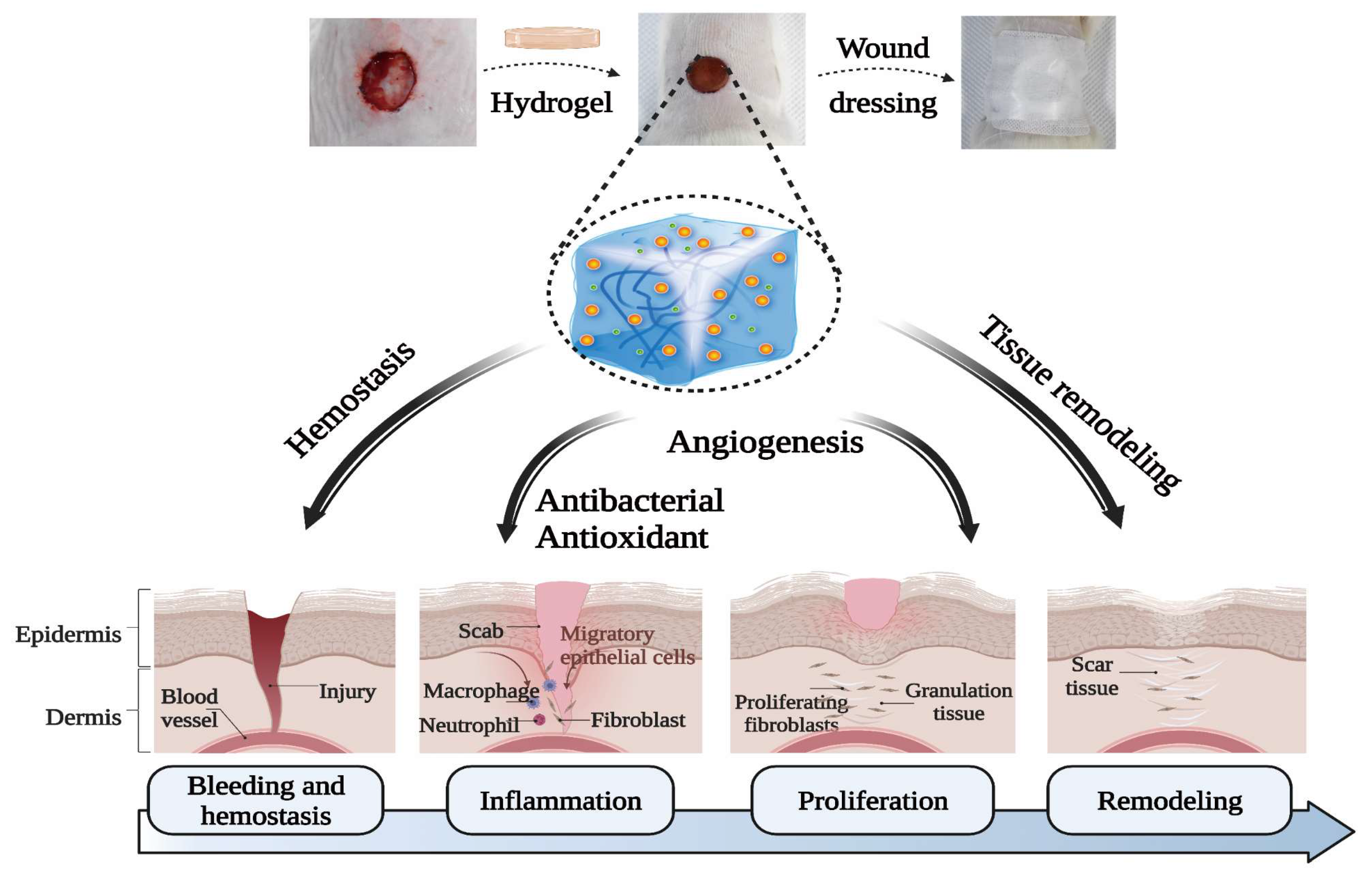
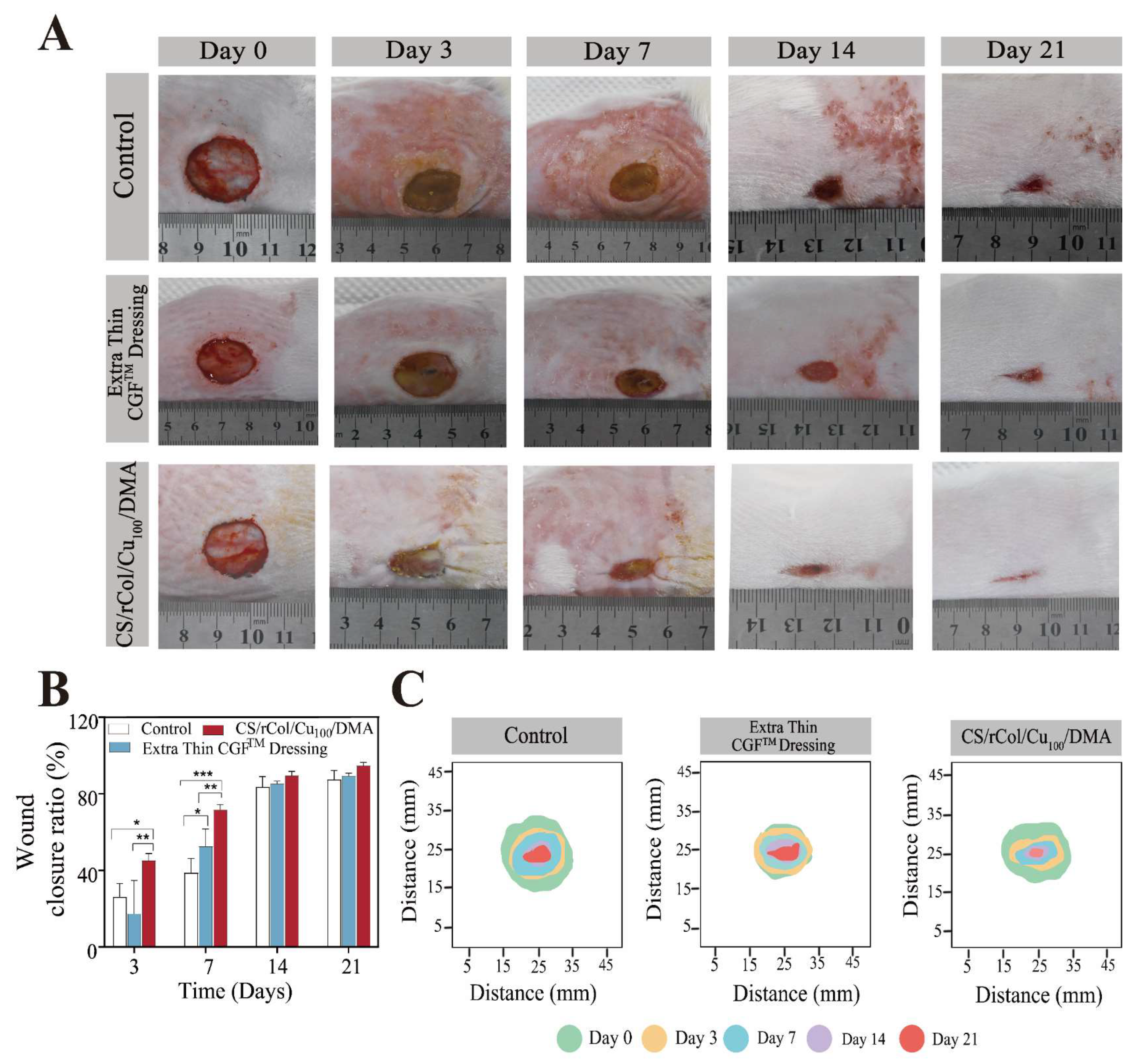
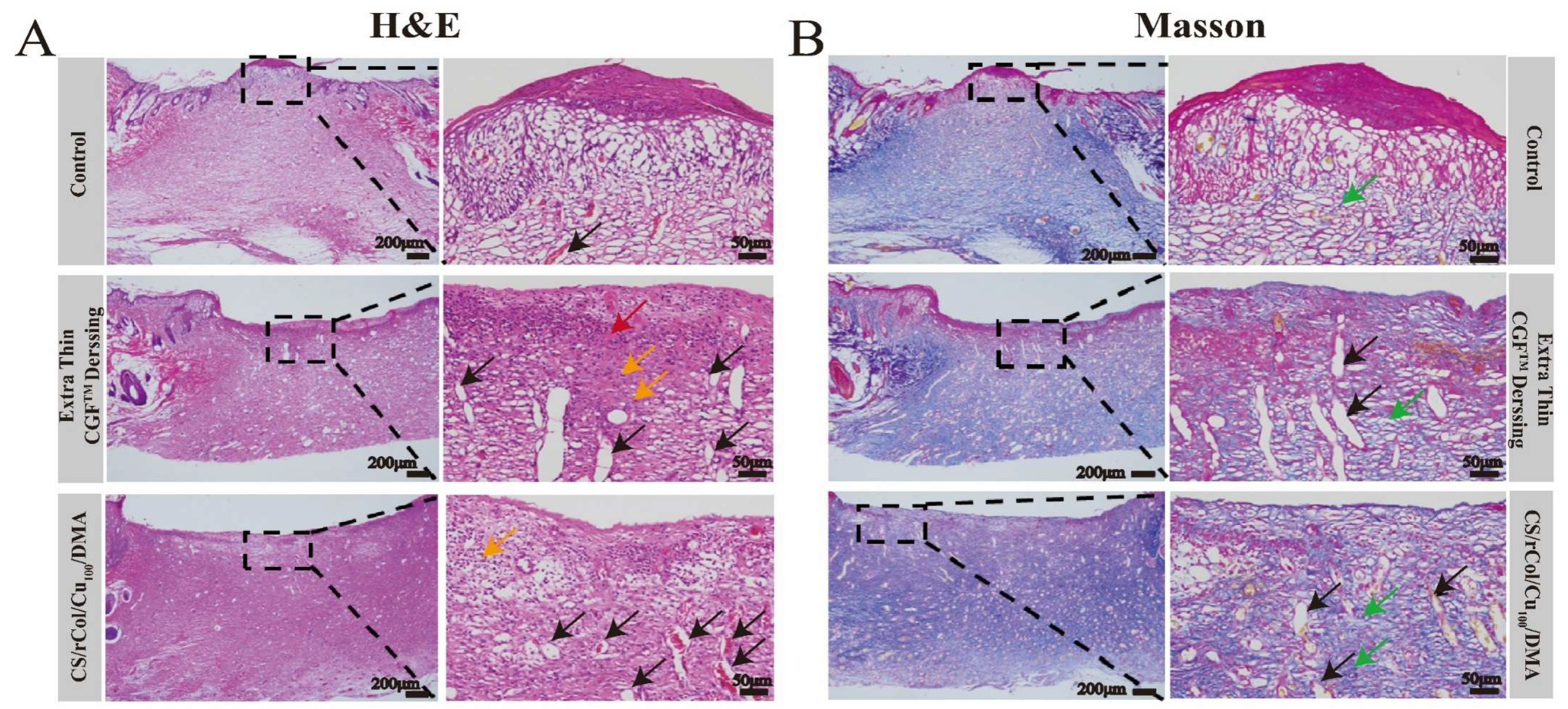
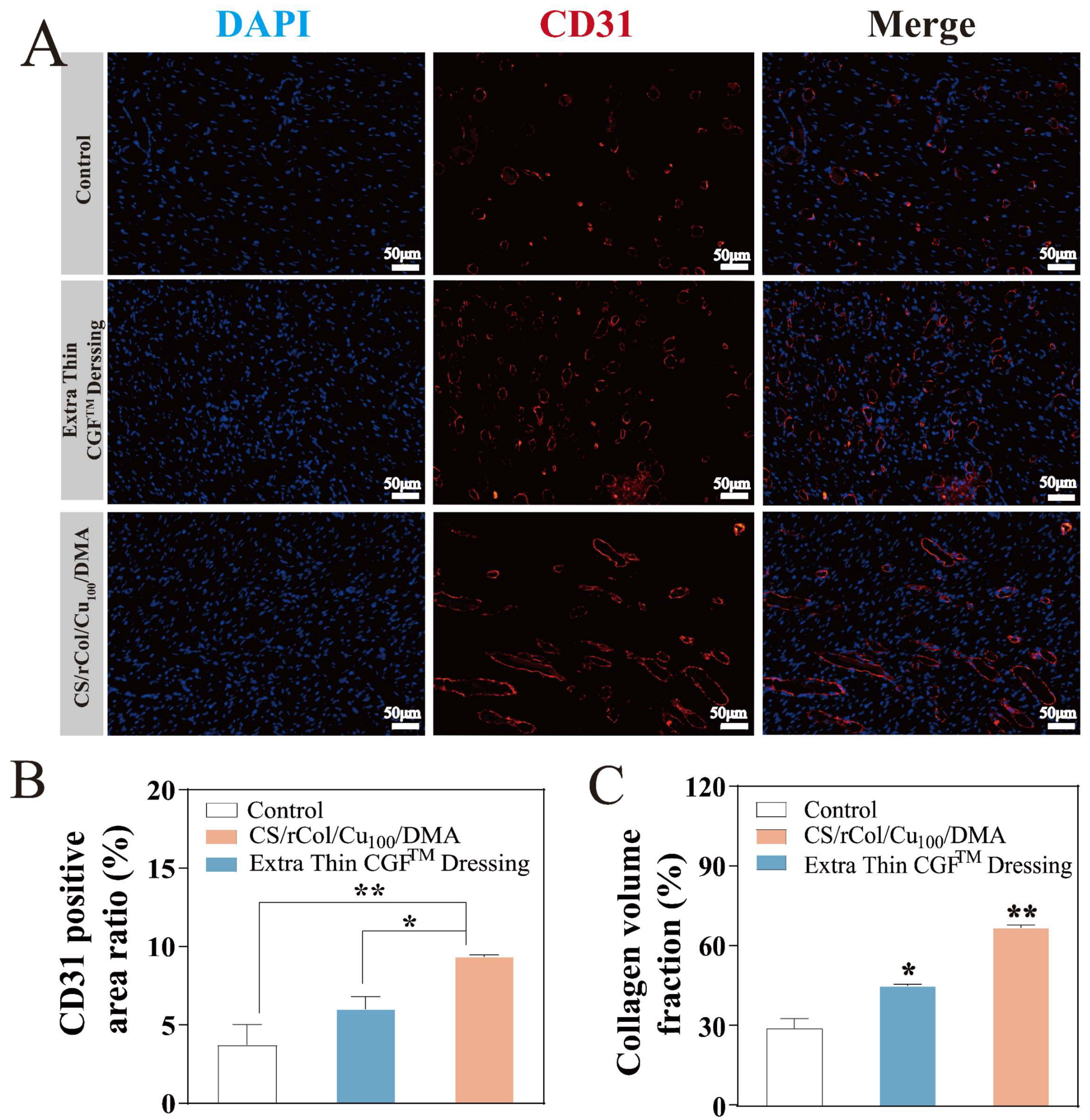
3.8. In Vivo Wound-Healing Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Du, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Injectable Self-Healing Adhesive Natural Glycyrrhizic Acid Bioactive Hydrogel for Bacteria-Infected Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 17562–17576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.G.; Jungvid, H.; Kumar, A. Skin tissue engineering for tissue repair and regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2008, 14, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Qin, D.; Sun, M.; Wang, T.; Chen, X. Research status of self-healing hydrogel for wound management: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2108–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendonca, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.; Shafiee, A. Wound Healing: From Passive to Smart Dressings. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.V.; Staidle, J.P.; Schoenfeld, J.; Benedetto, E.A.; Benedetto, P.X. Comparing the use of a novel antibiotic-free film-forming topical wound dressing versus a topical triple antibiotic in dermatologic surgical procedures including Mohs micrographic surgery. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Bacterial Growth-Induced Tobramycin Smart Release Self-Healing Hydrogel for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Infected Burn Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13022–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N. In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization Methods for Evaluation of Modern Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, C.; Cheng, C.; Shi, C.; Sun, M.; Hu, H.; Shi, T.; Chen, X.; He, X.; Zheng, X.; et al. Bioactive Injectable Hydrogel Dressings for Bacteria-Infected Diabetic Wound Healing: A “Pull-Push” Approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 26404–26417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, J. Assessment of biological properties of recombinant collagen-hyaluronic acid composite scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotz, C.; Schmid, F.F.; Oechsle, E.; Monaghan, M.G.; Walles, H.; Groeber-Becker, F. Cross-linked Collagen Hydrogel Matrix Resisting Contraction To Facilitate Full-Thickness Skin Equivalents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20417–20425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, B.D.; Stegemann, J.P. Strategies for directing the structure and function of three-dimensional collagen biomaterials across length scales. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, D.; Shang, L. Exploring the potential of the recombinant human collagens for biomedical and clinical applications: A short review. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 16, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Oliviero, M.; Vitale, G.A.; Lauritano, C.; D’Ambra, I.; Iannace, S.; de Pascale, D. Marine Collagen from Alternative and Sustainable Sources: Extraction, Processing and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.M.; Vidal, A.R.; Mello, R.O.; Mazutti, M.A.; Cansian, R.L.; Dornelles, R.C.P.; Demiate, I.M.; Kubota, E.H. Ultrasound as an alternative method to increase the extraction yield from chicken mecanically separated meatresidue collagen. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Kiick, K.L. Collagen-like peptides and peptide-polymer conjugates in the design of assembled materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2998–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, N.; Zhang, Y.N.; Assmann, A.; Sani, E.S.; Cheng, G.; Lassaletta, A.D.; Vegh, A.; Dehghani, B.; Ruiz-Esparza, G.U.; Wang, X.; et al. Engineering a highly elastic human protein-based sealant for surgical applications. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Chen, L.; Li, H.H.; Hu, Y.K.; Xiong, Y.H.; Huang, W.; Su, S.S.; Qi, S.H. [Research advances on the application of natural and recombinant collagen in wound repair]. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi 2022, 38, 978–982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, A.; Deng, A.; Yang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, S. Pore architecture and cell viability on freeze dried 3D recombinant human collagen-peptide (RHC)-chitosan scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 49, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, J.; Si, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, H.; Sheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J. A novel gene recombinant collagen hemostatic sponge with excellent biocompatibility and hemostatic effect. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 178, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, D.; Yang, C.; Bodo, M.; Chang, R.; Leigh, S.; Baez, J.; Carmichael, D.; Perala, M.; Hamalainen, E.R.; Jarvinen, M.; et al. Recombinant collagen and gelatin for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Annu; Ali, A.; Sheikh, J. A review on chitosan centred scaffolds and their applications in tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Biswas, S.; Nurus Sakib, M.; Rashid, T.U. Chitosan based bioactive materials in tissue engineering applications—A review. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ren, Y.; Chang, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Injectable Self-Healing Adhesive Chitosan Hydrogel with Antioxidative, Antibacterial, and Hemostatic Activities for Rapid Hemostasis and Skin Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 34455–34469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Yazdi, M.K.; Zarrintaj, P.; Stadler, F.J.; Ramsey, J.D.; Habibzadeh, S.; Hosseini Rad, S.; Naderi, G.; Saeb, M.R.; et al. Chitosan-based inks for 3D printing and bioprinting. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 62–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.Y.; Le Thi, P.; HwangBo, K.H.; Bae, J.W.; Park, K.D. Tunable and high tissue adhesive properties of injectable chitosan based hydrogels through polymer architecture modulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Dong, Y.; Su, Z.; Yin, R.; Song, A.; Li, S. Preparation, characteristics and assessment of a novel gelatin-chitosan sponge scaffold as skin tissue engineering material. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Ma, W.; Su, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, H. The osteogenic differentiation of dog bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a thermo-sensitive injectable chitosan/collagen/beta-glycerophosphate hydrogel: In vitro and in vivo. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Yan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells in vitro culture and in vivo differentiation in a temperature-sensitive chitosan/beta- glycerophosphate/collagen hybrid hydrogel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70 Pt 1, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, A.; Yang, Y.; Du, S.; Yang, X.; Pang, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, S. Preparation of a recombinant collagen-peptide (RHC)-conjugated chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Sun, J.; Wei, D.; Yuan, L.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X. Photo-crosslinked mono-component type II collagen hydrogel as a matrix to induce chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8707–8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Du, H.; Chai, N.; Sha, Z.; Geng, M.; Zhou, X.; He, C. Tannic acid-reinforced methacrylated chitosan/methacrylated silk fibroin hydrogels with multifunctionality for accelerating wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, J.; Hua, J.; Li, S.; Panchamukhi, A.; Yue, J.; Gou, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhu, L.; et al. A pulsatile release platform based on photo-induced imine-crosslinking hydrogel promotes scarless wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaraev, A.D.; Lerner, M.I.; Bakina, O.V.; Sidelev, D.V.; Tran, T.H.; Krinitcyn, M.G.; Malashicheva, A.B.; Cherempey, E.G.; Slepchenko, G.B.; Kozelskaya, A.I.; et al. Antibacterial Activity and Cytocompatibility of Electrospun PLGA Scaffolds Surface-Modified by Pulsed DC Magnetron Co-Sputtering of Copper and Titanium. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim Al-Khafaji, H.H.; Alsalamy, A.; Abed Jawad, M.; Ali Nasser, H.; Dawood, A.H.; Hasan, S.Y.; Ahmad, I.; Gatea, M.A.; Younis Albahadly, W.K. Synthesis of a novel Cu/DPA-MOF/OP/CS hydrogel with high capability in antimicrobial studies. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1236580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Ghule, N.W.; Bamer, A.H.; Kalaskar, M.G. Metal nanoparticles synthesis: An overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, N.R.; Lenz, M.; Wehrli, B.; Fent, K. Comparative effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and dissolved zinc on zebrafish embryos and eleuthero-embryos: Importance of zinc ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.; Xu, T.; Xing, W.; Ge, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; Ren, F.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Contact-Active Antibacterial Hydrogel with High Cell Affinity, Toughness, and Recoverability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1805964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Multifunctional Tissue-Adhesive Cryogel Wound Dressing for Rapid Nonpressing Surface Hemorrhage and Wound Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35856–35872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yu, R.; Guo, B. Dual-Dynamic-Bond Cross-Linked Antibacterial Adhesive Hydrogel Sealants with On-Demand Removability for Post-Wound-Closure and Infected Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7078–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas-Bartolome, M.; Benito-Garzon, L.; Fung, S.; Kohn, J.; Vazquez-Lasa, B.; San Roman, J. Bioadhesive functional hydrogels: Controlled release of catechol species with antioxidant and antiinflammatory behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 105, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Y.; Huang, B.X.; Wang, Q.H.; Wu, W.L.; Coates, P.; Sefat, F.; Lu, C.H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.M. A Mussel-Inspired Antibacterial Hydrogel with High Cell Affinity, Toughness, Self-Healing, and Recycling Properties for Wound Healing. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Frueh, J.; Shao, J.; Gai, M.; Hu, N.; He, Q. Guidable GNR-Fe3O4 -PEM@SiO2 composite particles containing near infrared active nanocalorifiers for laser assisted tissue welding. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 511, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; He, J.; Shi, M.; Liang, Y.; Guo, B. Injectable self-healing supramolecular hydrogels with conductivity and photo-thermal antibacterial activity to enhance complete skin regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Mu, X.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Nie, J.; Yang, D. The photocrosslinkable tissue adhesive based on copolymeric dextran/HEMA. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Chen, Z.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Kong, D.; et al. Construction and application of therapeutic metal-polyphenol capsule for peripheral artery disease. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, N.; Feng, L.; Zhao, M.; Wu, P.; Chai, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, P.; Guo, R. Multifunctional electrospun asymmetric wettable membrane containing black phosphorus/Rg1 for enhancing infected wound healing. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X.; Lei, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, G.; Kong, F.; Guo, J.; Duan, Y.; et al. Polyphenol-mediated biomimetic mineralization of sacrificial metal-organic framework nanoparticles for wound healing. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, M.; Guo, B. Anti-oxidant electroactive and antibacterial nanofibrous wound dressings based on poly(ε-caprolactone)/quaternized chitosan-graft-polyaniline for full-thickness skin wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuanthong, M.; Sirinupong, N.; Youravong, W. Triple helical structure of acid-soluble collagen derived from Nile tilapia skin as affected by extraction temperature. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2016, 96, 3795–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired adhesive antioxidant antibacterial hemostatic composite hydrogel wound dressing via photo-polymerization for infected skin wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, D.; Gan, W.; Zhu, S.; Li, W.; Tian, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Lu, L. Antibacterial poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate/chitosan hydrogels enhance mechanical adhesiveness and promote skin regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Wu, J.; Kirk, T.B.; Xu, J.; Xu, A.; Xue, W. Injectable and Self-Healing Hydrogels with Double-Dynamic Bond Tunable Mechanical, Gel-Sol Transition and Drug Delivery Properties for Promoting Periodontium Regeneration in Periodontitis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 61638–61652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Nthumba, P.M.; Gu, G.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, J. Engineering an adhesive based on photosensitive polymer hydrogels and silver nanoparticles for wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5756–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, M.; Bao, F.; Xing, M.; Wang, E.; Xu, Q.; Huan, Z.; Guo, F.; Chang, J. Multifunctional Zn doped hollow mesoporous silica/polycaprolactone electrospun membranes with enhanced hair follicle regeneration and antibacterial activity for wound healing. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6315–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balitaan, J.N.I.; Hsiao, C.D.; Yeh, J.M.; Santiago, K.S. Innovation inspired by nature: Biocompatible self-healing injectable hydrogels based on modified-beta-chitin for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.; Lin, E.J.; Tartar, D. Immunology of Wound Healing. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2018, 7, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Chen, B.; Yin, Z.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Adhesive Hemostatic Conducting Injectable Composite Hydrogels with Sustained Drug Release and Photothermal Antibacterial Activity to Promote Full-Thickness Skin Regeneration During Wound Healing. Small 2019, 15, e1900046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, E.; Ma, B.; Xu, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhang, M.; Pei, G.; Chang, J. A novel “hot spring”-mimetic hydrogel with excellent angiogenic properties for chronic wound healing. Biomaterials 2021, 264, 120414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. Efficient coexpression of recombinant human fusion collagen with prolyl 4-hydroxylase from Bacillus anthracis in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 70, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Ma, P.X. Stimuli-responsive supramolecular hydrogels with high extensibility and fast self-healing via precoordinated mussel-inspired chemistry. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7627–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozuyuk, U.; Yasa, O.; Yasa, I.C.; Ceylan, H.; Kizilel, S.; Sitti, M. Light-Triggered Drug Release from 3D-Printed Magnetic Chitosan Microswimmers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9617–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Li, K.K.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.X.; Wu, P.P.; Feng, L.B.; Deng, K.X.; Yu, C.J.; Deng, Y.Z.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) loaded gelatin/silk fibroin hydrogels for improving healing in a murine pressure ulcer model. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Biological Macromolecule Hydrogel Based on Recombinant Type I Collagen/Chitosan Scaffold to Accelerate Full-Thickness Healing of Skin Wounds. Polymers 2023, 15, 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193919
Kang D, Wang W, Li Y, Ma Y, Huang Y, Wang J. Biological Macromolecule Hydrogel Based on Recombinant Type I Collagen/Chitosan Scaffold to Accelerate Full-Thickness Healing of Skin Wounds. Polymers. 2023; 15(19):3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193919
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Duo, Wenhai Wang, Yanmei Li, Yi Ma, Yadong Huang, and Jufang Wang. 2023. "Biological Macromolecule Hydrogel Based on Recombinant Type I Collagen/Chitosan Scaffold to Accelerate Full-Thickness Healing of Skin Wounds" Polymers 15, no. 19: 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193919
APA StyleKang, D., Wang, W., Li, Y., Ma, Y., Huang, Y., & Wang, J. (2023). Biological Macromolecule Hydrogel Based on Recombinant Type I Collagen/Chitosan Scaffold to Accelerate Full-Thickness Healing of Skin Wounds. Polymers, 15(19), 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193919





