Biocompatibility and Antimicrobial Profile of Acid Usnic-Loaded Electrospun Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)—Magnetite Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning Deposition of PET Nanofibers
2.3. Magnetite (Fe3O4) Functionalized with Usnic Acid (UA) Synthesis
2.4. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)—Magnetite Nanofibers Functionalized with Usnic Acid Synthesis
2.5. Physico-Chemical Characterization
2.5.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
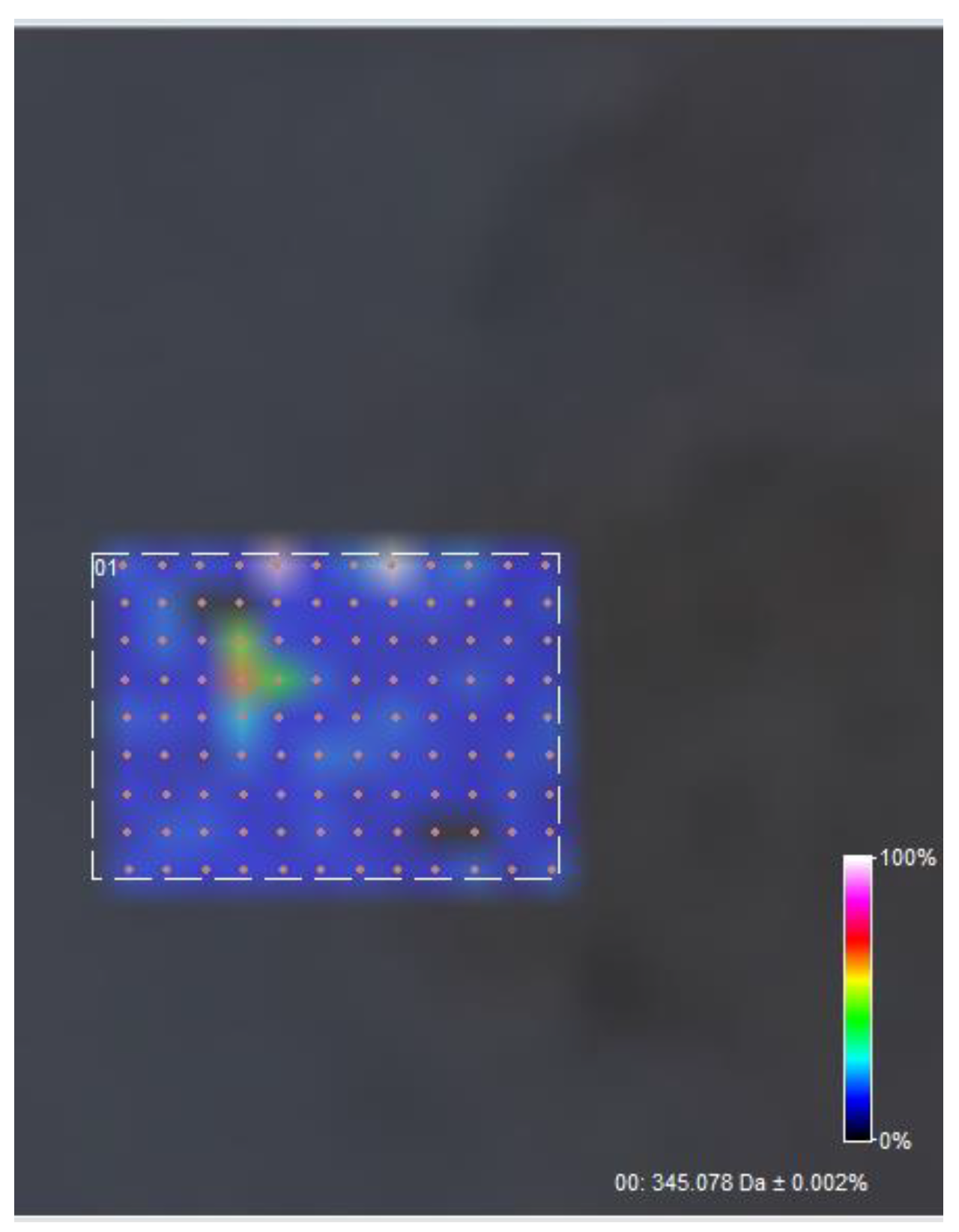
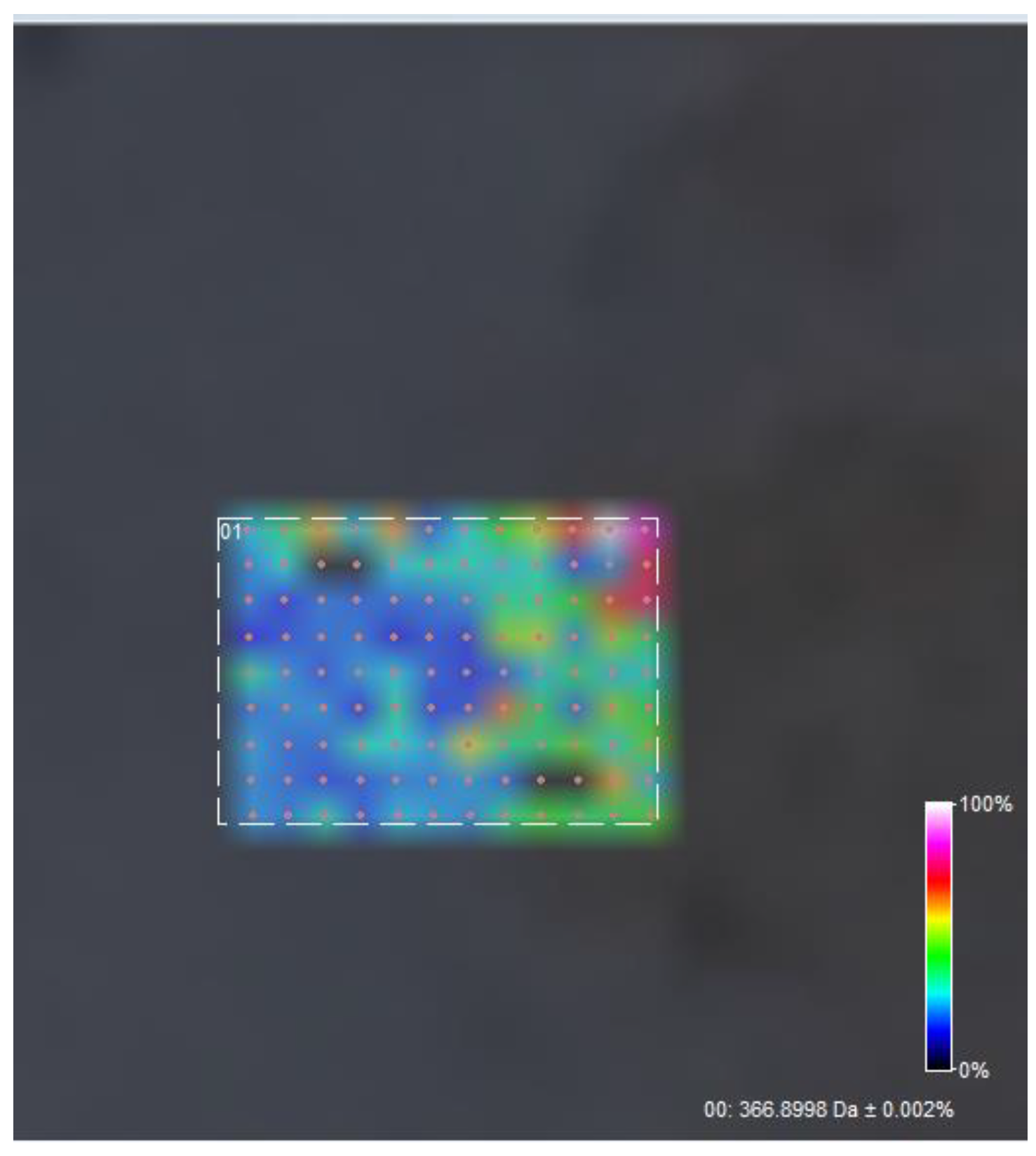
2.5.5. FT-ICR-MALDI
2.6. Biological Characterization
2.6.1. In Vitro Antibacterial Experiments
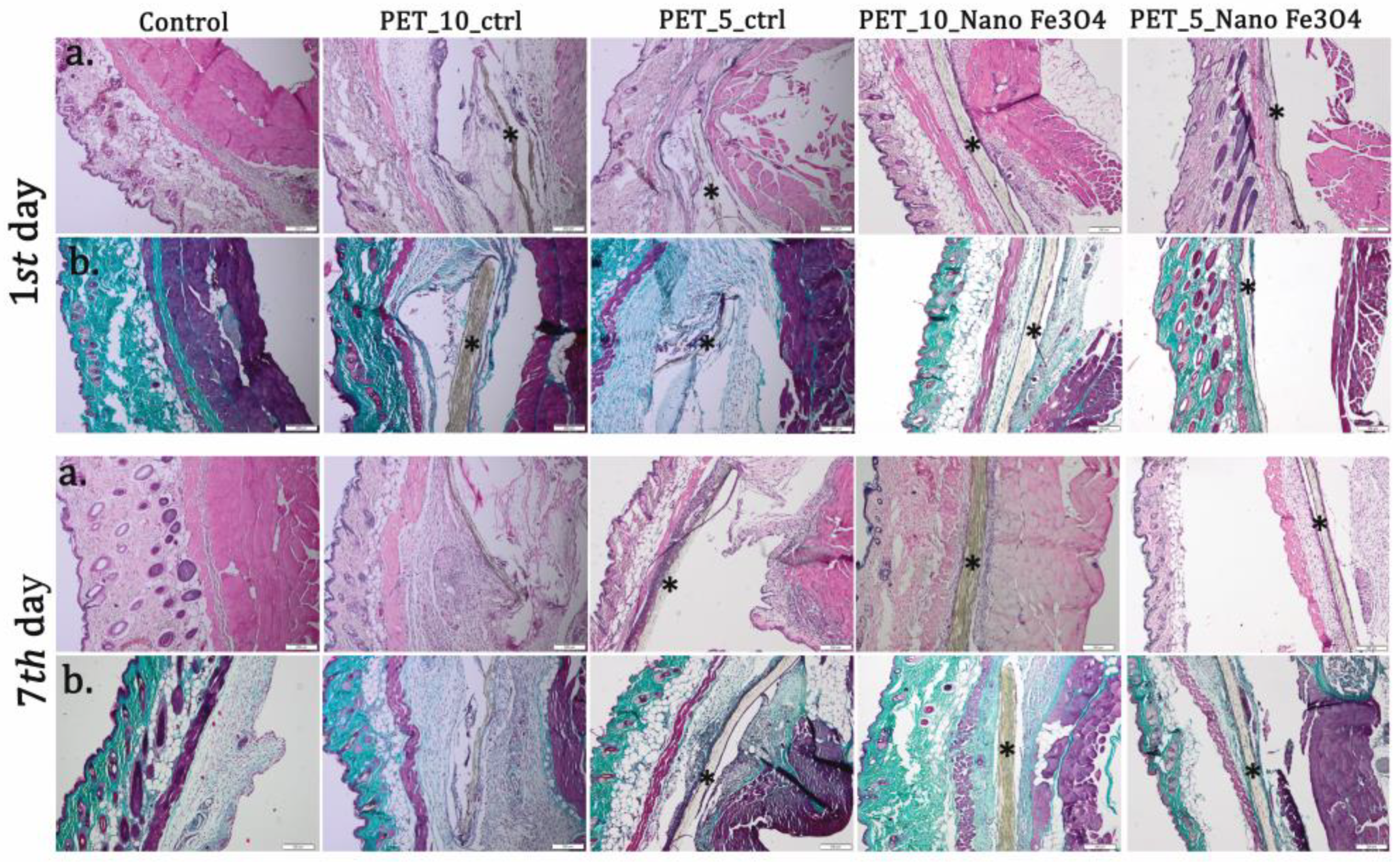
2.6.2. In Vivo Experiments
3. Results and Discussions
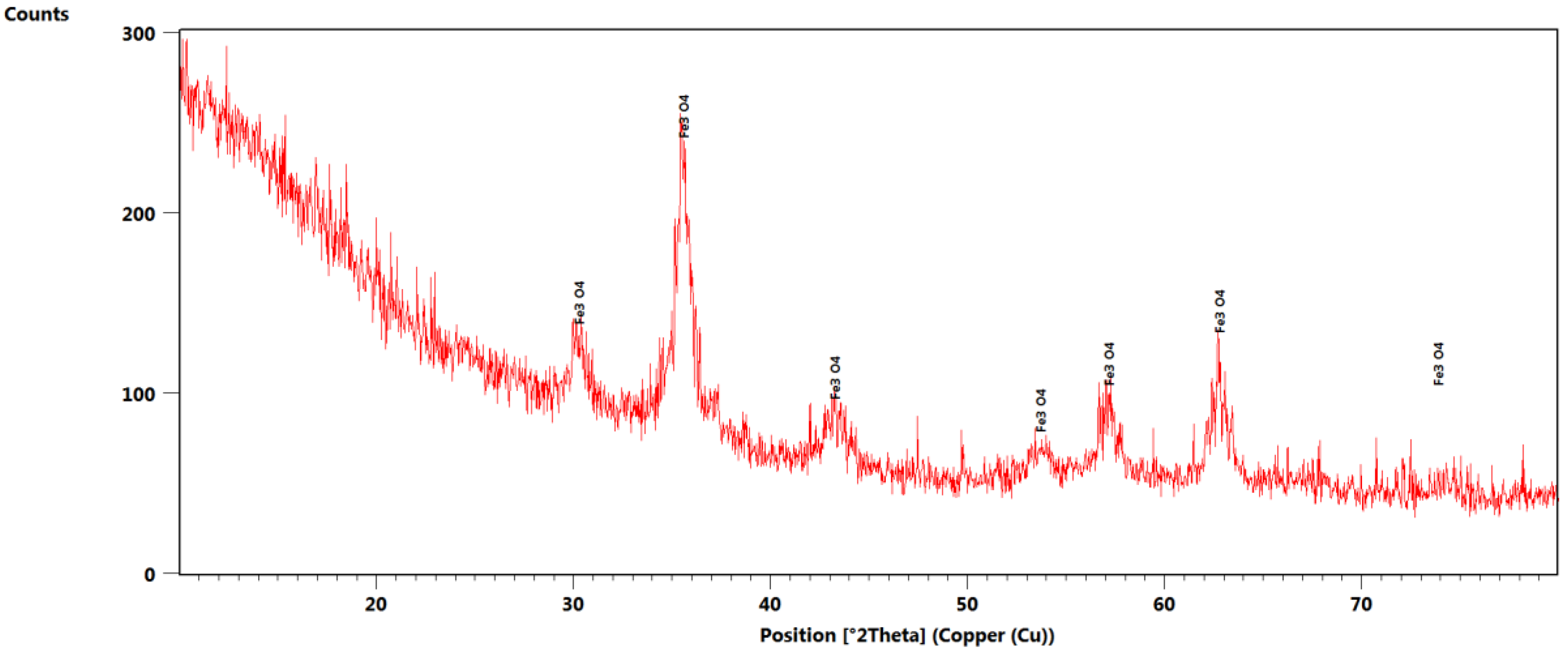
3.1. X-ray Diffraction
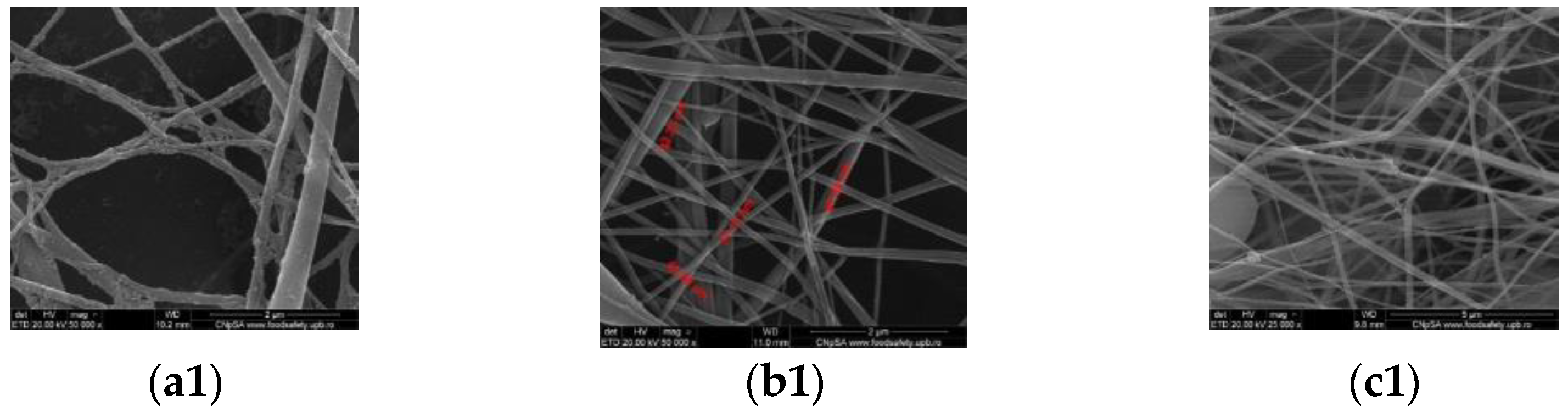
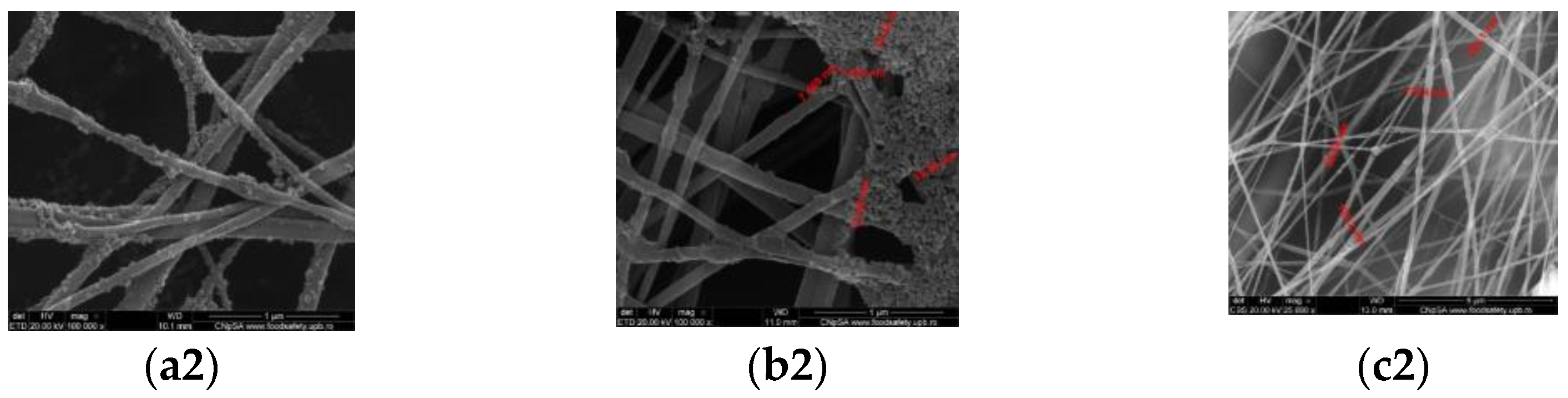
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
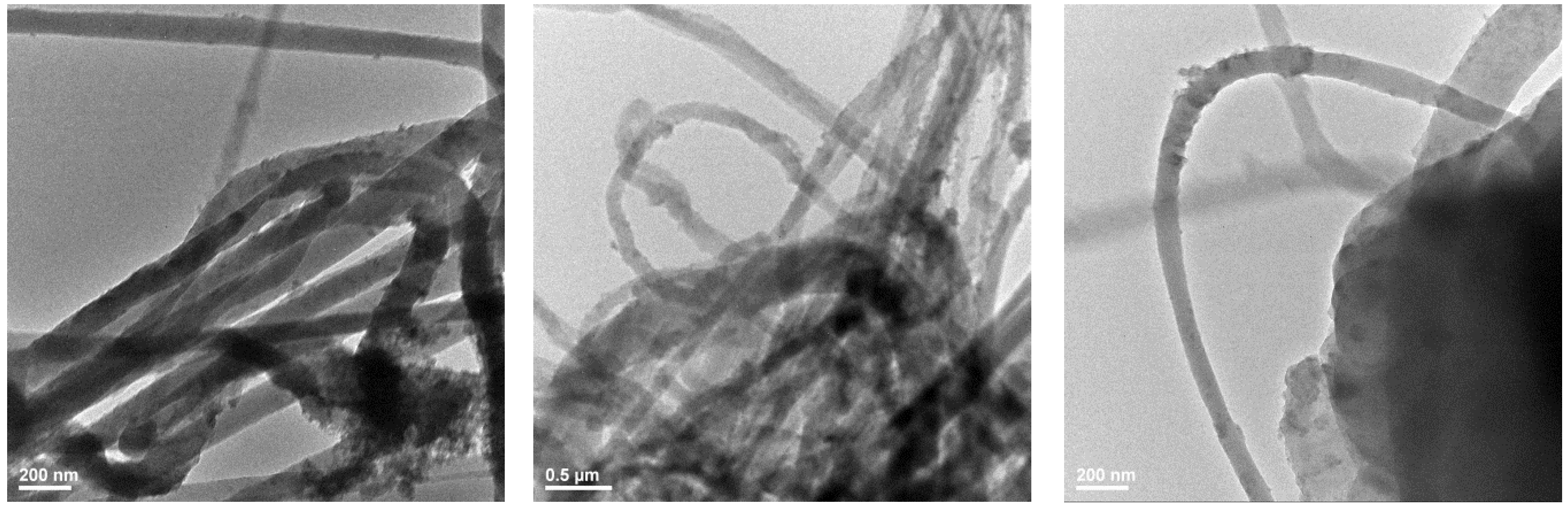
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
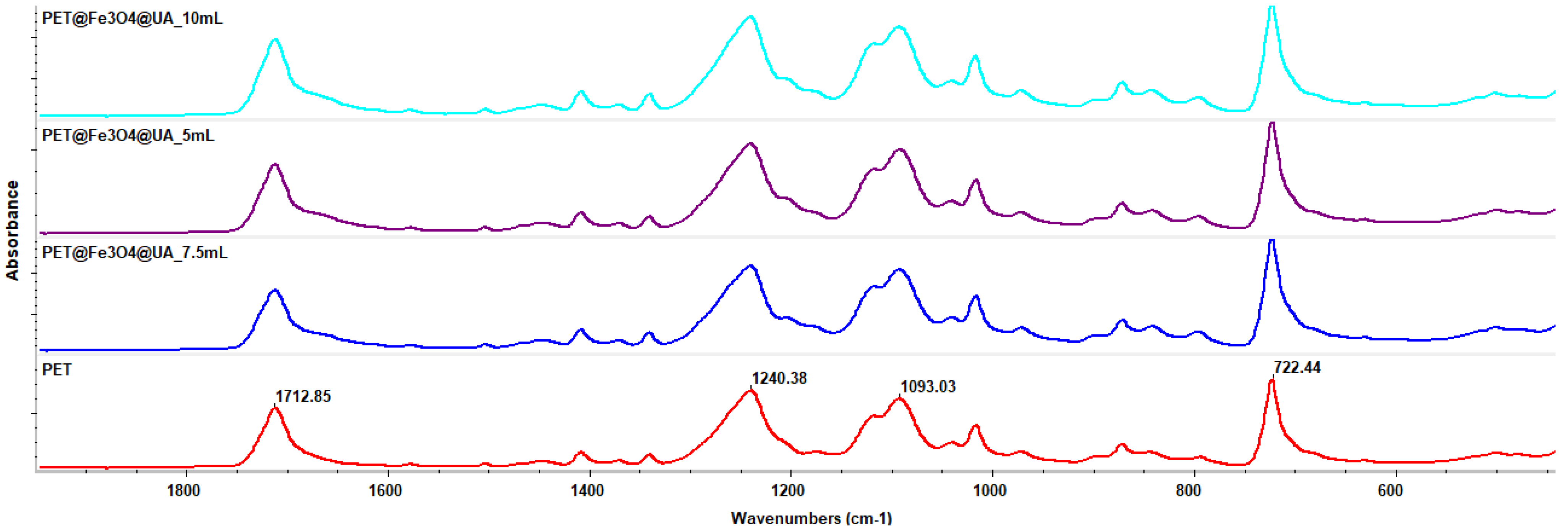
3.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.5. FT-ICR MALDI
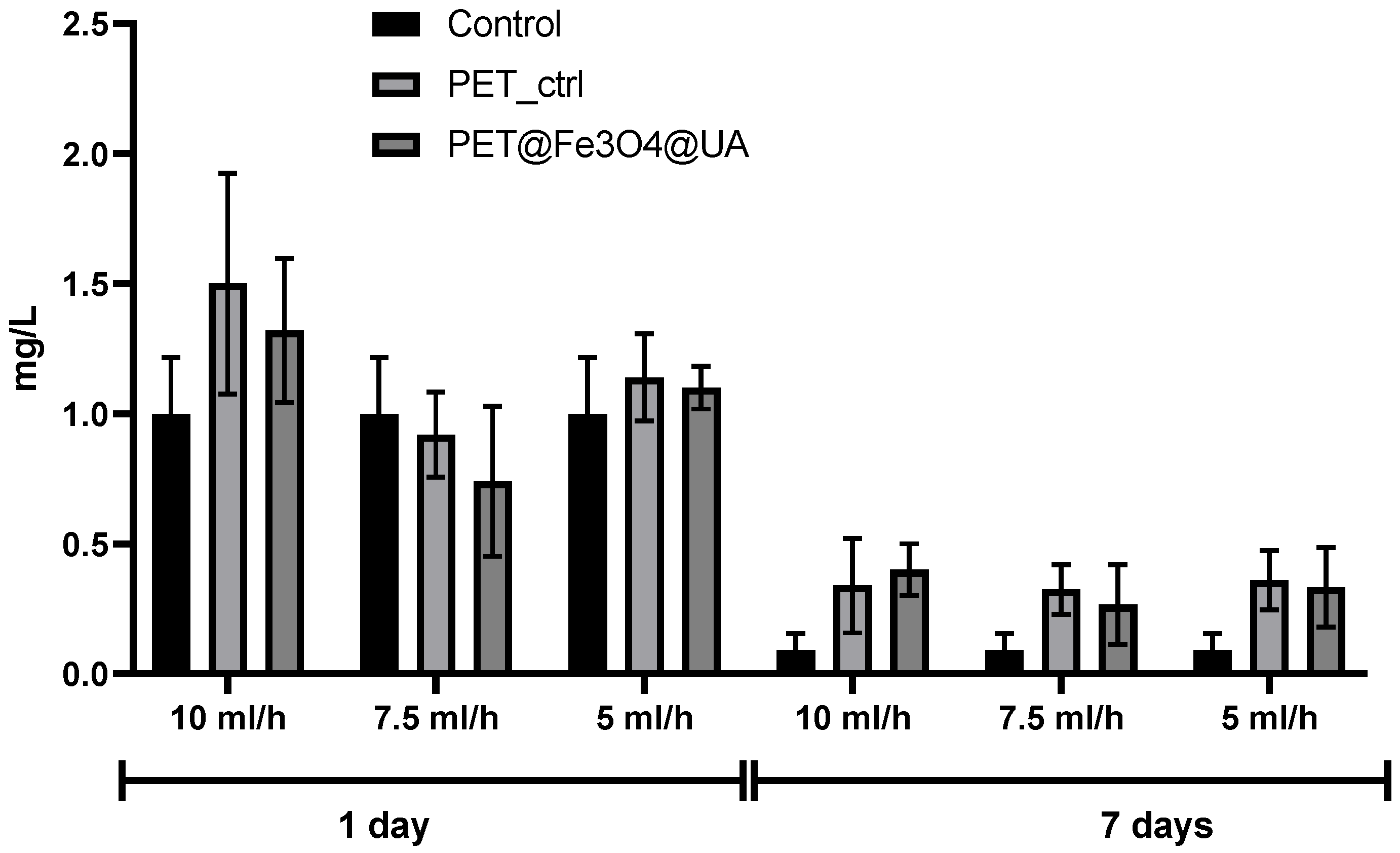
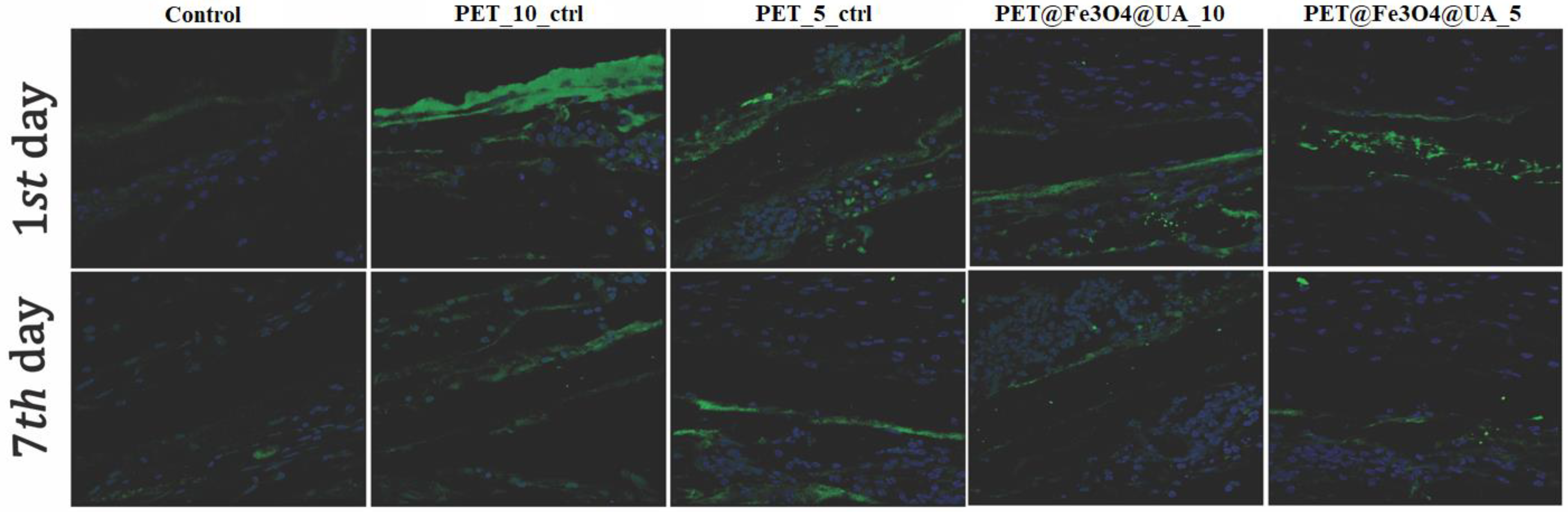
3.6. In Vitro Biocompatibility
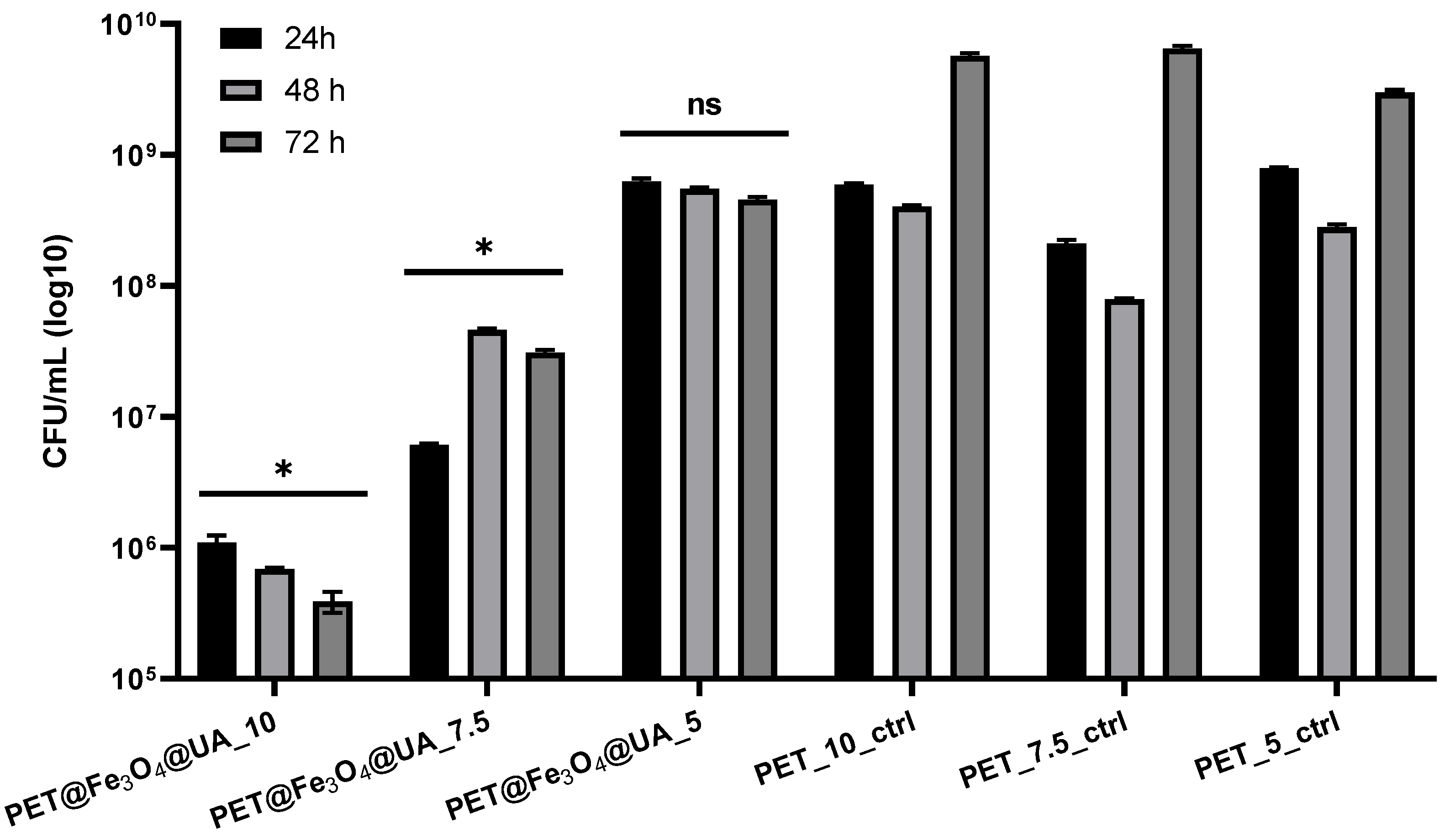
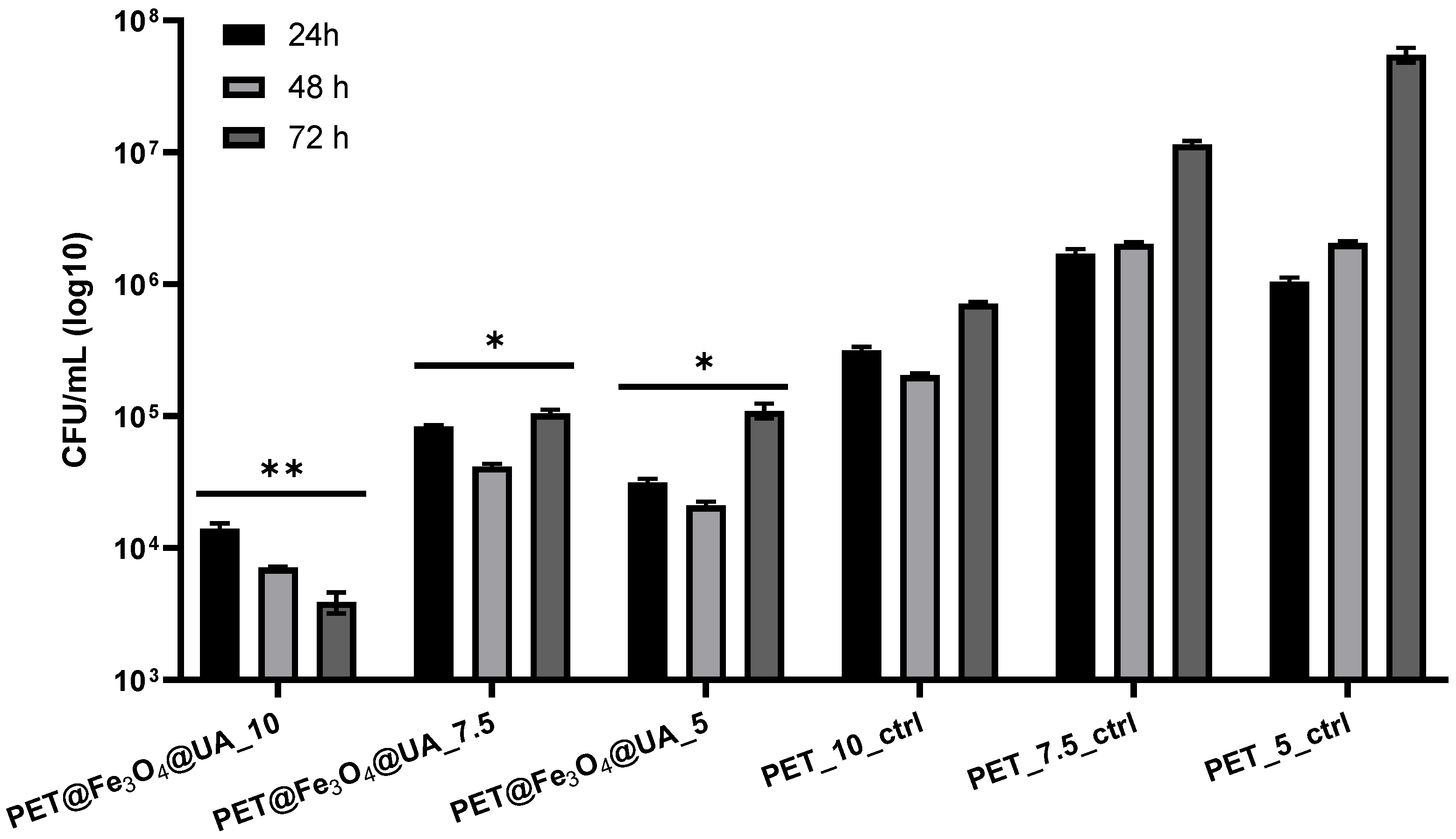
Antimicrobial Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prakash, P.; Sowmya, N.; Sudha, S.; Masilamani Selvam, M.; Pully, D.; Shobana, N.; Saigeetha, S.; Samrot, A.V. Isolation and Characterization of Chitin Nanofibers from Calocybe indica and its Applications. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2022, 11, 4105–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daels, N.; De Vrieze, S.; Sampers, I.; Decostere, B.; Westbroek, P.; Dumoulin, A.; Dejans, P.; De Clerck, K.; Van Hulle, S. Potential of a functionalised nanofibre microfiltration membrane as an antibacterial water filter. Desalination 2011, 275, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Kim, J.W.; Hyun, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Hattori, M.; Rah, D.K.; Park, Y.H. Electrospun three-dimensional silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffold. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 3922–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrash, H.; Nazeri, N.; Davoudi, P.; FaridiMajidi, R.; Ghanbari, H. Development of a Bioactive Scaffold based on NGF Containing PCL/Chitosan Nanofibers for Nerve Regeneration. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 12606–12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; You, T. Carbon nanofiber based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.; Saber, R.; Adabi, M.; Rasouli, R.; Douraghi, M.; Morshedi, M.; Farid-Majidi, R. Novel Competitive Voltam metric Aptasensor Based on Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers-Gold Nanoparticles Modified Graphite Electrode for Salmonella enterica serovar Detection. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 8702–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil, M.S.; Cha, D.I.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Bhattarai, N. Electrospun nanofibrous polyurethane membrane as wound dressing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2003, 67, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketabchi, N.; Dinarvand, R.; Adabi, M.; Gholami, M.; Firoozi, S.; Amanzadi, B.; Faridi-Majidi, R. Study of Third-Degree Burn Wounds Debridement and Treatment by Actinidin Enzyme Immobilized on Electrospun Chitosan/PEO Nanofibers in Rats. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 10358–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Ding, G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, M. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/poly (vinyl alcohol) composite nanofibers via electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 3026–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, B. Comparative analysis of superabsorbent properties of PVP and PAA nanofibres. Ind. Textila 2021, 72, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.; Jeddi, A.; Gharehaghaji, A. Fabrication and characterization of polyurethane electrospun nanofiber membranes for protective clothing applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 4135–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaci, U.D.; Peksel, A. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-based Electrospun Nanofibers: Characterization and Phytase Immobilization. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 7573–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoraibi, I.; Alomari, S. Different Methods for Nanofiber Design and Fabrication. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Barhoum, A., Bechelany, M., Makhlouf, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzarland, 2018; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Ding, B. Applications of electrospun fibers. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 2, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivri, Ç.; Haji, A. Nanofiber production from rose water and mate plant extract solutions using environmentally friendly electrospinning. Ind. Textila 2022, 73, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, S.; Venkatakrishnan, H.R.R.; Ravindran, J.; Sathyamoorthy, J.; Rangabashyam, K.A.; Ragini, Y.P.; Sathasivam, J. Hydrolytic Degradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate by Cutinase Enzyme Derived from Fungal Biomass-Molecular Characterization. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-R.; Chen, K.-S.; Tsai, J.-C.; Tseng, C.-C.; Lin, S.-F. The antibacterial activities of hydrophilic-modified nonwoven PET. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 20, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, N.; Yang, P.; Leng, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; Chu, P. The effects of amorphous carbon films deposited on polyethylene terephthalate on bacterial adhesion. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, R. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in the packaging industry. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, T.; Babar, A.A.; Ramzan, B.M.; Naeem, A.M.; Awais, M.; Anwar, F.; Fraz, A.; Abbas, M. Influence of rotor structure and process parameters on polyethylene oxide (PEO) nanofibers produced through centrifugal. Ind. Textila 2022, 73, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Ikladious, N. Depolymerization of poly (ethylene terephthalate) waste using 1, 4-butanediol and triethylene glycol. J. Elastomers Plast. 2003, 35, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samak, N.A.; Jia, Y.; Sharshar, M.M.; Mu, T.; Yang, M.; Peh, S.; Xing, J. Recent advances in biocatalysts engineering for polyethylene terephthalate plastic waste green recycling. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalakannan, S.; Kovendan, K.; Balachandar, V.; Naik, K.G.; Chauhan, A. Sources of Potential Fungi Generated Biogenic Nanoparticles for the Control of Diseases Transmitting Mosquitoes: A Review. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2022, 11, 3523–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, A.B. Biosynthesis of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanostructures using Vernonia Amygdalina Leaves Extract. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2021, 10, 2777–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H. Application of ferro-cobalt magnetic fluid for oil sealing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 267, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, S.; Sadighian, S.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Khalkhali, M. Theragnostic Magnetic Core-Shell Nanoparticle as Versatile Nanoplatform for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Drug Delivery. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 13276–13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Laibinis, P.E.; Hatton, T.A. Bilayer surfactant stabilized magnetic fluids: Synthesis and interactions at interfaces. Langmuir 1999, 15, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S. Magnetic Particles Weight as an Indicator for Heavy Metals Concentration. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2022, 11, 3770–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Xia, J.; Zhang, C.; Yin, D.; Häfeli, U.O. Preparation and radiolabeling of surface-modified magnetic nanoparticles with rhenium-188 for magnetic targeted radiotherapy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 277, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Wust, P.; Fähling, H.; Felix, R. Magnetic fluid hyperthermia (MFH): Cancer treatment with AC magnetic field induced excitation of biocompatible superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, D. Polymer-based nanofiber–nanoparticle hybrids and their medical applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Wust, P.; Schirra, H.; Schiestel, T.; Schmidt, H.; Felix, R. Endocytosis of dextran and silan-coated magnetite nanoparticles and the effect of intracellular hyperthermia on human mammary carcinoma cells in vitro. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 194, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Han, B.; Hu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, X. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their magnetic properties. Procedia Eng. 2012, 27, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadighian, S.; Sharifan, K.; Khanmohammadi, A.; Rohani, M.K. A Facile Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO for Curcumin Delivery. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 7994–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.R.; López-Abarrategui, C.; de la Serna Gómez, I.; Dias, S.C.; Otero-González, A.J.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial magnetic nanoparticles based-therapies for controlling infectious diseases. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 555, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Cruz, D.; Saleh, B.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Ajo, A.; Roy, A.K.; Webster, T.J. Chapter 22—Drug-delivery nanocarriers for skin wound-healing applications. In Wound Healing, Tissue Repair, and Regeneration in Diabetes; Bagchi, D., Das, A., Roy, S., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 439–488. [Google Scholar]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Stoica, A.E.; Dima-Bălcescu, M.-Ș.; Chircov, C.; Gharbia, S.; Baltă, C.; Roșu, M.; Herman, H.; Holban, A.M.; Ficai, A.; et al. Electrospun Polyethylene Terephthalate Nanofibers Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles: Novel Approach in Anti-Infective Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grumezescu, A.; Vasile, B.; Holban, A. Eugenol functionalized magnetite nanostructures used in anti-infectious therapy. Lett. Appl. Nanobiosci. 2013, 2, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Cotar, A.I.; Andronescu, E.; Ficai, A.; Ghitulica, C.D.; Grumezescu, V.; Vasile, B.S.; Chifiriuc, M.C. In vitro activity of the new water-dispersible Fe3O4@ usnic acid nanostructure against planktonic and sessile bacterial cells. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Chirea, M.; Grumezescu, V.; Socol, G.; Iordache, F.; Oprea, A.E.; Anghel, I.; Holban, A.M. MAPLE Fabricated Fe3O4@Cinnamomum verum Antimicrobial Surfaces for Improved Gastrostomy Tubes. Molecules 2014, 19, 8981–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, B.W.; Kang, T.J. Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanofibers with iron oxide nanoparticles and poly(ethylene terephthalate). Mater. Sci. 2012, 125, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.K.; Ahn, B.W.; Kang, T.J. Magnetic nanofibers with core (Fe3O4 nanoparticle suspension)/sheath (poly ethylene terephthalate) structure fabricated by coaxial electrospinning. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădulescu, M.; Andronescu, E.; Holban, A.M.; Vasile, B.S.; Iordache, F.; Mogoantă, L.; Mogoșanu, G.D.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Georgescu, M.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Antimicrobial Nanostructured Bioactive Coating Based on Fe3O4 and Patchouli Oil for Wound Dressing. Metals 2016, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Cheng, J.; Wei, Y. Preparation and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 microparticles with adjustable size and morphology. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 520, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolassi, A.C.C.; Nagarajan, S.; de Araújo Lima, B.; Guerra, V.G.; Aguiar, M.L.; Huon, V.; Soussan, L.; Cornu, D.; Miele, P.; Bechelany, M. Efficient nanoparticles removal and bactericidal action of electrospun nanofibers membranes for air filtration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lala, N.L.; Ramaseshan, R.; Bojun, L.; Sundarrajan, S.; Barhate, R.S.; Ying-jun, L.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of nanofibers with antimicrobial functionality used as filters: Protection against bacterial contaminants. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, J.A.; Said, I.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Yasin, S.A.; Ali, Z.A.; Ahmed, I.H. Electrospinning of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers: Optimization study using taguchi design of experiment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 454, 012130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kotaki, M.; Yong, T.; He, W.; Ramakrishna, S. Surface engineering of electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers towards development of a new material for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saftawy, A.A.; Elfalaky, A.; Ragheb, M.S.; Zakhary, S.G. Electron beam induced surface modifications of PET film. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 102, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairiah, B.; Lily, I.M.D.; Nur, A.A.A.J.S.M. Rigid Polyurethane Foam from Glyco lysed Polyethylene Terephthalate Dissolved in Palm-based Polyol. Sains Malays. 2013, 42, 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Paszkiewicz, S.; Szymczyk, A.; Pawlikowska, D.; Irska, I.; Taraghi, I.; Pilawka, R.; Gu, J.; Li, X.; Tu, Y.; Piesowicz, E. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ethylene terephthalate-co-1,4-cyclohexanedimethylene terephtlatate)-block-poly(tetramethylene oxide) copolymers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41745–41754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peltzer, M.A.; Simoneau, C. Report of an Interlaboratory Comparison from the European Reference Laboratory for Food Contact Materials; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, P.S. Antimicrobial Tolerance in Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curutiu, C.; Ditu, L.M.; Iordache, F.; Bleotu, C.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Lazar, V.; Paduraru, D.N.; Holban, A.M.J.B.R.I.A.C. Quorum Sensing molecules produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa impair attachment and biofilm formation in Candida albicans. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2017, 7, 2016–2020. [Google Scholar]
- Furiga, A.; Lajoie, B.; El Hage, S.; Baziard, G.; Roques, C. Impairment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm resistance to antibiotics by combining the drugs with a new quorum-sensing inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arakha, M.; Pal, S.; Samantarrai, D.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Mallick, B.C.; Pramanik, K.; Mallick, B.; Jha, S. Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fallahi, D.; Rafizadeh, M.; Mohammadi, N.; Vahidi, B. Effects of feed rate and solution conductivity on jet current and fiber diameter in electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile solutions. J. E-Polymers 2009, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zhu, L.T.; Deng, X.Y.; Chen, W.L. Effect of Experimental Parameters on Nanofiber Diameter from Electrospinning with Wire Electrodes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 230, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfim, D.P.F.; Cruz, F.G.S.; Guerra, V.G.; Aguiar, M.L. Development of Filter Media by Electrospinning for Air Filtration of Nanoparticles from PET Bottles. Membranes 2021, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, I.; Wu, Q.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Olsson, R.T.; Andersson, R.L. Electrospinning of recycled PET to generate tough mesomorphic fibre membranes for smoke filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, M.T.; Shahid, M.A.; Ali, A. Development of nanofibrous membrane from recycled polyethene terephthalate bottle by electrospinning. OpenNano 2022, 8, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, H.N.; Phong Vo, P.; Hayashi, K.; Kinashi, K.; Sakai, W.; Tsutsumi, N. Recycled PET as a PDMS-Functionalized electrospun fibrous membrane for oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



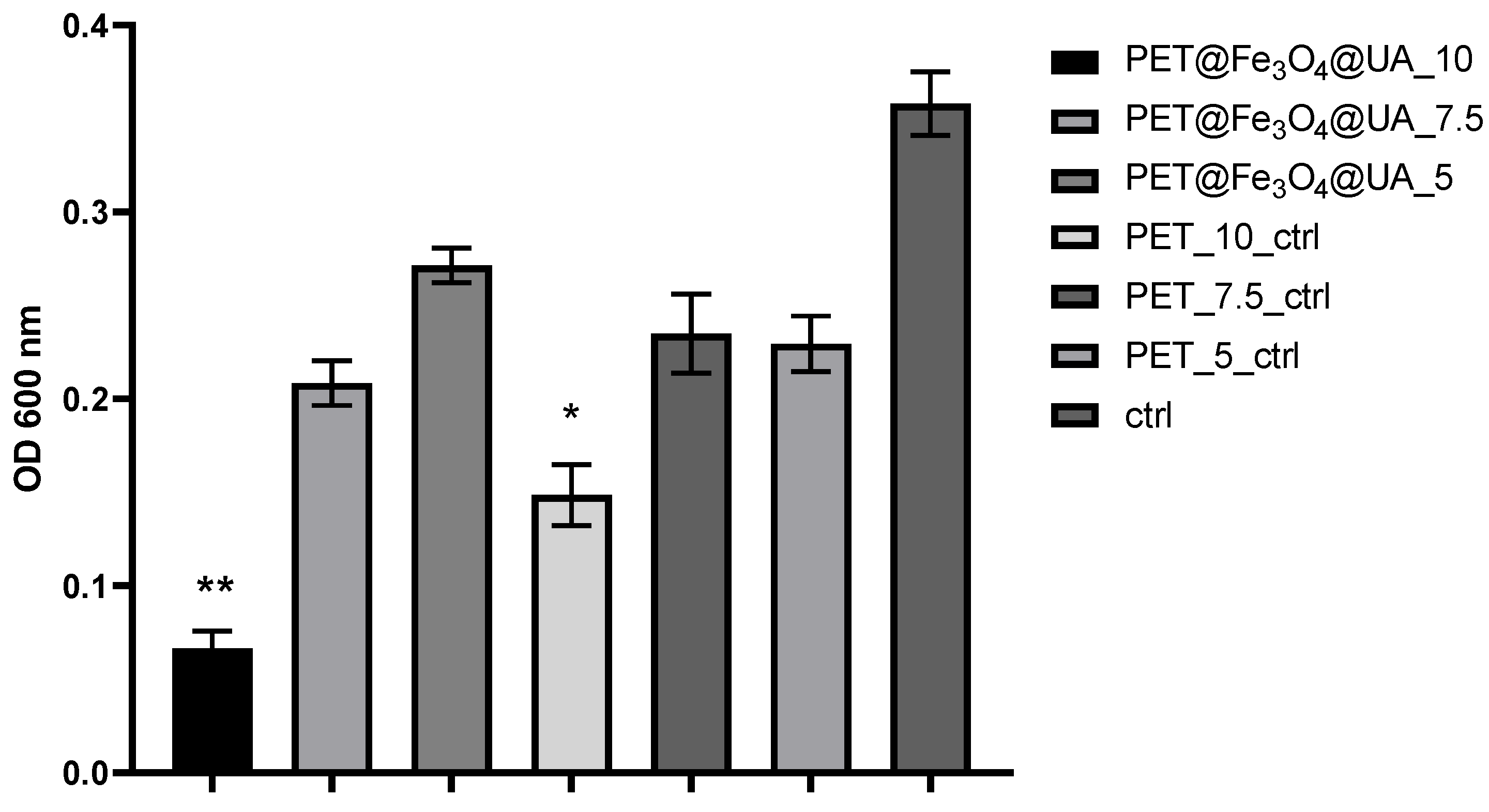

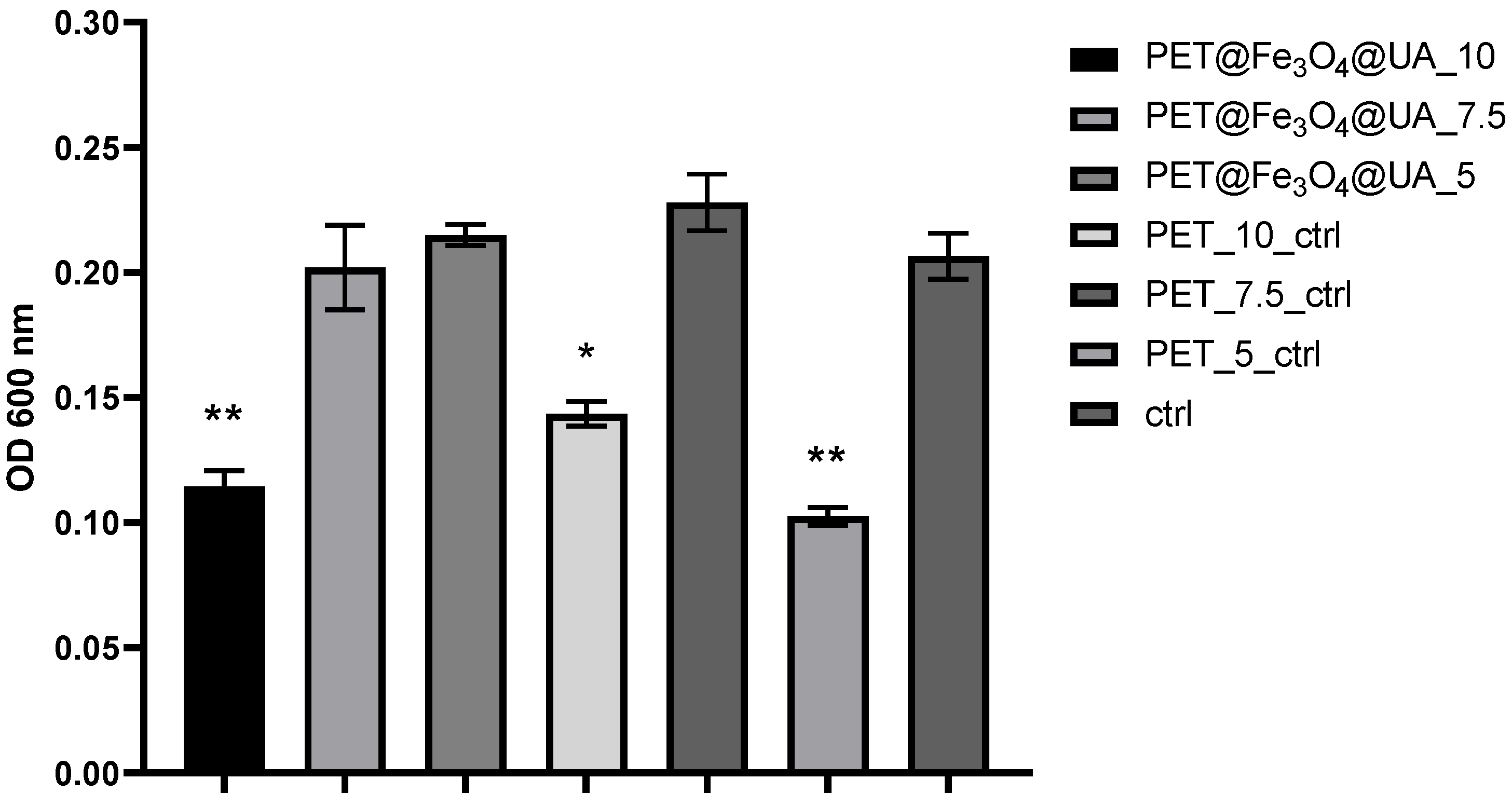

| Sample | Output 1 (kV) | Output 2 (kV) | Heat (kW) | Humidity (%) | Temperature (°C) | Feed Rate (mL/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET_5_ctrl | −5.73 | 17.53 | 0.6 | 35 | 27 | 5 |
| PET_7.5_ctrl | 7.5 | |||||
| PET_10_ctrl | 10 |
| Material | Implantation Period (Days) | Edema | PMN | M | F | NV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1 | − | + | − | − | − |
| 7 | − | − | + | − | − | |
| PET_10_ctrl | 1 | ++++ | +++ | ++ | + | − |
| 7 | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++++ | − | |
| PET_7.5_ctrl | 1 | +++ | +++ | + | + | − |
| 7 | ++ | + | +++ | +++ | − | |
| PET_5_ctrl | 1 | ++ | +++ | + | + | − |
| 7 | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | + | |
| PET@Fe3O4@UA_10 | 1 | + | ++ | + | + | − |
| 7 | − | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | |
| PET@Fe3O4@UA_7.5 | 1 | − | + | + | + | − |
| 7 | − | − | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| PET@Fe3O4@UA_5 | 1 | − | + | − | + | − |
| 7 | − | − | ++ | ++ | ++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoica, A.E.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Ficai, A.; Herman, H.; Cornel, B.; Roșu, M.; Gharbia, S.; Holban, A.M.; et al. Biocompatibility and Antimicrobial Profile of Acid Usnic-Loaded Electrospun Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)—Magnetite Nanofibers. Polymers 2023, 15, 3282. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153282
Stoica AE, Bîrcă AC, Mihaiescu DE, Grumezescu AM, Ficai A, Herman H, Cornel B, Roșu M, Gharbia S, Holban AM, et al. Biocompatibility and Antimicrobial Profile of Acid Usnic-Loaded Electrospun Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)—Magnetite Nanofibers. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3282. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153282
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoica (Oprea), Alexandra Elena, Alexandra Catalina Bîrcă, Dan Eduard Mihaiescu, Alexandru Mihai Grumezescu, Anton Ficai, Hildegard Herman, Baltă Cornel, Marcel Roșu, Sami Gharbia, Alina Maria Holban, and et al. 2023. "Biocompatibility and Antimicrobial Profile of Acid Usnic-Loaded Electrospun Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)—Magnetite Nanofibers" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3282. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153282
APA StyleStoica, A. E., Bîrcă, A. C., Mihaiescu, D. E., Grumezescu, A. M., Ficai, A., Herman, H., Cornel, B., Roșu, M., Gharbia, S., Holban, A. M., Vasile, B. Ș., Andronescu, E., & Hermenean, A. O. (2023). Biocompatibility and Antimicrobial Profile of Acid Usnic-Loaded Electrospun Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)—Magnetite Nanofibers. Polymers, 15(15), 3282. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153282












