Ketorolac Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Coating of AZ31 in the Treatment of Bone Fracture Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ketorolac Tromethamine Stability
2.3. Coating of AZ31 Alloy
2.4. Polymeric Film Production
2.5. Polymeric Films and Polymeric Coated AZ31 Characterization
2.6. In Vitro Release Study
2.7. Blank Polymeric Film Mass Loss
2.8. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
3. Results and Discussion
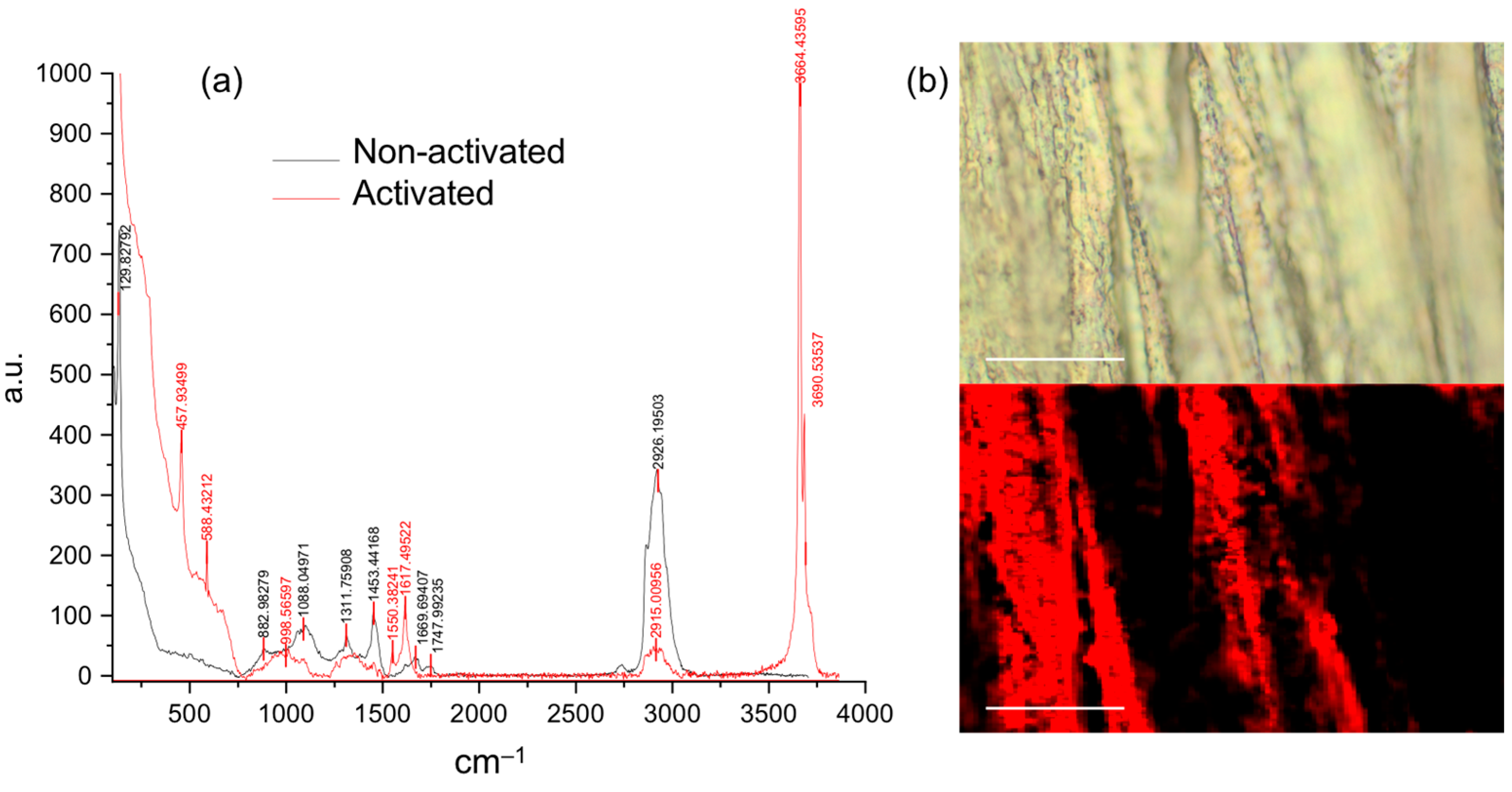
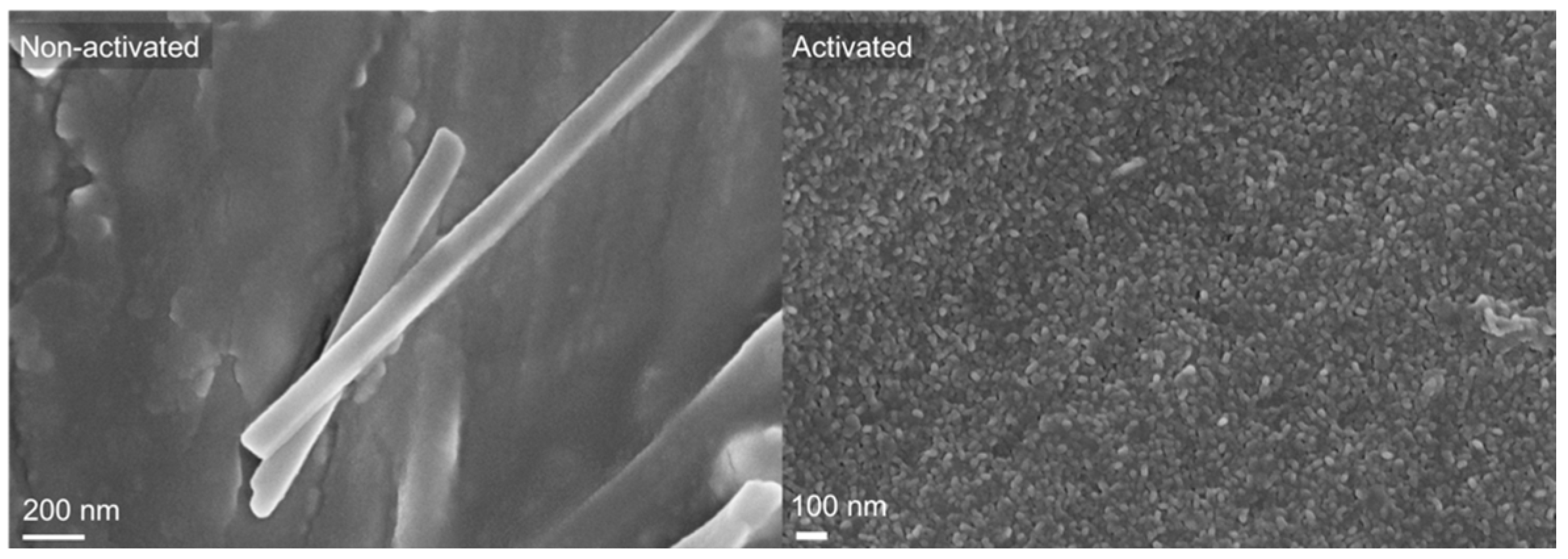
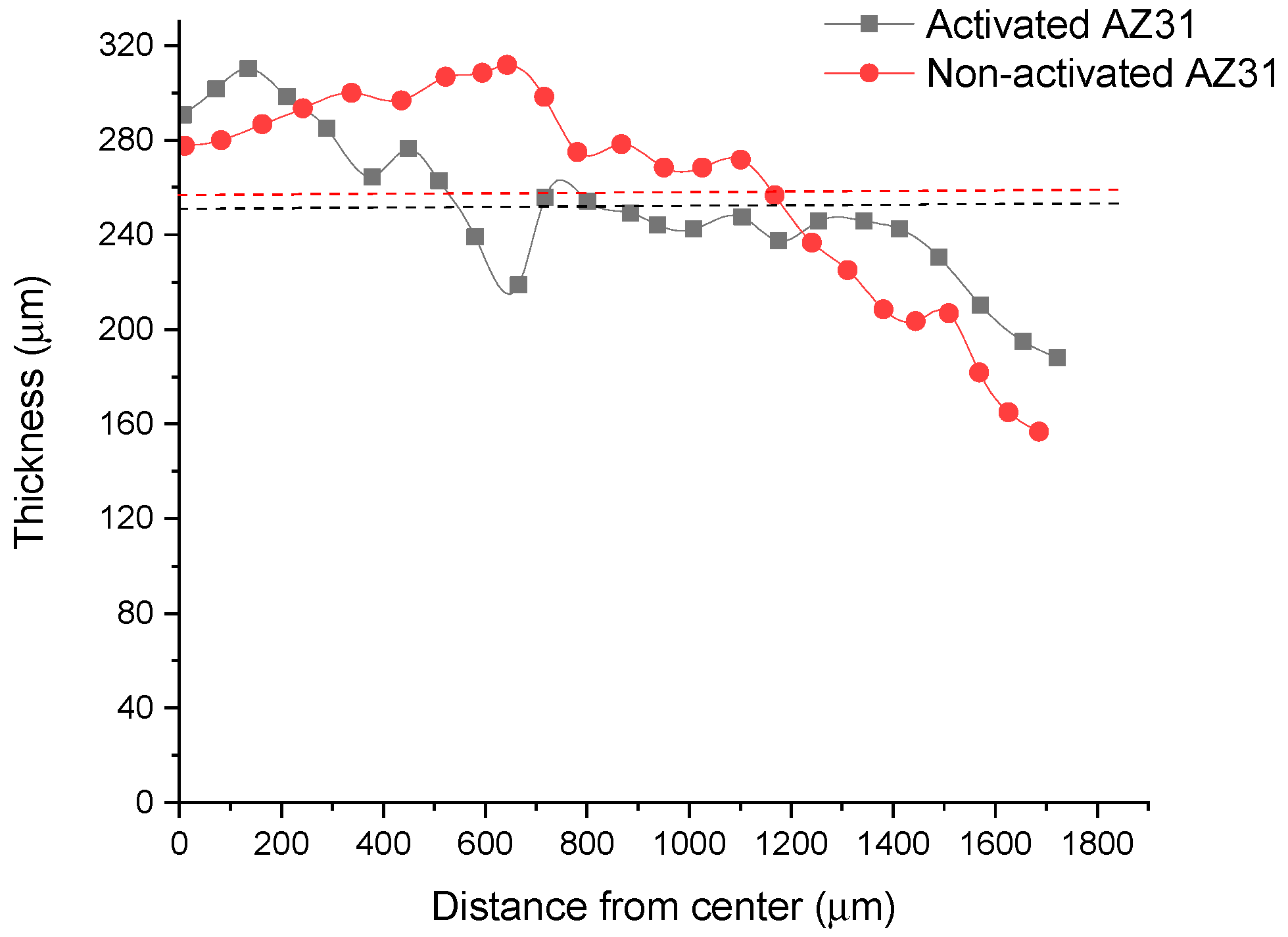
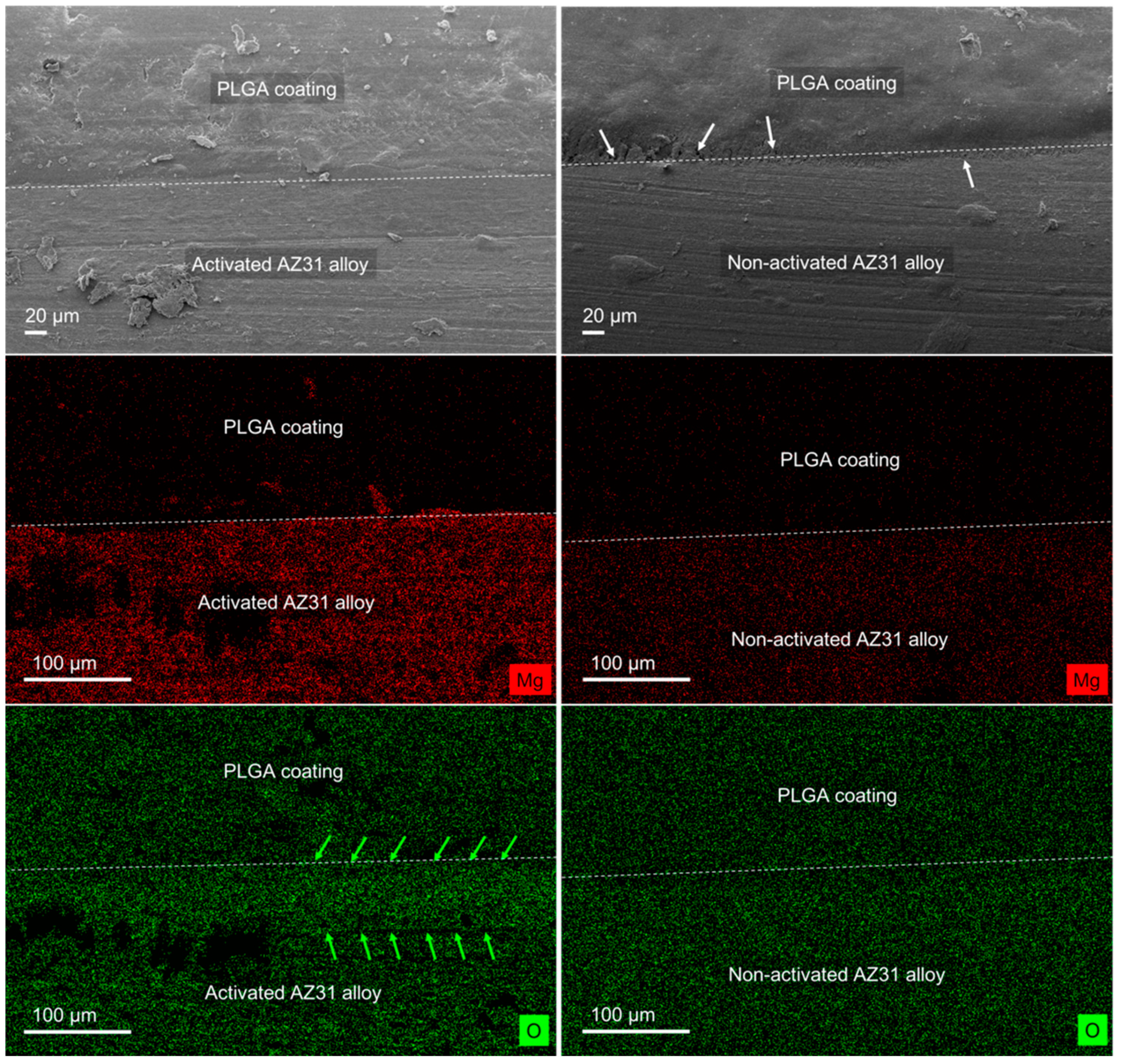
3.1. Polymeric Coated AZ31 Characterization
3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
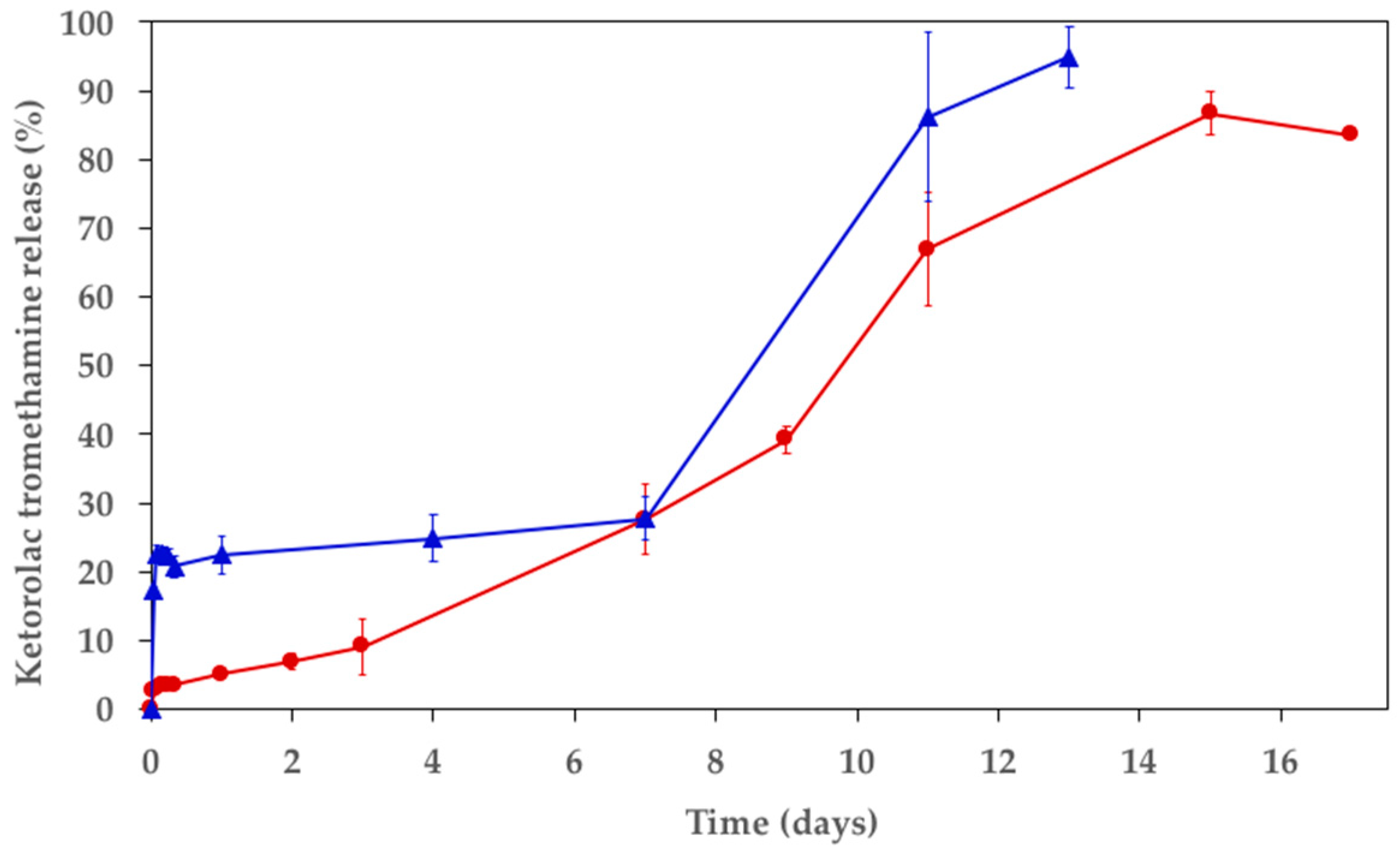
3.3. In Vitro Release Study and Polymer Mass Loss
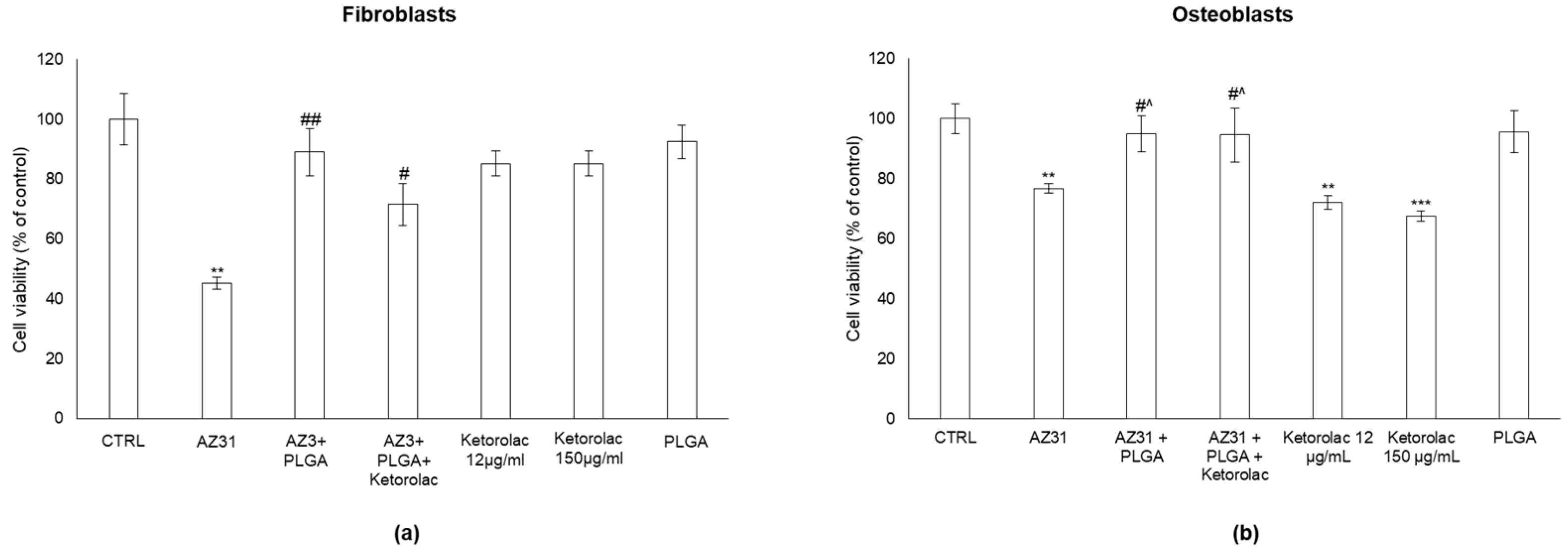
3.4. AZ31 Cytotoxicity in Human Fibroblasts and Osteoblasts
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, J. 1—Metallic Biomaterials: State of the Art and New Challenges. In Fundamental Biomaterials: Metals; Balakrishnan, P., Sreekala, M.S., Thomas, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 1–33. ISBN 978-0-08-102205-4. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, F.; Hort, N.; Vogt, C.; Cohen, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Degradable Biomaterials Based on Magnesium Corrosion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2008, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Curtin, J.; Duffy, B.; Jaiswal, S. Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys for Orthopaedic Applications: A Review on Corrosion, Biocompatibility and Surface Modifications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Shan, D.; Chen, R.; Zhang, F.; Han, E.-H. Biodegradable Behaviors of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy in Simulated Body Fluid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, K. A Review on Magnesium Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 953344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Xu, J.-K.; Hopkins, C.; Chow, D.H.-K.; Qin, L. Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Implants in Orthopedics-A General Review and Perspectives. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schranz, D.; Zartner, P.; Michel-Behnke, I.; Akintürk, H. Bioabsorbable Metal Stents for Percutaneous Treatment of Critical Recoarctation of the Aorta in a Newborn. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2006, 67, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, C.; Bodelón, O.G.; Montoya, R.; Clemente, C.; Garcia-Alonso, M.C.; Rubio, J.C.; Escudero, M.L. Fracture Bone Healing and Biodegradation of AZ31 Implant in Rats. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 025008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigheb, M.; Veneziano, M.; Tortia, R.; Bosetti, M.; Cochis, A.; Rimondini, L.; Grassi, F.A. Osteosynthesis Devices in Absorbable Magnesium Alloy in Comparison to Standard Ones: A Systematic Review on Effectiveness and Safety. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, T.; Fischerauer, S.F.; Hänzi, A.C.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F.; Weinberg, A.M. Magnesium Alloys for Temporary Implants in Osteosynthesis: In Vivo Studies of Their Degradation and Interaction with Bone. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, M.; Cassidy, J.; Duffy, B. Sol–Gel Sealing Characteristics for Corrosion Resistance of Anodised Aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Gao, L.; Fan, X.-L.; Zeng, R.-C.; Chen, D.-C.; Zhi, K.-Q. In Vitro Degradation and Cytocompatibility of a Low Temperature In-Situ Grown Self-Healing Mg-Al LDH Coating on MAO-Coated Magnesium Alloy AZ31. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Xu, D.; Liu, X. Mussel-Inspired Functionalization of PEO/PCL Composite Coating on a Biodegradable AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Tian, P.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B. In Vitro Degradation, Hemolysis, and Cytocompatibility of PEO/PLLA Composite Coating on Biodegradable AZ31 Alloy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yin, H.; Meng, H.; Sun, Z.; Sui, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, A.; Lu, S. In vivo degradation of magnesium alloys and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) and degradation evaluation of magnesium alloys using micro-ct. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2016, 30, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczenko, J.; Kajzer, W.; Grygiel-Pradelok, M.; Jaworska, J.; Jelonek, K.; Nowińska, K.; Gawliczek, M.; Libera, M.; Marcinkowski, A.; Kasperczyk, J. Corrosion Resistance of PLGA-Coated Biomaterials. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2017, 19, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schoubben, A.; Ricci, M.; Giovagnoli, S. Meeting the Unmet: From Traditional to Cutting-Edge Techniques for Poly Lactide and Poly Lactide-Co-Glycolide Microparticle Manufacturing. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Wang, F. PLGA-Based Micro/Nanoparticles: An Overview of Their Applications in Respiratory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, X.; Gu, J.; Yan, C.; Yin, S.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.; Geng, F. Polylactic-Co-Glycolic Acid-Based Nanoparticles Modified with Peptides and Other Linkers Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier for Targeted Drug Delivery. Nanomedicine 2023, 18, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotla, N.G.; Pandey, A.; Vijaya Kumar, Y.; Ramazani, F.; Fisch, A. Polyester-Based Long Acting Injectables: Advancements in Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Technological Insights. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, J.C.; Brogden, R.N. Ketorolac. A Reappraisal of Its Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Properties and Therapeutic Use in Pain Management. Drugs 1997, 53, 139–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massó González, E.L.; Patrignani, P.; Tacconelli, S.; García Rodríguez, L.A. Variability among Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs in Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.L.; Chang, J.K.; Wang, G.J. Effects of Ketorolac on Bone Repair: A Radiographic Study in Modeled Demineralized Bone Matrix Grafted Rabbits. Pharmacology 1998, 57, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.R.C.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated Biological Fluids with Possible Application in Dissolution Testing. Dissolut. Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, P.; Schoubben, A.; Giovagnoli, S.; Perioli, L.; Ricci, M.; Rossi, C. Ketoprofen Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Physical Interaction. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoubben, A.; Blasi, P.; Deluca, P.P. Effect of Agitation Regimen on the in Vitro Release of Leuprolide from Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic) Acid Microparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmin, F.; Blasi, P.; DeLuca, P.P. Accelerated Polymer Biodegradation of Risperidone Poly(d, l-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Microspheres. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, S.; Negri, P.; Coniglio, M.; Bruscoli, S.; Di Michele, A.; Marchetti, M.C.; Valenti, C.; Gambelunghe, A.; Fanasca, L.; Billi, M.; et al. Heat-Not-Burn Tobacco (IQOS), Oral Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes: Cytotoxicity, Morphological Analysis, Apoptosis and Cellular Cycle. An in Vitro Study. J. Periodontal Res. 2021, 56, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antognelli, C.; Marinucci, L.; Frosini, R.; Macchioni, L.; Talesa, V.N. Metastatic Prostate Cancer Cells Secrete Methylglyoxal-Derived MG-H1 to Reprogram Human Osteoblasts into a Dedifferentiated, Malignant-like Phenotype: A Possible Novel Player in Prostate Cancer Bone Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.; Macnair, R.; MacDonald, C.; Wykman, A.; Goldie, I.; Grant, M.H. In Vitro Biocompatibility Testing of Polymers for Orthopaedic Implants Using Cultured Fibroblasts and Osteoblasts. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambelunghe, A.; Giovagnoli, S.; Di Michele, A.; Boncompagni, S.; Dell’Omo, M.; Leopold, K.; Iavicoli, I.; Talesa, V.N.; Antognelli, C. Redox-Sensitive Glyoxalase 1 Up-Regulation Is Crucial for Protecting Human Lung Cells from Gold Nanoparticles Toxicity. Antioxidants 2020, 9, E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-H.; Lee, H.-P.; Yeh, M.-L. Characterization of a Sandwich PLGA-Gallic Acid-PLGA Coating on Mg Alloy ZK60 for Bioresorbable Coronary Artery Stents. Materials 2020, 13, E5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Morshed, M.; Labour, M.-N.; Hoey, D.; Duffy, B.; Curtin, J.; Jaiswal, S. Enhanced Corrosion Protection and Biocompatibility of a PLGA–Silane Coating on AZ31 Mg Alloy for Orthopaedic Applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 113871–113883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RSoniya, S.; Naiir, V.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanostructured Mg(OH)2 and MgO. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, K.; Fujima, N.; Komura, H. First-order Raman Scattering in MgO Microcrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ham, H.J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Suh, C.M. Thermal Conductivity of Magnesium Alloys in the Temperature Range from −125 °C to 400 °C. Int. J. Thermophys. 2013, 34, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.; Dixon, D. The Influence of Solvent Processing on Polyester Bioabsorbable Polymers. J. Biomater. Appl. 2012, 26, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, E.A.; Alb, A.M.; Nauman, E.A.; Reed, W.F.; Dee, K.C. Solvent Effects on the Microstructure and Properties of 75/25 Poly(D,L-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Tissue Scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 70, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.K.; Kavitha, K.; Rupeshkumar, M. Evaluation of Ketorolac Tromethamine Microspheres by Chitosan/Gelatin B Complex Coacervation. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.R.; Trehan, A. Development, Characterization, and Evaluation of Ketorolac Tromethamine-Loaded Biodegradable Microspheres as a Depot System for Parenteral Delivery. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, P.; D’Souza, S.S.; Selmin, F.; DeLuca, P.P. Plasticizing Effect of Water on Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide). J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, S.E.; Griesser, U.J. Physicochemical Properties of the Binary System Glibenclamide and Polyethylene Glycol 4000. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2004, 77, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsac, P.J.; Shamblin, S.L.; Taylor, L.S. Theoretical and Practical Approaches for Prediction of Drug-Polymer Miscibility and Solubility. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.R.; Trehan, A. Formulation, Characterization, and Evaluation of Ketorolac Tromethamine-Loaded Biodegradable Microspheres. Drug Deliv. 2005, 12, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulay, C.M.; Yaldiz, S.; Bilge, A. Do We Really Know the Duration of Pain after Rib Fracture? Kardiochir. Torakochirurgia Pol. 2018, 15, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadivelu, N.; Gowda, A.M.; Urman, R.D.; Jolly, S.; Kodumudi, V.; Maria, M.; Taylor, R.; Pergolizzi, J.V. Ketorolac Tromethamine—Routes and Clinical Implications. Pain Pract. 2015, 15, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvak, K.M.; McEvoy, G.K. Ketorolac, an Injectable Nonnarcotic Analgesic. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1991, 48, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocks, D.R.; Jamali, F. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Ketorolac Tromethamine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 23, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, D.I. Minimising the Adverse Effects of Ketorolac. Drug Saf. 2000, 22, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, L.; Van Hai, L.; Hoang, N.T.; Hanh, D.T.H.; Nam, N.V. In Vitro Biodegradation Behavior of Biodegradable Hydroxyapatite Coated AZ31 Alloy Treated at Various PH Values. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2021, 19, 22808000211010036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Shadanbaz, S.; Woodfield, T.B.F.; Staiger, M.P.; Dias, G.J. Magnesium Biomaterials for Orthopedic Application: A Review from a Biological Perspective. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1316–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvak, K.M.; McEvoy, G.K. Ketorolac, an Injectable Nonnarcotic Analgesic. Clin. Pharm. 1990, 9, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna-Bertos, E.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; García-Martínez, O.; Ruiz, C. Effects on Growth of Human Osteoblast-like Cells of Three Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Metamizole, Dexketoprofen, and Ketorolac. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2015, 17, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.L.; Bainbridge, N.J.; Jordan, N.R.; Sharpe, J.R. The Effect of Topical Analgesics on Ex Vivo Skin Growth and Human Keratinocyte and Fibroblast Behavior. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, A.; Yahata, C.; Takai, H. Cytocompatibility of Magnesium and AZ31 Alloy with Three Types of Cell Lines Using a Direct in Vitro Method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
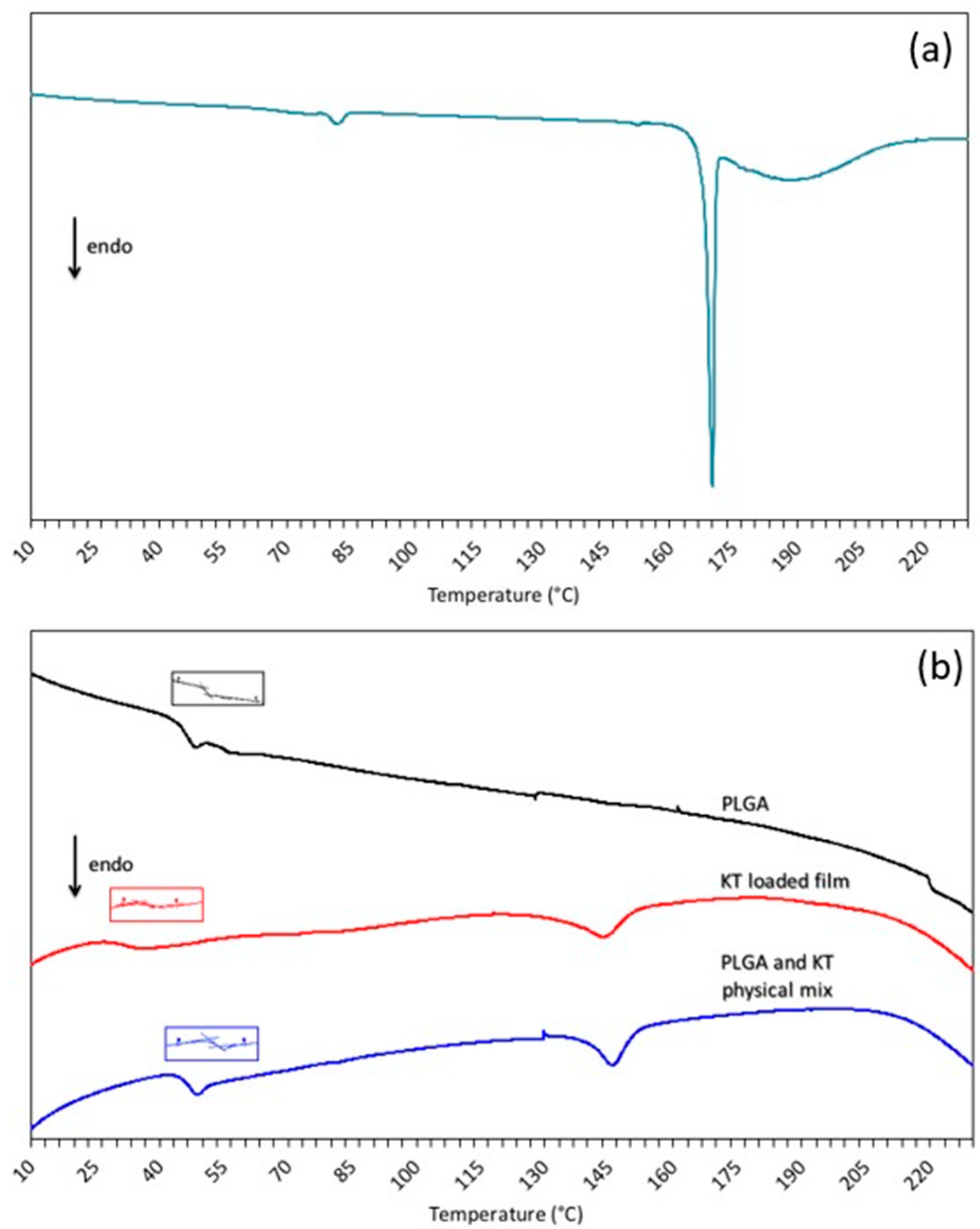

| Sample | Tg (°C) |
|---|---|
| PLGA RG 503 H | 45.73 |
| PLGA film loaded with 5% ketorolac tromethamine | 31.93 |
| Ketorolac tromethamine:PLGA physical mixture (5:100, w:w) | 45.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puccetti, M.; Cusati, E.; Antognelli, C.; Ricci, M.; Ambrogi, V.; Schoubben, A. Ketorolac Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Coating of AZ31 in the Treatment of Bone Fracture Pain. Polymers 2023, 15, 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102246
Puccetti M, Cusati E, Antognelli C, Ricci M, Ambrogi V, Schoubben A. Ketorolac Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Coating of AZ31 in the Treatment of Bone Fracture Pain. Polymers. 2023; 15(10):2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102246
Chicago/Turabian StylePuccetti, Matteo, Eleonora Cusati, Cinzia Antognelli, Maurizio Ricci, Valeria Ambrogi, and Aurélie Schoubben. 2023. "Ketorolac Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Coating of AZ31 in the Treatment of Bone Fracture Pain" Polymers 15, no. 10: 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102246
APA StylePuccetti, M., Cusati, E., Antognelli, C., Ricci, M., Ambrogi, V., & Schoubben, A. (2023). Ketorolac Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Coating of AZ31 in the Treatment of Bone Fracture Pain. Polymers, 15(10), 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102246