Zr-Based Biocomposite Materials as an Alternative for Fluoride Removal, Preparation and Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
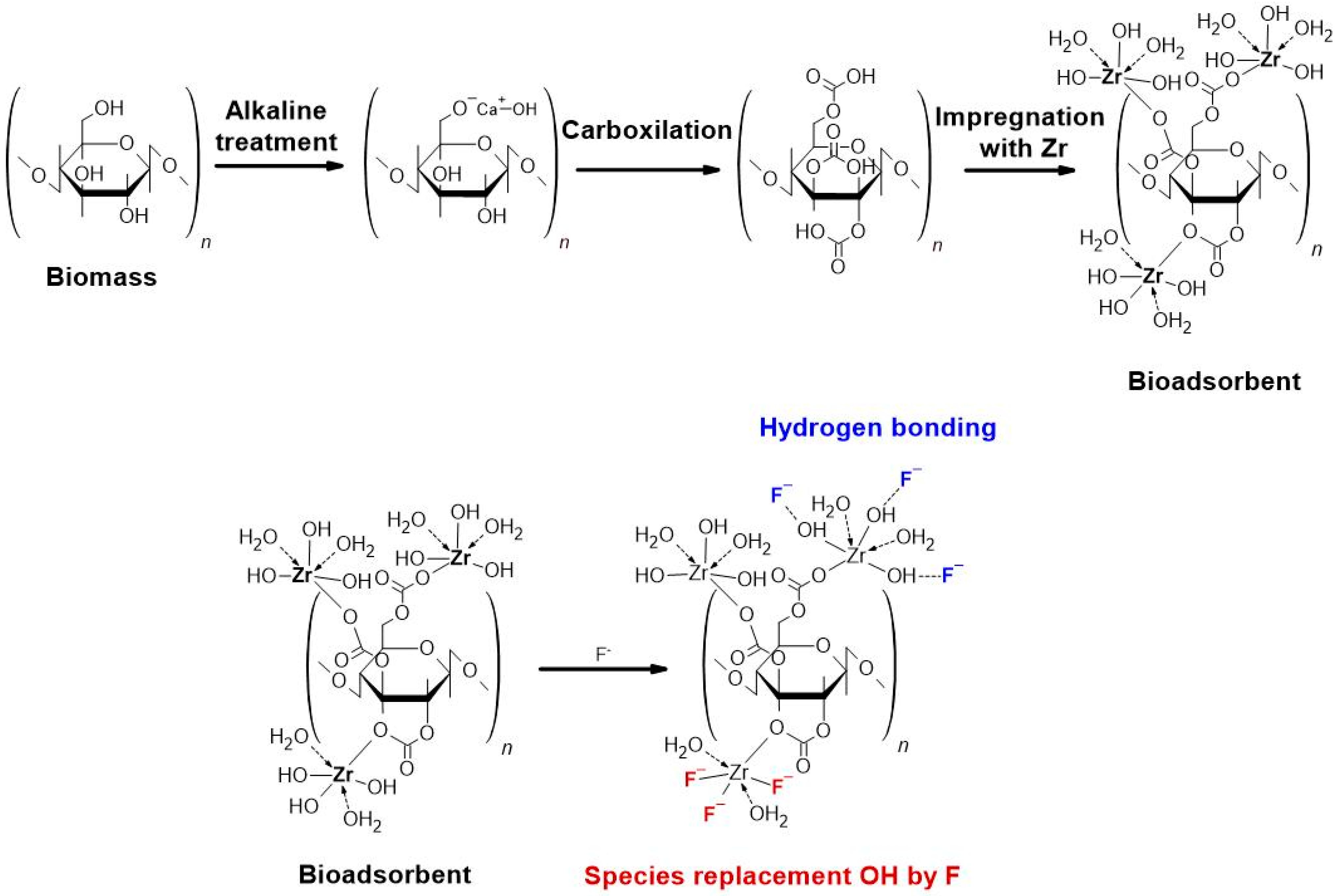
2.2. Preparation of the Composite Bioadsorbents
2.3. Characterization of Composite Bioadsorbents
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Surface, Morphological, and Structural Characterization of the Adsorbent Materials
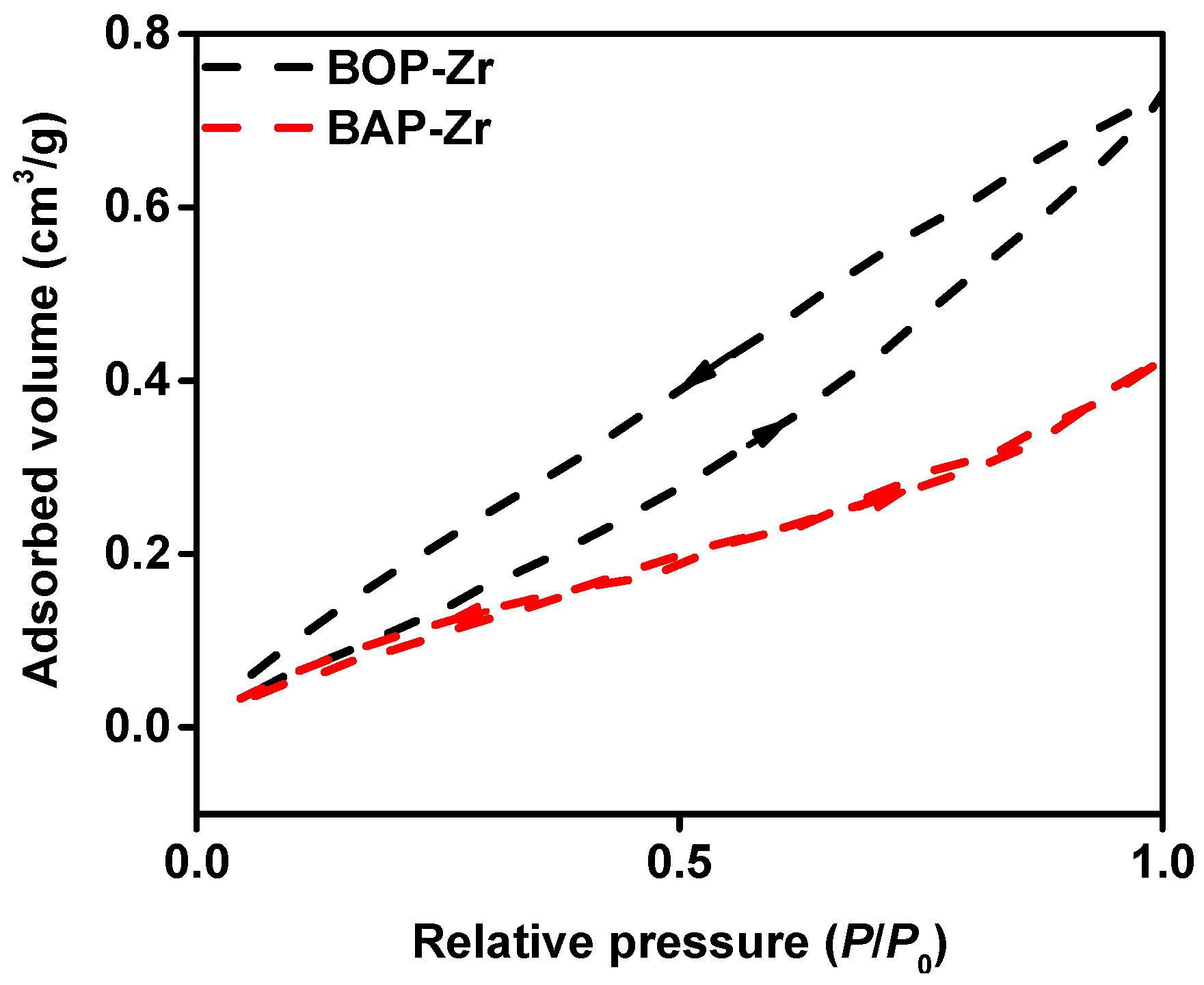
3.1.1. BET
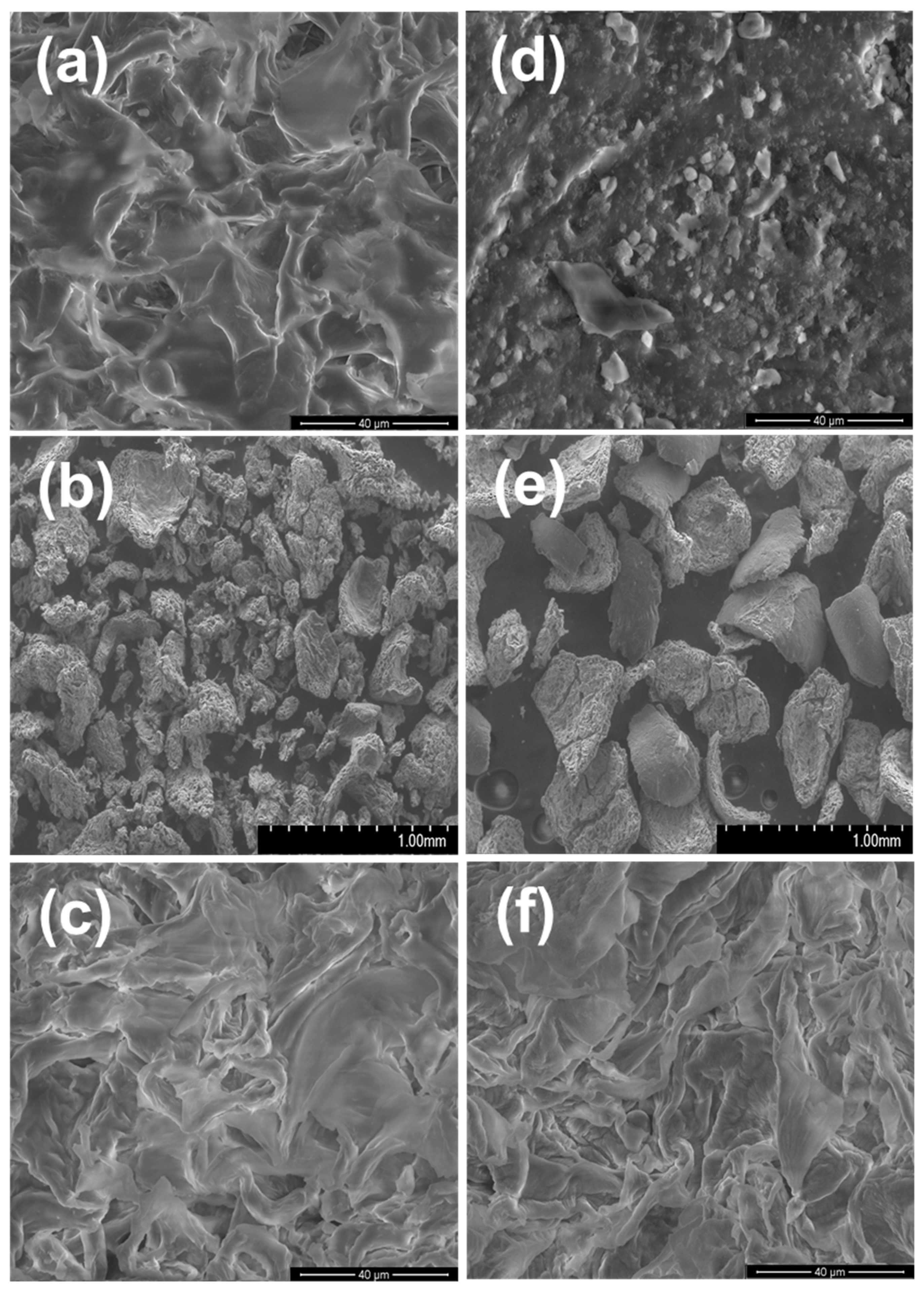
3.1.2. SEM-EDX
3.2. Composition Characterization of the Absorbents
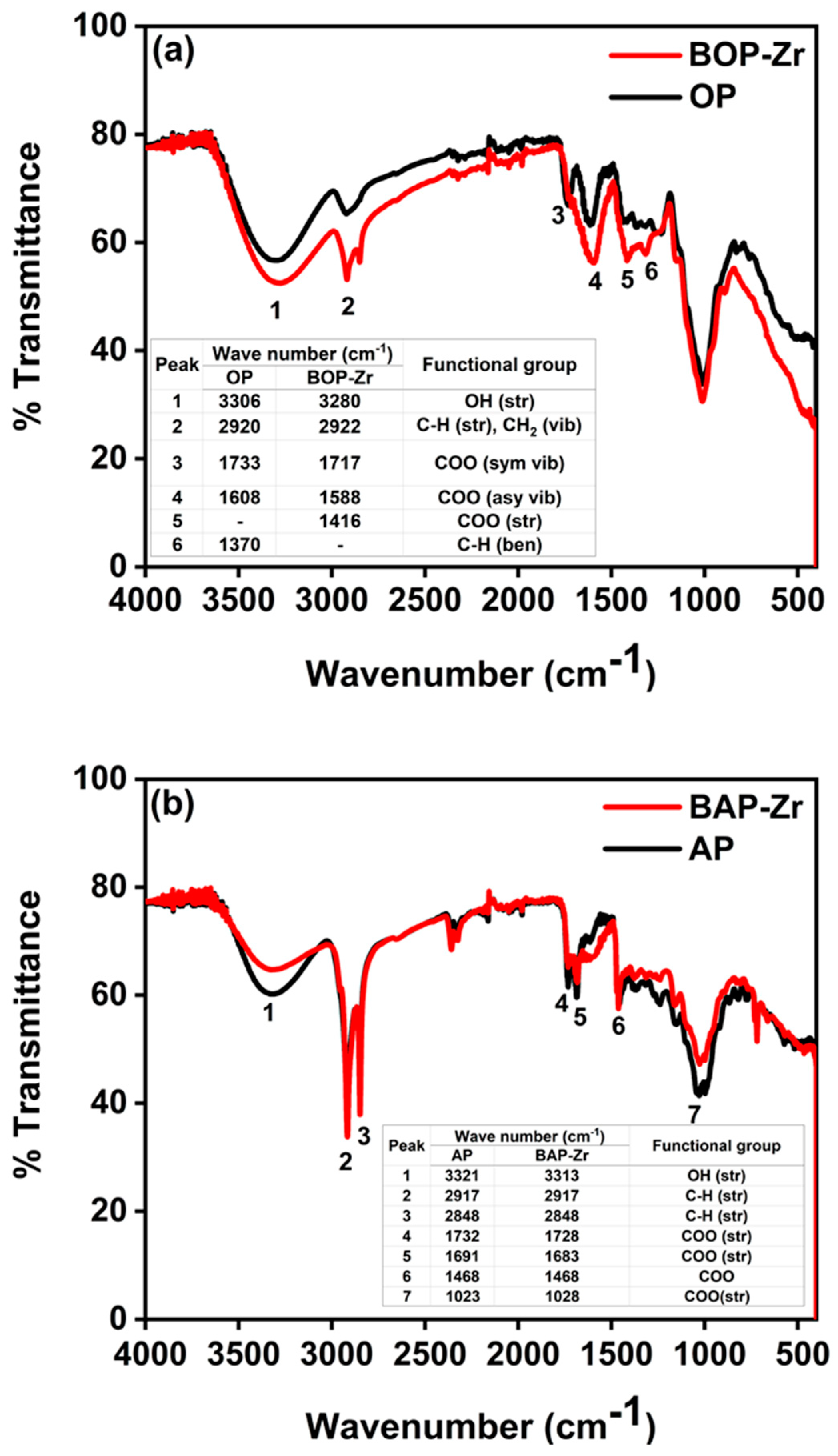
3.2.1. FTIR
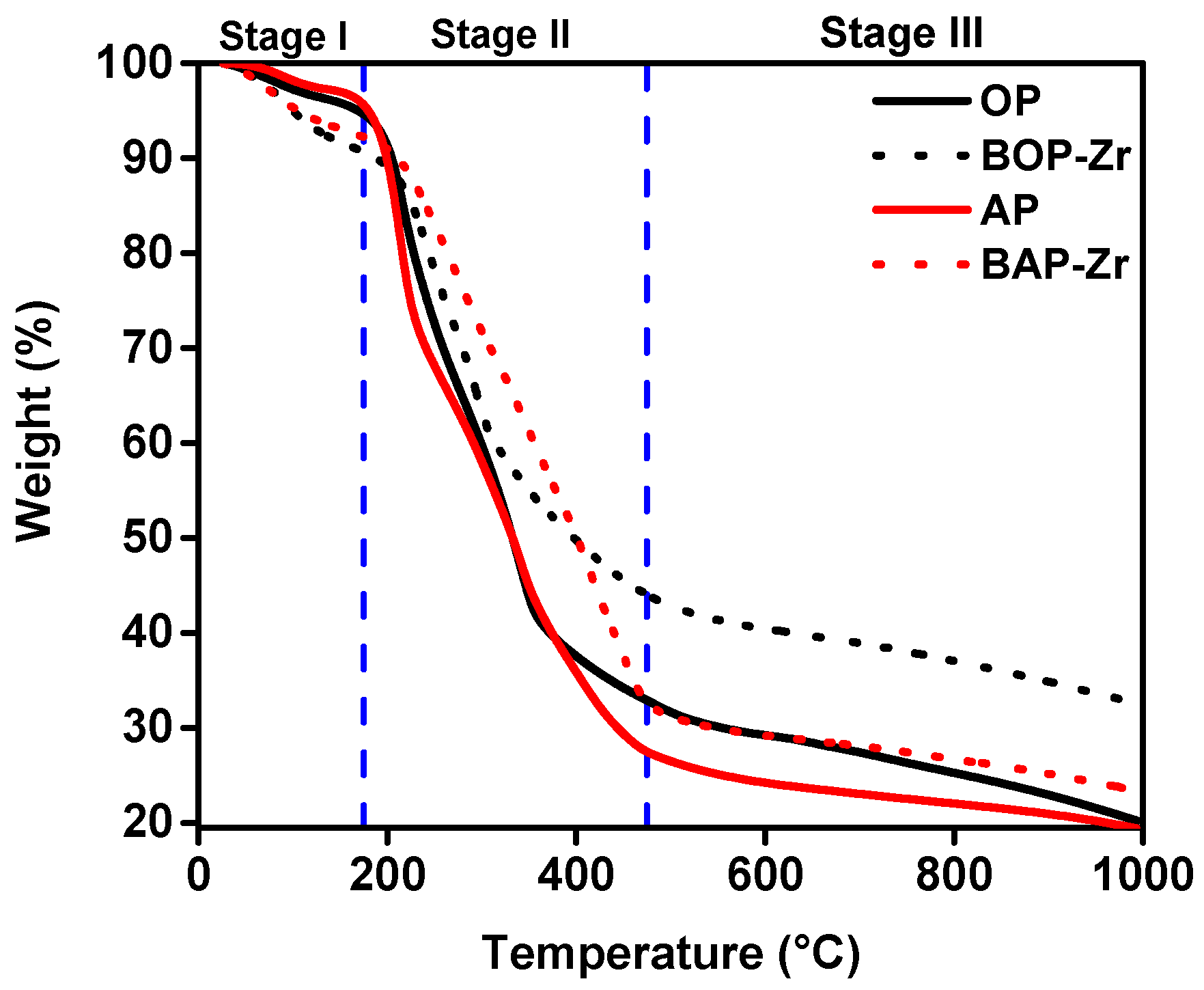
3.2.2. TGA
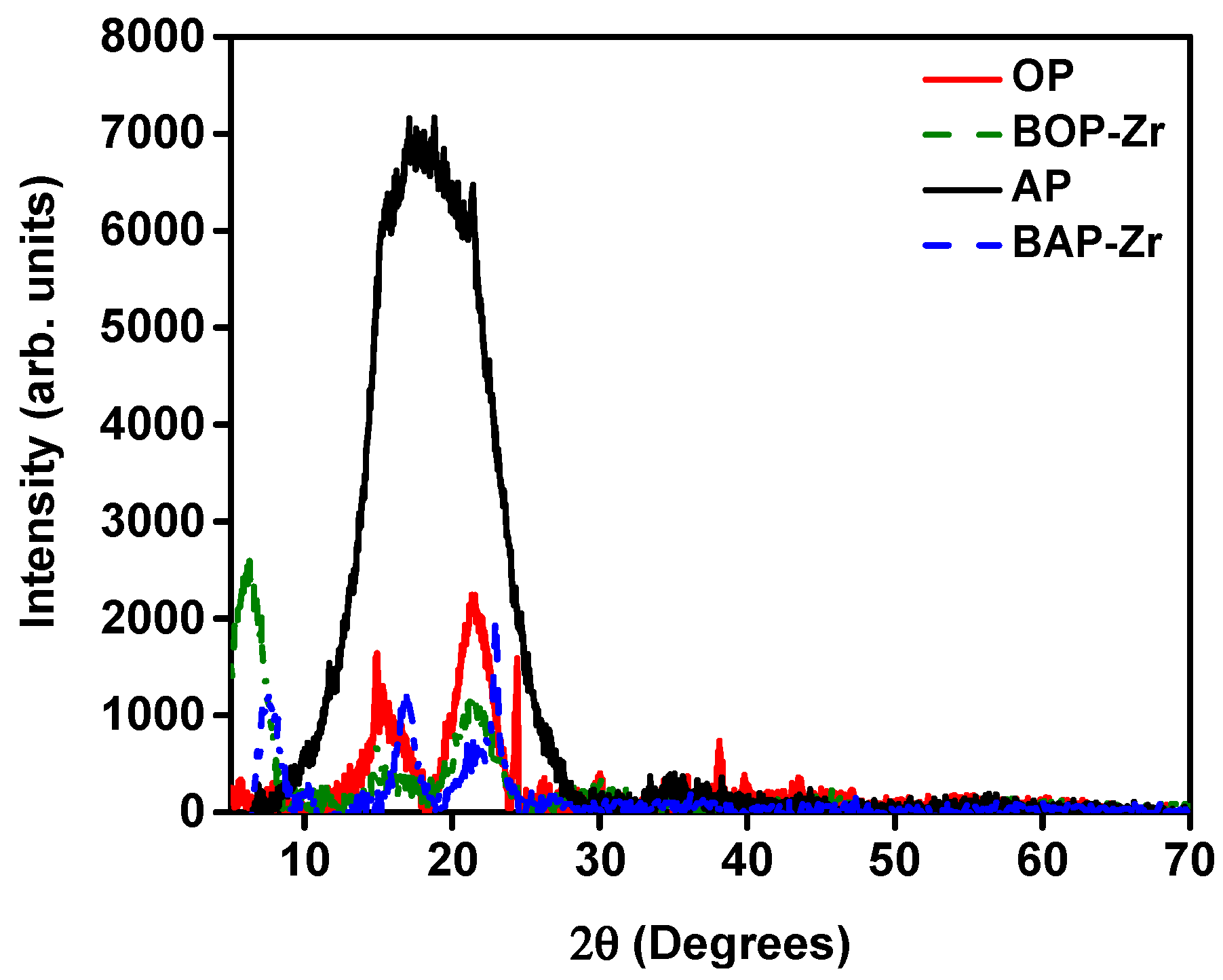
3.2.3. XRD
3.3. Fluoride Removal by Bioadsorbents
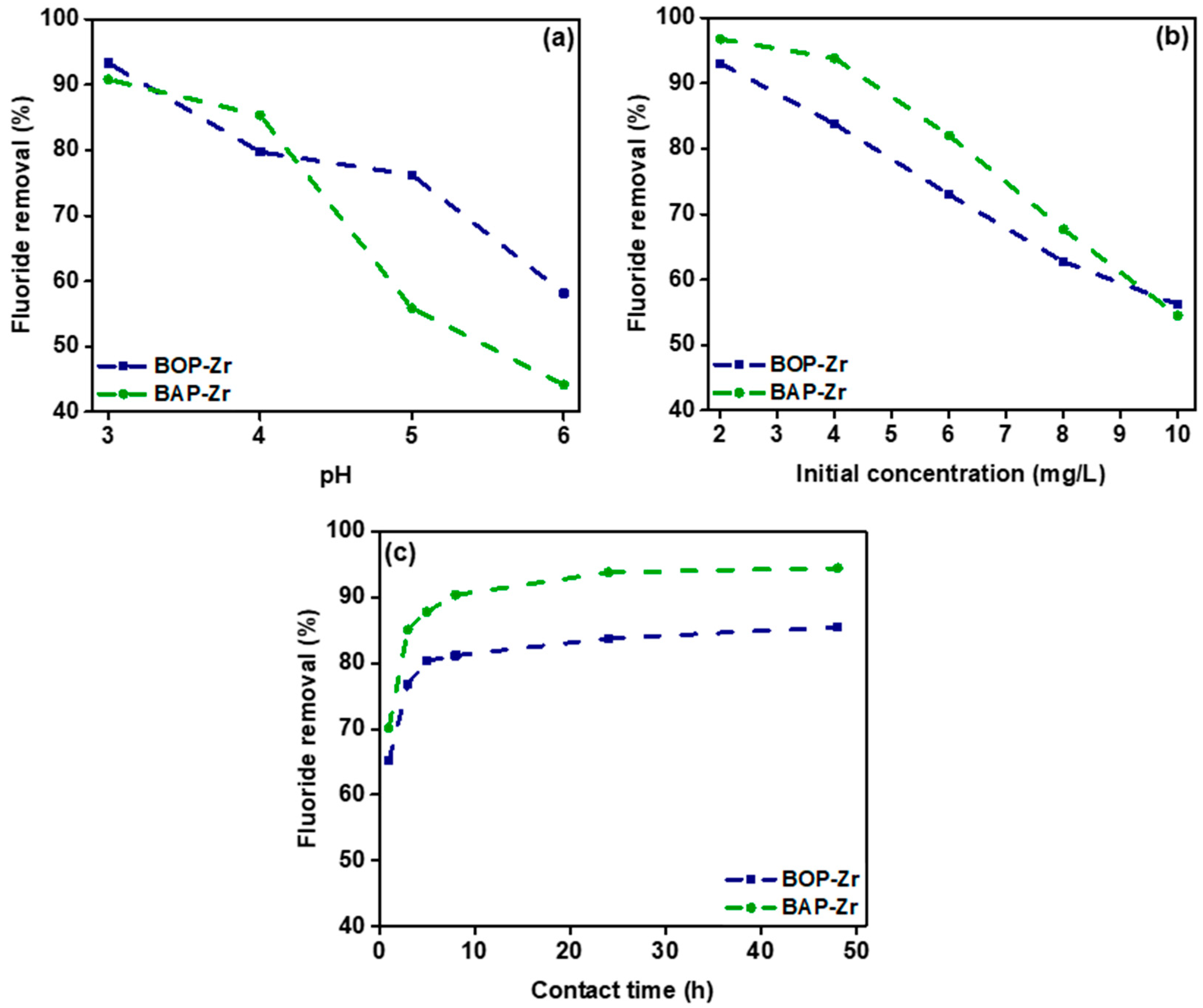
3.3.1. Influence of pH
3.3.2. Influence of the Initial Fluoride Concentration
3.3.3. Influence of Contact Time
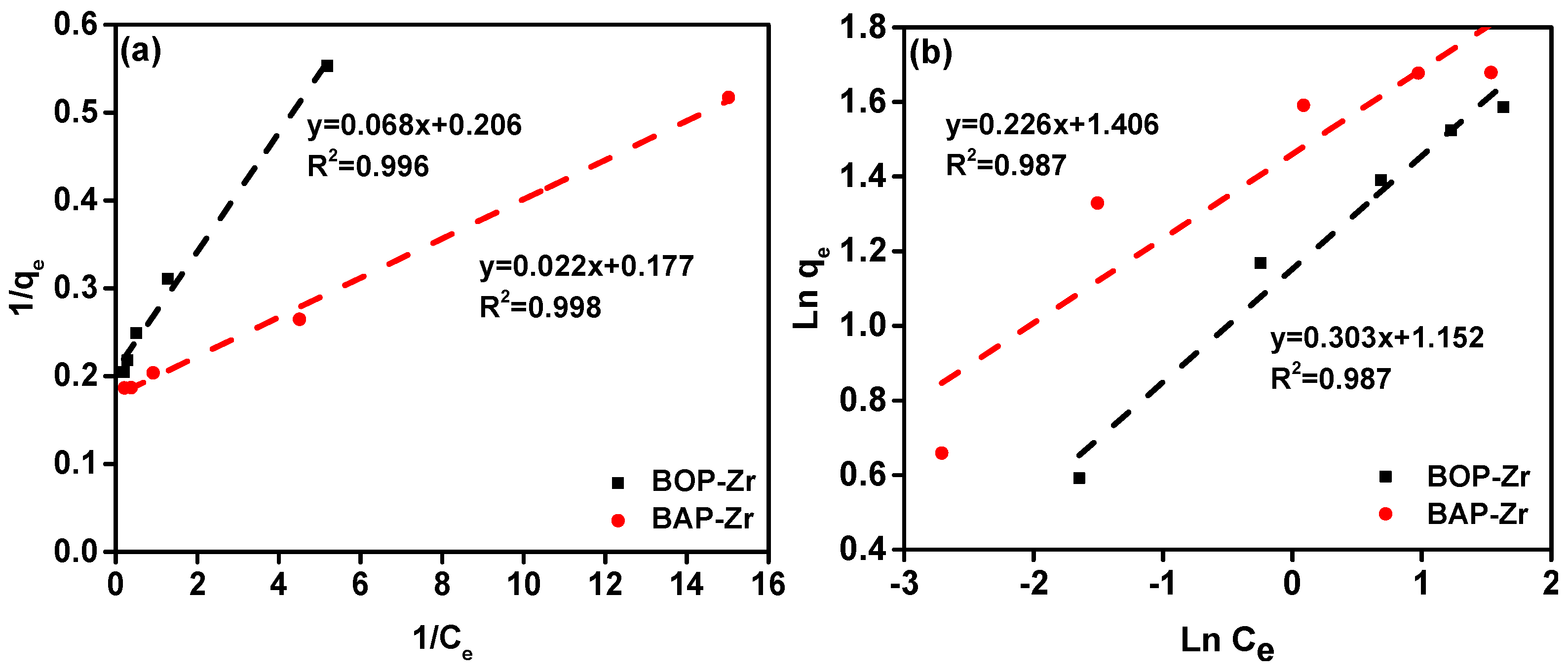
3.3.4. Adsorption Type and Capacity
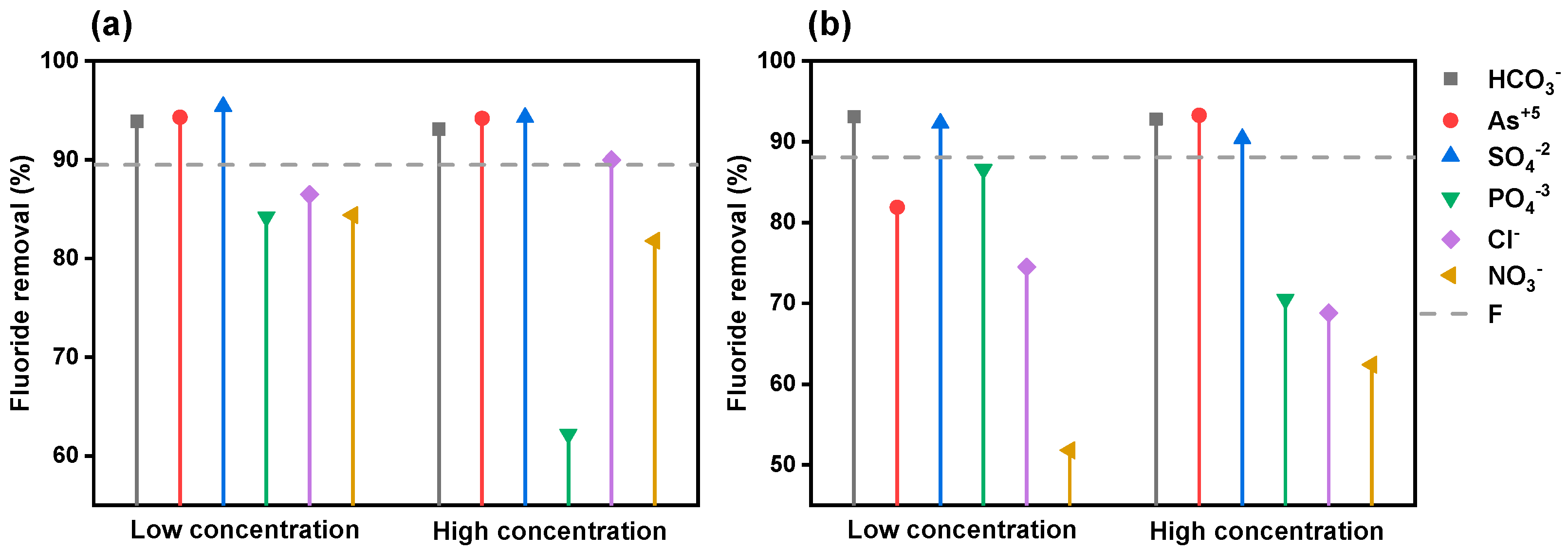
3.3.5. Co-Existing Ions
3.3.6. Fluoride Removal in Well Water
3.3.7. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alarcon-Herrera, M.T.; Martin-Alarcon, D.A.; Gutierrez, M.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L.; Martin-Dominguez, A.; Olmos-Marquez, M.A.; Bundschuh, J. Co-occurrence, possible origin, and health-risk assessment of arsenic and fluoride in drinking water sources in mexico: Geographical data visualization. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawell, J.; Bailey, K.; Chilton, J.; Dahi, L.; Fewtrell, L.; Magara, Y. Fluoride in drinking-water. In Who Drinking-Water Quality Series; World Health Organization titles with IWA Publishing; Bartram, L.F.a.J., Ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2006; p. 144. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Fluorine (Soluble Fluoride); Casrn 7782–41–4; Integrated Risk Information System; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1987.
- Manna, S.; Roy, D.; Adhikari, B.; Thomas, S.; Das, P. Biomass for water defluoridation and current understanding on biosorption mechanisms: A review. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2018, 37, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo-Peralta, A.; López-Guzmán, M.; Morales-Amaya, C.G.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L. Arsenic and fluoride in groundwater, prevalence and alternative removal approach. Processes 2021, 9, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhang, K.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Review of fluoride removal from water environment by adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habuda-Stanic, M.; Ravancic, M.E.; Flanagan, A. A review on adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. Materials 2014, 7, 6317–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaoui, M.; Jellali, S.; Zorpas, A.A.; Dutournie, P. Membrane technology for sustainable water resources management: Challenges and future projections. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 25, 100590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Agricultural waste peels as versatile biomass for water purification—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 244–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Haris, M.R.H.M. Application of biopolymer composites in arsenic removal from aqueous medium: A review. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Halde, G. A review on the sorptive elimination of fluoride from contaminated wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinhanmi, T.F.; Ofudje, E.A.; Adeogun, A.I.; Aina, P.; Joseph, I.M. Orange peel as low-cost adsorbent in the elimination of Cd(II) ion: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and optimization evaluations. Bioresour. Bioprocess 2020, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, P.; Bokare, M.; Pakade, Y.B. Methyl acrylate modified apple pomace as promising adsorbent for the removal of divalent metal ion from industrial wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 10454–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panic, M.; Andlar, M.; Tisma, M.; Rezic, T.; Sibalic, D.; Bubalo, M.C.; Redovnikovic, I.R. Natural deep eutectic solvent as a unique solvent for valorisation of orange peel waste by the integrated biorefinery approach. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D. The interaction between insoluble and soluble fiber. In Dietary Fiber for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease; Chapter 3—The Interaction Between Insoluble and Soluble; Samaa, F.R.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 35–59. [Google Scholar]
- Paudyal, H.; Pangeni, B.; Inoue, K.; Kawakita, H.; Ohto, K.; Ghimire, K.N.; Harada, H.; Alam, S. Adsorptive removal of trace concentration of fluoride ion from water by using dried orange juice residue. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, A.G.; Onifade, D.V.; Ighalo, J.O.; Adeoye, A.S. A review of coir fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 176, 107305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Jha, U.; Dey, R.K.; Mishra, S.; Swain, S.K. Fluoride sorption by zirconium (IV) loaded carboxylated orange peel. Desalin Water Treat. 2015, 53, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikoglu, A.Y.; SBilek, E.; Cesur, S. Optimum alkaline treatment parameters for the extraction of cellulose and production of cellulose nanocrystals from apple pomace. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, K.; Cai, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Jin, Z.; Meng, F.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; et al. A biocompatible and novelly-defined al-hap adsorption membrane for highly effective removal of fluoride from drinking water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, T.G.; Brahman, K.D.; Baig, J.A.; Afridi, H.I. A new efficient indigenous material for simultaneous removal of fluoride and inorganic arsenic species from groundwater. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 357, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.K. Natural banana (Musa acuminate) peel: An unconventional adsorbent for removal of fluoride from aqueous solution through batch study. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vargas, S.; Alfaro-Cuevas-Villanueva, R.; Huirache-Acuña, R.; Cortés-Martíne, R.Z. Removal of fluoride and arsenate from aqueous solutions by aluminum-modified guava seeds. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwakabona, H.T.; Mlay, H.R.; van der Bruggen, B.; Njau, K.N. Water defluoridation by Fe(III)-loaded sisal fibre: Understanding the influence of the preparation pathways on biosorbents’ defluoridation properties. J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 362, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, B.K.; Inoue, J.; Inoue, K.; Ghimire, K.N.; Harada, H.; Ohto, K.; Kawakita, H. Adsorptive removal of As(V) and As(III) from water by a Zr(IV)-loaded orange waste gel. J. Hazard Mater. 2008, 154, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallampati, R.; Valiyaveetti, S. Apple peels—A versatile biomass for water purification? ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 4443–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Singh, D.K.; Kumar, V.; Hasan, S.H. Effective removal of fluoride ions by rgo/zro2 nanocomposite from aqueous solution: Fixed bed column adsorption modelling and its adsorption mechanism. J. Fluor. Chem. 2017, 194, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, H.; Pangeni, B.; Inoue, K.; Matsueda, M.; Suzuki, R.; Kawakita, H.; Ohto, K.; Biswas, B.K.; Alam, S. Adsorption behavior of fluoride ions on zirconium(IV)-loaded orange waste gel from aqueous solution. Separ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Thommes, M. Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders Surface Area, Pore Size, and Density; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, T.; Misumi, Y.; Matsumoto, H. Pore size control for mesoporous titanium hydroxide prepared with mixed template molecules and its fluoride ion exchange property. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2009, 122, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Yenkie, M.K.N.; Labhsetwar, N.; Rayalu, S. Defluoridation of drinking water using chitosan based mesoporous alumina. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2011, 142, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Komarneni, S. Fluoride removal by ordered and disordered mesoporous aluminas. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2014, 197, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. Ionic Radii in Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 1475–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savari, A.; Hashemi, S.; Arfaeinia, H.; Dobaradaran, S.; Foroutan, R.; Mahvi, A.H.; Fouladvand, M.; Sorial, G.A.; Farjadfard, S.; Ramavandi, B. Physicochemical characteristics and mechanism of fluoride removal using powdered zeolite-zirconium in modes of pulsed& continuous sonication and stirring. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 3521–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigondo, M.; Paumo, H.K.; Bhaumik, M.; Pillay, K.; Maity, A. Rapid high adsorption performance of hydrous cerium-magnesium oxides for removal of fluoride from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, M.; Anand, S.; Mishra, B.K.; Giles, D.E.; Singh, P. Review of fluoride removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, V.; Khan, S.A.; Kumar, A. A review of emerging adsorbents and current demand for defluoridation of water: Bright future in water sustainability. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 80–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeniyi, A.G. A mini-review of the morphological properties of biosorbents derived from plant leaves. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, D.C.S.; Coseglio, B.B.; Pinto, L.A.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S. Development of spirulina/chitosan foam adsorbent for phenol adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayğılı, G.A.; Güzel, F. Chemical modification of a cellulose-based material to improve its adsorption capacity for anionic dyes. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2016, 38, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, H.; Pangeni, B.; Inoue, K.; Kawakita, H.; Ohto, K.; Harada, H.; Alam, S. Adsorptive removal of fluoride from aqueous solution using orange waste loaded with multi-valent metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, H.; Pangeni, B.; Ghimire, K.N.; Inoue, K.; Ohto, K.; Kawakita, H.; Alam, S. Adsorption behavior of orange waste gel for some rare earth ions and its application to the removal of fluoride from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 195, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Development, characterization, and utilization of magnetized orange peel waste as a novel adsorbent for the confiscation of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, P.; Pakade, Y.B. Removal of pb from water by adsorption on apple pomace: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics studies. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 164575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Fei, J.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Yao, J. Cellulose whiskers extracted from mulberry: A novel biomass production. Carbohyd. Polym. 2009, 76, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.A.F.M.; Jamaluddin, J.; Zainudin, Z.; Busheri, M.M.; Adrus, N.; Azim, F.S.S.; Hasham, R. The effect of alkaline treatment onto physical, thermal, mechanical and chemical properties of lemba leaves fibres as new resources of biomass. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 1531–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Orozco, R.; Hernández, P.B.; Morales, G.R.; Núñez, F.U.; Villafuerte, J.O.; Lugo, V.L.; Ramírez, N.F.; Díaz, C.E.B.; Vázquez, P.C. Characterization of lignocellulosic fruit wastre as an alternative feedstock for bioethanol production. Bioresources 2014, 9, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monte, L.S.; Escócio, V.A.; de Sousa, A.M.F.; Furtado, C.R.G.; Leite, M.C.A.M.; Visconte, L.L.Y.; Pacheco, E.B.A.V. Study of time reaction on alkaline pretreatment applied to rice husk on biomass component extraction. Biomass Convers. 2017, 8, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, H.; Pangeni, B.; Inoue, K.; Kawakita, H.; Ohto, K.; Alam, S. Adsorptive removal of fluoride from aqueous medium using a fixed bed column packed with Zr(IV) loaded dried orange juice residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norul Izani, M.A.; Paridah, M.T.; Anwar, U.M.K.; Nor, M.Y.M.; H’ng, P.S. Effects of fiber treatment on morphology, tensile and thermogravimetric analysis of oil palm empty fruit bunches fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Mohanty, A.K.; Drzal, L.T.; Askeñ, P.; Misra, M. Effects of alkali treatment on the structure, morphology and thermal properties of native grass fibers as reinforcements for polymer matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, R. Polímeros amorfos, semicristalinos, polímeros cristales líquidos y orientación. In Elementos Estructurales con Materiales Polímeros; Lafuente, Á.V., Ed.; Universidade de Coruna: Coruna, Spain, 1997; pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mulinari, D.R.; Cruz, T.G.; Cioffi, M.O.; Voorwald, H.J.; da Silva, M.L.; Rocha, G.J. Image analysis of modified cellulose fibers from sugarcane bagasse by zirconium oxychloride. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visakh, P.M.; Thomas, S. Preparation of bionanomaterials and their polymer nanocomposites from waste and biomass. Waste Biomass Valor. 2010, 1, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Sasaki, T.; Takagi, I.; Moriyama, H. Solubility of zirconium(IV) hydrous oxides. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2007, 44, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Abbassi, R.; Gupta, A.; Dadashzadeh, M. Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution and groundwater by wheat straw, sawdust and activated bagasse carbon of sugarcane. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.S.; Goel, S. Factors influencing arsenic and nitrate removal from drinking water in a continuous flow electrocoagulation (ec) process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, M.C.; Mandal, B.; Hazra, G.C. Nitrate and fluoride contamination in groundwater of an intensively managed agroecosystem: A functional relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2771–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, S.; Saha, P.; Roy, D.; Sen, R.; Adhikari, B. Defluoridation potential of jute fibers grafted with fatty acyl chain. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, S.; Nehra, S.; Kumar, D. Biopolymer scaffold of pectin and alginate for the application of health hazardous fluoride removal studies by equilibrium adsorption, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, K.; Ballav, N.; Debnath, S.; Pillay, K.; Maity, A. Hydrous zro2 decorated polyaniline nanofibres: Synthesis, characterization and application as an efficient adsorbent for water defluoridation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kang, D.; Yu, X.; Ge, M.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and characterization of mg–fe–la trimetal composite as an adsorbent for fluoride removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, S.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; Sun, X.; Gu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Modified hydrous zirconium oxide/pan nanofibers for efficient defluoridation from groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathibha, C.; Biswas, A.; Chunduri, L.A.A.; Reddy, S.K.; Loganathan, P.; Kalaruban, M.; Venkatarmaniah, K. Zr(IV) functionalized graphene oxide anchored sand as potential and economic adsorbent for fluoride removal from water. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 109, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, Z.; Xu, W. A low-cost and high efficient zirconium-modified-na-attapulgite adsorbent for fluoride removal from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Yang, S. Remediating fluoride from water using hydrous zirconium oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantano, C.G.; Brow, R.K. Hydrolysis reactions at the surface of fluorozirconate glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1988, 71, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piascik, J.R.; Wolter, S.D.; Stoner, B.R. Development of a novel surface modification for improved bonding to zirconia. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, e99–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolter, S.D.; Piascik, J.R.; Stoner, B.R. Characterization of plasma fluorinated zirconia for dental applications by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 10177–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahboun, N.; Veys-Renaux, D.; Rocca, E. Sealing mechanism of nanoporous alumina in fluorozirconate salt containing solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 541, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. Insight into mechanisms of fluoride removal from contaminated groundwater using lanthanummodified bone waste. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54291–54305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva-Moura, C.A.; Kretzman-Belmonte, G.; Guruprasad-Reddy, P.; Gonslaves, K.E.; Weibel, D.E. Euv photofragmentation study of hybrid nonchemically amplified resists containing antimony as an absorption enhancer. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 10930–10938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
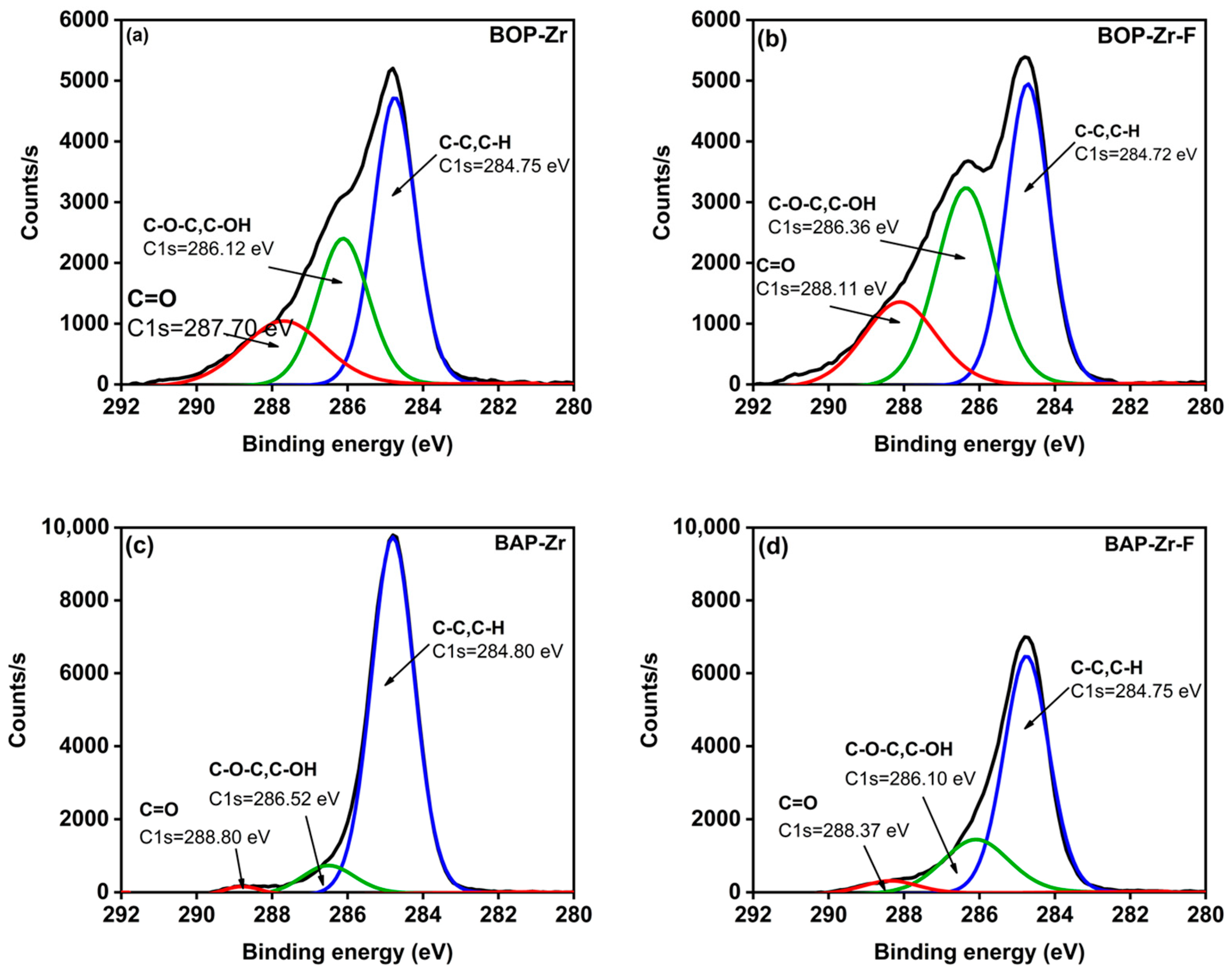
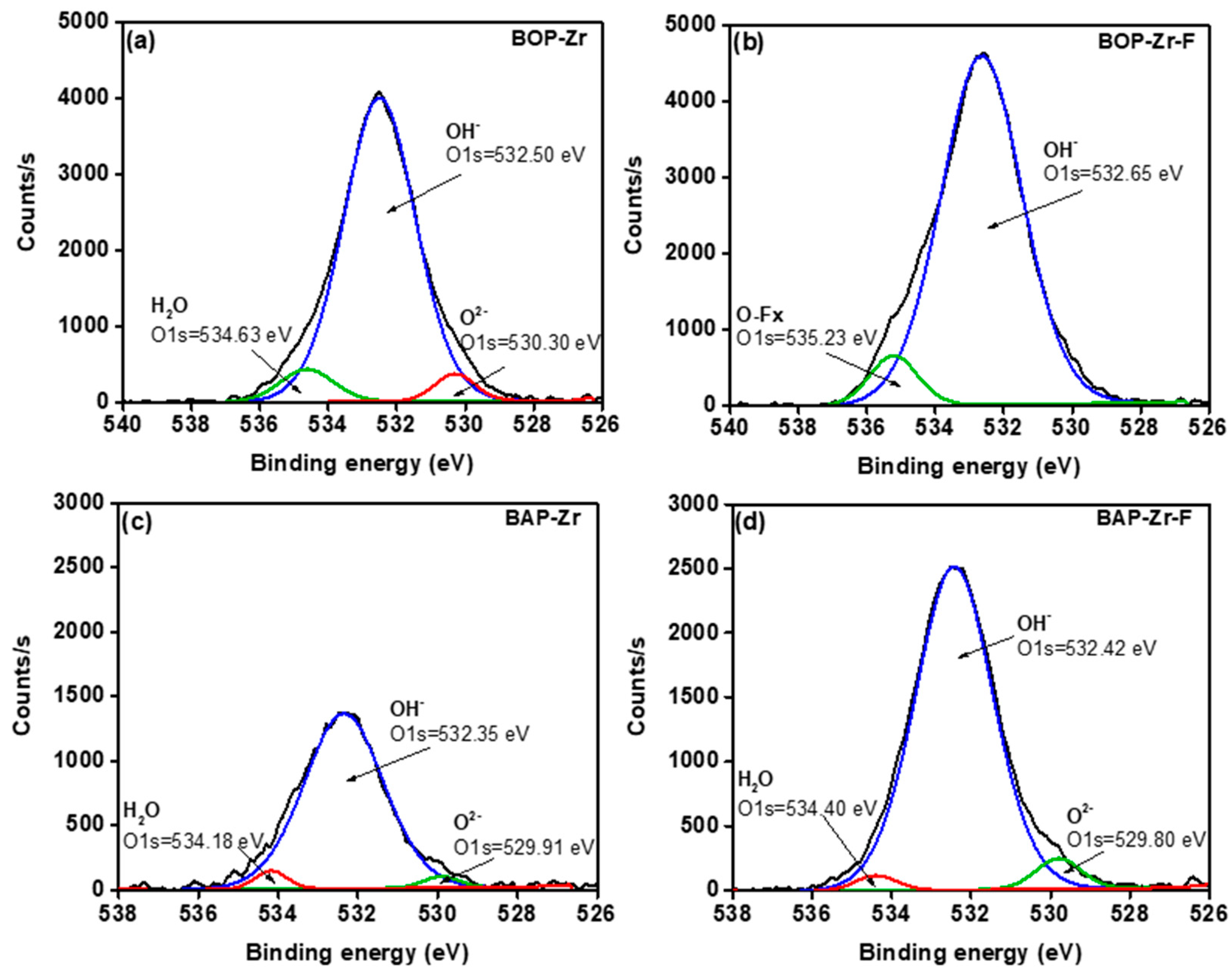
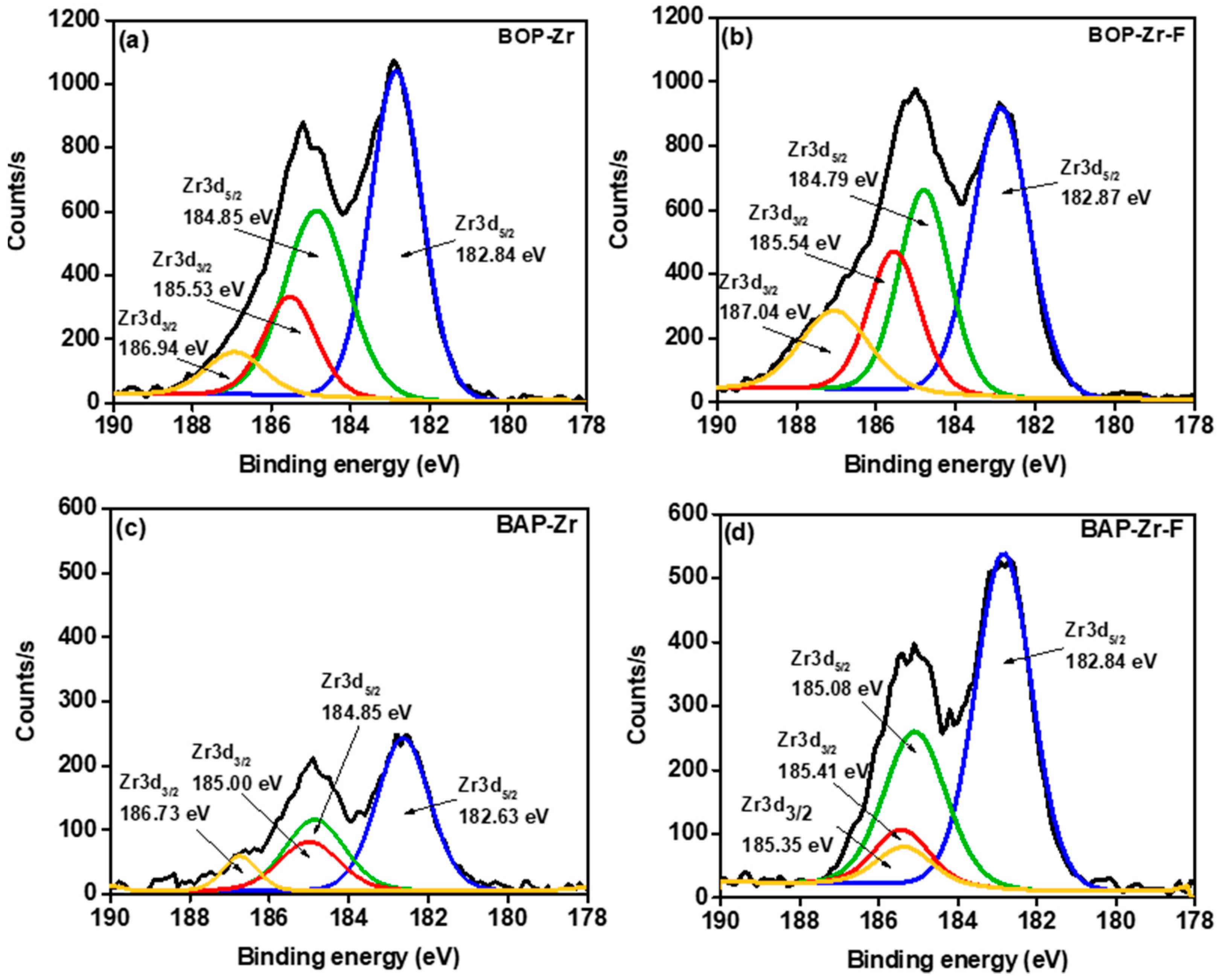
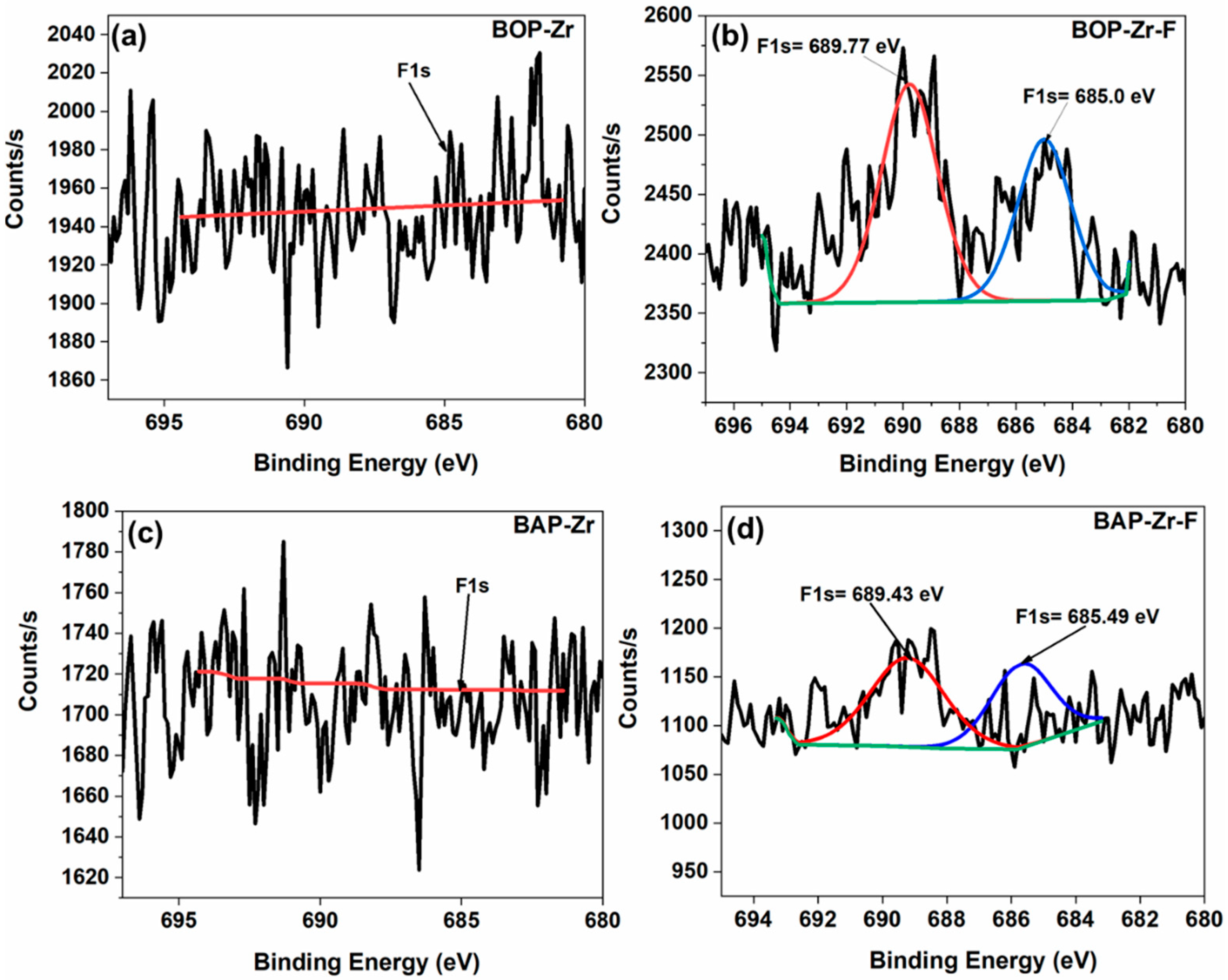
| Sample | Element (% Weight) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Ca | Cl | Zr | |
| OP | 55.72 ± 2.49 | 42.40 ± 2.44 | 0.41 ± 0.09 | ||
| BOP-Zr | 34.68 ± 1.12 | 30.85 ± 2.55 | 1.36 ± 0.18 | 33.08 ± 2.95 | |
| AP | 85.50 ± 0.47 | 14.51 ± 0.46 | |||
| BAP-Zr | 43.30 ± 1.29 | 32.57 ± 1.11 | 2.01 ± 0.09 | 22.01 ± 0.62 | |
| Bioadsorbent | Isotherm Model | qmax (mg/g) | Constant | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOP-Zr | Langmuir | 4.854 | KL 3.043 (L/mg) RL 0.08 | 0.996 |
| Freundlich | 3.297 | KF 3.165 (mg/g) | 0.987 | |
| BAP-Zr | Langmuir | 5.627 | KL 7.969 (L/mg) RL 0.03 | 0.998 |
| Freundlich | 4.413 | KF 4.308 (mg/g) | 0.987 |
| Bioadsorbent | Fluoride Removal 1 h (%) | Fluoride Removal 24 h (%) | Arsenic Removal 24 h (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well water | BOP-Zr | 85 | 95 | 81 |
| BAP-Zr | 69 | 93 | 84 | |
| Laboratory solution | BOP-Zr | 64 | 86 | 82 |
| BAP-Zr | 69 | 94 | 84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robledo-Peralta, A.; García-Quiñonez, L.V.; Rodríguez-Beltrán, R.I.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L. Zr-Based Biocomposite Materials as an Alternative for Fluoride Removal, Preparation and Characteristics. Polymers 2022, 14, 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081575
Robledo-Peralta A, García-Quiñonez LV, Rodríguez-Beltrán RI, Reynoso-Cuevas L. Zr-Based Biocomposite Materials as an Alternative for Fluoride Removal, Preparation and Characteristics. Polymers. 2022; 14(8):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081575
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobledo-Peralta, Adriana, Linda Viviana García-Quiñonez, René I. Rodríguez-Beltrán, and Liliana Reynoso-Cuevas. 2022. "Zr-Based Biocomposite Materials as an Alternative for Fluoride Removal, Preparation and Characteristics" Polymers 14, no. 8: 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081575
APA StyleRobledo-Peralta, A., García-Quiñonez, L. V., Rodríguez-Beltrán, R. I., & Reynoso-Cuevas, L. (2022). Zr-Based Biocomposite Materials as an Alternative for Fluoride Removal, Preparation and Characteristics. Polymers, 14(8), 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081575






