Abstract
A new synthetic chelating N–hydroxy–N–trioctyl iminophosphorane (HTIP) was prepared through the reaction of trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO) with N–hydroxylamine hydrochloride in the presence of a Lewis acid (AlCl3). Specifications for the HTIP chelating ligand were successfully determined using many analytical techniques, 13C–NMR, 1H–NMR, FTIR, EDX, and GC–MS analyses, which assured a reasonable synthesis of the HTIP ligand. The ability of HTIP to retain U(VI) ions was investigated. The optimum experimental factors, pH value, experimental time, initial U(VI) ion concentration, HTIP dosage, ambient temperature, and eluents, were attained with solvent extraction techniques. The utmost retention capacity of HTIP/CHCl3 was 247.5 mg/g; it was achieved at pH = 3.0, 25 °C, with 30 min of shaking and 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L. From the stoichiometric calculations, approximately 1.5 hydrogen atoms are released during the extraction at pH 3.0, and 4.0 moles of HTIP ligand were responsible for chelation of one mole of uranyl ions. According to kinetic studies, the pseudo–first order model accurately predicted the kinetics of U(VI) extraction by HTIP ligand with a retention power of 245.47 mg/g. The thermodynamic parameters ΔS°, ΔH°, and ΔG° were also calculated; the extraction process was predicted as an exothermic, spontaneous, and advantageous extraction at low temperatures. As the temperature increased, the value of ∆G° increased. The elution of uranium ions from the loaded HTIP/CHCl3 was achieved using 2.0 mol of H2SO4 with a 99.0% efficiency rate. Finally, the extended variables were used to obtain a uranium concentrate (Na2U2O7, Y.C) with a uranium grade of 69.93% and purity of 93.24%.
1. Introduction
The arrangement of the reactive center in a ligand has been the basis for many advances in inorganic as well as organometallic chemistry. Accordingly, significant time and effort have gone into designing and synthesizing ancillary ligands, besides studying the properties, reactivities, and geometries of the resulting complexes. In some cases, these efforts have resulted in new applications in stoichiometric chemistry, catalysis, and materials science [1,2,3]. A large number of structural studies for systems with phosphinimide ligands have been published in this area. These chelating and anionic ligands (R3PN) are easily obtained from neutral phosphinimine precursors, prepared utilizing the simple and long–established Staudinger reaction [4,5,6]. Iminophosphorane compounds, also known as phosphoranimines, phosphinimines, or phosphazenes, were detected in 1919; they are organic composites with the general structure R3P=NR. Iminophosphoranes contain nitrogen alongside phosphorus atoms, which coordinate to transition metals using the nitrogen atom’s lone pair of electrons. Multidentate ligands are produced by adding extra donor sites into the iminophosphorane ligand, and they are gaining popularity in both coordination chemistry and catalysis [7,8,9]. Iminophosphoranes are resonance hybrids of the two recognized forms A and B, and have a highly polarized P=N bond (Scheme 1). They can also integrate transition metals through the sp2–hybridized nitrogen atom’s lone pair, resulting in stable complexes (C in Scheme 1) [10]. Iminophosphoranes, which are primarily s–donor ligands with only minimal p–acceptor characteristics, have a limited inherent coordinating capability since they can be easily substituted by other ligands.
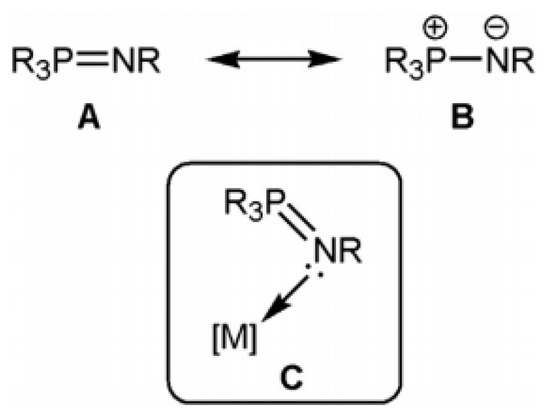
Scheme 1.
The recognized structures of an iminophosphorane and its coordination to a metal.
Polydentate mixed ligands, such as those found in the generic metal complex structures shown in Scheme 2 (D–G), can stabilize a wider range of metal ions than their monodentate R3P = NR counterparts due to the addition of further donor sites to the iminophosphoranes. The reactivity of the metal center can be modified as needed by selecting and adjusting these new donor sites, as well as the appropriate linkers. It is regarded as a critical component in achieving high levels of activity and selectivity [7].
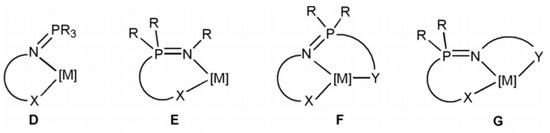
Scheme 2.
Common structures of complexes of metal with polydentate iminophosphorane–based ligands.
Several procedures for the production of iminophosphoranes are recognized; however, the most dominant and extensively used are the Staudinger as well as Kirsanov reaction (Scheme 3). A phosphine (PR3) is used as a starting material in both of them. The Staudinger reaction involves direct oxidation with an organic azide, whereas the Kirsanov reaction involves initial bromination and consecutive reaction of the resulting phosphine dibromide compound with a primary amine in the presence of a base [11,12,13].
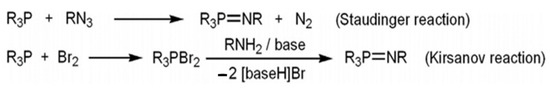
Scheme 3.
Principal techniques of iminophosphorane synthesis.
There are various methods for the synthesis of phosphazenes, such as the free radical process, thermal ring opening polymerization, substitution polymerization and cationic or anionic living polymerization, and solution polymerization method [14,15,16,17]. Phosphazenes have highly tunable chemical as well as physical properties that count on the substituents attached to the phosphorus atom. Therefore, they are employed in an enormous range of fields, such as rechargeable batteries [18], liquid crystals [19], membranes [20] and lubricants [21], anticancer agents [22], flame retardants [23], antibacterial reagents [24], biological materials [25], synthetic bones [26], photosensitive substrates [27], thermally stable macromolecules [28], a high limiting oxygen index (LOI) [29], coordination metal supports and reagents for organometallic chemistry [30], silicon-containing compounds [31], and catalysts [32].
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U, which belongs to the actinides. Due to its strategic significance in the energy sector, uranium became the most valuable heavy metal [32,33,34,35]. In nature, the Earth’s crust contains an average of 4.0 mg/L uranium [36]; however, it deposits in different types of rocks. It is a hexavalent state in the secondary minerals, such as kasolite, uranophane, autunite, etc., while it has a tetravalent oxidation state in the form of primary minerals, e.g., coffinite, pitchblende, uraninite, etc. Firstly, uranium is leached from its ore in an acidic or alkaline process, and extracted from the resulting leach liquor using an ion exchanger or a solvent extraction technique [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. Solvent extraction (SX) is a widely used technique for the recovery and separation of base metals and strategic metals in hydrometallurgy. Solvent extraction efficacy is subject to several factors including the type of separation apparatus (pulsed columns, mixer–settler, etc.), the type of feed solution, the applied flowsheets, the chemical composition of the organic solvent, the flow rates of both aqueous and organic phases in the extractions along with elution steps, etc. In the SX method, the extractant plays an essential role. It should have tremendous solubility in the organic solvent. Nevertheless, it must have an extremely low aqueous phase solubility. The solvent ought to be nonvolatile, industrially serviceable, nontoxic, nonflammable, and affordable for the element extraction process [48,49]. Previous studies have used several extractants for uranium extraction by solvent extraction. The derivatives of organophosphorus compounds have been employed since 1900 in uranium extraction processes. Compounds such as Cyanex 302, Cyanex 272, TBP, DEHPA, D2EHPA/TOPO mixtures, Primene JM–T/Alamine–336 mixture [50], DDPA, HDPA, CMPO, DNPPA, and DBBP, which are used to extract uranium from different matrices, were studied [51,52,53,54,55,56]. Several ligands with high selectivity are employed for uptake of uranium ions, comprising organic crown ethers [57], calixarenes [58], and Schiff bases. The long-chain amines have proven to be outstanding extractants for a large number of anionic metal complexes applied widely in uranium removal, such as Adogen–383, TOA, and Aliquate–336 [59,60,61].
Amides are deemed one of the outstanding as well as vital organic functional groups in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, polymers, and naturally occurring molecules. In addition, carboxamides have considerable value in coordination, medicinal, and organic chemistry. They can be obtained via the amidation process where a condensation reaction occurs between carboxylic acid and amine. One-pot synthesis of the chelating carboxamides using different catalysts were proposed. For instance, pyridine–2,6–dicarboxylic acid bis–(3–hydroxy phenyl) amide (Pydca) along with tetra–kis (2–ethylhexyl) pyridine–2,6–dicarboxamide (EHPyCA) were successfully synthesized and utilized for removal of thorium as well as uranium from leach liquors of ore samples in Egypt [62,63,64].
In this study, a new synthetic N–hydroxy–N–trioctyl iminophosphorane (HTIP) chelating ligand was synthesized using an effective alternative technique compared to the traditional Staudinger and Kirsanov methods and employed for uranium extraction from acidic solution. Both the removal and elution factors were optimized. Furthermore, the study dealt with the equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic characteristics of uranium extraction from G. Gattar leach fluid, North Eastern Desert of Egypt.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
The acidity and alkalinity of solutions were detected using a digital pH meter (VSTAR10 series, Thermo Scientific™, Waltham, MA, USA) with an error of ±0.1. An analytical balance (AUW220D Series, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with standard deviation of 0.05 mg was utilized to measure all samples. A Vibromatic-384 shaker was employed to mix the contents in separating funnels. The crystal structure of materials was examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique (D8 Discover Family, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). Quantitative analysis of U(VI) was executed with a double beam spectrometer (T80 UV/Vis, PG Instrument, Leicestershire, UK) using the arsenazo (III) indicator and 650 nm wavelength against an appropriate standard solution [65]. Furthermore, oxidometric titration against ammonium metavanadate and sodium diphenyl amine sulfonate as an indicator using automatic titrator [66,67] (SCOTT Instrument, GmbH, DE, Sialkot, Pakistan) was also employed to confirm the concentration of U(VI) ions. An ICP-OES spectrometer (OPTIMA 5300 DV, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) was applied to specify the concentration of uranium and metal ions of G. Gattar leachate. A Reichert Thermovar was used to determine the melting point. The elemental analysis of uranium concentrate product and HTIP ligand were recorded using EDX (JSM–7900F, Jeol, Tokyo, Japan). An FTIR spectrophotometer (IRPrestige–21, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) was employed to record the IR spectra using KBr disc. The 1H and 13C–NMR spectra were obtained at 500 MHz using an NMR spectrometer (Bruker Avance TM 500, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). The coupling constant (J) was measured in Hertz (Hz), while the chemical shift (δ) was measured in ppm. A mass spectrometer (Finnigan SSQ 7000 spectrometer, Thermo Finnigan, San Jose, CA, USA) was used for the molecular formula. The laboratories of National Research Center (NRC), Cairo, Egypt performed the FTIR, GC–MS, 1H, and 13C-NMR analyses.
2.2. Reagents
All of the reagents were made with analytical grade chemicals. HCl, H2SO4, NaOH, and HNO3 were purchased from POCH S.A., Gliwice, Poland. Trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO) and N–hydroxylamine hydrochloride were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific–Acros Organics Inc., Geel, Belgium. Ammonium metavanadate, sodium nitrite, FeSO4.7H2O, AlCl3, and urea were supplied by Scharlau Chemie. S.A., Barcelona, Spain. Uranyl acetate dihydrate, arsenazo III, and sodium diphenyl amine sulfonate were obtained from Merck, Darmstadt, Germany. Furthermore, methanol, DMF, and ethyl acetate were purchased from Fluka, Gillingham, UK. All reactions were performed utilizing flame-dried glassware. Thin paper chromatography (PC) was used to observe the reaction’s development. Ethanol plus ethyl acetate (50:50 v/v) was adopted as an eluent. A UV lamp was used to visualize spots on the PC plates (250 nm).
2.3. Synthesis of N–Hydroxy–N–Trioctyl Iminophosphorane (HTIP) Chelating Ligand
Two primary procedures were used to produce N–Hydroxy–N–trioctyl iminophosphorane (HTIP). The first stage in neutralization was to mix 0.1 mole of NaOH (5.0 g, over the stoichiometric quantity) with 0.1 mole of NH2OH.HCl (7.0 g) in 50.0 mL of DMF as diluent. For 2.0 h, the mixture was refluxed at 50 °C. The vital goal of the neutralization phase was to make NH2OH more nucleophilic. The second swelling process started with 0.1 mole trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO, 38.6 g) and 0.1 mole (13.3 g) AlCl3 hard Lewis acid in 50.0 mL DMF in a condenser for 2.0 h at 50 °C. Finally, the two additions were added to each other and allowed to condense for 6.0 h at 100 °C. The reaction was monitored using paper chromatography (PC) sheets and a solvent mixture of ethanol plus ethyl acetate 50:50 v/v. A UV lamp was used to detect the spots. The resulting HTIP appeared as a crystalline white to pale yellow solid with a density of ≈0.943 g/cm3. After completion of the reaction, the product was obtained by washing it several times with deionized water to remove any leftover DMF and AlCl3. The residue was washed, and the recrystallization procedure was performed with an ethanol/DMF mixture.
2.4. Preparation of U(VI) Standard Stock Solution
A 1000 mg/L (4.2 × 10−3 mol/L) U(VI) standard stock solution was prepared by dissolving 1.872 g of UO2(CH3COOH)2.2H2O in deionized water that had been acidified with 5.0 mL concentrated HNO3 to avoid hydrolysis in a 1000 mL volumetric flask. In addition, numerous standard stock solutions of 1000 mg/L of probable different ions during U(VI) extraction by HTIP/CHCl3 chelating ligand were generated by dissolving proper amounts of their salts in 1000 mL deionized water.
2.5. Extraction and Stripping Procedures
The pH value, shaking time, initial uranium(VI) conc., HTIP conc., temperature, and different ions were all tuned to optimize U(VI) ion extraction from synthetic solution by HTIP/CHCl3. In these experiments, 25.0 mL of a 100 mg/L (4.2 × 10−4 mol/L) synthetic U(VI) ions solution was mechanically shaken for a predefined period of time with 25.0 mL of varied concentrations of HTIP/CHCl3. Both the extraction distribution ratio D and stripping ratio D′ were calculated using the following Equation (1) [68]:
where Co and Ca (mg/L) correspond to the concentration of U(VI) in organic and aqueous phase, respectively. Moreover, the distribution coefficient (Kd) and extraction percentage (E%) were calculated using Equations (2) and (3), respectively:
where Ci and Ce (mg/L) symbolise for the initial and equilibrium concentration of U(VI) ions, respectively. Vo and Va (mL) represent organic and aqueous phase volumes, respectively. Nonetheless, the stripping procedures were performed by shaking different volumes of the loaded organic solvent with the eluent (2.0 mol H2SO4) for 10 min at ambient temperature. After equilibration, the two layers were entirely separated, and the U(VI) ion concentration was measured. The stripping percentage (S%) can be expressed using the next Equation (4):
2.6. Production of G. Gattar Granite Leach Solution
Uranium–rich ore sample was collected from G. Gattar granite, North Eastern Desert, Egypt. Percolation leaching technique was applied; H2SO4 was used as a leachant. The leaching parameters were optimized at 75.0 g/L of H2SO4, −100 mesh particle size for 4.0 h leaching time, and 1:1 S/L phase ratio at room temperature. ICP-OES and colorimetric analysis were used to detect the chemical composition of the G. Gattar ore sample and its leachate.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of N–Hydroxy–N–Trioctyl Iminophosphorane (HTIP) Chelating Ligand
The synthesis procedures for N–Hydroxy–N–trioctyl iminophosphorane (HTIP) chelating ligand and the suggested mechanism of the reaction are illustrated in Scheme 4. A very important clarification should be mentioned concerning the role of the Lewis acid (AlCl3) in the fabrication of HTIP ligand. The hard Lewis acid was characterized by a great charge density with vacant orbitals, which could attract electrons from the oxygen phosphine group. This operation facilitated the breaking of –P=O bonds. After that, the nucleophilic attack of NH2OH upon the phosphine group could take place easily, as the phosphorous atom acted as an electrophile. This method is considered as an effective alternative technique to the Staudinger and Kirsanov methods.
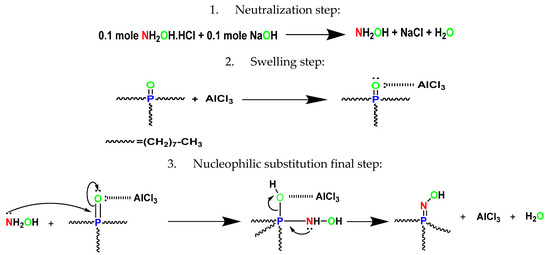
Scheme 4.
Synthesis of N–Hydroxy–N–trioctyl iminophosphorane (HTIP).
The obtained yield was ≈40.0 g (≈71.0%) with a melting point equal to 135–140 °C. Numerous functional groups in the synthesized HTIP were predicted using important observations in Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) [69]. Figure 1a displays the FTIR spectra of the HTIP and its complex with U(VI) ions. The HTIP had a strong peak, centered at roughly 3409.48 cm−1, which was linked to the OH group’s stretching mode. After chelation with U(VI) ions, the stretching vibration related to the OH group disappeared, indicating that the OH group took part in the chelation. The features located at 2850–2918, 701.38, 819.83, 1145.18 and 1464.72 cm−1 were more likely caused by the CH aliphatic, (CH2)n aliphatic, –P=N, –P–N, and N–O bonds, respectively. The frequency of –P=N and –P–N stretching vibrations in the HTIP–U(VI) complex were shifted to a lower frequency as compared with the free ligand (776.3 and 1118.41 cm−1), indicating that there was an appreciable chelation between HTIP and U(VI). The peak in the HTIP–U(VI) complex spectrum observed at 925 cm−1 corresponded to coordinated U=O bond [40,70].
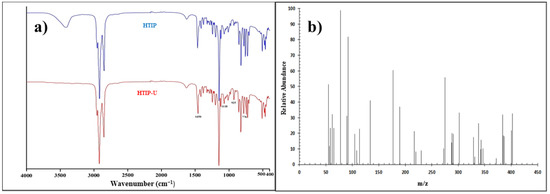
Figure 1.
(a) FTIR spectra of HTIP and HTIP–U(VI) complex; (b) GS–MS spectrum of HTIP chelating ligand.
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) is a powerful and effective tool for predicting chemical formulas and purity; the more stable fragment, [m/z]+, is an influential and strong tool. The synthetic ligand’s molecular weight was represented by the molecular ion peak with a value of 401.63. Some important fragmentation patterns related to the synthesized HTIP were observed, including [P=N–OH]˙ with a molecular weight of 61.98, [P=N–O]˙ with a molecular weight of 60.98, [CH3(CH2)7]˙ with a molecular weight of 113.25, and a fragment with a 384.66 molecular weight, which denoted the formation of the [(CH3(CH2)7)3P=N]˙ moiety. The results of the entire investigation indicated that the HTIP ligand could be synthesized successfully. Figure 1b demonstrates the GC–MS spectrum of the HTIP chelating ligand.
1H–NMR analysis with a 500.15 MHZ energy and CDCl3 as a diluent is a useful and efficient technology that provides important information about protons in the produced substance and aids in structure estimates. The primary δ (ppm) assignments were 7.259, 0.815–0.842, and 1.222–1.637 ppm, which corresponded to the protons of OH, methyl, and methylene, respectively. The assignments of the OH proton (δ = 7.259 ppm) were more deshielded than the assignments of the –CH2 and –CH3 protons, whereas –CH2 (δ = 1.222–1.637 ppm) was more deshielded than –CH3 (δ = 0.815–0.842 ppm). Figure 2a illustrates the 1H–NMR characterization of the HTIP chelating ligand.
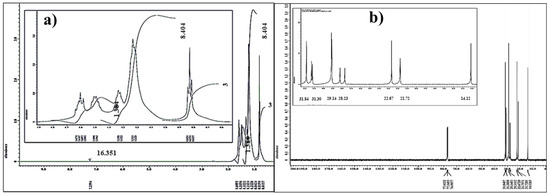
Figure 2.
(a) 1H–NMR spectrum; (b) 13C–NMR spectrum of HTIP chelating ligand.
13C–NMR analysis with a 125.76 MHZ energy and CDCl3 as a diluent is a useful method for determining the number of carbon atoms in an HTIP ligand. The major δ (ppm), which is connected to alkyl carbon, occurred at 14.126–31.848 ppm (Figure 2b). The –CH3 carbon appeared at 14.126 ppm, which was more protected than the other –CH2 carbons that appeared in chemical shift ranges of 21.728–31.848 ppm.
A characteristic EDX analysis was performed to illustrate the elements composing HTIP chelating ligand after and before uranyl ion chelation. A significant peak from 0–0.5 keV represented carbon, oxygen and nitrogen atoms, while the peak at 1.65 keV represented the phosphorous atom. The appearance of uranium gave an obvious sign for the chelation of uranyl ions by HTIP chelating ligand. The identification of HTIP and HTIP–U(VI) complex by EDX spectrum is presented in Figure 3.
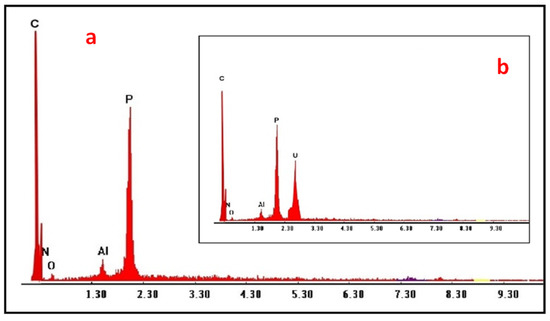
Figure 3.
EDX spectra of (a) HTIP; (b) HTIP–U(VI) complex.
3.2. Extraction Procedures
3.2.1. The Influence of pH
The role of pH was very important in the retention of U(VI) on the ligand’s active sites because it impacted the form of uranium in aqueous media as well as the features of the active sites of the HTIP ligand. Figure 4 shows the species of uranyl ions in the HYDRA–MEDUSA program at different pH vales. There are many U(VI) species in solution, according to earlier research [71,72]. Uranium can be found in cationic, neutral, or anionic species. Until pH 5.0, uranium is primarily present in the cationic forms UO22+, UO2(OH)+, and (UO2)2(OH)22+, whilst UO2SO4, UO3.2H2O, UO2(OH)3–, and UO2(OH)42– are neutral and anionic species that are identified till pH 12.0.
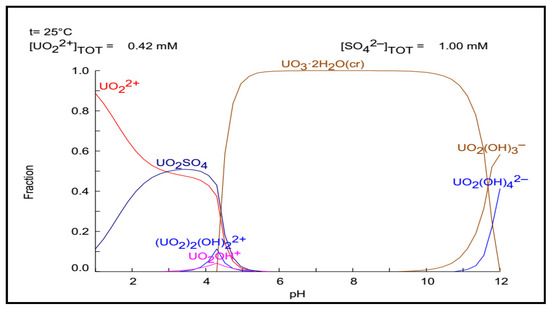
Figure 4.
The HYDRA–MEDUSA diagram of uranyl ions at different pH values.
The retention of U(VI) on HTIP was examined using 25.0 mL of a 4.2 × 10−4 mol/L U(VI) solution (100 mg/L) and 25.0 mL of 0.99 × 10−4 mol/L HTIP/CHCl3 (10 mg of HTIP in 25.0 mL CHCl3) at pH ranges from 0.25–6.0 and room temperature for 30 min. Figure 5a depicts the acquired data, which reveal that the retention capacity was enhanced from pH 0.25 (qe = 12.5 mg/g) to pH 3.0 (qe = 247.5 mg/g) and remained constant up to pH 6.0. It was noticed that in highly acidic medium, pH 0.25–1.0, there was a small variation in HTIP retention due to the high conc. of hydrogen ions, which may compete with uranyl ions and protonated HTIP ligand. The ultimate retention of U(VI) was detected at pH 3.0 (qe = 247.5 mg/g) because UO22+, UO2(OH)+, and (UO2)2(OH)22+ species are predominant in this range. Therefore, pH 3.0 has been proposed as the best pH value for U(VI) ion retention on HTIP/CHCl3, with qe = 247.5 mg/g retention capacity (99.0%). A graph of logD versus pH shows a straight line with a slope of 1.5 and an intersection of 2.7157 in linear regression analysis (slope analysis), as displayed in Figure 5b. The value of slope represents the amount of hydrogen ions set free in the aqueous medium during the formation of the HTIP–U(VI) complex, indicating that about 1.5 moles of hydrogen ions were released during the extraction procedure. Moreover, at pH value 3.0 (logβ = 2.7157), the stability constant (β) of the HTIP–U(VI) complex was computed and found to be 519.63; it showed that the HTIP ligand had a high affinity for uranyl ions.
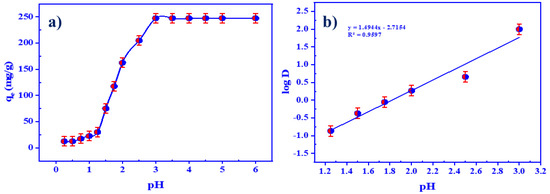
Figure 5.
(a) The influence of pH on the retention of uranium by HTIP chelating ligand; (b) the regression analysis of U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP at various pH values. (U(VI) conc.: 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L, HTIP/CHCl3 conc.: 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L (10 mg/25 mL), A/O 1:1, T: 25 °C, time: 30 min).
Lastly, based on the preceding analysis, the suggested complex structure and chelation mechanism are presented in Scheme 5. It is clear that the first mechanism mainly depends on the pH value. Competition occurs in highly acidic media between both hydrogen and uranyl ions, causing the tendency of equilibrium to shift towards the left, but in slightly acidic, neutral and alkaline medium, may cause hydrogen ion withdrawal with increased chelation effect and uptake capacity of the HTIP ligand. The second mechanism depends on pH value and the affinity of the HTIP ligand for uranyl ions. The third mechanism is a mixture between the two later mechanisms.
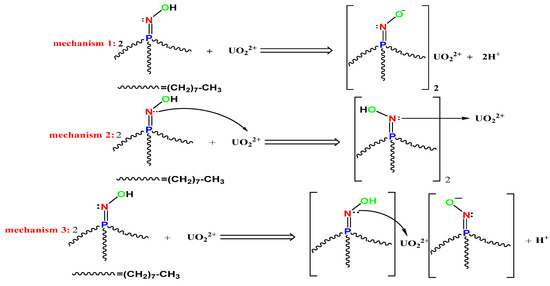
Scheme 5.
Proposed mechanisms of UO22+ ion extraction by HTIP chelating ligand.
3.2.2. The Influence of Equilibration Time
Contact time is one of the highly essential factors on the financial side. The effect of equilibrium time on U(VI) retention was examined using 9.96 × 10−4 mol/L (10 mg/25.0 mL) HTIP/CHCl3 and a 25.0 mL aqueous uranium(VI) ion solution with a concentration of 0.42 ×10−3 mol/L at pH 3.0. U(VI) ion retention rose with rising equilibrium time and reached an ultimate value (247.5 mg/g, 99.0%) after 30 min, which remained roughly constant for the next 120 min, as shown in Figure 6. As a result, 30 min was deemed sufficient for achieving equilibrium in subsequent testing, and it was applied in all successive investigations.
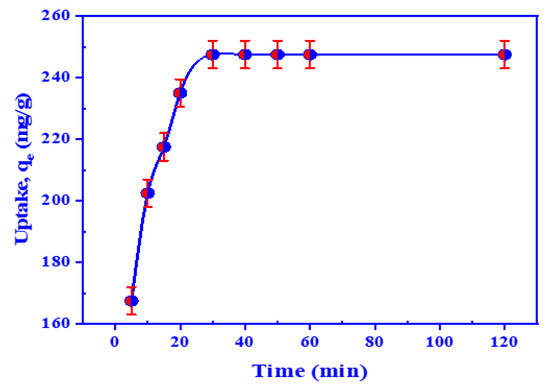
Figure 6.
The influence of time on the retention of uranium by HTIP chelating ligand. (U(VI) conc.: 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L, HTIP/CHCl3 conc.: 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L (10 mg/25 mL), pH 3.0, A/O 1:1, T: 25 °C).
Kinetic studies were used to express the rate of uranyl ion entrapment using HTIP/CHCl3, providing crucial information for the design and modeling of the extraction process. Both pseudo first order (PFO) and second order (PSO) kinetic models were employed to identify the mechanism of U(VI) ion entrapment using HTIP/CHCl3 and the rate constant of the process. The PFO model is presented by the equation below [73]:
where qe and qt (mg/g) correspond to the quantity of U(VI) ions entrapped per unit mass at equilibrium and time t, respectively, and k1 (min−1) denotes the rate constant. Figure 7a displays a straight line plot of log(qe − qt) against t; the values of both k1 and qe were calculated from the slope and intercept, respectively. The calculated value of qe was 245.47 mg/g, and of k1, 0.1648 min−1, with R2 = 0.9586. It is obvious that the calculated value of qe was extremely close to the practical retention capacity of 247.5 mg/g (Table 1). Nonetheless, the PSO kinetic model was calculated using the equation below [74]:
where k2 (g/mg.min) is in agreement with the rate constant. Figure 7b demonstrates the straight line of graphing t/qt vs. t; it has a slope of 1/qe and an intercept of 1/k2qe2. The PSO model was found to be ineffective in explaining the practical data. Table 1 illustrates the calculated value of qe as 277.47 mg/g, which was somewhat greater than the experimental retention capacity, whereas the value of k2 was 0.001 min−1 with R2 equal to 0.9991. Therefore, the PFO kinetic model was more reliable in characterizing the extraction process of U(VI) ions using HTIP/CHCl3, as it was appropriate for the experimental data.
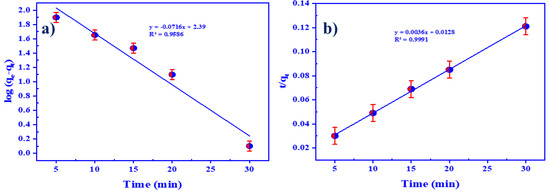
Figure 7.
(a) PFO Kinetic model; (b) PSO kinetic model of U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP chelating ligand. (U(VI) conc.: 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L, HTIP/CHCl3 conc.: 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L (10 mg/25 mL), pH 3.0, A/O 1:1, T: 25 °C).

Table 1.
The kinetic constants of U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP chelating ligand.
3.2.3. The Impact of Initial U(VI) Ion Concentration
The impact of the initial concentration of U(VI) ions on extraction efficiency is crucial to investigate since it helps us to anticipate retention power. A diagram of retention power against different initial U(VI) concentrations is shown in Figure 8. Two different stages can be noted. In the first stage, the retention power of HTIP ligand increases conspicuously from 24.75 to 247.5 mg/g with the rising initial concentration of U(VI) ions because the number of active points on the HTIP ligand exceeds the number of uranyl ions in solution. On the other hand, the retention capacity remains constant in the second stage, when the concentration of uranyl ions increases from 100 to 300 mg/L U(VI), because uranyl ions have entirely interacted with the HTIP active sites. The number of active HTIP sites is less than that of uranyl ions. At an initial U(VI) concentration of 100 mg/L, the maximum value of U(VI) ion retention on HTIP/CHCl3 is 247.5 mg/g (99.0%).
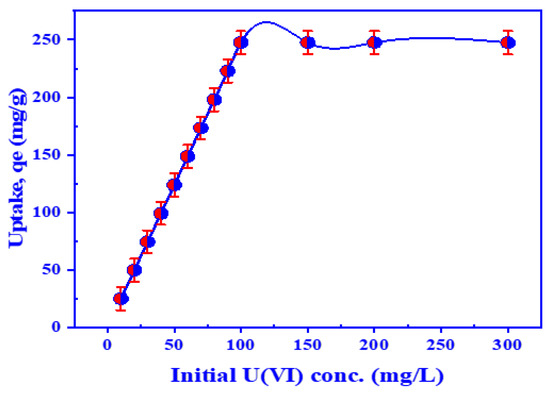
Figure 8.
The influence of initial U(VI) ion concentration on the retention of uranium by HTIP chelating ligand. (pH 3.0, HTIP/CHCl3 conc.: 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L (10 mg/25 mL), time: 30 min, A/O 1:1, T: 25 °C).
3.2.4. The Influence HTIP Dose
The HTIP amount is important for better uranyl ion sequestration because it impacts the equilibrium of the system. The effect of HTIP doses varying from 0.0025 to 0.1 g/25.0 mL CHCl3 on U(VI) retention efficiency was investigated. Figure 9a shows that augmenting the HTIP quantity from 0.0025 to 0.01 g/25.0 mL CHCl3 improved U(VI) ion retention efficiency, followed by retention diminishing from 0.025 g to 0.1 g/25.0 mL CHCl3 because the number of HTIP incorporation sites surpassed the number of uranyl ions. The retention capacity of 0.01 g/25.0 mL HTIP/CHCl3 was 247.5 mg/g with a 99.0% removal efficiency. As a consequence, the best concentration for consequent extraction studies was 0.01 g/25.0 mL HTIP/CHCl3. It is obvious that the retention efficiency of HTIP is higher than that of other materials reported in earlier studies, as shown in Table 2.
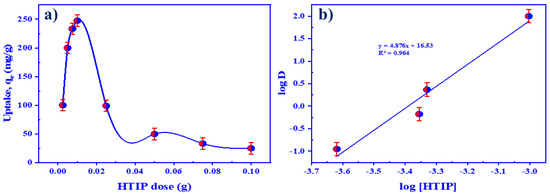
Figure 9.
(a) The influence of HTIP dose on the retention of uranium; (b) the regression analysis of U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP at different concentrations. (U(VI) conc.: 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L, pH 3.0, Time: 30 min, A/O 1:1, T: 25 °C).

Table 2.
Comparison of retention efficiency of different materials.
The regression analysis was studied to guarantee the configuration of the HTIP–U(VI) complex formed. Figure 9b illustrates a straight line with a slope of 4.876 and R2 = 0.964 when plotting logD versus logHTIP. The linear regression analysis (slope analysis) can elaborate the stoichiometry mechanism between HTIP chelating ligand and U(VI) ions, which suggests that 1.0 mole of U(VI) ions is chelated by 4.0 moles of HTIP.
3.2.5. U(VI) Ion Distribution Isotherm (McCabe–Thiele Isotherm)
Figure 10a demonstrates the McCabe–Thiele diagram of the extraction distribution isotherm of U(VI) ions by HTIP in a system consisting of U(VI) concentration 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L, HTIP/CHCl3 conc. 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L (10 mg/25.0 mL), 3.0 pH value, and A/O phase ratio 1:1 for 30 min. It was observed that two theoretical extraction phases are required to extract nearly all of the U(VI) ions. Furthermore, the elution of U(VI) ions from the HTIP–U(VI) complex was conducted using 2.0 M of H2SO4. The HTIP/CHCl3 organic phase had a concentration of U(VI) ions of 95.0 mg/L. Figure 10b depicts the McCabe–Thiele diagram of the U(VI) ion stripping distribution isotherm; to release almost all of the entrapped U(VI) ions from the HTIP–U(VI) complex, four theoretical stripping stages are required with a 2:1 A/O phase ratio.
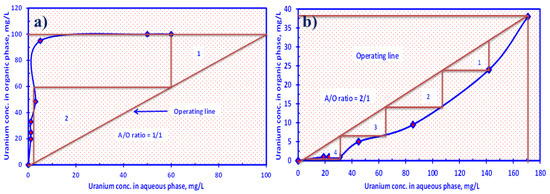
Figure 10.
McCabe–Thiele diagram of (a) U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP chelating ligand; (b) U(VI) ion stripping isotherm from HTIP–U(VI) complex. (U(VI) conc.: 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L, HTIP/CHCl3 conc.: 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L (10 mg/25 mL), pH 3.0, time: 30 min, T: 25 °C).
3.2.6. The Influence Temperature
The effectiveness of temperature on the removal of U(VI) ions using HTIP/CHCl3 was investigated by mixing 25.0 mL of 0.99 × 10−4 mol/L (10 mg/25.0 mL) HTIP/CHCl3 and 25.0 mL of uranium(VI) ion solution with a concentration of 4.2 × 10−4 mol/L (100 mg/L) for 30 min at pH 3.0 and agitation temperature varying from 25–65 °C. The uptake efficiency of HTIP/CHCl3 for U(VI) ions dropped from 247.5 mg/g to 200 mg/g when the temperature was elevated from 25 to 65 °C, (Figure 11a). The pattern suggests that the process of extracting U(VI) ions through HTIP is exothermic.
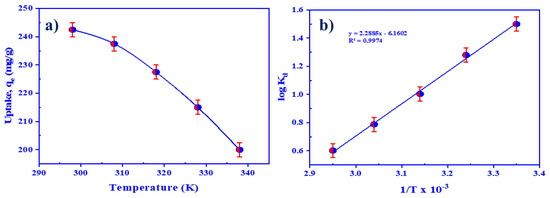
Figure 11.
(a) The influence of temperature on the retention of uranium by HTIP chelating ligand; (b) thermodynamic study of U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP chelating ligand (U(VI) conc.: 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L, HTIP/CHCl3 conc.: 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L (10 mg/25 mL), pH 3.0, A/O 1:1, time: 30 min).
Thermodynamic analysis was also carried out to characterize the extraction mechanism using the Gibbs free energy formula [82,83,84]:
where ∆G° (kJ/mol) points to Gibbs free energy, ∆H° (kJ/mol) is attributed to enthalpy change, ∆S° (J/mol.K) is defined as entropy change, T (K) stands for the temperature, and R (8.314 J/mol.K) corresponds to the universal gas constant. Figure 11b displays a logKd versus 1/T graph with R2 = 0.9974; ∆H° and ∆S° were generated by the slope and intercept, respectively.
The fact that ∆G° is negative implies that the retention of U(VI) on HTIP is thermodynamically spontaneous and attainable (Table 3). In addition, the rise in ∆G° values as temperature rises, from −8.646 kJ/mol at 298 K to −3.926 kJ/mol at 338 K, suggests that the retention of uranium at low temperature is desirable. Moreover, the negative value of ∆H° indicates that U(VI) ion retention on HTIP is an exothermic process, suggesting that heat is produced during the extraction. Finally, the negative value of ∆S° affirms that the capture of U(VI) ions on HTIP is more practicable and less disorganized.

Table 3.
Thermodynamic analysis of U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP chelating ligand.
The Arrhenius equation was employed to predict the activation energy (Ea) of entrapped U(VI) ions at various temperatures using the slope of the straight line in Figure 11b. The Arrhenius equation was estimated by the subsequent equation [85]:
where Ea (kJ/mol) corresponds to the activation energy of extraction and A correlates with the pre-exponential factor, which is independent of temperature. According to calculations, the extraction of U(VI) ions on HTIP ligand requires an activation energy of −8.261 kJ/mol; this implies that the extraction procedure occurs spontaneously and exothermically at room temperature, with no need for activation energy.
3.2.7. The Influence of Co-Ions
The investigated co-ions were identified as co-ions accompanied by U(VI) during the leaching process. The impact of co-existing ions was examined separately under optimal extraction conditions by introducing each one into 25.0 mL of a 4.2 × 10−4 mol/L (100 mg/L) U(VI) ion solution. Each ion was identified as an interfering ion when the extraction efficiency differed by more than ±5.0%. Thus, the co-ion concentration that produced a ±5.0% error in uranyl extraction efficiency was used to set the tolerance limit. Table 4 shows that none of the studied co-ions had a negative impact on the retention of U(VI) ions. The findings emphasize the selective extraction of U(VI) on HTIP chelating ligand, which could be used to extract U(VI) ions from leachates of ores in the presence of other ions.

Table 4.
The influence of co-ions on U(VI) ion extraction by HTIP chelating ligand.
3.3. Stripping and Precipitation
Three types of acids with different concentrations ranging from 0.025–2.0 M were utilized as stripping agents for stripping of U(VI) ions from the HTIP–U(VI) complex; the experiments were carried out using 10.0 mL acid volume for 25.0 mL of HTIP–U(VI) complex, shaking well for 10 min at 25 °C. According to the data listed in Table 5, the U(VI) stripping efficiency dropped at low acidic concentrations, but increased when the acid concentration was higher. It was notable that 99.0% stripping efficiency could be achieved with 10.0 mL of 0.5 M HCl, 0.5 M HNO3, or 2.0 M H2SO4. Subsequently, the eluted solution was precipitated with 30.0% NaOH solution until pH 7.0–8.0 was attained, where uranium precipitated as sodium diuranate (Na2U2O7), yielding a final uranium concentrate (yellow cake). The precipitate was left to settle for 24.0 h and filtered. Lastly, the precipitate was dried for 3.0 h at 110 °C in an electrical oven to obtain the uranium concentrate as a final product.

Table 5.
Effect of stripping agent conc. on U(VI) ion elution from HTIP–U(VI) complex.
3.4. Case Study: U(VI) Recovery from G. Gattar Ore Sample by HTIP Chelating Ligand
The previous data suggest that the HTIP chelating ligand can extract uranium from leachates of geological ores. Accordingly, this hypothesis was investigated using G. Gattar granite leach liquor [85,86]. Uranium (1340 mg/kg) was leached from a G. Gattar ore sample using the percolation leaching technique. The leachate contained approximately 0.45 g/L (450 mg/L) of uranium ions in the presence of a variety of metal ion impurities (Table 6 and Table 7). The recovery experiment was carried out by mixing 1.0 L of HTIP/CHCl3 (0.99 × 10−3 mol/L) with 1.0 L of leach liquor under the previously defined optimum conditions (pH 3.0, 1:1 A/O phase ratio, 30 min, and 25 °C). According to the study, the extraction efficiency of U(VI) reached 99.0%. In addition, it was affirmed that the released U(VI) ions from the HTIP–U(VI) complex could be easily eluted in 10 min using 2.0 M H2SO4.

Table 6.
Chemical composition of G. Gattar granite ore sample.

Table 7.
The chemical analysis of G. Gattar granite leach liquor.
After the elution process, 30.0% NaOH was used to precipitate U(VI) ions as sodium diuranate precipitate Na2U2O7 by adjusting the pH to 7.0–8.0. The uranium concentrate was characterized using XRD and EDX, in addition to ICP-OES analysis techniques in order to determine the U(VI) content alongside other associated metal ions. The results are given in Figure 12, as well as Table 8. According to the analyses, the uranium(VI) content in the uranium concentrate product “yellow cake’’ was 69.93%, with a purity of 93.24%. Figure 13 demonstrates a flow chart of the recovery of U(VI) ions from G. Gattar granite ore mineralization using HTIP chelating ligand.
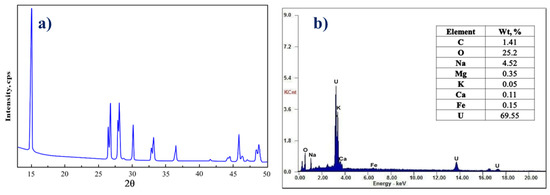
Figure 12.
(a) XRD spectrum; (b) EDX spectrum of Na2U2O7 product from G. Gattar granite ore sample.

Table 8.
ICP-OES analysis of Na2U2O7 product from G. Gattar granite ore sample.
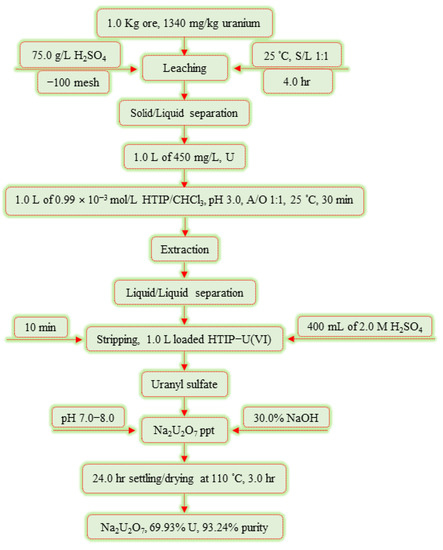
Figure 13.
Flow chart illustrating the production of Na2U2O7 from G. Gattar granite ore sample using HTIP chelating ligand.
4. Conclusions
A novel synthetic chelating agent, N–hydroxy–N–trioctyl–iminophosphorane (HTIP), was synthesized using an effective substitutional technique compared to the conventional methods and was utilized to uptake U(VI) ions from leach liquor of G. Gattar, North Eastern Desert, Egypt. Characterization was performed successfully using numerous analytical techniques, including 1H–NMR, 13C–NMR, FTIR, EDX, and GC–MS analyses. The uranium sequestration procedures were optimized by mixing 25.0 mL of U(VI) ion solution containing 0.42 × 10−4 mol/L with 0.99 × 10−3 mol/L HTIP/CHCl3 at pH 3.0, 1:1 A/O phase ratio, at 25 °C for 30 min. The utmost retention capacity of HTIP/CHCl3 was 247.5 mg/g. From the stoichiometric calculations, approximately 1.5 hydrogen atoms were released during the extraction at pH 3.0, and 4.0 moles of HTIP ligand were responsible for chelation of 1 mole of uranyl ions. The kinetic modeling data were well-suited to the pseudo first-order model. Furthermore, thermodynamic study demonstrated a negative ΔS° value, indicating that the uptake process is less disordered. Moreover, the rise in ΔG° value pointed to the spontaneousness and possibility of removing U(VI) ions at low temperatures. The elution of uranium loaded on HTIP was achieved using 2.0 M of H2SO4 as uranyl sulfate with 99.0% efficiency. Lastly, uranium concentrate (Na2U2O7, Y.C) with a purity of 93.24% was obtained by adding 30.0% NaOH to the elution and adjusting the pH to 7.0–8.0 with continuous stirring for 2 h.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.M.A. and A.K.S.; methodology, B.M.A. and A.K.S.; software, B.M.A., A.K.S. and M.F.C.; validation, M.Y.H. and M.I.S.; formal analysis, B.M.A. and A.K.S.; investigation, A.K.S.; resources, B.M.A. and A.K.S.; data curation, M.A.G., H.S.E.-G. and N.M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, B.M.A.; writing—review and editing, A.K.S.; visualization, B.M.A. and A.K.S.; supervision, E.M.E.-S. and M.F.C.; project administration, A.K.S., E.M.E.-S. and M.F.C.; funding acquisition, J.S.A.-O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors express their gratitude for the support from Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2022R13), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude for the support from Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2022R13), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dehnicke, K.; Krieger, M.; Massa, W. Phosphoraneiminato complexes of transition metals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 182, 19–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnicke, K.; Weller, F. Phosphorane iminato complexes of main group elements. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1997, 158, 103–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, H.; Meyer, J. Über neue organische Phosphorverbindungen III. Phosphinmethylenderivate und Phosphinimine. Helv. Chim. Acta 1919, 2, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephan, D.W. Sterically Demanding Phosphinimides: Ligands for Unique Main Group and Transition Metal Chemistry. Adv. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 54, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröb, T.; Geiseler, G.; Harms, K.; Greiner, A.; Dehnicke, K. Phosphaniminato-Komplexe des Zirconiums: Die Kristallstrukturen von [ZrCl3(NPPh3)(HNPPh3)2] und [ZrCl2(NPPh3)2(HNPPh3)2]. Z. Für Anorg. Und Allg. Chem. 2002, 628, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gololobov, Y.G.; Kasukhin, L.F. Recent advances in the staudinger reaction. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 1353–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, J.; García-Garrido, S.E.; Cadierno, V. Iminophosphorane–phosphines: Versatile ligands for homogeneous catalysis. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 751, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allcock, H.R. Chemistry and Applications of Polyphosphazenes; Wiley Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 1–725. [Google Scholar]
- Gleria, M.; De Jaeger, R. Applicative Aspects of Poly (Organophosphazenes), UK ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 1–308. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, A.; Zacchini, S.; Richards, P.I. From neutral iminophosphoranes to multianionic phosphazenates. The coordination chemistry of imino–aza-P(V) ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 227, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gololobov, Y.G.; Zhmurova, I.N.; Kasukhin, L.F. Sixty years of staudinger reaction. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berkel, S.S.; van Eldijk, M.B.; van Hest, J.C.M. Staudinger Ligation as a Method for Bioconjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8806–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, L.A.; Ferguson, N.M. Phosphorus-Nitrogen Compounds II: Some p-Toluidine Derivatives. J. Pharm. Sci. 1964, 53, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Huo, J.; Gao, J.; Xiao, A. Recent Research Progress in the Synthesis of Polyphosphazene and Their Applications. Des. Monomers Polym. 2009, 12, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothemund, S.; Teasdale, I. Preparation of polyphosphazenes: A tutorial review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5200–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strasser, P.; Teasdale, I. Main-Chain Phosphorus-Containing Polymers for Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.-X.; Lu, Q.; Yu, B.-T.; Wen, L. Inorganic polymer phosphazene disulfide as cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Krogman, N.R.; Sethuraman, S.; Nair, L.S.; Sturgeon, J.L.; Brown, P.W.; Laurencin, C.T.; Allcock, H.R. Effect of side group chemistry on the properties of biodegradable L-alanine cosubstituted polyphosphazenes. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, K.; Kruszyński, R.; Bartczak, T.J.; Porwolik-Czomperlik, I. AIDS-related lymphoma screen results and molecular structure determination of a new crown ether bearing aziridinylcyclophosphazene, potentially capable of ion-regulated DNA cleavage action. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2001, 322, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.A.; Saba, C.S. Oxidative Stability and Degradation Mechanism of a Cyclotriphosphazene Lubricant. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 3489–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarcı, D.; Beşli, S.; Demirbas, E. Synthesis of a series of triple-bridged cyclotriphosphazene hexa-alkoxy derivatives and investigation of their structural and mesomorphic properties. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cil, E.; Tanyildizi, M.A.; Ozen, F.; Boybay, M.; Arslan, M.; Gorgulu, A.O. Synthesis, characterization, and biological-pharmacological evaluation of new phosphazenes bearing dioxybiphenyl and schiff base groups. Arch. Der Pharm. 2012, 345, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, H.R.; Kwon, S. Covalent linkage of proteins to surface-modified poly(organophosphazenes): Immobilization of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and trypsin. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Synthesis and Performance of Cyclomatrix Polyphosphazene Derived from Trispiro-Cyclotriphosphazene as a Halogen-Free Nonflammable Material. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greish, Y.E.; Bender, J.D.; Lakshmi, S.; Brown, P.W.; Allcock, H.R.; Laurencin, C.T. Low temperature formation of hydroxyapatite-poly(alkyl oxybenzoate)phosphazene composites for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolus, P.; Gleria, M. Photochemistry and photophysics of poly(organophosphazenes) and related compounds: A review. I. Monomolecular processes. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 1994, 4, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, J.P.; Knight, G.J.; Wright, W.W. Heat-Resistant Polymers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; pp. 1–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, P.; De Jaeger, R. Polyphosphazenes: Synthesis, structures, properties, applications. Eur. Polym. J. 1991, 27, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, V.; Thomas, K.R.J. Coordination and organometallic chemistry of cyclophosphazenes and polyphosphazenes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 7, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, R.; Allcock, H.R. Telechelic Syntheses of the First Phosphazene Siloxane Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 6390–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleria, M.; De Jaeger, R. Aspects of Phosphazene Research. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2001, 11, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, M.; Atia, B.; Morcy, A. The role of graphene oxide anchored 1-amino-2-naphthol-4-sulphonic acid on the adsorption of uranyl ions from aqueous solution: Kinetic and thermodynamic features. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 99, 996–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, A.K.; Mohamed, S.A.; Mira, H.I.; Cheira, M.F. Successive leaching of uranium and rare earth elements from El Sela mineralization. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2018, 5, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Cao, M.; Gao, J.; Gui, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Ma, F.; Yan, Y.; Qiu, M. Electroadsorption of uranium on amidoxime modified graphite felt. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, Z.; Wang, W.; Song, J.; Li, P.; Liang, J.; Fan, Q. Light Promotes the Immobilization of U(VI) by Ferrihydrite. Molecules 2022, 27, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, C.R. The Elements, in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 81st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cheira, M.F.; El-Didamony, A.M.; Mahmoud, K.F.; Atia, B.M. Equilibrium and Kinetic Characteristics of Uranium Recovery by the Strong Base Ambersep 920U Cl Resin. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 7, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.R.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yoon, H.-S. A Brief Review on Solvent Extraction of Uranium from Acidic Solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2011, 40, 77–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, G. Hydrometallurgy of strategic metals. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2000, 18, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheira, M.F.; Mira, H.I.; Sakr, A.K.; Mohamed, S.A. Adsorption of U(VI) from acid solution on a low-cost sorbent: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic assessments. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2019, 30, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, M.A.; Negm, S.H.; Youssef, M.A.; Sakr, A.K.; Mira, H.I.; Mohammaden, T.F.; Al-Otaibi, J.S.; Hanfi, M.Y.; Sayyed, M.I.; Cheira, M.F. Sustainable Remedy Waste to Generate SiO2 Functionalized on Graphene Oxide for Removal of U(VI) Ions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, M.A.; El-Gendy, H.S.; Cheira, M.F.; Atia, B.M. Uranium ions extraction from the waste solution by thiosemicarbazide anchored cellulose acetate. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ouyang, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Adesina, A.A. Selective biosorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution by ion-imprinted honeycomb-like chitosan/kaolin clay composite foams. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Xiong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W. Immobilization of U(VI) in wastewater using coal fly ash aerogel (CFAA) as a low-cost adsorbent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Y.; Lv, Z.; Fang, M.; Tan, X. A green and economical MgO/biochar composite for the removal of U(VI) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 180, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Dai, Y.; Le, Z.; Adesina, A.A. Nanofabricated chitosan/graphene oxide electrodes for enhancing electrosorptive removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tan, K.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Z.; Tan, W.; Xu, Y. The adsorption of U(VI) by albite during acid in-situ leaching mining of uranium. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, S.; Chagnes, A.; Courtaud, B.; Thiry, J.; Cote, G. Solvent extraction of uranium from acidic sulfate media by Alamine® 336: Computer simulation and optimization of the flow-sheets. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari Nasab, M. Solvent extraction separation of uranium(VI) and thorium(IV) with neutral organophosphorus and amine ligands. Fuel 2014, 116, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.C.B.S.; Morais, C.A. Thorium and uranium extraction from rare earth elements in monazite sulfuric acid liquor through solvent extraction. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sole, K.C.; Cole, P.M.; Feather, A.M.; Kotze, M.H. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange Applications in Africa’s Resurging Uranium Industry: A Review. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2011, 29, 868–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Singh, D.K.; Anitha, M.; Sharma, J.N.; Hubli, R.C.; Singh, H. New synergistic solvent mixture of DNPPA and bidentate octyl (phenyl) CMPO for enhanced extraction of uranium (VI) from phosphoric acid medium. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 147–148, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.E.; Wilkins, D.; Soldenhoff, K.H. Solvent extraction of uranium from saline leach liquors using DEHPA/Alamine 336 mixed reagent. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 134–135, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, D.; Chagnes, A.; Haddad, M.; Laureano, H.; Mokhtari, H.; Courtaud, B.; Jugé, S.; Cote, G. Solvent extraction studies of uranium(VI) from phosphoric acid: Role of synergistic reagents in mixture with bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 144–145, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Pranolo, Y.; Cheng, C.Y. Uranium recovery from strong acidic solutions by solvent extraction with Cyanex 923 and a modifier. Miner. Eng. 2016, 89, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaballa, H.; Steed, J.W.; Junk, P.C.; Elsegood, M.R.J. Formation of Lanthanide and Actinide Oxonium Ion Complexes with Crown Ethers from a Liquid Clathrate Medium. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 4666–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, L.; Thuéry, P.; Ephritikhine, M. Uranium(iv) complexes of calix[n]arenes (n = 4, 6 and 8). Chem. Commun. 2006, 8, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopo, H.; Goljahanpoor, K.; Sillanpää, R. Aminoalkylbis(phenolate) [O,N,O] donor ligands for uranyl(VI) ion coordination: Syntheses, structures, and extraction studies. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nadi, Y.A.; Daoud, J.A.; Aly, H.F. Modified leaching and extraction of uranium from hydrous oxide cake of Egyptian monazite. Int. J. Miner. Processing 2005, 76, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Pranolo, Y.; Cheng, C.Y. Uranium Solvent Extraction and Separation From Vanadium in Alkaline Solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiller, P.E.; Mariet, C. Luminescence of uranium(VI) after liquid-liquid extraction from HCl by Aliquat® 336 in n-dodecane:1-decanol by time-resolved laser-induced luminescence spectroscopy. Radiochim. Acta 2020, 108, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, B.M.; Khawassek, Y.M.; Hussein, G.M.; Gado, M.A.; El-Sheify, M.A.; Cheira, M.F. One-pot synthesis of pyridine dicarboxamide derivative and its application for uranium separation from acidic medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, B.M.; Gado, M.A.; Cheira, M.F.; El-Gendy, H.S.; Yousef, M.A.; Hashem, M.D. Direct synthesis of a chelating carboxamide derivative and its application for thorium extraction from Abu Rusheid ore sample, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spjuth, L.; Liljenzin, J.O.; Skålberg, M.; Hudson, M.J.; Chan, G.Y.S.; Drew, M.G.B.; Feaviour, M.; Iveson, P.B.; Madic, C. Extraction of Actinides and Lanthanides from Nitric Acid Solution by Malonamides. Radiochim. Acta 1997, 78, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahem, K.A.; Taher, M.A.; Cheira, M.F. Peculiarities of u (vi) adsorption from acidic solution using chitin-derived chitosan as a low-priced bio-adsorbent. Al-Azhar Bull. Sci. 2021, 32, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, K.; Bürger, S.; Vogt, S.; Mason, P.; Morales-Arteaga, M.; Narayanan, U. Uranium assay determination using Davies and Gray titration: An overview and implementation of GUM for uncertainty evaluation. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2009, 282, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheira, M.F. Solvent extraction of uranium and vanadium from carbonate leach solutions of ferruginous siltstone using cetylpyridinium carbonate in kerosene. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 2247–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.; Anaya, S.S.; Hagenbach, A.; Abram, U. Rhenium(V) and Technetium(V) Complexes with Phosphoraneimine and Phosphoraneiminato Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 3172–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sakr, A.K.; Schlöder, T.; Klein, S.; Beckers, H.; Kitsaras, M.-P.; Snelling, H.V.; Young, N.A.; Andrae, D.; Riedel, S. Searching for Monomeric Nickel Tetrafluoride: Unravelling Infrared Matrix Isolation Spectra of Higher Nickel Fluorides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6391–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bo, F.; Aksenov, S.M.; Hatert, F.; Burns, P.C. Synthesis, IR spectroscopy and crystal structure of [(UO2)2{Be(H2O)2(PO4)2}]·(H2O), the first compound with a trimer beryllophosphate anion. Z. Für Krist. Cryst. Mater. 2018, 233, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekhunguni, P.M.; Tavengwa, N.T.; Tutu, H. Sorption of uranium(VI) onto hydrous ferric oxide-modified zeolite: Assessment of the effect of pH, contact time, temperature, selected cations and anions on sorbent interactions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Brendler, V.; Foerstendorf, H. Aqueous Uranium(VI) Hydrolysis Species Characterized by Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 10127–10134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Geleel, M.; Atwa, S.T.; Sakr, A.K. Removal of Cr (III) from aqueous waste using Spent Activated Clay. J. Am. Sci. 2013, 9, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, E.M.; Lashen, T.A.; Abou El-Enein, S.A.; Hassanin, M.A.; Sakr, A.K.; Hanfi, M.Y.; Sayyed, M.I.; Al-Otaibi, J.S.; Cheira, M.F. Cetylpyridinium Bromide/Polyvinyl Chloride for Substantially Efficient Capture of Rare Earth Elements from Chloride Solution. Polymers 2022, 14, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhoum, A.A.; Eisa, W.H.; El-Tantawy El-Sayed, I.; Tolba, A.A.; Shalaby, Z.M.; Mohamady, S.I.; Muhammad, S.S.; Hussien, S.S.; Akashi, T.; Guibal, E. A new route for manufacturing poly(aminophosphonic)-functionalized poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-magnetic nanocomposite-Application to uranium sorption from ore leachate. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Z.; et al. Nitrogen-rich carbon nitrogen polymers for enhancing the sorption of uranyl. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujar, R.B.; Lakshmi, D.S.; Figoli, A.; Mohapatra, P.K. Polymeric beads containing Cyanex 923 for actinide uptake from nitric acid medium: Studies with uranium and plutonium. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayyas, M.; Al-Harahsheh, M.; Wei, X.-Y. Solid phase extractive preconcentration of Uranium from Jordanian phosphoric acid using 2-hydroxy-4-aminotriazine-anchored activated carbon. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 149, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayambashi, A.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. Solid phase extraction of uranium (VI) from phosphoric acid medium using macroporous silica-based D2EHPA-TOPO impregnated polymeric adsorbent. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Magied, A.F. Solid phase extraction of uranium from phosphoric acid: Kinetic and thermodynamic study. Radiochim. Acta 2017, 105, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A. Sorption of U(VI) ions from aqueous solution by eggplant leaves: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2021, 138, 103829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, E.M.; Lashen, T.A.; Abou El-Enein, S.A.; Hassanin, M.A.; Sakr, A.K.; Cheira, M.F.; Almuqrin, A.; Hanfi, M.Y.; Sayyed, M.I. Rare Earth Group Separation after Extraction Using Sodium Diethyldithiocarbamate/Polyvinyl Chloride from Lamprophyre Dykes Leachate. Materials 2022, 15, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, A.K.; Cheira, M.F.; Hassanin, M.A.; Mira, H.I.; Mohamed, S.A.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Eed, E.M.; Sayyed, M.I.; Hanfi, M.Y. Adsorption of Yttrium Ions on 3-Amino-5-Hydroxypyrazole Impregnated Bleaching Clay, a Novel Sorbent Material. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.S.; Atwa, S.T.; Sakr, A.K.; Abdel Geleel, M. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of the adsorption of Ni (II) using Spent Activated clay Mineral. N. Y. Sci. J. 2012, 5, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zidan, I.H.; Cheira, M.F.; Bakry, A.R.; Atia, B.M. Potentiality of uranium recovery from G. Gattar leach liquor using Duolite ES-467 chelating resin: Kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm features. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 100, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, B.M. 1,5-Diphenylthiocarbazone-Modified Amberlite XAD-7: A Chelating Collector for Upgrading Uranium Concentrate Produced from G. Gattar Pilot Plant, North Eastern Desert, Egypt. Radiochemistry 2019, 61, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).