Extraction of Nanocellulose for Eco-Friendly Biocomposite Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Nanocellulose from Palm Fiber
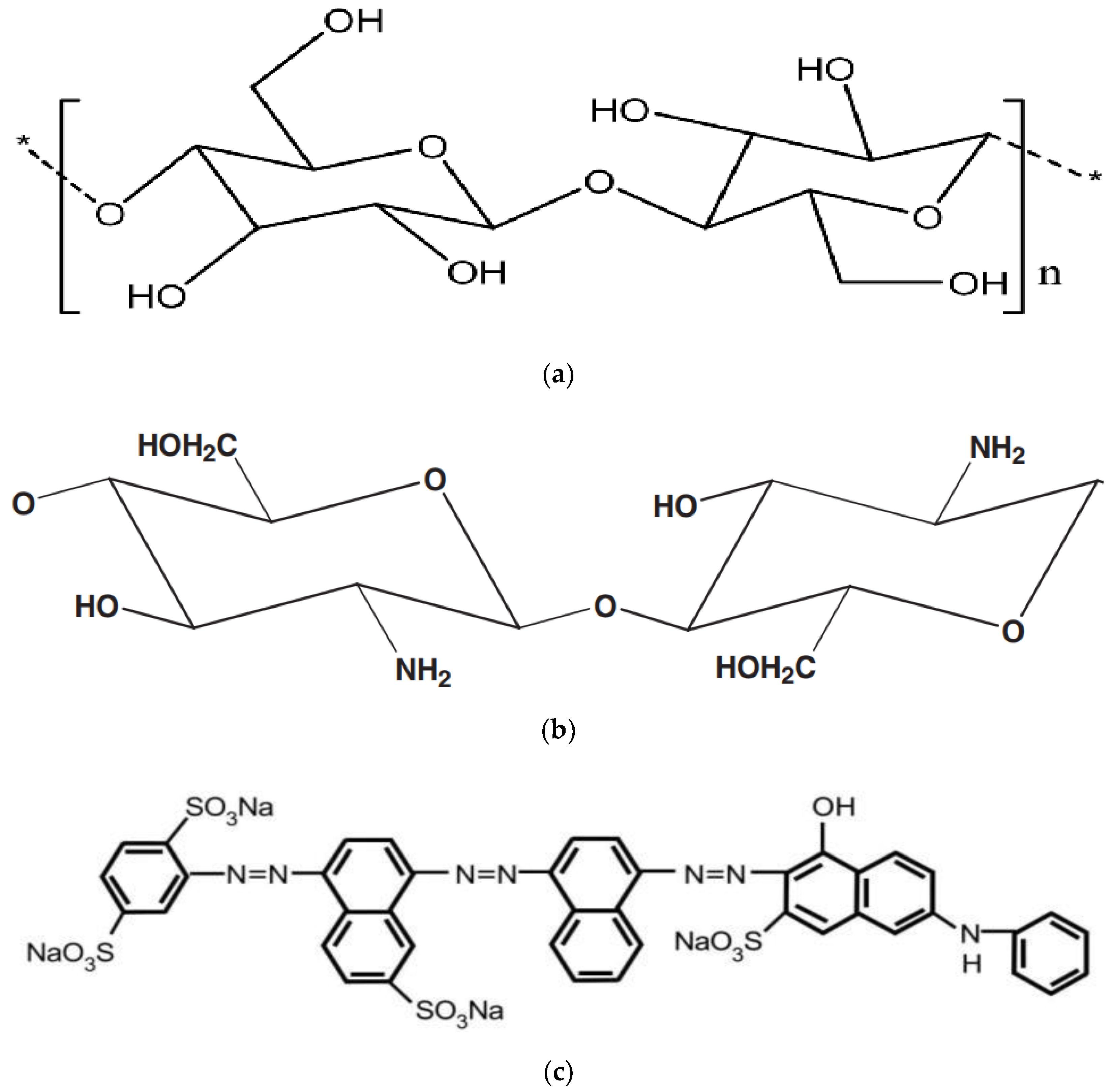
2.2. Chitosan and Dyes
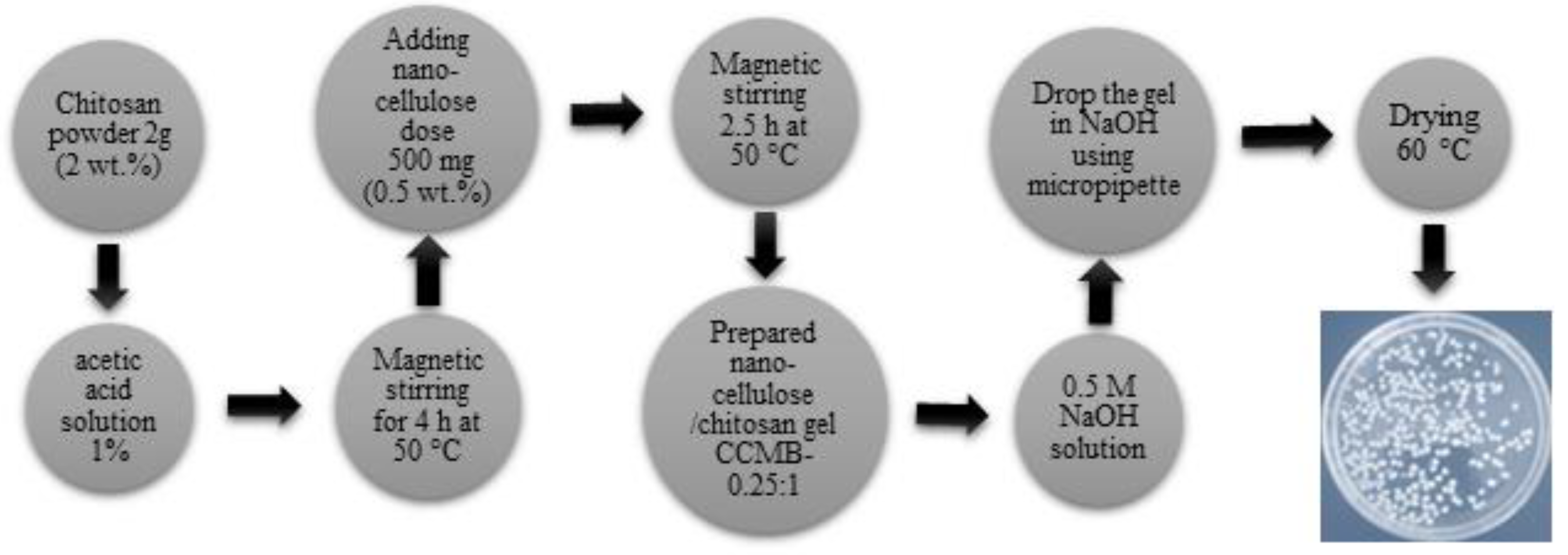
2.3. Preparation of Nanocellulose/Chitosan Microbeads (CCMB)
2.4. Adsorption Studies
Nanocellulose and Chitosan Nanocomposites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Nanocellulose
3.1.1. Size of Nanocellulose
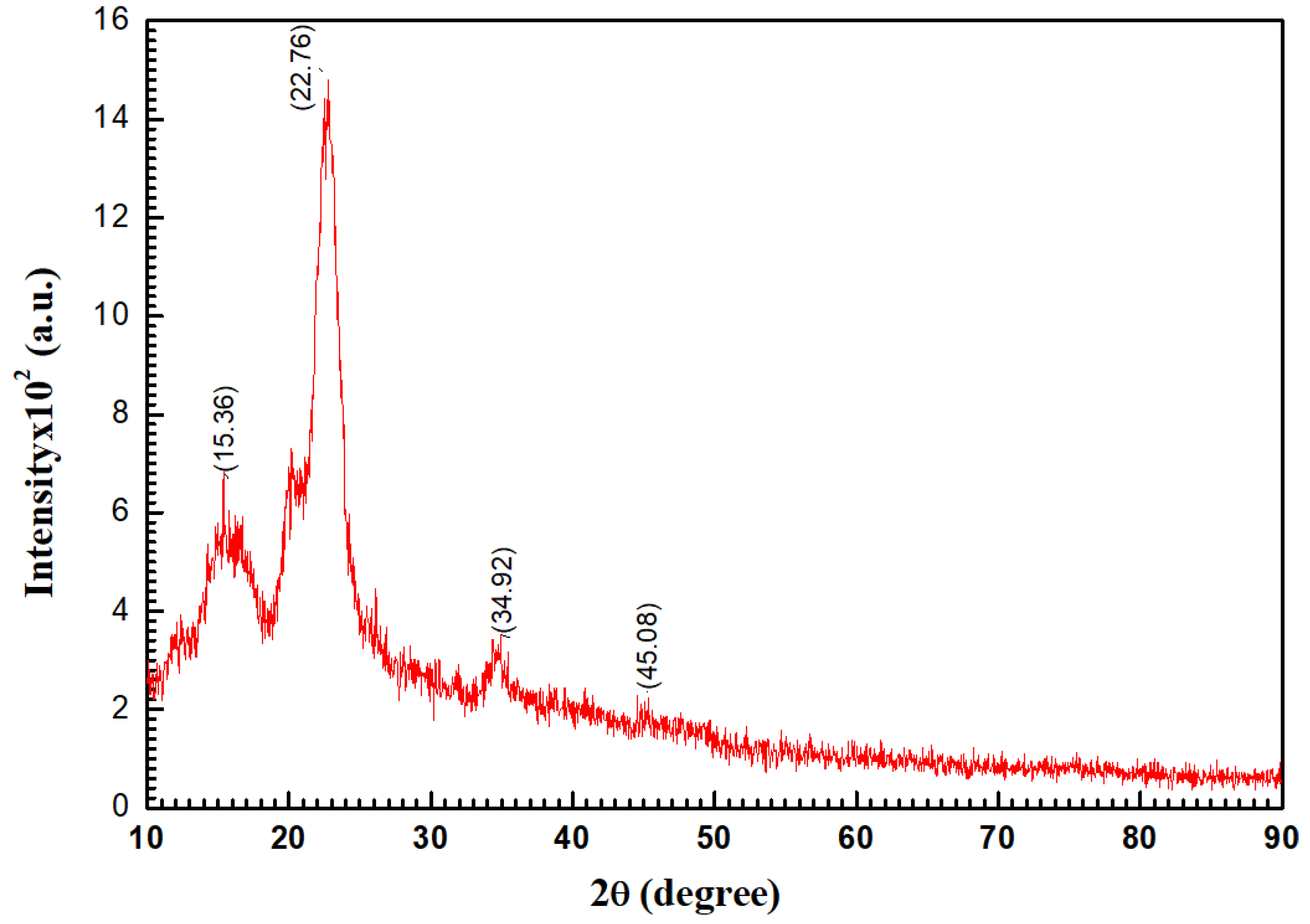
3.1.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
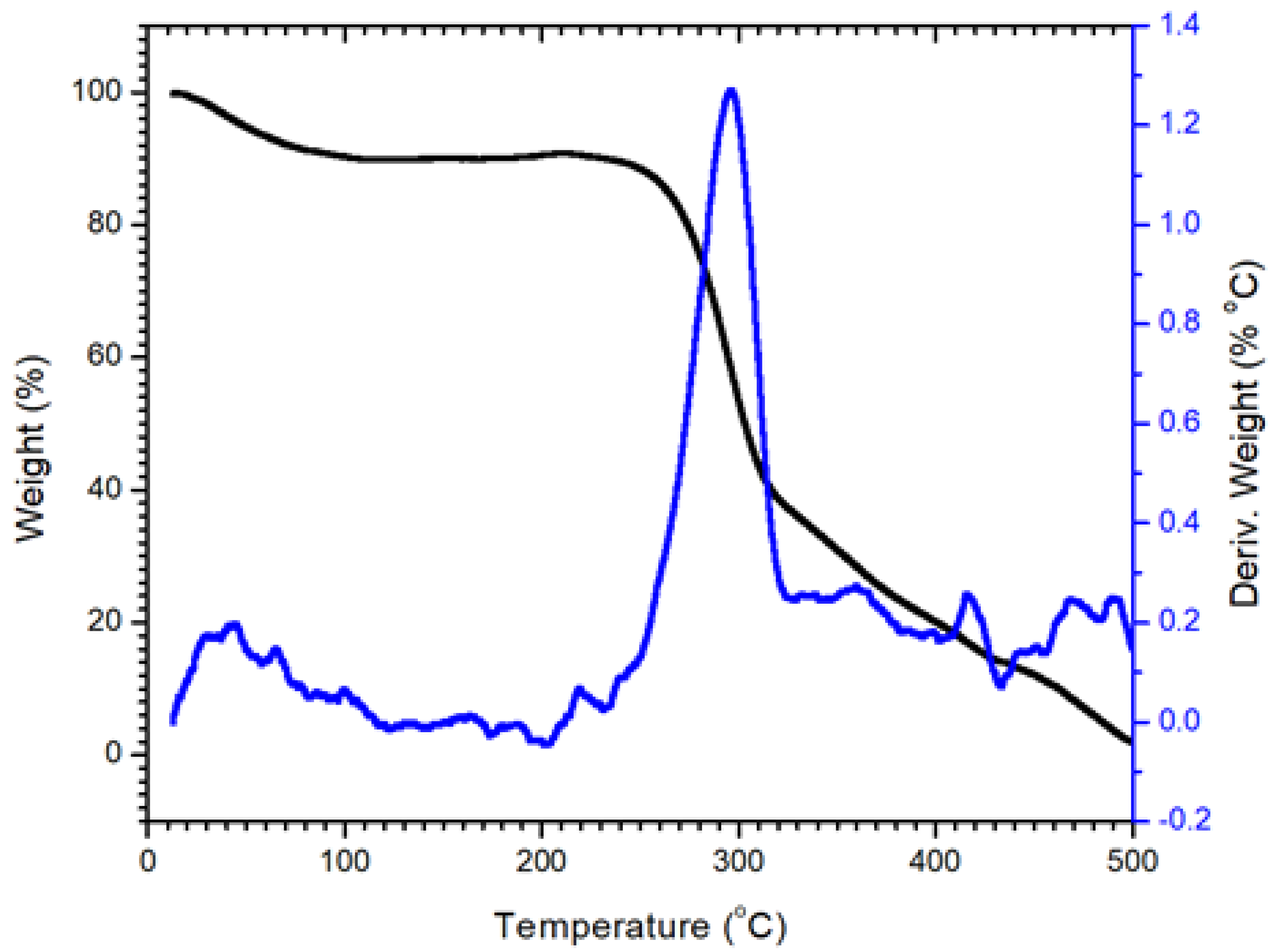
3.1.3. Thermal Analysis of Nanocellulose
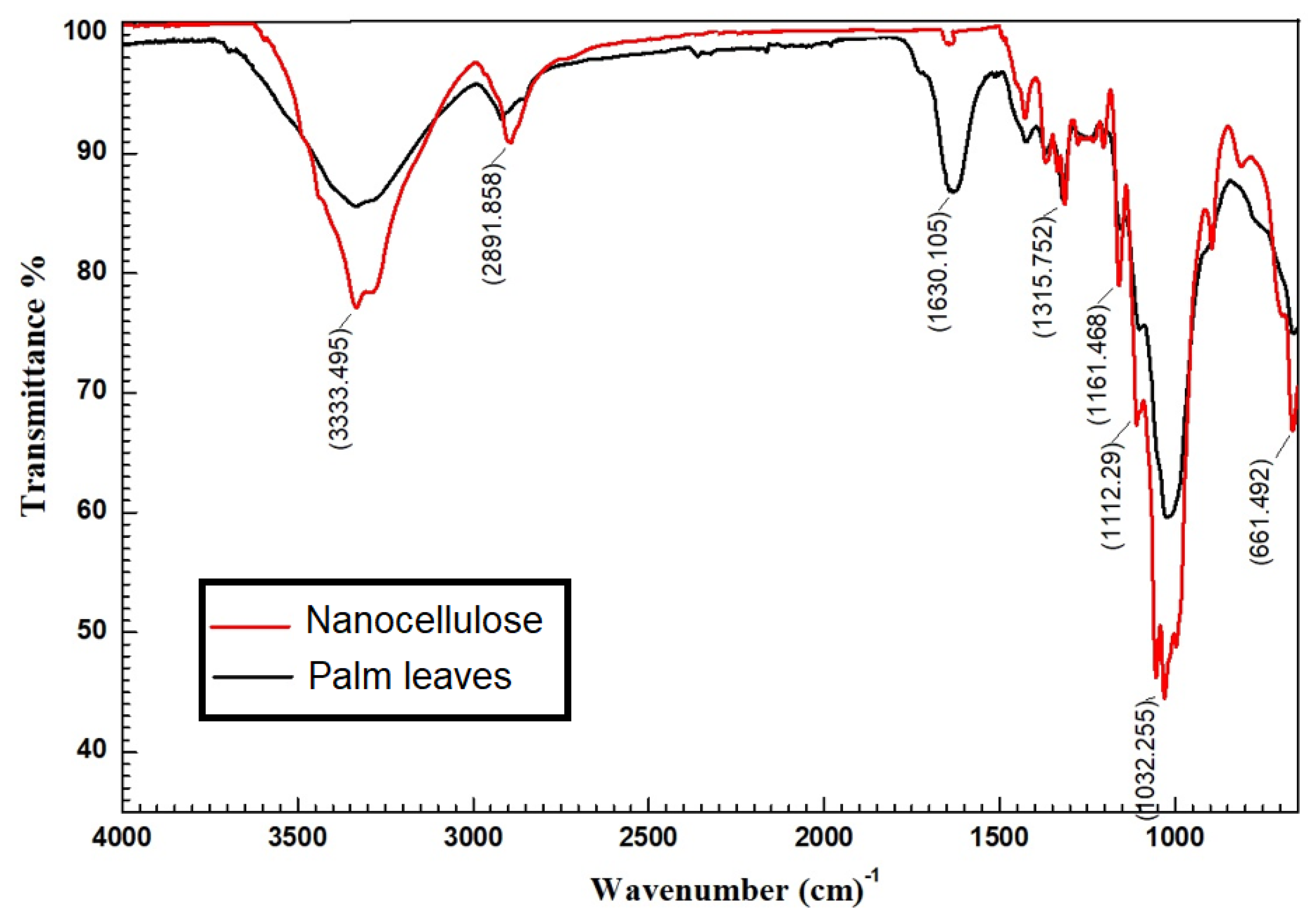
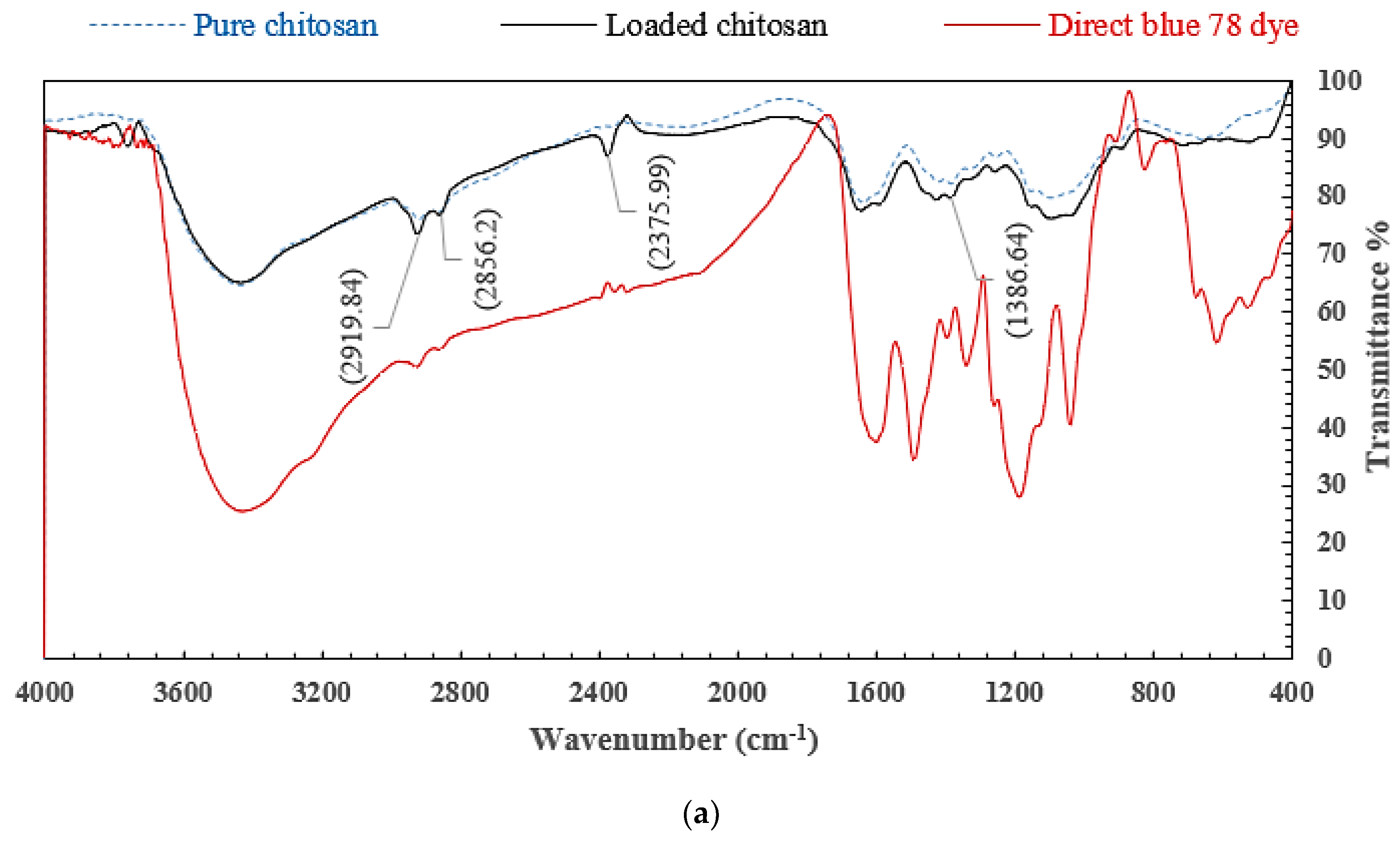
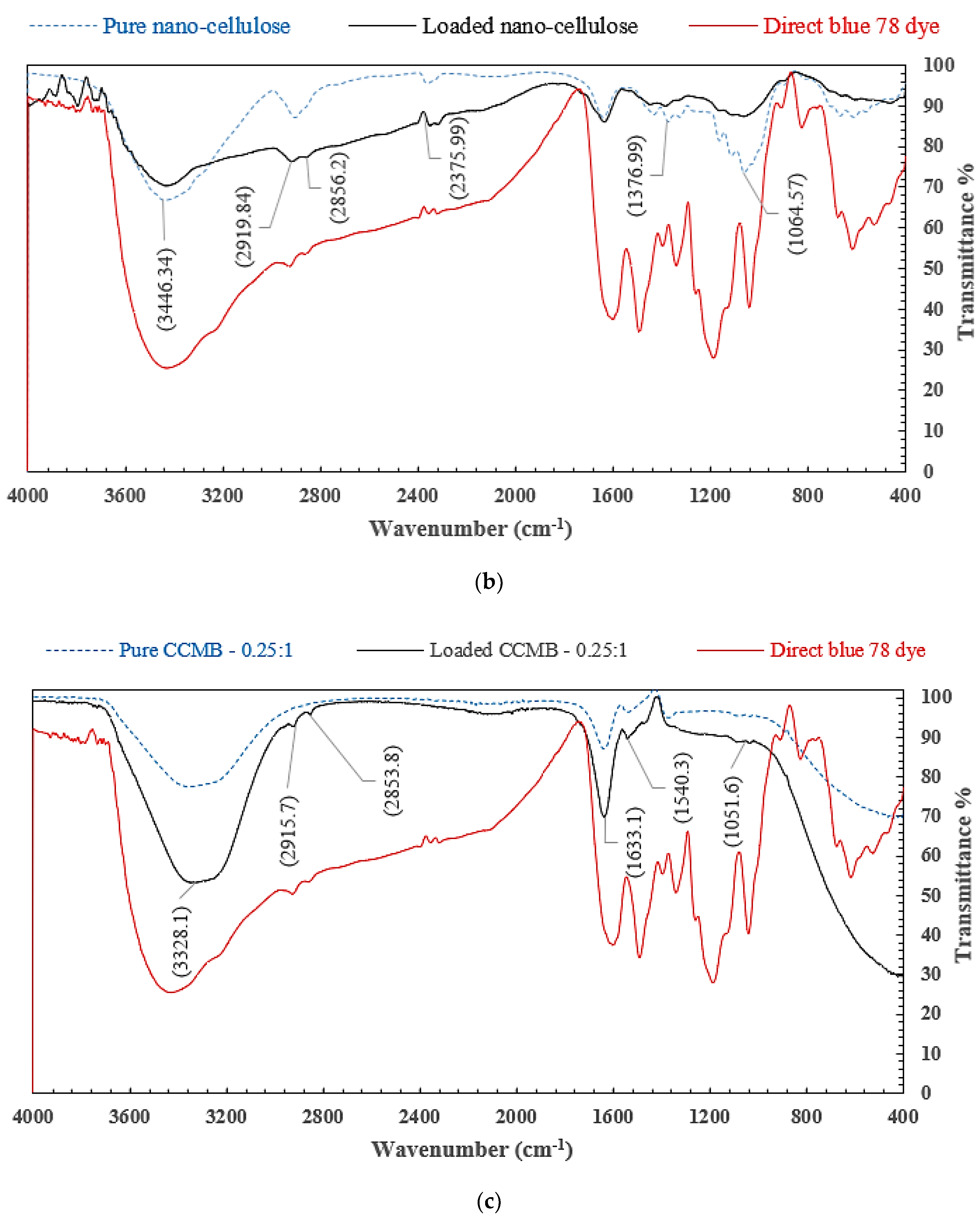
3.1.4. FTIR Analysis
3.2. Characterization of Nanocomposites
Surface Morphology of Nanocomposites
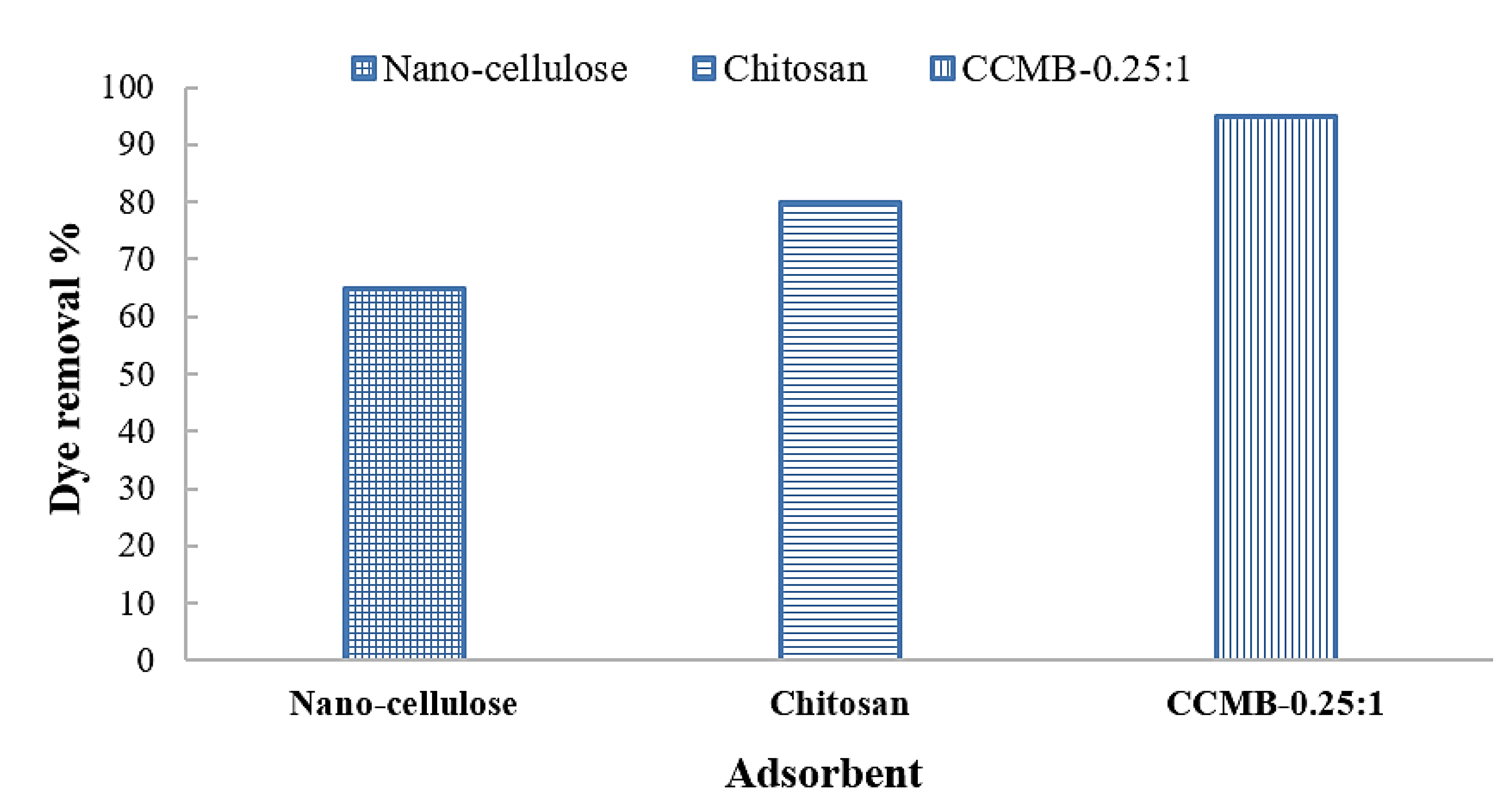
3.3. Adsorption Tests
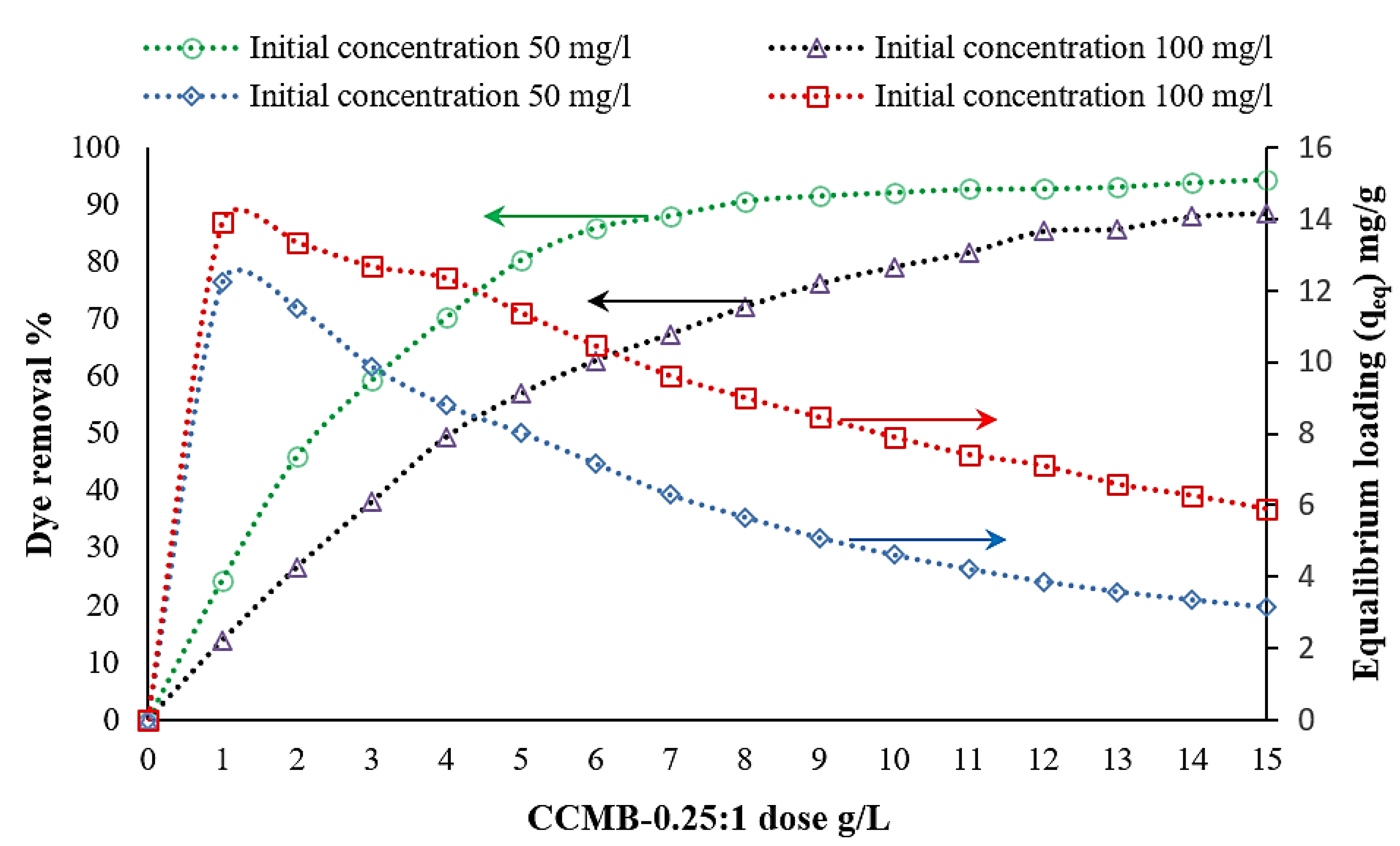
3.3.1. Effect of Adsorbent Concentration on DB78 Dye Removal Efficiency
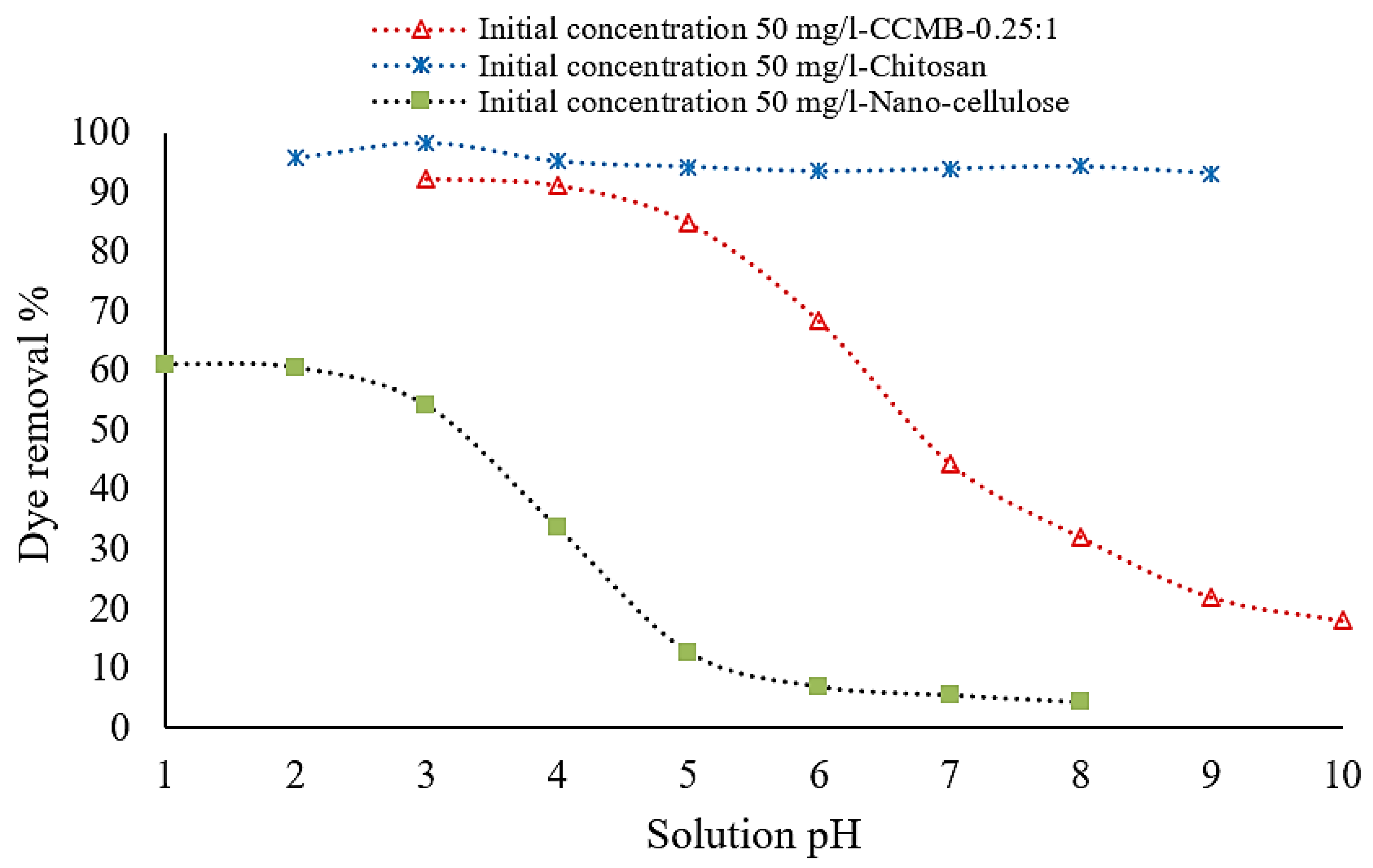
3.3.2. Effect of Solution pH on DB78 Dye Removal Efficiency
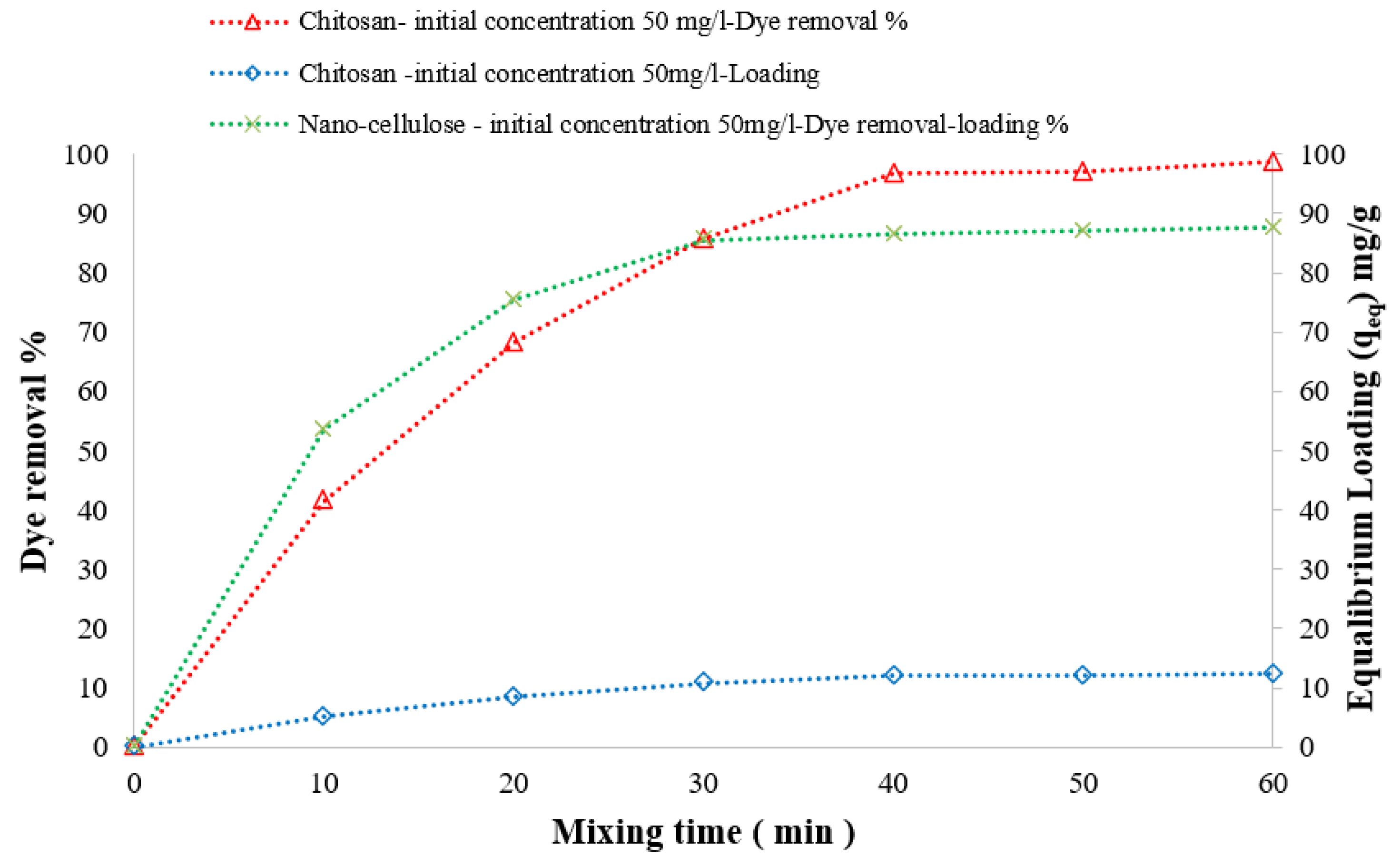
3.3.3. Effect of Mixing Time on DB78 Dye Removal Efficiency
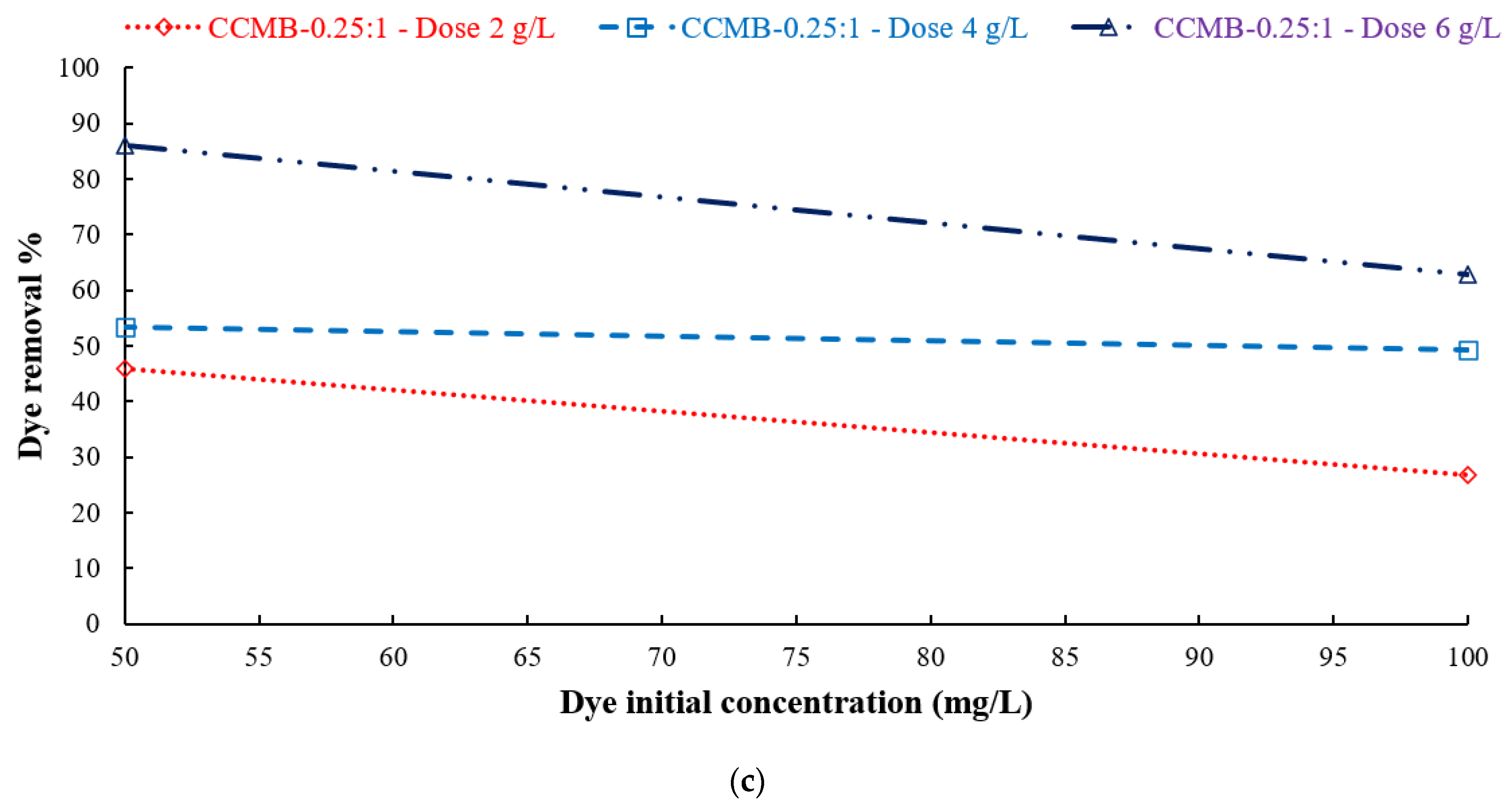
3.3.4. Effect of Dye Initial Concentration Removal Efficiency
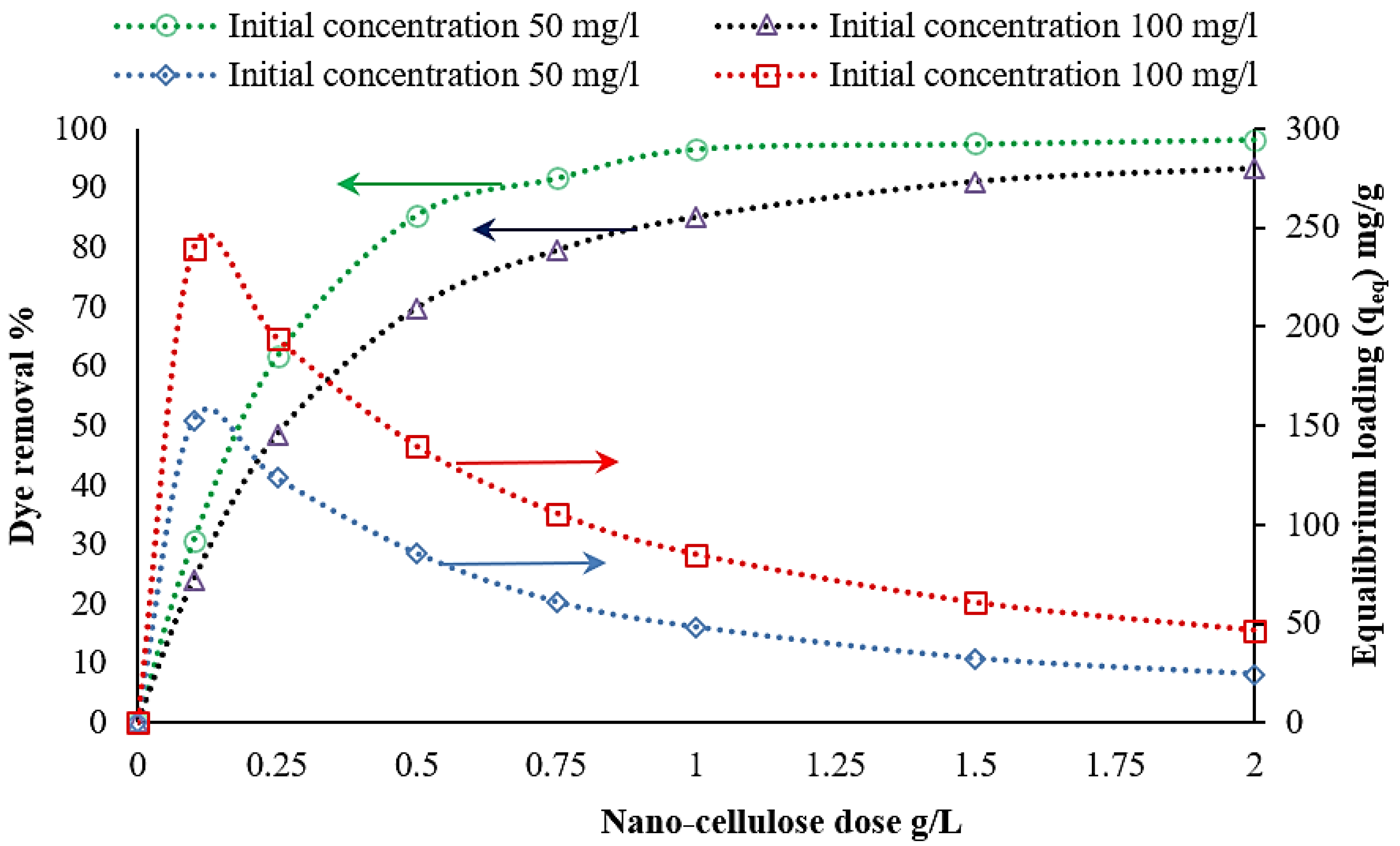
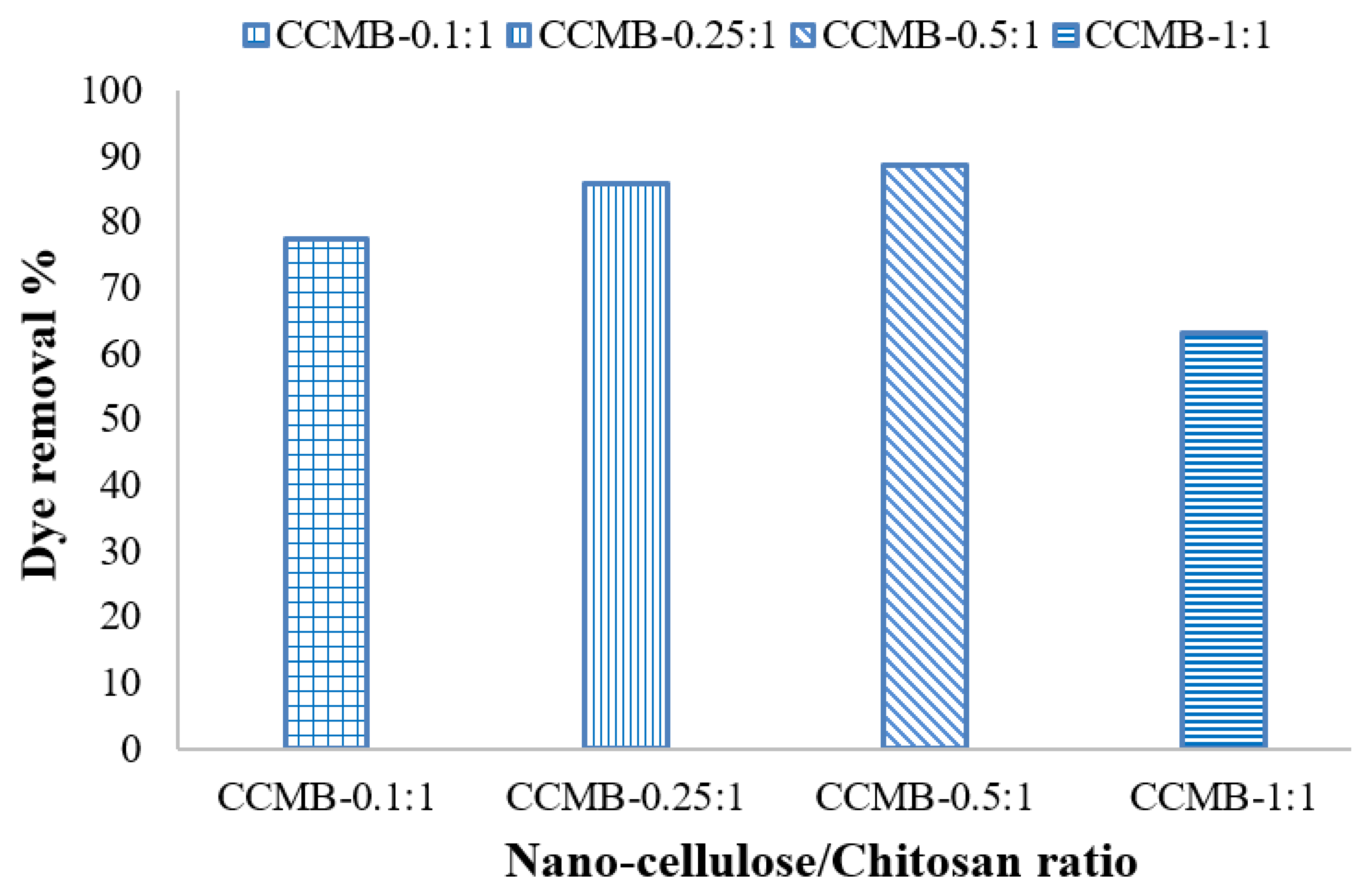
3.3.5. Effect of Nanocellulose Concentration on Removal Efficiency
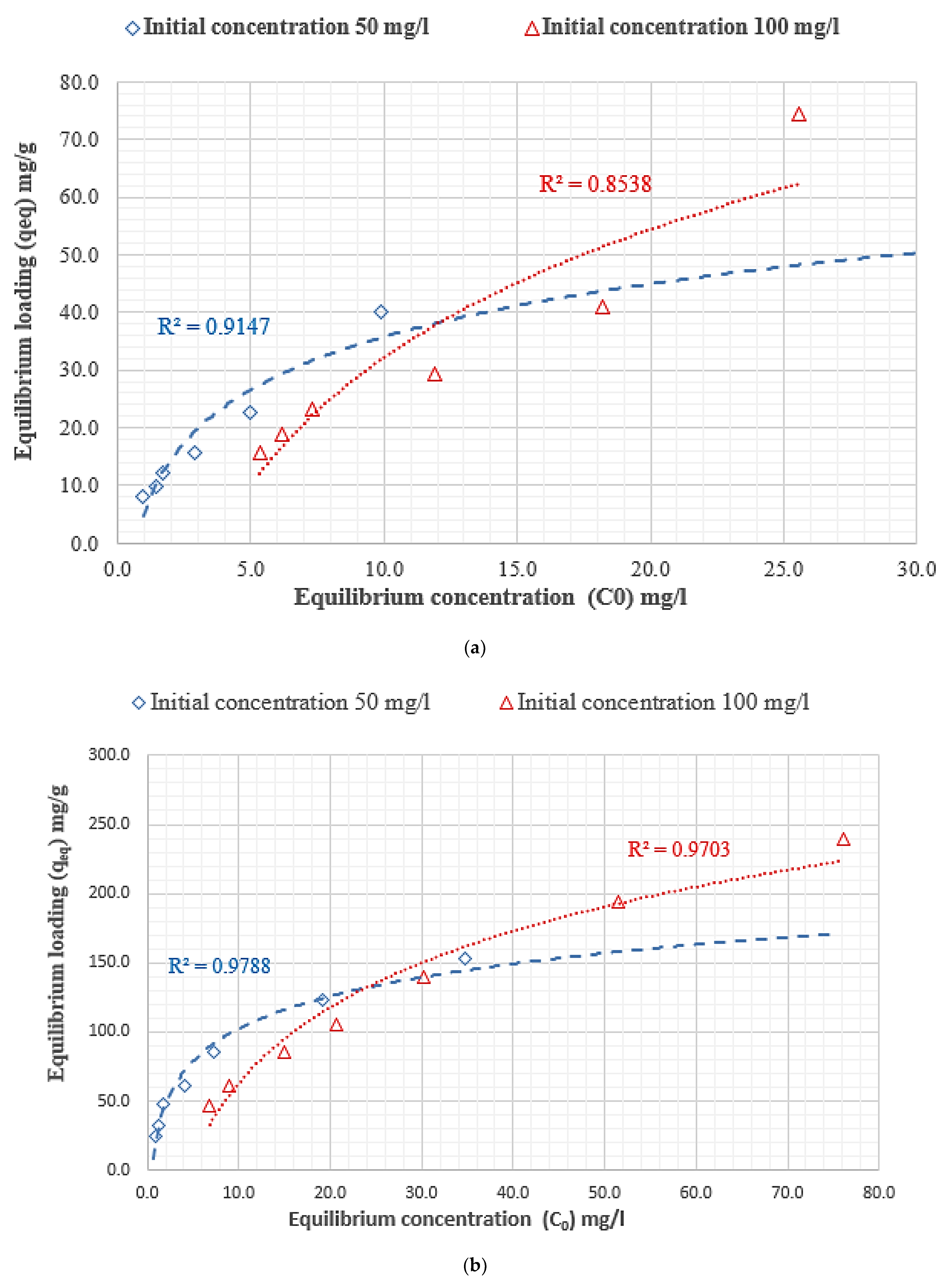
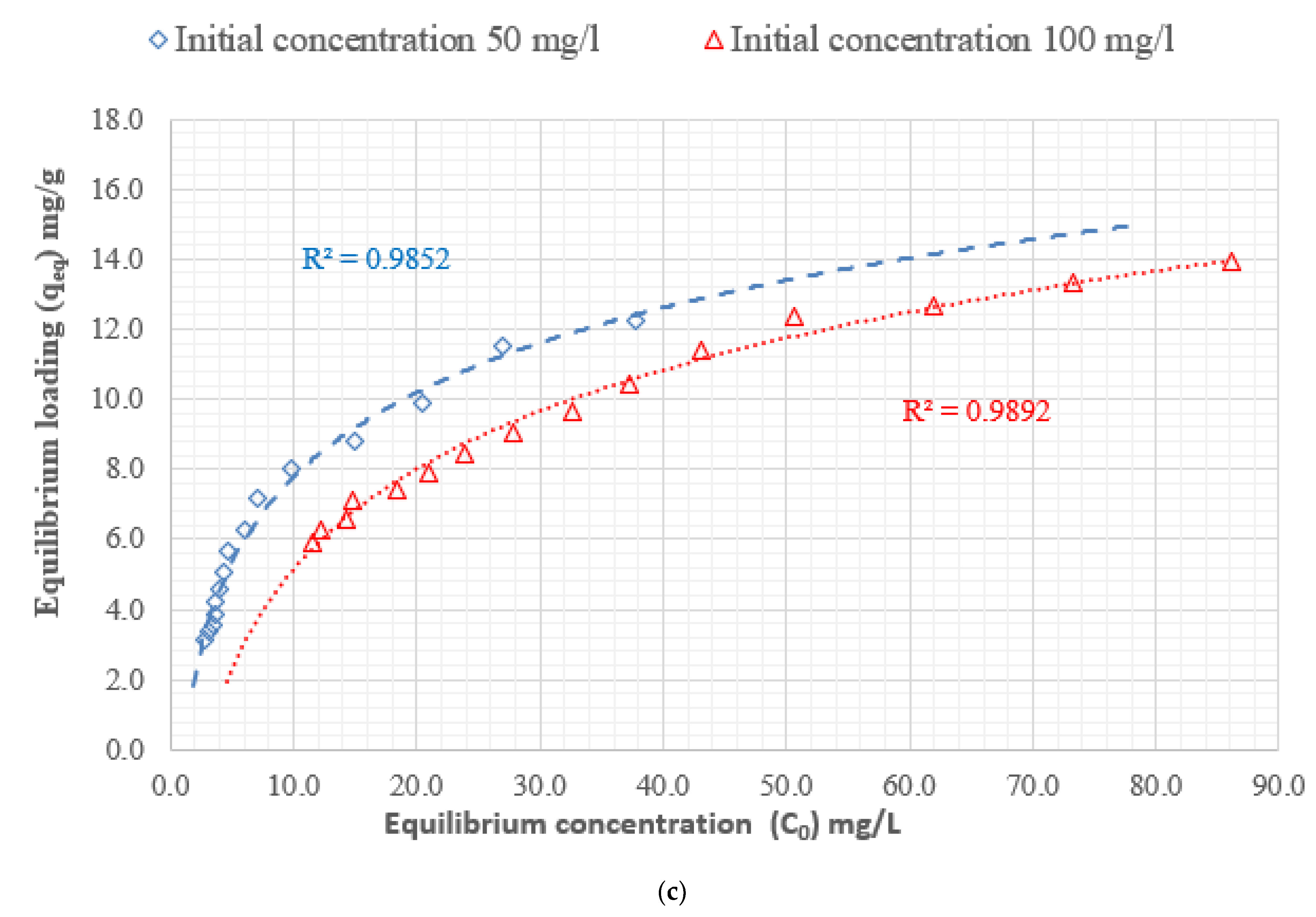
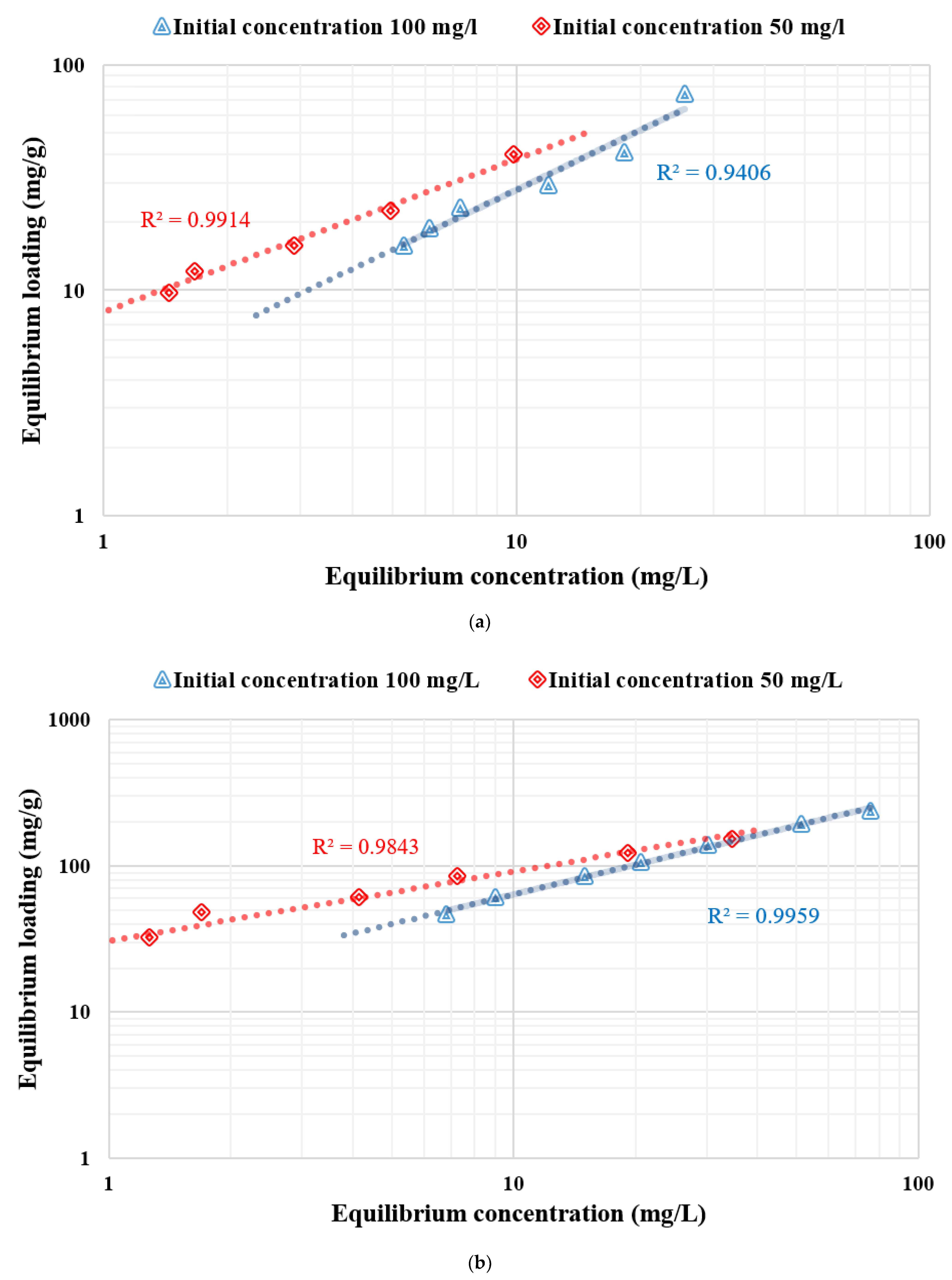
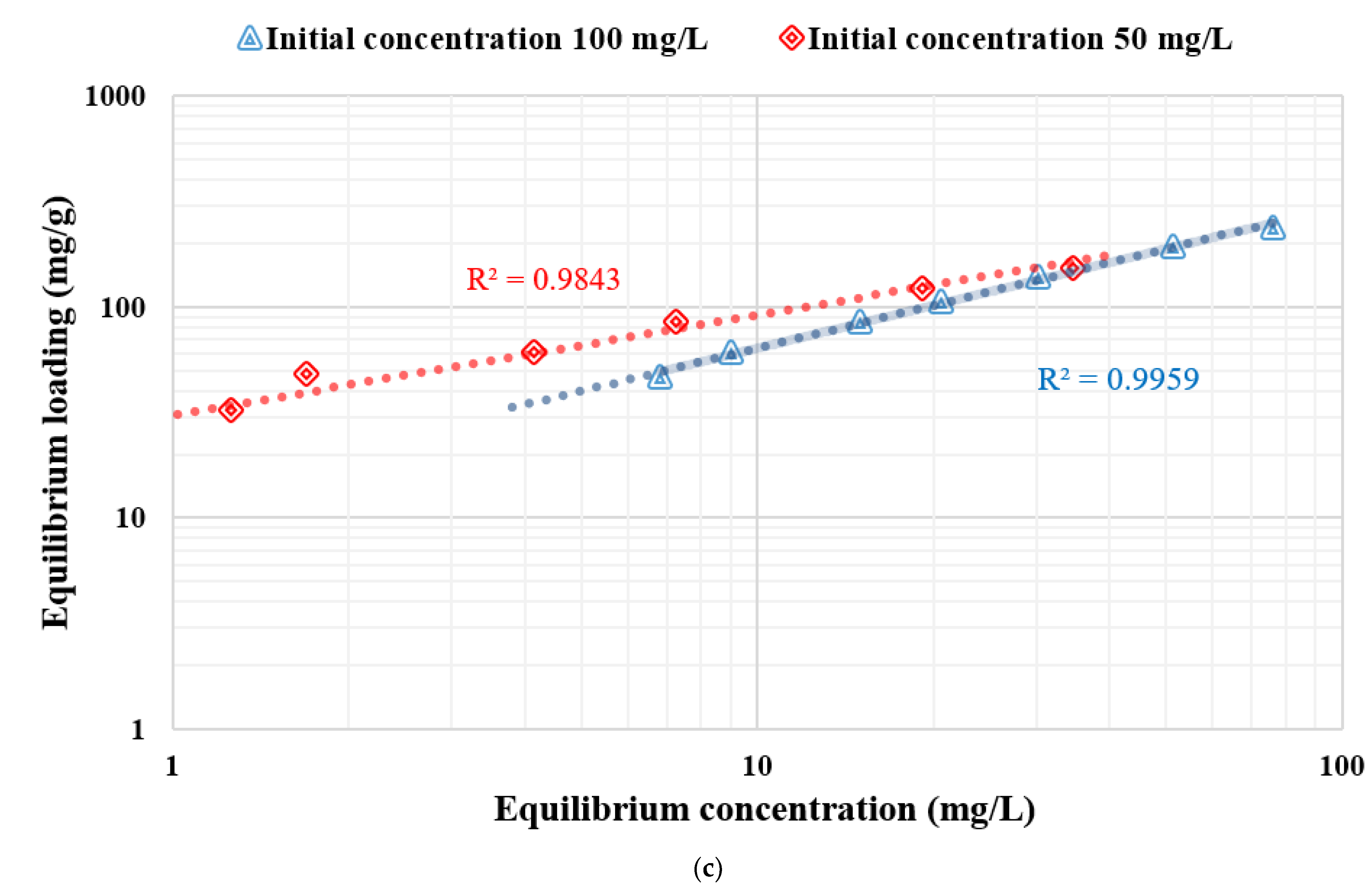
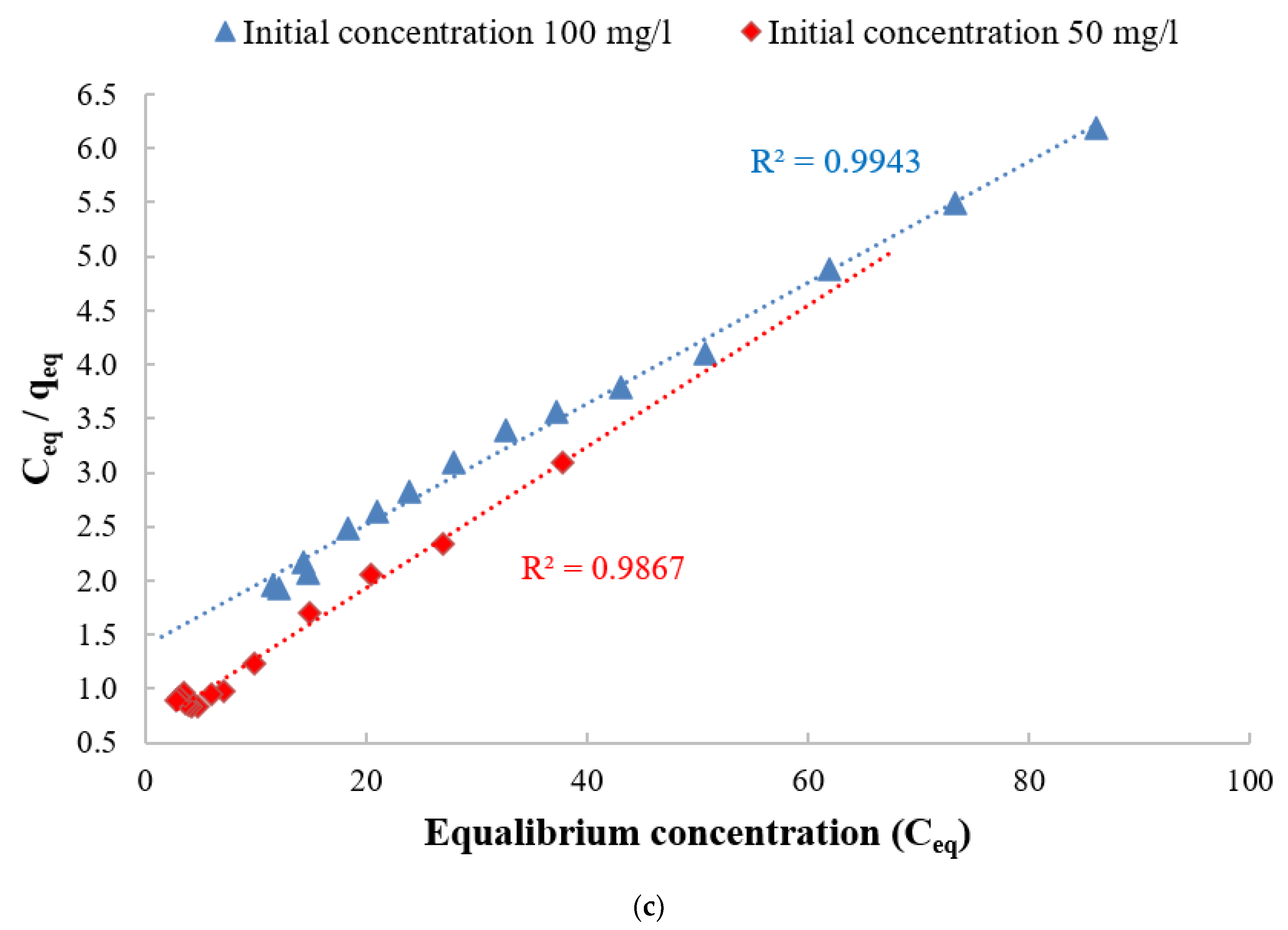
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm
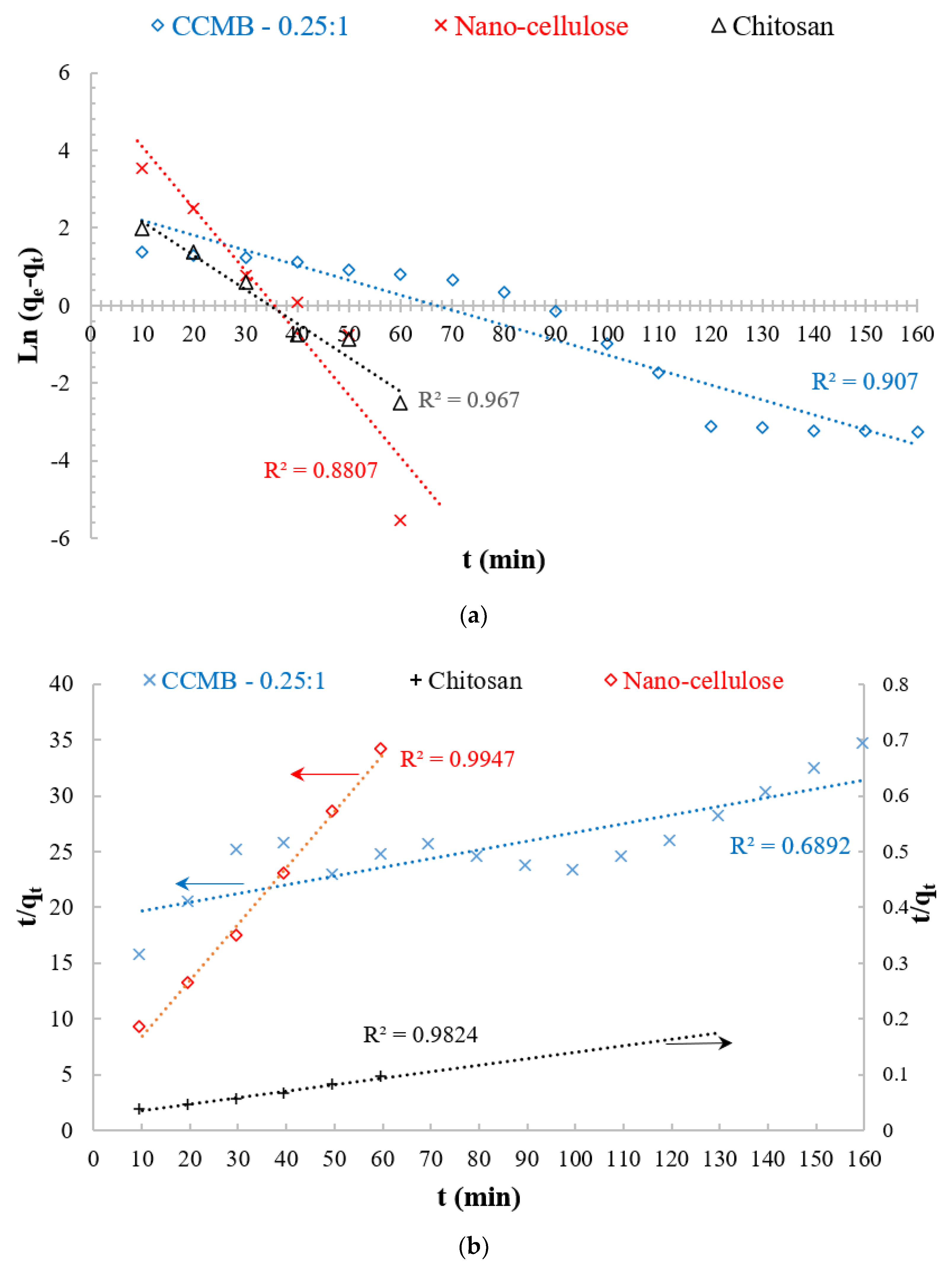
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramya, M.; Karthika, M.; Selvakumar, R.; Raj, B.; Ravi, K. A facile and efficient single step ball milling process for synthesis of partially amorphous Mg-Zn-Ca alloy powders for dye degradation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 696, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, V.; Larrechi, M.; Callao, M. Kinetic and adsorption study of acid dye removal using activated carbon. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandid, A.M.; Bassyouni, M.; Nehari, D.; Elhenawy, Y. Experimental and simulation study of multichannel air gap membrane distillation process with two types of solar collectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 243, 114431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoromba, M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H. Ecofriendly method to synthesize poly (o-aminophenol) based on solid state polymerization and fabrication of nanostructured semiconductor thin film. Polymers 2017, 120, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhenawy, Y.; Elminshawy, N.A.S.; Bassyouni, M.; Alhathal Alanezi, A.; Drioli, E. Experimental and theoretical investigation of a new air gap membrane distillation module with a corrugated feed channel. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.K.; Kumar, B.V.; Kalaiarasan, G.; Babu, P.J. TiO2 nanosheet incorporated polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes for dye removal. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 107, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhady, S.; Bassyouni, M.; Mansour, R.A.; Elzahar, M.H.; Abdel-Hamid, S.; Elhenawy, Y.; Saleh, M.Y. Oily Wastewater Treatment Using Polyamide Thin Film Composite Membrane Technology. Membranes 2020, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mehalmey, W.A.; Safwat, Y.; Bassyouni, M.; Alkordi, M.H. Strong Interplay between Polymer Surface Charge and MOF Cage Chemistry in Mixed-Matrix Membrane for Water Treatment Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27625–27631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoromba, M.S.; Ismail, M.I.; Bassyouni, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Salah, N.; Alshahrie, A.; Memic, A. Fabrication and characterization of poly (aniline-co-o-anthranilic acid)/magnetite nanocomposites and their application in wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 520, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Zoromba, M.S.; Abdel-Hamid, S.M.S.; Drioli, E. A review of polymeric nanocomposite membranes for water purification. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 73, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrasheedy, A.; Nady, N.; Bassyouni, M.; El-Shazly, A. Metal Organic Framework Based Polymer Mixed Matrix Membranes: Review on Applications in Water Purification. Membranes 2019, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; El-Ashtoukhy, E.-S.; Zoromba, M.S.; Bassyouni, M.; Sedahmed, G. Removal of nitrates from water by electrocoagulation using a cell with horizontally oriented Al serpentine tube anode. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 82, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, M.; Mansi, A.E.; Elgabry, A.; Ibrahim, B.A.; Kassem, O.A.; Alhebeshy, R. Utilization of carbon nanotubes in removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review of the CNTs’ potential and current challenges. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 126, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eteba, A.; Bassyouni, M.; Saleh, M. Removal of Hazardous Organic Pollutants Using Fly Ash. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2021, 9, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Yu, S.; Guo, S.; Du, K. High-strength and low-swelling chitosan/cellulose microspheres as a high-efficiency adsorbent for dye removal. Cellulose 2021, 28, 9323–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, T.; Woo, S.H. Adsorption of Congo Red from Aqueous Solutions Using Chitosan Hydrogel Beads Formed by Various Anionic Surfactants. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroń, P.; Chwastowski, J. Raphia-Microorganism Composite Biosorbent for Lead Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2021, 14, 7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroń, P.; Płecka, A.; Chwastowski, J. Lead Sorption by Chrysanthemum indicum: Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Desorption Studies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroń, P.; Sorys, P.; Chwastowski, J. Equilibrium and Kinetic Study of Ammonium Sorption by Raphia farinifera. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; Abdellatif, F.H.; Hasanin, M.S.; Abdellatif, M.M. Fabrication, characterization, and potential application of modified sawdust sorbents for efficient removal of heavy metal ions and anionic dye from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 332, 130021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, S.; Peinado, S.; Morillas-Gutiérrez, F.; La Rubia, M.D.; Moya, A.J. Nanocellulose from Agricultural Wastes: Products and Applications—A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.H.; Hasanin, M.; Kamel, S.; Dacrory, S. A new approach for antimicrobial and antiviral activities of biocompatible nanocomposite based on cellulose, amino acid and graphene oxide. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 209, 112172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, A.; Hasanin, M.; El-Aziz, M.A.; Turky, G. Conducting chitosan/hydroxylethyl cellulose/polyaniline bionanocomposites hydrogel based on graphene oxide doped with Ag-NPs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 167, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, A.A.; El-Aziz, M.A.; Hasanin, M.; Kamel, S. A novel electromagnetic biodegradable nanocomposite based on cellulose, polyaniline, and cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacrory, S.; Hashem, A.H.; Hasanin, M. Synthesis of cellulose based amino acid functionalized nano-biocomplex: Characterization, antifungal activity, molecular docking and hemocompatibility. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Rivkin, A.; Cao, Y.; Nevo, Y.; Abraham, E.; Ben-Shalom, T.; Lapidot, S.; Shoseyov, O. Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 39, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, J.P.S.; Rosa, M.F.; Filho, M.M.S.; Nascimento, L.D.; Nascimento, D.M.; Cassales, A.R. Extraction and characterization of nanocellulose structures from raw cotton linter. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul Rahman, N.H.; Chieng, B.W.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Abdul Rahman, N. Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from tea leaf waste fibers. Polymers 2017, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iskandar, M.A.; Yahya, E.B.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Rahman, A.A.; Ismail, M.A. Recent Progress in Modification Strategies of Nanocellulose-Based Aerogels for Oil Absorption Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, M.; Jahn, E.; Mautner, A.; Veigel, S.; Böhmdorfer, S.; Potthast, A.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Rosenau, T. Facile Preparation of Mechanically Robust and Functional Silica/Cellulose Nanofiber Gels Reinforced with Soluble Polysaccharides. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo-Martín, R.; Espinosa, E.; Rabasco-Vílchez, L.; Sanchez, L.M.; de Haro, J.; Rodríguez, A. Cellulose Nanofiber-Based Aerogels from Wheat Straw: Influence of Surface Load and Lignin Content on Their Properties and Dye Removal Capacity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelraof, M.; El Saied, H.; Hasanin, M.S. Green Immobilization of Glucanobacter xylinum onto Natural Polymers to Sustainable Bacterial Cellulose Production. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2022, 13, 2053–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellette, R.J.; Rawn, J.D. Organic Chemistry: Structure, Mechanism, Synthesis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nia, M.H.; Tavakolian, M.; Kiasat, A.R.; van de Ven, T.G. Hybrid Aerogel Nanocomposite of Dendritic Colloidal Silica and Hairy Nanocellulose: An Effective Dye Adsorbent. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11963–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.F.; Ching, Y.C.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Muhamad, F.; Hai, N.D.; Choo, J.H.; Hassan, C.R. Adsorbents for removal of cationic dye: Nanocellulose reinforced biopolymer composites. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivod, V.; Neral, B.; Mihelič, A.; Kokol, V. Highly efficient film-like nanocellulose-based adsorbents for the removal of loose reactive dye during textile laundering. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putro, J.N.; Santoso, S.P.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S.; Ju, Y.-H. Nanocrystalline cellulose from waste paper: Adsorbent for azo dyes removal. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, A.; Hamid, A.; Muhammad, N.; Naseer, A.; Ghauri, M.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, N.S. Cellulose-based Materials for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater–An Overview. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.; Luzzi, E.; Salzano de Luna, M.; Aprea, P.; Ambrogi, V.; Filippone, G. Chitosan/Zeolite Composite Aerogels for a Fast and Effective Removal of Both Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Water. Polymers 2021, 13, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Barbosa, N.; Campaña, A.L.; Cruz, J.C.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Osma, J.F. Enhanced Catalytic Dye Decolorization by Microencapsulation of Laccase from P. Sanguineus CS43 in Natural and Synthetic Polymers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-W.; Wu, M.-T.; Lee, J.C.-M.; Cheng, T.-Y. Isothermal Adsorption Properties for the Adsorption and Removal of Reactive Blue 221 Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Cross-Linked β-Chitosan Glycan as Acid-Resistant Adsorbent. Polymers 2018, 10, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayyouh, M.H.; Al-Blehed, M.S.; Attia, A.M. The effect of alkaline and polymer additives on phase behaviour of surfactant-oil-brine system at high salinity conditions. Rev. De L’institut Français Du Pétrole 1993, 48, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, E.; Harada, H.; Mitoma, Y.; Yonemura, S.; A Halem, H.I. Rapid Removal of Acid Red 88 by Zeolite/Chitosan Hydrogel in Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2022, 14, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Mitropoulos, A. Chitosan adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkayawong, N.; Thiravetyan, P.; Nakbanpote, W. Adsorption mechanism of synthetic reactive dye wastewater by chitosan. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.L.; Tan, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chong, W.C. A State-of-the-Art Review on Biowaste Derived Chitosan Biomaterials for Biosorption of Organic Dyes: Parameter Studies, Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamics. Polymers 2021, 13, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsamman, M.T.; Sánchez, J. Chitosan- and Alginate-Based Hydrogels for the Adsorption of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Water. Polymers 2022, 14, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Duarte, R.G.; López-Cervantes, J.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; Correa-Murrieta, M.A.; Núñez-Gastélum, J.A.; Rodríguez-Núñez, J.R. Chitosan-based adsorbents gels for the removal of tris-azo dye: Isotherms and kinetics studies. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2016, 15, 2469–2478. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, P.; Pal, A. Dye removal using waste beads: Efficient utilization of surface-modified chitosan beads generated after lead adsorption process. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elmageed, A.A.I.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Bourezgui, A.; Al-Hossainy, A.F. Synthesis, DFT studies, fabrication, and optical characterization of the [ZnCMC] TF polymer (organic/inorganic) as an optoelectronic device. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 8621–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arletti, R.; Quartieri, S.; Vezzalini, G. Elastic behavior of zeolite boggsite in silicon oil and aqueous medium: A case of high-pressure-induced over-hydration. Am. Miner. 2010, 95, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santmartí, A.; Lee, K.-Y. Crystallinity and Thermal Stability of Nanocellulose. In Nanocellulose and Sustainability: Production, Properties, Applications, and Case Studies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Y. Adsorptive removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions using microgel based on nanocellulose and polyvinylamine. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouillat, S.; Pla, F. State of the Art Manufacturing and Engineering of Nanocellulose: A Review of Available Data and Industrial Applications. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 4, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Movaghgharnezhad, S.; Mirabi, A.; Toosi, M.R.; Rad, A.S. Synthesis of cellulose nanofibers functionalized by dithiooxamide for preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of Cd(II) ions in water samples. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8885–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimova, O.L.; Evdokimova, A.V.; Kusova, T.V.; Agafonov, A.V. Preparation of hybrid nanocomposites based on nanoscale cellulose and magnetic nanoparticles with photocatalytic properties. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2020, 11, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolian, M.; Wiebe, H.; Sadeghi, M.A.; Van De Ven, T.G. Dye Removal Using Hairy Nanocellulose: Experimental and Theoretical Investigations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 5040–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, B. Adsorption behaviour of congo red by cellulose/chitosan hydrogel beads regenerated from ionic liquid. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 16970–16980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Peng, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X. Removal of Anionic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions by Cellulose-Based Adsorbents: Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 3266–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.A.; Yusra, A.I.; Bhat, A.H.; Jawaid, M. Cell wall ultrastructure, anatomy, lignin distribution, and chemical composition of Malaysian cultivated kenaf fiber. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 31, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Queiroz, M.; Melo, K.R.T.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Does the Use of Chitosan Contribute to Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation? Mar. Drugs 2014, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Lee, H.V.; Hamid, S.B.A. Preparation of Nanostructured Cellulose via Cr(III)- and Mn(II)-Transition Metal Salt Catalyzed Acid Hydrolysis Approach. BioResources 2016, 11, 7224–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamaming, J.; Hashim, R.; Leh, C.P.; Sulaiman, O.; Sugimoto, T.; Nasir, M. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from parenchyma and vascular bundle of oil palm trunk (Elaeis guineensis). Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán, J.I.; Alvarez, V.A.; Cyras, V.P.; Vázquez, A. Cyras, Analia Va’zquez, extraction of cellulose and preparation of nanocellulose from sisal fibers. Cellulose 2008, 15, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlita, Y.; Lee, H.V.; Hamid, S.B.A. Hamid, Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals Bio-Polymer From Agro-Industrial Wastes: Separation and Characterization. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2016, 24, 719–728. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, M.; Hashim, R.; Sulaiman, O.; Nordin, N.A.; Lamaming, J.; Asim, M. Laccase, an Emerging Tool to Fabricate Green Composites: A Review. BioResources 2015, 10, 6262–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, E.; Deepa, B.; Pothan, L.A.; Jacob, M.; Thomas, S.; Cvelbar, U.; Anandjiwala, R. Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: A novel approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Farooq, A.; Bassyouni, M.I.; Sait, H.H.; El-Wafa, M.A.; Hasan, S.W.; Ani, F.N. Pyrolysis of Saudi Arabian date palm waste: A viable option for converting waste into wealth. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutub, S.A.; Bassyouni, M. Dissolved solids adsorption of freshwater using synthesized bio-foam composite. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Murcia-Salvador, A.; Pellicer, J.A.; Fortea, M.I.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Adsorption of Direct Blue 78 Using Chitosan and Cyclodextrins as Adsorbents. Polymers 2019, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Symmetry Compound | 2θ | d | hkl | Observed | Calculated | FWHM | Dav | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2θ | 2d | 2θ | 2d | ||||||
| Parameters | 15.453 | 5.7296 | 111 | 15.331 | 5.882 | 0 | 1.3 × 10−5 | 5.7296 | 83.04 |
| a = 15.96 Å; b = 7.85 Å; c = 10.87 Å | 20.332 | 4.4253 | 051 | 20.332 | 4.425 | 0 | 4 × 10−6 | 1.7565 | 270.86 |
| α = γ = 90, β = 97.931° | 22.655 | 3.9201 | 020 | 22.635 | 3.974 | 0 | 0 | 3.9201 | 121.37 |
| V = 1400 (22), rmse (a) = 1.05 × 10−3 | 34.575 | 2.5920 | 23 | 34.575 | 2.613 | 0 | −1 × 10−6 | 2.5920 | 183.56 |
| Machine error = −0.48 | |||||||||
| Average | 3.5995 | 164.71 | |||||||
| Adsorbent | Initial Concentration 50 mg/L | Initial Concentration 100 mg/L | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (g/L) | Loading (mg/g) | Removal % | Dose (g/L) | Loading (mg/g) | Removal % | |
| Chitosan | 3 | 15.7 | 94.2 | 5 | 18.77 | 93.85 |
| Nanocellulose | 1 | 48.3 | 96.6 | 2 | 46.6 | 935 |
| CCMB-0.25:1 | 9 | 5.08 | 91.52 | 14 | 5.9 | 88.4 |
| Adsorbent | DB78 Dye Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Langmuir Isothermal | Freundlich Isothermal | Followed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q0 (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 | Kf (mg/g) | 1/n | R2 | |||
| Chitosan | 50 | 73.5 | 0.107 | 0.8514 | 8.02 | 0.67 | 0.9914 | Freundlich |
| 100 | 384.6 | 0.0074 | 0.1658 | 3.65 | 0.88 | 0.9406 | Freundlich | |
| Nanocellulose | 50 | 175.4 | 0.16 | 0.9867 | 30.6 | 0.47 | 0.9843 | Langmuir |
| 100 | 400 | 0.018 | 0.988 | 13.49 | 0.67 | 0.9959 | Freundlich | |
| CCMB-0.25:1 | 50 | 15.31 | 1.0306 | 0.9867 | 2.18 | 0.51 | 0.9428 | Langmuir |
| 100 | 17.79 | 0.0404 | 0.9943 | 2.12 | 0.43 | 0.9841 | Langmuir | |
| Kinetic Model Parameters | Pseudo First-Order Model | Pseudo Second-Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (1/min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | K2 (g/mg min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | |
| CCMB-0.25:1 | 0.0385 | 12.8 | 0.907 | 0.0003 | 13.2 | 0.689 |
| Nanocellulose | 0.1594 | 292 | 0.8807 | 0.0015 | 99 | 0.9947 |
| Chitosan | 0.0867 | 20.9 | 0.967 | 2.807 | 17.27 | 0.9824 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bassyouni, M.; Zoromba, M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Mosly, I. Extraction of Nanocellulose for Eco-Friendly Biocomposite Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091852
Bassyouni M, Zoromba MS, Abdel-Aziz MH, Mosly I. Extraction of Nanocellulose for Eco-Friendly Biocomposite Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091852
Chicago/Turabian StyleBassyouni, Mohamed, Mohamed Sh. Zoromba, Mohamed H. Abdel-Aziz, and Ibrahim Mosly. 2022. "Extraction of Nanocellulose for Eco-Friendly Biocomposite Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091852
APA StyleBassyouni, M., Zoromba, M. S., Abdel-Aziz, M. H., & Mosly, I. (2022). Extraction of Nanocellulose for Eco-Friendly Biocomposite Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment. Polymers, 14(9), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091852









