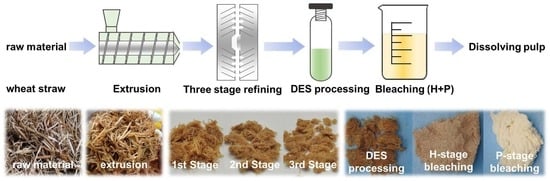
Preparation of Dissolving Pulp by Combined Mechanical and Deep Eutectic Solvent Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Wheat Straw Raw Material and Preparation of DES
2.3. Optimization of DES Processing Conditions
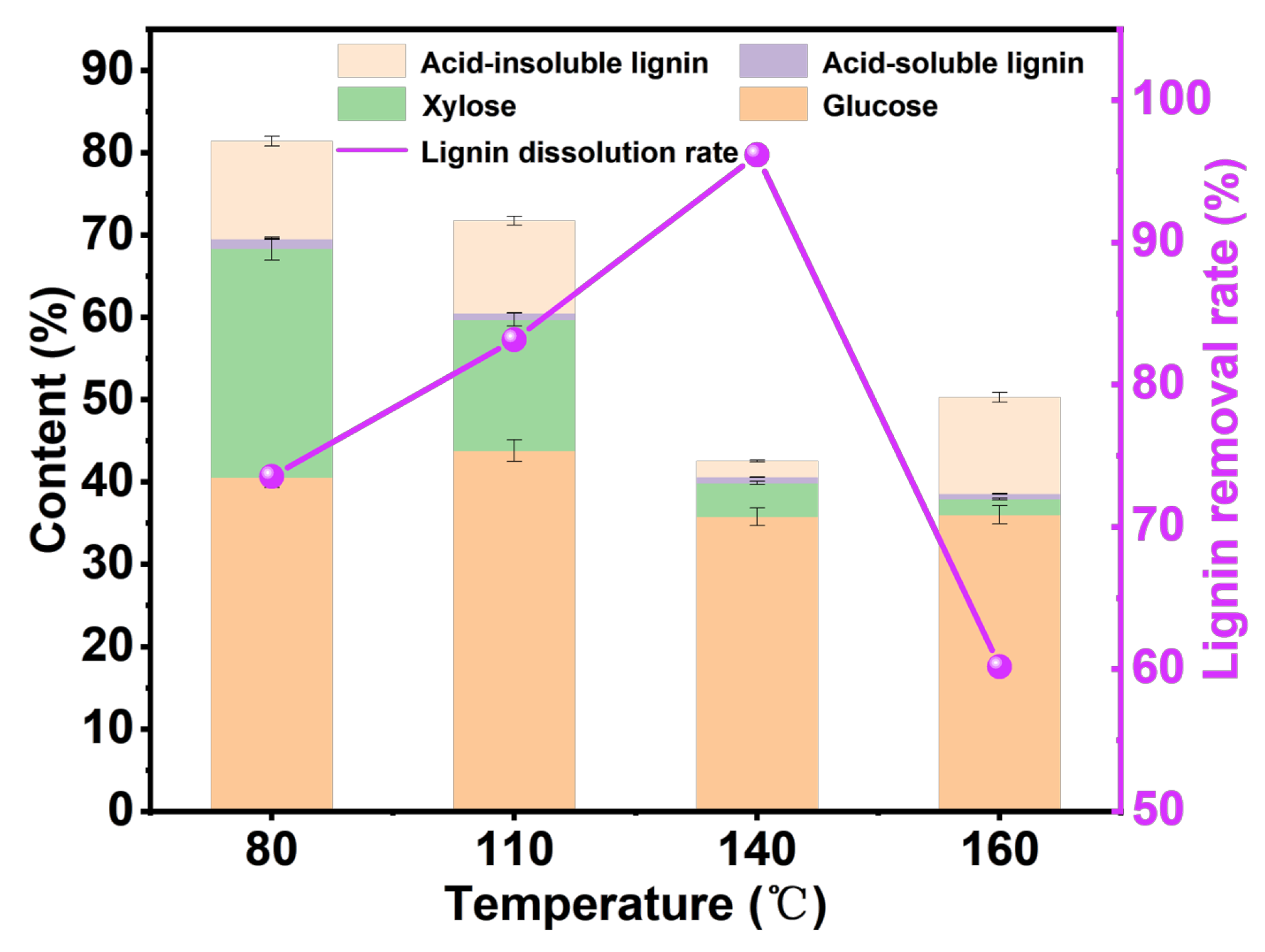
2.3.1. Different Temperatures
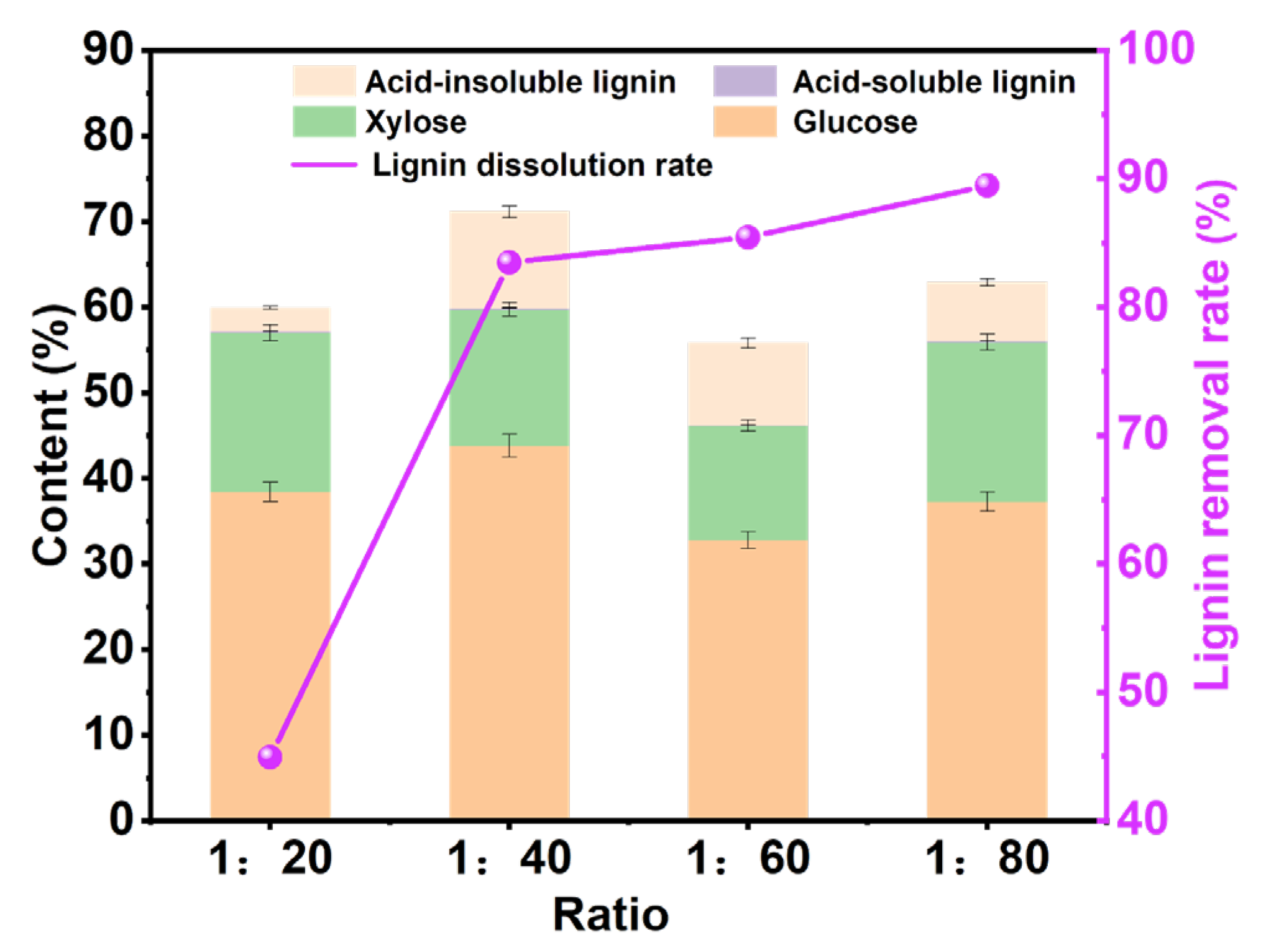
2.3.2. Different Solid–Liquid Ratios
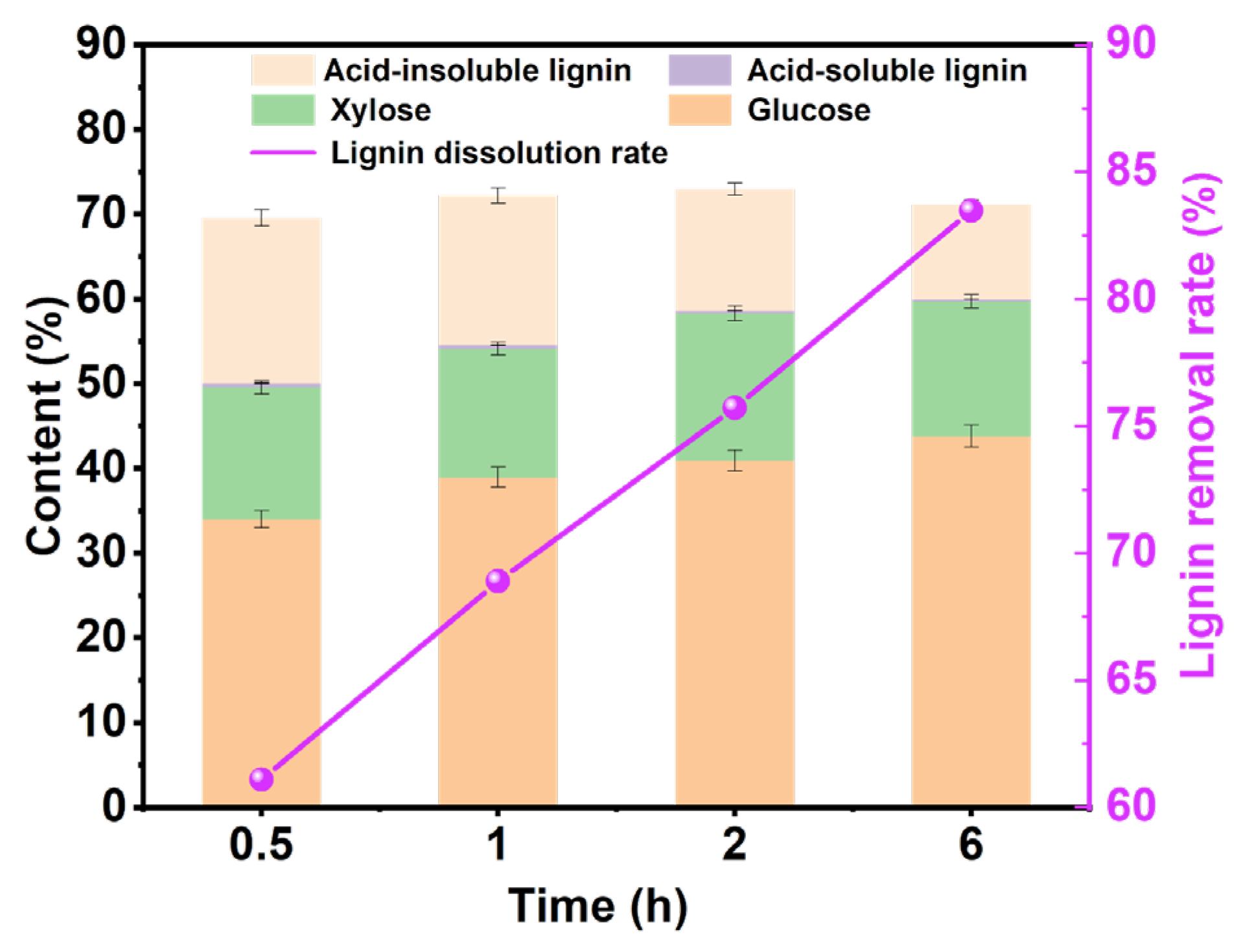
2.3.3. Different Times
2.4. Lignin Recovery and DES Regeneration
2.5. Pulp Bleaching
2.6. Characterizations
2.6.1. SEM
2.6.2. FT-IR
2.6.3. XRD
2.6.4. UV-Vis
2.6.5. Cellulose Component Analysis
2.6.6. Pulp Property Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Mechanical Treatment on Pulp Components
3.2. Optimization of Processing Conditions Using the OFAT Method
3.2.1. Effect of Processing Temperature
3.2.2. Effect of Processing Time
3.2.3. Effect of Solid–Liquid Ratio
3.3. SEM Analysis
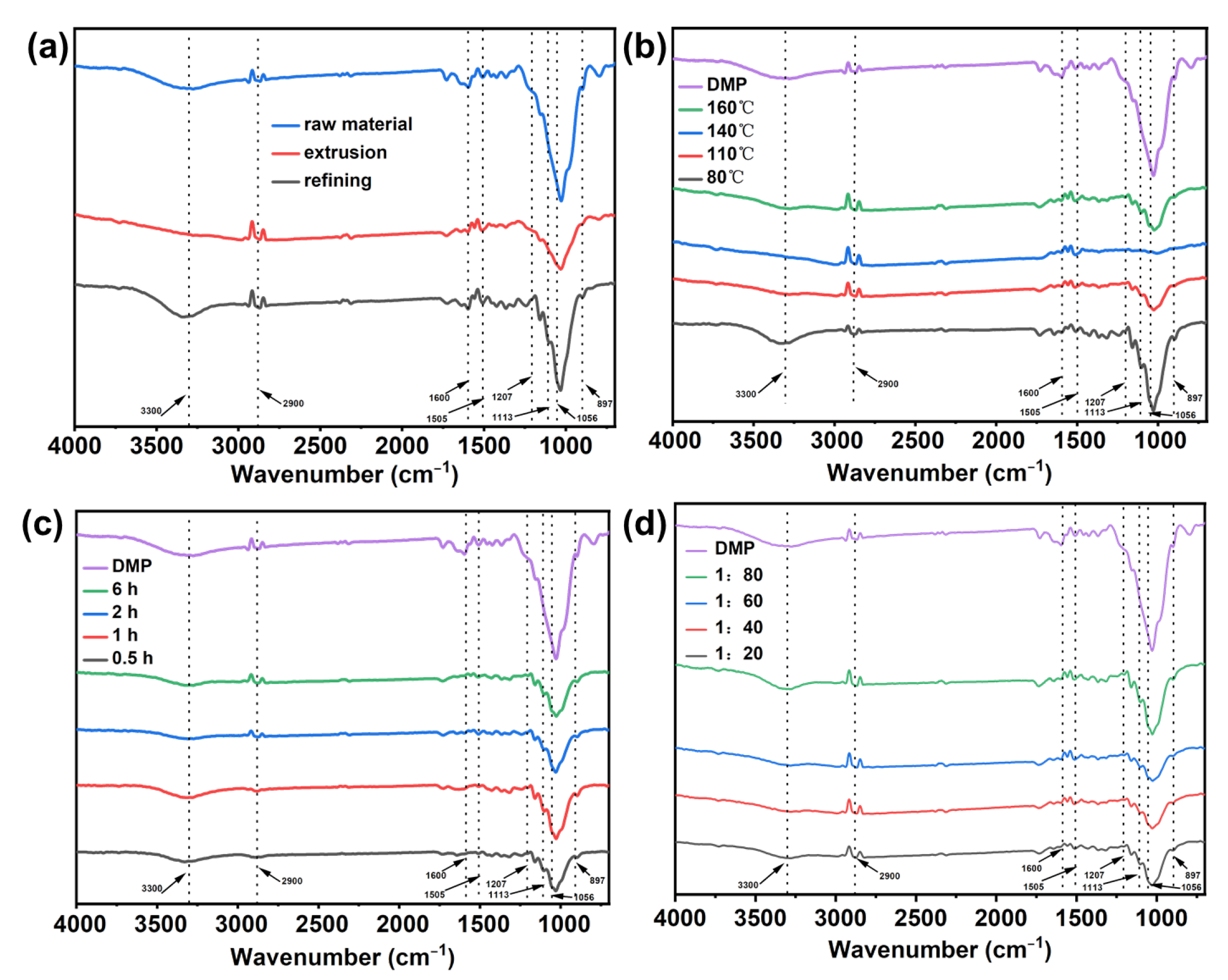
3.4. FT-IR Analysis
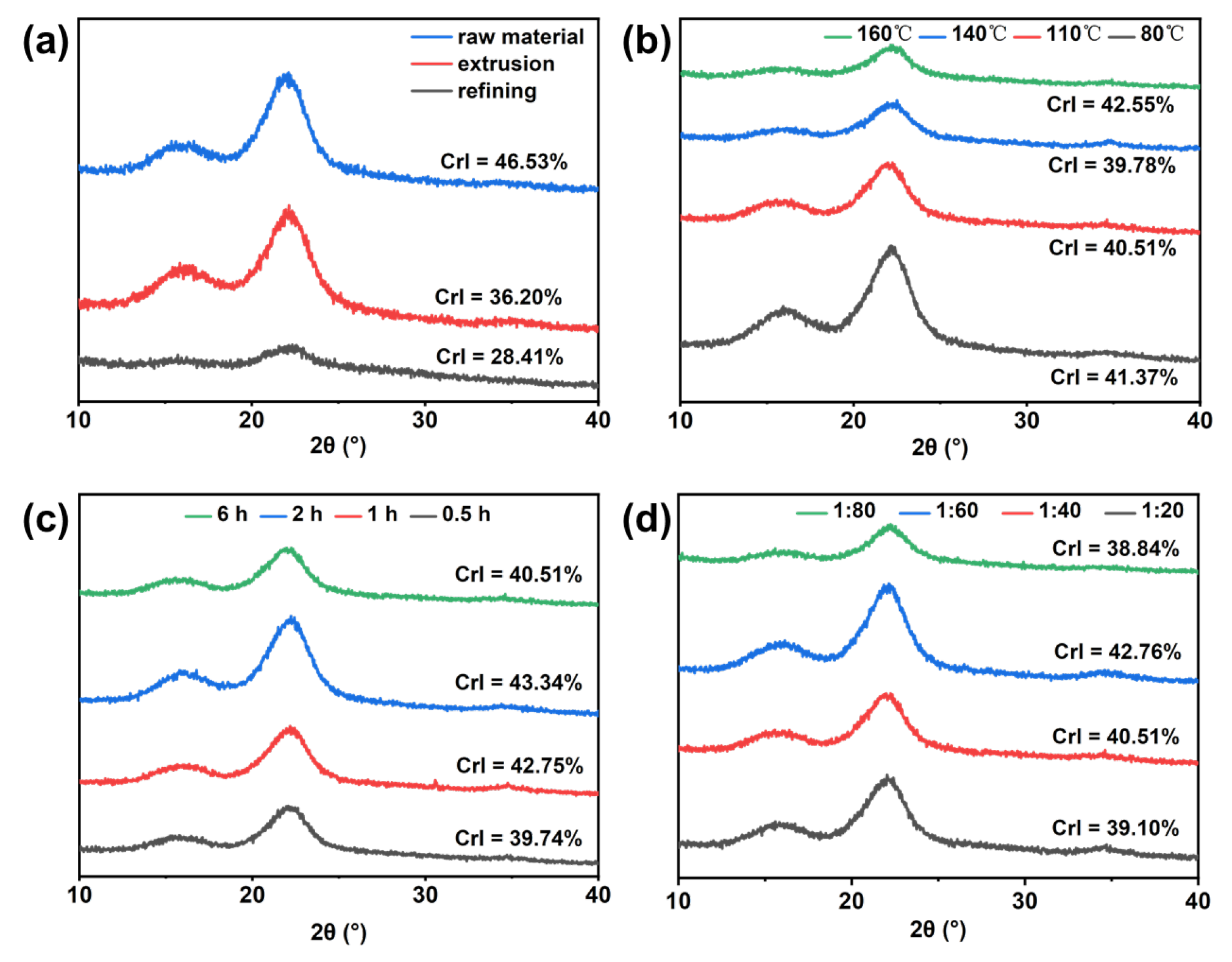
3.5. XRD Analysis
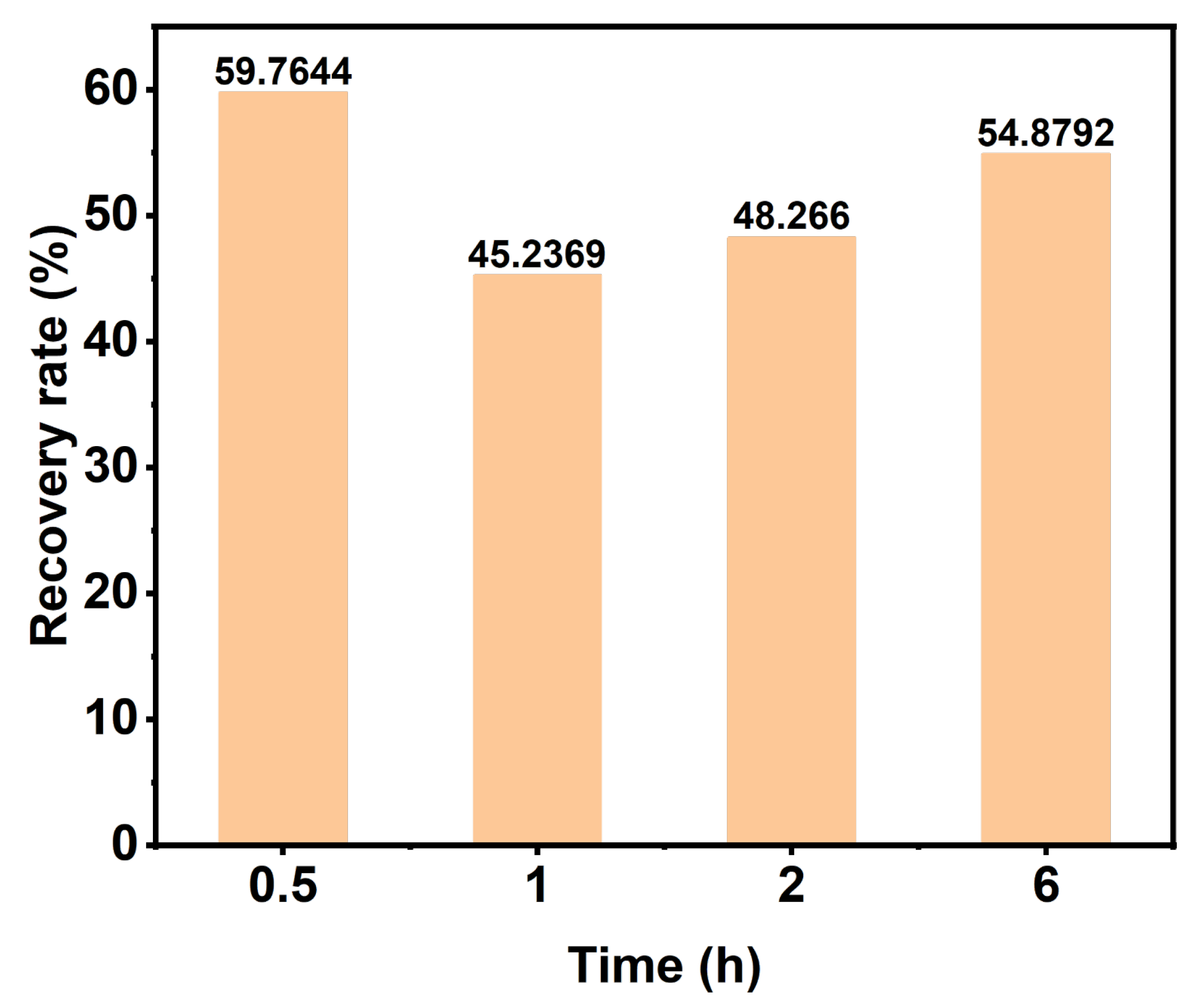
3.6. DES Recovery Analysis
3.7. Pulp Bleaching
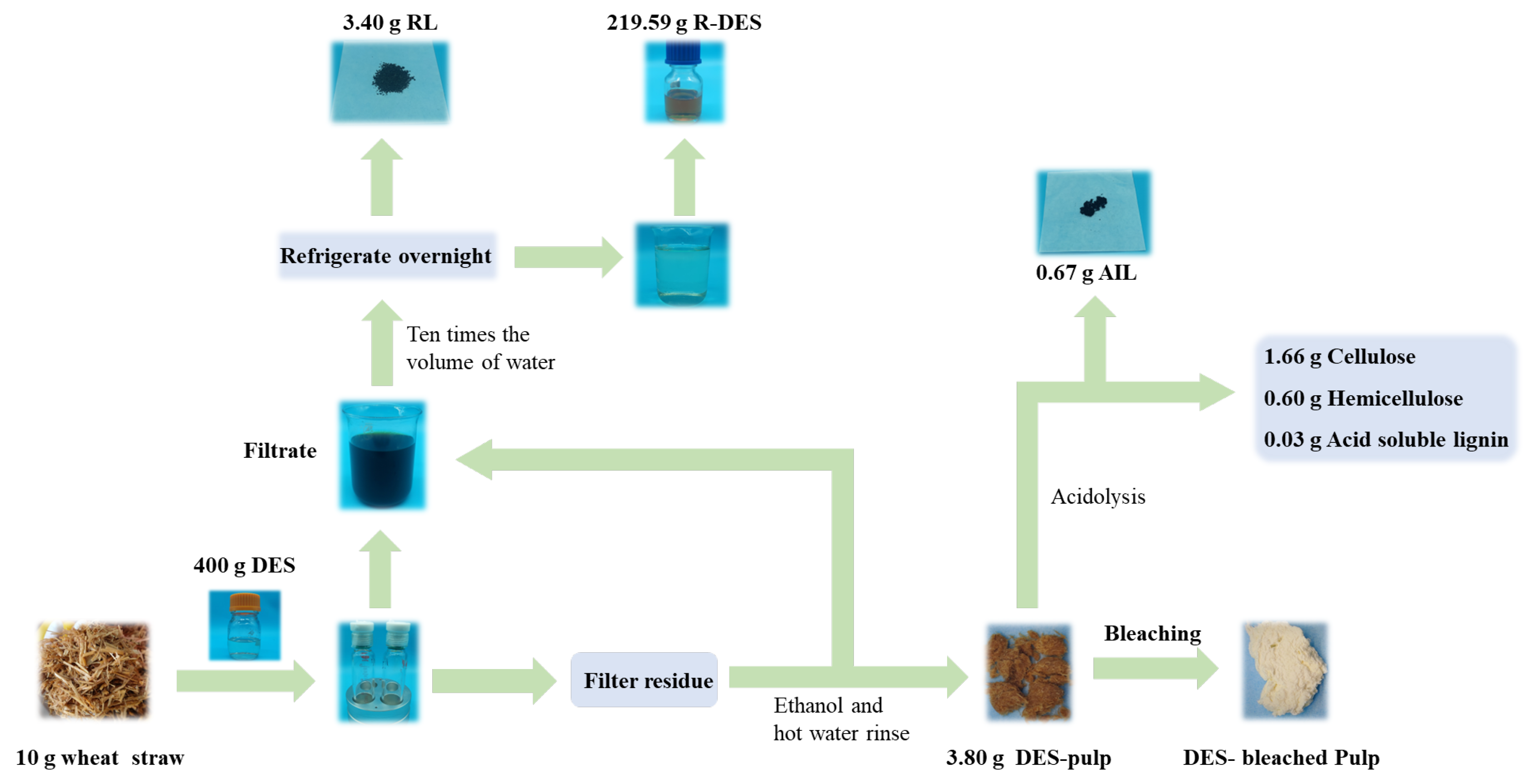
3.8. Mass Balance in the Preparation Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabemanolontsoa, H.; Saka, S. Various pretreatments of lignocellulosics. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessbesell, L.; Paleologou, M.; Leitch, M.; Pulkki, R.; Xu, C. Global lignin supply overview and kraft lignin potential as an alternative for petroleum-based polymers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 123, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourmaud, A.; Shah, D.U.; Beaugrand, J.; Dhakal, H.N. Property changes in plant fibres during the processing of bio-based composites. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 154, 112705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghifar, H.; Venditti, R.; Jur, J.; Gorga, R.E.; Pawlak, J.J. Cellulose-Lignin Biodegradable and Flexible UV Protection Film. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 5, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Y.; Yin, X.; Lei, B. A facile strategy for preparing lignocellulose-based bioplastic by grafting with quaternary ammonium salts. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 174, 114160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Luo, L.; Zhang, F.; Yi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Lü, X. A review on recycling techniques for bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 149, 111370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Arya, S.K. A review on management of rice straw by use of cleaner technologies: Abundant opportunities and expectations for Indian farming. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Kardam, S.K.; Kadam, A.A.; Kumar, V.; Gaikwad, K.K. Green and energy-efficient extraction of cellulose nano-fibrils from rice straw and its coating to improve functional properties of rice straw paperboard made via refiner mechanical pulping. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 165, 106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P. Concerns of the Conventional Pulping Methods. In Environmentally Benign Pulping; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.-J.; Wen, J.-L.; Mei, Q.-Q.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Yuan, T.-Q.; Sun, R.-C. Facile fractionation of lignocelluloses by biomass-derived deep eutectic solvent (DES) pretreatment for cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis and lignin valorization. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xiong, J.; Huang, Z.; Cao, S.; Zong, M.; Lou, W. Improving biocatalysis of cefaclor with penicillin acylase immobilized on magnetic nanocrystalline cellulose in deep eutectic solvent based co-solvent. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Cao, D.; Bi, W.; Chen, D.D.Y. Extraction of Natural Products by Direct Formation of Eutectic Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 12049–12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, S.; Mao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Ren, X.; Yu, Z. High electrochemical activity of a Ti/SnO2-Sb electrode electrodeposited using deep eutectic solvent. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, S.K.; Park, S.; Song, W.; Myung, S.; Jung, H.K.; Lee, S.S.; Yoon, D.H.; An, K.S. Chemically Stabilized and Functionalized 2D—MXene with Deep Eutectic Solvents as Versatile Dispersion Medium. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Mahmood, W.M.A.; Lorwirachsutee, A.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M. Polyol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Extraction of Natural Polyphenolic Antioxidants from Chlorella vulgaris. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5018–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. New natural and renewable low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs): Screening as solvents for lignocellulosic biomass processing. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, C.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Tan, Z. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent systems as a pretreatment for nanofibrillation of ramie fibers. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3069–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo Dugoni, G.; Mezzetta, A.; Guazzelli, L.; Chiappe, C.; Ferro, M.; Mele, A. Purification of Kraft cellulose under mild conditions using choline acetate based deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8680–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Feng, X.; Tian, C.; Tian, G.; Nie, S. Acidic deep eutectic solvent treatment for viscosity control and reactivity enhancement of bamboo dissolving pulp. Cellulose 2023, 30, 2097–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ling, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, F. Integration of facile deep eutectic solvents pretreatment for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis and lignin valorization from industrial xylose residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Tian, C.; Feng, X.; Tian, G.; Liu, X.; Ni, Y. Ultrafast process of microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent to improve properties of bamboo dissolving pulp. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Yu, Y.; Wan, Z.; Zargar, S.; Wu, J.; Bi, R.; Sokhansanj, S.; Tu, Q.; Rojas, O.J. Energy pellets from whole-wheat straw processed with a deep eutectic solvent: A comprehensive thermal, molecular and environmental evaluation. Renew. Energy 2022, 194, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Suopajarvi, T.; Sun, S.; Mankinen, O.; Mikkelson, A.; Huttunen, H.; Komulainen, S.; Romakkaniemi, I.; Ahola, J.; Telkki, V.V.; et al. High-purity lignin fractions and nanospheres rich in phenolic hydroxyl and carboxyl groups isolated with alkaline deep eutectic solvent from wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, R.; Ma, R.; Lin, K.-t.; Ahamed, A.; Zhang, X. Facile Extraction of Wheat Straw by Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) to Produce Lignin Nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10248–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suopajärvi, T.; Ricci, P.; Karvonen, V.; Ottolina, G.; Liimatainen, H. Acidic and alkaline deep eutectic solvents in delignification and nanofibrillation of corn stalk, wheat straw, and rapeseed stem residues. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 145, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.-D.; Lin, K.-P.; Li, A.-L.; Yang, L.-M.; Fu, M.-H. Effect of constituents molar ratios of deep eutectic solvents on rice straw fractionation efficiency and the micro-mechanism investigation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 120, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, K.; He, Z.; Wu, T.; Huang, C.; Liang, L.; Fang, G. Deep eutectic solvent recycling to prepare high purity dissolving pulp. Cellulose 2021, 28, 11503–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C. Efficient removal of lignin from vegetable wastes by ultrasonic and microwave-assisted treatment with ternary deep eutectic solvent. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 149, 112357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yi, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Tan, Z. Light-colored cellulose nanofibrils produced from raw sisal fibers without costly bleaching. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 172, 114009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E.; Conrad, C.M. An Empirical Method for Estimating the Degree of Crystallinity of Native Cellulose Using the X-Ray Diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 2677.8-1994; Fibrous Raw Material. Determination of Acid-Insoluble Lignin. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1994.
- Duan, C.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Stavik, J.; Ni, Y. Comparison of acid sulfite (AS)- and prehydrolysis kraft (PHK)-based dissolving pulps. Cellulose 2015, 22, 4017–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C. Improvement in the Fock test for determining the reactivity of dissolving pulp. Tappi J. 2013, 12, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Fan, L.; An, X. Microwave assisted ionic liquid pretreatment of medicinal plants for fast solvent extraction of active ingredients. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 83, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Bolf, N. Research on Wheat Straw Pulping with Ionic Liquid 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazole Bromide. Kem. U Ind. 2016, 65, 579–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, P.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, S.; Ragauskas, A. Pseudo-lignin and pretreatment chemistry. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1306–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.-L.; Gunny, A.A.N.; Kasim, F.H.; AlNashef, I.M.; Arbain, D. Alkaline deep eutectic solvent: A novel green solvent for lignocellulose pulping. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4085–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, T.; Fu, Q.-J.; Bai, Y.-Y.; Peng, F.; Yao, C.-L. Choline chloride-lactic acid deep eutectic solvent for delignification and nanocellulose production of moso bamboo. Cellulose 2019, 26, 9447–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Escobar, N.; Ospina-Acero, D.; Velasquez-Cock, J.A.; Gomez-Hoyos, C.; Serpa Guerra, A.; Ganan Rojo, P.F.; Velez Acosta, L.M.; Escobar, J.P.; Correa-Hincapie, N.; Triana-Chavez, O.; et al. Use of Fourier Series in X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) for Estimation of Crystallinity in Cellulose from Different Sources. Polymers 2022, 14, 5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achaby, M.; Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Fayoud, N.-E.H.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Trabadelo, V.; Draoui, K.; Ben Youcef, H. Bio-sourced porous cellulose microfibrils from coffee pulp for wastewater treatment. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3873–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinivu, E.C. Protic Ionic Liquids for Lignin Extraction-A Lignin Characterization Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, K.K.; Leppänen, M.; Ceccherini, S.; Seitsonen, J.; Väisänen, S.; Altgen, M.; Johansson, L.S.; Maloney, T.; Ruokolainen, J.; Vuorinen, T. Chemical characterization and ultrastructure study of pulp fibers. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatah, I.; Khalil, H.; Hossain, M.; Aziz, A.; Davoudpour, Y.; Dungani, R.; Bhat, A. Exploration of a Chemo-Mechanical Technique for the Isolation of Nanofibrillated Cellulosic Fiber from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch as a Reinforcing Agent in Composites Materials. Polymers 2014, 6, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Ji, X.; Wang, Q. Production and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibrils from Different Chemical and Mechanical Pulps. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2018, 38, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zheng, G.W.; Zong, M.H.; Li, N.; Lou, W.Y. Recent progress on deep eutectic solvents in biocatalysis. Bioresour. Bioprocess 2017, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liang, L.; Ran, M.; Wu, T.; Wang, B.; Zou, X.; Zhao, M.; Fang, G.; Shen, K. Comparative Evaluation of Organic Acid Pretreatment of Eucalyptus for Kraft Dissolving Pulp Production. Materials 2020, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Pulp Classification | Brightness (%ISO) | Viscosity (mL/g) | α-Cellulose Content (%) | Fock Reactivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES Pulp | 28.64 | 623 | 61.82 | 44.24 |
| DES Bleached Pulp | 73.46 | 472 | 81.79 | 55.85 |
| Pulp Classification | Average Length (mm) | Fines Content (%) | Average Width (µm) | Curl (%) | Kink Angle (°) | Fibrillation (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lc(n) | Lc(l) | Lc(w) | ||||||
| DES Pulp | 0.52 | 0.82 | 1.32 | 86.76 | 29.81 | 5.21 | 37.84 | 1.74 |
| DES Bleached Pulp | 0.49 | 0.71 | 1.05 | 84.63 | 34.44 | 7.30 | 38.84 | 1.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Yang, G. Preparation of Dissolving Pulp by Combined Mechanical and Deep Eutectic Solvent Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163476
Li X, Chen J, Wang B, Zhang L, Zhang K, Yang G. Preparation of Dissolving Pulp by Combined Mechanical and Deep Eutectic Solvent Treatment. Polymers. 2023; 15(16):3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163476
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xincai, Jiachuan Chen, Baobin Wang, Lei Zhang, Kai Zhang, and Guihua Yang. 2023. "Preparation of Dissolving Pulp by Combined Mechanical and Deep Eutectic Solvent Treatment" Polymers 15, no. 16: 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163476
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, J., Wang, B., Zhang, L., Zhang, K., & Yang, G. (2023). Preparation of Dissolving Pulp by Combined Mechanical and Deep Eutectic Solvent Treatment. Polymers, 15(16), 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163476