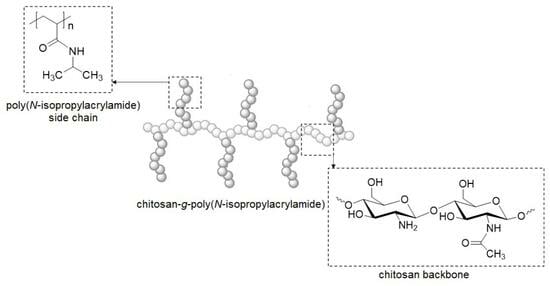
Synthesis and Characterization of Thermoresponsive Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
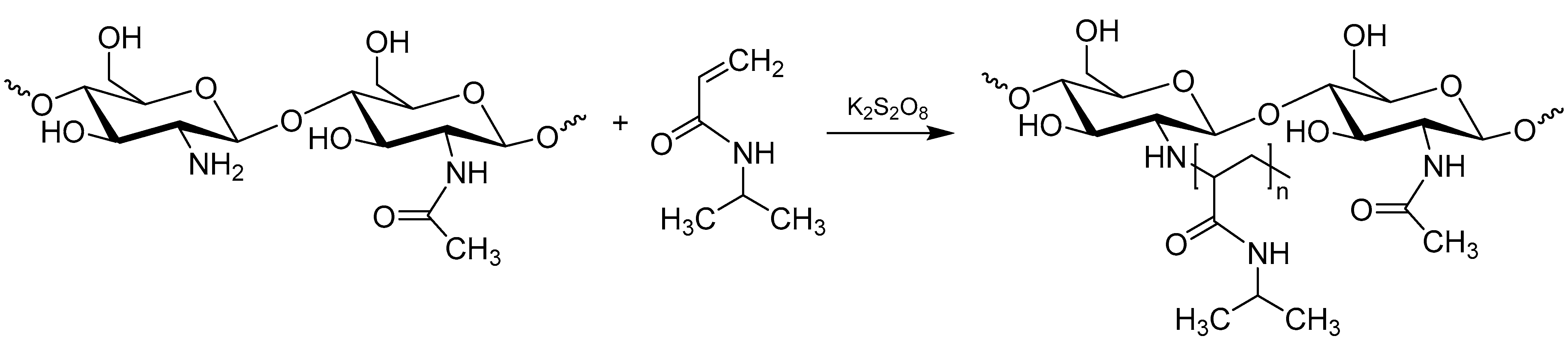
2.2. Synthesis of Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers
2.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
2.4. FT-IR Analysis
2.5. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.6. TG Analysis
2.7. LCST Determination of the Synthesized Copolymer Solutions
2.8. Particle Size Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers
3.2. Characterization of Graft Copolymers
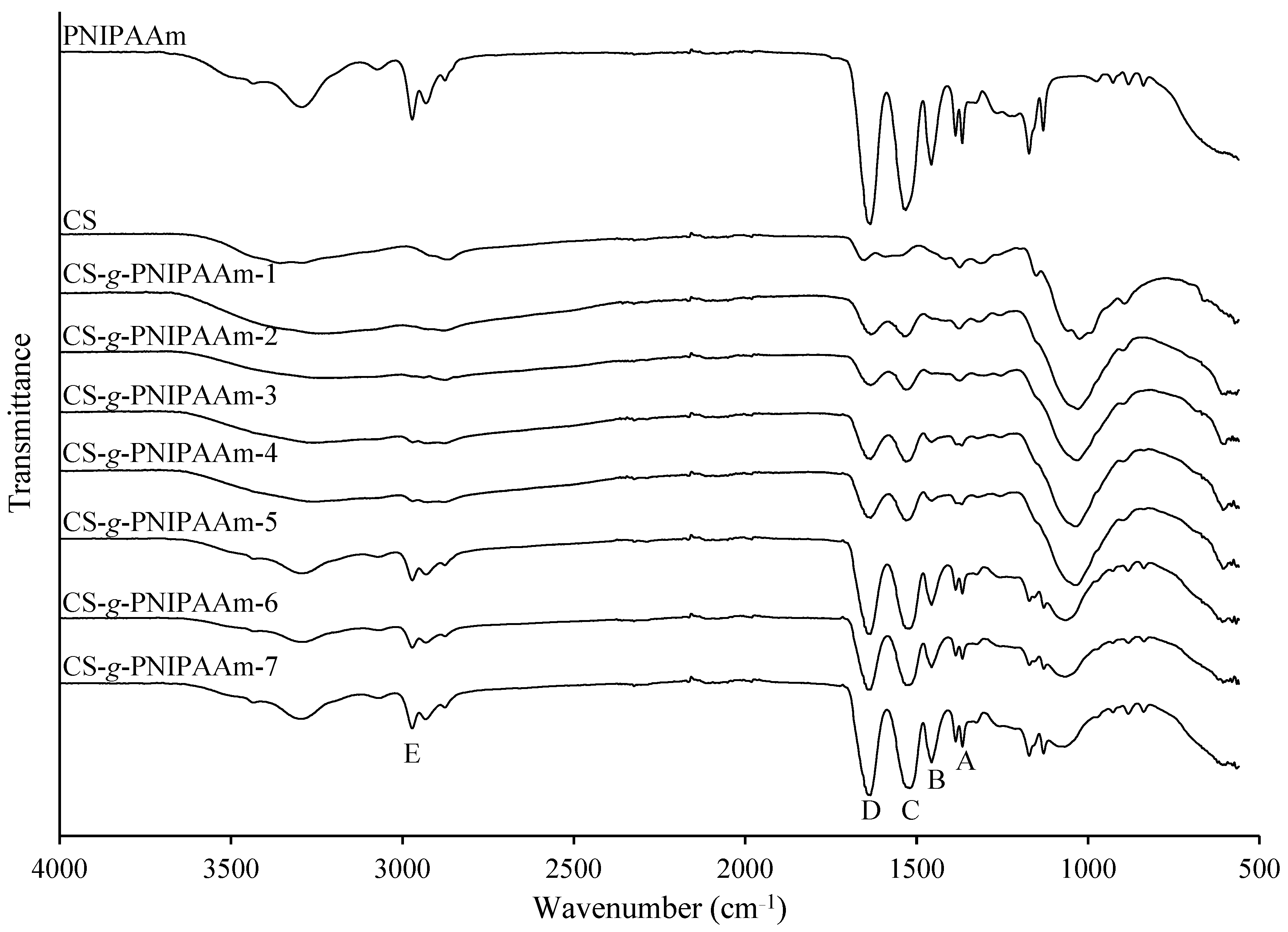
3.2.1. FT-IR Analysis
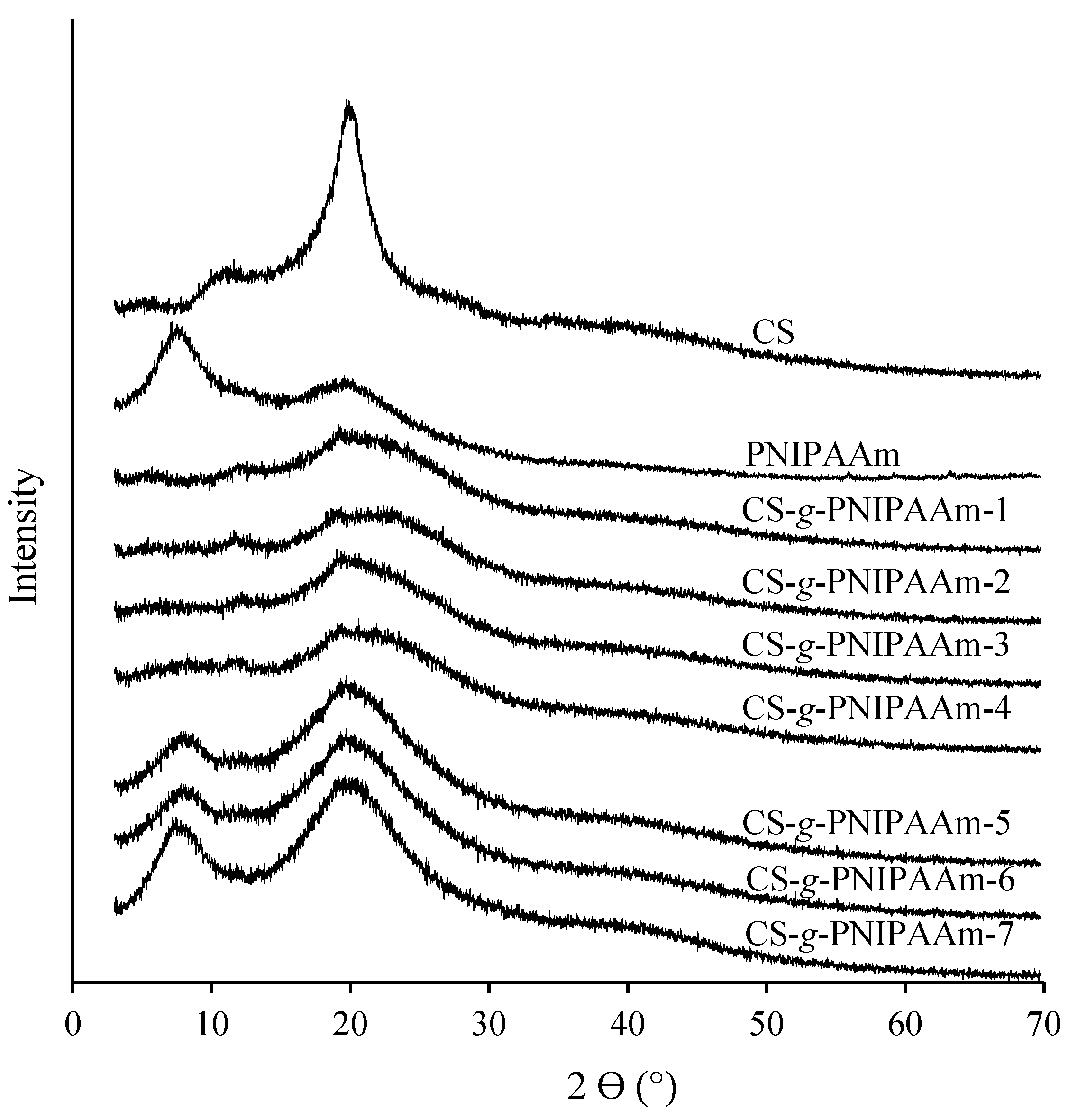
3.2.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.2.3. TG Analysis
3.3. Termoresponsive Behavior of Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers
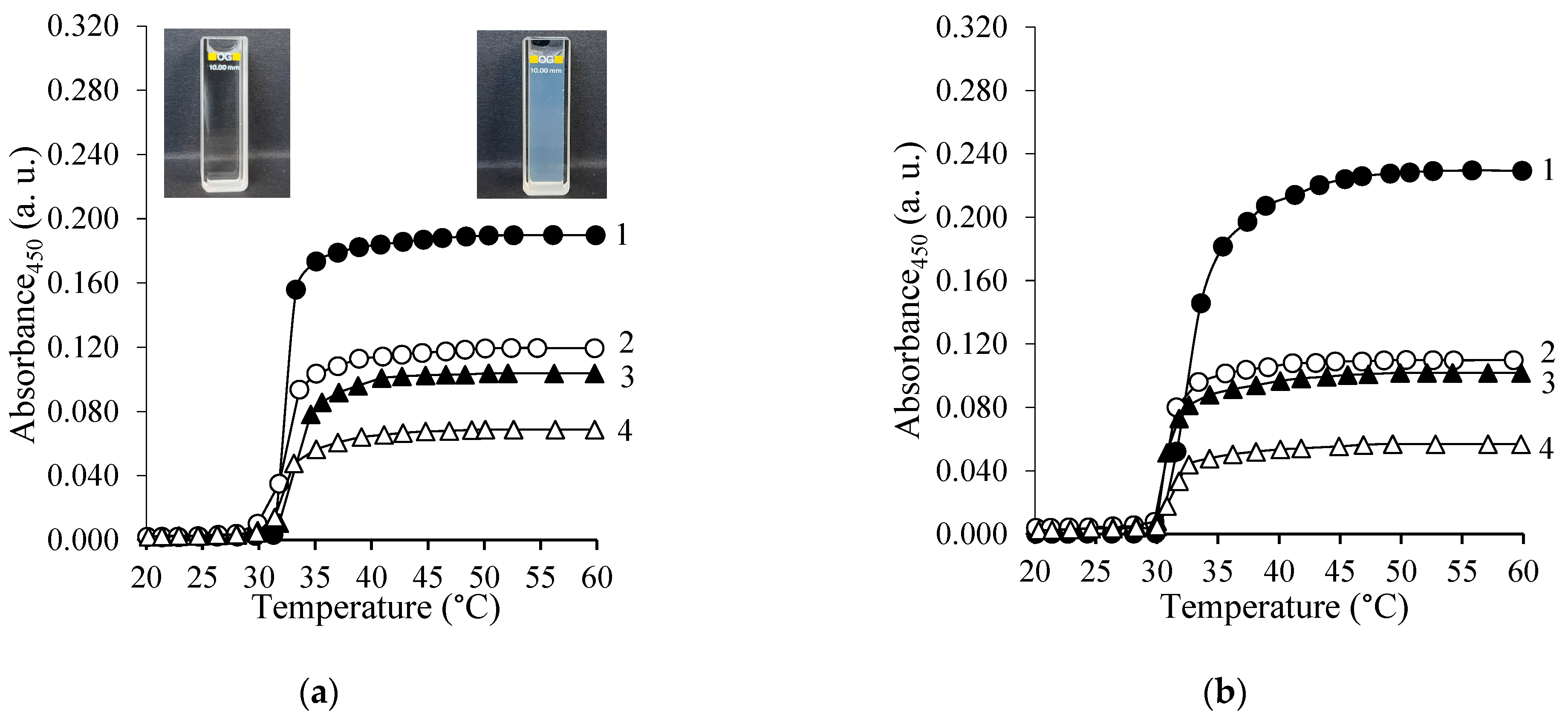
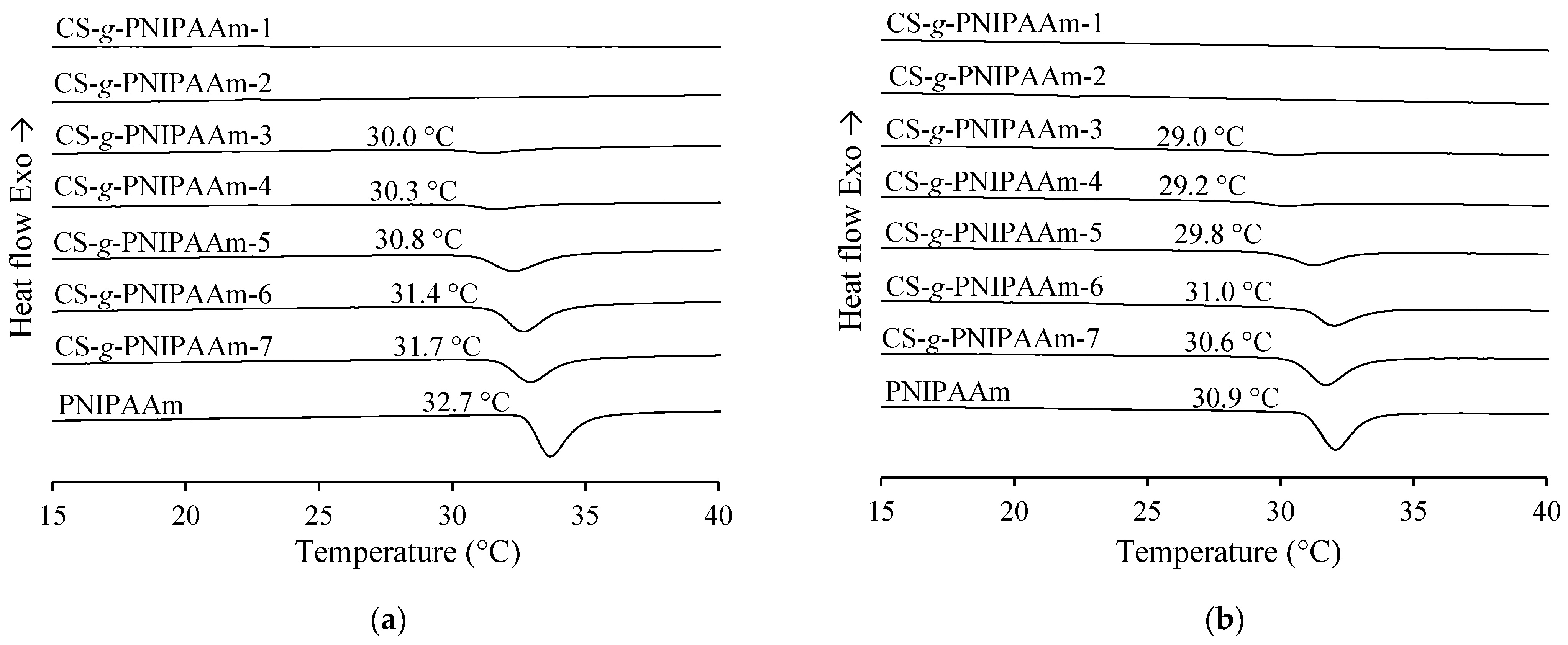
3.3.1. Determination of LCST of the Copolymer Solutions
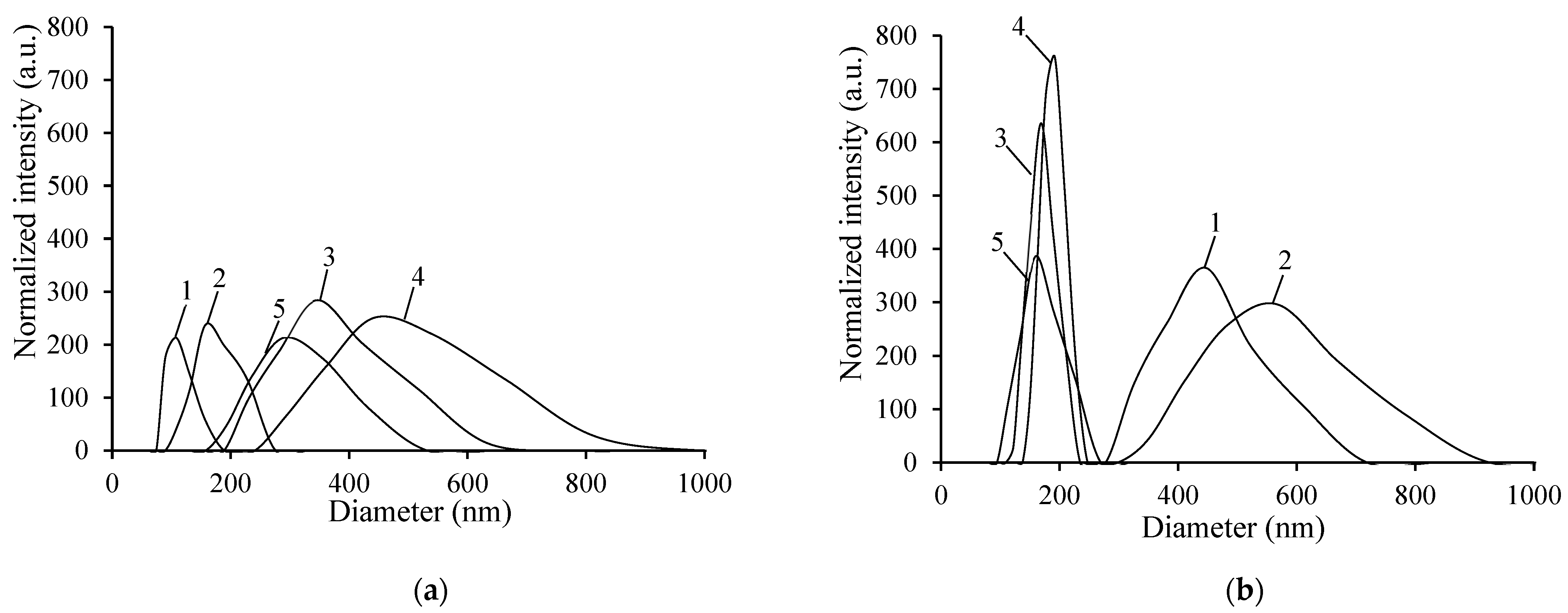
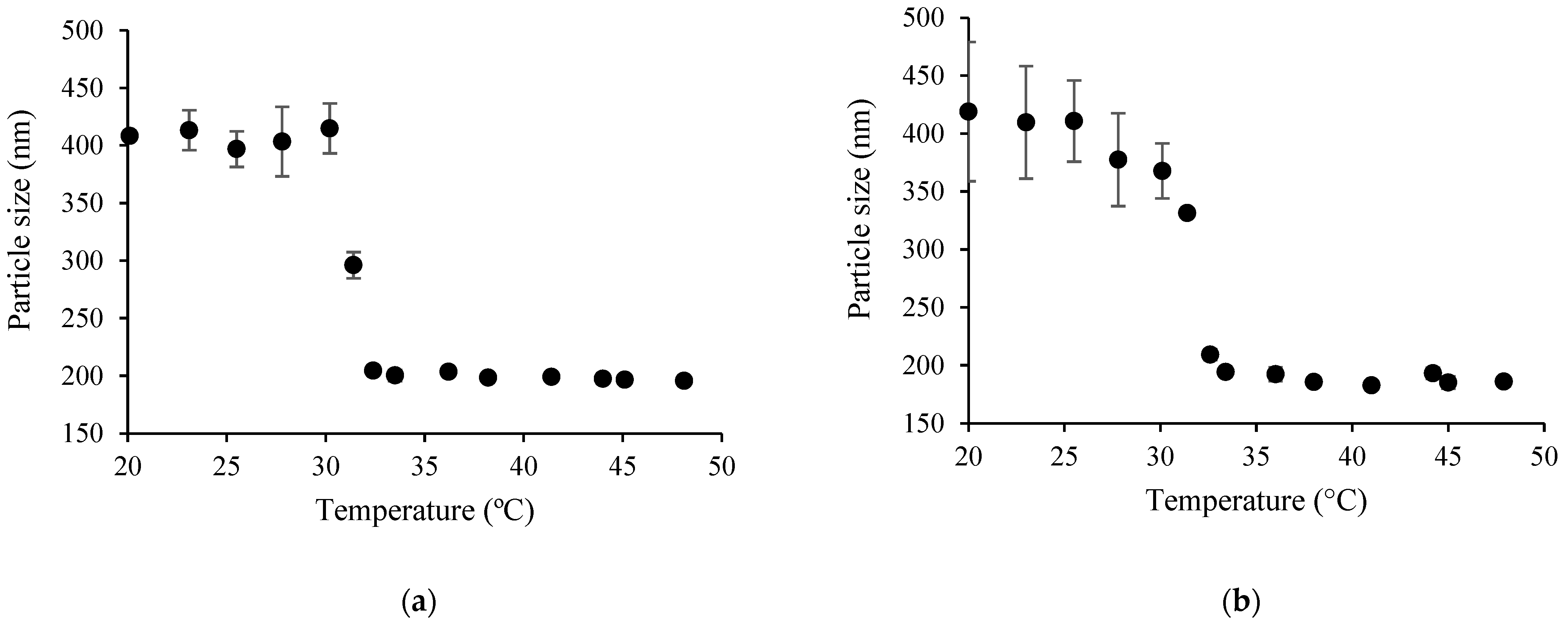
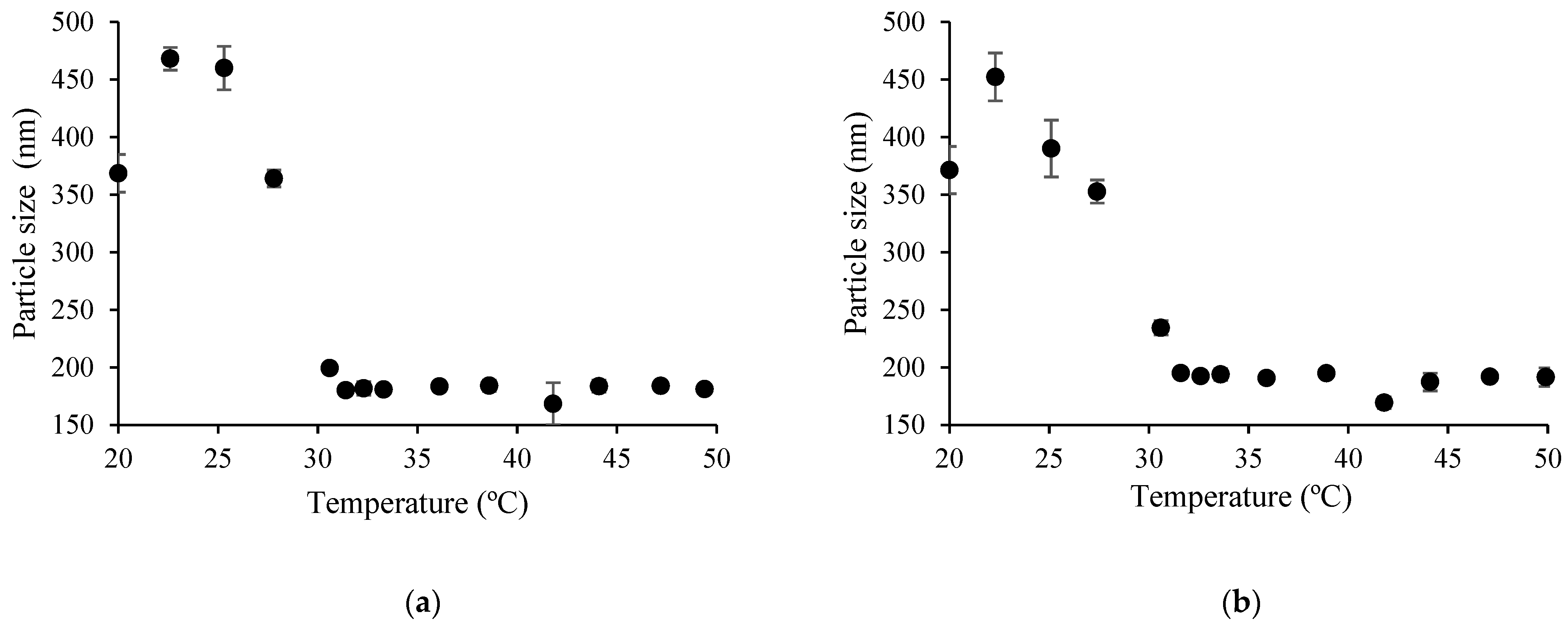
3.3.2. Particle Size Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmaljohann, D. Thermo- and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaruwa, H.; Tavengwa, N.T. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications in separation sciencre. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 175, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Musuc, M. Polymer Gels: Classification and Recent Developments in Biomedical Applications. Polym. Gels Netw. 2023, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.S. Stimuli-responsive polymers: Biomedical applications and challenges for clinical translation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, J.H.; John, R.; Alex, A.; Anoop, K.R. Smart polymers for the controlled delivery of drugs—a concise overview. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-J.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Lin, S.-H.; Hsu, S.-H. Smart polymers for cell therapy and precision medicine. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Trzebicka, B.; Müller, A.H.E.; Dworak, A.; Tsvetanov, C.B. Thermosensitive water-soluble copolymers with doubly responsive reversibly interacting entities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1275–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamies, R.; Zhu, K.; Kjøniksen, A.; Nyström, B. Thermal response of low molecular weight poly-(N-isopropylacrylamide) polymers in aqueous solution. Polym. Bull. 2009, 62, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.K.; Banerjee, R.; Pradhan, P.; Bahadur, D. Thermal behavior of magneticall modalized poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-chitosan based nanohydrogel. Colloids Surf. 2010, 81, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsili, L.; Dal Bo, M.; Berti, F.; Toffoli, G. Chitosan-based biocompatible copolymers for thermoresponsive drug delivery systems: On the development of a standardization systems. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 13, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, J.; Song, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, J. Smart hydrogel formed by alginate-g-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and chitosan through polyelectrolyte complexation and its controlled release properties. Gels 2022, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, S.D.; Jafar Mazumder, M.A.; Lasowski, F.; Fitzpatrick, L.E.; Sheardown, H. PNIPAAm-Grafted-Collagen as an injectable, in situ gelling, bioactive cell delivery ccaffold. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2261–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, C.; Yang, X.; Shen, B.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Sun, H.; Yu, K.; Yang, B.; et al. PH- and Temperature-sensitive hydrogel nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence for bioprobes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5856–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Guan, X.; Zheng, J.; Guo, H.; Wu, K.; Liang, L.; Lu, M. Biodegradable, thermoresponsive PNIPAA-based hydrogel scaffolds for the sustained release of levofloxacin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32967–32978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Yao, M.; Ding, Z.; Xuan, J.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Xia, Y.; Cao, M. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-based thermoresponsive composite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Su, Y.; Wang, D. Mechanical properties of PNIPAA based hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.N.; Ferreira, L.M.B.; Cardoso, V.M.O.; Boni, F.I.; Souza, A.L.R.; Gremião, M.P.D. Recent advances in smart hydrogels for biomedical applications: From self-assembly to functional approaches. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Rajendrran, R.R.; Mohanto, S.; Agarwal, U.; Panda, K.; Dhotre, K.; Manne, R.; Deepak, A.; Zafar, A.; Yasir, M.; et al. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based hydrogels for biomedical applications: A review of the state-of-the-art. Gels 2022, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüelles-Monal, W.M.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Fernández-Quiroz, D.; Recillas-Mota, M.T.; Montiel-Herrera, M. Review: Chitosan derivatives: Introducing new functionalities with a controlled molecular architecture for innovative materials. Polymers 2018, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Bumbu, G.G.; Petronela, D.R.; Staikos, G. Comparative study of the behavior of carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers and their equivalent physical blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokias, G.; Mylonas, Y.; Staikos, G.; Bumbu, G.G.; Vasile, C. Synthesis and aqueous solution properties of novel thermoresponsive graft copolymers based on a carboxymethylcellulose backbone. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 4958–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziminska, M.; Wilson, J.J.; McErlean, E.; Dunne, N.; McCarthy, H.O. Synthesis and evaluation of a thermoresponsive degradable chitosan-grafted PNIPAAm hydrogel as a “smart” gene delivery system. Materials 2020, 13, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yu, W. Preparation and characterization of CS-g-PNIPAAm microgels and application in water vapor-permeable fabric. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recillas, M.; Silva, L.L.; Peniche, C.; Goycoolea, M.F.; Rinaudo, M.; Argüelles-Monal, M. Thermoresponsive behavior of chitosan-g-N-isopropylacrylamide copolymer solutions. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.-Y.; Don, T.-M.; Chiu, W.-Y. Synthesis of chitosan-based thermo- and pH-responsive porous nanoparticles by temperature-dependent self-assembly method and their application in drug release. J. Polym. Sci. 2009, 47, 5126–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalina, N.; Cheaburu, Y. On the Development of chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) by raft polymerization technique. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2020, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, S.J. Thermo- and pH-responsive behaviors of graft copolymer and blend based on chitosan and N-isopropylacrylamide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-W.; Liu, X.; Miller, A.L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Yeh, M.-L.; Lu, L. Strengthening injectable thermo-sensitive NIPAAm-g-chitosan hydrogels using chemical cross-linking of disulfide bonds as scaffolds for tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y. Synthesis and characterization of thermosensitive graft copolymer of N-isopropylacrylamide with biodegradable carboxymethylchitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Dextran-grafted-PNIPAAm as an artificial chaperone for protein refolding. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 27, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Nita, L.E. Novel multi-stimuli responsive sodium alginate-grafted-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers: II. Dilute solution properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalanqui, M.; Pentlavalli, S.; McCrudden, C.; Chambers, P.; Ziminska, M.; Dunne, N.; McCarthy, H. Influence of alginate backbone on efficacy of thermo-responsive alginate-g-P(NIPAAm) hydrogel as a vehicle for sustained and controlled gene delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 95, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; She, Z.; Wang, M.; Fang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q. Thermo-sensitive alginate-based injectable hydrogel for tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, J.; Delattre, C.; Michaud, P.; de Baynast, H. Optimization of chitosan properties with the aim of a water resistant adhesive development. Polymers 2021, 13, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaci, M.; Kaya, I. Preparation of biodegradable, and pH-sensitive poly(azomethine)-chitosan hydrogels for potential application of 5-fluoro uracil delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 158, 110680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaci, M.; Kaya, İ. Biodegradable and antibacterial poly(azomethine-urethane)-chitosan hydrogels for potential drug delivery application. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-based stimuli-responsive materials for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2023, 4, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangyekan, C.; Aht-Ong, D.; Srikulkit, K. Preparation and properties evaluation of chitosan-coated cassava starch films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günister, E.; Pestreli, D.; Ünlü, C.H.; Atıcı, O.; Güngör, N. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-MMT biocomposite systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K.; Ikeda, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Shimojoh, M.; Harata, M. Chemoselective protection of the amino groups of chitosan by controlled phthaloylation: Facile preparation of a precursor useful for chemical modifications. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnik, A.; Imperiale, J.C.; Vázquez-González, B.; Raskin, M.M.; Muñoz-Muñoz, F.; Burillo, G.; Cedillo, G.; Bucio, E. Mucoadhesive thermo-responsive chitosan-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) polymeric micelles via a one-pot gamma-radiation-assisted pathway. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 136, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Shi, L.; Tao, Q.; Hui, B.; Li, J. The effect of pH on the LCST of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid). Biomater. Sci. 2004, 15, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.F.G.; Lima, R.M.L.; Feitosa, P.A.J.; Paula, C.B.H.; Paula, C.M.R. Influence of galactomannan molar mass on particle size galactomannan grafted-poly-N-isopropylacrylamide copolymer. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Jang, M.-K.; Nah, J. Synthesis and characterization of thermosensitive nanoparticles based on PNIPAAm core and chitosan shell structure. Macromol. Res. 2009, 17, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, T.; Song, K.; Wu, S.; Fan, X. Effect of intermolecular and intramolecular forces on hydrodynamic diameters of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 127, 4280–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


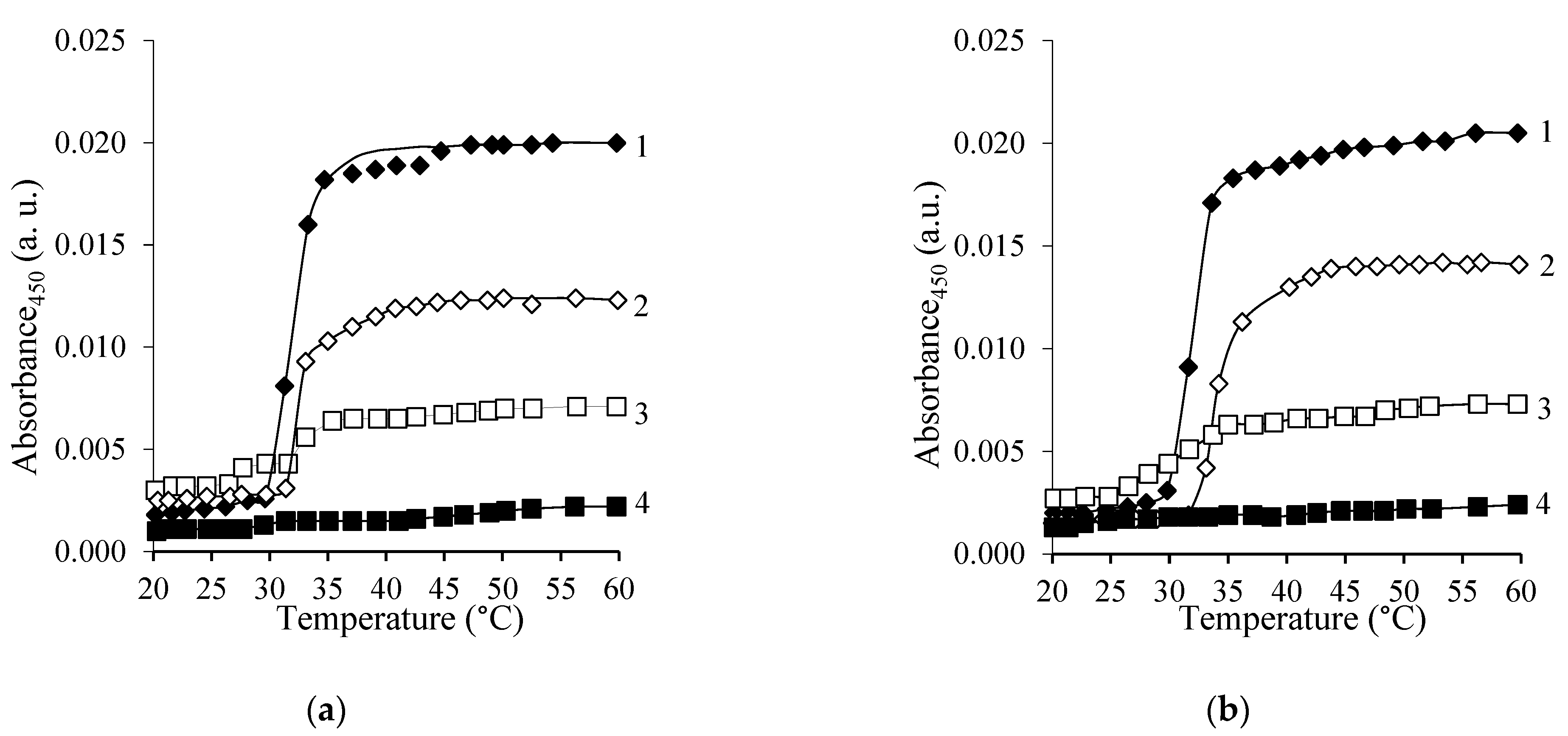
| Copolymer Sample | Molar Ratio of Reagents | Comonomer Molar Ratio in Feed, % | Reaction Yield, % | Comonomer Molar Ratio in Copolymer, % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | NIPAAm | PPS | CS | NIPAAm | CS | NIPAAm | ||
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 80.0 | 20.0 | 55.2 | 92.6 | 7.4 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.16 | 66.7 | 33.3 | 53.9 | 88.0 | 12.0 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-3 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.16 | 55.6 | 44.4 | 55.1 | 81.7 | 18.3 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-4 | 1 | 1 | 0.16 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 57.2 | 79.5 | 20.5 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-5 | 1 | 3 | 0.16 | 25.0 | 75.0 | 57.8 | 74.5 | 25.5 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-6 | 1 | 5 | 0.16 | 16.7 | 83.3 | 63.6 | 62.7 | 37.3 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-7 | 1 | 10 | 0.16 | 9.1 | 90.9 | 77.3 | - | - |
| Sample | Decomposition Onset Temperature, °C | Residual Mass, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Step | Second Step | ||
| CS | 277 | - | 36.4 ± 0.2 |
| PNIPAAm | 371 | - | 0.8 ± 0.3 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-1 | 201 | 254 | 36.2 ± 0.2 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-2 | 203 | 258 | 35.8 ± 0.3 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-3 | 200 | 258 | 35.4 ± 0.2 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-4 | 203 | 260 | 33.0 ± 0.4 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-5 | 238 | 373 | 12.9 ± 0.3 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-6 | 236 | 379 | 12.5 ± 0.2 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-7 | 247 | 386 | 7.0 ± 0.4 |
| In Aqueous Solution | In Aqueous 1% Acetic Acid Solution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | LCST, °C (Cloud Point) | LCST, °C (DSC) | Enthalpy, J/g | LCST, °C (cloud point) | LCST, °C (DSC) | Enthalpy, J/g |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-2 | 29.7 a | - | - | 29.2 a | - | - |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-3 | 30.9 a | 30.0 | 5.41 | 30.2 a | 29.0 | 5.12 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-4 | 31.0 a | 30.3 | 6.36 | 29.9 a | 29.2 | 5.32 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-5 | 31.0 b | 30.8 | 25.74 | 30.1 b | 29.8 | 21.10 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-6 | 31.6 b | 31.4 | 33.81 | 30.0 b | 31.0 | 23.86 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-7 | 31.0 b | 31.7 | 29.32 | 30.0 b | 30.6 | 35.83 |
| PNIPAAm | 31.4 b | 32.7 | 44.26 | 30.6 b | 30.9 | 43.65 |
| Copolymer Sample | Particle Diameter, nm | PDI | Particle Diameter, nm | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 45 °C | |||
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-3 a | 164 ± 98 | 0.34 ± 0.11 | 634 ± 215 | 0.27 ± 0.07 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-4 a | 267 ± 46 | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 554 ± 114 | 0.16 ± 0.03 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-5 b | 408 ± 1 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 197 ± 10 | 0.15 ± 0.04 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-6 b | 419 ± 60 | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 185 ± 5 | 0.07 ± 0.04 |
| CS-g-PNIPAAm-7 b | 383 ± 43 | 0.44 ± 0.06 | 157 ± 15 | 0.20 ± 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babelyte, M.; Peciulyte, L.; Navikaite-Snipaitiene, V.; Bendoraitiene, J.; Samaryk, V.; Rutkaite, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Thermoresponsive Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers. Polymers 2023, 15, 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153154
Babelyte M, Peciulyte L, Navikaite-Snipaitiene V, Bendoraitiene J, Samaryk V, Rutkaite R. Synthesis and Characterization of Thermoresponsive Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153154
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabelyte, Migle, Laura Peciulyte, Vesta Navikaite-Snipaitiene, Joana Bendoraitiene, Volodymyr Samaryk, and Ramune Rutkaite. 2023. "Synthesis and Characterization of Thermoresponsive Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153154
APA StyleBabelyte, M., Peciulyte, L., Navikaite-Snipaitiene, V., Bendoraitiene, J., Samaryk, V., & Rutkaite, R. (2023). Synthesis and Characterization of Thermoresponsive Chitosan-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Copolymers. Polymers, 15(15), 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153154