Cassava Starch-Based Thermo-Responsive Pb(II)-Imprinted Material: Preparation and Adsorption Performance on Pb(II)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Preparation of CPIT
2.4. Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of CPIT
2.5. Desorption and Regeneration of CPIT
2.6. Selective Adsorption of CPIT
3. Results and Discussion
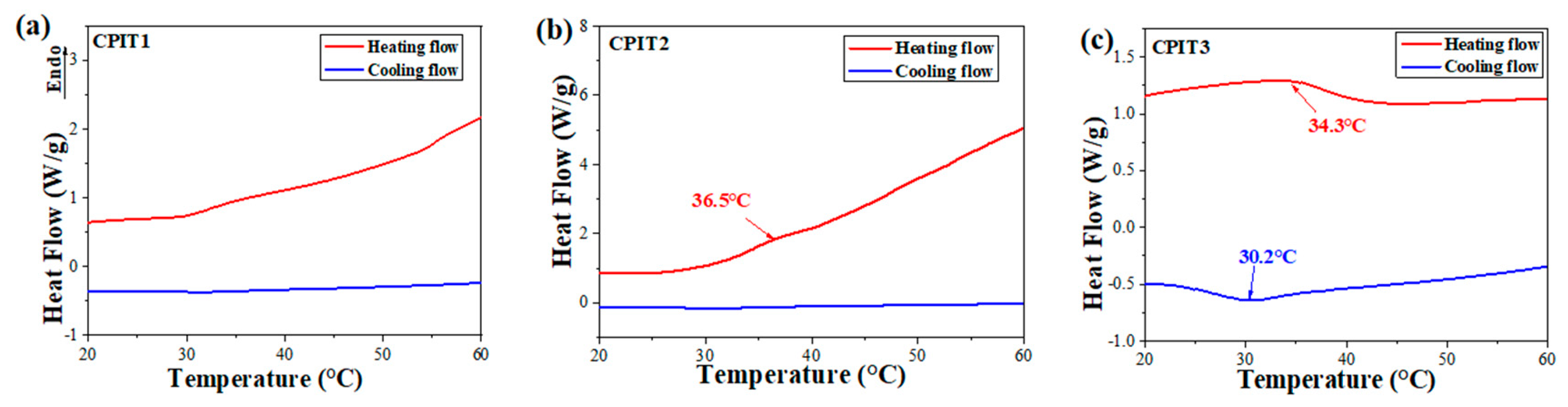
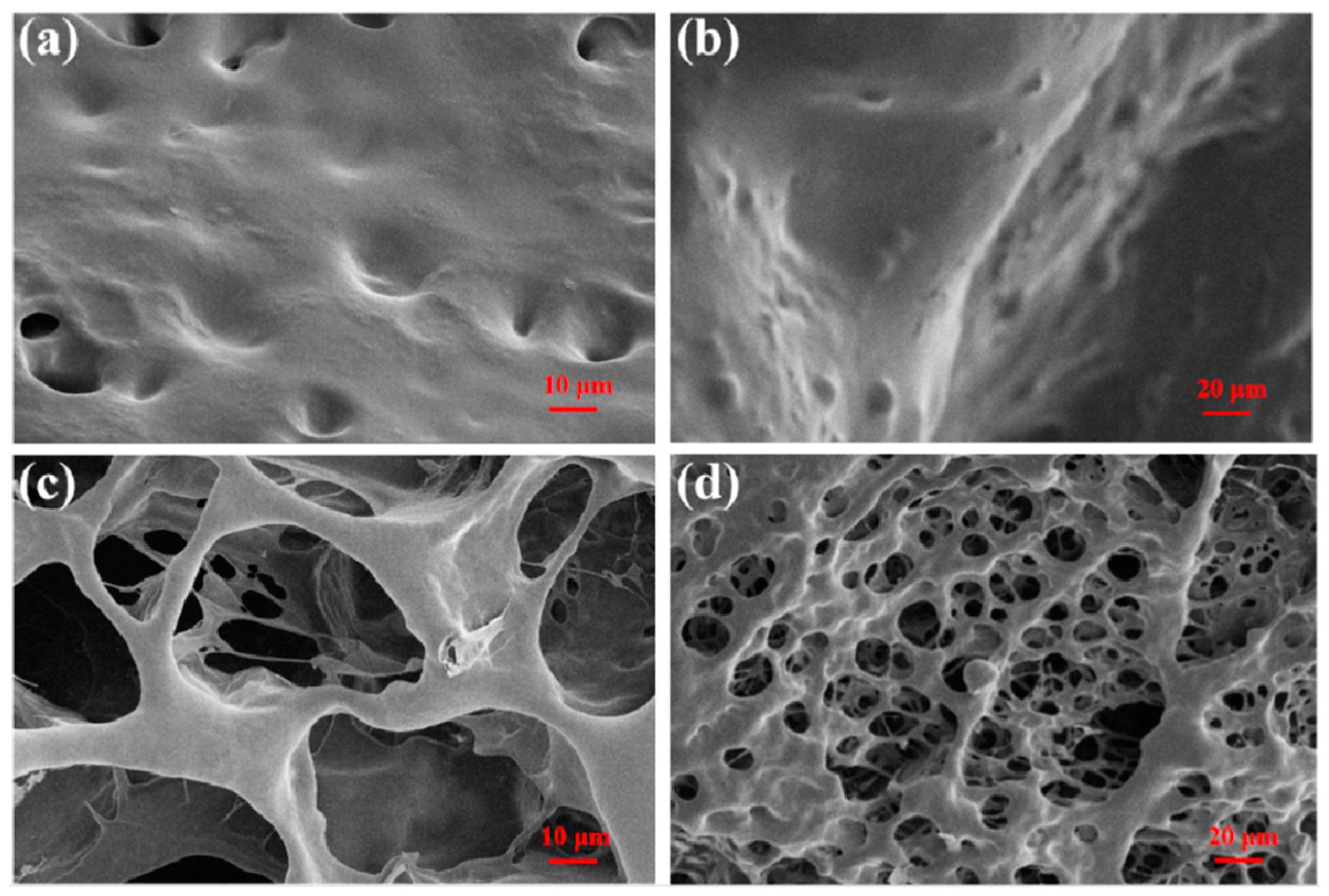
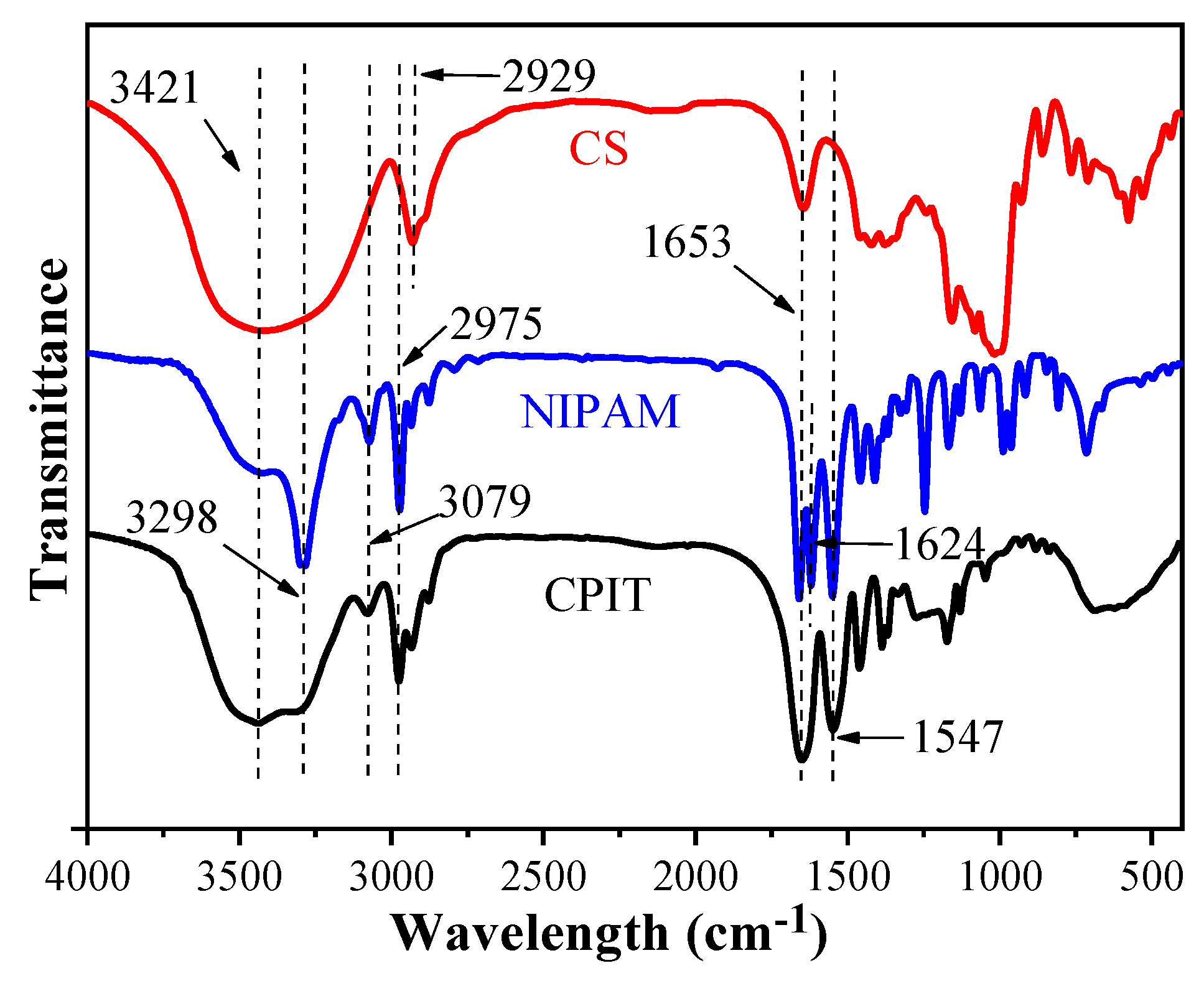
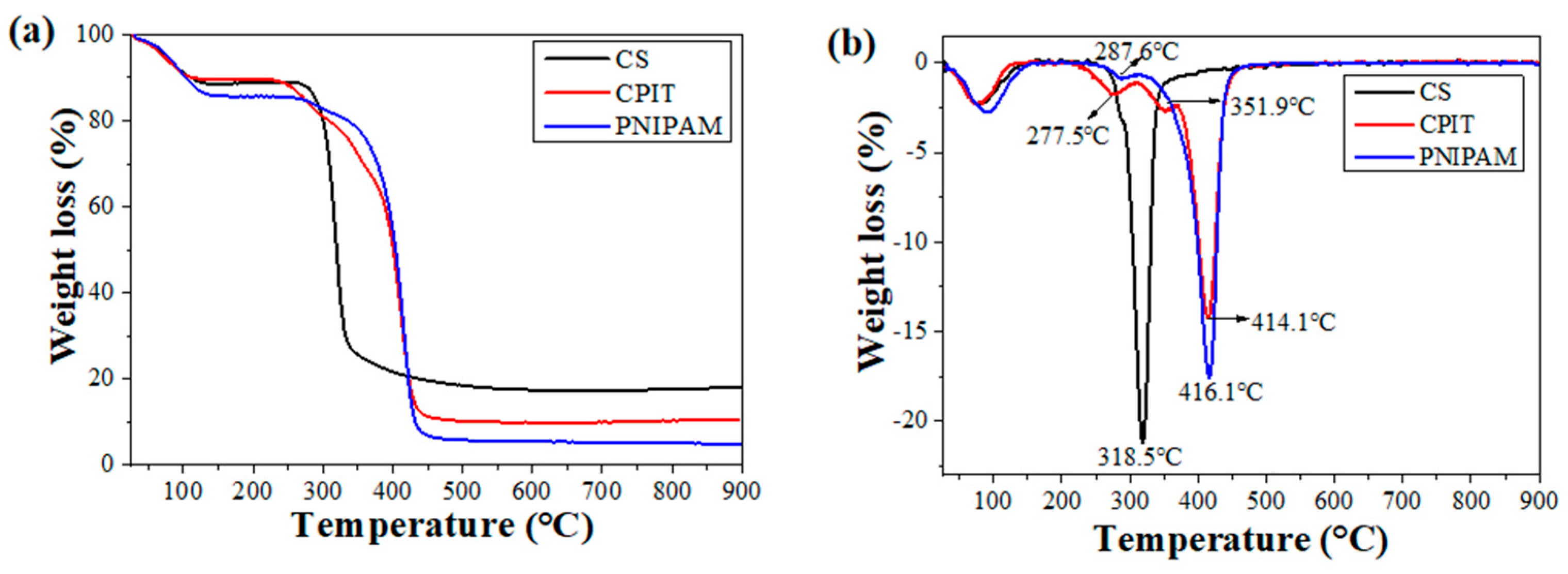
3.1. Characterization of CPIT
3.2. Adsorption Performance of CPIT on Pb(II)
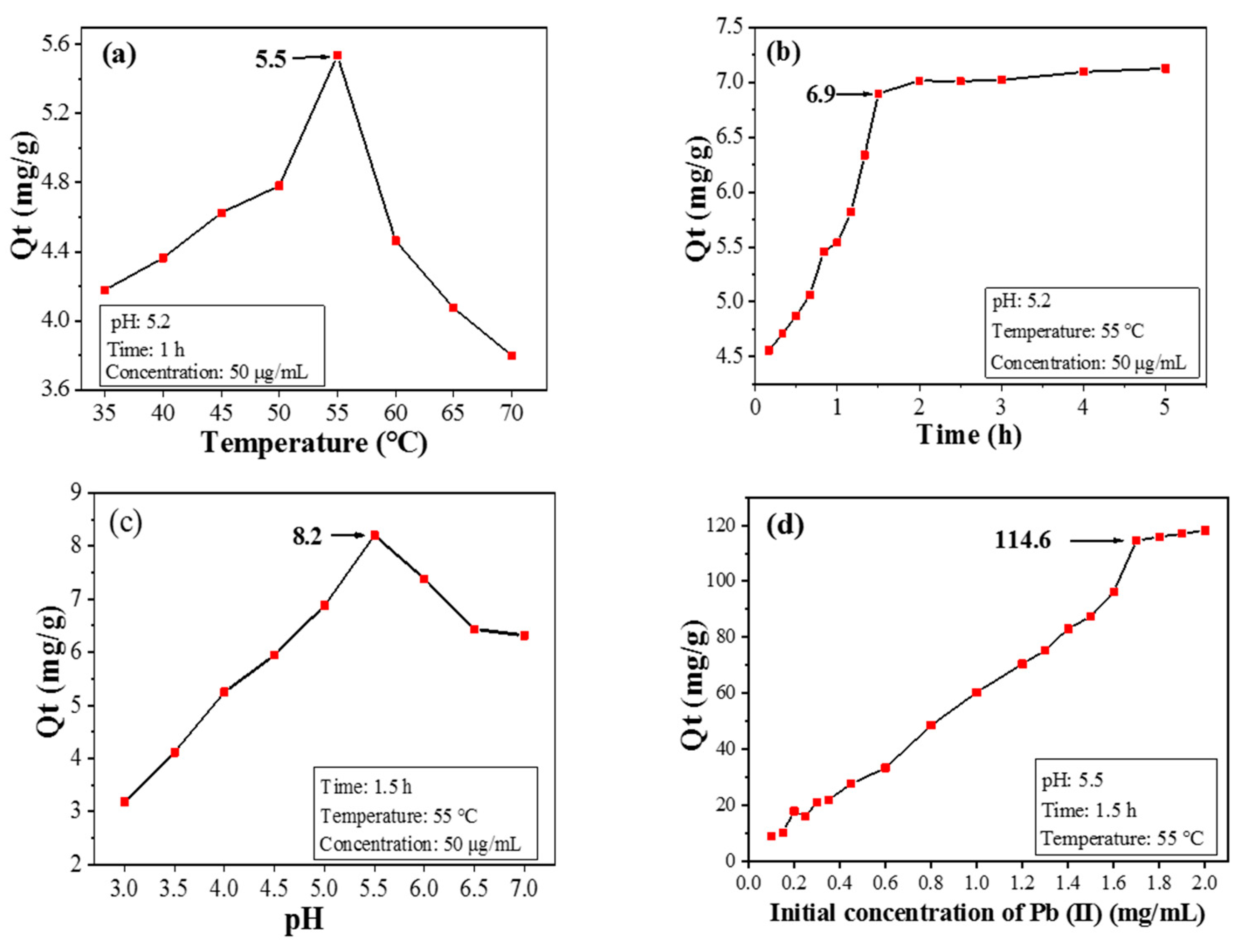
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature on Pb(II) Adsorption by CPIT
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorption Time on Pb(II) Adsorption by CPIT
3.2.3. Effect of pH Value on Pb(II) Adsorption by CPIT
3.2.4. Effect of Initial Pb(II) Concentration on Pb(II) Adsorption by CPIT
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism of CPIT
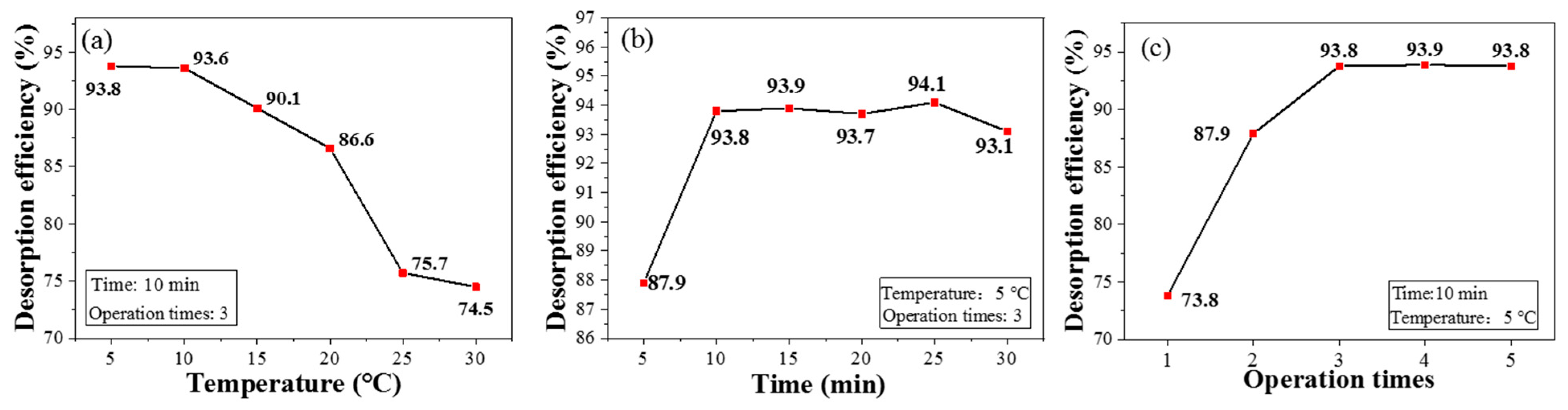
3.4. Desorption Performance of CPIT
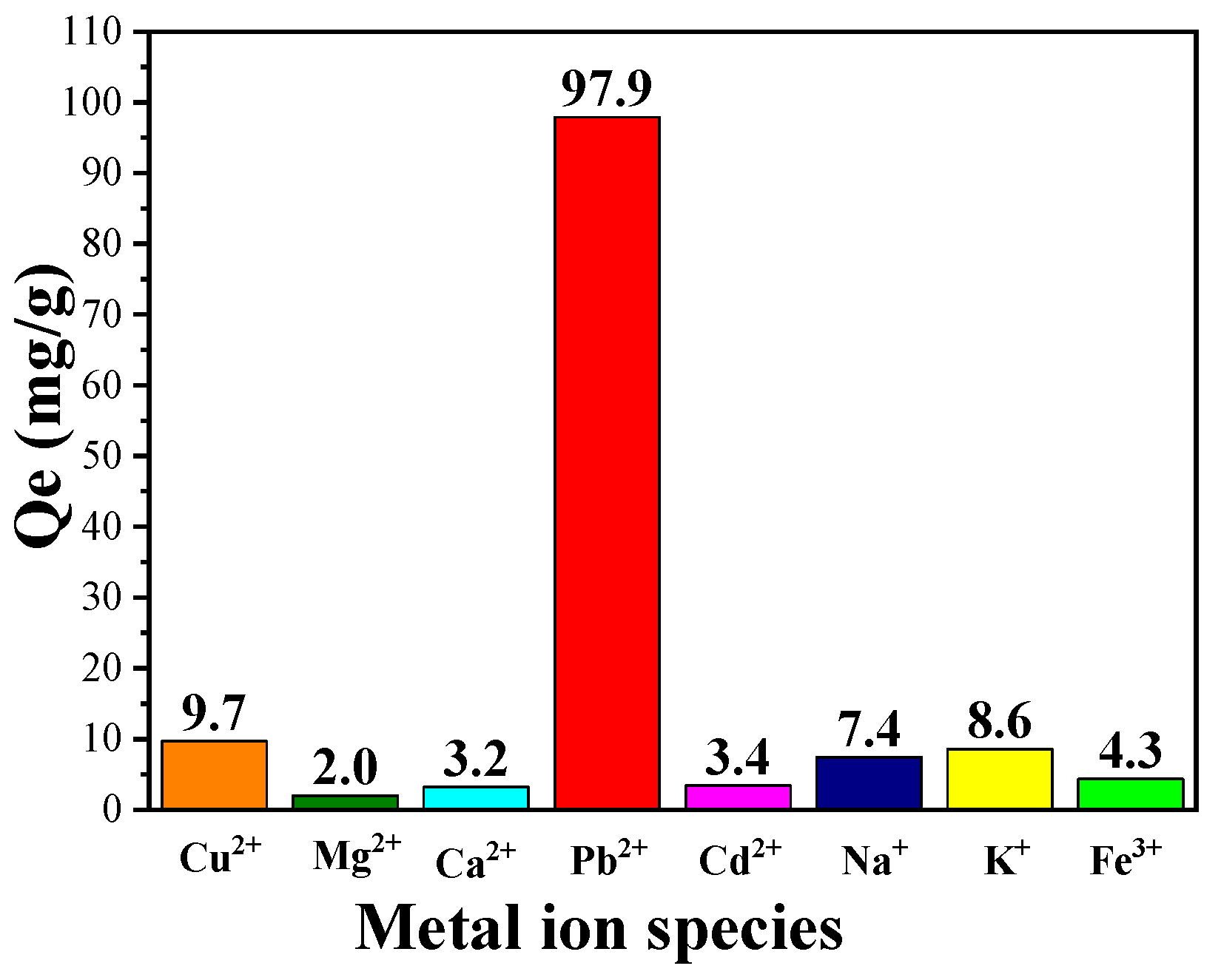
3.5. Selective Adsorption Capacity of CPIT
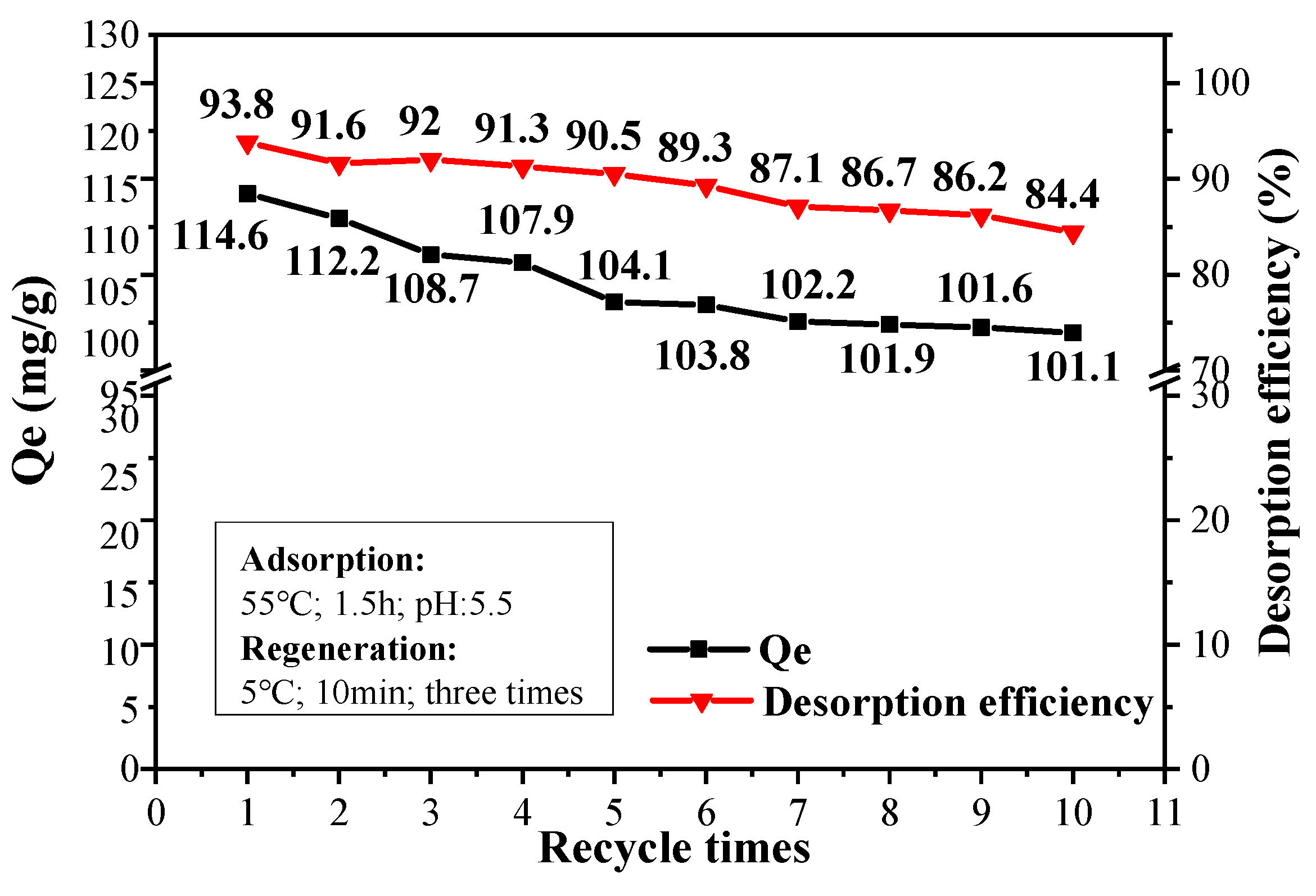
3.6. Regeneration of CPIT
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Huang, B.; Tang, X.; Wang, S.; Hua, Q.; Yan, Z. Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) onto chitosan-pyromellitic dianhydride modified biochar. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onditi, M.; Adelodun, A.A.; Changamu, E.O.; Ngila, J.C. Removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from drinking water using polysaccharide extract isolated from cactus pads (Opuntia ficus indica). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, Z.; Usman, M.; Anastopoulos, I.; Qadeer, A.; Zhu, R.; Wakeel, A.; Dong, R. Use of nano-/micro-magnetite for abatement of cadmium and lead contamination. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 264, 110477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Cai, C.; Chi, H.; Reid, B.J.; Coulon, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y. Remediation of cadmium and lead polluted soil using thiol-modified biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chai, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W. Simultaneous immobilization of lead, cadmium, and arsenic in combined contaminated soil with iron hydroxyl phosphate. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 17, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesali-Naseh, M.; Vesali Naseh, M.R.; Ameri, P. Adsorption of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions using carbon nanotubes: A systematic review. J. Cleaner Prod. 2021, 291, 125917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Li, M.; Li, L. Synthesis, application and mechanisms of Ferro-Manganese binary oxide in water remediation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Bakry, B.M.; Adlii, A.; Yakout, S.M.; El-Zaidy, M.E. Facile conversion of kaolinite into clay nanotubes (KNTs) of enhanced adsorption properties for toxic heavy metals (Zn(2+), Cd(2+), Pb(2+), and Cr(6+)) from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Tavengwa, N.T.; Tutu, H.; Chimuka, L. Green aspects in molecular imprinting technology: From design to environmental applications. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 17, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René, W.; Lenoble, V.; Chioukh, M.; Branger, C. A turn-on fluorescent ion-imprinted polymer for selective and reliable optosensing of lead in real water samples. Sens. Actuators, B 2020, 319, 128252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Shao, N.; Hou, L.; Zhu, X. Fabrication of an efficient surface ion-imprinted polymer based on sandwich-like graphene oxide composite materials for fast and selective removal of lead ions. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 566, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, X.; Wei, X.; Tang, L.; Wei, S. Metal-ion-imprinted thermo-responsive materials obtained from bacterial cellulose: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption evaluation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11742–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yang, C.; Rao, X.; Hu, L.; Bao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, X. Fabrication of recoverable magnetic surface ion-imprinted polymer based on graphene oxide for fast and selective removal of lead ions from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 625, 126949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Xu, H.; Chen, C.; Shi, F.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Hu, S. A novel dual crosslinked polysaccharide hydrogel with self-healing and stretchable properties. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 6134–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.-H.; Ibrahim, I.; Arun, D.; Holtzl, T.; Dumée, L.F.; Lim, H.N.; Szekely, G. Architecting neonicotinoid-scavenging nanocomposite hydrogels for environmental remediation. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Li, W.; Cheng, M.; Tang, W.; Xiong, Z. A responsive pure DNA hydrogel for label-free detection of lead ion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1157, 338400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Ahmad, A.L.; Lim, J.K.; Ooi, B.S. Facile synthesis and characterization of thermo-magneto-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-magnetite composite hydrogel and its adsorption-desorption study on chromium (III). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 218, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cseri, L.; Hardian, R.; Anan, S.; Vovusha, H.; Schwingenschlogl, U.; Budd, P.M.; Sada, K.; Kokado, K.; Szekely, G. Bridging the interfacial gap in mixed-matrix membranes by nature-inspired design: Precise molecular sieving with polymer-grafted metal-organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 23793–23801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksendzov, E.A.; Nikishau, P.A.; Zurina, I.M.; Presniakova, V.S.; Timashev, P.; Rochev, Y.A.; Kotova, S.; Kostjuk, S.V. Graft Copolymers of N-Isopropylacrylamide with Poly(D,L-lactide) or Poly(ε-caprolactone) Macromonomers: A Promising Class of Thermoresponsive Polymers with a Tunable LCST. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Tang, L.; Li, M.; Liang, Z.; Yin, X.; Wei, S. Ion-imprinted thermosensitive chitosan derivative for heavy metal remediation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.H.; Fan, Y.Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, H.; Ma, L.J.; Huang, X.J.; Liu, Y. Structural Characterization of Controlled Decrystallization of Cassava Starch. Starch-Stärke 2019, 72, 1900049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travalini, A.P.; Lamsal, B.; Magalhaes, W.L.E.; Demiate, I.M. Cassava starch films reinforced with lignocellulose nanofibers from cassava bagasse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickenheisser, M.; Paul, T.; Janiak, C. Prospects of monolithic MIL-MOF@poly(NIPAM)HIPE composites as water sorption materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 220, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, R.K. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose based adsorbents for removal of Ni(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 140, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Cheng, X.; Peng, Q.; Li, W. Temperature/pH dual-responsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)/chitosan-coated luminescent composite nanospheres: Fabrication and controllable luminescence. Opt. Mater. 2018, 86, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Sharma, N. Efficiency of Superparamagnetic Nano Iron Oxide Loaded Poly(Acrylamide-co-Maleic acid) Hydrogel in Uptaking Cu2+ Ions from Water. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of Copper (II) onto Different Adsorbents. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, L.; Köhler, M.; Sobotta, F.H.; Enke, M.T.; Brendel, J.C.; Schacher, F.H. Poly(2-acrylamidoglycolic acid) (PAGA): Controlled Polymerization Using RAFT and Chelation of Metal Cations. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 7284–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.R. pH mediated rheological modulation of chitosan hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, M.; Ezzatzadeh, E.; Jalilian, R.; Taheri, A. Micro solid phase extraction of cadmium and lead on a new ion-imprinted hierarchical mesoporous polymer via dual-template method in river water and fish muscles: Optimization by experimental design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, K. Study on the adsorption behavior of glutaric acid modified Pb(II) imprinted chitosan-based composite membrane to Pb(II) in aqueous solution. Mater. Lett. 2019, 251, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Song, M.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Qin, R.; He, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, M. Characterization and adsorption properties of cross-linked yeast/β-cyclodextrin polymers for Pb(II) and Cd(II) adsorption. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31542–31554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusof, N.F.; Mehamod, F.S.; Mohd Suah, F.B. Fabrication and binding characterization of ion imprinted polymers for highly selective Co2+ ions in an aqueous medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatabi, J.; Sarrafi, Y.; Lakouraj, M.M.; Taghavi, M. Facile and efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by chitosan-lead ion imprinted polymer network. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ren, S.; Zhang, T.; Wei, X.; Li, M.; Yin, X.; Wei, S. UO22+-imprinted thermoresponsive hydrogel for accumulation of uranium from seawater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by magnetic activated carbon and its mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, L.; Du, K. Proteinaceous porous nanofiber membrane-type adsorbent derived from amyloid lysozyme protofilaments for highly efficient lead(II) biologic scavenging. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhao, P.; Xi, M.; Li, Y. Synthesis of Copper and Lead Ion Imprinted Polymer Submicron Spheres to Remove Cu2+ and Pb2+. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 4628–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

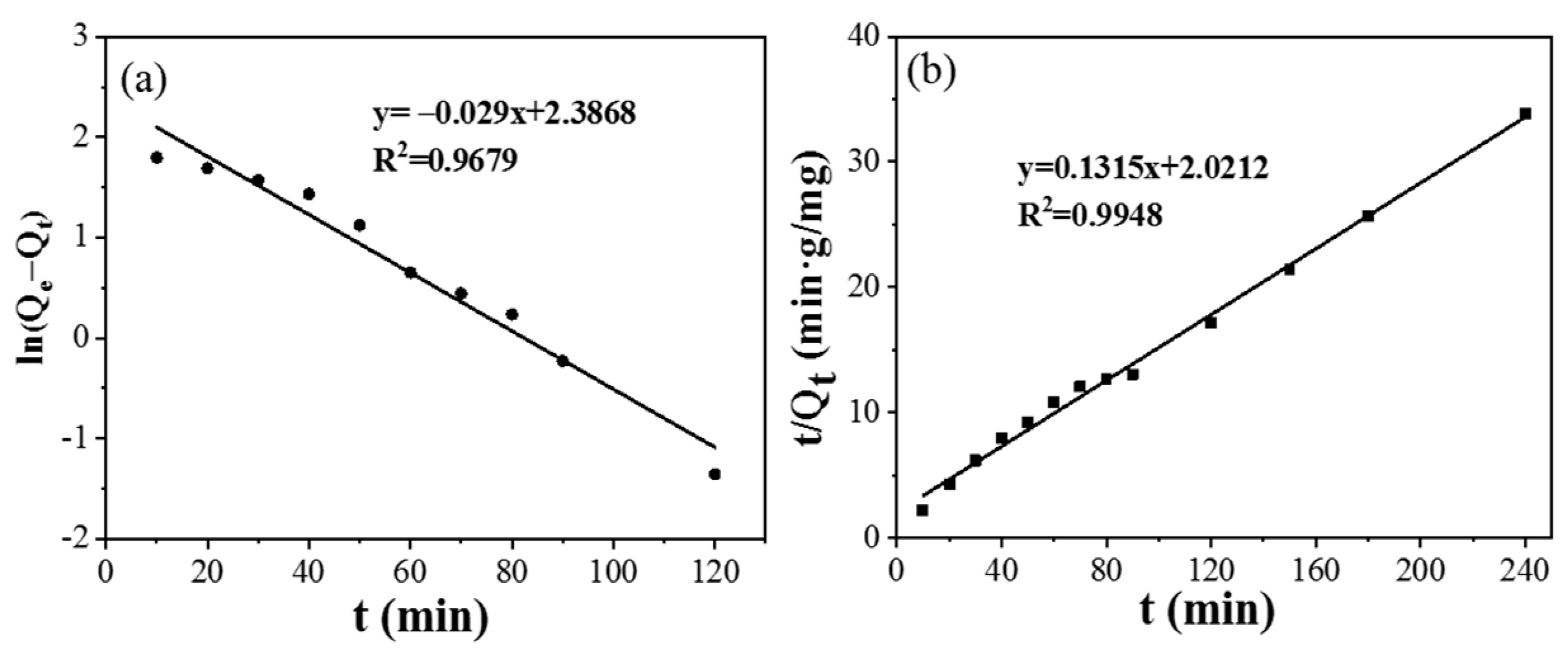
| Samples | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Second-Order Dynamic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | R2 | Qe | k2 | R2 | Qe | |
| CPIT | 0.0005 | 0.9502 | 7.0554 | 0.0086 | 0.9948 | 7.6046 |
| Adsorption Isotherms of Pb(II) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
| KL (L/mg) | Qm (mg/g) | RL2 | KF (L/mg) | n | RF2 | |
| CPIT | 0.0008 | 189.39 | 0.9250 | 0.5006 | 1.3298 | 0.9839 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, M.; Du, Y.; Zhang, T.; Du, X.; Yin, X. Cassava Starch-Based Thermo-Responsive Pb(II)-Imprinted Material: Preparation and Adsorption Performance on Pb(II). Polymers 2022, 14, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040828
Lv M, Du Y, Zhang T, Du X, Yin X. Cassava Starch-Based Thermo-Responsive Pb(II)-Imprinted Material: Preparation and Adsorption Performance on Pb(II). Polymers. 2022; 14(4):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040828
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Meiyuan, Yuhan Du, Tingting Zhang, Xueyu Du, and Xueqiong Yin. 2022. "Cassava Starch-Based Thermo-Responsive Pb(II)-Imprinted Material: Preparation and Adsorption Performance on Pb(II)" Polymers 14, no. 4: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040828
APA StyleLv, M., Du, Y., Zhang, T., Du, X., & Yin, X. (2022). Cassava Starch-Based Thermo-Responsive Pb(II)-Imprinted Material: Preparation and Adsorption Performance on Pb(II). Polymers, 14(4), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040828





