Acoustic Emission Signal Characterisation of Failure Mechanisms in CFRP Composites Using Dual-Sensor Approach and Spectral Clustering Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
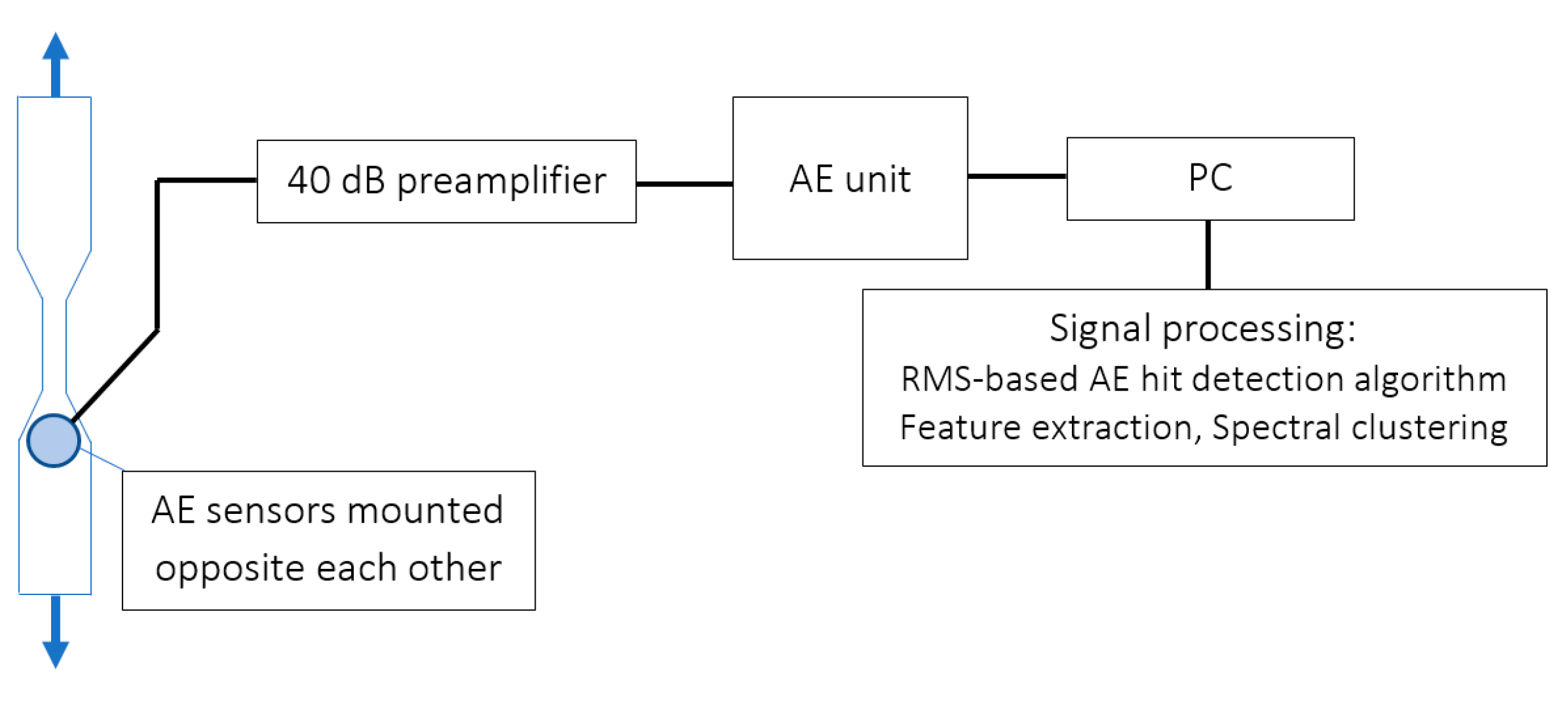
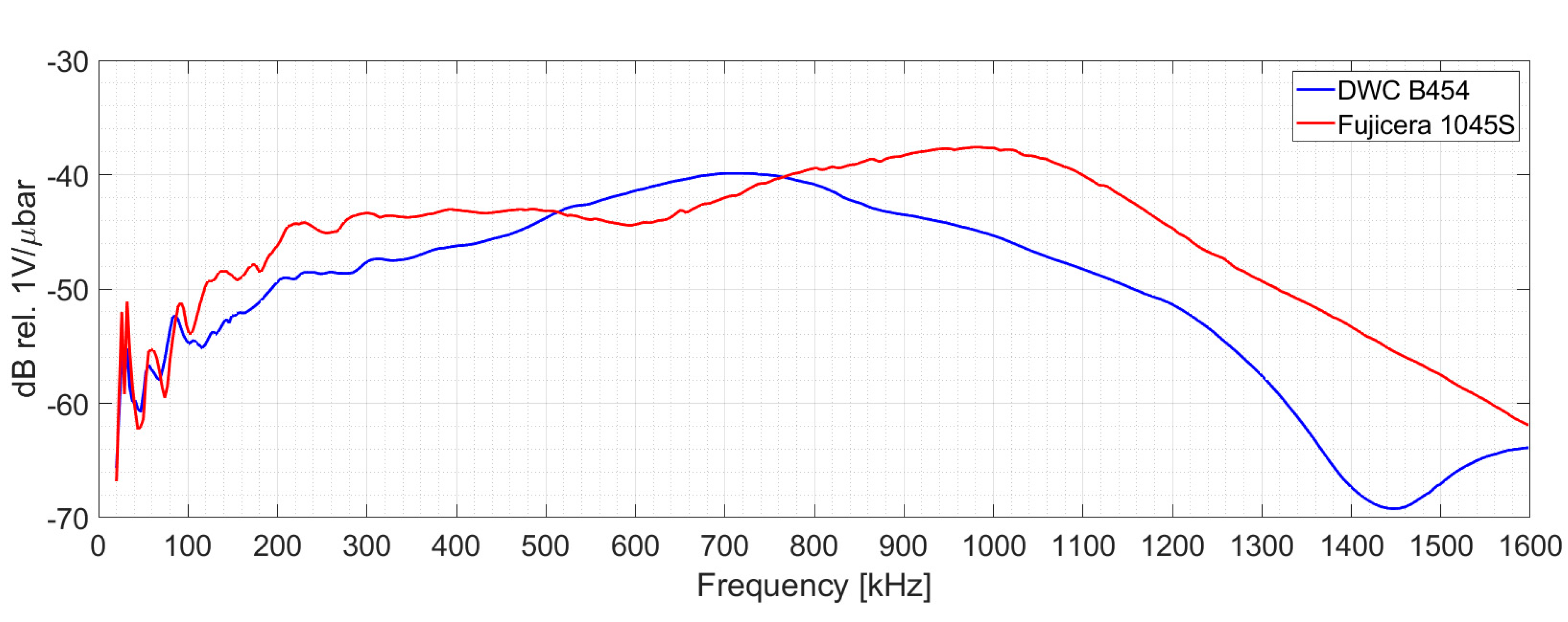
2.1. Acoustic Emission Monitoring
- The AE activity was recorded at a fixed threshold value of 28 dBAE, while the duration discrimination time (DDT) and rearm time (RAT) were set to 100 µs;
- 2
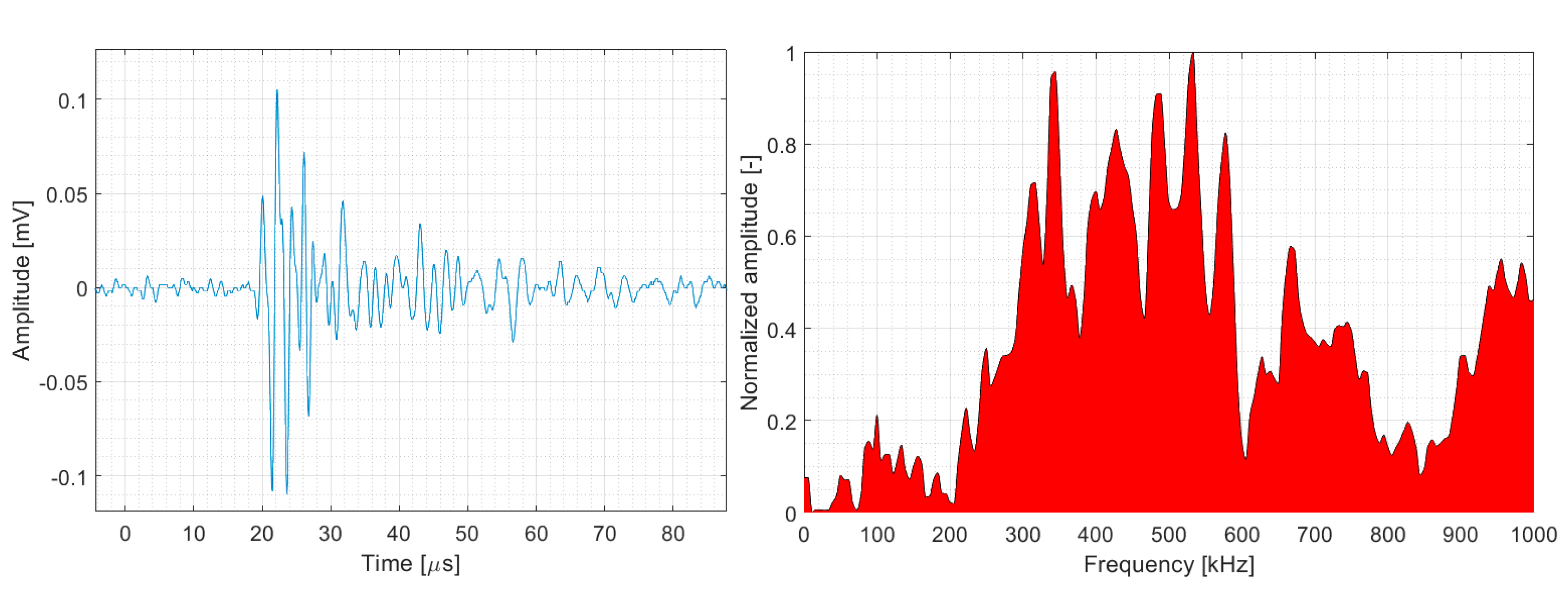
- The recorded wave transients were subsequently subjected to an additional hit segmentation process with the following parameters: width of the RMS window = 10 µs, fixed value of the RMS threshold = 10 dBAE. The floating value of the RMS threshold is given by:where rmsmean is the mean value of the RMS before the start of the AE hit (mean value from the first 10 samples before the hit start), max(rms) is the maximum value of the RMS recording for the given AE hit, and peak/valley ratio = 0.25 (maximum) for valid pairs exceeding the principal threshold of 28 dBAE.
2.2. Failure Mechanisms
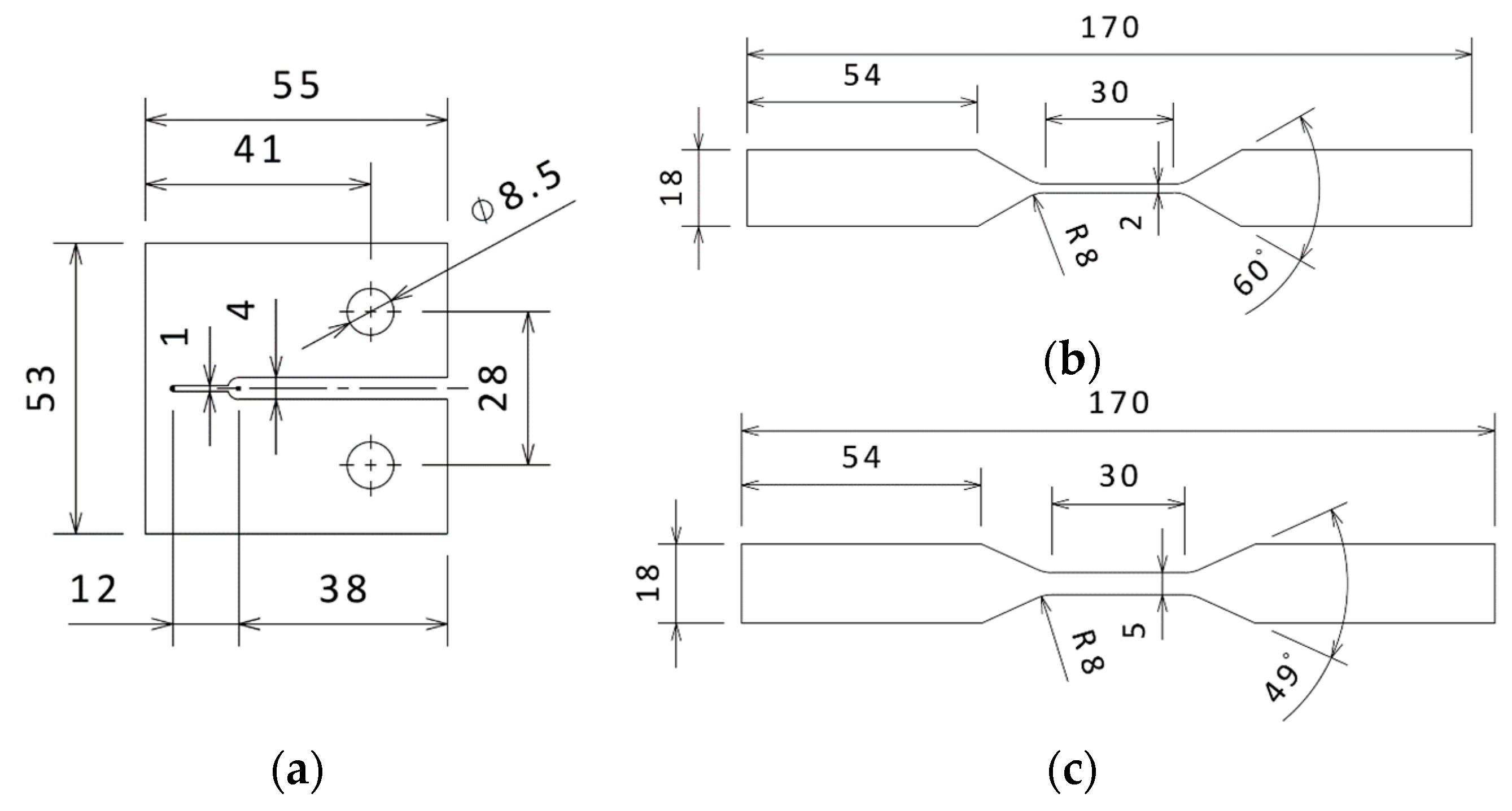
2.2.1. Tensile Test of Fibre Bundles and Compact Tension Test of Bulk Resin
2.2.2. Compact Tension Test of Unidirectional Specimens
2.2.3. Compact Tension and Tensile Test of 0–90° Cross-Ply Specimens
2.2.4. Tensile Test of ± 45° Cross-ply Specimens
3. Pattern Recognition Technique
3.1. Feature Selection
- For a given matrix Kn × p containing normalised input data, construct the nearest neighbour graph. Afterwards, define pairwise distances di,j for all points in the neighbourhood;
- 2.
- Generate the similarity matrix S using the kernel transformation , where is the scale factor for the kernel and is the pairwise distance between two arbitrary nodes i and j ( refers to the Euclidian distance in our case);
- 3.
- Perform the centring of each feature using its mean , where is the degree matrix and ;
- 4.
- For each feature, compute the score ;
3.2. Clustering Technique
- Assemble the similarity graph for a given set of points defined by X;
- Calculate the similarity (or adjacency) matrix S, with where is the scale factor for the kernel and is the pairwise distance between two arbitrary nodes i and j ( is the Euclidian distance in our case);
- Construct the Laplacian matrix , where denotes the degree matrix;
- Find , the h smallest eigenvectors of matrix , and form matrix by stacking the eigenvectors into columns;
- Treat each row in as a point and perform k-means clustering;
- Assign the original points in X to the same clusters as their corresponding rows in .
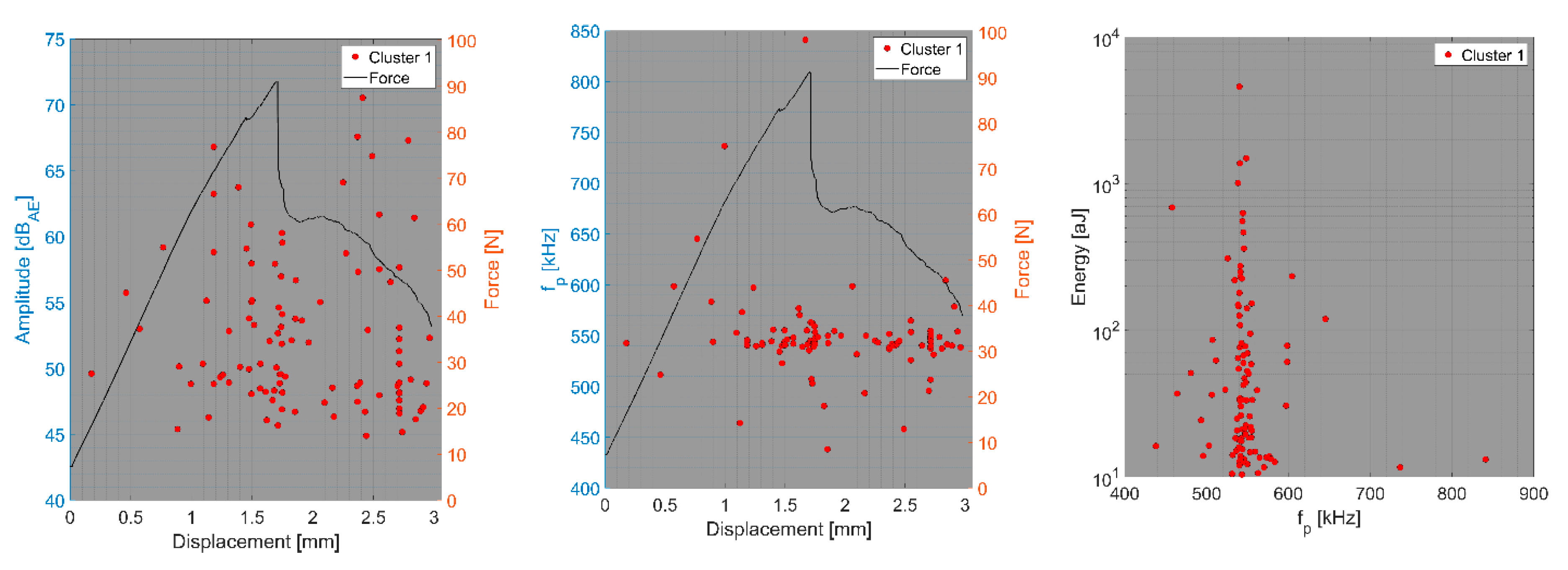
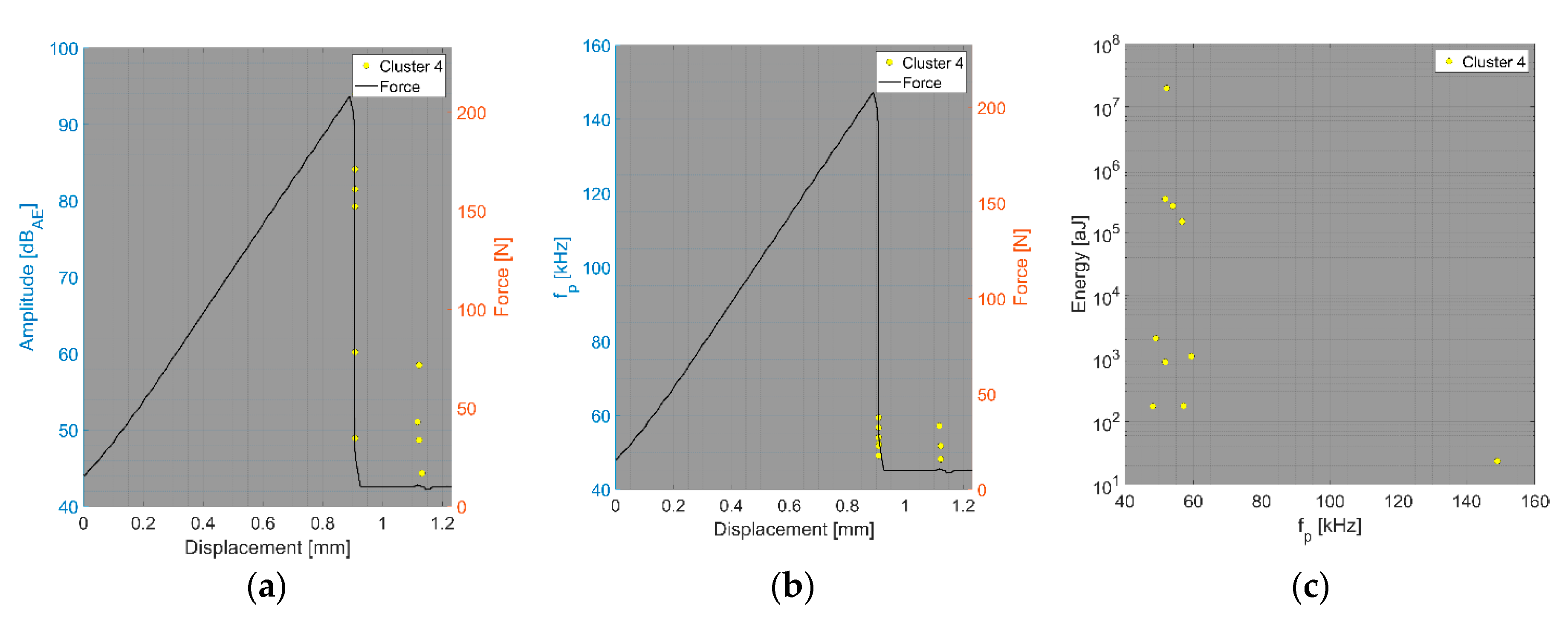
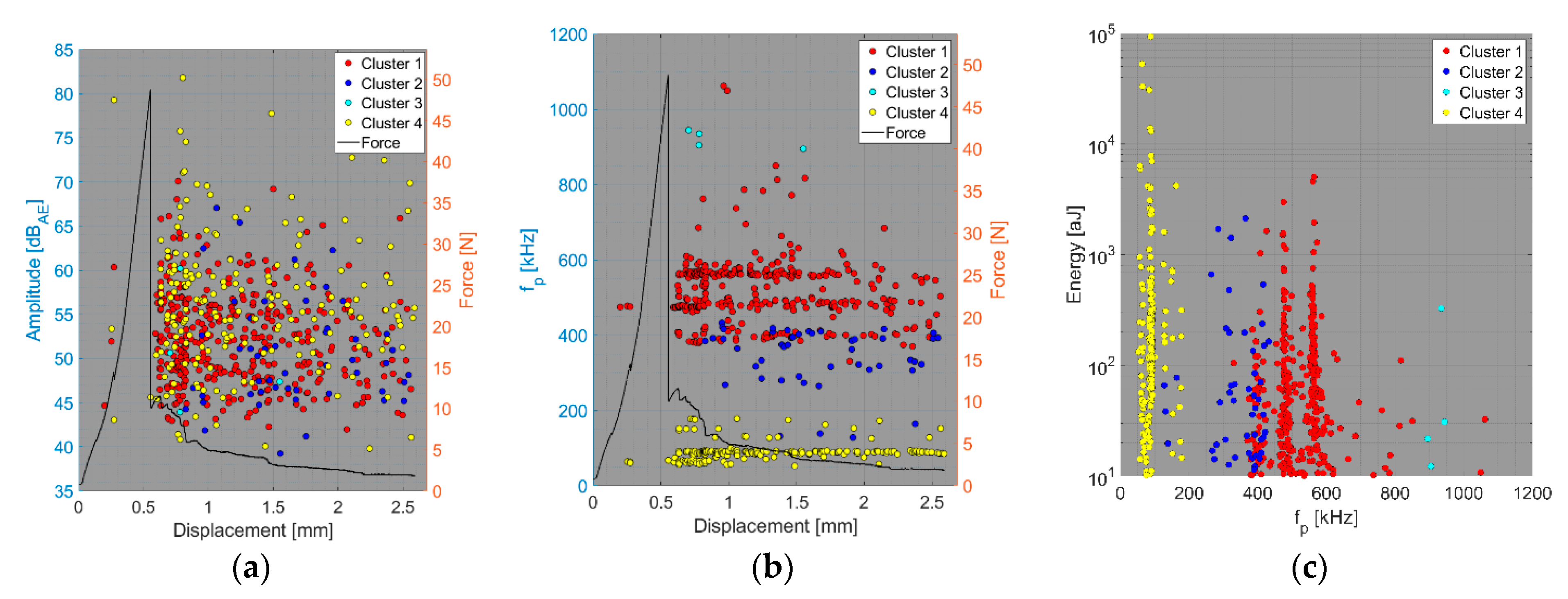
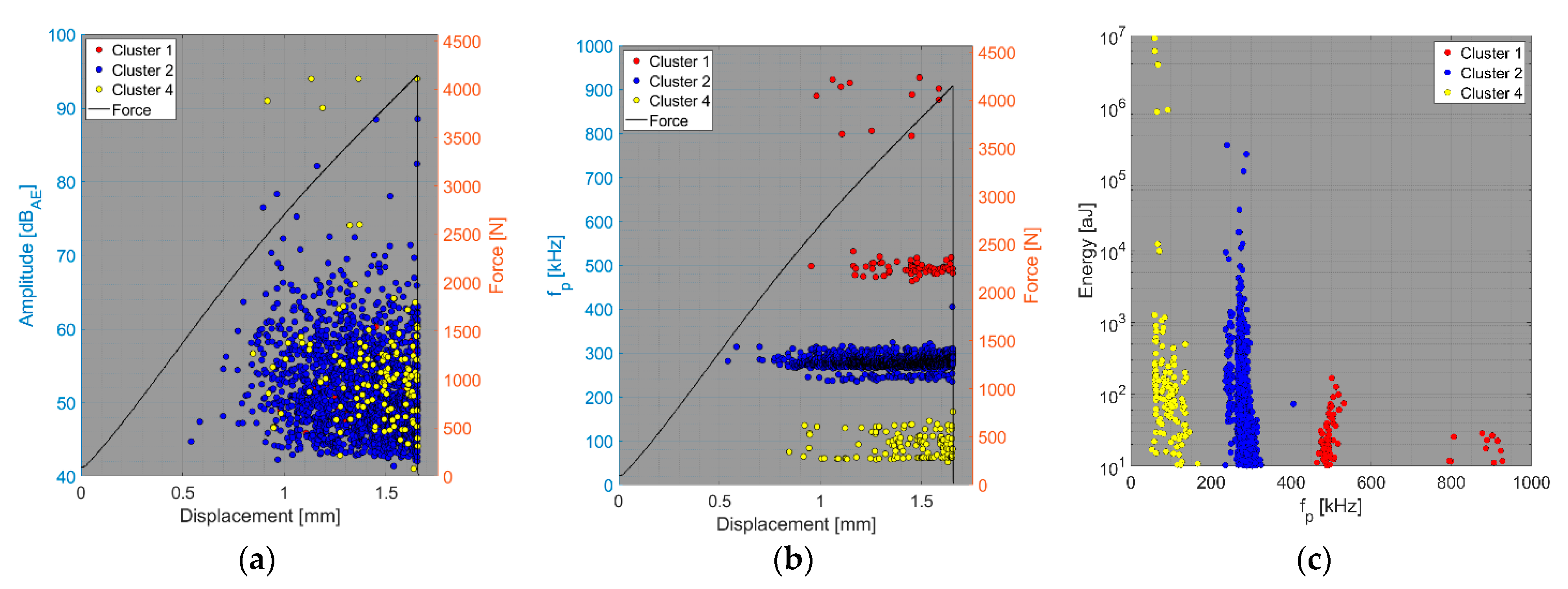
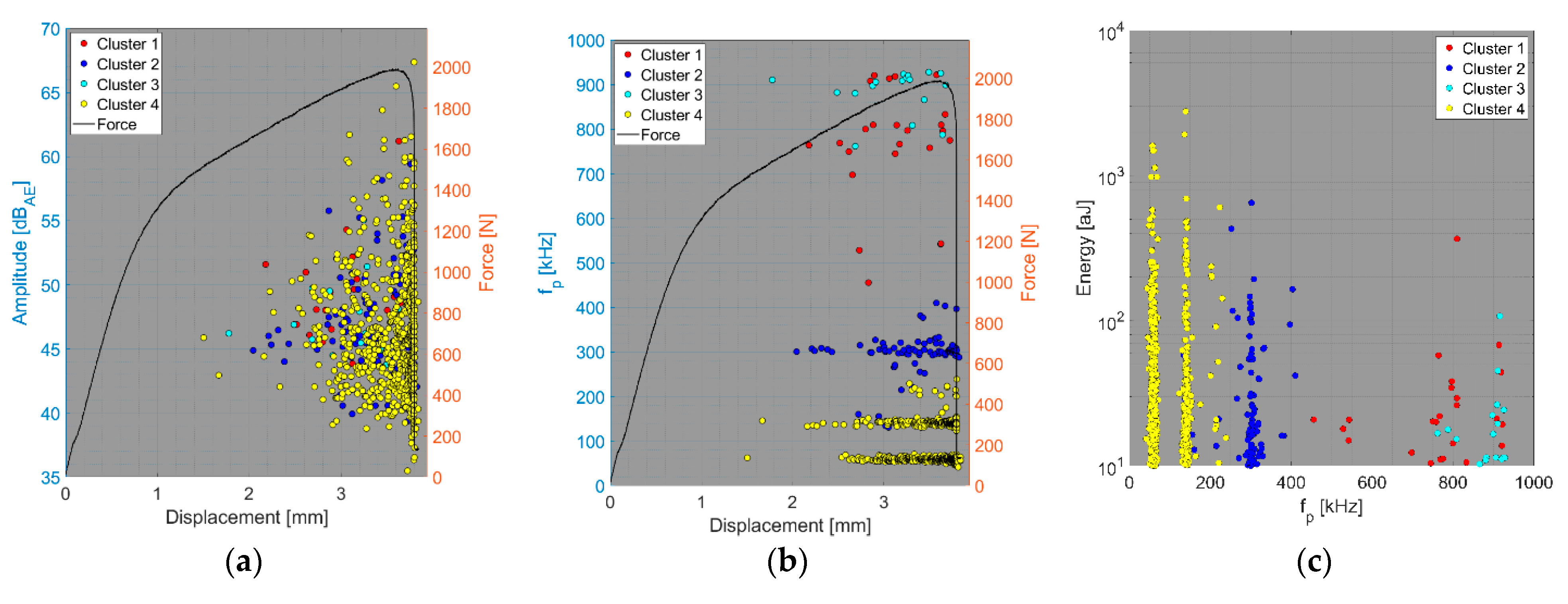
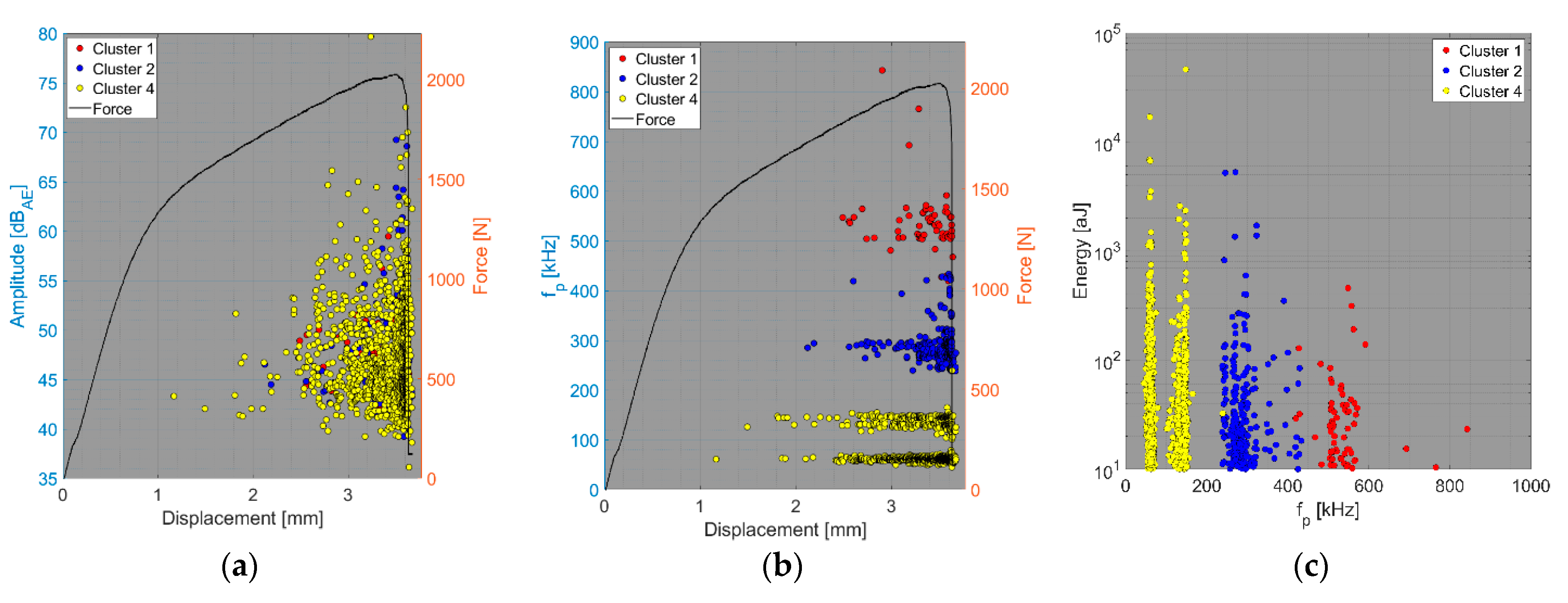
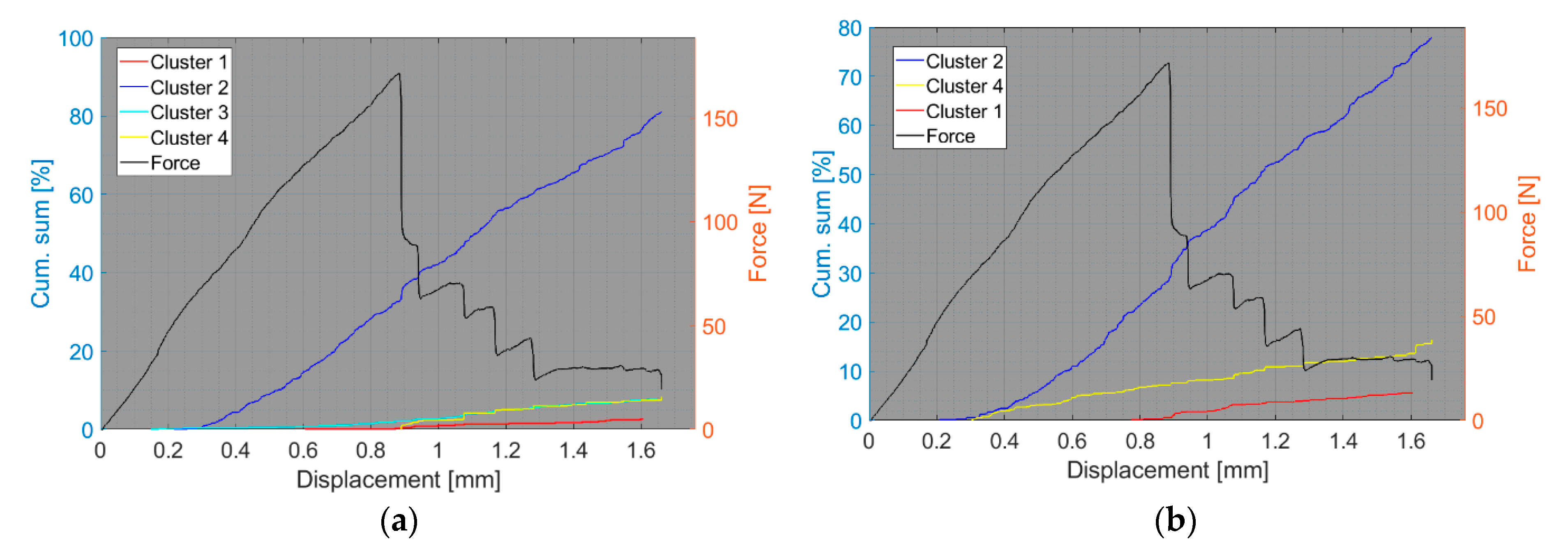
4. Results and Discussion
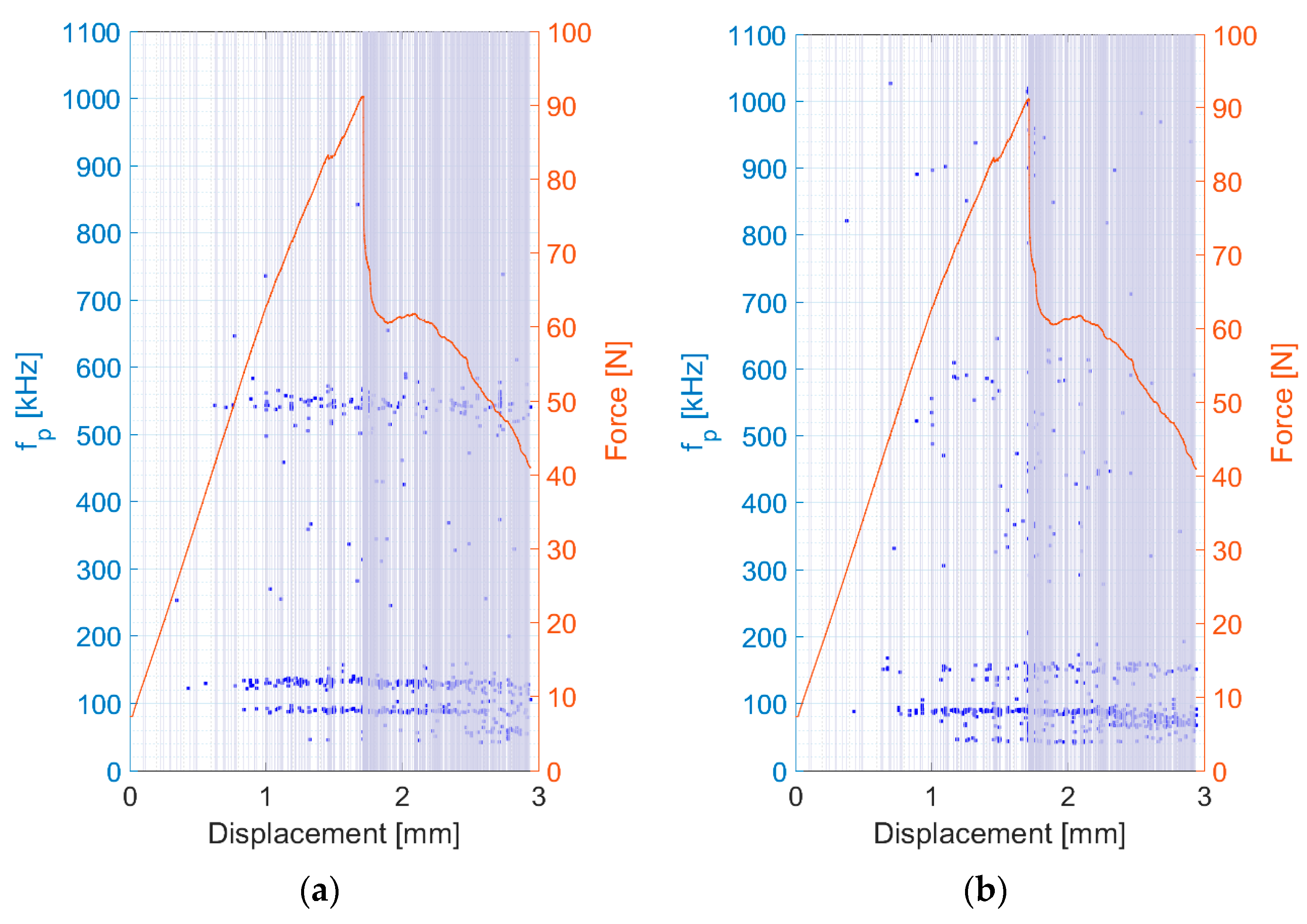
- Relationship between amplitude and force versus displacement (a);
- Relationship between peak frequency and force versus displacement (b);
- Relationship between AE hit energy versus peak frequency (c).
4.1. Delamination and Matrix Cracking
4.2. Fibre/Matrix Debonding
4.3. Fibre Failure
4.4. Fibre Pull-Out
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Šofer, M.; Cienciala, J.; Fusek, M.; Pavlíček, P.; Moravec, R. Damage analysis of composite CFRP tubes using acoustic emission monitoring and pattern recognition approach. Materials 2021, 14, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Han, Q.; Liu, X. Damage pattern recognition and damage evolution analysis of unidirectional CFRP tendons under tensile loading using acoustic emission technology. Compos. Struct. 2020, 238, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, V.; Sidharth, A.A.P.; Santulli, C. Failure modes characterization of impacted carbon fibre reinforced plastics laminates under compression loading using acoustic emission. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Kim, B.; Locquet, A.; McKeon, P.; Declercq, N.; Citrin, D.S. Nondestructive evaluation of forced delamination in glass fiber reinforced composites by terahertz and ultrasonic waves. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 79, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, H.; Schulze, M.; Pooch, M.; Gäbler, S.; Nocke, A.; Bardl, G. Review on quality assurance along the CFRP value chain—Nondestructive testing of fabrics, preforms and CFRP by HF radio wave techniques. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 77, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Withers, P.J. X-ray computed tomography of polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiuk, K.; Dudzik, K. Determining the stages of deformation and destruction of composite materials in a static tensile test by acoustic emission. Materials 2022, 15, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinánd, M.; Várdai, R.; Móczó, J.; Pukánszky, B. Deformation and failure mechanism of particulate filled and short fiber reinforced thermoplastics: Detection and analysis by acoustic emission testing. Polymers 2021, 13, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Mansouri, H.; Nikbakht, A.; Saghafi, H.; Fotouhi, M. Applying acoustic emission technique for detecting various damages occurred in PCL nanomodified composite laminates. Polymers 2021, 13, 3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Salazar, O.F.; Wakayama, S.; Can-Herrera, L.A.; Dzul-Cervantes, M.A.A.; Ríos-Soberanis, C.R.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M. Damage evolution and fracture events sequence analysis of core-shell nanoparticle modified bone cements by acoustic emission technique. Polymers 2020, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yuxia, C.; Liu, D.; Li, D. Acoustic emission-based study to characterize the crack initiation point of wood fiber/HDPE composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šofer, M.; Kučera, P.; Mazancová, E.; Krejčí, L. Acoustic emission and fractographic analysis of seamless steel pressure cylinders with artificial flaws under hydrostatic burst testing. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoubi, S.; Dahmene, F.; Bouzenad, A.; el Mountassir, M.; Aouini, M. Modal acoustic emission for composite structures health monitoring: Issues to save computing time and algorithmic implementation. Compos. Struct. 2018, 183, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, N.; Huguet, S.; Gaertner, R. Integration of the Kohonen’s self-organising map and k-means algorithm for the segmentation of the AE data collected during tensile tests on cross-ply composites. NDTE Int. 2005, 38, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shateri, M.; Ghaib, M.; Svecova, D.; Thomson, D. On acoustic emission for damage detection and failure prediction in fiber reinforced polymer rods using pattern recognition analysis. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, C.U.; Ohtsu, M. Acoustic Emission Testing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 3540699724. [Google Scholar]
- Fotouhi, M.; Najafabadi, M.A. Acoustic emission-based study to characterize the initiation of delamination in composite materials. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014, 29, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sause, M.G.R.; Müller, T.; Horoschenkoff, A.; Horn, S. Quantification of failure mechanisms in mode-I loading of fiber reinforced plastics utilizing acoustic emission analysis. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongsheng, L.; Qian, H.; Jinping, O. Fatigue damage evolution and monitoring of carbon fiber reinforced polymer bridge cable by acoustic emission technique. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2012, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, R.; Najafabadi, M.A.; Saeedifar, M.; Yousefi, J.; Minak, G. Correlation of acoustic emission with finite element predicted damages in open-hole tensile laminated composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 108, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norden, H.E.; Zheng, S.; Steven, R.L.; Manli, C.W.; Hsing, H.S.; Quanan, Z.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar]
- Sause, M.G.R. In-Situ Monitoring of Fiber-Reinforced Composites: Theory, Basic Concepts, Methods, and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9783319309538. [Google Scholar]
- Roundi, W.; el Mahi, A.; el Gharad, A.; Rebiere, J.-L. Acoustic emission monitoring of damage progression in Glass/Epoxy composites during static and fatigue tensile tests. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 132, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, M.B.; el Mahi, A.; Rebiere, J.-L.; Gimenez, I.; Beyaoui, M.; Abdennadher, M.; Haddar, M. Investigation and identification of damage mechanisms of unidirectional carbon/flax hybrid composites using acoustic emission. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 216, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tabrizi, I.E.; Kefal, A.; Zanjani, J.S.M.; Akalin, C.; Yildiz, M. Experimental and numerical investigation on fracture behavior of glass/carbon fiber hybrid composites using acoustic emission method and refined zigzag theory. Compos. Struct. 2019, 223, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Swolfs, Y.; Straumit, I.; Yan, X.; Lomov, S.V. Cluster analysis of acoustic emission signals for 2D and 3D woven carbon fiber/epoxy composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 50, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidane, E.H.; Scida, D.; Assarar, M.; Ayad, R. Damage mechanisms assessment of hybrid flax-glass fibre composites using acoustic emission. Compos. Struct. 2017, 174, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marec, A.; Thomas, J.H.; el Guerjouma, R. Damage characterization of polymer-based composite materials: Multivariable analysis and wavelet transform for clustering acoustic emission data. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2008, 22, 1441–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashmforoush, F.; Khamedi, R.; Fotouhi, M.; Hajikhani, M.; Ahmadi, M. Damage classification of sandwich composites using acoustic emission technique and k-means genetic algorithm. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2014, 33, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedifar, M.; Najafabadi, M.A.; Zarouchas, D.; Toudeshky, H.H.; Jalalvand, M. Clustering of interlaminar and intralaminar damages in laminated composites under indentation loading using acoustic emission. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 144, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskouei, A.R.; Heidary, H.; Ahmadi, M.; Farajpur, M. Unsupervised acoustic emission data clustering for the analysis of damage mechanisms in glass/polyester composites. Mater. Des. 2012, 37, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedifar, M.; Zarouchas, D. Damage characterization of laminated composites using acoustic emission: A review. Compos. Part B 2020, 195, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, P.J.; Wijnen, P.A.M.; Janssen, R.B.F. Real-time frequency determination of acoustic emission for different fracture mechanisms in carbon/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1995, 55, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutkin, R.; Green, C.J.; Vangrattanachai, S.; Pinho, S.T.; Robinson, P.; Curtis, P.T. On acoustic emission for failure investigation in CFRP: Pattern recognition and peak frequency analyses. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boominathan, R.; Arumugam, V.; Santulli, C.; Sidharth, A.A.P.; Sankar, R.A.; Sridhar, B.T.N. Acoustic emission characterization of the temperature effect on falling weight impact damage in carbon/epoxy laminates. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schull, P.J. Nondestructive Evaluation: Theory, Techniques, and Applications; M. Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sause, M.G.R.; Gribov, A.; Unwin, A.R.; Horn, S.; Schull, P.J. Pattern recognition approach to identify natural clusters of acoustic emission signals. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Cui, J. Acoustic emission RA-value and granite fracture modes under dynamic and static loads. In Advances in Acoustic Emission Technology; Springer Proceedings in Physics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 218, WCAE 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R. Fiber bridging in composite laminates: A literature review. Compos. Struct. 2019, 229, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, C.; Casavola, C.; Pappalettera, G.; Kannan, V.P. Laplacian score and K-means data clustering for damage characterization of adhesively bonded CFRP composites by means of acoustic emission technique. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichenihi, A.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Rao, Y. Feature selection and clustering of damage for pseudo-ductile unidirectional carbon/glass hybrid composite using acoustic emission. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Cai, D.; Niyogi, P. Laplacian score for feature selection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2005, 18, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Lomov, S.V.; Yan, X.; Carvelli, V. Cluster analysis of acoustic emission signals for 2D and 3D woven glass/epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2014, 116, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia, A.; Fantozzi, G.; Godin, N.; Osmani, H.; Reynaud, P. Mechanical behaviour of jute fibre-reinforced polyester composite: Characterization of damage mechanisms using acoustic emission and microstructural observations. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 3377–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://uk.mathworks.com/help/stats/fsulaplacian.html (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Ahmed, M.; Seraj, R.; Islam, S.M.S. The k-means Algorithm: A Comprehensive survey and performance evaluation. Electronics 2020, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Luxburg, U. A Tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat. Comput. 2007, 17, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.; Weiss, Y. On spectral clustering: Analysis and an algorithm. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 14; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/stats/spectralcluster.html (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Chaimontree, S.; Atkinson, K.; Coenen, F. Best clustering configuration metrics: Towards multiagent based clustering. In Advanced Data Mining and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, L.; Rousseeuw, P.J. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]


















| Reference | Matrix Cracking | Delamination | Fibre/Matrix Debonding | Fibre Breakage | Fibre Pull-Out |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Frequency [kHz] | |||||
| [3] | 80–120 | 120–170 | 170–200 | ~250 | - |
| [33] | 90–180 | - | 240–310 | >300 | 180–240 |
| [34] | <50 | 50–150 | 200–300 | 400–500 | 500–600 |
| [30] | <150 | 150–300 | - | >400 | - |
| [35] | 60–120 | 120–210 | - | 200–350 | - |
| Sample Identification | Material Parameters |
|---|---|
| Bulk resin (BRCT) | LH 385 epoxy resin with curing agent H512 E = 3.1 GPa (ex), Rm = 58 MPa (ex) |
| Unidirectional (UCT) Cross-ply (CPT, CPCT, CPTS) | carbon/epoxy prepreg CM-Preg T-C-230/600 CP004 39 nominal ply thickness = 0.25 mm, resin content = 39% E(0°) = 135 GPa (mmd), Rm(0°) = 1900 MPa (mmd) |
| Carbon fibre bundle (CFB) | E = 240 GPa (mmd), Rm = 4 GPa (mmd) |
| Type of Test | Name/Number of Specimens | Stacking Sequence | Thickness [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile test | Carbon fibre bundle (CFB)/4 | - | - |
| Tensile test | Cross-ply (CPT)/4 | (90°, 0°)4S | 2 |
| Tensile test | Cross-ply (CPTS)/4 | (45°, −45°)4S | 2 |
| Compact tension | Unidirectional (UCT)/4 | (90°)4 | 1 |
| Compact tension | Cross-ply (CPCT)/4 | (90°, 0°)4S | 2 |
| Compact tension | Bulk resin (BRCT)/4 | - | 5 |
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Amplitude (E) | Largest voltage peak of the given AE hit (in dBAE) (dB rel. to 1 µV before the input to the preamplifier). |
| Risetime (E) | Time interval (in µs) between the first threshold crossing and the reached maximum amplitude (in µs). |
| Duration (E) | Time interval (in µs) between the first and last threshold crossings (in µs). |
| Energy (E) | Integral of the squared AE signal over time (, refers to the AE hit duration) (in aJ). |
| fp—Peak frequency (E) | Frequency corresponding to the maximum magnitude in the frequency spectrum (in kHz). |
| fc—Frequency centroid (E) | Centre of mass of the frequency spectrum (in kHz). |
| fpw—Weighted peak frequency (C) | Square root of the product between the peak frequency and frequency centroid [37], namely (in kHz). |
| RA—RA value (C) pfI ÷ pfVI—Partial power (C) | Risetime/peak amplitude ratio (in µs/dBAE) [38]. (RA is sometimes called the rise angle). Non-dimensionalised ratio between the power in the frequency interval I÷VI and the power of the entire frequency spectrum, that is, within the ⟨50, 1100⟩ [kHz] frequency interval. Note: . |
| Failure Mechanism | A [dBAE] | E [aJ] | Peak Frequency [kHz] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delamination/Matrix cracking | 40÷94 (occas. 100) | <107 | 50÷200 |
| Fibre/Matrix debonding | 40÷70 (occas. 85) | <105 (occas. 106) | 200÷400 |
| Fibre failure | <80 | <104 | 400÷600(1000) |
| Fibre pull-out | <60 | <103 | >700 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šofer, M.; Šofer, P.; Pagáč, M.; Volodarskaja, A.; Babiuch, M.; Gruň, F. Acoustic Emission Signal Characterisation of Failure Mechanisms in CFRP Composites Using Dual-Sensor Approach and Spectral Clustering Technique. Polymers 2023, 15, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010047
Šofer M, Šofer P, Pagáč M, Volodarskaja A, Babiuch M, Gruň F. Acoustic Emission Signal Characterisation of Failure Mechanisms in CFRP Composites Using Dual-Sensor Approach and Spectral Clustering Technique. Polymers. 2023; 15(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠofer, Michal, Pavel Šofer, Marek Pagáč, Anastasia Volodarskaja, Marek Babiuch, and Filip Gruň. 2023. "Acoustic Emission Signal Characterisation of Failure Mechanisms in CFRP Composites Using Dual-Sensor Approach and Spectral Clustering Technique" Polymers 15, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010047
APA StyleŠofer, M., Šofer, P., Pagáč, M., Volodarskaja, A., Babiuch, M., & Gruň, F. (2023). Acoustic Emission Signal Characterisation of Failure Mechanisms in CFRP Composites Using Dual-Sensor Approach and Spectral Clustering Technique. Polymers, 15(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010047







