Effect of Nano-SiO2 on Different Stages of UHMWPE/HDPE Fiber Preparation via Melt Spinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
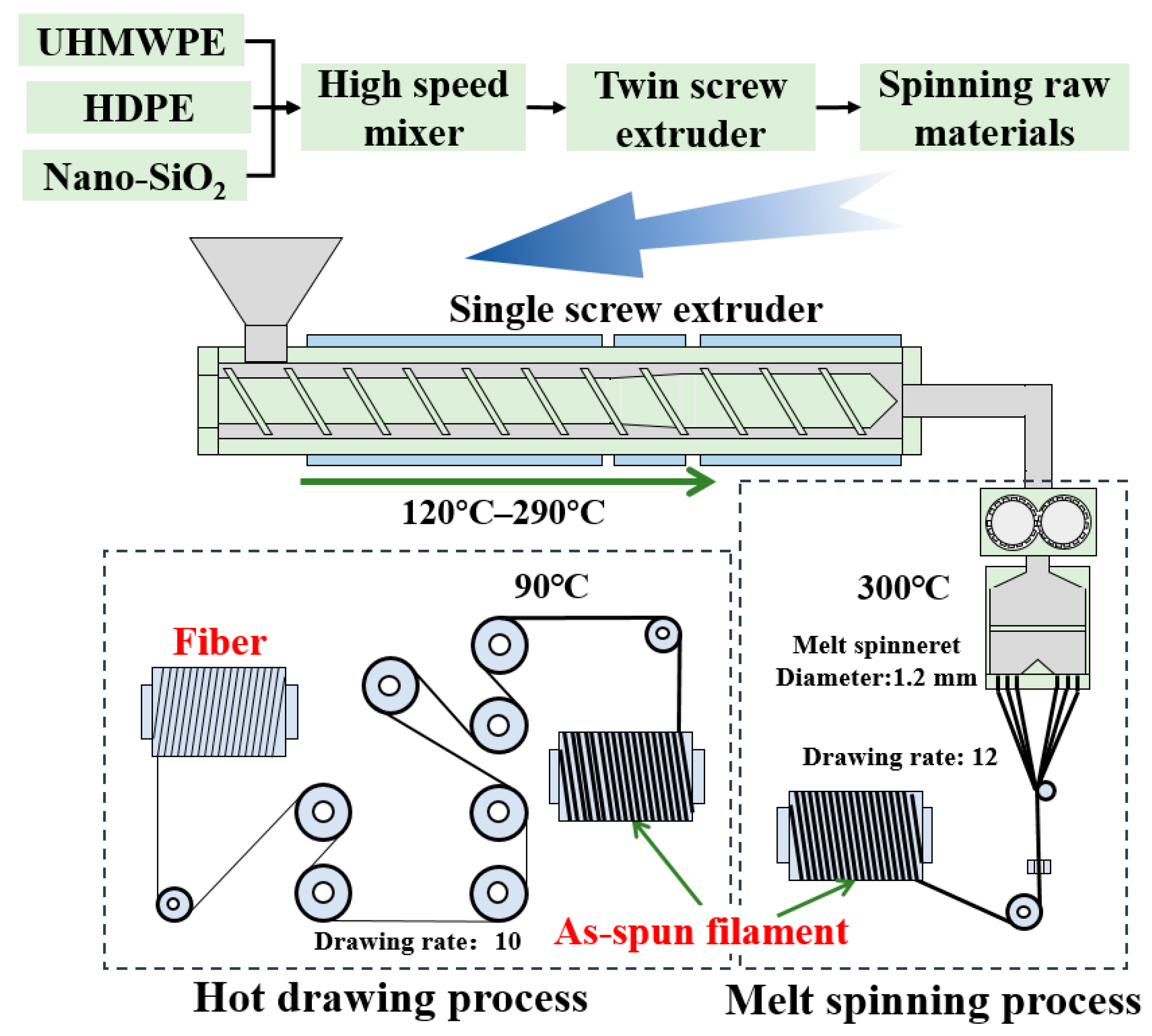
2.2. Preparation Procedures
2.3. Characterizations and Measurements
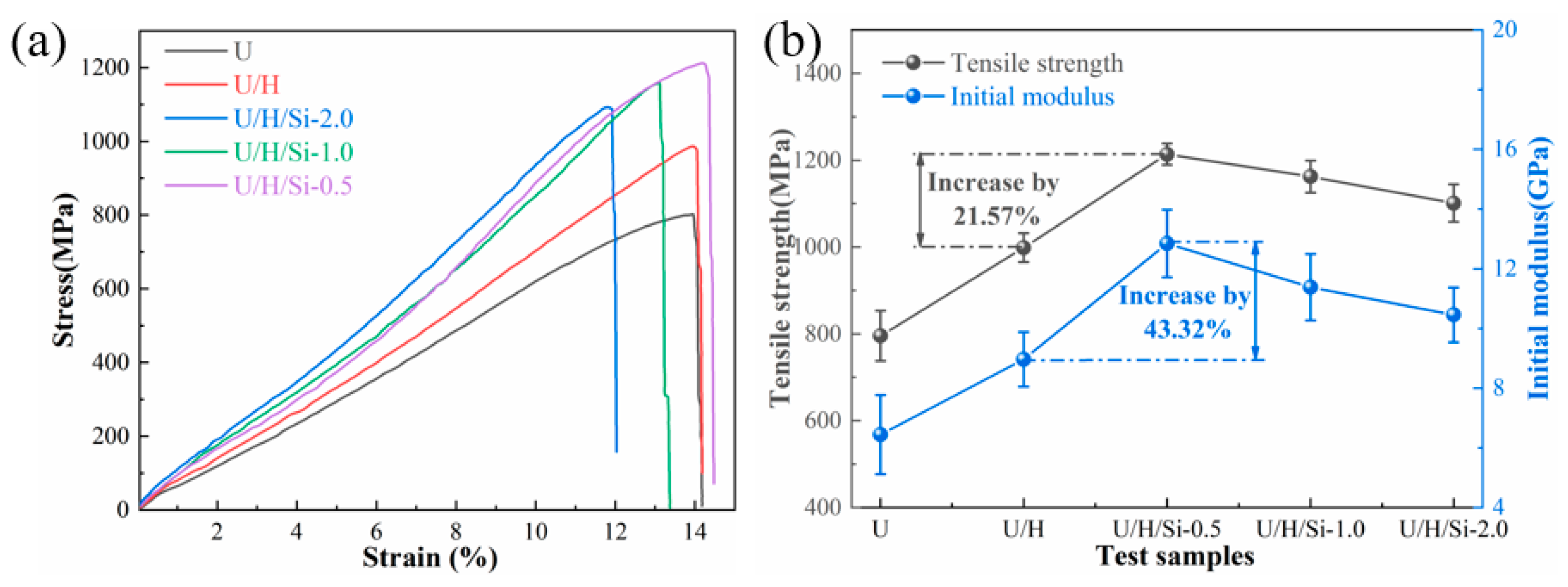
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Property
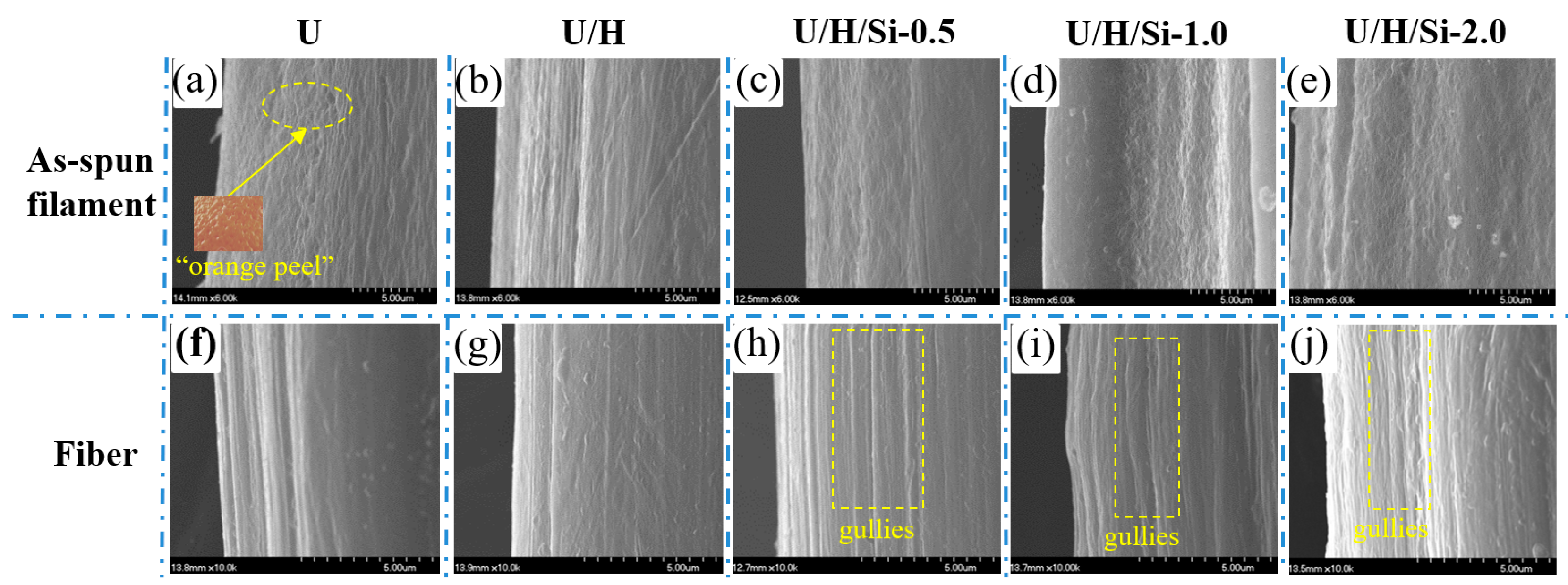
3.2. SEM Observation
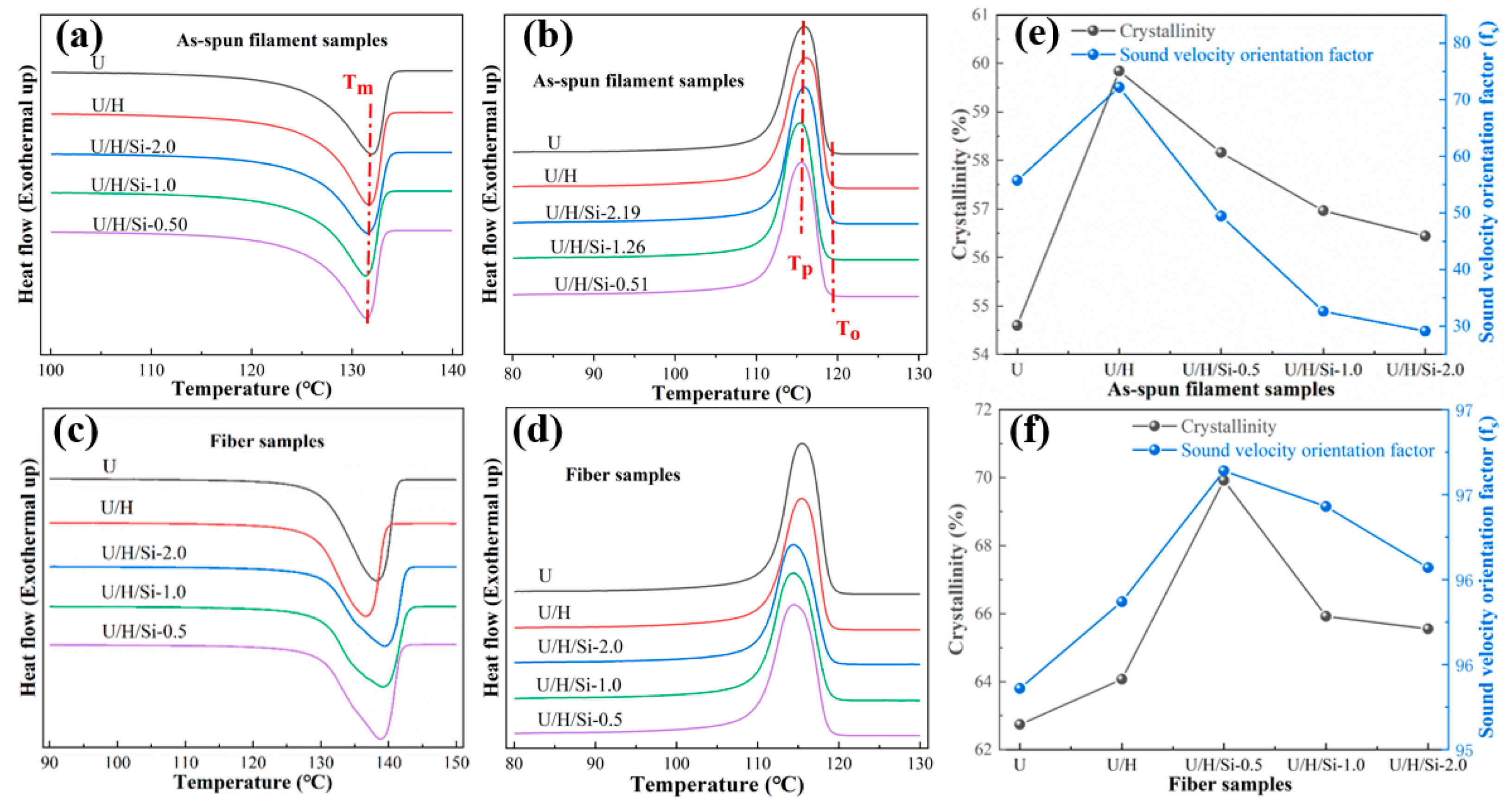
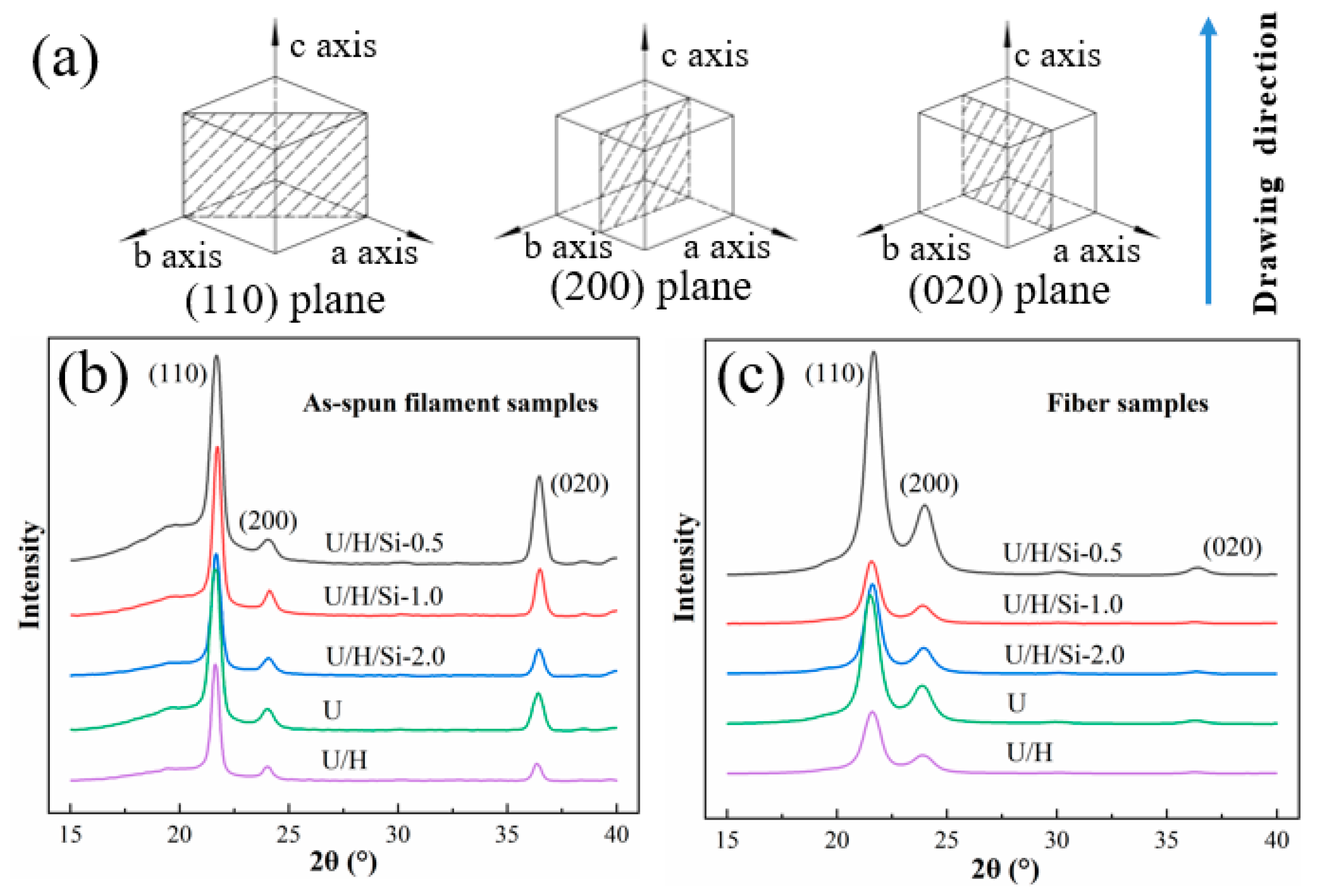
3.3. Crystallization and Molecular Chain Orientation
3.4. Grain Size
3.5. Mechanical Property
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The incorporation of nano-SiO2 improves the flowability of the UHMWPE/PE blend. However, under the effect of high shear rate, the content of nano-SiO2 had no obvious effect on the viscosity for matrix material, the apparent viscosity and the complex viscosity tends to be the identical.
- (2)
- The addition of nano-SiO2 restrains the crystallization and molecular chain orientation in the as-spun filament, and both reduces with the addition of nano-SiO2 content. After hot drawing, the crystallinity and molecular chain orientation of nanocomposite fiber are higher than those of UHMWPE/PE fiber and are most obvious when the nano-SiO2 content is 0.5 wt%.
- (3)
- In the extrusion stage of as-spun filament, the addition of nano-SiO2 increase the entanglement points of the molecular chain, which caused the as-spun filament grain size of nanocomposite to be smaller than that of the UHMWPE/HDPE as-spun filament. However, after hot drawing, the nano-SiO2 have a promotion effect on grain refinement and the grain size becomes larger, continuing the addition of nanoparticles does not have a significant promotion effect.
- (4)
- Since both the crystallinity and molecular chain orientation are improved and the grain size is refined, when the content is 0.51 wt%, UHMWPE/HDPE/modified nano-SiO2 shows the best mechanical property with tensile strength and initial modulus of 1211 MPa and 12.81 GPa, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, J.H.; Rutledge, G.C. 50th Anniversary Perspective: Advanced Polymer Fibers: High Performance and Ultrafine. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 5627–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Chen, X.; Wan, C.; Su, F.; Ji, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Li, L. Deformation of Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene Precursor Fiber: Crystal Slip with or without Melting. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 6385–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.; Kurek, A.; Thomann, R.; Schwabe, J.; Mark, S.; Enders, M.; Hees, T.; Mülhaupt, R. Tailored Nanostructured HDPE Wax/UHMWPE Reactor Blends as Additives for Melt-Processable All-Polyethylene Composites and in Situ UHMWPE Fiber Reinforcement. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 8129–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. Surface amine-functionalization of UHMWPE fiber by bio-inspired polydopamine and grafted hexamethylene diamine. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Alves, A.L.; Cassiano Nascimento, L.F.; Suarez, J.C.M. Influence of weathering and gamma irradiation on the mechanical and ballistic behavior of UHMWPE composite armor. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, J.S.; Detrez, F.; Cherkaoui, M.; Cantournet, S.; Ku, D.N.; Corte, L. Hydrogel fibers for ACL prosthesis: Design and mechanical evaluation of PVA and PVA/UHMWPE fiber constructs. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y. Structure evolution of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene/montmorillonite nanocomposite fibers prepared by melt spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3930–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Bao, J.; Wang, G.; Lu, W.; Chen, W. Structure and properties of gel-spun ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers obtained from industrial production line. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, Y.; Murase, H.; Ohta, Y. Dyneema®: Super Fiber Produced by the Gel Spinning of a Flexible Polymer. In High-Performance and Specialty Fibers: Concepts, Technology and Modern Applications of Man-Made Fibers for the Future; The Society of Fiber Science and Technology, Ed.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 109–132. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Wyatt, T.; Hong, Y.; Yao, D. Gel spinning of UHMWPE fibers with polybutene as a new spin solvent. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufenus, R.; Yan, Y.; Dauner, M.; Kikutani, T. Melt-Spun Fibers for Textile Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Yoon, K.W.; Burger, C.; Sics, I.; Fang, D.F.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. In-situ X-ray scattering studies of a unique toughening mechanism in surface-modified carbon nanofiber/UHMWPE nanocomposite films. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3883–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Xue, P.; Jia, M.; Sun, H. A Study of the Mechanical Behavior and Crystal Structure of UHMWPE/HDPE Blend Fibers Prepared by Melt Spinning. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. 2018, 13, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiage, M.; Fukagawa, D. Preparation of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene fibers by combination of melt-spinning and melt-drawing. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Y.Z.; Ma, L.; Adachi, R.; Kurosu, H.; Matsuo, M. Ultra-drawing of low molecular weight polyethylene—Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene blend films prepared by gelation/crystallization from semi-dilute solutions. Polymer 2001, 42, 8125–8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyu, T.; Vadhar, P. Cocrystallization and miscibility studies of blends of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene with conventional polyethylenes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1986, 32, 5575–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.-D.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Liu, S.-M.; Jiang, Z.-J.; Zhao, J.-Q. Preparation of HDPE/UHMWPE/MMWPE blends by two-step processing way and properties of blown films. Polym. Bull. 2006, 58, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Li, H. Viscosity reduction and disentanglement in ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene melt: Effect of blending with polypropylene and poly(ethylene glycol). Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-T.; Wang, C.-K.; Yeh, A.; Huang, L.-K.; Wang, W.-H.; Hsieh, K.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-N. Preparation and characterization of novel ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composite fibers filled with nanosilica particles. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-t.; Wang, C.-K.; Tsai, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-N.; Huang, K.-S.; Chiu, S.-H. Ultradrawing properties of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene/hydrochloric acid treated attapulgite fibers. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yeh, J.-t.; Wang, C.-K.; Huang, L.-K.; Tsai, C.-C.; Lai, W.-Y. Ultradrawing and Ultimate Tenacity Properties of Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene Composite Fibers Filled with Nanosilica Particles with Varying Specific Surface Areas. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 146718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-T.; Wang, C.-K.; Hu, P.; Lai, Y.-C.; Huang, L.-K.; Tsai, F.-C. Ultradrawing properties of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene/attapulgite fibers. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, C.; Chen, L.; Hu, Z. Preparation, morphology, and adhesive and mechanical properties of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene/SiO2nanocomposite fibers. Polym. Compos. 2009, 31, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Gao, P.; Yu, T.X. Ultra-strong gel-spun UHMWPE fibers reinforced using multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Polymer 2006, 47, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, Y.-T.T.; Aminuddin, N.; Young, J. Melt Spinning Blends of UHMWPE and HDPE and Fibers Made Therefrom. U.S. Patent US8057897B2, 15 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, R.Y.; Chen, Q. Dispersion of Inorganic Nanoparticles in Polymer Matrices: Challenges and Solutions. In Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials; Kalia, S., Haldorai, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Šupová, M.; Martynková, G.S.; Barabaszová, K. Effect of Nanofillers Dispersion in Polymer Matrices: A Review. Science of Adv. Mater. 2011, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Xue, P.; Jia, M. Crystal Structure Evolution of UHMWPE/HDPE Blend Fibers Prepared by Melt Spinning. Polymers 2017, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaggi, H.S.; Kumar, S.; Das, D.; Satapathy, B.K.; Ray, A.R. Morphological correlations to mechanical performance of hydroxyapatite-filled HDPE/UHMWPE composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Vimal, K.K.; Kapur, G.S.; Sharma, S.; Choudhary, V. High-density polyethylene/halloysite nanocomposites: Morphology and rheological behaviour under extensional and shear flow. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xu, L.; Cao, W.; Wu, S. A study on the orientation structure and mechanical properties of polyacrylonitrile precursors. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2005, 16, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, G.; Zhong, W.H.; Ren, X.; Wang, X.Q.; Yang, X.P. Structure, mechanical properties and friction behavior of UHMWPE/HDPE/carbon nanofibers. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-D.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Liu, B.-G.; Du, Z.-J.; Li, H.-Q. Crystallization Behavior and Crystal Morphology of Linear/Long Chain Branching Polypropylene Blends. Polym. J. 2008, 40, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lan, L.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, H.; Guo, S.; Lin, C.; He, G. Constructing highly oriented and condensed shish-kebab crystalline structure of HDPE/UHMWPE blends via intense stretching process: Achieving high mechanical properties and in-plane thermal conductivity. Polymer 2022, 241, 124532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, Q.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Xue, P. Thermal actuation shape memory of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) with molecular orientation. Mater. Lett. 2022, 325, 132813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.; Deng, Y. Gel-spun fibers from magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles and UHMWPE nanocomposite: The physical and flammability properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 51, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, M.M.; Woo, D.; Mumpower, E.L.; Benicewicz, B.C. Poly(alkyl methacrylate)-grafted silica nanoparticles in polyethylene nanocomposites. Polymer 2017, 109, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, V.M.; Xu, J.; Melian, C.; Demco, D.E.; Möller, M.; Simmelink, J. Morphology, Chain Dynamics, and Domain Sizes in Highly Drawn Gel-Spun Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene Fibers at the Final Stages of Drawing by SAXS, WAXS, and1H Solid-State NMR. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9254–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Lv, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Wang, Z. Effect of Gel Solution Concentration on the Structure and Properties of Gel-Spun Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene Fibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8357–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fu, Q.; Niu, L.; Shi, Z. Enhancement of the tensile strength in poly(p-phenylene sulfide) and multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites by hot-stretching. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Mass Ratio of UHMWPE/HDPE | Content of Nano-SiO2 (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| U | 1 | 0 |
| U/H | 6/4 | 0 |
| U/H/Si-0.5 | 6/4 | 0.5 |
| U/H/Si-1.0 | 6/4 | 1.0 |
| U/H/Si-2 | 6/4 | 2.0 |
| As-Spun Filament Sample | (°C) | (°C) | (°C) | (°C) | (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | 115.9 | 118.62 | 2.72 | 131.97 | 16.07 |
| U/H | 116.12 | 118.79 | 2.67 | 131.67 | 15.55 |
| U/H/Si-0.5 | 115.55 | 118.38 | 2.83 | 131.43 | 15.88 |
| U/H/Si-1.0 | 115.41 | 118.43 | 2.83 | 131.36 | 15.95 |
| U/H/Si-2.0 | 115.94 | 118.79 | 2.85 | 131.57 | 15.63 |
| As-Spun Filament Samples | Grain Size(nm) | Fiber Samples | Grain Size(nm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110 Plane | 200 Plane | 020 Plane | Average | 110 Plane | 200 Plane | 020 Plane | Average | ||
| U | 15.4 | 13.0 | 15.1 | 14.5 | U | 9.7 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 8.5 |
| U/H | 20.2 | 18.4 | 19.4 | 19.3 | U/H | 9.5 | 7.6 | 10.0 | 9.0 |
| U/H/Si-0.5 | 16.9 | 13.4 | 16.3 | 15.5 | U/H/Si-0.5 | 10.2 | 8.2 | 9.1 | 9.2 |
| U/H/Si-1.0 | 17.2 | 14.1 | 17.0 | 16.1 | U/H/Si-1.0 | 10.6 | 8.4 | 9.2 | 9.4 |
| U/H/Si-2.0 | 17.6 | 14.3 | 17.4 | 16.4 | U/H/Si-2.0 | 10.7 | 8.5 | 8.7 | 9.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Xue, P.; Liu, L. Effect of Nano-SiO2 on Different Stages of UHMWPE/HDPE Fiber Preparation via Melt Spinning. Polymers 2023, 15, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010186
Yang Q, Zhang R, Liu M, Xue P, Liu L. Effect of Nano-SiO2 on Different Stages of UHMWPE/HDPE Fiber Preparation via Melt Spinning. Polymers. 2023; 15(1):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010186
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qun, Run Zhang, Mingfei Liu, Ping Xue, and Lichao Liu. 2023. "Effect of Nano-SiO2 on Different Stages of UHMWPE/HDPE Fiber Preparation via Melt Spinning" Polymers 15, no. 1: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010186
APA StyleYang, Q., Zhang, R., Liu, M., Xue, P., & Liu, L. (2023). Effect of Nano-SiO2 on Different Stages of UHMWPE/HDPE Fiber Preparation via Melt Spinning. Polymers, 15(1), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010186






