Nano Delivery Chitosan-Protein/Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain (PHGPB) Synthesized by Colloidal-Spray Drying Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Protein Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain (PHGPB)
2.2.2. Protein Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain (PHGPB) Characterization
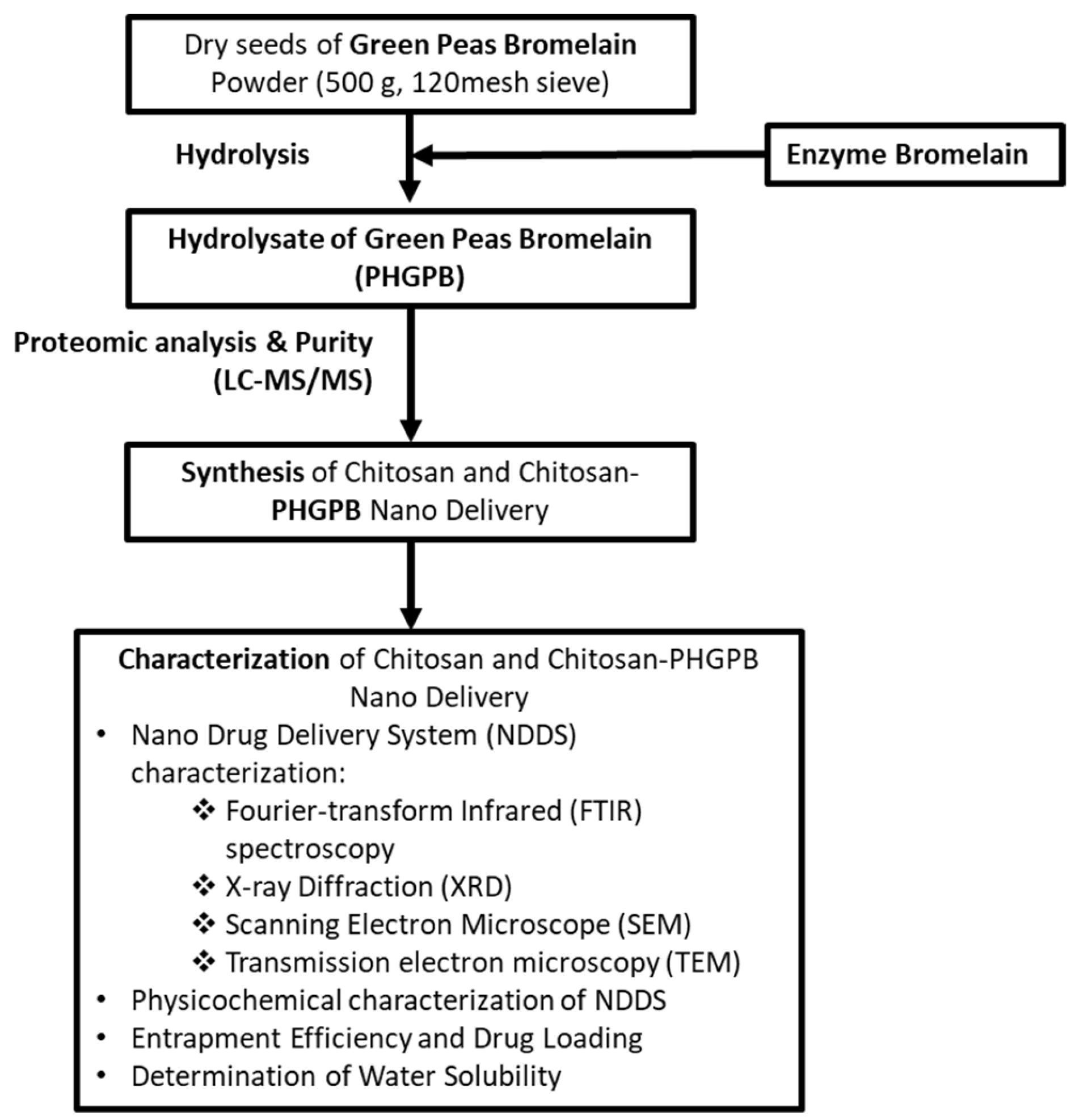
2.2.3. Synthesis of Chitosan and Chitosan/PHGPB
2.2.4. Nano Drug Delivery System (NDDS) Characterization
2.2.5. Physiochemical of NDDS Characterization
2.2.6. Entrapment Efficiency and Drug Loading
2.2.7. Determination of Water Solubility
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- RISKESDAS. Riset Kesehatan Dasar. Badan Penelitian dan Kesehatan Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. In Penyakit Ginjal Kronis 2018; Departemen Kesehatan RI: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Universitas Kristen Maranatha. Pembuatan dan Pengujian Hidrolisat Protein Kacang Polong Hijau (Pisum sativum) sebagai Antifibrosis untuk Terapi Penyakit Ginjal. Kronis Patent IDP 000078605, 24 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayat, M.; Prahastuti, S.; Afifah, E.; Widowati, W.; Yusuf, M.; Hasan, K. The role of green peas protein hydrolysate in TGF/SMAD signaling to prevent renal fibrosis. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101920. [Google Scholar]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C.W. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Surface Chemistry on Biological Systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques, International Scholarly Research Network. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, F.; Lin, W. Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Kidney Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 683247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madni, A.; Kousar, R.; Naeem, N.; Wahid, F. Recent advancements in applications of chitosan-based biomaterials for skin tissue engineering. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Raziyeva, K.; Tabyldiyeva, L.; Berikova, K.; Zhumagul, D.; Temirkhanova, K.; Saparov, A. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambiliyagodage, C.; Jayanetti, M.; Mendis, A.; Ekanayake, G.; Liyanaarachchi, H.; Vigneswaran, S. Recent Advances in Chitosan-Based Applications-A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatullayeva, S.; Tagiyev, D.; Zeynalov, N.; Mammadova, S.; Aliyeva, E. Recent advances of chitosan-based polymers in biomedical applications and environmental protection. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochima, E.; Azhary, S.Y.; Pratama, R.; Panatarani, C.; Joni, I.M. Preparation and Characterization of Nano Chitosan from Crab Shell Waste by Beads-milling Method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 193, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyaboonchai, W. Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Promising System for. Drug Delivery. Naresuan Univ. J. 2003, 11, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, G.; Madhan, B.; Narendrakumar, U.; Kumar, R.V.S.; Manjubala, I. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Li, T.; Song, X.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, P.; Gong, X.; Chen, C.; Sun, L. Preparation and characterization of methacrylated gelatin/bacterial cellulose composite hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Regener. Biomater. 2019, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdiana, Y.; Wathoni, N.; Shamsuddin, S.; Joni, I.M.; Muchtaridi, M. Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles of Targeted Drug Delivery System in Breast Cancer Treatment. Polymers 2021, 13, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, B.; Luigi, D.; Nardo Silvia, F. Thermo-Responsive Methylcellulose Hydrogels: From Design to Applications as Smart Biomaterials. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2021, 27, 486–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhary, S.Y.; Purnama, D.; Florena, F.F.; Vanitha, M.; Muchtaridi; Panatarani, C.; Joni, I.M. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan:SiO2, nanocomposite by ultrasonic spray drying. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 550, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathoni, N.; Rusdin, A.; Motoyama, K.; Joni, I.M.; Lesmana, R.; Muchtaridi, M. Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for α-Mangostin. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2020, 13, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Cai, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, F.; Lin, W. A review of the application of nanoparticles in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic kidney disease. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geo, H.N.; Murugan, D.D.; Chik, Z.; Norazit, A.; Foo, Y.Y.; Leo, B.F.; Teo, Y.Y.; Kadir, S.Z.S.B.S.A.; Chan, Y.; Chai, H.J.; et al. Renal Nano-drug delivery for acute kidney Injury: Current status and future perspectives. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, M. Preparation and Examination of Hydrolysate Protein of Green Peas by Bromelain for Improvement Kidney Function; Universitas Kristen Maranatha: Bandung, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Harlow, E.; Lane, D. Bradford assay. CSH Protoc. 2006, 2006, pdb.prot4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, M.; Prahastuti, S.; Rakasiwi, A.S.; Prisilia, S.; Hasan, K. Sub-chronic toxicity study of green peas protein hydrolysate in rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, M.; Pangastuti, R.; Prahastuti, S.; Hasan, K. Protein Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain Attenuates Kidney Fibrosis in Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Rats: Emphasis on Anti-Inflammatory Activities. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2022, 30, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizo, R.R.; Miranda, O.R.; Moyano, D.F.; Walden, C.A.; Giri, K.; Bhattacharya, R.; Robertson, J.D.; Rotello, V.M.; Reid, J.M.; Mukherjee, P. Modulating Pharmacokinetics, Tumor Uptake and Biodistribution by Engineered Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.-R.; Zhao, Z. Comparative study of the in vitro and in vivo characteristics of cationic and neutral liposomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 16, 2271–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; He, C.; Riviere, J.E.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Lin, Z. Meta-Analysis of Nanoparticle Delivery to Tumors Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation Approach. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3075–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tsui, C.; Tang, C.; Yang, M.; Gu, L. Surface charge switchable and pH-responsive chitosan/polymer core-shell composite nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 121, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Mayanovic, R.A. A Review of the Preparation, Characterization, and Applications of Chitosan Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdiana, Y.; Wathoni, N.; Shamsuddin, S.; Muchtaridi, M. Drug release study of the chitosan-based nanoparticles. Heliyon 2021, 8, e08674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jafernik, K.; Ładniak, A.; Blicharska, E.; Czarnek, K.; Ekiert, H.; Wiącek, A.E.; Szopa, A. Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles as Effective Drug Delivery Systems—A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




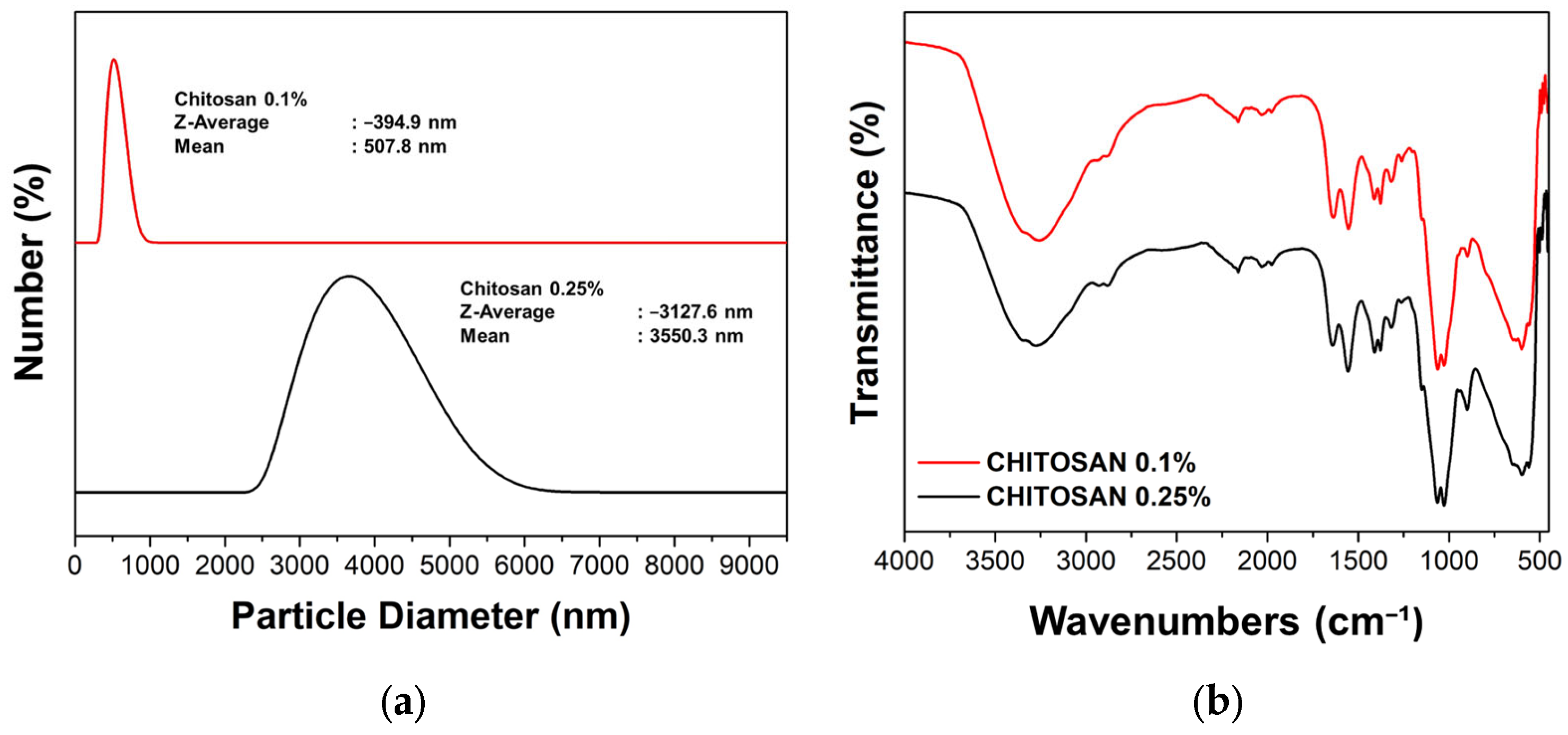

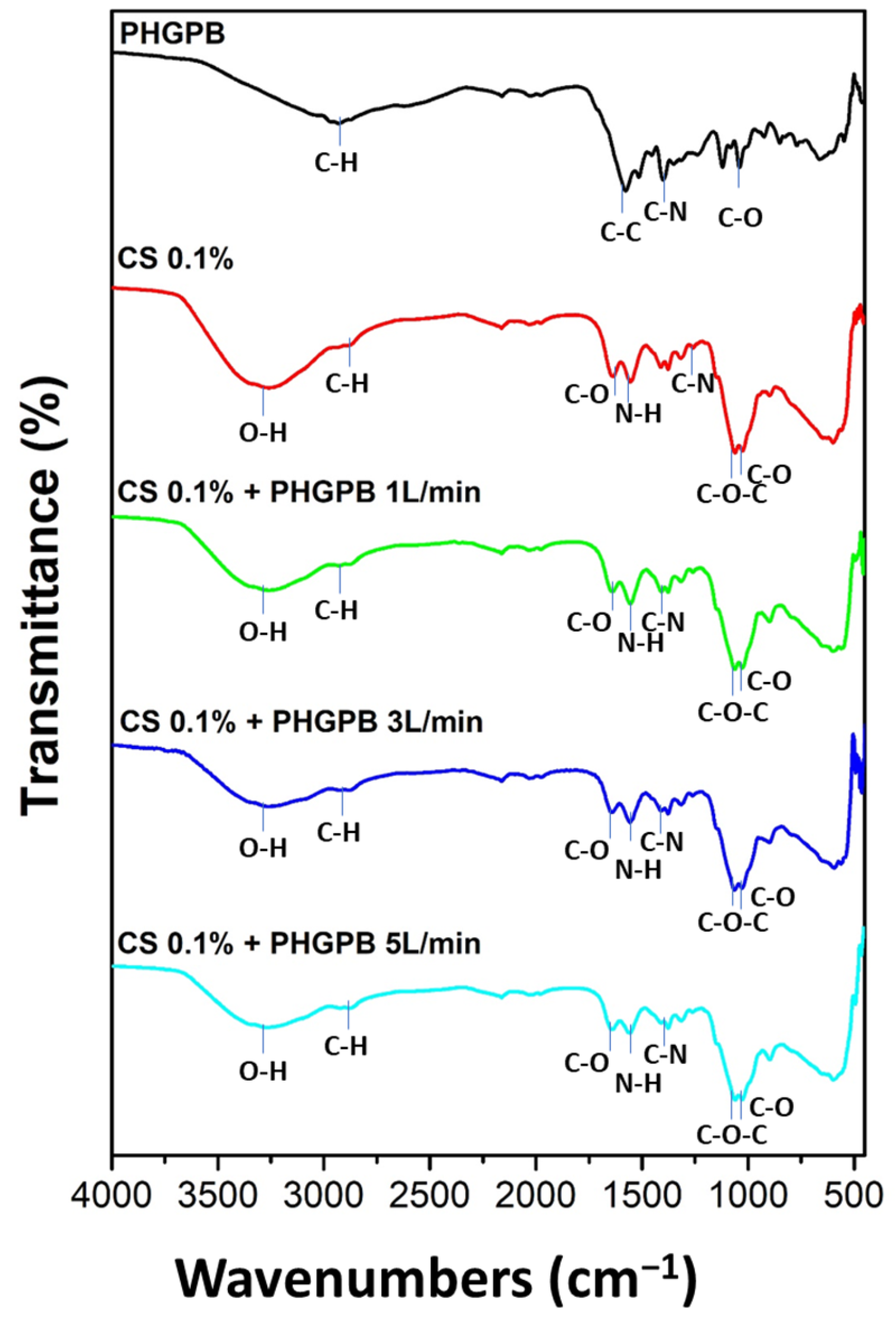


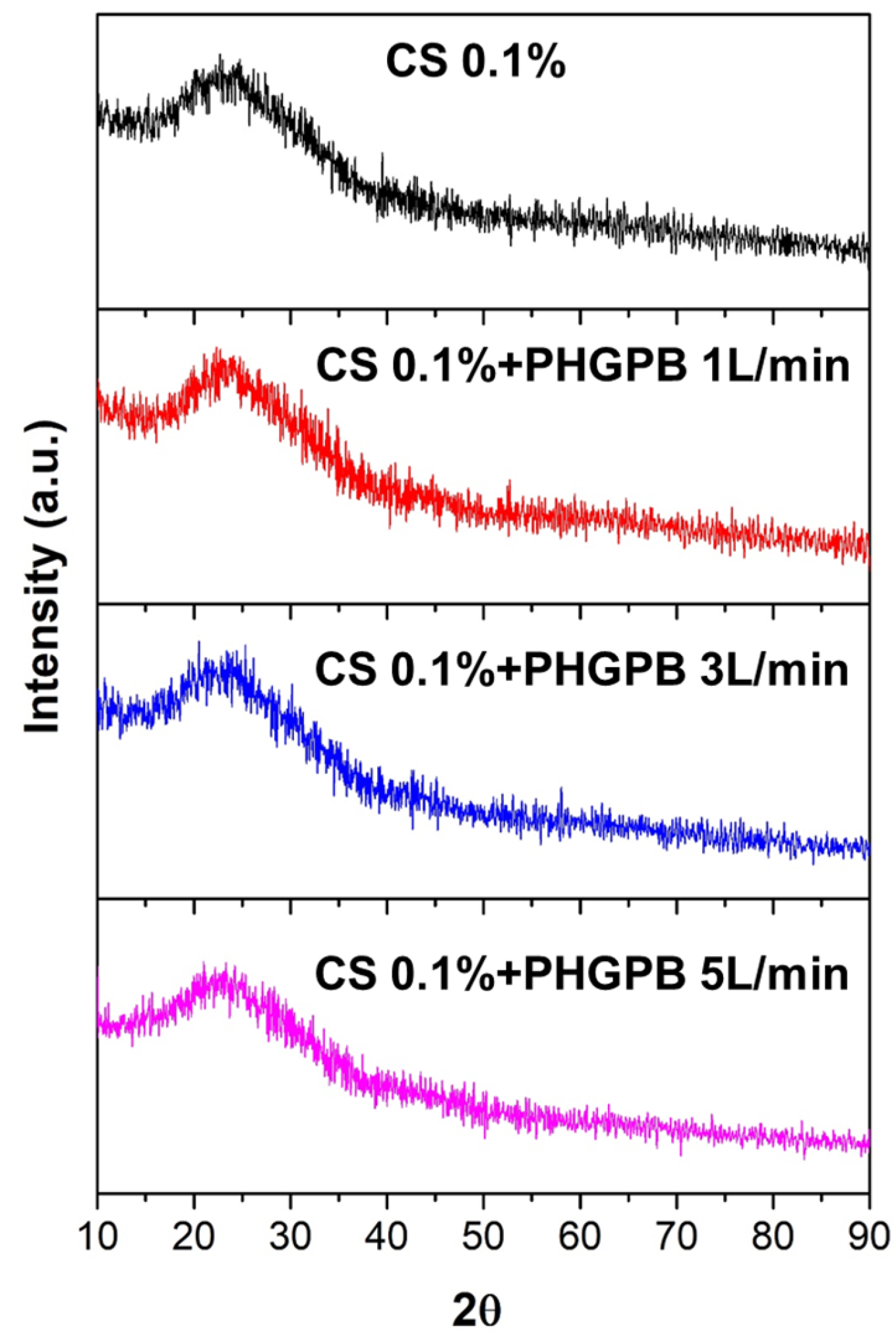

| No. | Samples Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chitosan 0.1% | Chitosan 0.1% |
| 2 | Chitosan 0.1% + PHGPB 1 L/min | Chitosan 0.1% + PHGPB, synthesis at flow rate 1 L/min |
| 3 | Chitosan 0.1% + PHGPB 3 L/min | Chitosan 0.1% + PHGPB, synthesis at flow rate 3 L/min |
| 4 | Chitosan 0.1% + PHGPB 5 L/min | Chitosan 0.1% + PHGPB synthesis at flow rate 5 L/min |
| No | Accession | Description | Coverage | Peptide | PSMs | Unique | Protein | AAs | MW (kda) | Calc.pl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q5ZGL2 | Seed albumin2 (Fragment) OS = Pisum sativum OX = 3888 GN = pa2 PE = 4SV = 1 | 67 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 51 | 5.7 | 8.5 |
| 2 | P08688 | Albumin-2 OS = Pisum sativum OX = 3888 PE = 2SV = 1 | 38 | 7 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 231 | 26.2 | 5.35 |
| 3 | ADA161AT60 | Non-specific lipid = transfer protein 1 OS = Pisum sativum OX = 3888 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 120 | 12.2 | 8.65 |
| 4 | Q53WT6 | P139 protein OS = Pisum sativum OX = 3888 GN = p139 PE = 2 SV = 1 | 19 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 74 | 8.2 | 6.48 |
| 5 | Q76KV8 | Short chain alcohol dehydrogenase A (Fragment) OS = Pisum sativum OX = 3888 GN = sadA PE = 2 SV = 1 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 277 | 29.2 | 6 |
| 6 | PO2867 | Lectin OS = Pisum sativum OX 3888 GN = LECA PE = 1 SV = 1 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 275 | 30.3 | 5.03 |
| 7 | PO2855 | Provicilin (Fragment) OS = Pisum sativum OX 3888 GN = LECA PE = 3 SV = 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 275 | 31.5 | 5.76 |
| 8 | O24294 | Legumin (Minor small) OS = Pisum sativum OX 3888 GN = LegS PE = 2 SV = 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 566 | 64.8 | 5.55 |
| 9 | P15838 | Legumin A2 OS = Pisum sativum OX 3888 GN = LEGA 2 PE = 3 SV = 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 520 | 59.2 | 6.62 |
| 10 | Q9M3X6 | Convicilin OS = Pisum sativum OX 3888 GN = cvc PE = 2 SV = 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6123 | 72 | 5.6 |
| 11 | P09918 | Seed linoleate 95-Lipoxygenase-3 OS = Pisum sativum OX 3888 GN = LOX1.3 PE = 2 SV = 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 861 | 97.6 | 6.51 |
| Formulae | Entrapment Efficiency (%) | Drug Loading (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CS 0.1% + PHGPB 1 L/min | 87.92 ± 0.91 | 4.61 ± 0.35 |
| CS 0.1% + PHGPB 3 L/min | 83.84 ± 0.00 | 6.17 ± 0.00 |
| CS 0.1% + PHGPB 5 L/min | 86.17 ± 1.26 | 5.28 ± 0.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hidayat, M.; Hasan, K.; Yusuf, M.; Sriwidodo, S.; Panatarani, C.; Joni, I.M. Nano Delivery Chitosan-Protein/Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain (PHGPB) Synthesized by Colloidal-Spray Drying Method. Polymers 2023, 15, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112546
Hidayat M, Hasan K, Yusuf M, Sriwidodo S, Panatarani C, Joni IM. Nano Delivery Chitosan-Protein/Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain (PHGPB) Synthesized by Colloidal-Spray Drying Method. Polymers. 2023; 15(11):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112546
Chicago/Turabian StyleHidayat, Meilinah, Khomaini Hasan, Muhamad Yusuf, Sriwidodo Sriwidodo, Camellia Panatarani, and I Made Joni. 2023. "Nano Delivery Chitosan-Protein/Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain (PHGPB) Synthesized by Colloidal-Spray Drying Method" Polymers 15, no. 11: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112546
APA StyleHidayat, M., Hasan, K., Yusuf, M., Sriwidodo, S., Panatarani, C., & Joni, I. M. (2023). Nano Delivery Chitosan-Protein/Hydrolysate of Green Peas Bromelain (PHGPB) Synthesized by Colloidal-Spray Drying Method. Polymers, 15(11), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112546






