Evaluation of Touch and Durability of Cotton Knit Fabrics Treated with Reactive Urethane-Silicone Softener
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Development of Urethane–Silicone Softener
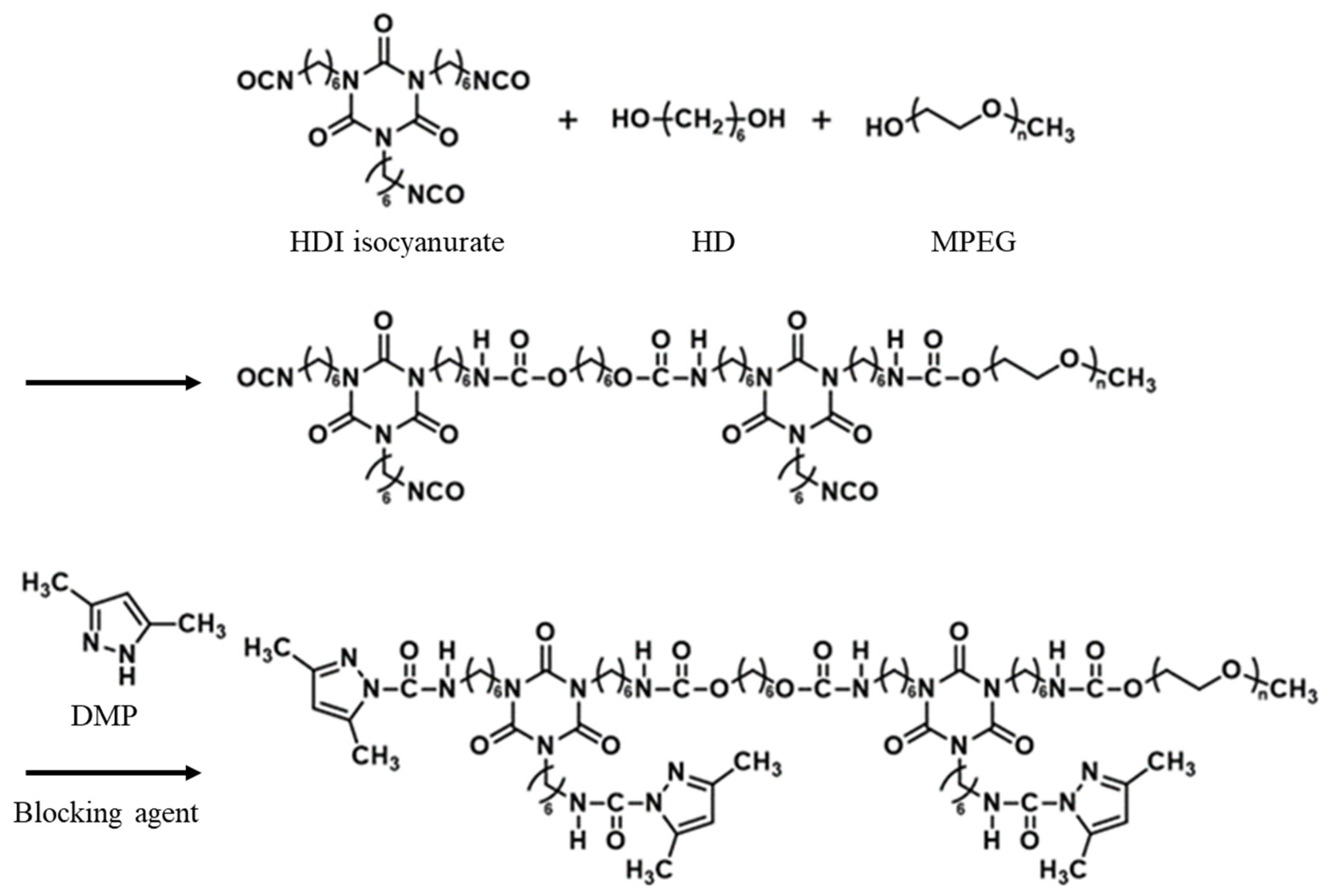
2.2.1. Synthesis of Blocked Isocyanate
2.2.2. Urethane–Silicone Softener Manufacturing
2.2.3. Determination of NCO Content
- B: amount of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid solution by blank test (mL).
- S: amount of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid solution used in the sample (mL).
- 42: molecular weight of NCO (g/mol).
- N: normal concentration (N) of the hydrochloric acid solution used.
- f: factor of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid solution.
- w: mass of sample (g).
2.3. Softening Finishes
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Particle Size Analysis
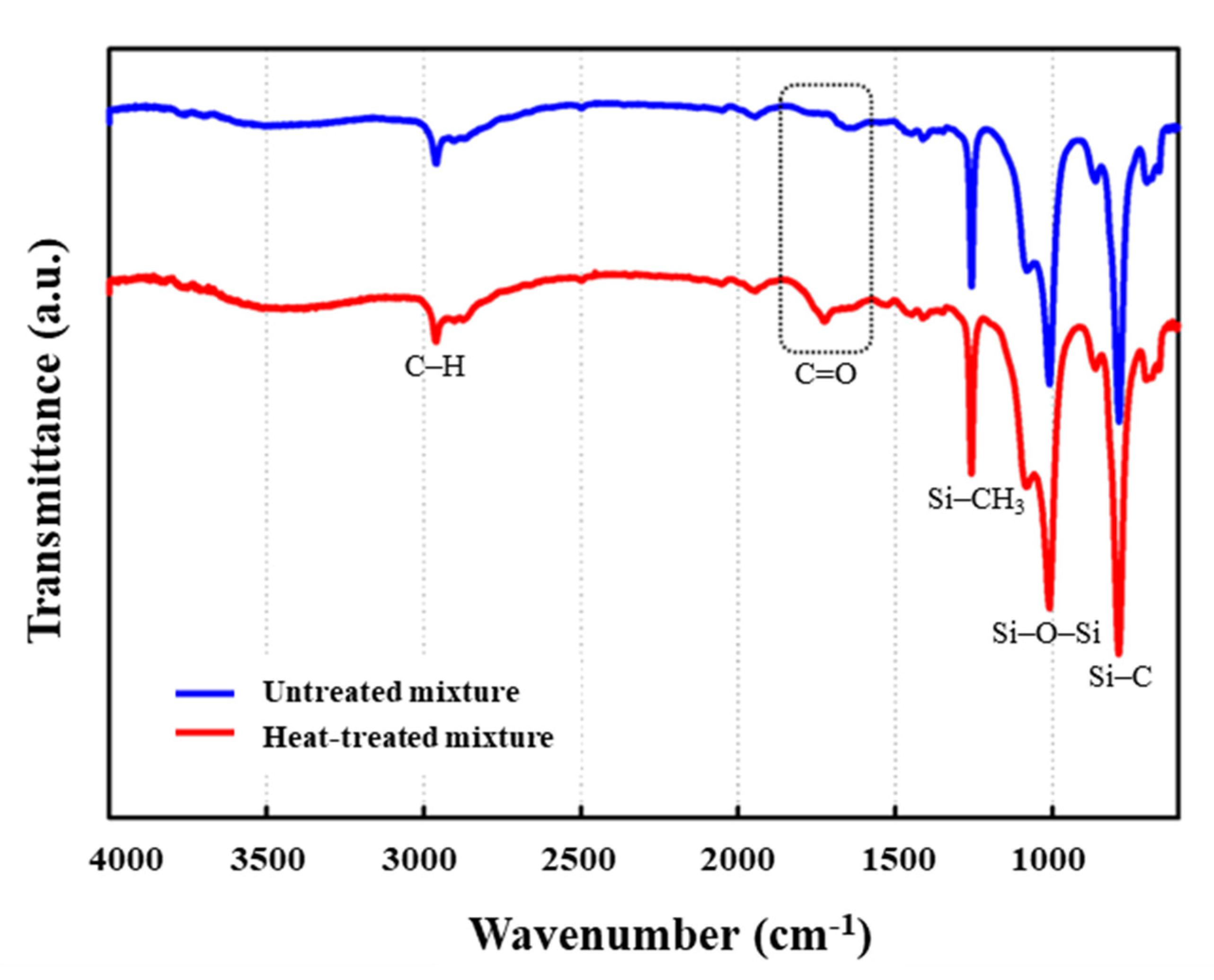
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and KES-FB System Analysis of Cotton Knitwear Treated with Urethane–Silicone Softener
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Blocked Isocyanate
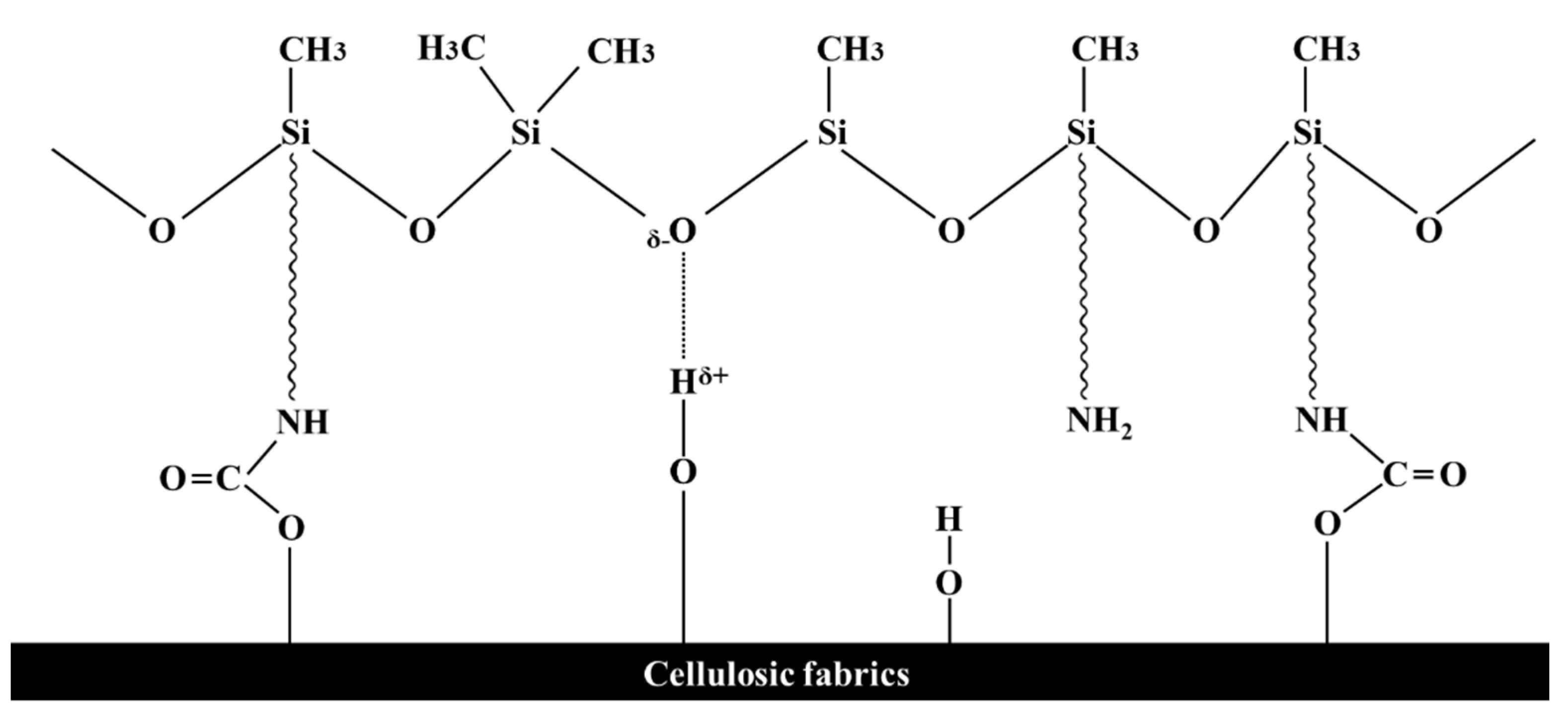
3.2. Characterization of Urethane–Silicone Softener
3.3. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and KES-FB System Analysis
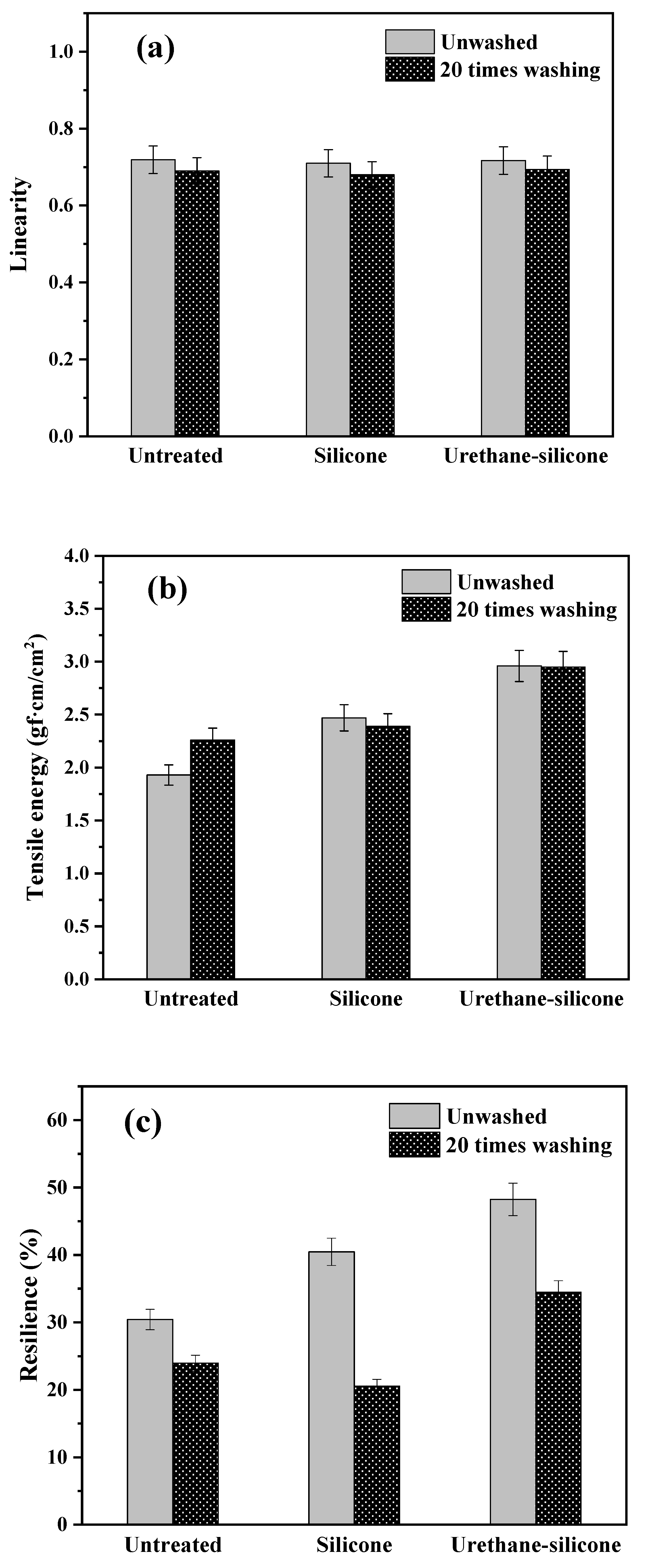
3.3.1. Tensile Properties of Cotton Knitwear after Softener Treatment
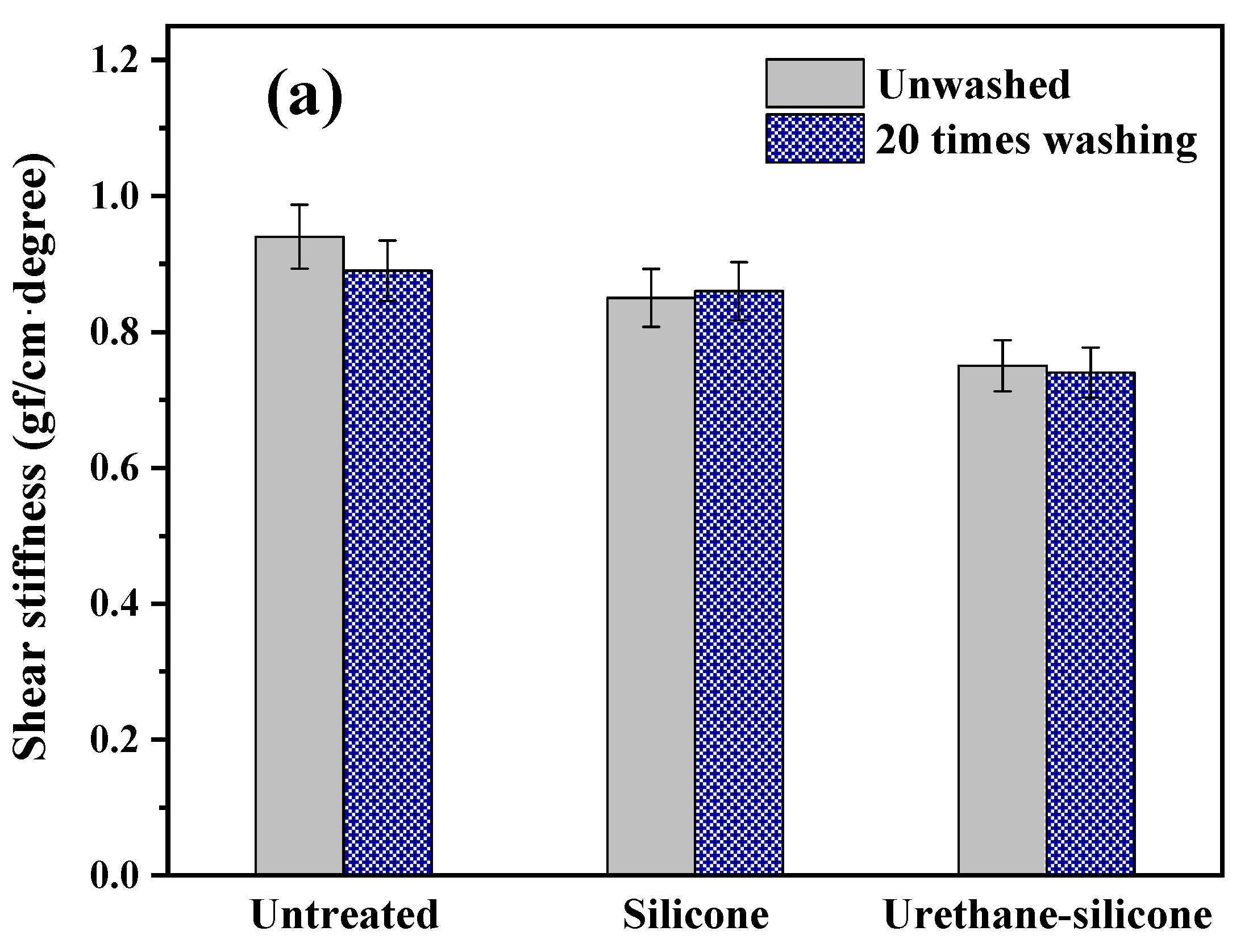
3.3.2. Shear Properties of Cotton Knitwear after Softener Treatment
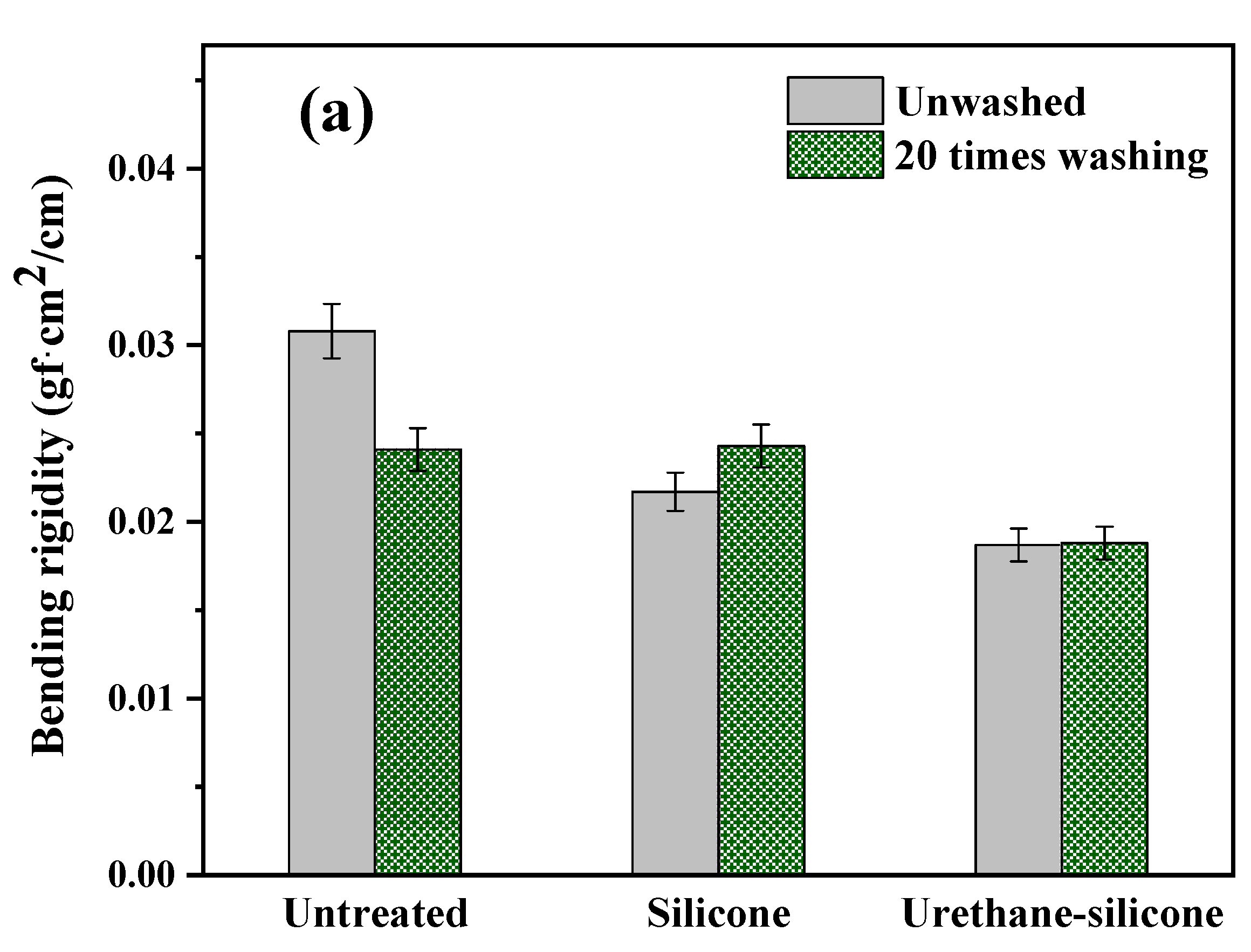
3.3.3. Bending Properties of Cotton Knitwear after Softener Treatment
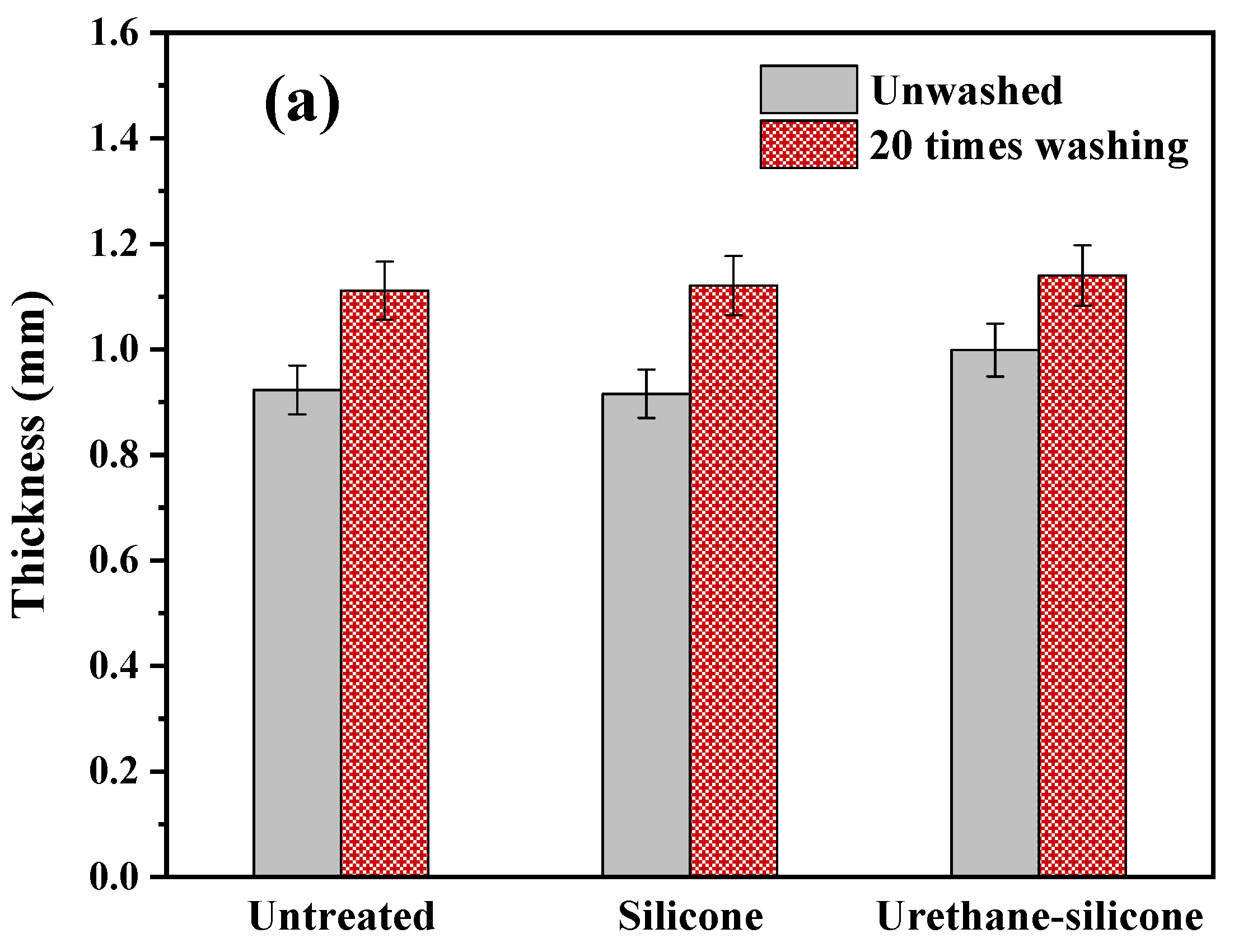
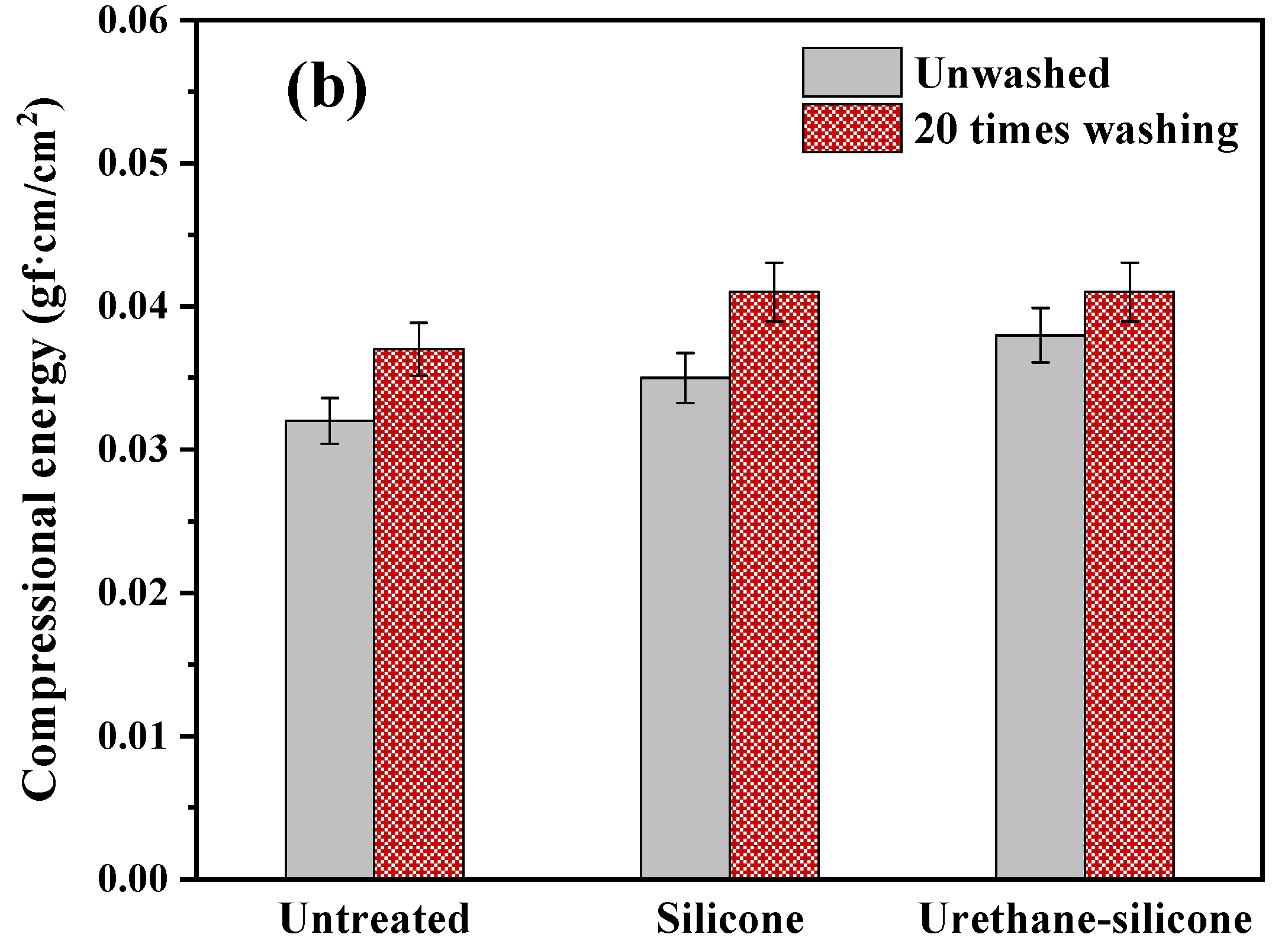
3.3.4. Compression Properties of Cotton Knitwear after Softener Treatment
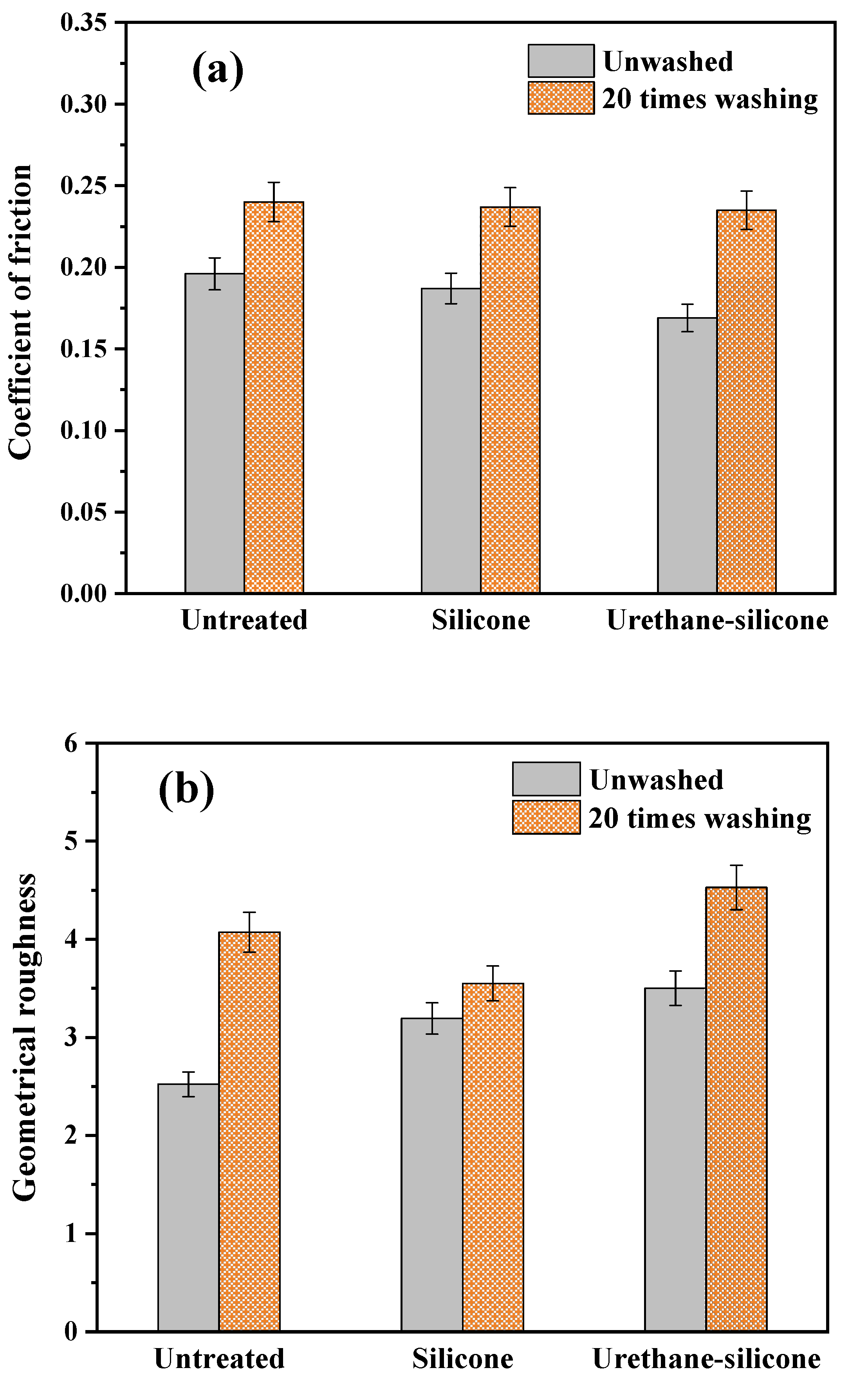
3.3.5. Surface Properties of Cotton Knitwear after Softener Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bevilacqua, M.; Ciarapica, F.E.; Mazzuto, G.; Paciarotti, C. Environmental analysis of a cotton yarn supply chain. J. Clean Prod. 2014, 82, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Cordeiro, A.; de Alencar Nääs, I.; Neto, P.L.D.O. The sustainability awareness of Brazilian consumers of cotton clothing. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 215, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaković, M.; Popović, D.M.; Mladenović, N.; Poparić, G.B.; Stanković, S.B. Development of comfortable and eco-friendly cellulose based textiles with improved sustainability. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 267, 122154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Xing, T.; Chen, G. Improving the anti-pilling performance of cellulose fiber blended knitted fabrics with 2, 4, 6-trichloropyrimidine treatment. Coatings 2020, 10, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, L.; Anand, S.C.; Hall, M.E.; Holmes, D.A. Factors during tumble drying that influence dimensional stability and distortion of cotton knitted fabrics. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2003, 15, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munden, D.L. Dimensional stability of plain-knit fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 1960, 51, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Thangamani, K. Establishing the effect of loop length on dimensional stability of single jersey knitted fabric made from cotton/lycra core spun yarn. Indian. J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 3, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.R.; Chatterjee, B.; Saha, S.; Shaw, K. Comparison of performances of macro, micro and nano silicone softeners. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Islam, A.; Huiyu, J. Silicone softener synthesis and application on knit and woven white cotton fabrics. Am. J. Polym. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Shimizu, K.; Igarashi, T.; Nakamura, K.; Takatera, M. Effect of fabric softener on crossing torque and compression properties of cotton yarn. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.S. Fabric softener technology: A review. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2015, 18, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obendorf, S.K.; Dixit, V.; Woo, D.J. Microscopy study of distribution of laundry fabric softener on cotton fabric. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2009, 12, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, M.; Ramesh Kumar, M. Effect of fabric softener on thermal comfort of cotton and polyester fabrics. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2007, 32, 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- Sadek, R. Effect of fabric softener on properties of a single jersey knitted fabric made of cotton and spandex yarn. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, M.; Hashemikia, S. Application of polyurethane/citric acid/silicone softener composite on cotton/polyester knitted fabric producing durable soft and smooth surface. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 4141–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.P.; Vyas, D.D. Effect of silicone nano-emulsion softener on physical properties of cotton fabric. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2010, 35, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Saraf, N.M.; Alat, D.V. Yellowing of white fabrics and garments. Colourage 2007, 54, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Duru, S.C.; TUFAN, H.A.; Şahin, U.K. Assessing Color Differences of Cotton Fabrics Made from Different Yarns After Abrasion. Text. Appar. 2020, 30, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Parvinzadeh, M.; Hajiraissi, R. Effect of nano and micro emulsion silicone softeners on properties of polyester fibers. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2008, 45, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, H.; Avinc, O.; Khoddami, A. Comparison of softened polylactic acid and polyethylene terephthalate fabrics using KES-FB. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2013, 3, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.J.; Lee, J.S. Mechanical properties and sensibility of Tencel Jacquard fabrics treated with Ginkgo biloba extract and silicon softener. Sci. Emot. Sensibil. 2010, 13, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata, S.; Niwa, M. Objective measurement of fabric mechanical property and quality: Its application to textile and clothing manufacturing. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 1991, 3, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.J.; Song, W.; Zheng, Y.Y.; He, X.Z. Improvement of method for determination of isocyanate group content in polyurethane prepolymer. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Freienbach, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 303, pp. 2533–2536. [Google Scholar]
- Gurunathan, T.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Isocyanate terminated castor oil-based polyurethane prepolymer: Synthesis and characterization. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 80, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Long, X.; Ye, Z.; Qu, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, C. Scanning Electron Microscopy Investigation for Monitoring the Emulsion Deteriorative Process and Its Applications in Site-Directed Reaction with Paper Fabric. Molecules 2021, 26, 6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, S.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.H. New development of polyurethane dispersion derived from blocked aromatic diisocyanate. Prog. Org. Coat. 2003, 48, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Kim, J.; Bae, J.Y. Towards the development of thermally latent novolac-based char formers for ABS resins. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2006, 91, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hong, W.; Chen, X. Continuous production of water-borne polyurethanes: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delebecq, E.; Pascault, J.P.; Boutevin, B.; Ganachaud, F. On the versatility of urethane/urea bonds: Reversibility, blocked isocyanate, and non-isocyanate polyurethane. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 80–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomölder, R.; Plogmann, F.; Speier, P. Selectivity of isophorone diisocyanate in the urethane reaction influence of temperature, catalysis, and reaction partners. J. Coat. Technol. 1997, 69, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; De-Ning, W.; Sheng-Kang, Y. Hydrogen-bonding properties of segmented polyether poly (urethane urea) copolymer. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 4405–4409. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Qiang, S.; Yang, F.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Yin, Y. Synthesis of blocked and branched waterborne polyurethanes for pigment printing applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: An overview. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebukawa, Y.; Nakashima, S.; Otsuka, T.; Nakamura-Messenger, K.; Zolensky, M.E. Rapid contamination during storage of carbonaceous chondrites prepared for micro FTIR measurements. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2009, 44, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Feng, L.; Diao, S.; Feng, S.; Zhang, C. Study on the synthesis and thermal degradation of silicone resin containing silphenylene units. Thermochim. Acta. 2011, 521, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.T. Deposition behavior of hexamethydisiloxane films based on the FTIR analysis of Si–O–Si and Si–CH3 bonds. Thin Solid Films 1997, 311, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalie, D.; Gideon, R.K.; Ferede, A.; Tesinova, P.; Lenfeldova, I. Tactile comfort and low-stress mechanical properties of half-bleached knitted fabrics made from cotton yarns with different parameters. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.; Fan, J.; Siu, T.; Siu, L.Y.C. Effects of repeated laundering on the performance of garments with wrinkle-free treatment. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebpour, F.; Holme, I. Effects of silicone-based softener on the easy-care finished cotton fabric. IJFTR 2006, 31(3), 444–449. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Lewis, J.E.; Stewart, N.M.; Qian, L.; Boyter, H. Effect of finishing methods on washing durability of microencapsulated aroma finishing. J. Text. Inst. 2008, 99, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, C.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zeng, Z. Antibacterial cotton fabrics coated by biodegradable cationic silicone softeners. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 22, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, J.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Manoharan, S. A study of knitted fabrics from polyester microdenier fibres. J. Text. Inst. 2007, 98, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoddami, A.; Avinc, O.; Mallakpour, S. A novel durable hydrophobic surface coating of poly (lactic acid) fabric by pulsed plasma polymerization. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 67, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avinc, O.; Wilding, M.; Gong, H.; Farrington, D. Effects of softeners and laundering on the handle of knitted PLA filament fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J. Blending Effect on the Mechanical and Hand Properties of Wool/Acrylic Blend Knits. Int. J. Costume Cult. 2005, 8, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Khoddami, A.; Gong, H.; Ghadimi, G. Effect of wool surface modification on fluorocarbon chain re-orientation. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, G.; Koehl, L.; Perwuelz, A.; Lee, K.S. Interaction of textile parameters, wash-ageing and fabric softener with mechanical properties of knitted fabrics and correlation with textile-hand. I. Interaction of textile parameters with laundry process. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.H.; Kan, C.W. Effect of heat setting parameters on some properties of PLA knitted fabric. Fiber. Polym. 2013, 14, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalie, D.; Ferede, A.; Rotich, G.K. Effect of weft yarn twist level on mechanical and sensorial comfort of 100% woven cotton fabrics. Fash. Text. 2019, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaynor, L.; Takahashi, M.; Nakajima, M. Effects of laundering on the surface properties and dimensional stability of plain knitted fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2000, 70, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Properties | Symbols | Characteristic Values | Unit | Measuring Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile properties | LT | Linearity | - | Max. Load: 50 gf/cm Tensile speed: 0.1 mm/s Measuring length: 2.5 cm |
| WT | Tensile energy | gf·cm/cm2 | ||
| RT | resilience | % | ||
| Shear properties | G | shear stiffness | gf/cm·degree | Shear deformation: ±4° |
| 2HG | Hysteresis at ϕ = 4° | gf/cm | ||
| Bending properties | B | Bending rigidity | gf·cm2/cm | Bending curvature (K): ±2.5 cm |
| 2HB | Hysteresis | gf·cm/cm | ||
| Compression properties | T0 | Thickness of fabric | mm | Max. Load: 10 gf/cm2 Compression speed: 50 mm/s Compression area: 2 cm2 |
| WC | Compressional energy | gf·cm/cm2 | ||
| Surface properties | MIU | Coefficient of friction | - | Friction static load: 50 g Roughness static load: 5 g |
| SMD | Geometrical roughness | micron |
| Sample | Particle Size (um) |
|---|---|
| Blocked isocyanate emulsion | 0.059213 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Woo, J.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Shim, E.; Youk, J.H. Evaluation of Touch and Durability of Cotton Knit Fabrics Treated with Reactive Urethane-Silicone Softener. Polymers 2022, 14, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091873
Cho HS, Yoon HJ, Lee BH, Woo JC, Choi HY, Shim E, Youk JH. Evaluation of Touch and Durability of Cotton Knit Fabrics Treated with Reactive Urethane-Silicone Softener. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091873
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hang Sung, Hye Jun Yoon, Bum Hoon Lee, Jang Chang Woo, Hyeong Yeol Choi, Euijin Shim, and Ji Ho Youk. 2022. "Evaluation of Touch and Durability of Cotton Knit Fabrics Treated with Reactive Urethane-Silicone Softener" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091873
APA StyleCho, H. S., Yoon, H. J., Lee, B. H., Woo, J. C., Choi, H. Y., Shim, E., & Youk, J. H. (2022). Evaluation of Touch and Durability of Cotton Knit Fabrics Treated with Reactive Urethane-Silicone Softener. Polymers, 14(9), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091873






