Synthesis of Silver Nanocomposites for Stereolithography: In Situ Formation of Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
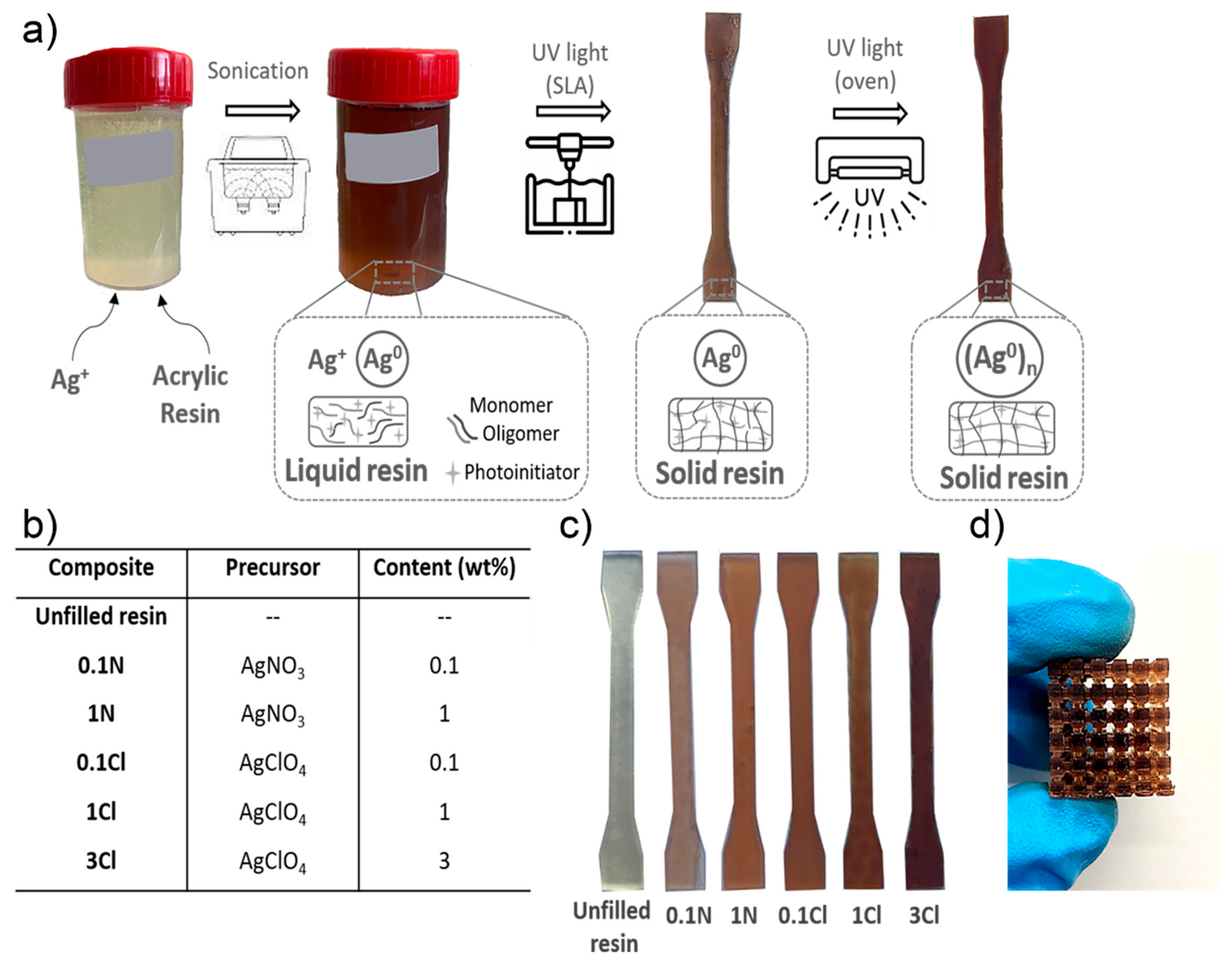
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization
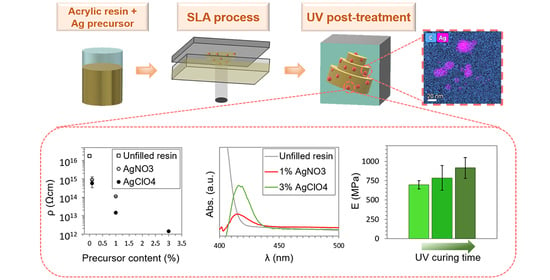
3. Results
3.1. Fabrication of Nanocomposites
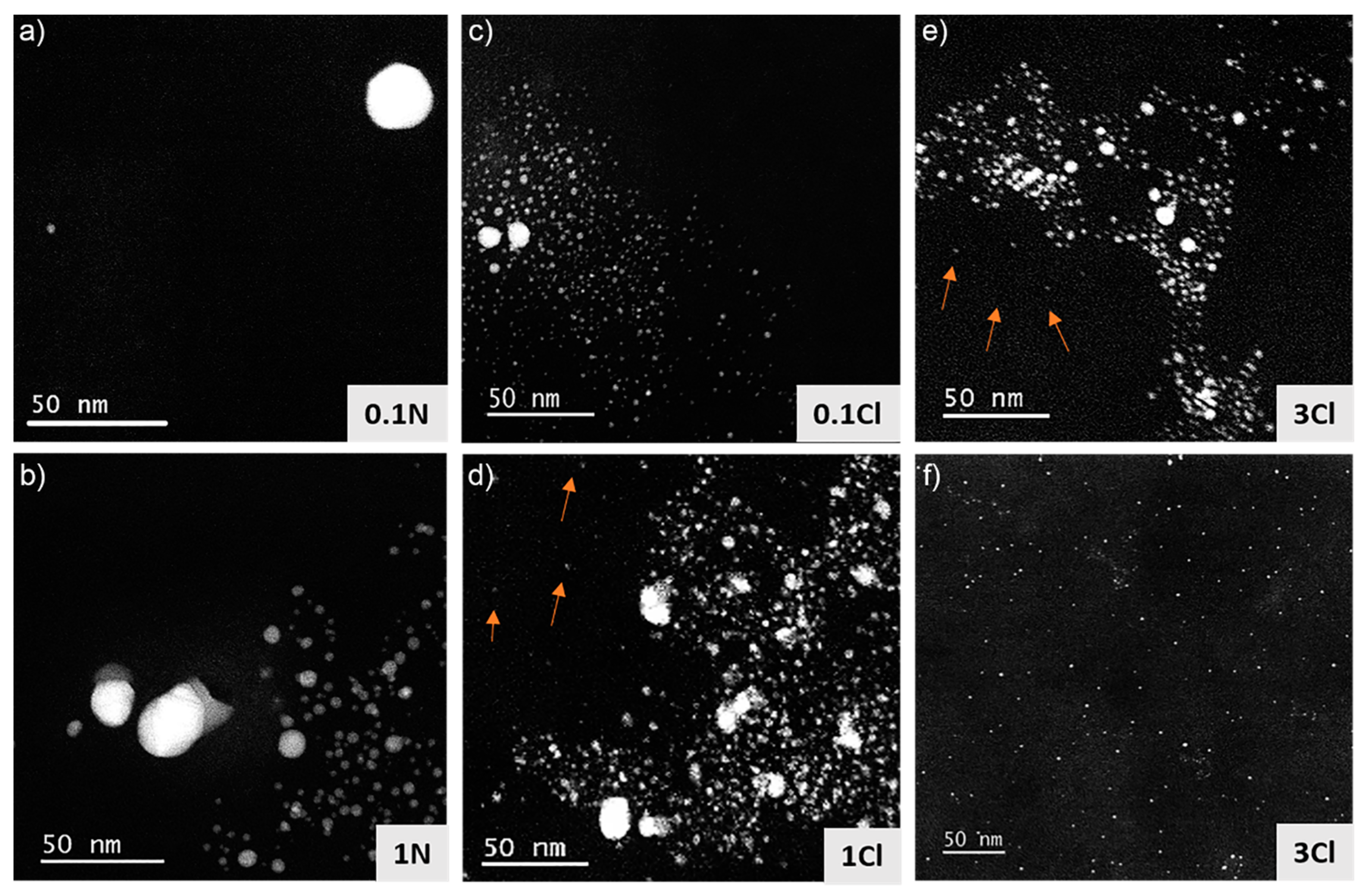
3.2. Structural and Compositional Characterization
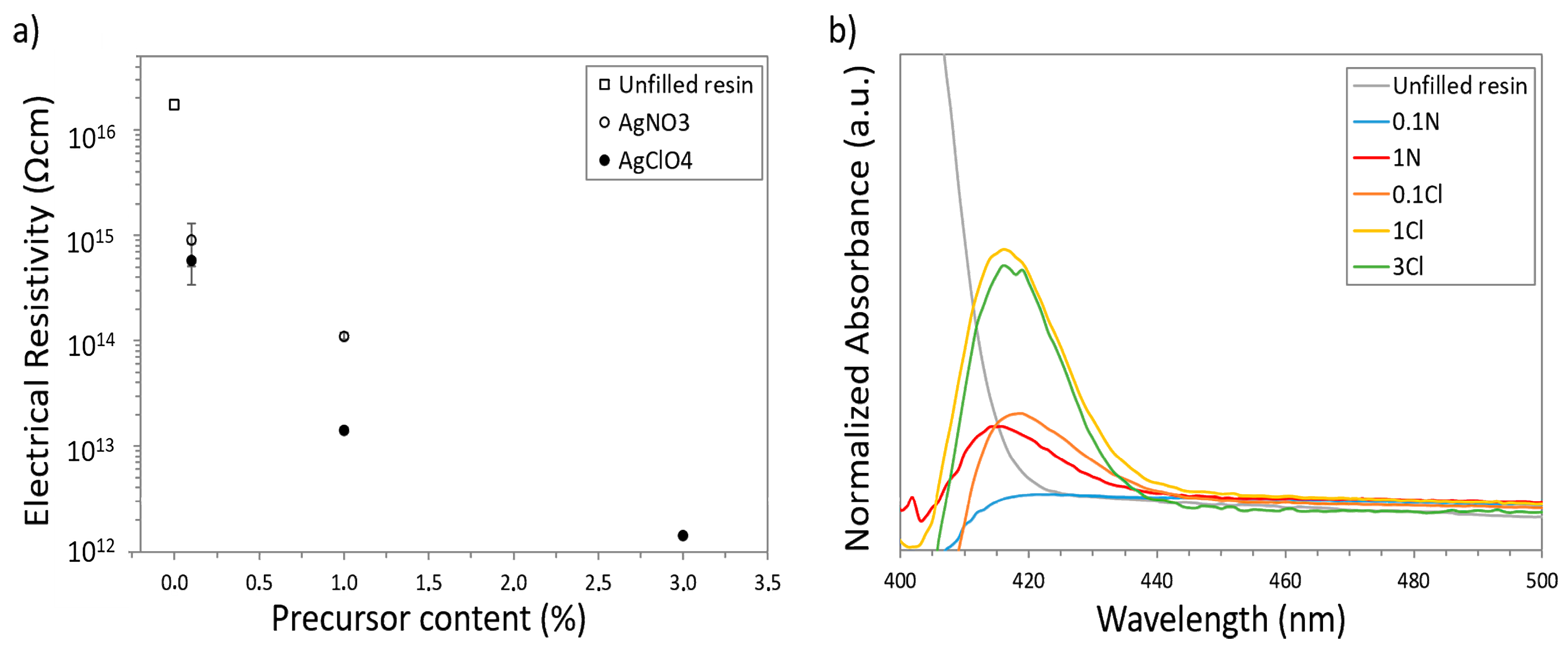
3.3. Analysis of the Electrical and Optical Properties
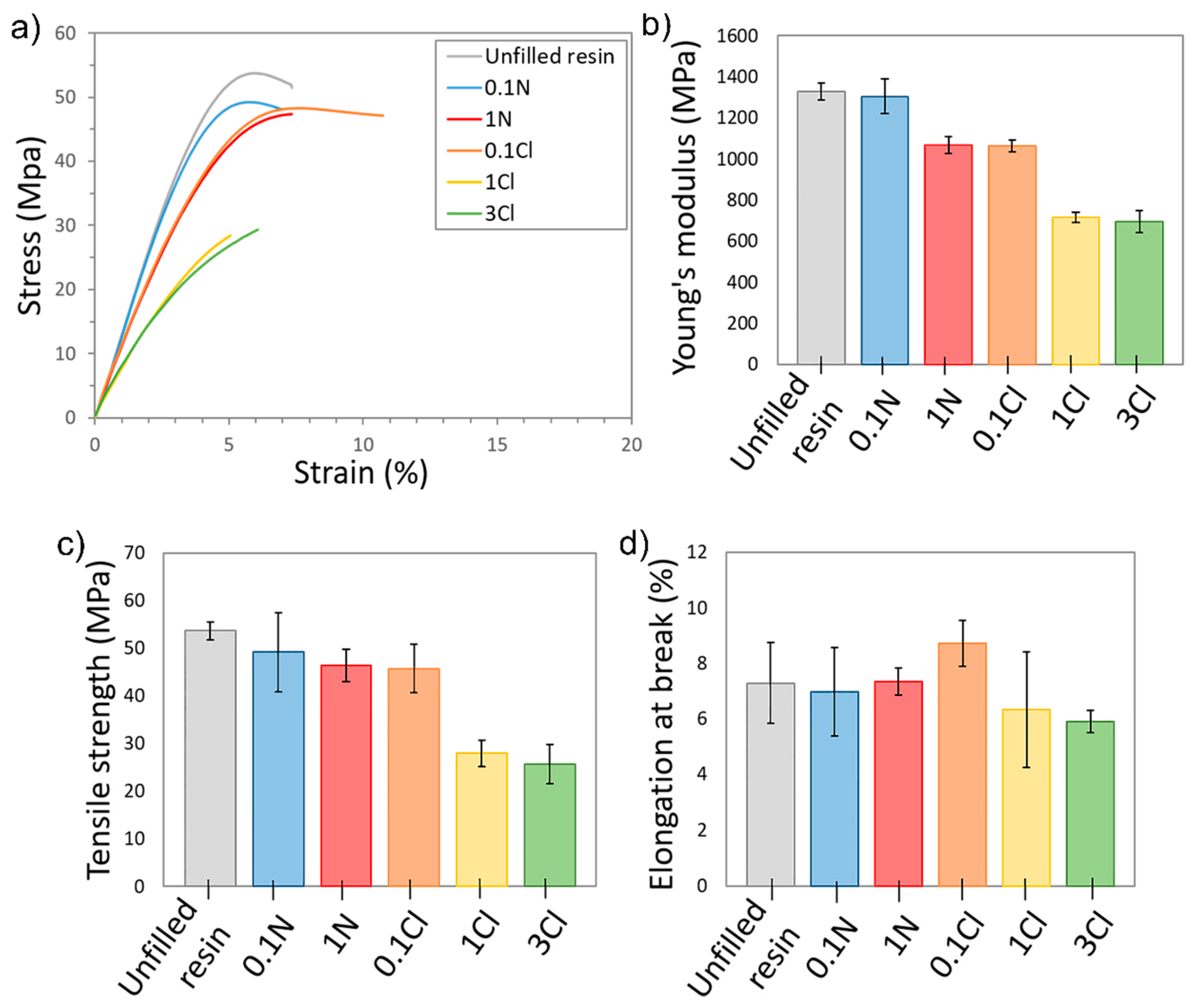
3.4. Mechanical Characterization
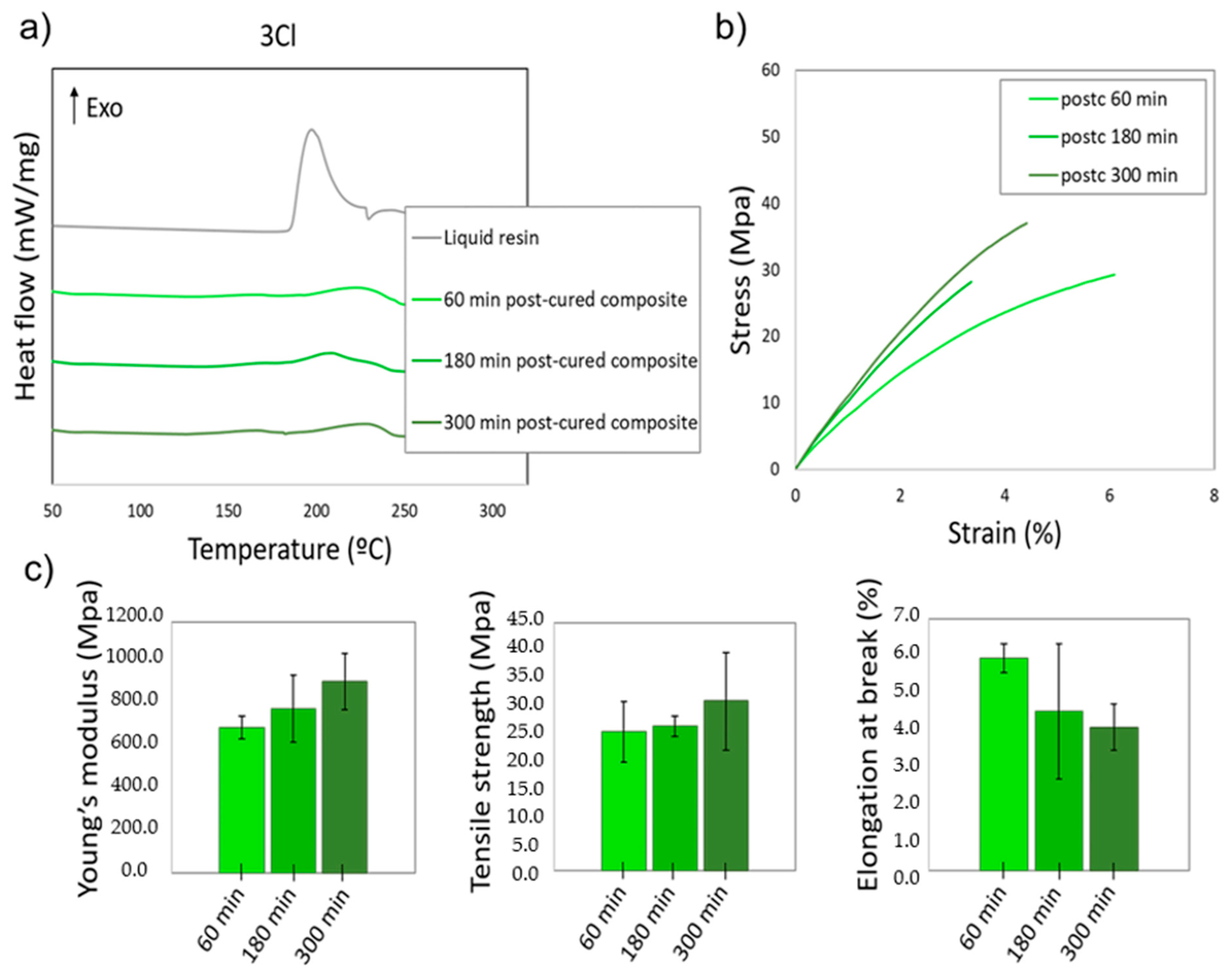
3.5. Analysis of the Degree of Cure of the Nanocomposites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taormina, G.; Sciancalepore, C.; Messori, M.; Bondioli, F. 3D printing processes for photocurable polymeric materials: Technologies, materials, and future trends. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2018, 16, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farahani, R.D.; Dubé, M.; Therriault, D. Three-Dimensional Printing of Multifunctional Nanocomposites: Manufacturing Techniques and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5794–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boparai, K.S.; Singh, R.; Singh, H. Development of rapid tooling using fused deposition modeling: A review. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2016, 22, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, G.; Qin, R.; Liu, W.; Xiong, H.; Shi, G.; Blackburn, J. Progress in additive manufacturing on new materials: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 242–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, J.; Collan, M. How Additive Manufacturing Technology Changes Business Models?—Review of Literature. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, S.; Tokita, E.; Neupane, R.; Ghosh, U. 3D printed nanomaterial-based electronic, biomedical and bioelectronic devices. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 172001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challagulla, N.V.; Rohatgi, V.; Sharma, D.; Kumar, R. Recent developments of nanomaterial applications in additive manufacturing: A brief review. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.W.; Stucker, B. Rapid Prototyping to Direct Digital Manufacturing; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781441911193. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, M. 3D printing gets a boost and opportunities with polymer materials. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.C.; Erkal, J.L.; Lockwood, S.Y.; Chen, C.; Spence, D.M. Evaluation of 3D printing and its potential impact on biotechnology and the chemical sciences. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3240–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, A. 3D Printing of Optical Components; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 233, ISBN 978-3-030-58959-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Song, X.; Zhu, B.; Hsiai, T.; Wu, P.I.; Xiong, R.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Three dimensional printing of high dielectric capacitor using projection based stereolithography method. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sa, L.; Kaiwu, L.; Shenggui, C.; Junzhong, Y.; Yongguang, J.; Lin, W.; Li, R. 3D printing dental composite resins with sustaining antibacterial ability. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhamannil, R.V.; Govindan, P. Current state and future scope of additive manufacturing technologies via vat photopolymerization. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 43, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Photo-curing 3D printing technique and its challenges. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Qin, Q.; Wang, J. A review of stereolithography: Processes and systems. Processes 2020, 8, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fahy, W.P.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Zhao, N.; Pilato, L.; Kafi, A.; Bateman, S.; Koo, J.H. Recent developments in polymers/polymer nanocomposites for additive manufacturing. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 111, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiao, T.; Lu, G.; Liu, J. Photocurable modification of inorganic fillers and their application in photopolymers for 3D printing. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 6350–6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manapat, J.Z.; Mangadlao, J.D.; Tiu, B.D.B.; Tritchler, G.C.; Advincula, R.C. High-Strength Stereolithographic 3D Printed Nanocomposites: Graphene Oxide Metastability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10085–10093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosi, A.; Pumera, M. Self-Contained Polymer/Metal 3D Printed Electrochemical Platform for Tailored Water Splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, B.; Arshad, M.; Ullah, A.; Mertiny, P.; Qureshi, A.J. Additive manufacturing ferromagnetic polymers using stereolithography—Materials and process development. Manuf. Lett. 2019, 21, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.A.; Kudryashov, A.; Agareva, N.; Afanasiev, A.; Gusev, S.; Tatarskiy, D.; Bityurin, N. In-situ monitoring of the evolution of the optical properties for UV LED irradiated polymer-based photo-induced nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 486, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedzińska, D.; Gieleta, R.; Popławski, A. Experimental study on influence of curing time on strength behavior of sla-printed samples loaded with different strain rates. Materials 2020, 13, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsoom, U.; Peristyy, A.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Paull, B. A 3D printable diamond polymer composite: A novel material for fabrication of low cost thermally conducting devices. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 38140–38147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melessanaki, K.; Mateo, M.; Ferrence, S.C.; Betancourt, P.P.; Anglos, D. The application of LIBS for the analysis of archaeological ceramic and metal artifacts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 197–198, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jembrih-Simbürger, D.; Neelmeijer, C.; Schalm, O.; Fredrickx, P.; Schreiner, M.; De Vis, K.; Mäder, M.; Schryvers, D.; Caen, J. The colour of silver stained glass—Analytical investigations carried out with XRF, SEM/EDX, TEM, and IBA. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.; Vilarigues, M.; Alves, L.C.; da Silva, R.C. Stained glasses from Monastery of Batalha: Non-destructive characterisation of glasses and glass paintings. J. Cult. Herit. 2008, 9, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrie, B.H. Rethinking the history of artists’ pigments through chemical analysis. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, C.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Birke, G.; Martinez, E.; Reyes, P. Conversion of methanol to formaldehyde on TiO2 supported Ag nanoparticles. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2010, 55, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, A.; Eränen, K.; Lemus-Yegres, L.J.; Voss, B.; Gabrielsson, A.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y. Ethylene epoxidation over supported silver catalysts—Influence of catalyst pretreatment on conversion and selectivity. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyne, D.A.; Savage, A.M.; Orlicki, J.A.; Beyer, F.L.; Griep, M.H. Macroscopic Alignment of Silver Nanoplates in an Adaptable Dichroic Polarizer. Plasmonics 2019, 14, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaveliya, N.; Lenke, S.; Köhler, J.M. Composite Sensor Particles for Tuned SERS Sensing: Microfluidic Synthesis, Properties and Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10742–10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jaakola, J.; Säynätjoki, A.; Tervonen, A.; Honkanen, S. Sers-active silver nanoparticles in ion-exchanged glass. J. Nonlinear Opt. Phys. Mater. 2010, 19, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawish, S.M.; Mosleh, S. Antimicrobial Polypropylene Loaded by Silver Nano Particles. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantino, E.; Chiappone, A.; Roppolo, I.; Manfredi, D.; Bongiovanni, R.; Pirri, C.F.; Calignano, F. 3D Printing of Conductive Complex Structures with in Situ Generation of Silver Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3712–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taormina, G.; Sciancalepore, C.; Bondioli, F.; Messori, M. Special resins for stereolithography: In situ generation of silver nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aktitiz, İ.; Varol, R.; Akkurt, N.; Saraç, M.F. In-situ synthesis of 3D printable mono- and Bi-metallic (Cu/Ag) nanoparticles embedded polymeric structures with enhanced electromechanical properties. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, S.; Dhamodharan, D.; Kale, M.B.; Divakaran, N.; Senthil, T.; Wu, L.; Wang, J. A Novel Approach to Enhance Mechanical and Thermal Properties of SLA 3D Printed Structure by Incorporation of Metal–Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siengchin, S.; Boonyasopon, P.; Sadanand, V.; Rajulu, A.V. Nanocomposite cellulose fabrics with in situ generated silver nanoparticles by bioreduction method. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeksha, B.; Sadanand, V.; Hariram, N.; Rajulu, A.V. Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocomposite fabrics with in situ generated silver nanoparticles by bioreduction method. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantino, E.; Chiappone, A.; Calignano, F.; Fontana, M.; Pirri, F.; Roppolo, I. In situ thermal generation of silver nanoparticles in 3D printed polymeric structures. Materials 2016, 9, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Flores, G.A.; Bertana, V.; Chiappone, A.; Roppolo, I.; Scaltrito, L.; Marasso, S.L.; Cocuzza, M.; Massaglia, G.; Quaglio, M.; Pirri, C.F.; et al. Single-Step 3D Printing of Silver-Patterned Polymeric Devices for Bacteria Proliferation Control. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roppolo, I.; Castellino, M.; Bejtka, K.; Rizza, G.; Perrone, D.; Coulon, P.E.; Chiappone, A.; Rajan, K.; Bocchini, S.; Ricciardi, C.; et al. Resistive Switching in Polymer Nanocomposites by Matrix-Controlled in Situ Nanoparticles Generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 14285–14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciancalepore, C.; Moroni, F.; Messori, M.; Bondioli, F. Acrylate-based silver nanocomposite by simultaneous polymerization–reduction approach via 3D stereolithography. Compos. Commun. 2017, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhainsa, K.C.; D’Souza, S.F. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 47, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hada, H.; Yonezawa, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kurakake, A. Photoreduction of silver ion in aqueous and alcoholic solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1976, 80, 2728–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, A.; Accorsi, G.; Armaroli, N. Luminescent complexes beyond the platinum group: The d10 avenue. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Król-Gracz, A.; Michalak, E.; Nowak, P.M.; Dyonizy, A. Photo-induced chemical reduction of silver bromide to silver nanoparticles. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2011, 9, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libera, M.R.; Egerton, R.A.Y.F. Advances in the Transmission Electron Microscopy of Polymers. Polym. Rev. 2010, 50, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A. Surface plasmons in metallic nanoparticles: Fundamentals and applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 283001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Rycenga, M.; Skrabalak, S.E.; Wiley, B.; Xia, Y. Chemical synthesis of novel plasmonic nanoparticles. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2009, 60, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.K.; Shin, M.; Kim, B.; Park, J.W.; Lee, H. A visible light-curable yet visible wavelength-transparent resin for stereolithography 3D printing. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Tian, C.; Zheng, C.; Wang, L.; Fu, H. A simple and large-scale strategy for the preparation of Ag nanoparticles supported on resin-derived carbon and their antibacterial properties. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 025603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatenko, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Suzuki, M. Synthesis of spherical silver nanoparticles with controllable sizes in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 7910–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; McMahon, J.M.; Schatz, G.C.; Gray, S.K.; Sun, Y. Reversing the size-dependence of surface plasmon resonances. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14530–14534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De León, A.S.; Molina, S.I. Influence of the degree of cure in the bulk properties of graphite nanoplatelets nanocomposites printed via stereolithography. Polymers 2020, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valencia, L.M.; Herrera, M.; de la Mata, M.; de León, A.S.; Delgado, F.J.; Molina, S.I. Synthesis of Silver Nanocomposites for Stereolithography: In Situ Formation of Nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061168
Valencia LM, Herrera M, de la Mata M, de León AS, Delgado FJ, Molina SI. Synthesis of Silver Nanocomposites for Stereolithography: In Situ Formation of Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2022; 14(6):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061168
Chicago/Turabian StyleValencia, Luisa M., Miriam Herrera, María de la Mata, Alberto S. de León, Francisco J. Delgado, and Sergio I. Molina. 2022. "Synthesis of Silver Nanocomposites for Stereolithography: In Situ Formation of Nanoparticles" Polymers 14, no. 6: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061168
APA StyleValencia, L. M., Herrera, M., de la Mata, M., de León, A. S., Delgado, F. J., & Molina, S. I. (2022). Synthesis of Silver Nanocomposites for Stereolithography: In Situ Formation of Nanoparticles. Polymers, 14(6), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061168