Wound Dressing Double-Crosslinked Quick Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Modified Nanocellulose
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Oxidation of Cellulose Nanocrystals
2.3. Functionalization of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Nanofibers
2.4. Preparation of DACNC/CMC Hydrogels and CMC/ DACNC/ HCNF Hydrogels
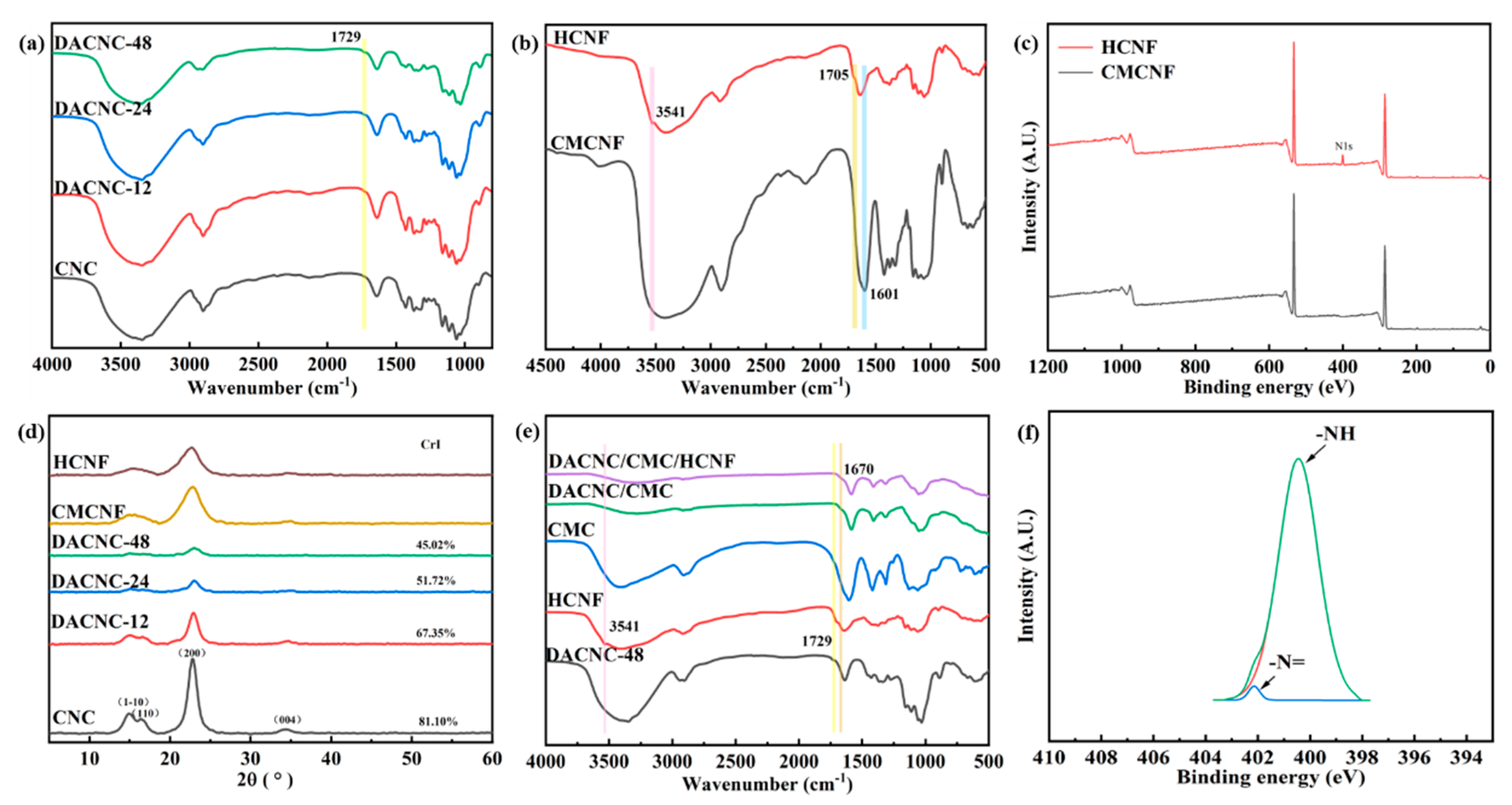
2.5. Verification of Modified Raw Materials and Hydrogels
2.6. Self-Healing Research
2.7. In Vitro Cytocompatibility Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
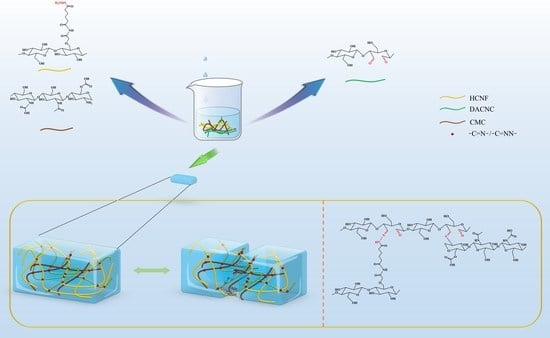
3.1. Formation of CMC/DACNC/HCNF Hydrogels
3.2. Fluid Absorption Capacity
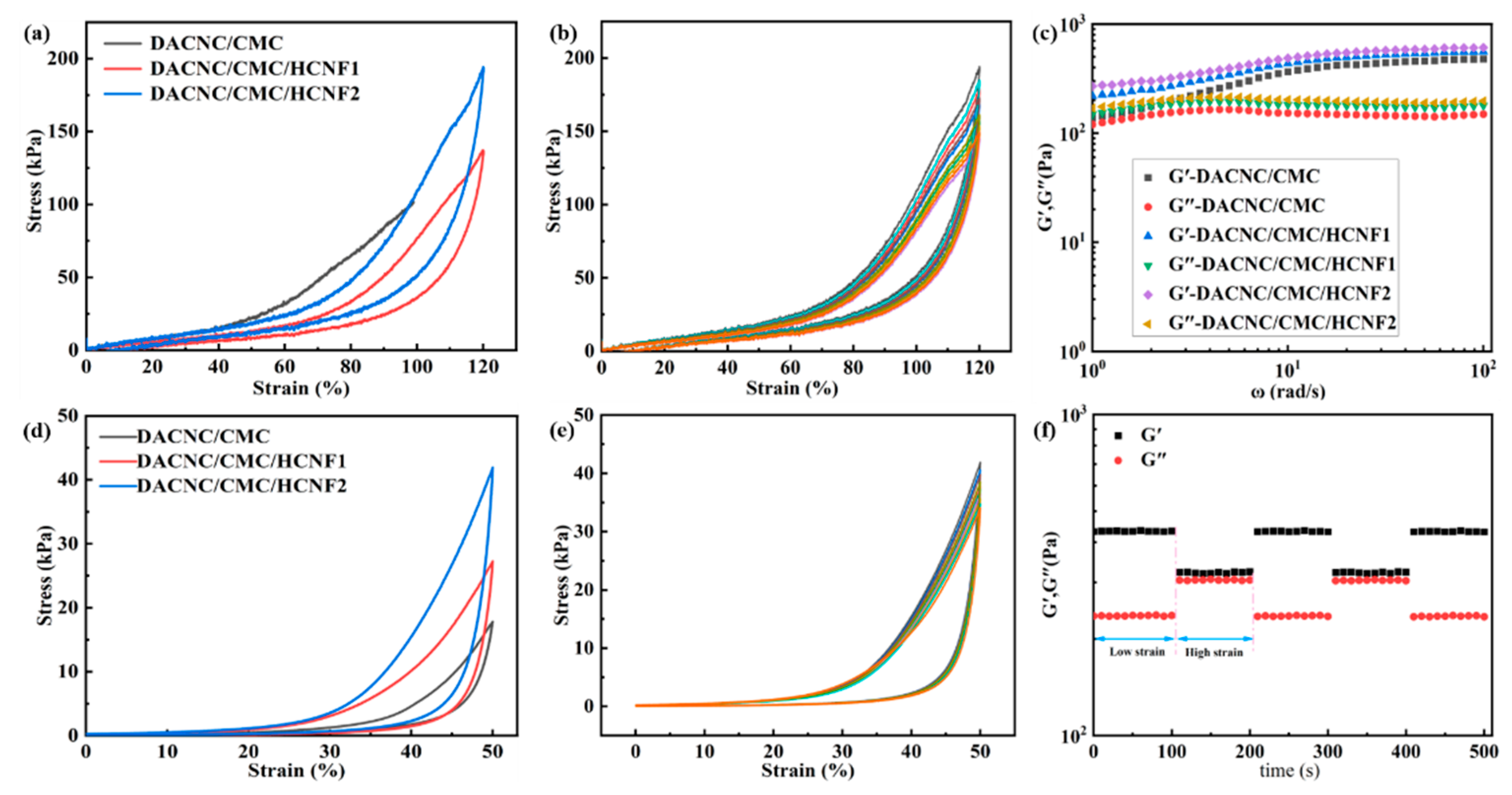
3.3. Mechanical Strength
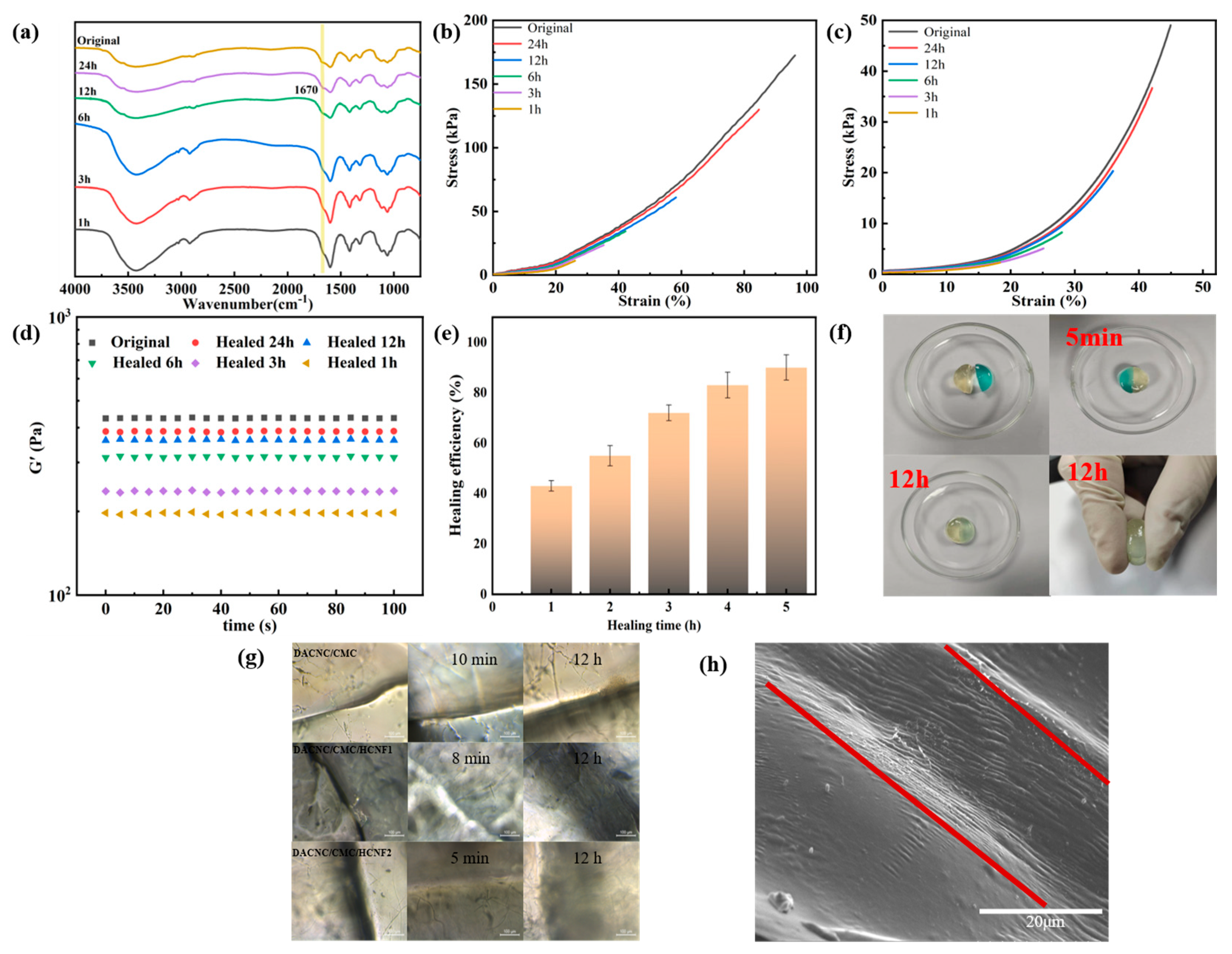
3.4. Self-Healing Performance
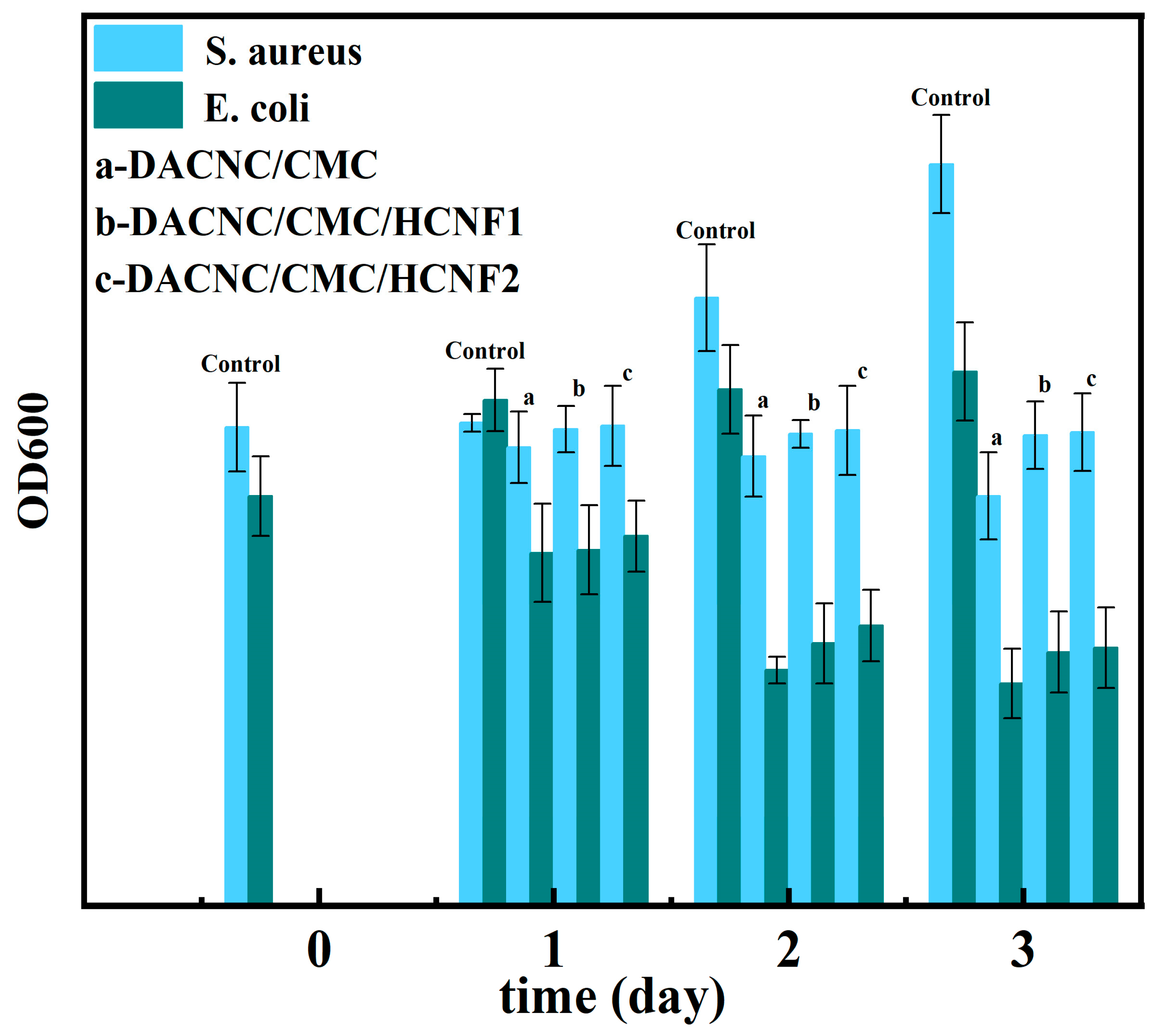
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
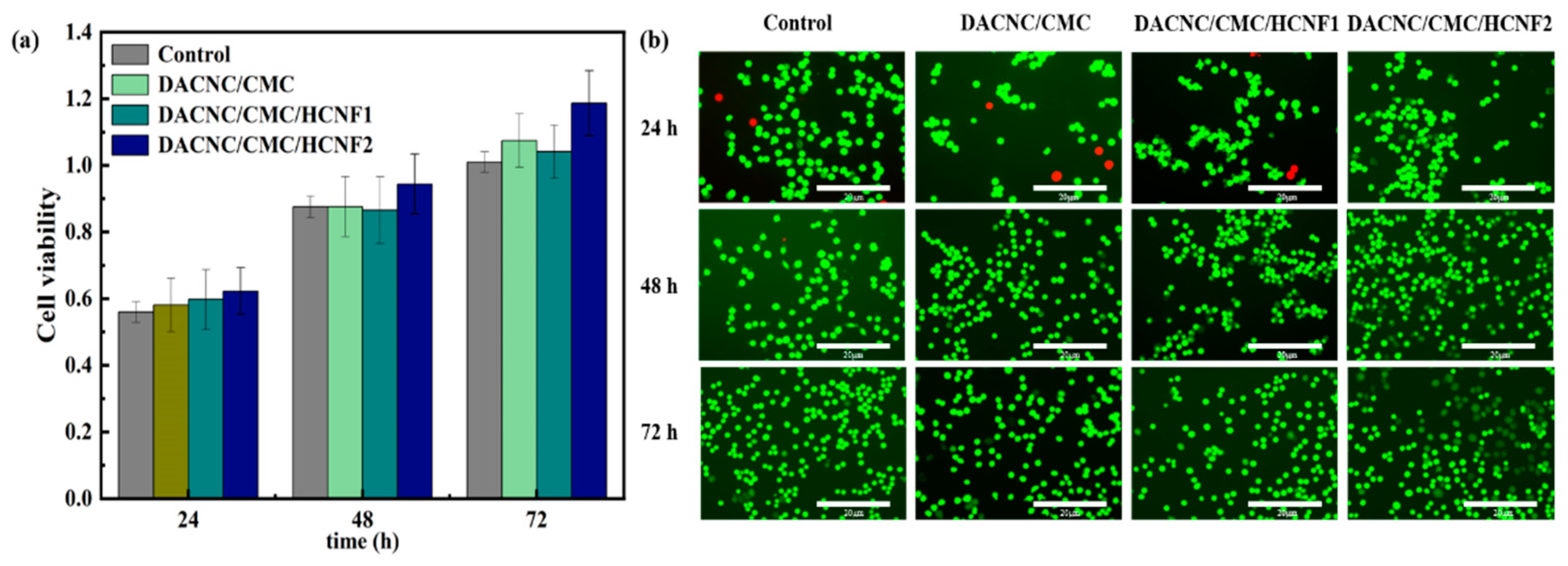
3.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dąbrowska, A.; Spano, F.; Derler, S.; Adlhart, C.; Spencer, N.; Rossi, R. The relationship between skin function, barrier properties, and body-dependent factors. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monavarian, M.; Kader, S.; Moeinzadeh, S.; Jabbari, E. Regenerative Scar-Free Skin Wound Healing. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2019, 25, 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimova, N.; Lyundup, A.; Lyubimov, R.; Mel’Nichenko, G.; Nikolenko, V. Pathophysiological aspects of wound healing in normal and diabetic foot. Ann. Russ. Acad. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portou, M.; Baker, D.; Abraham, D.; Tsui, J. The innate immune system, toll-like receptors and dermal wound healing: A review. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Xu, F.-J. Rational design and latest advances of polysaccharide-based hydrogels for wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 2084–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Mohamad, N.; Low, W.-L.; Martin, C.; Amin, M.C.I.M. Microwaved bacterial cellulose-based hydrogel microparticles for the healing of partial thickness burn wounds. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Fu, Y.V.; Xu, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Lee, C. A Novel Double-Crosslinking-Double-Network Design for Injectable Hydrogels with Enhanced Tissue Adhesion and Antibacterial Capability for Wound Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veld, R.C.O.; Walboomers, X.F.; Jansen, J.A.; Wagener, F.A. Design Considerations for Hydrogel Wound Dressings: Strategic and Molecular Advances. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2020, 26, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, P.; Cheng, Q.; He, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J. Ultrafast Fabrication of Self-Healing and Injectable Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Dressing for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 24095–24105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X. Alginate hydrogel dressings for advanced wound management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Mao, L.; Yuan, M.; Liao, W. Novel fenugreek gum-cellulose composite hydrogel with wound healing synergism: Facile preparation, characterization and wound healing activity evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Rehman, H.U.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Ultratough, Self-Healing, and Tissue-Adhesive Hydrogel for Wound Dressing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33523–33531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, J.; Ran, L.; Yu, K.; Lu, B.; Lan, G.; Dai, F.; Lu, F. An injectable self-healing hydrogel with adhesive and antibacterial properties effectively promotes wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. On-Demand Dissolvable Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Cellulose Nanocrystal for Deep Partial Thickness Burn Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41076–41088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Wei, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sheng, N.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S. All-natural injectable hydrogel with self-healing and antibacterial properties for wound dressing. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2637–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Peng, Y.; Chen, L.; Fu, S. Effects of cellulose nanofibrils on dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose based dual responsive self-healing hydrogel. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8813–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardean, C.; Davidescu, C.M.; Nemeş, N.S.; Negrea, A.; Ciopec, M.; Duteanu, N.; Negrea, P.; Duda-Seiman, D.; Musta, V. Factors Influencing the Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan and Chitosan Modified by Functionalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.S.; Mohammadi, Z.; Amini, M.; Yousefi, M.; Tarighi, P.; Eftekhari, S.; Tehrani, M.R. Thiolated chitosan-lauric acid as a new chitosan derivative: Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia, Z. Carboxymethyl chitosan: Properties and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, M.E.; Li, K.; Qian, J.; Wang, L.; Lavoine, N.; Newman, R.; Gardner, D.J.; Li, T.; Hu, L.; Ragauskas, A.J.; et al. Recent Advances in Functional Materials through Cellulose Nanofiber Templating. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2005538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Javaid, M.U.; Pan, C.; Yu, G.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Self-healing stimuli-responsive cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishkewich, N.; Mohammed, N.; Tang, J.; Tam, K.C. Recent advances in the application of cellulose nanocrystals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 29, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, P.; Sherje, A.P. Cellulose nanocrystals: Fundamentals and biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.K.; Frollini, E.; Thakur, V.K. Cellulose nanocrystals: Pretreatments, preparation strategies, and surface functionalization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1554–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Miri, N.; Heggset, E.B.; Wallsten, S.; Svedberg, A.; Syverud, K.; Norgren, M. A comprehensive investigation on modified cellulose nanocrystals and their films properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, S.P.; Langer, R.; Fink, G.R.; Kohane, D.S. Injectable in situ cross-linking hydrogels for local antifungal therapy. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Singh, A.K.; Dravid, A.; Bellare, J.R. Multiscale Porosity in Compressible Cryogenically 3D Printed Gels for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20437–20452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Fawal, G.F.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Elnouby, M.S. Hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel for wound dressing: Fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, T.; Hossain, M.; Rahaman, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Gwon, J.-G.; Lee, B.-T. Multi-functional nanocellulose-chitosan dressing loaded with antibacterial lawsone for rapid hemostasis and cutaneous wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 272, 118482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Patwa, R.; Zandraa, O.; Saha, N.; Saha, P. Preparation and characterization of injectable self-antibacterial gelatin/carrageenan/bacterial cellulose hydrogel scaffolds for wound healing application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, A.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C. Wound Dressing Double-Crosslinked Quick Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Modified Nanocellulose. Polymers 2023, 15, 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163389
Huang A, Chen Y, Wu C. Wound Dressing Double-Crosslinked Quick Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Modified Nanocellulose. Polymers. 2023; 15(16):3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163389
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Anshan, Yehong Chen, and Chaojun Wu. 2023. "Wound Dressing Double-Crosslinked Quick Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Modified Nanocellulose" Polymers 15, no. 16: 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163389
APA StyleHuang, A., Chen, Y., & Wu, C. (2023). Wound Dressing Double-Crosslinked Quick Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Modified Nanocellulose. Polymers, 15(16), 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163389